Abstract
A detailed electron microscopy study was performed to clarify the fracture mechanism of WC particles reinforced with FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy coatings at 600 °C. Large-sized fibers and elemental segregation formed in the coating, triggering high local stress in the matrix alloy and resulting in a low tensile strength of 150 MPa. High temperature promoted the homogenization process of elemental segregation, but also facilitated the dissolution of large-sized fibers, resulting in the growth of slim fibers and nanofibers. Both the structural homogenization and multi-scale fiber strengthening led to an enhanced tensile strength of 242 MPa at 600 °C. These current findings provide an understanding of the fracture mechanism of HEA/WC coatings during high-temperature exposure.
1. Introduction
Particle-reinforced metal matrix composite coatings have received widespread attention because of their good mechanical and excellent anti-wear properties [1,2,3]. Up to now, different hard particles, such as TiC, Al2O3 and WC, have been added into metal matrix coatings [4,5,6]. Unfortunately, the poor wettability of the metal matrix coatings severely diminishes the interface bonding strength between the hard phase and the metal matrix, leading to unsatisfactory wear resistance [7]. High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have superior mechanical properties at elevated temperatures [8,9], but also show good wettability with hard particles [10,11], which indicates that HEAs show promise for potential use as a metal matrix material.
The fabrication and wear behaviors of the hard phases of reinforced HEA coatings are the research focus of this study. Zhang et al. [7] prepared the HEA/WC coating through laser cladding (LC). They reported that this coating with a WC proportion of 60% showed the greatest hardness and the best wear resistance. They also investigated the wear behaviors of HEA/WC coatings fabricated through LC and plasma cladding (PC) [12]. Their results revealed that the LC coating possessed better wear resistance than the PC coating. However, relatively little research on the fracture behavior of this coating has been reported. Here, a detailed characterization was performed to investigate the fracture behavior of this coating at room temperature (RT) and 600 °C. The fracture mechanism of the coating was further discussed systematically.
2. Materials and Methods
FeCoCrNiMn/WC HEA composite coatings were fabricated on 45# steel through plasma cladding (DML-V03AD). FeCoCrNiMn powder was prepared by the nitrogen vacuum aerosol process, and its diameter ranged from 45 μm to 105 μm, while the spherical WC powder had a diameter of approximately 53–150 um. These powders were heated and dried at a temperature of 80 °C for 2 h, and then uniformly mixed in a ball mill according to the predetermined WC mass fraction of 80%. The plasma cladding parameters are displayed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Plasma cladding parameters of the coatings.
The phase structure of the coating was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, X’ Pert Powder, PANalytical B.V., Almelo, The Netherlands) with a Cu-Kα radiation source. In order to enhance the resolution, a graphite crystal monochromator was incorporated into the optical path to eliminate Kβrays. The surface morphology of the coating was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Zeiss ∑IGMA HD, Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). The local compositions of the coating were detected by an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS, Bruker instrument, Karlsruhe, Germany) equipped on the SEM instrument. The cross-sectional elemental mappings of the coating were characterized by a transmission electron microscope (TEM, Thermofisher Talos F200X, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an EDS (Thermofisher Super-X G2 EDS Detector, Waltham, MA, USA). The fracture behaviors of the coating were tested by tensile testing (Fule Instrument Technology Co., Ltd., FL4304GL, Shanghai, China). The temperatures were at RT and 600 °C. The fracture images of the coatings were observed by the SEM.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1 displays the XRD result of the coating. The diffraction peaks located at 43.4°, 50.2° and 74.3° correspond to the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, while the diffraction peaks located at 30.9°, 35.2° and 48.4° are attributed to the WC phases [7]. In addition, the Fe3W3C phases are characterized at 32.1°, 39.7°, 42.3°, 46.3°, 59.6°, 64.4° and 72.3° [7], while the W2C phases are identified at 39.7°, 52.3°, 61.8° and 69.3° [7]. The appearance of Fe3W3C and W2C implies the decomposition of the WC particles during the surfacing process.
