Understanding the Fracture Failure Mechanism of WC Particle-Reinforced FeCoCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Coatings at 600 °C
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
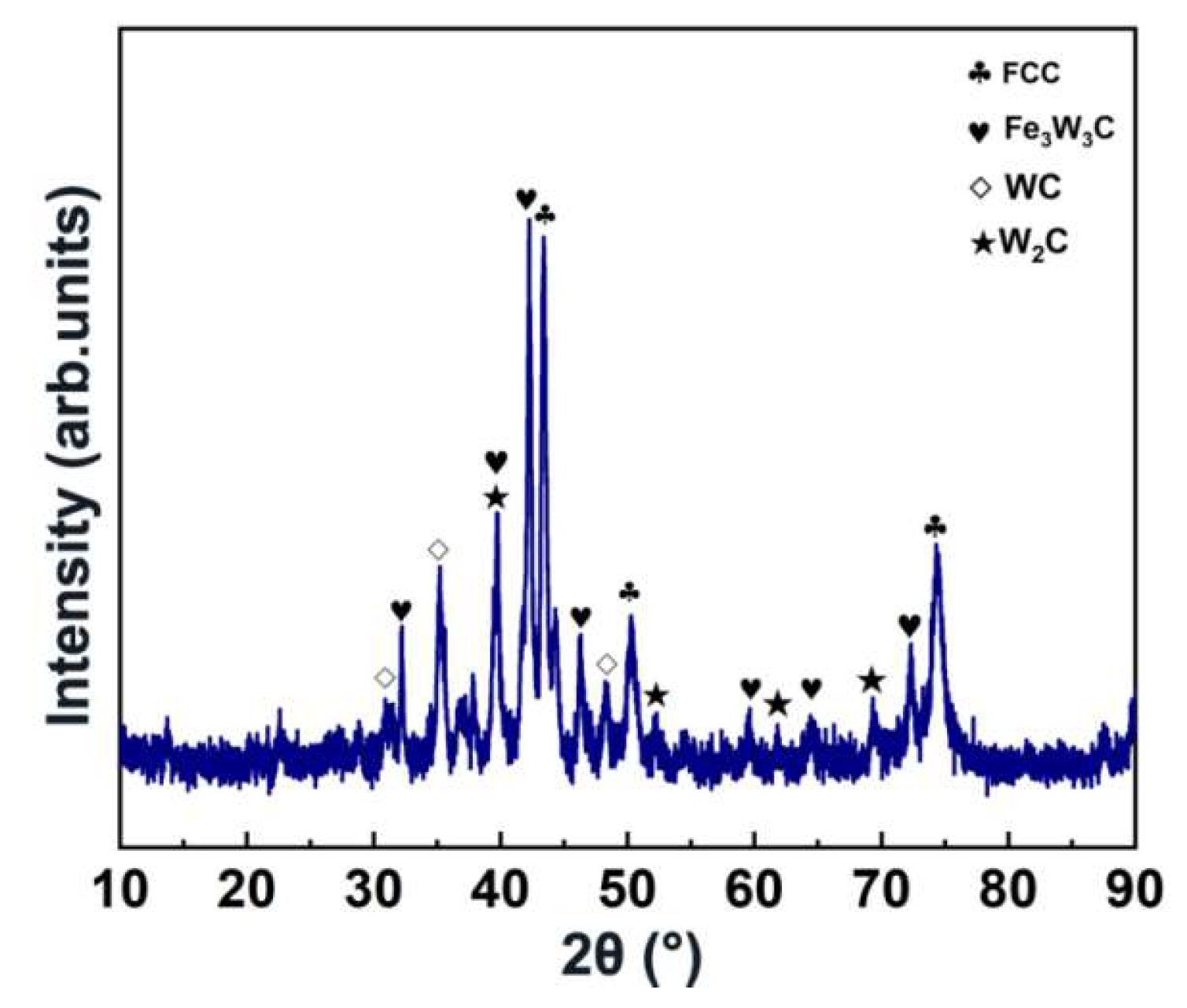
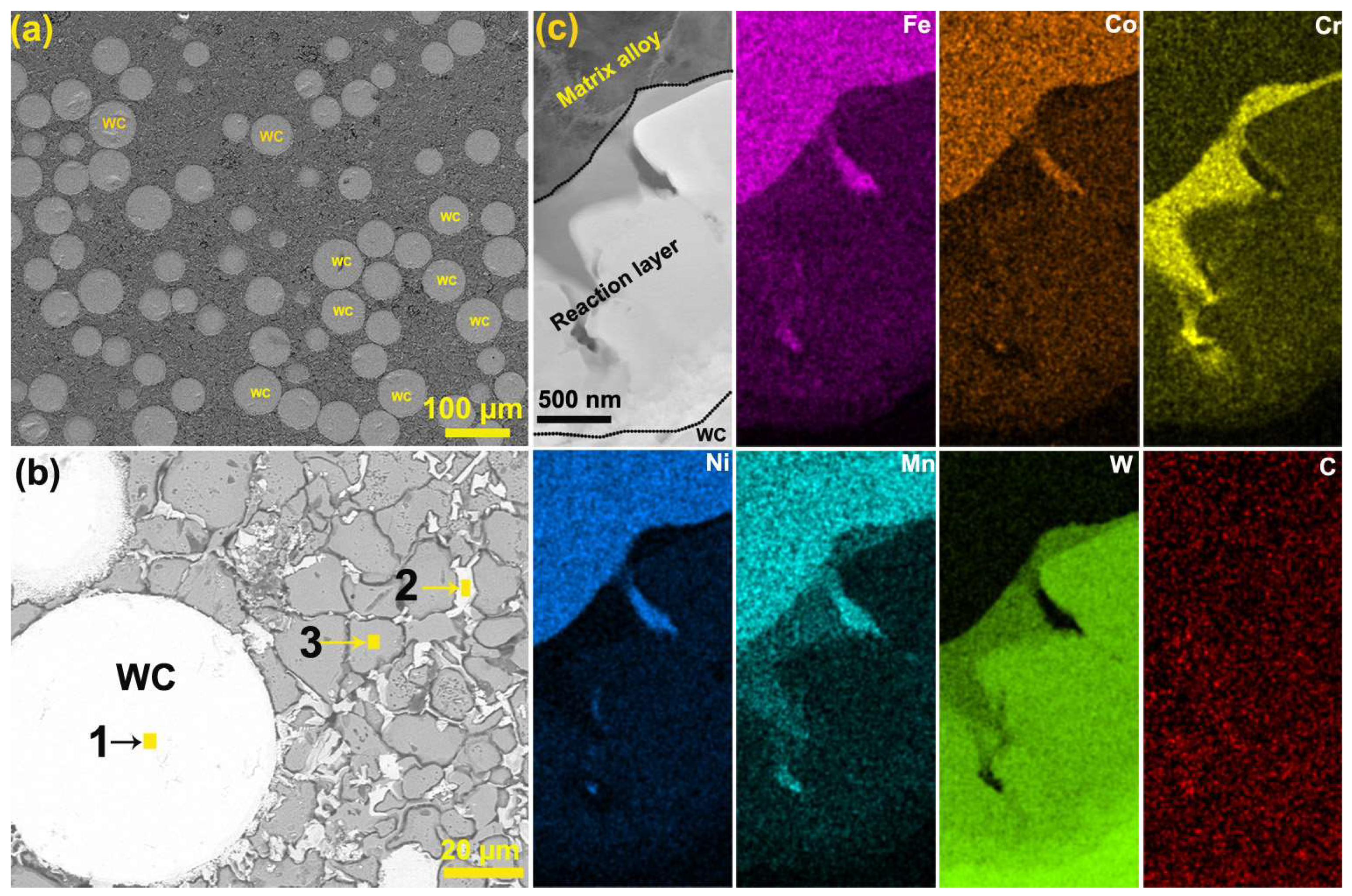
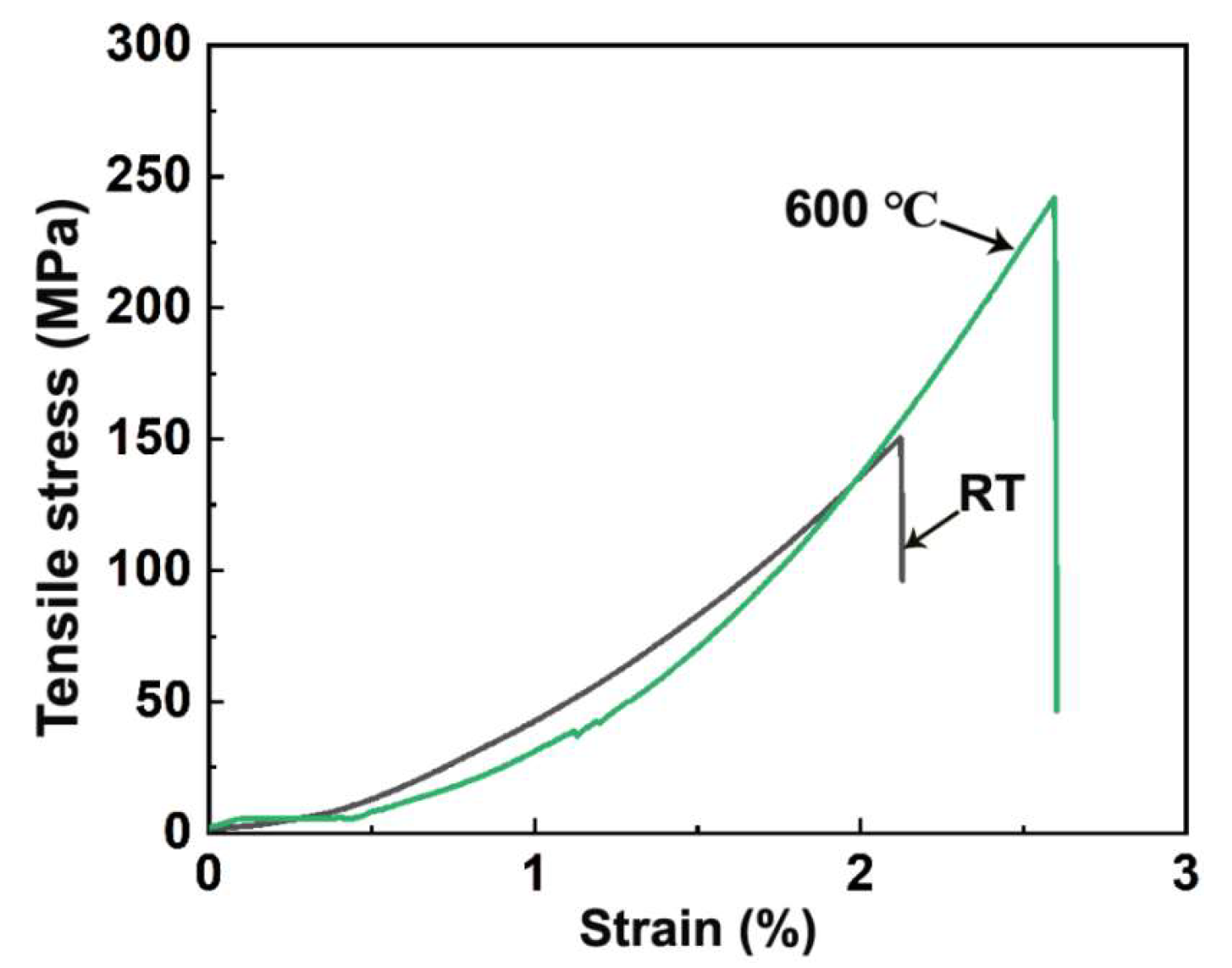
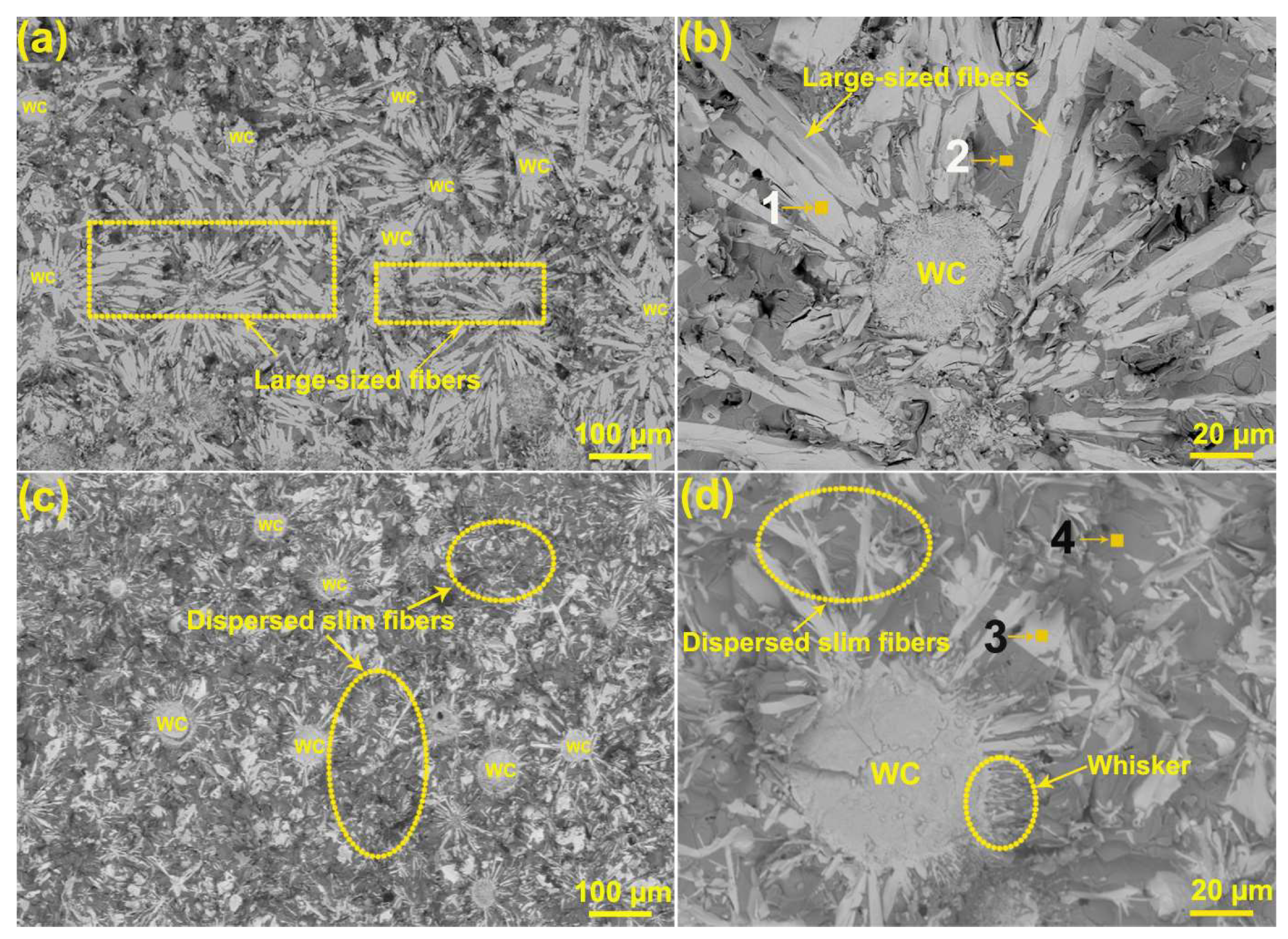
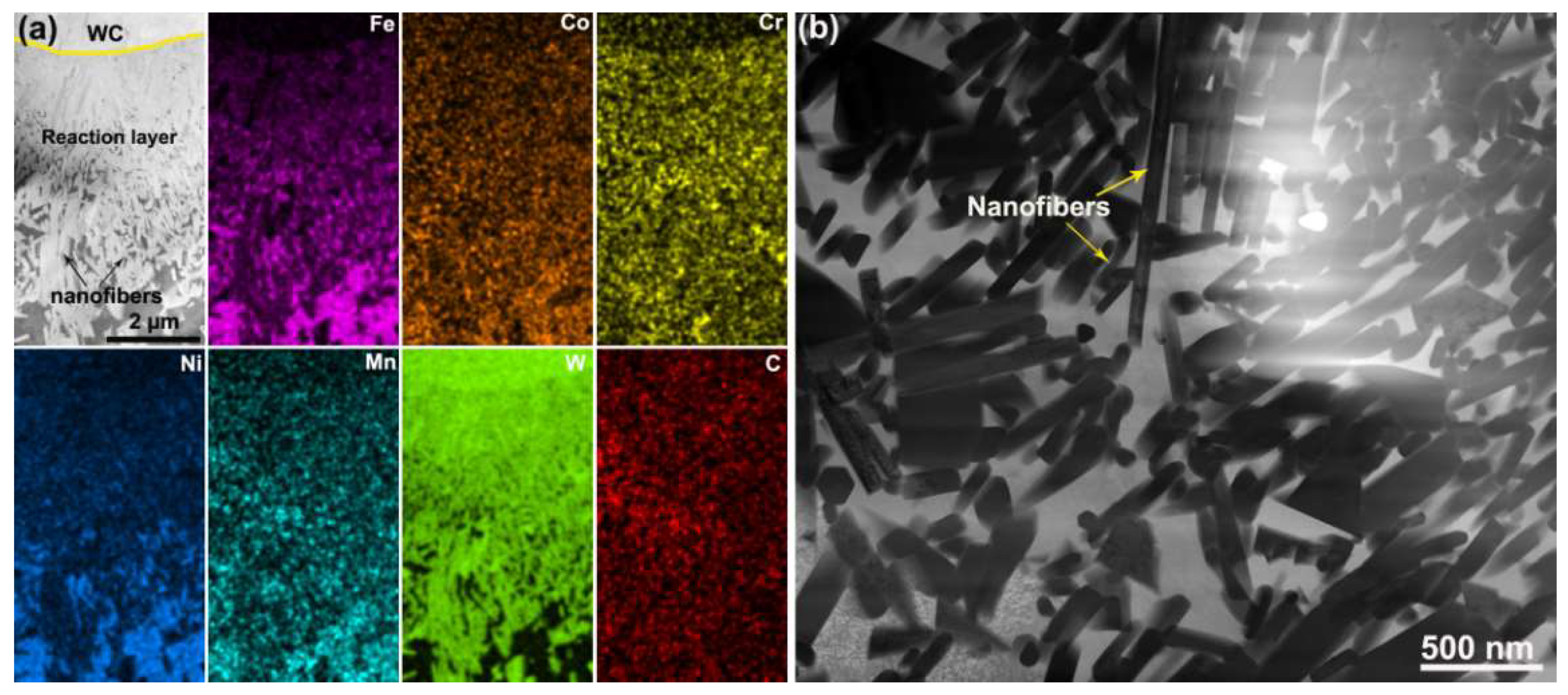
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbari, M.K.; Baharvandi, H.R.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K. Tensile and fracture behavior of nano/micro TiB2 particle reinforced casting A356 aluminum alloy composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Guo, F.; Huang, X.; Li, K.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Gong, F. Understanding the anti-wear mechanism of SiCp/WE43 magnesium matrix composite. Vacuum 2020, 172, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Yan, F.; Duan, R.; Huang, Y. Effect of