Salicylic-Zinc Nanocomposites with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
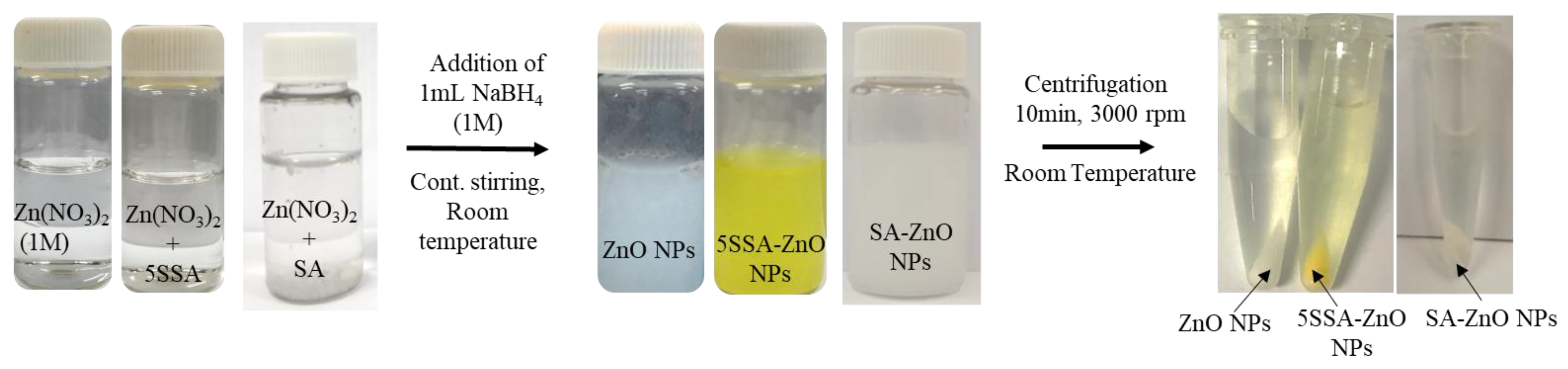
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of SA-ZnO and 5-SSA-ZnO NPs
2.3. Investigation of Antimicrobial Activity
2.4. Cell Toxicity Profiling
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
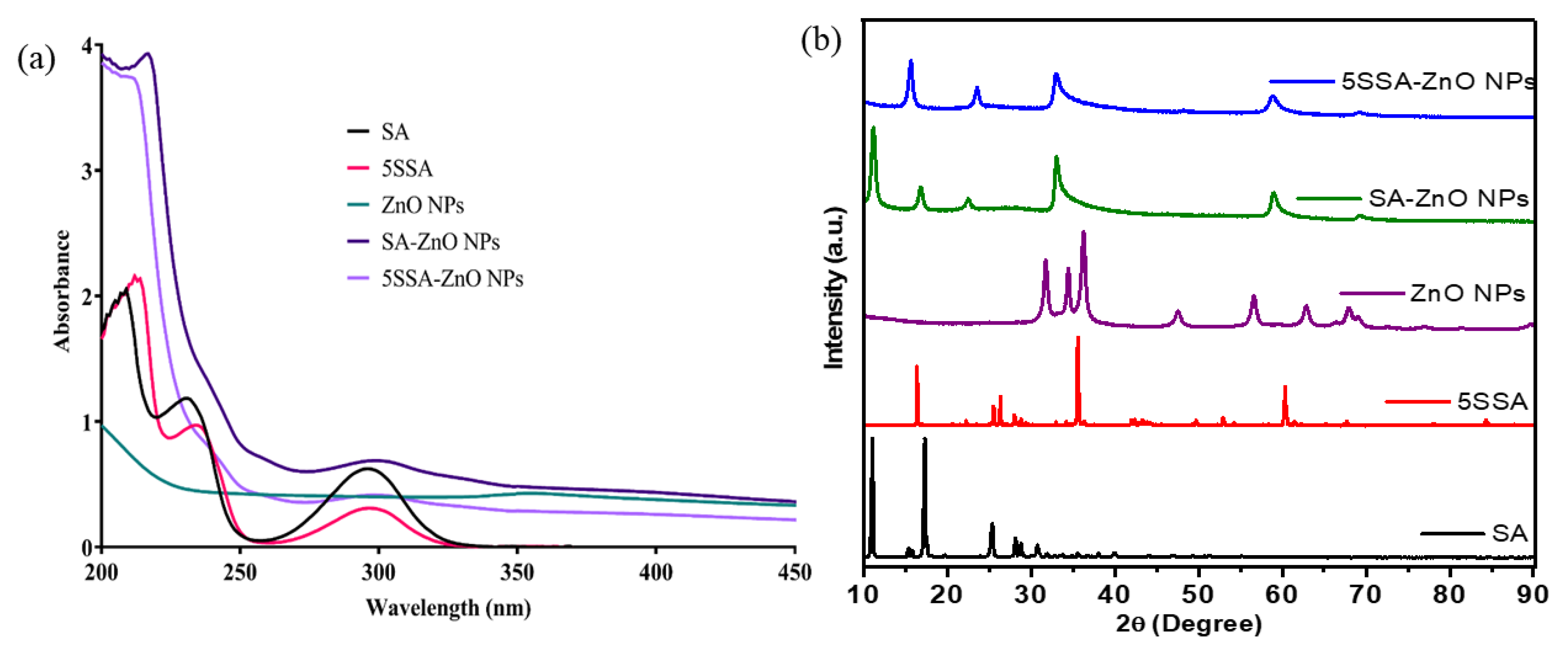
3.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
3.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Nanocomposites
