Chitosan Gel Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Membranes: A Novel Approach for the Remediation of Cadmium in Aqueous Solutions and Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Analysis
2.2. Stability in the Solution
2.3. Morphological Analysis
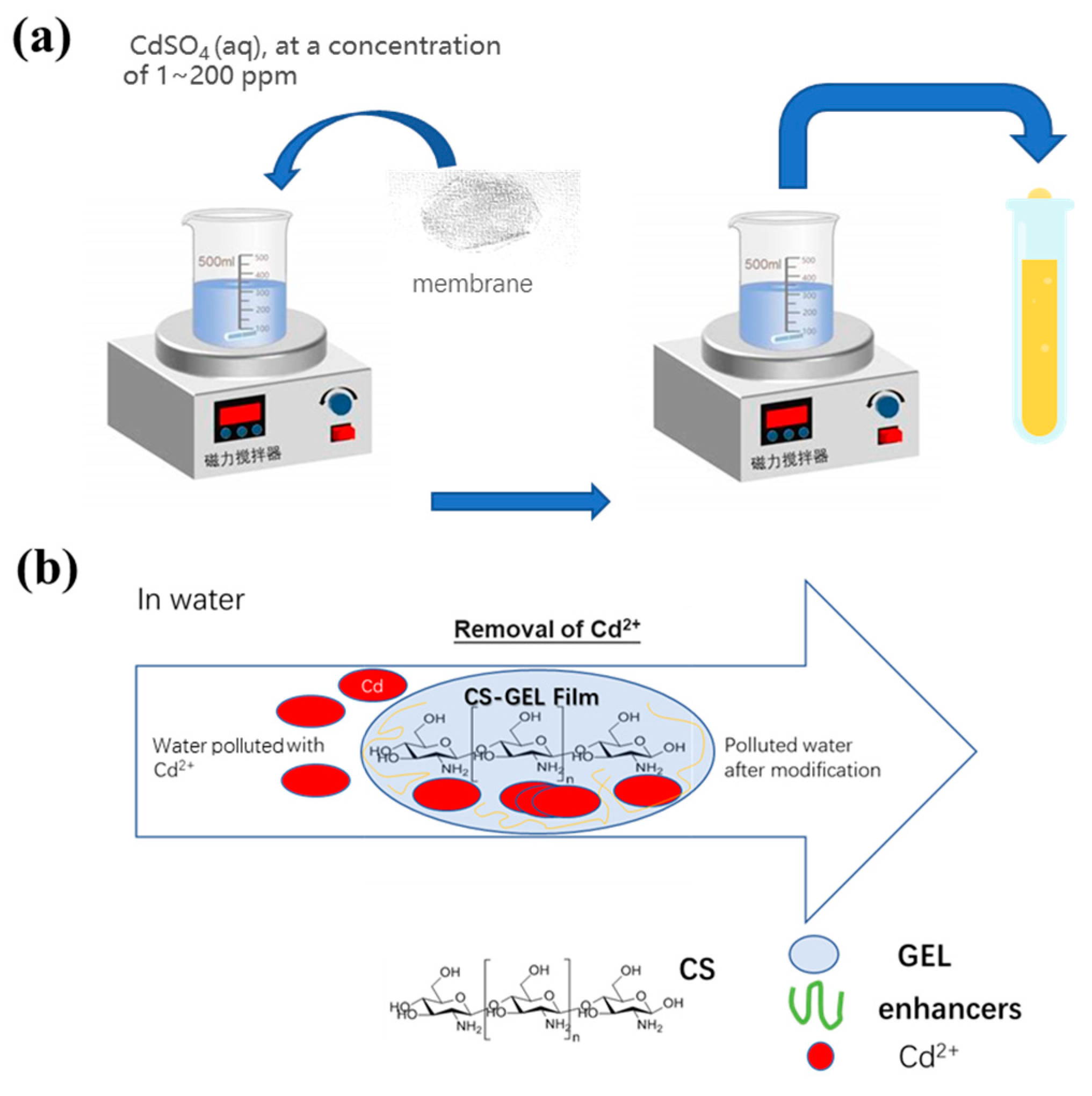
2.4. Application of Cd2+ Ion Sorption in Water Solution
2.5. Application of Soil Remediation
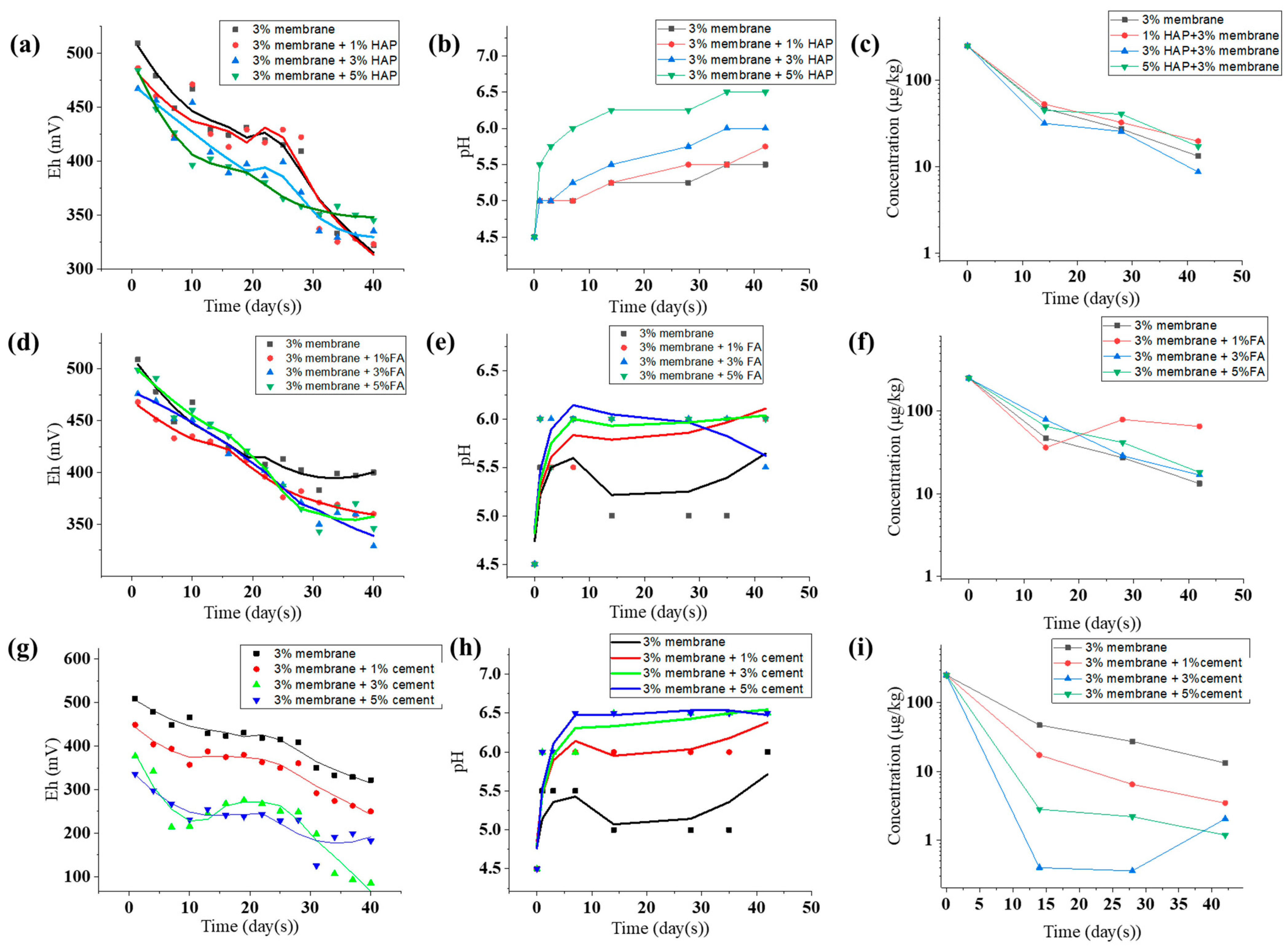
2.6. Optimized Application via Compound Use with Other Additives
2.7. Soil pH and CaCl2-Extractable Cd Concentration
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Membranes
3.3. Structural Characterization
3.4. Morphological Characterization
3.5. Adsorption Studies
3.6. Desorption Studies
3.7. Application in Soil Remediation
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, J.; Lin, Q.; Yao, X.; Yin, G. Removal of Cd from aqueous solution by chitosan coated MgO-biochar and its in-situ remediation of Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaney, W.R.; Strickland, R.C.; Lamoreaux, R.J. Phytotoxicity of cadmium inhibited by lime. Plant Soil 1977, 47, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. Effects of low-levels of dietary cadmium in animals—Review. J. Environ. Qual. 1977, 6, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, L. Cadmium and the kidney. Environ. Health Perspect. 1984, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandervoet, E.; Vanegmond, L.; Kleijn, R.; Huppes, G. Cadmium in the European-community: A policy-oriented analysis. Waste Manag. Res. 1994, 12, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, M.M.; Howerton, B.S.; Atwood, D.A. Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4757–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocher, C.; Dorda, J.; Mavrov, V.; Chmiel, H.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Matis, K.A. Hybrid flotation—Membrane filtration process for the removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4018–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, A.; Hubicki, Z.; Podkoscielny, P.; Robens, E. Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, M.R.; Fritt-Rasmussen, J.; Nielsen, S.; Ottosen, L.M. Electrodialytic removal of cadmium from wastewater sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 106, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, E.; Karapinar, N.; Donat, R. The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 280, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khraisheh, M.A.M.; Al-Degs, Y.S.; McMinn, W.A.M. Remediation of wastewater containing heavy metals using raw and modified diatomite. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 99, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobya, M.; Demirbas, E.; Senturk, E.; Ince, M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from apricot stone. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, J. Hematite enhances the immobilization of copper, cadmium and phosphorus in soil amended with hydroxyapatite under flooded conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by advanced carbon nanotubes: Critical review of adsorption applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Guo, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W. Biomass chitosan/sodium alginate colorimetric imprinting hydrogels with integrated capture and visualization detection for cadmium(II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 331, 121841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.G.; Ayuso, E.A.; De Blas, O.J. Sorption of heavy metals from industrial waste water by low-cost mineral silicates. Clay Miner. 1999, 34, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, C.; Feng, D. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater effluents by biosorptive flotation. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizares, P.; Perez, A.; Camarillo, R. Recovery of heavy metals by means of ultrafiltration with water-soluble polymers: Calculation of design parameters. Desalination 2002, 144, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, I.N.; Iyengar, L.; Rao, A.V.S.P. Removal of Cadmium Using Chitosan. J. Environ. Eng. 1988, 114, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.R.; Davids, W.G.; MacRae, J.D.; Amirbahman, A. Kinetics of cadmium uptake by chitosan-based crab shells. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, Z. Removal of heavy metal ions using chitosan and modified chitosan: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Shi, X.; Zhou, N.; Liu, K.; Ma, J.; Yu, F.; Li, Y. Mechanism underlying how a chitosan-based phosphorus adsorbent alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Bidens pilosa L. and its impact on soil microbial communities: A field study. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, M.; Adnan Ramzani, P.M.; Rasool, B.; Khan, M.A.; Ur-Rahman, M.; Akhtar, I.; Turan, V.; Tauqeer, H.M.; Farhad, M.; Khan, S.A.; et al. Efficacy of chitosan-coated textile waste biochar applied to Cd-polluted soil for reducing Cd mobility in soil and its distribution in moringa (Moringa oleifera L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, P.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, H. Remediation of Cd (II) ions in aqueous and soil phases using novel porous cellulose/chitosan composite spheres loaded with zero-valent iron nanoparticles. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 173, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, K.; Fan, Z.; Wang, P.; Xu, Z.; Ren, X.; Hu, S.; Gao, Z. Fabrication of double crosslinked chitosan/gelatin membranes with Na+ and pH dual-responsive controlled permeability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 115963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubilar, J.F.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Osorio, F.; Pedreschi, F. Physical properties of emulsion-based hydroxypropyl methylcellulose/whey protein isolate (HPMC/WPI) edible films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, W.; Li, S. Influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, methylcellulose, gelatin, poloxamer 407 and poloxamer 188 on the formation and stability of soybean oil-in-water emulsions. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ban, X.; Cheng, L.