Influence of Current Duty Cycle and Voltage of Micro-Arc Oxidation on the Microstructure and Composition of Calcium Phosphate Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Micro-Arc Oxidation of Titanium
2.3. Coating Research Methods
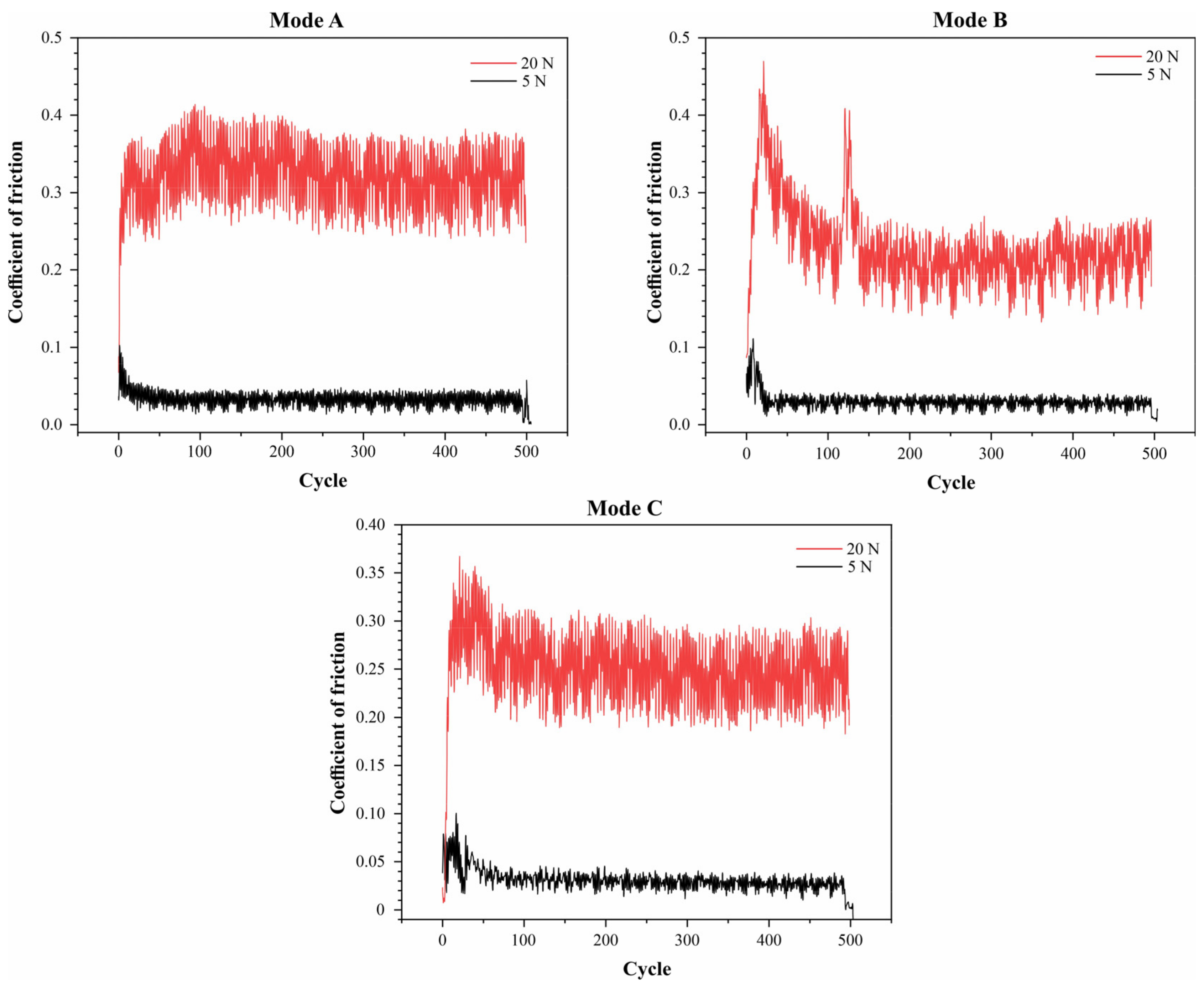
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Calcium phosphate coatings were successfully deposited on a titanium substrate using the micro-arc oxidation method at different duty cycles and voltages in an aqueous solution of orthophosphoric acid with hydroxyapatite and calcium carbonate.
- The linear increase in voltage at the duty cycles used determined the size of the particles formed in the coating. Morphological analysis of the coatings showed that the morphology changes depending on the duty cycles, ranging from sponge-like with needles to flower-like structures.