3.3. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis of Nanocomposites
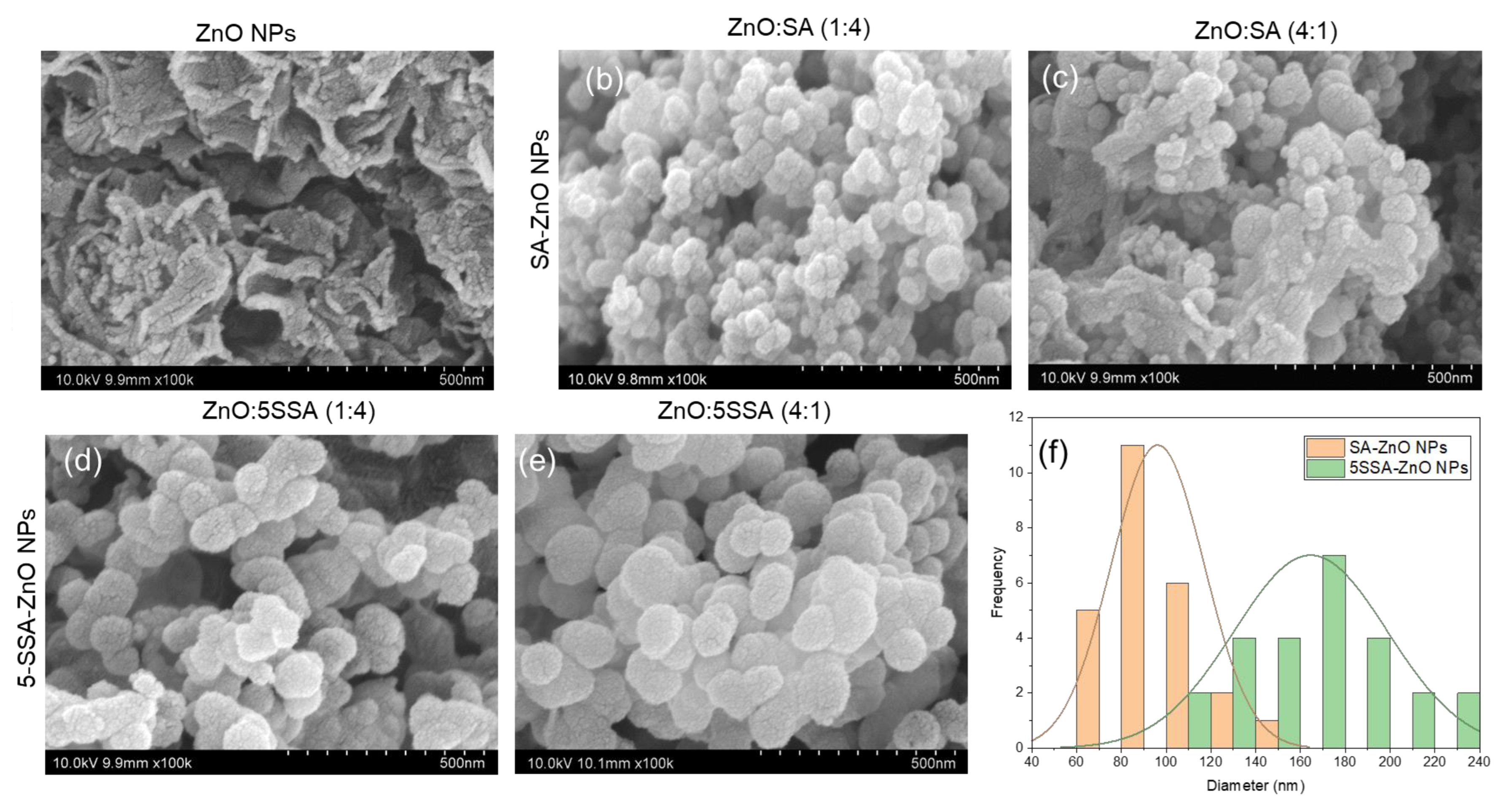
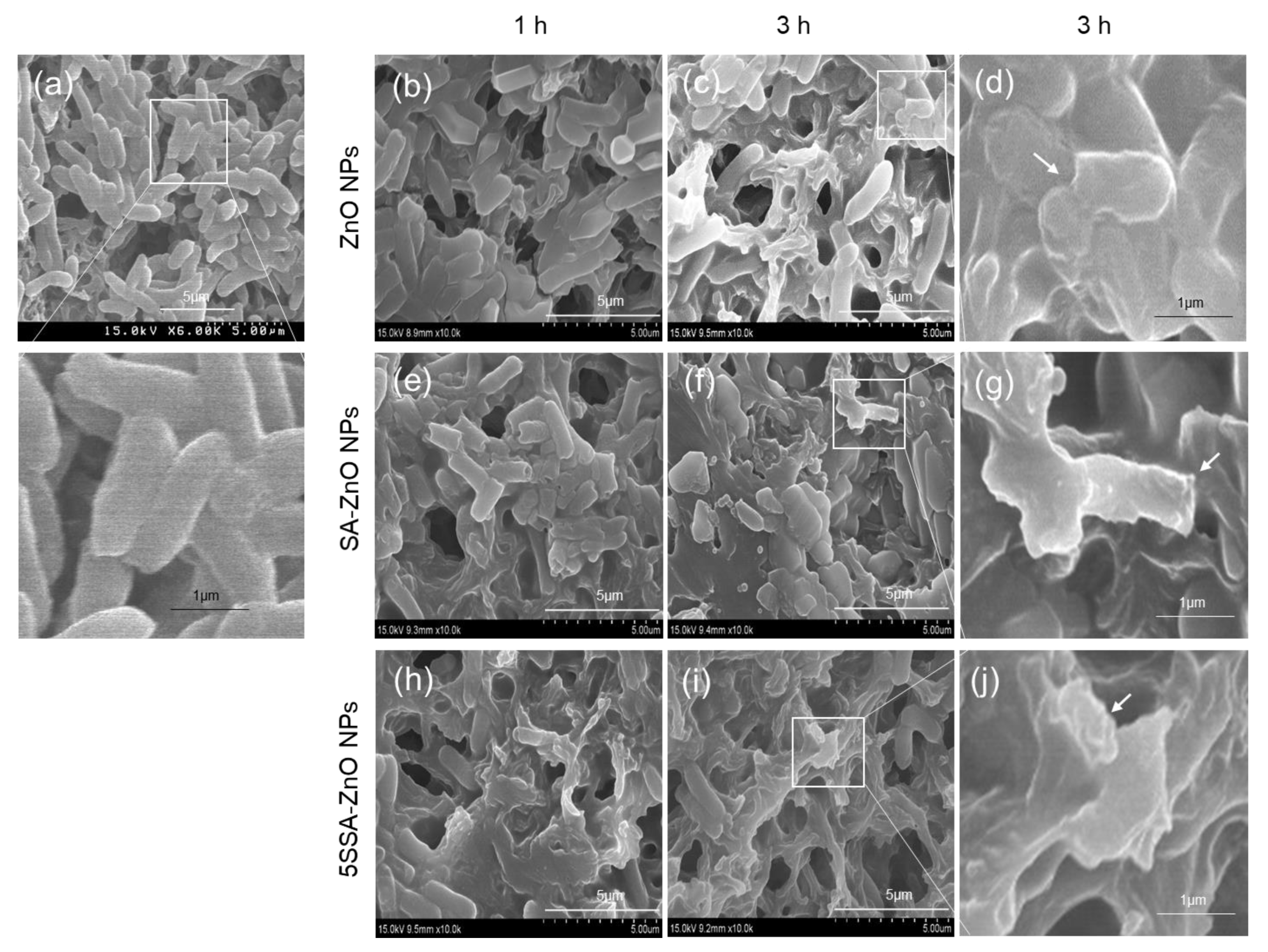
3.4. Nanostructures of Nanocomposites
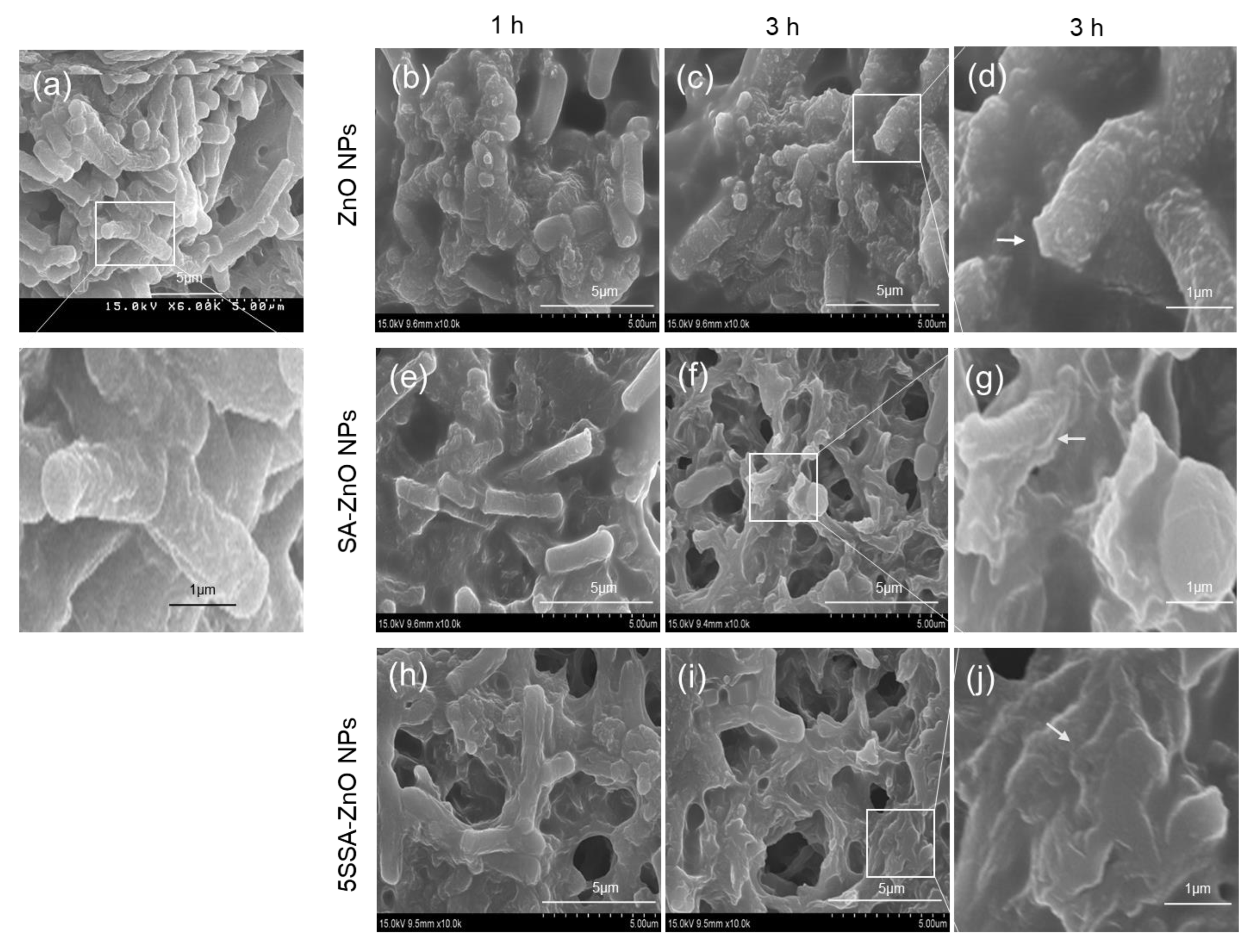
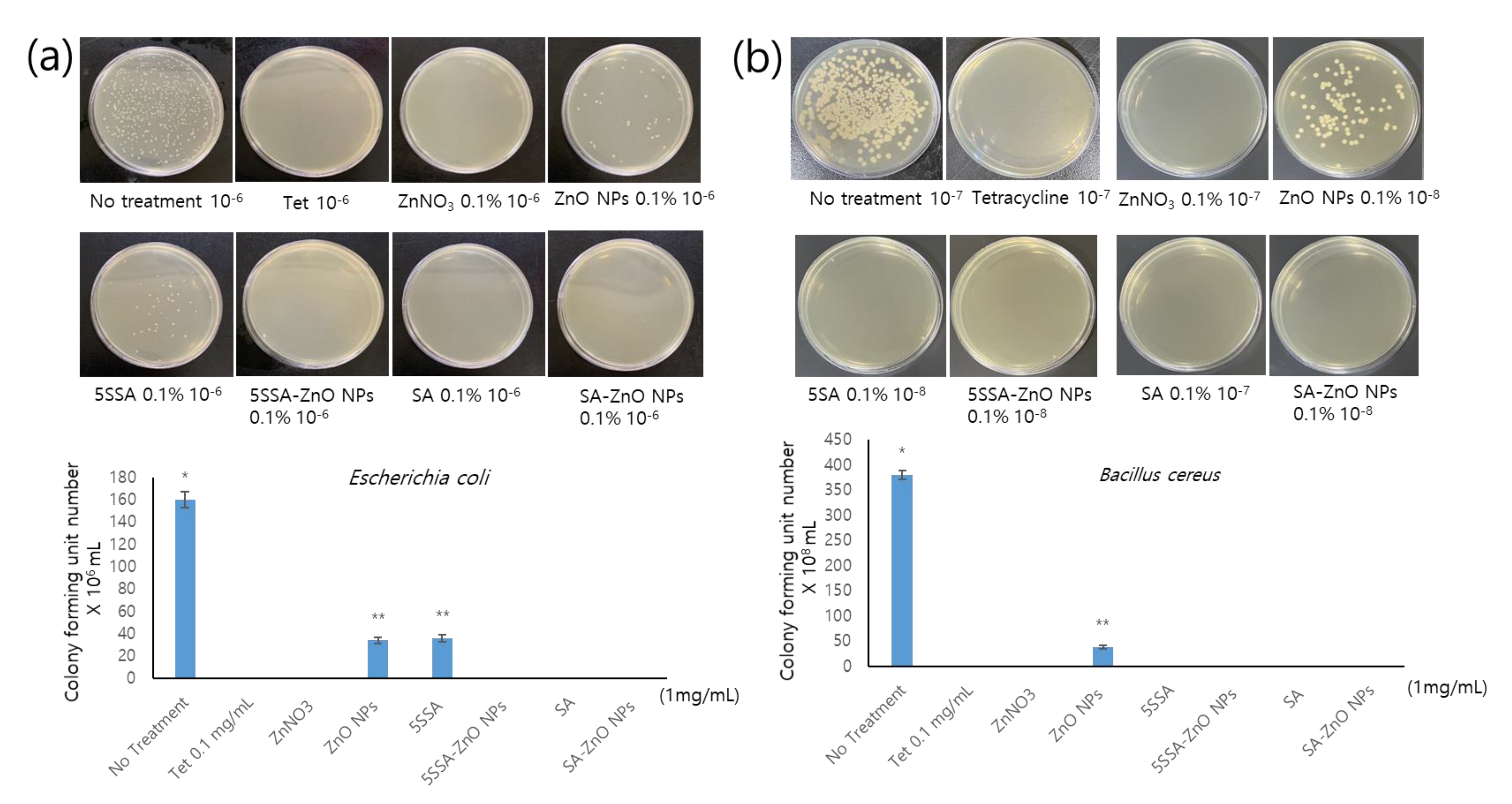
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity of NPs against E. coli and B. cereus
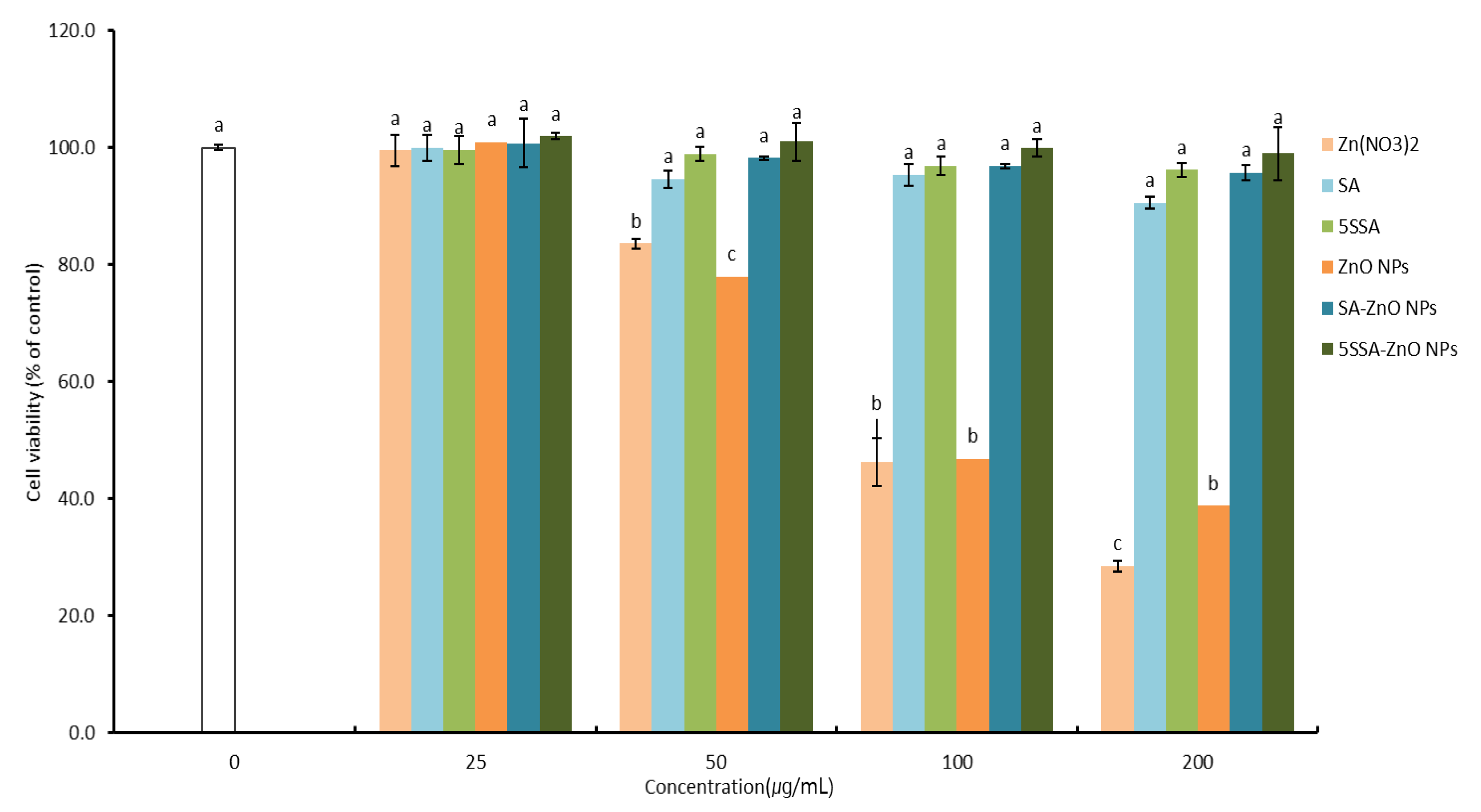