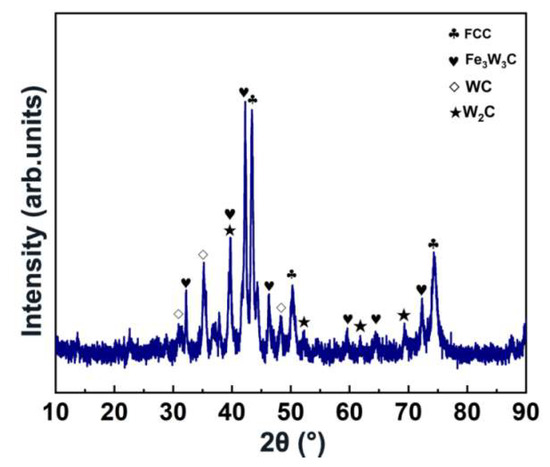
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of the prepared coating.
Figure 2a shows the surface SEM image of the coating. It can be found that this coating has a typical composite structure, and plenty of WC particles are embedded in the alloy matrix. The local magnified image in Figure 2b reveals that the matrix alloy presents a network structure accompanied with many white dispersed phases. The EDS result in point 1 confirms a high W content of 41.43 at. % and a high C content of 52.39 at. %, corresponding to the WC particles. However, the compositions of the white dispersed phases in point 2 are 25.27 at. % W, 29.60 at. % C, 12.77 at. % Cr, 13.60 at. % Ni, 6.74 at. % Fe, 5.09 at. % Co and 1.29 at. % Mn, indicating that these WC particles experience decomposition during the cladding process, resulting in the formation of alloy phases enriched with W and C. In addition, a high C content of 20.70 at. % is detected in point 3, indicating a rapid diffusion of C atoms in the alloy matrix. WC decomposition is further confirmed by the TEM result in Figure 2c, showing that a clear reaction layer forms between the WC particles and the matrix alloy.
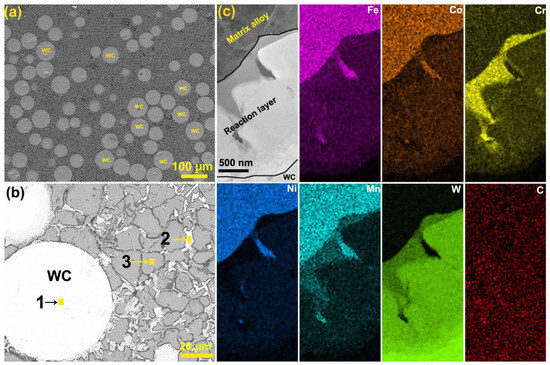
Figure 2.
(a,b) Surface and local magnified SEM image of the coating; (c) cross-sectional TEM element mappings of the WC particles.
Figure 3 displays the tensile stress–strain curves of the coating at RT and 600 °C. The tensile strength of the coating is about 150 MPa at RT, but reaches a higher value of 242 MPa as the temperature increases to 600 °C. In addition, this coating possesses a strain of 2.1% at RT, but displays a higher strain of 2.6% at 600 °C. The tensile test results clearly confirm that this coating exhibits an enhanced fracture resistance at 600 °C.
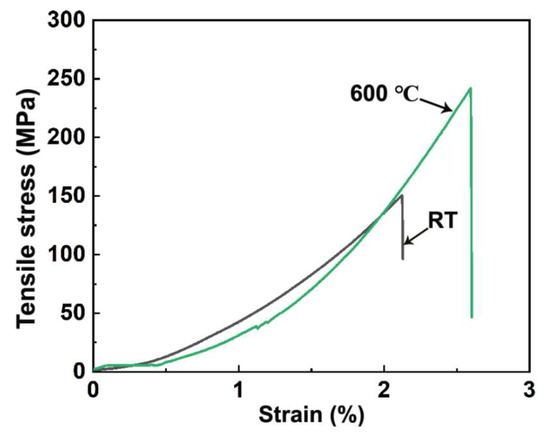
Figure 3.
Tensile stress–strain curves of the coating at evaluated temperatures.