- Using different duty cycles of micro-arc treatment, amorphous/crystalline structures were formed containing phases such as CaPO3(OH), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O, and γ–Ca2P2O7, which are biocompatible phases.
- Regarding the crystallinity of the calcium phosphate coatings and the Ca/P ratio, the duty cycle of mode C allowed us to obtain coatings with relatively high indicators: crystallinity up to 60.3% and Ca/P ratio up to 0.62.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Hady Gepreel, M.; Niinomi, M. Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paital, S.R.; Dahotre, N.B. Calcium phosphate coatings for bio-implant applications: Materials, performance factors, and methodologies. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 66, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, R.B. Structure, properties, and biomedical performance of osteoconductive bioceramic coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipovna, M.A.; Karaulovich, K.A.; Vladimirovich, P.A.; Zhanuzakovich, A.Z.; Bolatovna, K.B.; Wieleba, W.; Leśniewski, T.; Bakhytuly, N. The study of the tribological properties under high contact pressure conditions of TiN, TiC and TiCN coatings deposited by the magnetron sputtering method on the AISI 304 stainless steel substrate. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2023, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhaliyev, B.K. Innovative technologies providing enhancement of non-ferrous, precious, rare and rare earth metals extraction. Kompleks. Ispolz. Miner. Syra = Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2019, 310, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagul, U.; Bagdaulet, K.; Murat, O.; Azamat, Y.; Kaysar, K. Investigations of waste sludge of titanium production and its leaching by nitric acid. In Proceedings of the 19th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM 2019, Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June–6 July 2019; Volume 19, pp. 861–868. [Google Scholar]
- Ramazanova, Z.; Zamalitdinova, M.; Kovalenko, M. Investigation of the properties of oxide coatings on titanium alloys obtained by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Kompleks. Ispolz. Miner. Syra = Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2022, 321, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K. Biomaterials and interface with bone. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Li, Y.; Munir, K.; Wen, C. Calcium Phosphate-Based Composite Coating by Micro-Arc Oxidation (MAO) for Biomedical Application: A Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 43, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Xu, W.; Hu, W.; Hodgson, P. Hydroxyapatite/titania sol–gel coatings on titanium–zirconium alloy for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oirschot, B.A.