Coating of Neural Electrodes with Platinum Nanoparticles Reduces and Stabilizes Impedance In Vitro and In Vivo in a Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
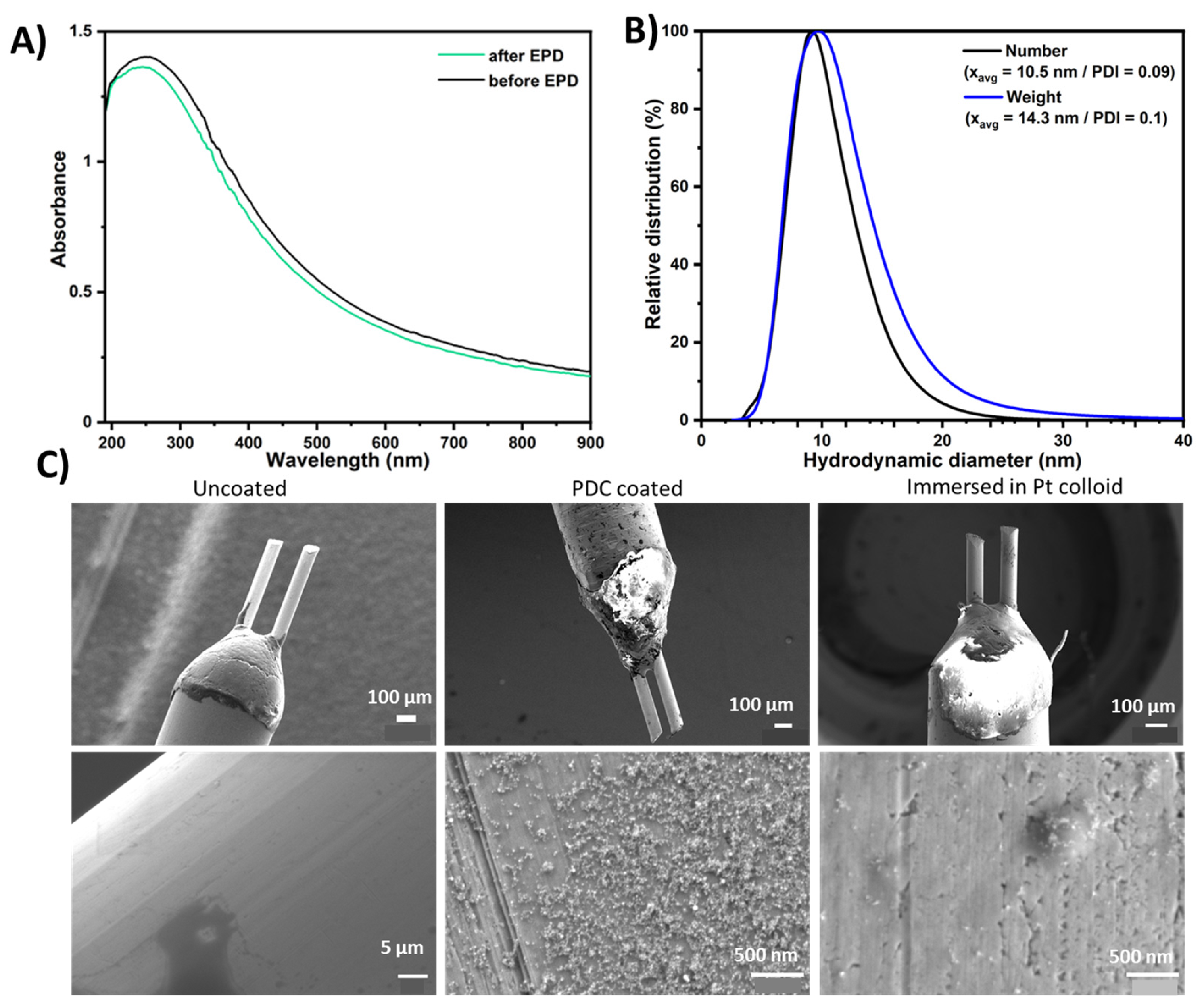
2.1. Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.2. Electrodes and Coating
2.3. Impedance Measurement
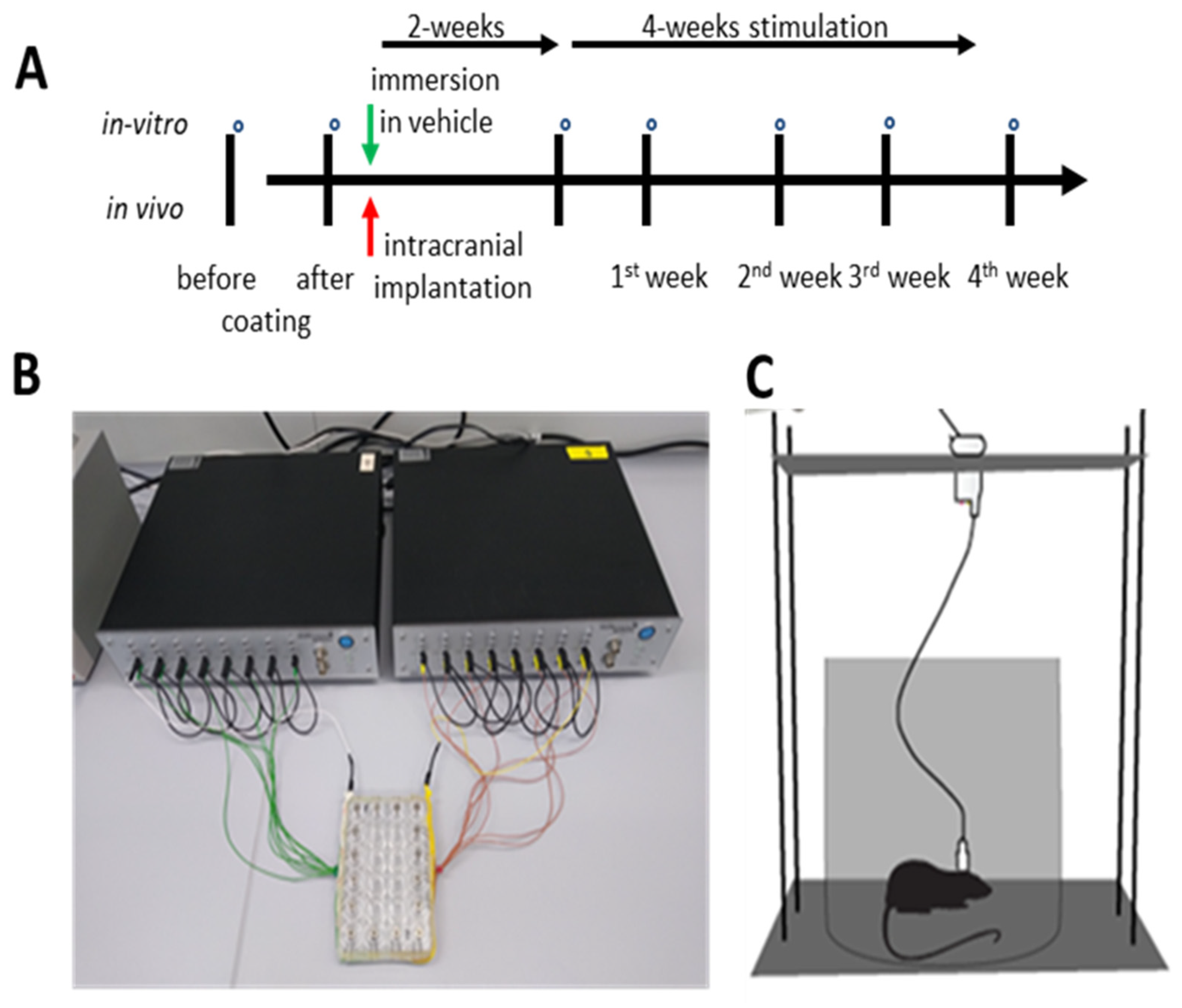
2.4. Animals
2.5. Surgery
2.6. Electrostimulation
2.7. Histology
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nanoparticles and Electrode Coatings
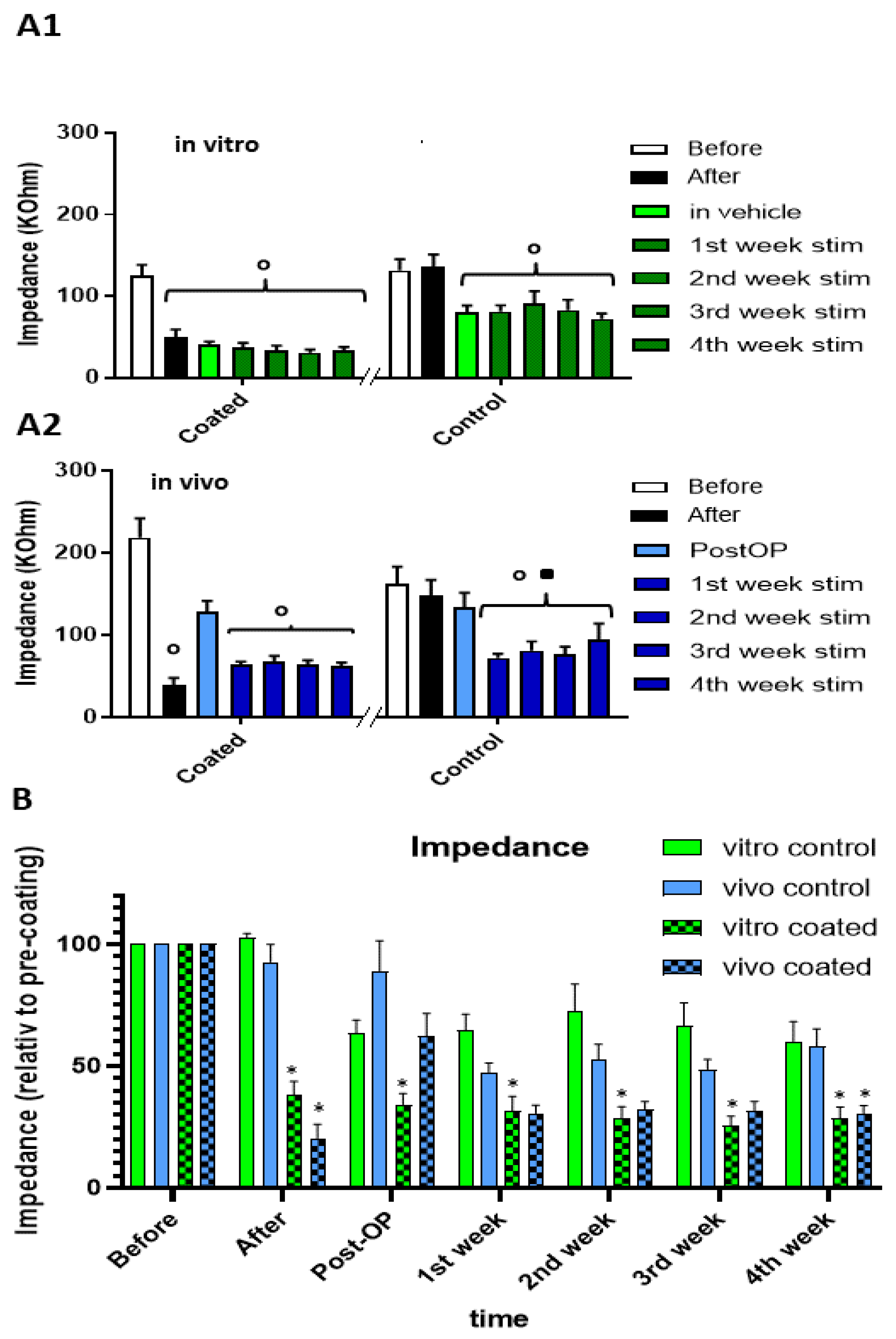
3.2. Impedance In Vitro
3.3. Impedance In Vivo
3.4. Normalized Data
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulder, M.; Mishra, A.; Mammis, A.; Horn, A.; Boutet, A.; Blomstedt, P.; Chabardes, S.; Flouty, O.; Lozano, A.M.; Neimat, J.S.; et al. Advances in Technical Aspects of Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2023, 101, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, J.K.; Lipsman, N.; Aziz, T.; Boutet, A.; Brown, P.; Chang, J.W.; Davidson, B.; Grill, W.M.; Hariz, M.I.; Horn, A.; et al. Technology of Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Status and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P.; Chabardes, S.; Chang, J.W.; Matthews, K.; McIntyre, C.C.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Schulder, M.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation: Current Challenges and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, M.S.; Foss, M.; Besenbacher, F. Influence of Nanoscale Surface Topography on Protein Adsorption and Cellular Response. Nano Today 2010, 5, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemo, B. Biological Surface Science. Surf. Sci. 2002, 500, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.; Wilkinson, C. Nantotechniques and Approaches in Biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehler, C.; Stieglitz, T.; Asplund, M. Nanostructured Platinum Grass Enables Superior Impedance Reduction for Neural Microelectrodes. Biomaterials 2015, 67, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehler, C.; Vieira, D.M.; Egert, U.; Asplund, M. NanoPt-A Nanostructured Electrode Coating for Neural Recording and Microstimulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14855–14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.; Wilkinson, C. Topographical Control of Cells. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, I.R.; Yu, C.; Sambangi, J.; Lee, C.D.; Whalen, J.J.; Petrossians, A.; Grill, W.M. Electrodeposited Platinum-Iridium Coating Improves In Vivo Recording Performance of Chronically Implanted Microelectrode Arrays. Biomaterials 2019, 205, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountas, K.N.; Smith, J.R.; Murro, A.M.; Politsky, J.; Park, Y.D.; Jenkins, P.D. Implantation of a Closed-Loop Stimulation in the Management of Medically Refractory Focal Epilepsy: A Technical Note. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2005, 83, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelov, S.D.; Koenen, S.; Jakobi, J.; Heissler, H.E.; Alam, M.; Schwabe, K.; Barcikowski, S.; Krauss, J.K. Electrophoretic Deposition of Ligand-Free Platinum Nanoparticles on Neural Electrodes Affects Their Impedance in Vitro and in Vivo with No Negative Effect on Reactive Gliosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristenpart, W.D.; Aksay, I.A.; Saville, D.A. Electrohydrodynamic Flow around a Colloidal Particle near an Electrode with an Oscillating Potential. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 575, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, V.; Rehbock, C.; Giera, B.; Karnes, J.J.; Forien, J.-B.; Angelov, S.D.; Schwabe, K.; Krauss, J.K.; Barcikowski, S. Comparing Direct and Pulsed-Direct Current Electrophoretic Deposition on Neural Electrodes: Deposition Mechanism and Functional Influence. Langmuir 2021, 37, 9724–9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, V.; Stratmann, N.; Schaufler, V.; Angelov, S.D.; Nordhorn, I.D.; Heissler, H.E.; Martínez-Hincapié, R.; Čolić, V.; Rehbock, C.; Schwabe, K.; et al. Mechanical Stability of Nano-Coatings on Clinically Applicable Electrodes, Generated by Electrophoretic Deposition. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, S.; Rehbock, C.; Heissler, H.E.; Angelov, S.D.; Schwabe, K.; Krauss, J.K.; Barcikowski, S. Optimizing in Vitro Impedance and Physico-Chemical Properties of Neural Electrodes by Electrophoretic Deposition of Pt Nanoparticles. Chemphyschem Eur. J. Chem. Phys. Phys. Chem. 2017, 18, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulbaki, A.; Doll, T.; Helgers, S.; Heissler, H.E.; Voges, J.; Krauss, J.K.; Schwabe, K.; Alam, M. Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation Restores Motor and Sensorimotor Cortical Neuronal Oscillatory Activity in the Free-Moving 6-Hydroxydopamine Lesion Rat Parkinson Model. Neuromodulation 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; ISBN 9780080475158. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, W.T.; Sasaki, T.; Koshizaki, N. Laser Ablation of a Platinum Target in Water. I. Ablation Mechanisms. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streubel, R.; Bendt, G.; Gökce, B. Pilot-Scale Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles by High-Speed Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 205602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streich, C.; Koenen, S.; Lelle, M.; Peneva, K. Influence of Ligands in Metal Nanoparticle Electrophoresis for the Fabrication of Biofunctional Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 348, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, S.; Streubel, R.; Jakobi, J.; Schwabe, K.; Krauss, J.K.; Barcikowski, S. Continuous Electrophoretic Deposition and Electrophoretic Mobility of Ligand-Free, Metal Nanoparticles in Liquid Flow. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, D174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidian, M.R.; Corey, J.M.; Kipke, D.R.; Martin, D.C. Conducting-Polymer Nanotubes Improve Electrical Properties, Mechanical Adhesion, Neural Attachment, and Neurite Outgrowth of Neural Electrodes. Small 2010, 6, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattahi, P.; Yang, G.; Kim, G.; Abidian, M.R. A Review of Organic and Inorganic Biomaterials for Neural Interfaces. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1846–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.A.; Langhals, N.B.; Joseph, M.D.; Richardson-Burns, S.M.; Hendricks, J.L.; Kipke, D.R. Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) Polymer Coatings Facilitate Smaller Neural Recording Electrodes. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butson, C.R.; Maks, C.B.; McIntyre, C.C. Sources and Effects of Electrode Impedance during Deep Brain Stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.B.; Achyuta, A.K.H.; Murthy, S.K. Bridging the Divide between Neuroprosthetic Design, Tissue Engineering and Neurobiology. Front. Neuroeng. 2010, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; McCreery, D.B.; Carter, R.R.; Bullara, L.A.; Yuen, T.G.; Agnew, W.F. Stability of the Interface between Neural Tissue and Chronically Implanted Intracortical Microelectrodes. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1999, 7, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolelis, M.A.L.; Dimitrov, D.; Carmena, J.M.; Crist, R.; Lehew, G.; Kralik, J.D.; Wise, S.P. Chronic, Multisite, Multielectrode Recordings in Macaque Monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11041–11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polikov, V.S.; Tresco, P.A.; Reichert, W.M. Response of Brain Tissue to Chronically Implanted Neural Electrodes. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 148, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenbuerger, M.; Nolte, K.W.; Coenen, V.A.; Burgunder, J.-M.; Krauss, J.K.; Weis, J. Brain Alterations with Deep Brain Stimulation: New Insight from a Neuropathological Case Series. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.F.; Grill, W.M. Impedance Characteristics of Deep Brain Stimulation Electrodes in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 046008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satzer, D.; Yu, H.; Wells, M.; Padmanaban, M.; Burns, M.R.; Warnke, P.C.; Xie, T. Deep Brain Stimulation Impedance Decreases Over Time Even When Stimulation Settings Are Held Constant. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 584005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Gunduz, A.; Shute, J.; Eisinger, R.; Cernera, S.; David Ho, K.W.; Martinez-Ramirez, D.; Almeida, L.; Wilson, C.A.; Okun, M.S.; et al. Longitudinal Follow-up of Impedance Drift in Deep Brain Stimulation Cases. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2018, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bärsch, N.; Jakobi, J.; Weiler, S.; Barcikowski, S. Pure Colloidal Metal and Ceramic Nanoparticles from High-Power Picosecond Laser Ablation in Water and Acetone. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 445603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, J.A.; Maddux, B.L.S.; Hutchison, J.E. Toward Greener Nanosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2228–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, A.; Koenen, S.; Schwabe, K.; Rehbock, C.; Barcikowski, S. How Electrophoretic Deposition with Ligand-Free Platinum Nanoparticles Affects Contact Angle. Key Eng. Mater. 2015, 654, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobi, J.; Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Chakravadhanula, V.S.K.; Kienle, L.; Wagener, P.; Barcikowski, S. Stoichiometry of Alloy Nanoparticles from Laser Ablation of PtIr in Acetone and Their Electrophoretic Deposition on PtIr Electrodes. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 145601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, V.; Giera, B.; Karnes, J.J.; Stratmann, N.; Schaufler, V.; Li, Y.; Rehbock, C.; Barcikowski, S. Electrophoretic Deposition of Platinum Nanoparticles Using Ethanol-Water Mixtures Significantly Reduces Neural Electrode Impedance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 022504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.A.; Hadzhieva, Z.; Dlouhý, I.; Boccaccini, A.R. Electrophoretic Deposition and Characterization of Functional Coatings Based on an Antibacterial Gallium (III)-Chitosan Complex. Coatings 2020, 10, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besra, L.; Liu, M. A Review on Fundamentals and Applications of Electrophoretic Deposition (EPD). Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, J.; Sridhar, K.; Liegey, J.; Brady, J.; Jahns, H.; Lowery, M. Stimulation-Induced Changes at the Electrode-Tissue Interface and Their Influence on Deep Brain Stimulation. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 19, 046004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, M.; Unsworth, C.P.; Gouws, G.J.; Plank, N.O.V. Synthesis of Encapsulated ZnO Nanowires Provide Low Impedance Alternatives for Microelectrodes. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.J.; Oswald, J.; Krüger, T. Electrophoretic Deposition of Dielectric Film on Stimulation Electrodes for the Use in Intraoperative Neuromonitoring. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 4, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Biest, O.O.; Vandeperre, L.J. Electrophoretic Deposition of Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1999, 29, 327–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| In Vitro | In Vivo | |
|---|---|---|
| mean ± SD, impedance in kΩ coated/uncoated (ctl) | 33.8 ± 12.7/82.0 ± 29.9 | 64.8 ± 13.2/81.3 ± 31.9 |
| LEVENE | F(1,58) = 12.126, p = 0.001 | F(1,54) = 5.521, p = 0.0225 |
| BARTELETT | χ2 = 18.050, p < 0.0001 | χ2 = 18.342 p < 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelov, S.D.; Rehbock, C.; Ramesh, V.; Heissler, H.E.; Alam, M.; Barcikowski, S.; Schwabe, K.; Krauss, J.K. Coating of Neural Electrodes with Platinum Nanoparticles Reduces and Stabilizes Impedance In Vitro and In Vivo in a Rat Model. Coatings 2024, 14, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030352
Angelov SD, Rehbock C, Ramesh V, Heissler HE, Alam M, Barcikowski S, Schwabe K, Krauss JK. Coating of Neural Electrodes with Platinum Nanoparticles Reduces and Stabilizes Impedance In Vitro and In Vivo in a Rat Model. Coatings. 2024; 14(3):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030352
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelov, Svilen D., Christoph Rehbock, Vaijayanthi Ramesh, Hans E. Heissler, Mesbah Alam, Stephan Barcikowski, Kerstin Schwabe, and Joachim K. Krauss. 2024. "Coating of Neural Electrodes with Platinum Nanoparticles Reduces and Stabilizes Impedance In Vitro and In Vivo in a Rat Model" Coatings 14, no. 3: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030352
APA StyleAngelov, S. D., Rehbock, C., Ramesh, V., Heissler, H. E., Alam, M., Barcikowski, S., Schwabe, K., & Krauss, J. K. (2024). Coating of Neural Electrodes with Platinum Nanoparticles Reduces and Stabilizes Impedance In Vitro and In Vivo in a Rat Model. Coatings, 14(3), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030352