strengthening particles on the dry sliding wear behavior of Al2O3-M7C3/Fe metal matrix composite coatings produced by laser cladding. Wear 2015, 324–325, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Dai, X.Q. Laser induction hybrid rapid cladding of WC particles reinforced NiCrBSi composite coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4708–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Deng, Q.L.; Zheng, J.F.; Dong, G.; Yang, J.G. Microstructure and wear behaviour of laser clad NiCrBSi+Ta composite coating. Surf. Eng. 2011, 28, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Tan, Y.F.; Wang, X.L.; Jing, Q.F.; Hong, X. Tribological properties of laser cladding TiB2 particles reinforced Ni-base alloy composite coatings on aluminum alloy. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, S. Effect of WC content on microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high-entropy alloy/WC composite coatings by plasma cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Chen, R.R.; Liu, T.; Gao, X.F.; Qin, G.; Wu, S.P.; Guo, J.J. Unraveling the oxidation mechanism of Y-doped AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy at 1100 °C. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 652, 159316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, W.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Peng, Y.B.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, Y. Interfacial structures and mechanical properties of a high entropy alloy-diamond composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 86, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Peng, Y.B.; Liu, F.Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, Y. Effect of Ti/Ni coating of diamond particles on microstructure and properties of high-entropy alloy/diamond composites. Entropy 2019, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.C.