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; van den Beucken, J.J.; Meijer, G.; Jansen, J.; Junker, R. A systematic review on the long-term success of calcium phosphate plasma-spray-coated dental implants. Odontology 2016, 104, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albayrak, O.; El-Atwani, O.; Altintas, S. Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate by electrophoretic deposition method: Effects of titanium dioxide inner layer on adhesion strength and hydroxyapatite decomposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2482–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhodub, L.F.; Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Sukhodub, L.B.; Sagidugumar, A.; Kistaubayeva, A.S.; Savitskaya, I.S.; Turlybekuly, A. Antibacterial and physical characteristics of silver-loaded hydroxyapatite/alginate composites. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2021, 3, 045010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, C.; Denis, C.; Pullar, R.; Binions, R.; Parkin, I.; Darr, J.; Castro, P. Aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition of hydroxyapatite-embedded titanium dioxide composite thin films. J. Photcohem. Phobiol. A Chem. 2017, 332, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Miyake, A.; Tashiro, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Blank, D.H.; Rijnders, G. Relationship between the Ca/P ratio of hydroxyapatite thin films and the spatial energy distribution of the ablation laser in pulsed laser deposition. Mater. Lett. 2016, 165, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, G.; Wu, G.; Jin, W.; Wu, H.; Chu, P.K. Plasma and ion-beam modification of metallic biomaterials for improved anti-bacterial properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 306, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaeva, A.; Kenzhegulov, A.; Kowalewski, P.; Wieleba, W. Investigation of hydroxyapatite-titanium composite properties during heat treatment. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2017, 19, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, G.; He, K.; Yuan, Y.F. Effect of sandblasting intensity on microstructures and properties of pure titanium micro-arc oxidation coatings in an optimized composite technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaeva, A.A.; Kenzhegulov, A.K.; Panichkin, A.V.; Shah, A. Obtaining hydroxyapatite coatings by mechanochemical interaction. Kompleks. Ispolz. Miner. Syra = Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2020, 314, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhadilov, B.; Baizhan, D. Creation of bioceramic coatings on the surface of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation followed by gas detonation spraying. Coatings 2021, 11, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.