Effects of Ti/N Ratio on Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone Microstructure Evolution and Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of High Heat Input Welding Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
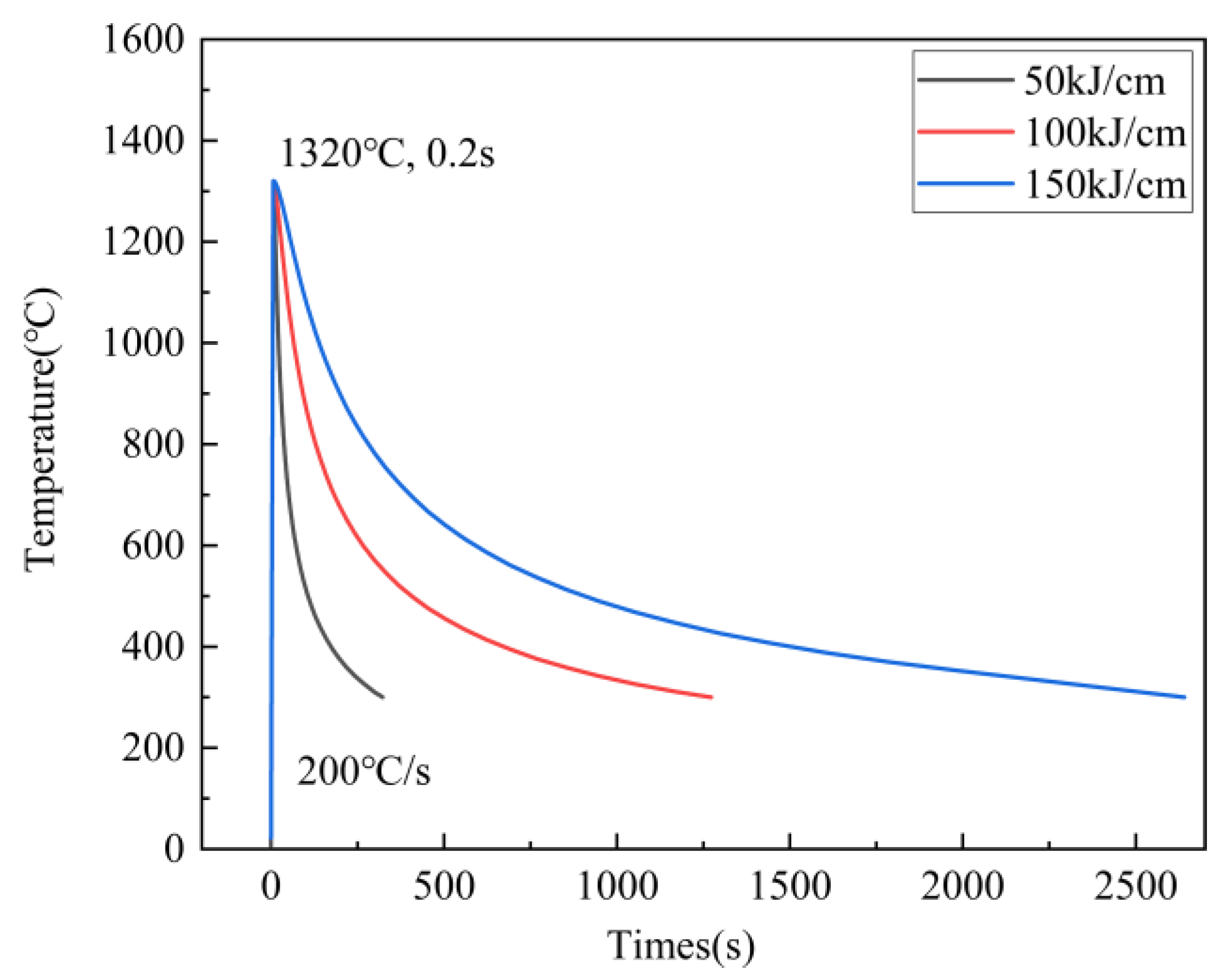
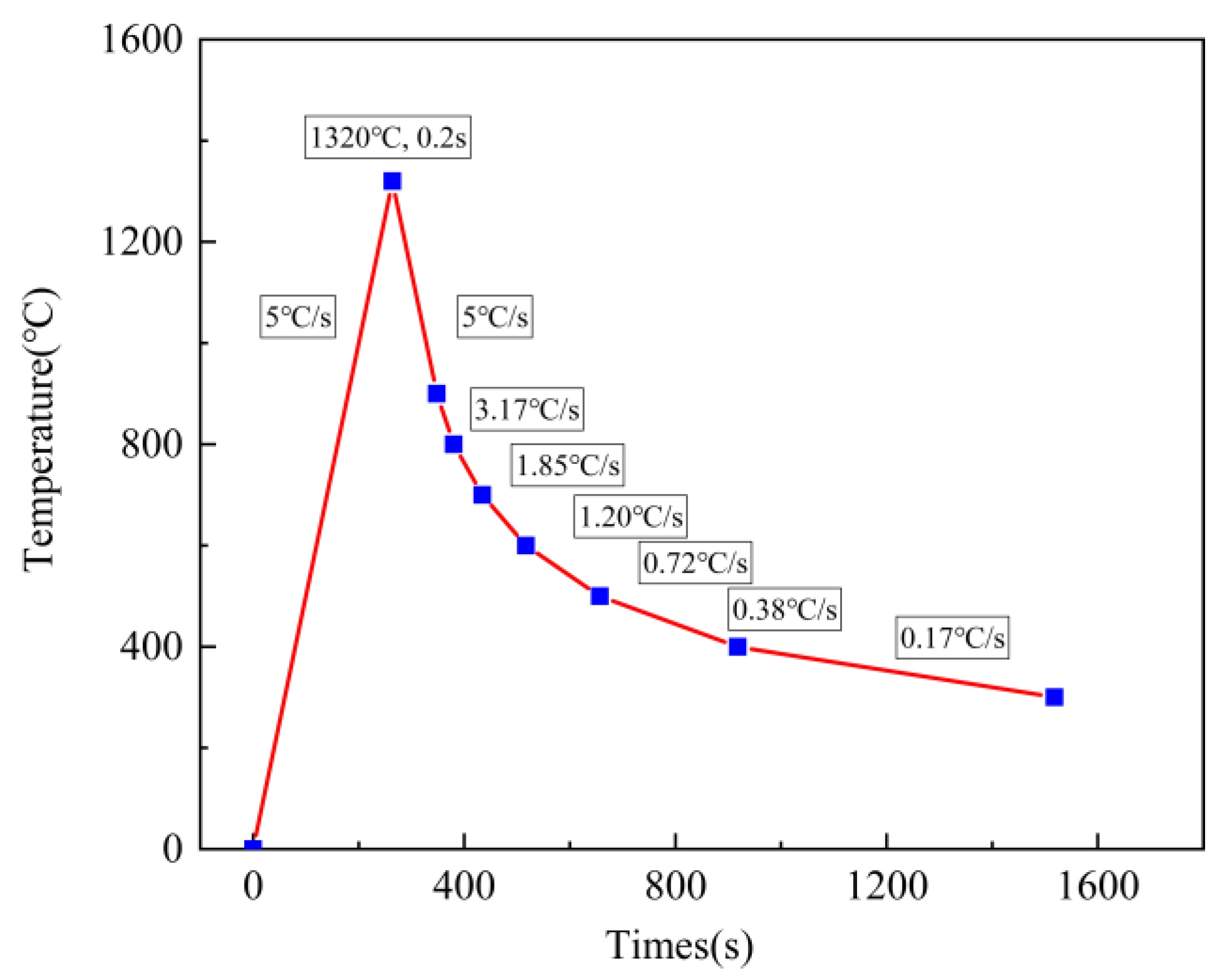
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
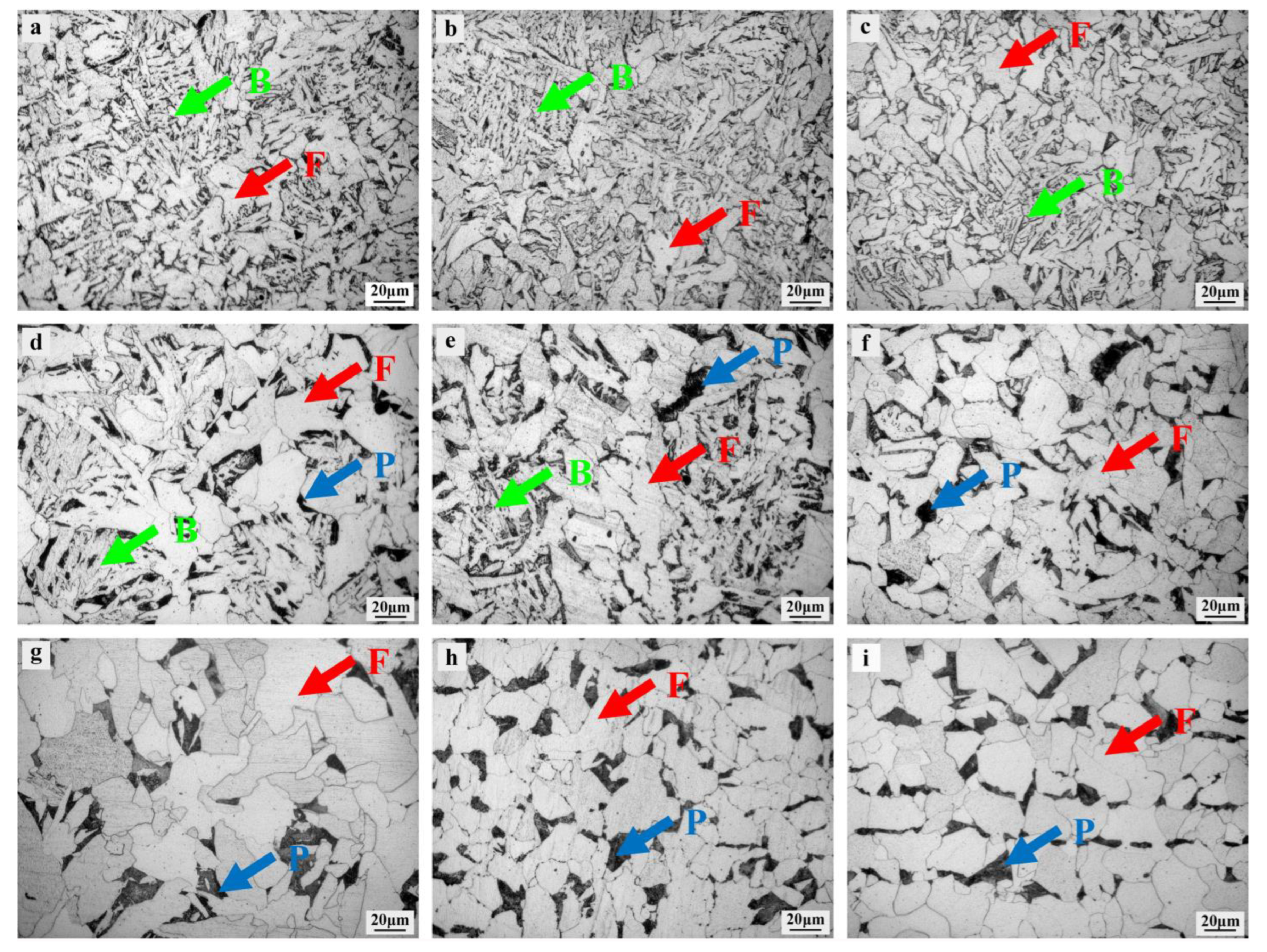
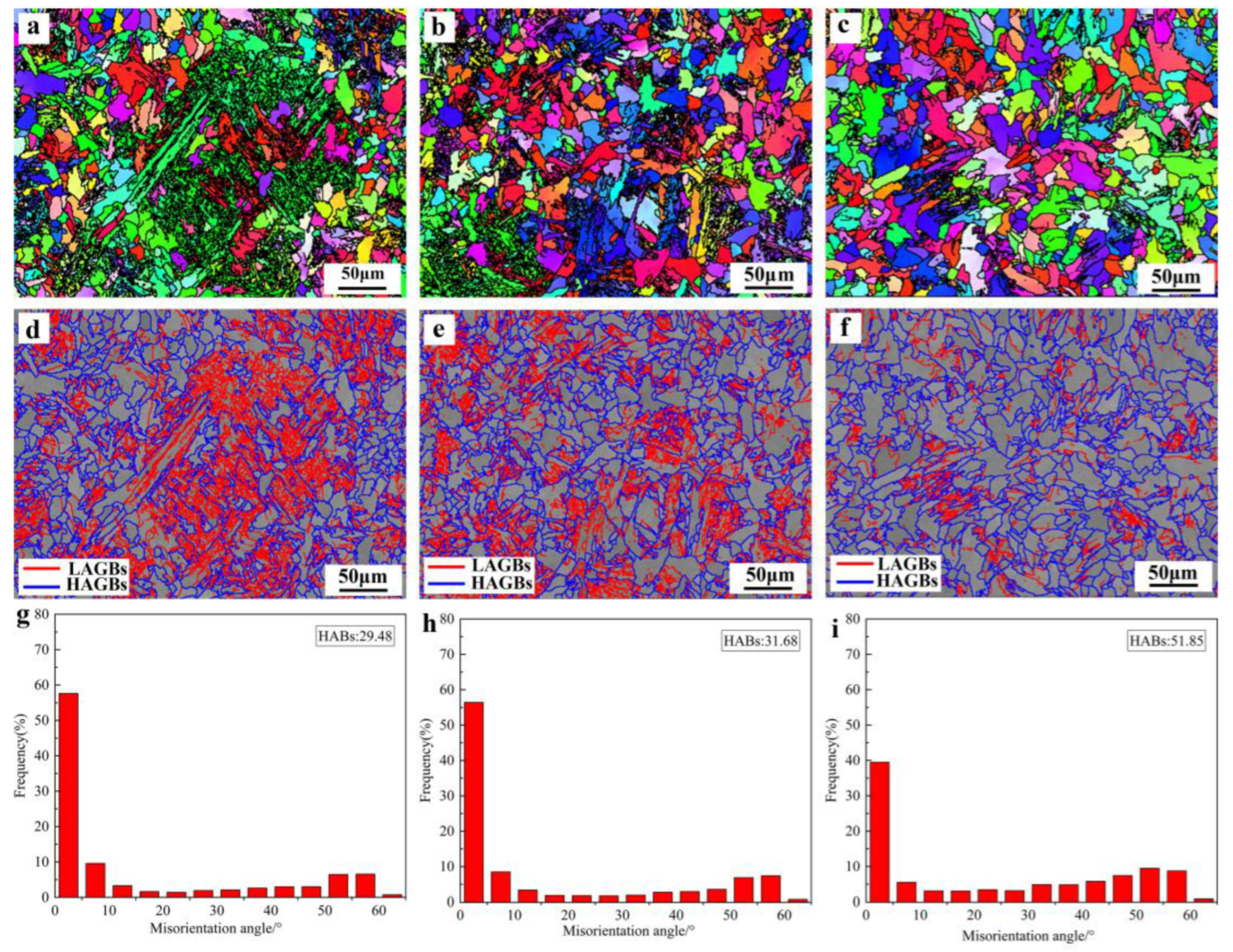
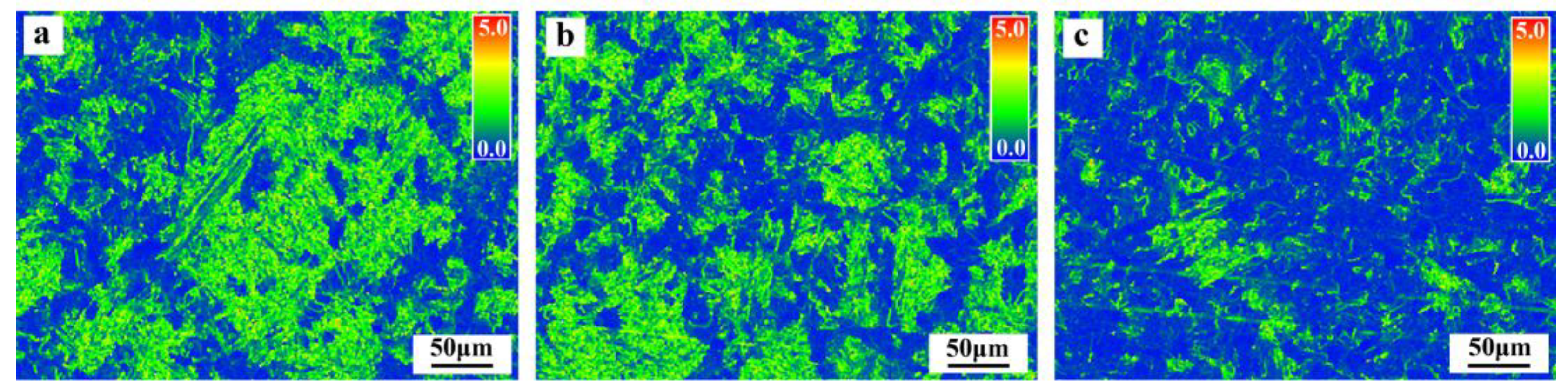
3.1. Microstructure