Figure 4a,b present the fracture morphology of the coating at RT. This coating possesses a typical brittle fracture. Plenty of large-sized fibers appear on the fracture. Compared with the SEM surface image of the coating, these large-sized fibers form in the middle of the coating, which mainly originates from a relatively slow cooling rate that provides sufficient dendrite precipitation time. In addition, the compositions of point 1 are 26.05 at. % W, 24.20 at. % C, 5.31 at. % Cr, 15.17 at. % Ni, 16.92 at. % Fe, 4.84 at. % Co and 12.92 at. % Mn, which proves that these fibers are the white phases. In contrast, the matrix alloy contains a high C content of 22.99 at. % (point 2), confirming rapid diffusion of C atoms during the cladding. As shown in Figure 4c, this coating also exhibits a brittle fracture at 600 °C, but these large-sized fibers have disappeared and have been replaced by numerous slim fibers. The SEM image in Figure 4d shows that these slim fibers are randomly distributed in the matrix alloy. Plenty of whiskers also form at the edge of the WC particles. According to the EDS result of point 3, a high W of 28.03 at. % and a high C content of 27.85 at. % are detected in the slim texture, but a higher C of 28.57 at. % and a higher Ni of 25.36 at. % are detected in the matrix alloy (point 4). Apparently, prominent homogenization of both the dispersed phase and the matrix alloy occurs during the 600 °C tensile test.
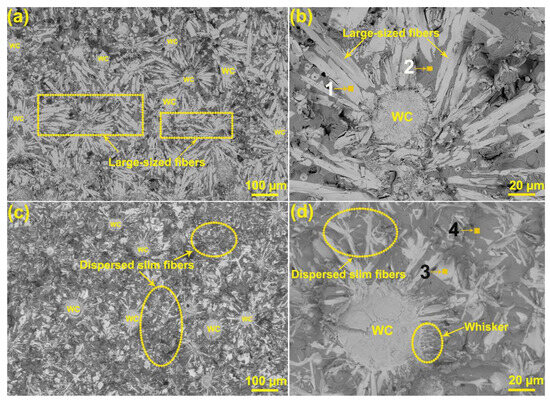

Figure 4.
Fracture images of the coating at evaluated temperatures: (a,b) RT; (c,d) 600 °C.
TEM characterizations are performed to clarify the homogenization behavior of the coating during the 600 °C tensile test. As shown in Figure 5a, a clear dissolution of WC particles occurs, reflected by a widened diffusion layer between the WC particles and the matrix alloy. Meanwhile, high-density nanofibers form in the reaction layer. As shown in Figure 5b, these nanofibers also appear in the matrix alloy. Apparently, these WC particles experience aggravated decomposition at 600 °C, and eventually result in the growth of nanofibers.
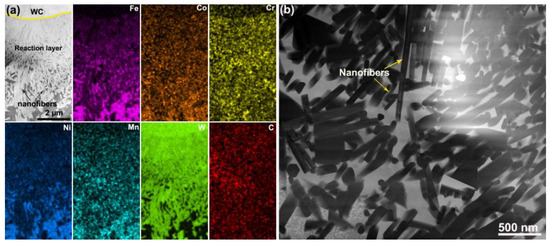
Figure 5.
Cross-sectional TEM characterization results of the coating after the 600 °C tensile test: (a) elemental mappings of WC particles; (b) TEM image of the matrix alloy.
Based on the characterization results, this coating illustrates unsatisfactory fracture resistance at RT, which likely originates from its non-uniform structure. As reported by a previous study [13], the plasma surfacing technique includes a high heat input and fast cooling. The high-temperature molten pool benefits the growth of coarse textures, while a fast cooling time delays the elemental diffusion, leading to local segregation. As identified by the results of Figure 2b and Figure 4a, during the surfacing process, WC decomposition induces the formation of large-sized fibers and local elemental segregation, triggering high local stress in the matrix alloy, and eventually results in poor tensile properties. However, this coating possesses an enhanced fracture resistance at 600 °C, which is mainly attributed to the structural homogenization and fiber strengthening. As identified by the SEM images of Figure 4, during the 600 °C tensile test, the high temperature promotes the structural homogenization process, but also drives the dissolution of large-sized fibers, resulting in the growth of slim fibers. As identified by the TEM images of Figure 5, the high temperature aggravates WC decomposition and induces the formation of numerous nanofibers. The homogenized structure is expected to relieve local high stress, while these slim fibers and nanofibers induce a prominent nailing effect and reinforce the matrix alloy. Therefore, the strong synergistic effect of structural homogenization and muti-scale fiber strengthening eventually leads to a significant enhancement in the fracture resistance of the coating at 600 °C.