-J.; Choe, H.-C. Surface morphology and cell behavior of Zn-coated Ti–6Al–4V alloy by RF-sputtering after PEO-treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 361, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Z. Review of the biocompatibility of micro-arc oxidation coated titanium alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Wang, F.; Shimizu, T.; Igarashi, K.; Zhao, L. Formation characterization of hydroxyapatite of titanium by microarc oxidation and hydrothermal treatment. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Xu, D.; Liu, X. Mussel-inspired functionalization of PEO/PCL composite coating on a biodegradable AZ31 magnesium alloy. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 141, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Zhang, J.W.; Ye, F.; Lv, W.G.; Lu, S.; Sun, L.; Jiang, X.Z. Properties of micro-arc oxidation coating fabricated on magnesium under two steps current-decreasing mode. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdu, S.; Deniz, O.F.; Kutbay, I.; Usta, M. Characterization and formation of hydroxyapatite on Ti6Al4 V coated by plasma electrolytic oxidation. J. Alloys Comp. 2013, 551, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Q.; Ivanisenko, Y.; Diemant, T.; Caron, A.; Chuvilin, A.; Jiang, J.Z.; Valiev, R.Z.; Qi, M.; Fecht, H.J. Synthesis and properties of hydroxyapatite-containing porous titania coating on ultrafine-grained titanium by micro-arc oxidation. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamaeva, A.A.; Panichkin, A.V.; Kenzhegulov, A.K.; Kalipbekova, M.A. Preparation of calcium phosphate coatings on a titanium substrate under microarc processing conditions. Kompleks. Ispolz. Miner. Syra = Complex Use Miner. Resour. 2017, 2, 33–40. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.H.; Jun, Y.K.; Han, Y.; Hong, S.H. Biomimetic apatite coatings on micro-arc oxidized titania. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Han, Y.; Huang, X. Hydroxyapatite coatings prepared by micro-arc oxidation in Ca- and P-containing electrolyte. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5655–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Yuan, M. Effect of Pulse Duty Cycle and Oxidation Time on Microstructure and Properties of Micro-arc Oxidation Coatings on Ti6Al4V Alloy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2419, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Kung, H.-P.; Lin, H.-C. Effects of Electrical Parameters on Micro-Arc Oxidation Coatings on Pure Titanium. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, K.; Chen, J.; Zuo, Y. The influences of duty cycle on the bonding strength of AZ31B magnesium alloy by microarc oxidation treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1789–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafili, F.; Chaharmahali, R.; Babaei, K.; Fattah-alhosseini, A. Duty cycle influence on the corrosion behavior of coatings created by plasma electrolytic oxidation on AZ31B magnesium alloy in simulated body fluid. Corros. Commun. 2021, 3, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, E.G.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Sedelnikova, M.B.; Prosolov, K.A.; Khlusov, I.A.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M. Zn- or Cu-Containing CaP-Based Coatings Formed by Micro-arc Oxidation on Titanium and Ti-40Nb Alloy: Part I–Microstructure, Composition and Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIN 51834-1:2010-11; Testing of Lubricants—Tribological Test in the Translatory Oscillation Apparatus—Part 1: General Working Principles. German Institute for Standardisation: Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, F.Q. Influence of anions in phosphate and tetraborate electrolytes on growth kinetics of microarc oxidation coatings on Ti6Al4V alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baizhan, D.R.; Rakhadilov, B.K.; Aldabergenova, T.M.; Bayatanova, L.B.; Kurbanbekov, S.R.; Buitkenov, D.B. Obtaining of calcium-phosphate coatings on the titanium surface by micro-arc oxidation. Eurasian Phys. Tech. J. 2023, 20, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ling, L.I. Kinetic characteristics of phosphorus adsorption on surface coatings in natural water. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2013, 33, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Soballe, K.; Hansen, E.S.; Rasmussen, H.B.; Jorgensen, P.H.; Beunger, C. Tissue ingrowth into titanium and hydroxyapatite-coated implants during stable and unstable mechanical conditions. J. Orthop. Res. 1992, 10, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, M.; Dehghanian, C.; Shokouhfar, M.; Baradaran, A. Investigation of the voltage and time effects on the formation of hydroxyapatite-containing titania prepared by plasma electrolytic oxidation on Ti-6Al-4 V alloy and its corrosion behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7268–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiraharjo, R.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T. Hydroxyapatite-coated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffolds for promoting osteoblast and stem cell differentiation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2012, 366, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Hong, S.H.; Xu, K. Structure and in vitro bioactivity of titania-based films by micro-arc oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 168, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, B.; Liang, C.