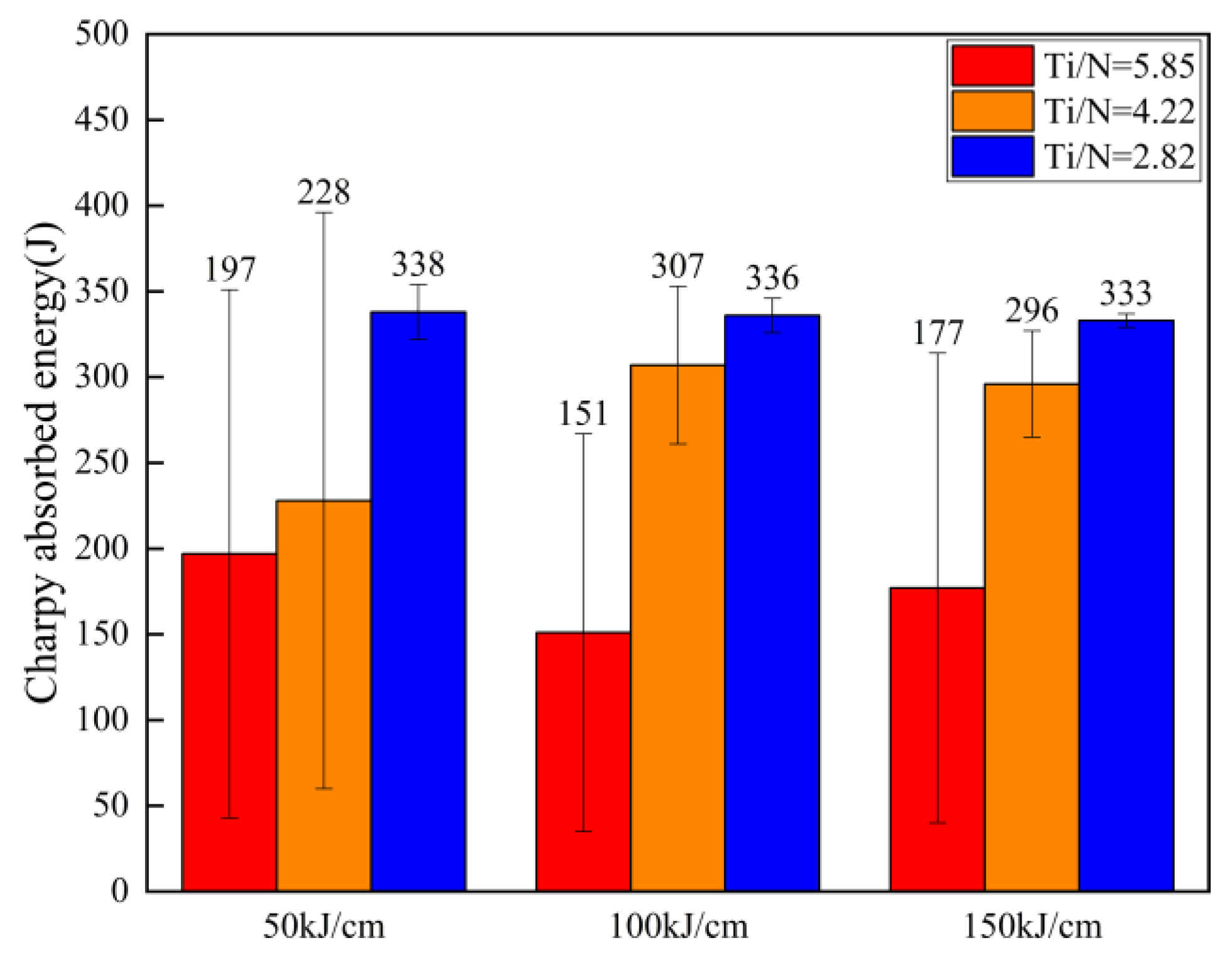
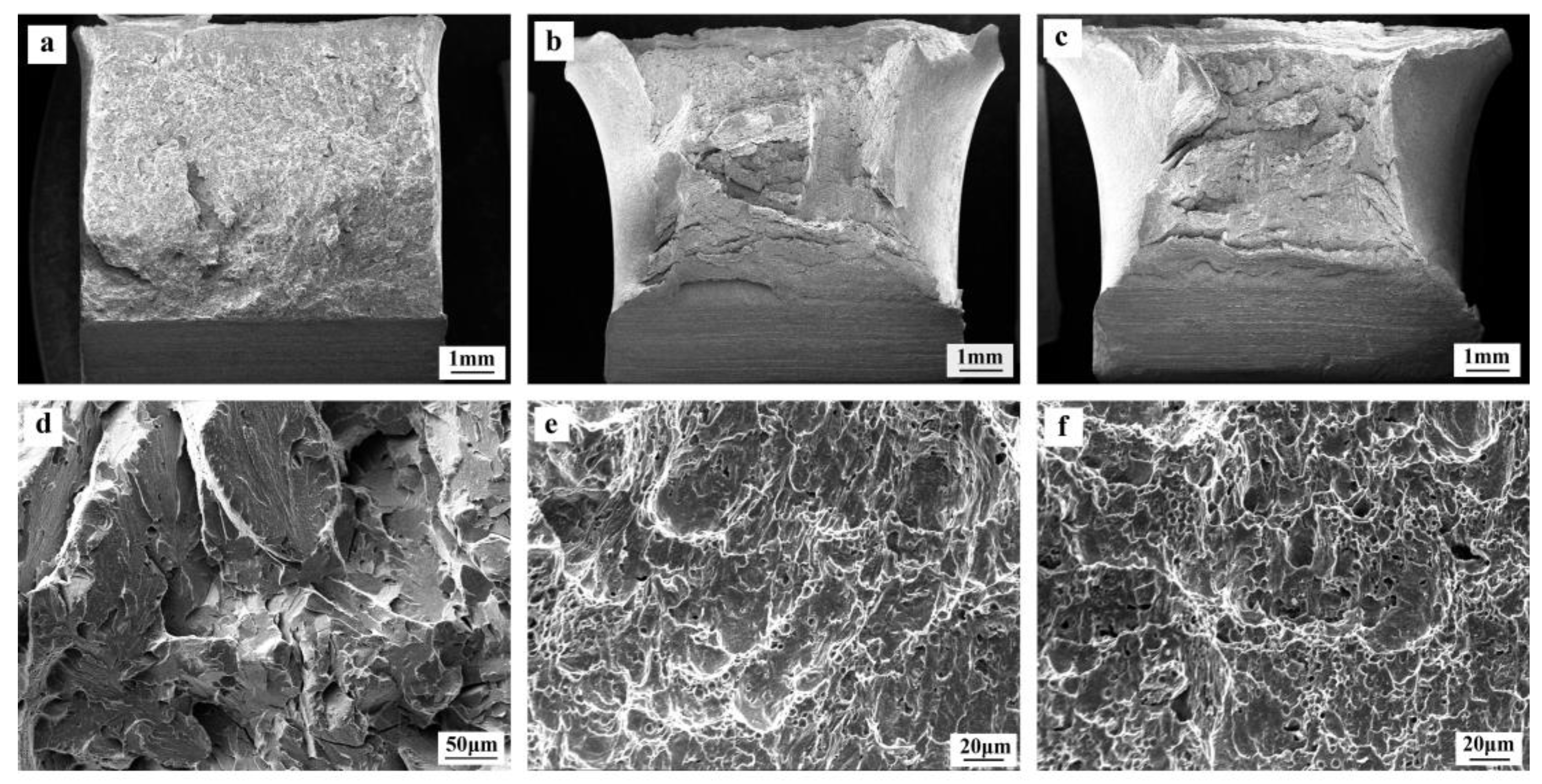
3.2. Mechanical Properties
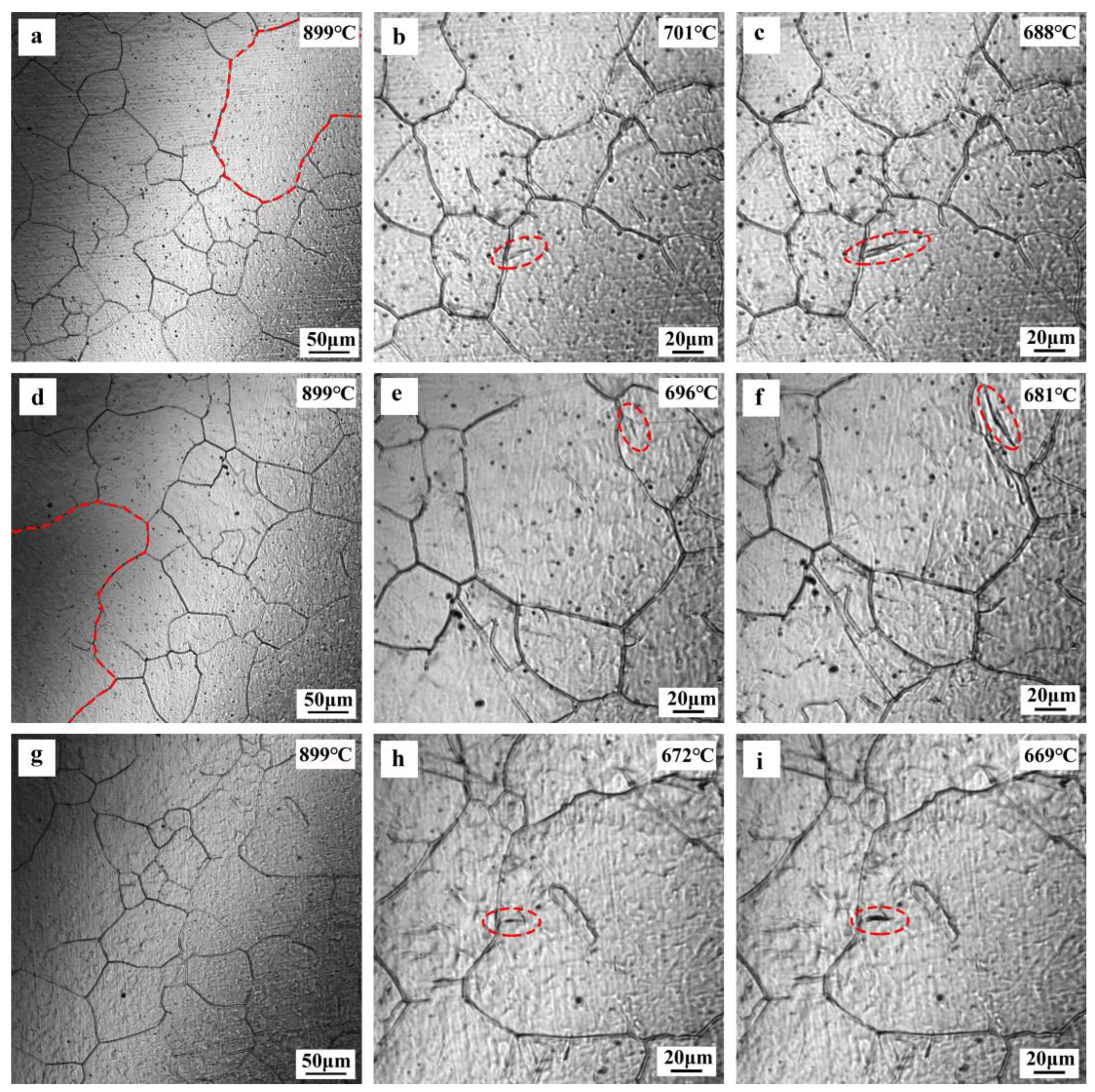
3.3. In Situ Observation
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of the Ti/N Ratio on Austenite Grain Growth
4.2. Effect of the Ti/N Ratio on CGHAZ Microstructure and Toughness
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- A lower Ti/N ratio reduced the size of TiN particles, which made the distribution of TiN particles more uniform. A higher Ti/N ratio promoted the appearance of coarse TiN particles in the steel.
- (2)
- A lower Ti/N ratio refined the microstructure of the CGHAZ, increased the proportion of ductile microstructure and the content of high-angle grain boundaries, and reduced the generation of local high strain structure.
- (3)
- The coarse TiN particles formed by a higher Ti/N ratio weakened the pinning of the grain boundary, resulting in an increase in the formation temperature of lath ferrite and the coarsening of the CGHAZ microstructure.