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.; Li, Z. Co-supported hydrocolloids improve the structure and texture quality of gluten-free bread. LWT 2021, 152, 112248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, A.; Mucha, M. Thermogravimetric and FTIR studies of chitosan blends. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 396, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Su, C.; Wu, M.; Wei, X.; Jiang, L.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) reduces the hardening of fructose-containing and maltitol-containing high-protein nutrition bars during storage. LWT 2022, 163, 113607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, L.; Abdolmaleki, K.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Bahmaei, M. Characterization of sodium caseinate/Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose concentrated emulsions: Effect of mixing ratio, concentration and wax addition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abdullah, O.G.; Hussein, S.A.; Ahmed, H.M. Effect of PVA Blending on Structural and Ion Transport Properties of CS:AgNt-Based Polymer Electrolyte Membrane. Polymers 2017, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowtham, G.K.; Hegde, V.N.; Meshk, S.; Sukrutha, S.K.; Somashekar, R. Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Soot Particles Doped HPMC Polymer Composites. J. Res. Updates Polym. Sci. 2015, 4, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, K.; Asadpour, G. Effects of HCl Hydrolyzed Cellulose Nanocrystals from Waste Papers on the Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose/Cationic Starch Biofilms. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demappa, T. Influence of KI Salt Concentration on the Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Films: Optical Study. Opt. Mater. 2022, 129, 112474. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, S.E.; Angeli, V.W.; Souza, K.C.B.d.; Miron, D.d.S.; Carvalho, G.d.A.; Santos, V.d.; Brandalise, R.N. Evaluation of the solubility of the HPMC: PVA blends in biological fluids in vitro. Mater. Res. 2011, 14, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elanchezhiyan, S.S.; Sivasurian, N.; Meenakshi, S. Enhancement of oil recovery using zirconium-chitosan hybrid composite by adsorptive method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 145, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B. Residual oil and suspended solid removal using natural adsorbents chitosan, bentonite and activated carbon: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 108, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E. Water treatment of hexavalent chromium by gelatin-impregnated-yeast (Gel–Yst) biosorbent. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elanchezhiyan, S.S.; Prabhu, S.M.; Meenakshi, S. Effective adsorption of oil droplets from oil-in-water emulsion using metal ions encapsulated biopolymers: Role of metal ions and their mechanism in oil removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichi, A.; Eliazyan, G.; Kazarian, S. Study of the Degradation and Conservation of Historical Leather Book Covers with Macro Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Imaging. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7150–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Graft copolymerization kinetics of ethyl acrylate onto hydroxypropyl methylcellulose using potassium persulphate as initiator in aqueous medium. Iran. Polym. J. 2006, 15, 467–475. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Guan, W.; Shi, S.; Blersch, D. Adsorption model development for mass transport characteristics of MFEP structure by physisorption method. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onundi, Y.; Mamun, A.; Al Khatib, M.; Al Saadi, M.; Suleyman, A. Heavy metals removal from synthetic wastewater by a novel nano-size composite adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 8, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhu, S. Competitive adsorption of copper (II), cadmium (II), lead (II) and zinc (II) onto basic oxygen furnace slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Fan, Y.; Yi, Q.; Li, R.; Zhou, J. Effects of goethite on the fractions of Cu, Cd, Pb, P and soil enzyme activity with hydroxyapatite in heavy metal-contaminated soil. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 45869–45877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Composition | pH 2 | pH 3 | pH 4 | pH 5 | pH 6 | pH 7 | pH 8 | pH 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGH-0 | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Stable |
| CGH-1 | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Unstable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable |
| CGH-2 | Unstable | Unstable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable |
| CGH-3 | Unstable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable |
| CGH-4 | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable |
| CGH-5 | Unstable | Unstable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, G.; Sun, J.; Kang, F.; Lv, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Ren, X. Chitosan Gel Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Membranes: A Novel Approach for the Remediation of Cadmium in Aqueous Solutions and Soils. Coatings 2024, 14, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14040421
Cai G, Sun J, Kang F, Lv Q, Liu J, Wang J, Gao Z, Ren X. Chitosan Gel Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Membranes: A Novel Approach for the Remediation of Cadmium in Aqueous Solutions and Soils. Coatings. 2024; 14(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14040421
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Guanyu, Jing Sun, Fei Kang, Qilin Lv, Jin Liu, Jie Wang, Zideng Gao, and Xueqin Ren. 2024. "Chitosan Gel Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Membranes: A Novel Approach for the Remediation of Cadmium in Aqueous Solutions and Soils" Coatings 14, no. 4: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14040421
APA StyleCai, G., Sun, J., Kang, F., Lv, Q., Liu, J., Wang, J., Gao, Z., & Ren, X. (2024). Chitosan Gel Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Membranes: A Novel Approach for the Remediation of Cadmium in Aqueous Solutions and Soils. Coatings, 14(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14040421