4. Conclusions
This work investigated the fracture failure behavior of FeCoCrNiMn/WC HEA composite coatings at RT and 600 °C. The high temperature molten pool induced WC decomposition and triggered the formation of large-sized fibers. Fast cooling led to elemental segregation due to insufficient diffusion, both of which triggered high stress initiation and resulted in poor fracture resistance of the coating. During the 600 °C tensile test, thermal drive promoted the coating’s homogenization, but also aggravated the dissolution of large-sized fibers and WC particles. Numerous slim fibers and nanofibers formed in the matrix alloy, triggering a prominent nailing effect. The strong synergy of structural homogenization and muti-scale fiber strengthening resulted in enhanced fracture resistance of the coating at 600 °C. Therefore, for potential engineering applications, a very necessary vacuum annealing treatment should be employed to improve the mechanical properties of the WC-reinforced HEA coating.
Author Contributions
X.W., investigation and writing—original draft preparation; S.Z., investigation and methodology; F.Z., data curation and investigation; Z.W., conceptualization, and writing—reviewing and editing; Z.X., conceptualization, and writing—reviewing and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors appreciate the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2018YFA0707305), the Key R&D program of Shanxi Province (No. 202102050201001), the Shanxi Key Research and Development Program (No. 202101120401008), the Shanxi Youth Science Foundation Project (No. 201901D211291), the 2023 Open R&D project of the Research Institute of Haian Taiyuan University of Technology (No. 2023HA-TYUTKFYF012), and the Graduate Education Innovation Project of Taiyuan University of Science and Technology (No. BY 2022005).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Institute of Electron Microscope Center of Shenzhen University for their TEM technical supports.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Akbari, M.K.; Baharvandi, H.R.; Shirvanimoghaddam, K. Tensile and fracture behavior of nano/micro TiB2 particle reinforced casting A356 aluminum alloy composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Guo, F.; Huang, X.; Li, K.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Gong, F. Understanding the anti-wear mechanism of SiCp/WE43 magnesium matrix composite. Vacuum 2020, 172, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Luo, Z.; Li, Y.; Yan, F.; Duan, R.; Huang, Y. Effect of strengthening particles on the dry sliding wear behavior of Al2O3-M7C3/Fe metal matrix composite coatings produced by laser cladding. Wear 2015, 324–325, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Dai, X.Q. Laser induction hybrid rapid cladding of WC particles reinforced NiCrBSi composite coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4708–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Deng, Q.L.; Zheng, J.F.; Dong, G.; Yang, J.G. Microstructure and wear behaviour of laser clad NiCrBSi+Ta composite coating. Surf. Eng. 2011, 28, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Tan, Y.F.; Wang, X.L.; Jing, Q.F.; Hong, X. Tribological properties of laser cladding TiB2 particles reinforced Ni-base alloy composite coatings on aluminum alloy. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, S. Effect of WC content on microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high-entropy alloy/WC composite coatings by plasma cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Chen, R.R.; Liu, T.; Gao, X.F.; Qin, G.; Wu, S.P.; Guo, J.J. Unraveling the oxidation mechanism of Y-doped AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy at 1100 °C. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 652, 159316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.H.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, W.R.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, J.W. Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6308–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Peng, Y.B.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, Y. Interfacial structures and mechanical properties of a high entropy alloy-diamond composite. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 86, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Peng, Y.B.; Liu, F.Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, Y. Effect of Ti/Ni coating of diamond particles on microstructure and properties of high-entropy alloy/diamond composites. Entropy 2019, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.B.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.C.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Hu, S.H.; Hu, Y. Microstructures and mechanical properties of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy/WC reinforcing particles composite coatings prepared by laser cladding and plasma cladding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 84, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefedyev, S.P.; Vdovin, K.N.; Emelyushin, A.N. Peculiarities of forming of the wear-resistant cast iron coating structure on steel 45 upon plasma-powder surfacing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 870, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).