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Z. Formation mechanism and adhesive strength of a hydroxyapatite/TiO2 composite coating on a titanium surface prepared by micro-arc oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fang, Y.J.; Zheng, H.; Tan, G.; Cheng, H.; Ning, C. Effect of applied voltage on phase components of composite coatings prepared by micro-arc oxidation. Thin Solid Films 2013, 544, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, P.K. Effects of micropitted/nanotubular titania topographies on bone mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2629–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.T.; Huang, J.W.; Lin, W.T.; Kuo, T.Y.; Chien, C.-S.; Chang, C.-P.; Lin, Y.D. Effects of Micro-Arc Oxidation Discharge Parameters on Formation and Biomedical Properties of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Flower-like Structure Coatings. Materials 2023, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, H. Influence of surface structures on biocompatibility of TiO2/HA coatings prepared by MAO. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 215, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Verma, V.; Rashid, H.; Glogauer, M. Biodegradable materials for bone repair and tissue engineering applications. Materials 2015, 8, 5744–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.L.; Chen, J.; Cao, B.B.; Xu, L.; Lu, S. Effects of interaction of (NaPO3)6 and NaH2PO4 on Ca/P of MAO Bio-ceramic coating of ZK60 Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2013, 745, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauskojus, W.; Wied, J.K.; Litterscheid, C.F.; Mangstl, M.; Schmedt auf der Günne, J. Crystal Structure of γ-Ca2P2O7. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2022, 648, e202200196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, L.; Gbureck, U.; Bhaduri, S.B.; Sikder, P. Monetite, an important calcium phosphate compound–Its synthesis, properties and applications in orthopedics. Acta Biomater. 2021, 127, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.; Jiang, Y. Bio-Aggregates Based Building Materials: State-of-the-Art Report of the RILEM Technical Committee 236-BBM; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2017; pp. 39–71. [Google Scholar]