- (4)
- For the steel with a Ti/N ratio of 2.82, the average impact toughness was higher and more stable. For the steel with a Ti/N of 5.85, the impact toughness was lower and clearly fluctuated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Y.; Leng, J.; Wang, C. On the heterogeneous microstructure development in the welded joint of 12MnNiVR pressure vessel steel subjected to high heat input electrogas welding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcaro, R.R.; Faria, G.L.; Godefroid, L.B.; Apolonio, G.R.; Cândido, L.C.; Pinto, E.S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a flash butt welded pearlitic rail. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 270, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, R.; Su, H.; Chai, F.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C. Effect of nitrogen content on the second phase particles in V–Ti microalloyed shipbuilding steel during weld thermal cycling. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, B.; Mao, J. Effect of Ca on the evolution of inclusions and the formation of acicular ferrite in Ti–Mg killed EH36 steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Lee, H.C. Effect of plastic deformation on the formation of acicular ferrite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 360, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Kiyose, A.; Uemori, R.; Minagawa, M.; Hoshino, M.; Nakashima, T.; Ishida, K.; Yasui, H. Super High HAZ Toughness Technology with Fine Microstructure Imparted by Fine Particles. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2004, 90, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Sun, J.; Matsuura, H.; Wang, C. Profiling Microstructure Evolution Roadmap in Heat-Affected Zones of EH36 Shipbuilding Steel Under Controlled Thermal Simulation. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Shi, G.; Peng, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. N-induced microstructure refinement and toughness improvement in the coarse grain heat-affected zone of a low carbon Mo–V–Ti–B steel subjected to a high heat input welding thermal cycle. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Fan, H.; Shi, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R. Effect of Welding Heat Input on Microstructure and Impact Toughness in the Simulated CGHAZ of Low Carbon Mo-V-Ti-N-B Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, W.; Ge, Z.; Luo, G.; Peng, J. Effect of high heat input welding on the microstructures, precipitates and mechanical properties in the simulated coarse grained heat affected zone of a low carbon Nb-V-Ti-N microalloyed steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 199, 112849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Kang, J.; Wang, G.; Misra, D.; Yuan, G. Relationship Between Impact Toughness and Microstructure for the As-Rolled and Simulated HAZ of Low-Carbon Steel Containing Ti-Ca Oxide Particles. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Sumi, H.; Kitani, Y. High tensile strength steel plates and welding consumables for architectural construction with excellent toughness in welded joint-“JFE EWEL” technology for excellent quality in HAZ of high heat input welded joints. JFE Tech. Rep. 2005, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.H.; Du, K.; Gao, P.; Zhang, J. Microstructure Evolution and Toughness Variation of Simulation HAZ with Large Heat Input Welding for E40 Ship Plate Steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 382, 032010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Saito, N.; Tsuzuki, T.; Tokunaga, Y.; Okamoto, K. Improvement in HAZ Toughness of Steel by TiN-MnS Addition. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.-l.; Wu, K.-M.; Huang, G.; Wei, R.; Cheng, L. In situ observation of austenite grain growth behavior in the simulated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of Ti-microalloyed steels. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2014, 21, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Yang, K. Effect of TiN inclusions on the impact toughness of low-carbon microalloyed steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Marimuthu, M.; Kuzmikova, L.; Li, H.J.; Barbaro, F.; Zheng, L.; Bai, M.Z.; Jones, C. Influence of Ti/N ratio on simulated CGHAZ microstructure and toughness in X70 steels. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 18, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Ma, X.; Subramanian, S.V.; Shang, C. Influence of Martensite–Austenite constituents formed at different intercritical temperatures on toughness. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Terasaki, H.; Komizo, Y.I. In situ observation of the formation of intragranular acicular ferrite at non-metallic inclusions in C–Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wu, K.; Cheng, L.; Wei, R. In-situ Observations of Acicular Ferrite Growth Behavior in the Simulated Coarse-grained Heat-affected Zone of High-strength Low-alloy Steels. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Sun, J.; Matsuura, H.; Wang, C. In Situ Observation of the Nucleation and Growth of Ferrite Laths in the Heat-Affected Zone of EH36-Mg Shipbuilding Steel Subjected to Different Heat Inputs. