Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained from Moringa oleifera Seed Cake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of M. oleifera Cake Extracts
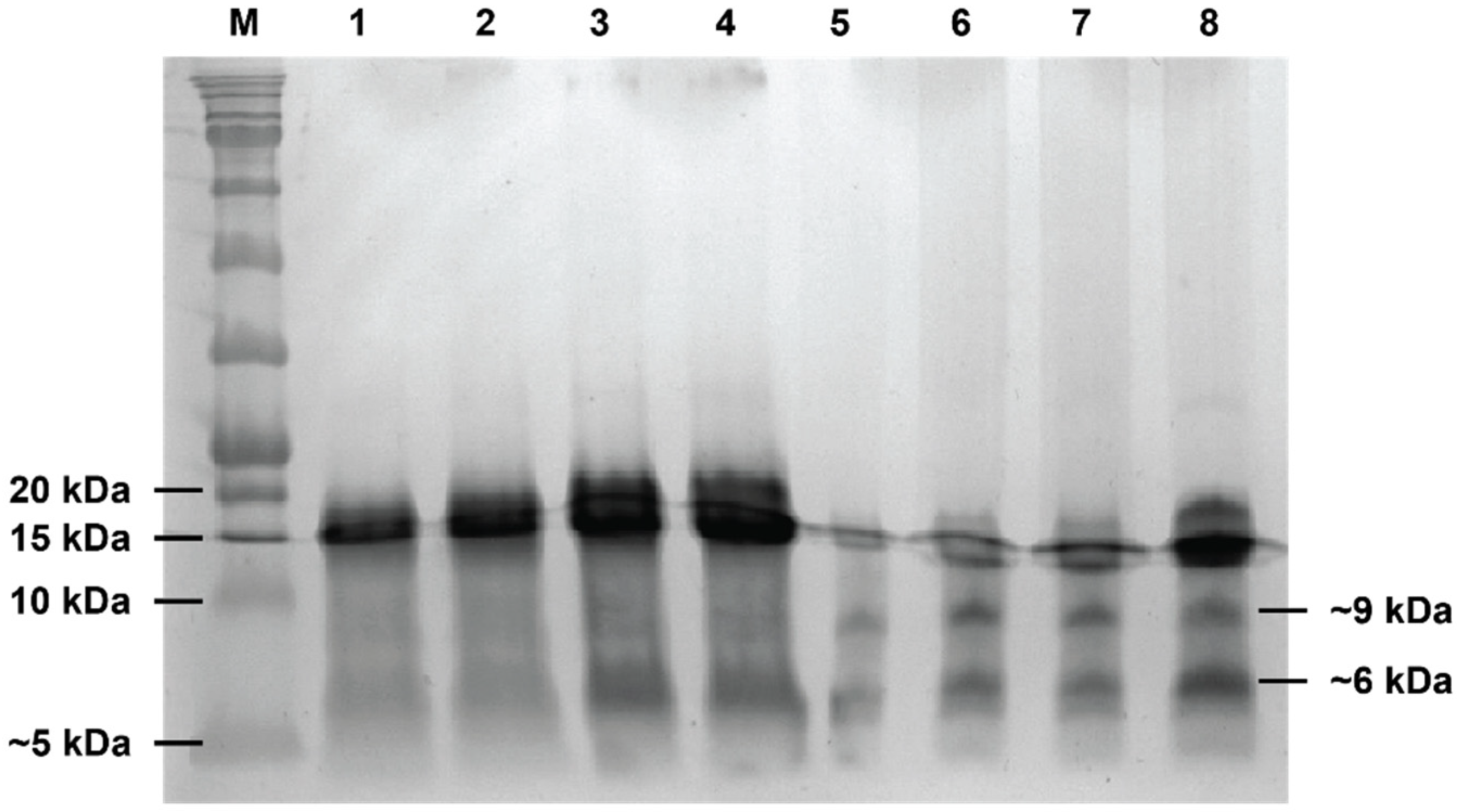
2.2. Characterization of the Seed Cake Extracts by SDS-PAGE
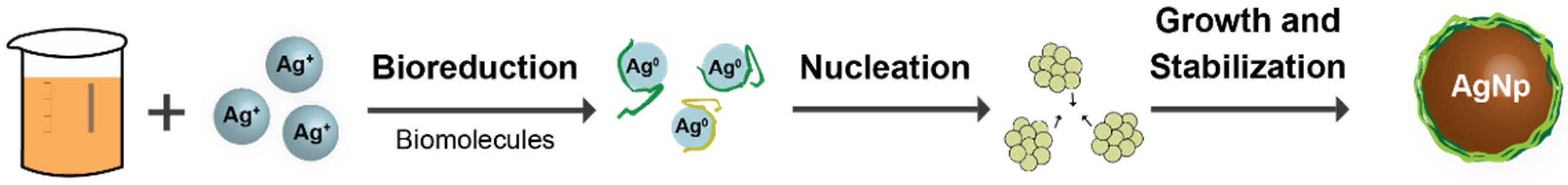
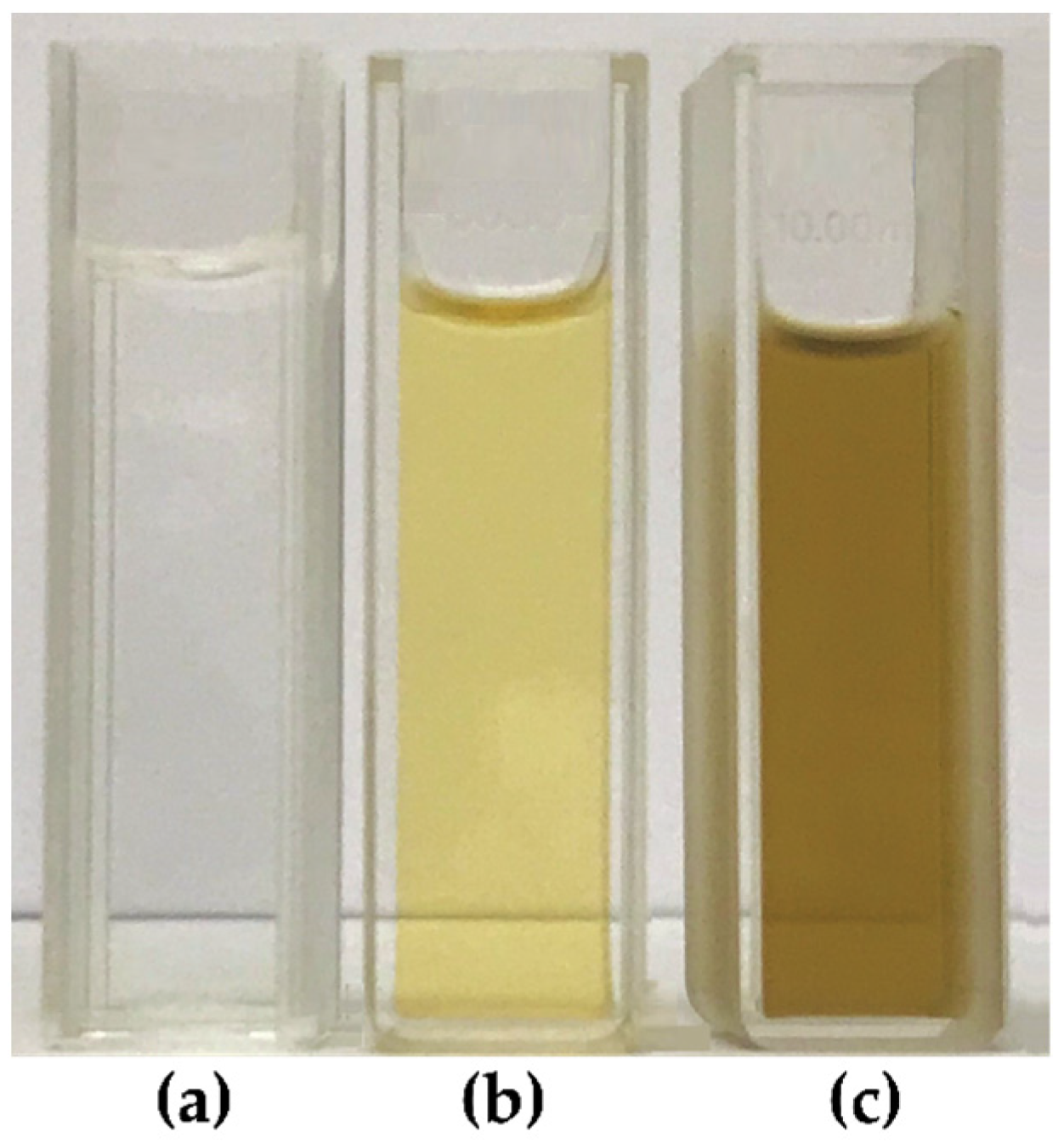
2.3. Green Synthesis of AgNPs
2.4. Characterization of AgNPs
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity of AgNPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Seed Cake Extracts
3.2. Characterization of AgNPs
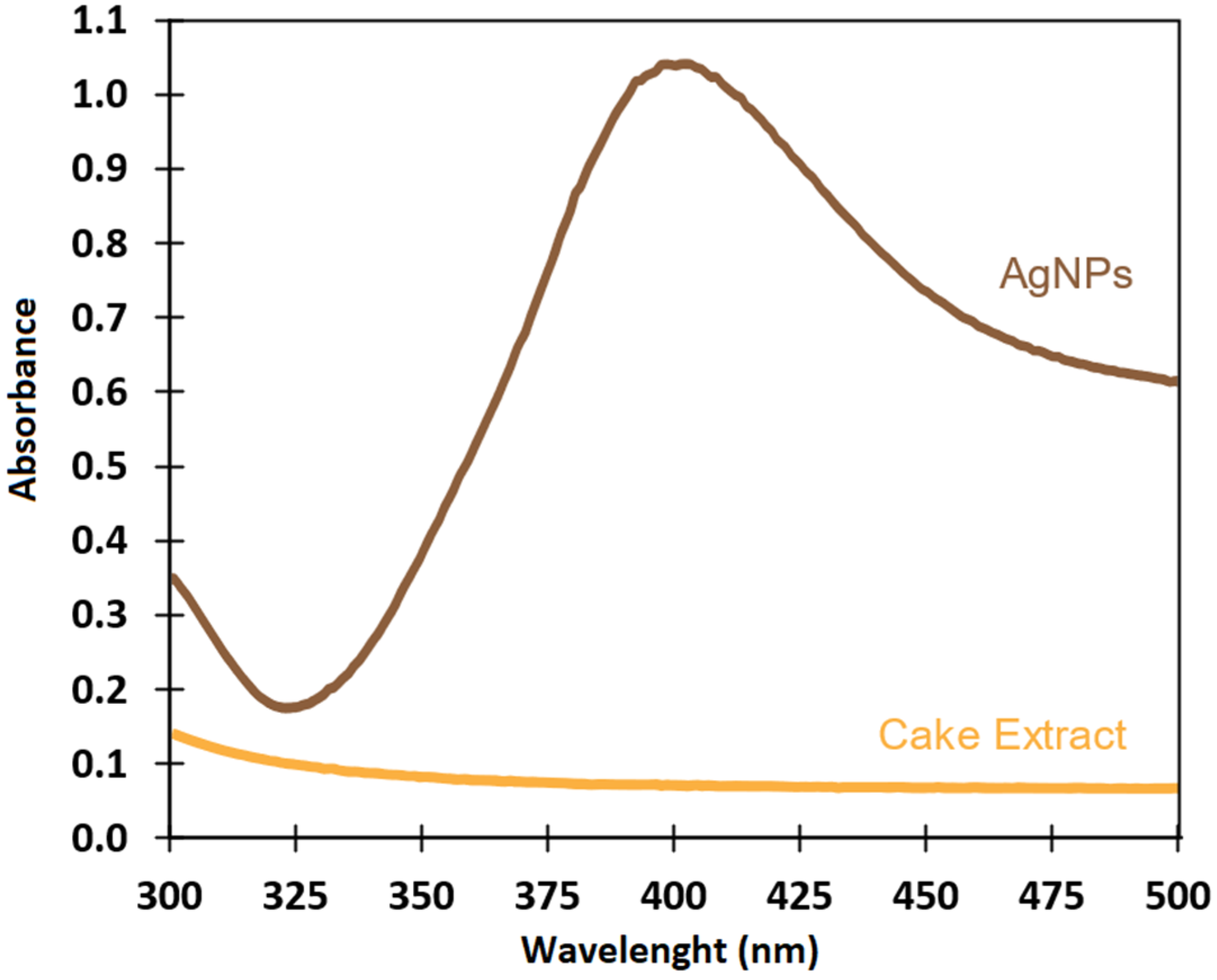
3.2.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
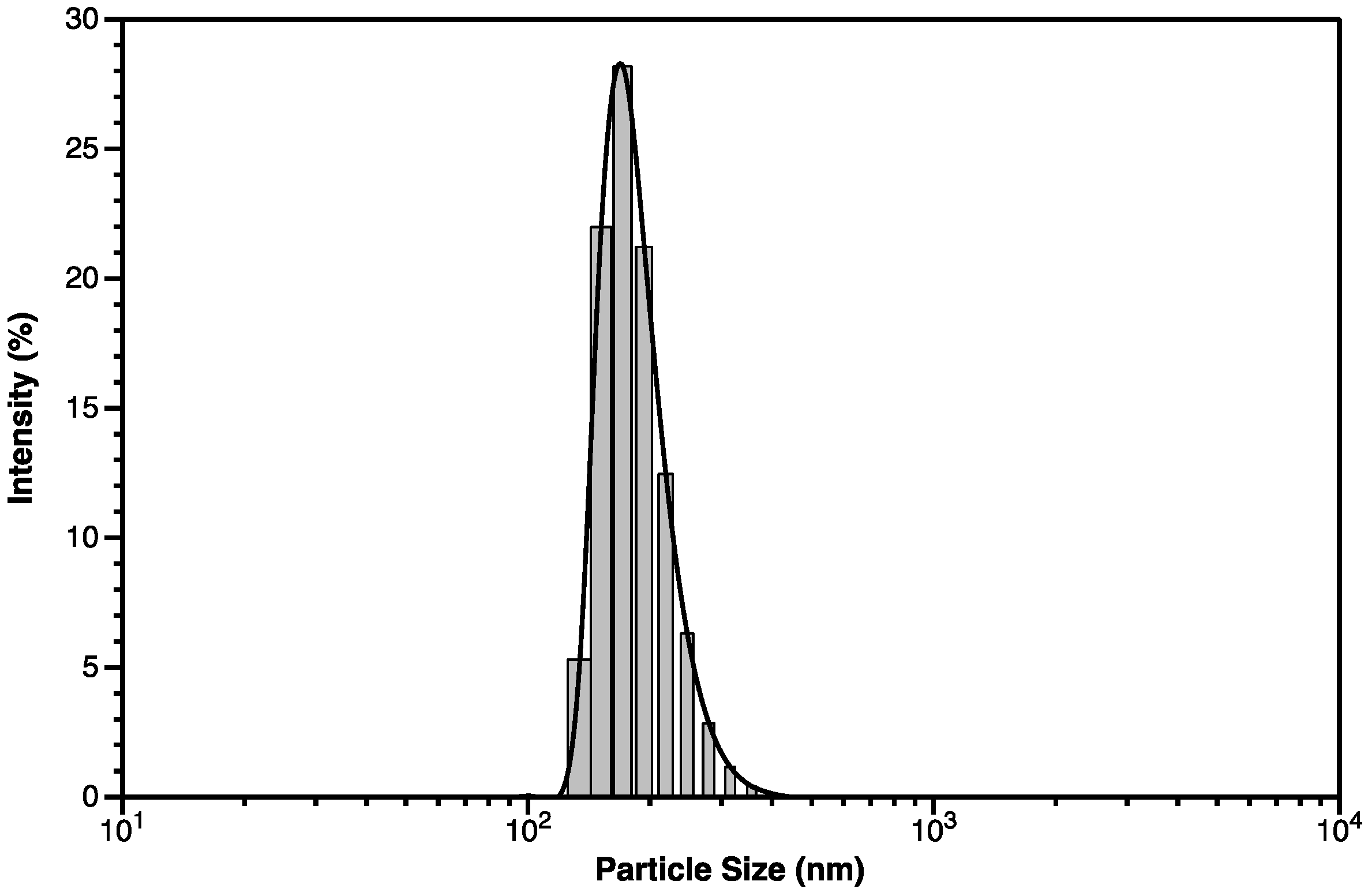
3.2.2. DLS Spectroscopy
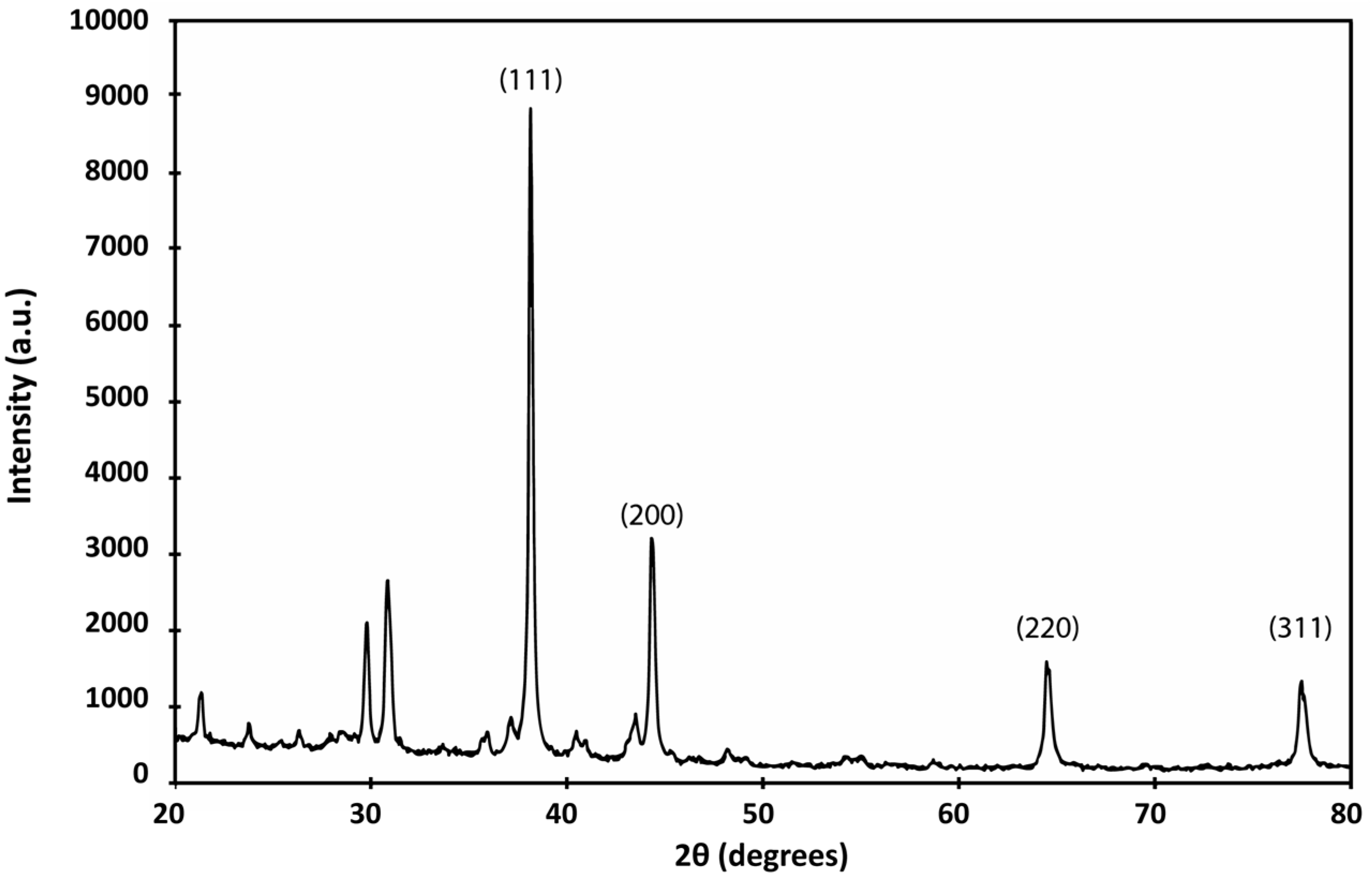
3.2.3. XRD
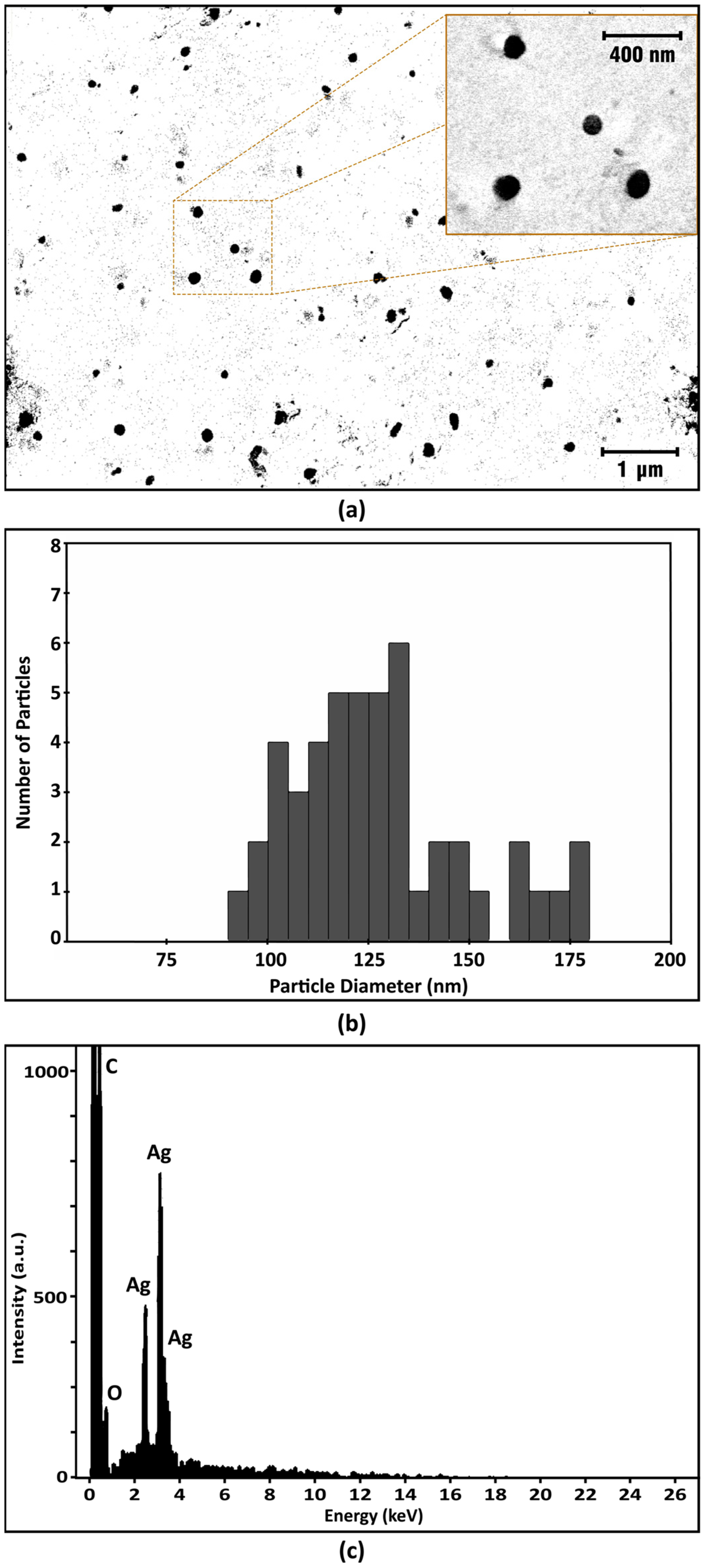
3.2.4. SEM-EDX
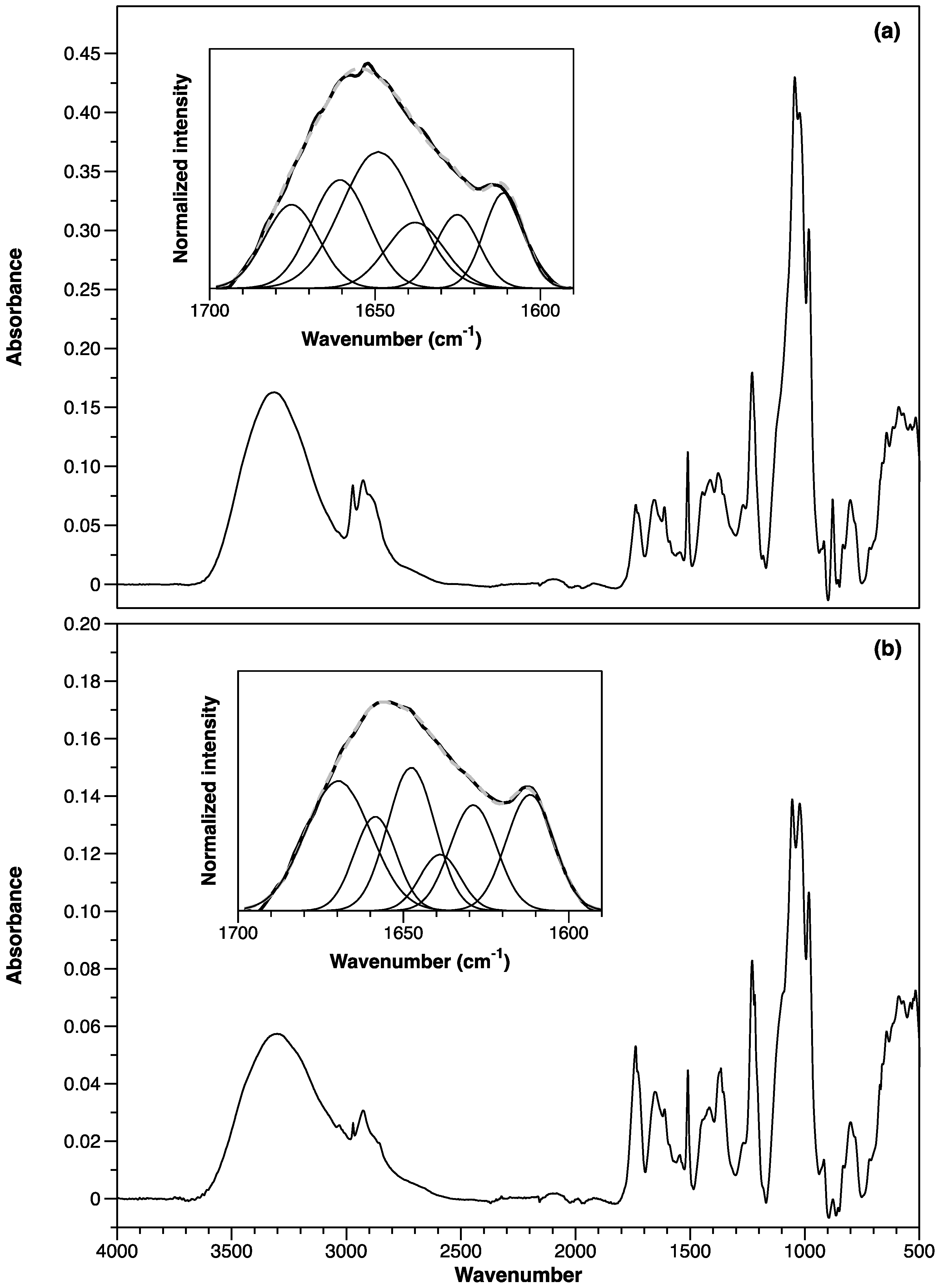
3.2.5. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
3.2.6. Antibacterial Activity of AgNPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rana, A.; Yadav, K.; Jagadevan, S. A comprehensive review on green synthesis of nature-inspired metal nanoparticles: Mechanism, application and toxicity. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, P.K.; Kumar, J.; Das, A.K.; Sadhu, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Kim, B.S. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Applications and limitations. Catalysts 2021, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shafey, A.M. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 304–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.; Bhagare, A.; Ali, I.H.; Dhayagude, A.; Lokhande, D.; Aher, J.; Jameel, M.; Dutta, M. Role of Moringa oleifera on green synthesis of metal/metal oxide nanomaterials. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 2147393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Abou El-ezz, D.; Abd–El Sayed, M.A.; Zikry, M.M.; Abu-Dief, A.M. Green biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Moringa oleifera: Access to a powerful antimicrobial, anticancer, pesticidal and catalytic agents. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 1422–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinise, N.; Fuku, X.G.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Mayedwa, N.; Maaza, M. ZnO nanoparticles via Moringa oleifera green synthesis: Physical properties & mechanism of formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 406, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwumulo, H.F.; Muwonge, H.; Ibingira, C.; Lubwama, M.; Kirabira, J.B.; Ssekitoleko, R.T. Greensynthesis and characterization of iron-oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera: A potential protocol for use in low and middle income countries. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, N.; Kaur, A.; Mann, S.; Garg, M.K.; Sofi, S.A.; Panghal, A. Bioactive compounds, associated health benefits and safety considerations of Moringa oleifera L.: An updated review. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 51, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, C.; Castelló, M.L.; Ortolá, M.D.; García-Mares, F.J.; Soriano, M.D. Moringa oleifera: An unknown crop in developed countries with great potential for industry and adapted to climate change. Foods 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azlan, U.K.; Mediani, A.; Rohani, E.R.; Tong, X.; Han, R.; Misnan, N.M.; Jam, F.A.; Bunawan, H.; Sarian, M.N.; Hamezah, H.S. A comprehensive review with updated future perspectives on the ethnomedicinal and pharmacological aspects of Moringa oleifera. Molecules 2022, 27, 5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, C.; Ankola, M.; Upadhyay, T.K.; Sharangi, A.B.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Al-Saeed, F.A.; Muzammil, K.; Saeed, M. Moringa oleifera: Miracle plant with a plethora of medicinal, therapeutic, and economic importance. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Chu, X.; Sun, K. Nutritional compositions of Indian Moringa oleifera seed and antioxidant activity of its polypeptides. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzuvor, C.K.O.; Pan, S.; Amanze, C.; Amuzu, P.; Asakiya, C.; Kubi, F. Bioactive components from Moringa oleifera seeds: Production, functionalities and applications—A critical review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Selvasekaran, P.; Kapoor, S.; Barbhai, M.D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Saurabh, V.; Potkule, J.; Changan, S.; ElKelish, A.; Selim, S.; et al. Moringa oleifera Lam. seed proteins: Extraction, preparation of protein hydrolysates, bioactivities, functional food properties, and industrial application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebek, K.; Schantz, A.B.; Sines, I.; Lauser, K.; Velegol, S.; Kumar, M. The flocculating cationic polypeptide from Moringa oleifera seeds damages bacterial cell membranes by causing membrane fusion. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4496–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, H.D.; Werkneh, A.A.; Bezabh, H.K.; Ambaye, T.G. Synthesis paradigm and applications of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), a review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2017, 13, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, H.; Ciğerci, İ.H.; Ali, M.M.; Hazman, O.; Liman, R.; Colă, F.; Bonciu, E. Cytotoxic and genotoxic evaluation of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera on MCF-7 and HUVEC cell lines. Plants 2022, 11, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althomali, A.; Daghestani, M.H.; Almukaynizi, F.B.; Al-Zahrani, S.A.; Awad, M.A.; Merghani, N.M.; Bukhari, W.I.; Ibrahim, E.M.; Alzahrani, S.M.; Altowair, N.; et al. Anti-colon cancer activities of green-synthesized Moringa oleifera—AgNPs against human colon cancer cells. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, C.V.; Villa, C.C. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles, influence of capping agents, and dependence on size and shape: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Hossain, K.F.B.; Banik, S.; Hosokawa, T.; Saito, T.; Kurasaki, M. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: Physicochemical properties and perspectives. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salayová, A.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Daneu, N.; Baláž, M.; Bujňáková, Z.L.; Balážová, Ľ.; Tkáčiková, Ľ. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using various medicinal plant extracts: Morphology and Antibacterial Efficacy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The Scherrer equation versus the “Debye-Scherrer Equation”. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwietering, M.H.; Jongenburger, I.; Rombouts, F.M.; van’t Riet, K. Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.B.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Gifoni, J.M.; Pereira, M.L.; Almeida, M.G.G.; Gomes, V.M.; Da Cunha, M.; Ribeiro, S.F.F.; Dias, G.B.; Beltramini, L.M.; et al. New insights into the structure and mode of action of Mo-CBP3, an antifungal Chitin-binding protein of Moringa oleifera seeds. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, J.E.C.; Moreno, F.B.M.B.; Monteiro-Júnior, J.E.; Sousa, A.J.S.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Monteiro-Moreira, A.C.O.; Rocha, B.A.M.; Grangeiro, T.B. Mo-CBP3, a 2S albumin from Moringa oleifera, is a complex mixture of isoforms that arise from different post-translational modifications. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 140, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Mandal, C.; Habib, A. Antibacterial potential of synthesized silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Moringa oleifera. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, D.E.; Side, S.; Nisa, N.A.T. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera L. leaf extract as bioreductor. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 967, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashrai, A.; Dar, A.M.; Sherwani, M.A.; Singh, B.R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles as a platform for biomedicinal application. J. Nanosci. Nanomed. 2018, 2, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Moodley, J.S.; Krishna, S.B.N.; Pillay, K.; Sershen; Govender, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera leaf extracts and its antimicrobial potential. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 015011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, P.; Martin, J.; Nguyen, L.-H.; He, Y.; Gehring, A.; Chen, C.-Y. Antimicrobial activity of spherical silver nanoparticles prepared using a biocompatible macromolecular capping agent: Evidence for induction of a greatly prolonged bacterial lag phase. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailova, E.O. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of action and probable bio-application. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Culture | λ (h) | (h−1) | A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.34 ± 0.17 | 0.078 ± 0.005 | 0.469 |
| 2.5 mg/mL AgNP | 2.11 ± 0.18 | 0.073 ± 0.005 | 0.440 |
| 7.5 mg/mL AgNP | 3.26 ± 0.27 | 0.070 ± 0.010 | 0.312 |
| 10.0 mg/mL AgNP | 4.55 ± 0.10 | 0.068 ± 0.004 | 0.237 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, N.; Jacinto, J.P.; Silva, R.; Soares, J.C.; Pereira, A.S.; Tavares, P. Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained from Moringa oleifera Seed Cake. Coatings 2023, 13, 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081439
Coelho N, Jacinto JP, Silva R, Soares JC, Pereira AS, Tavares P. Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained from Moringa oleifera Seed Cake. Coatings. 2023; 13(8):1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081439
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, Nuno, João P. Jacinto, Rodrigo Silva, Jéssica C. Soares, Alice S. Pereira, and Pedro Tavares. 2023. "Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained from Moringa oleifera Seed Cake" Coatings 13, no. 8: 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081439
APA StyleCoelho, N., Jacinto, J. P., Silva, R., Soares, J. C., Pereira, A. S., & Tavares, P. (2023). Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Obtained from Moringa oleifera Seed Cake. Coatings, 13(8), 1439. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081439