- Seesanong, S.; Seangarun, C.; Boonchom, B.; Sronsri, C.; Laohavisuti, N.; Chaiseeda, K.; Boonmee, W. Recrystallization of triple superphosphate produced from oyster shell waste for agronomic performance and environmental issues. Minerals 2022, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchom, B.; Danvirutai, C. The morphology and thermal behavior of Calcium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (Ca(H2PO4)2•H2O) obtained by a rapid precipitation route at ambient temperature in different media. J. Optoelectron. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Xu, X.; Song, Y. A phosphoric anion layer inhibits electronic current generation and nanotube growth during anodization of titanium. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 4597–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisca, G.D.O.; Vitoriano, J.D.O.; Alves-Junior, C. Controlling plasma electrolytic oxidation of titanium using current pulses compatible with the duration of microdischarges. Results Mater. 2022, 15, 100310. [Google Scholar]
- Lukić, M.; Stojanović, Z.; Škapin, S.D.; Maček-Kržmanc, M.; Mitrić, M.; Marković, S.; Uskoković, D. Dense fine-grained biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) bioceramics designed by two-step sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, I.U.; Choudhry, Q.; Mahmood, A.; Gilani, Z.A.; Shahid, S.A.; Farooq, M. Structural, morphological and electrical properties of heat treated CaHPO4 biomaterials. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 2015, 9, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
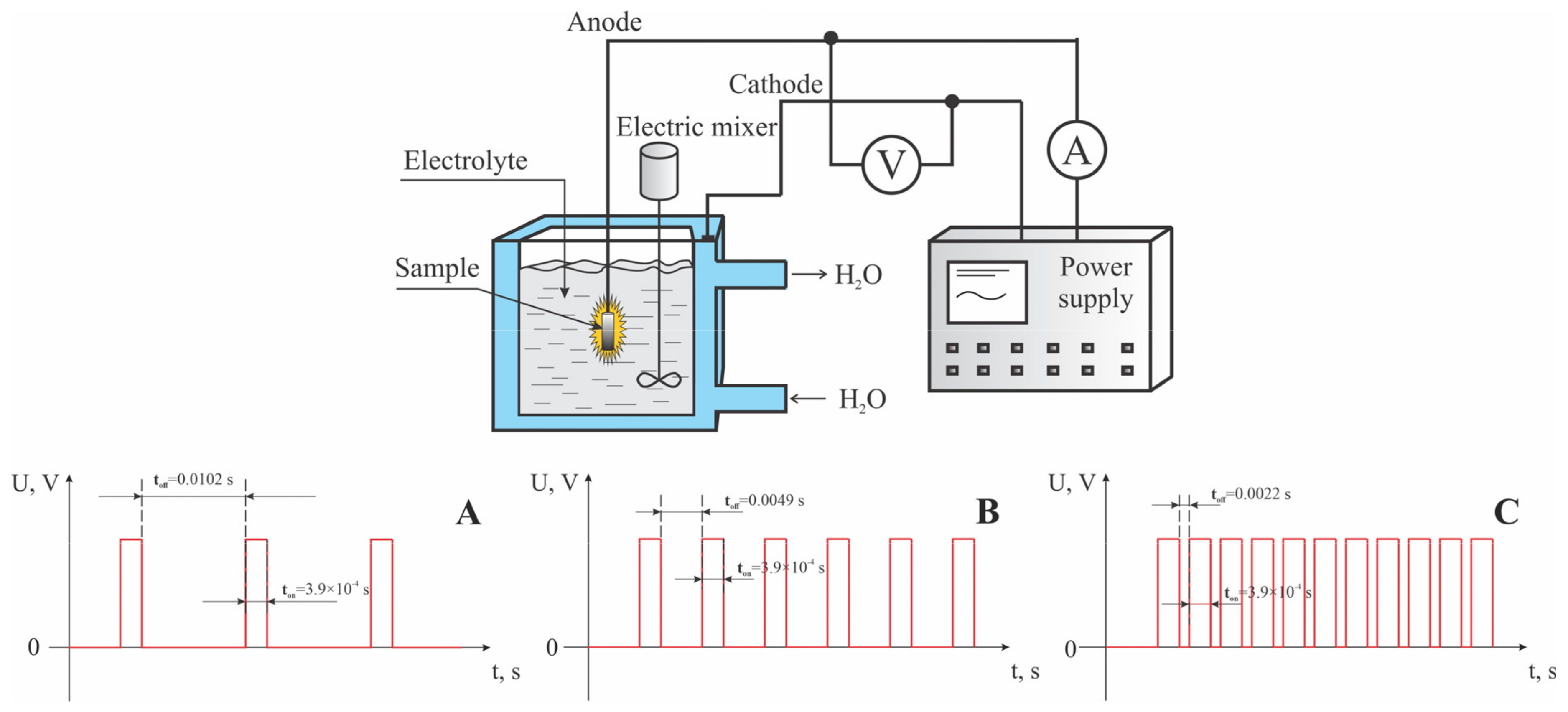

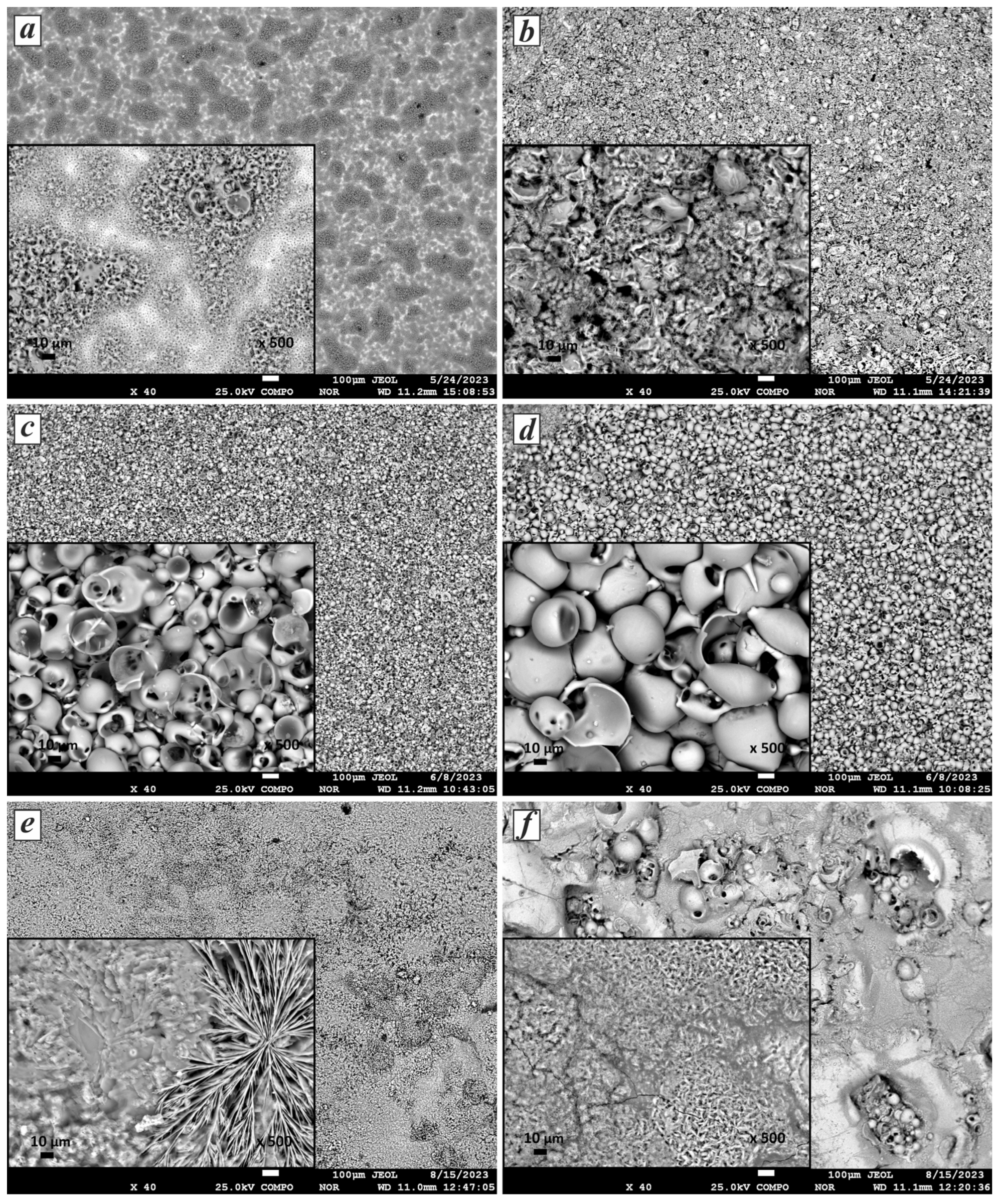
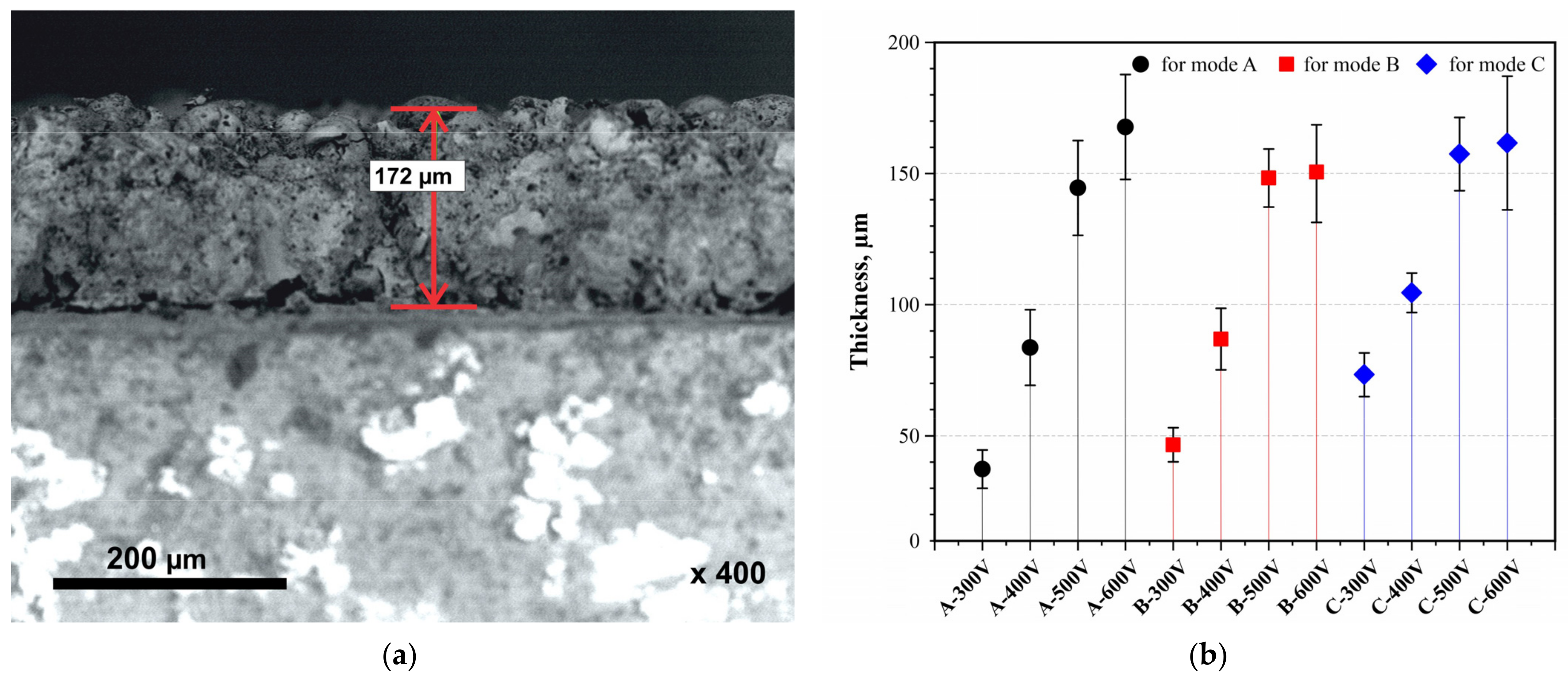

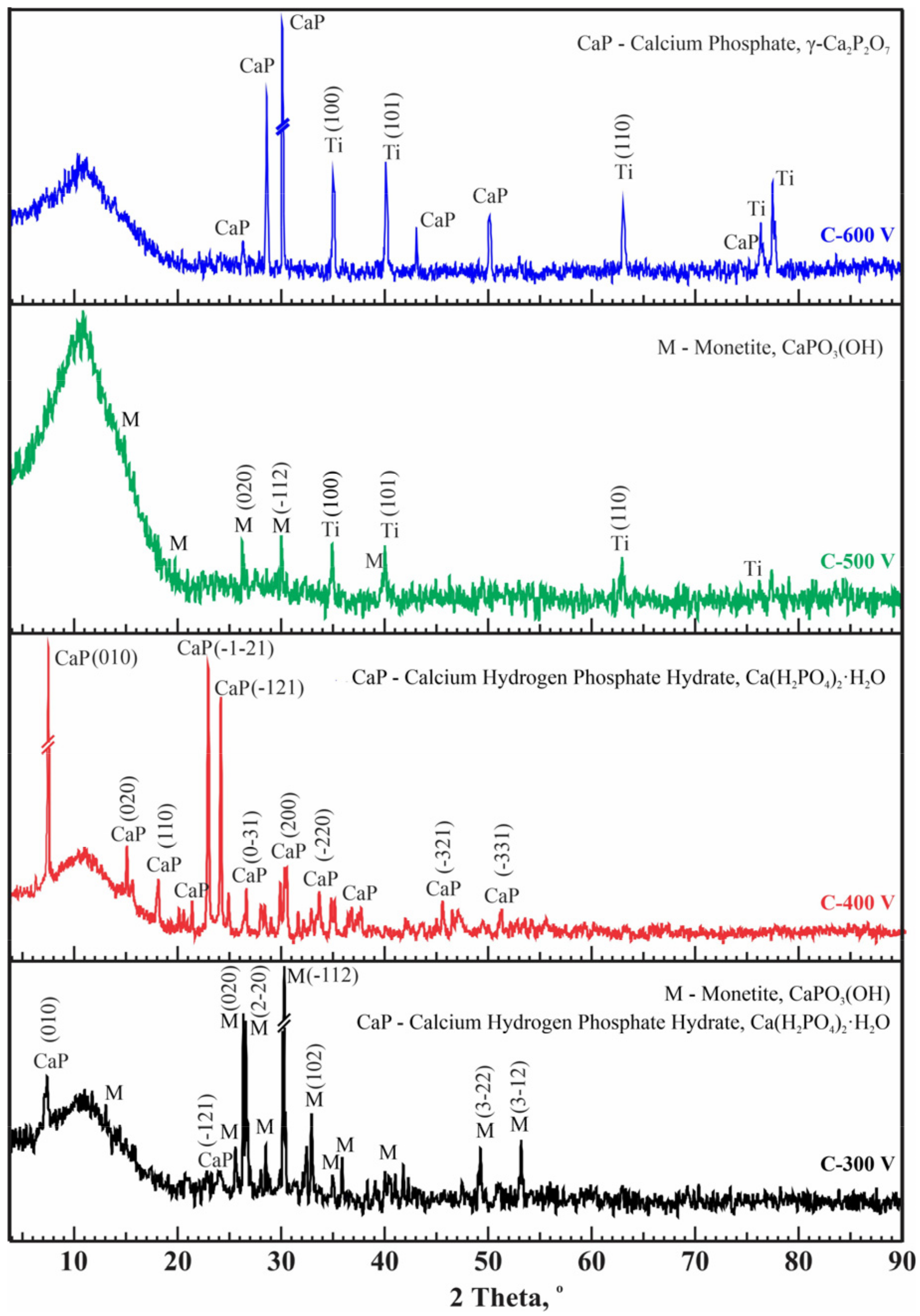
| Sample | Duration of Period (s) | Duty Cycle (%) | Voltage (V) | Treatment Duration (min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ton | Toff | ||||
| A–300 V | 0.00039 | 0.0102 | 35 | 300 | 10 |
| A–400 V | 400 | ||||
| A–500 V | 500 | ||||
| A–600 V | 600 | ||||
| B–300 V | 0.00039 | 0.0049 | 17.3 | 300 | 10 |
| B–400 V | 400 | ||||
| B–500 V | 500 | ||||
| B–600 V | 600 | ||||
| C–300 V | 0.00039 | 0.0022 | 8.3 | 300 | 10 |
| C–400 V | 400 | ||||
| C–500 V | 500 | ||||
| C–600 V | 600 | ||||
| Sample | Elemental Composition, at.% | Ca/P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | P | O | Ti | ||
| A–300 V | 3.16 | 10.44 | 78.82 | 7.58 | 0.3 |
| A–400 V | 3.14 | 12.02 | 77.14 | 7.7 | 0.26 |
| A–500 V | 4.11 | 11.33 | 78.01 | 6.55 | 0.36 |
| A–600 V | 3.57 | 10.99 | 77.59 | 7.85 | 0.32 |
| B–300 V | 4.63 | 12.18 | 77.41 | 5.78 | 0.38 |
| B–400 V | 4.78 | 12.22 | 79.91 | 3.09 | 0.39 |
| B–500 V | 4.93 | 10.85 | 78.93 | 5.29 | 0.45 |
| B–600 V | 3.95 | 12.03 | 75.33 | 8.31 | 0.32 |
| C–300 V | 4.55 | 12.19 | 77.21 | 6.05 | 0.37 |
| C–400 V | 6.08 | 13.93 | 76.03 | 3.96 | 0.43 |
| C–500 V | 5.95 | 11.97 | 75.17 | 6.91 | 0.49 |