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, G.; Misra, R.D.; Wang, G. A Comparative Study of Acicular Ferrite Transformation Behavior between Surface and Interior in a Low C–Mn Steel by HT-LSCM. Metals 2021, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.C.; Wen, G.H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Guo, J.L.; Tang, P. Modification for prediction model of austenite grain size at surface of microalloyed steel slabs based on in situ observation. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 28, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, A. Effect of Welding Peak Temperature on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Heat-Affected Zone of Q690 High Strength Bridge Steel. Materials 2021, 14, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, M.; Di, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D. Toughening mechanism of inter-critical heat-affected zone in a 690 MPa grade rack plate steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Chong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J. Effect of solution treatment on mechanical properties and microstructure of welded joints of Fe-29Mn-9Al-0.9C low-density steel. J. Micromech. Mol. Phys. 2020, 5, 2050006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Ohnuma, I.; Ohtani, H.; Ishida, K.; Nishizawa, T. Solubility Product of TiN in Austenite. ISIJ Int. 1998, 38, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gamsjäger, E.; Schider, S.; Khanbareh, H.; van der Zwaag, S. In situ observation of austenite–ferrite interface migration in a lean Mn steel during cyclic partial phase transformations. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2414–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Yokoyama, H.; Yamada, K.; Niikura, M. Effects of the Austenite Grain Size and Deformation in the Unrecrystallized Austenite Region on Bainite Transformation Behavior and Microstructure. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Z.; Misra, R.D.; Shang, C. The Effects of Prior Austenite Grain Refinement on Strength and Toughness of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel. Metals 2021, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Jönsson, P.G.; Nakajima, K. Prediction of intragranular ferrite nucleation from TiO, TiN, and VN inclusions. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 51, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.C.F.; Bott, I.S.; Souza, L.F.G.; Mendes, M.C.; Araújo, L.S.; Evans, G.M. Mechanical and microstructural behavior of C-Mn steel weld deposits with varying titanium contents. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4659–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, K.; Dong, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, D.; Jin, X.; Liu, H.; Tai, M. Effect of Heat-Input on Microstructure and Toughness of CGHAZ in a High-Nb-Content Microalloyed HSLA Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

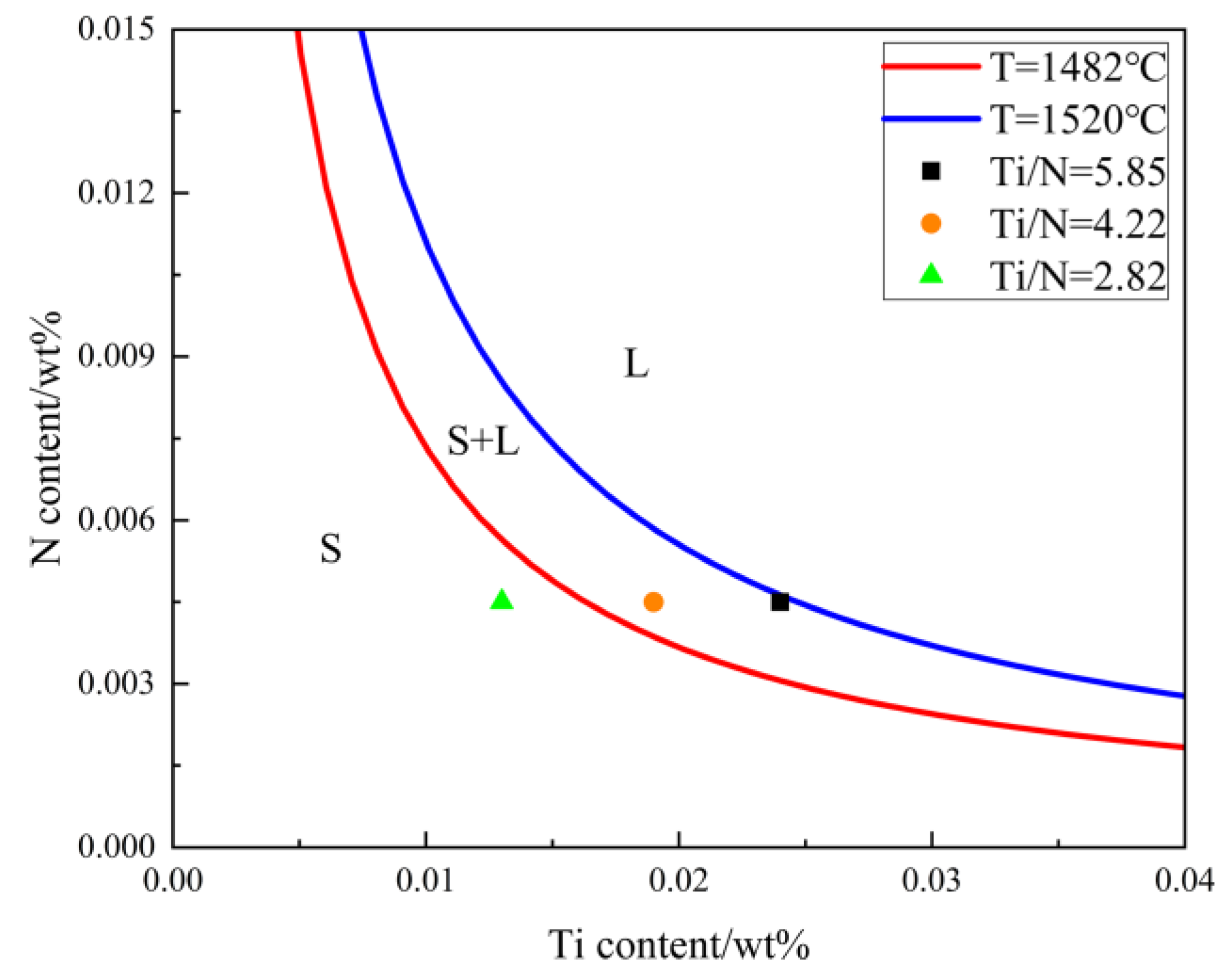

| Steels | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Ti | N | Als | Ti/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.084 | 1.43 | 0.26 | 0.0074 | 0.0017 | 0.024 | 0.0041 | 0.016 | 5.85 |
| B | 0.084 | 1.45 | 0.27 | 0.0079 | 0.0017 | 0.019 | 0.0045 | 0.017 | 4.22 |
| C | 0.083 | 1.45 | 0.26 | 0.0067 | 0.0018 | 0.013 | 0.0046 | 0.015 | 2.82 |
| Ti/N | KAM Distribution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0°–1° | 1°–2° | 2°–3° | 3°–4° | 4°–5° | Ave | |
| 5.85 | 0.570 | 0.305 | 0.106 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 1.030 |
| 4.22 | 0.632 | 0.265 | 0.086 | 0.015 | 0.002 | 0.939 |
| 2.82 | 0.864 | 0.108 | 0.024 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.562 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Fu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y. Effects of Ti/N Ratio on Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone Microstructure Evolution and Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of High Heat Input Welding Steel. Coatings 2023, 13, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081347
Liu J, Wang J, Hu F, Fu K, Zhang Z, Wu Y. Effects of Ti/N Ratio on Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone Microstructure Evolution and Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of High Heat Input Welding Steel. Coatings. 2023; 13(8):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081347
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jin, Jiaji Wang, Fengya Hu, Kuijun Fu, Zhiqiang Zhang, and Yumin Wu. 2023. "Effects of Ti/N Ratio on Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone Microstructure Evolution and Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of High Heat Input Welding Steel" Coatings 13, no. 8: 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081347
APA StyleLiu, J., Wang, J., Hu, F., Fu, K., Zhang, Z., & Wu, Y. (2023). Effects of Ti/N Ratio on Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone Microstructure Evolution and Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of High Heat Input Welding Steel. Coatings, 13(8), 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081347