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, Y. Microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy/WC reinforcing particles composite coatings prepared by laser cladding and plasma cladding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 84, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedyev, S.P.; Vdovin, K.N.; Emelyushin, A.N. Peculiarities of forming of the wear-resistant cast iron coating structure on steel 45 upon plasma-powder surfacing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 870, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Welding current (A) | 150 |
| Powder feeding capacity (rad/min) | 40 |
| Protective gas flow rate (L/min) | 1 |
| Powder feeding gas flow rate (L/min) | 4 |
| Ion gas flow rate (L/min) | 2 |
| Welding speed (mm/min) | 170 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Z. Understanding the Fracture Failure Mechanism of WC Particle-Reinforced FeCoCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Coatings at 600 °C. Coatings 2024, 14, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030339
Wang X, Zhang S, Zhao F, Wu Z, Xie Z. Understanding the Fracture Failure Mechanism of WC Particle-Reinforced FeCoCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Coatings at 600 °C. Coatings. 2024; 14(3):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030339
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinbo, Shihan Zhang, Fei Zhao, Zhisheng Wu, and Zhiwen Xie. 2024. "Understanding the Fracture Failure Mechanism of WC Particle-Reinforced FeCoCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Coatings at 600 °C" Coatings 14, no. 3: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030339
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, S., Zhao, F., Wu, Z., & Xie, Z. (2024). Understanding the Fracture Failure Mechanism of WC Particle-Reinforced FeCoCrNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Coatings at 600 °C. Coatings, 14(3), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14030339