| C–600 V | 8.43 | 13.41 | 74.63 | 3.03 | 0.62 |
| Sample | CaP Coating Phase Compositions (%) | Crystallinity, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaPO3(OH) | Ti(PO3)3 | H2Ti2O5·H2O | |||
| A–500 V | 96.6 | 3.4 | – | 53.4 | |
| A–600 V | 76.4 | 5.3 | 18.3 | 51.3 | |
| CaPO3(OH) | Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O | TiP2O7 | Ti | ||
| B–500 V | 4.6 | 6.2 | 39.8 | 49.5 | 47.3 |
| B–600 V | – | – | 24.7 | 75.3 | 42.2 |
| CaPO3(OH) | Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O | γ–Ca2P2O7 | Ti | ||
| C–300 V | 89.5 | 10.5 | – | – | 59.4 |
| C–400 V | – | 100 | – | – | 60.3 |
| C–500 V | 64.4 | – | – | 35.6 | 55.4 |
| C–600 V | – | – | 83.1 | 16.9 | 48.2 |
| Sample | Dominant CaP Phase | hkl | Average Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A–500 V | CaPO3(OH) | 020 | 123.9 |
| 2−20 | |||
| −112 | |||
| A–600 V | CaPO3(OH) | 020 | 157.7 |
| 2−20 | |||
| −112 | |||
| B–500 V | Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O | 010 | 129.9 |
| −1−21 | |||
| −121 | |||
| B–600 V | Amorphous | ||
| C–300 V | CaPO3(OH) | 020 | 166.2 |
| 2−20 | |||
| −112 | |||
| C–400 V | Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O | 010 | 124.9 |
| −1−21 | |||
| −121 | |||
| C–500 V | CaPO3(OH) | 002 | 355 |
| 200 | |||
| C–600 V | γ–Ca2P2O7 | – | 209 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamaeva, A.; Kenzhegulov, A.; Panichkin, A.; Abdulvaliyev, R.; Fischer, D.; Bakhytuly, N.; Toiynbaeva, N. Influence of Current Duty Cycle and Voltage of Micro-Arc Oxidation on the Microstructure and Composition of Calcium Phosphate Coating. Coatings 2024, 14, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060766
Mamaeva A, Kenzhegulov A, Panichkin A, Abdulvaliyev R, Fischer D, Bakhytuly N, Toiynbaeva N. Influence of Current Duty Cycle and Voltage of Micro-Arc Oxidation on the Microstructure and Composition of Calcium Phosphate Coating. Coatings. 2024; 14(6):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060766
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamaeva, Axaule, Aidar Kenzhegulov, Aleksander Panichkin, Rinat Abdulvaliyev, Dametken Fischer, Nauryzbek Bakhytuly, and Nazgul Toiynbaeva. 2024. "Influence of Current Duty Cycle and Voltage of Micro-Arc Oxidation on the Microstructure and Composition of Calcium Phosphate Coating" Coatings 14, no. 6: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060766
APA StyleMamaeva, A., Kenzhegulov, A., Panichkin, A., Abdulvaliyev, R., Fischer, D., Bakhytuly, N., & Toiynbaeva, N. (2024). Influence of Current Duty Cycle and Voltage of Micro-Arc Oxidation on the Microstructure and Composition of Calcium Phosphate Coating. Coatings, 14(6), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14060766