3.6. Growth and Proliferation of HaCaT Cells Treated with SA-ZnO or 5-SSA-ZnO NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makabenta, J.M.V.; Nabawy, A.; Li, C.-H.; Schmidt-Malan, S.; Patel, R.; Rotello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Goudoulas, T.B.; Jeevanandam, J.; Tan, K.X.; Chowdhury, S.; Danquah, M.K. Therapeutic Applications of Metal and Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles: Dermato-Cosmetic Perspectives. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 724499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayagam, R.; Lee, K.E.; David, E.; Matin, M.N.; Kang, S.G. Facile green preparation of PLGA nanoparticles using wedelolactone: Its cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 129, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide—From synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niska, K.; Zielinska, E.; Radomski, M.W.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Metal nanoparticles in dermatology and cosmetology: Interactions with human skin cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 295, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.; Hashim, M.; Malik, S.A.; Khan, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hano, C. Recent Advances in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for Cancer Diagnosis, Target Drug Delivery, and Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Garg, R.; Kumari, A. A review on biogenic synthesis, applications and toxicity aspects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1325. [Google Scholar]
- Abdussalam-Mohammed, W. Comparison of chemical and biological properties of metal nanoparticles (Au, Ag), with metal oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) and their applications. Adv. J. Chem. Sect. A 2020, 3, 192–210. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.-Y.; Logue, M.; Robinson, N. Antimicrobial resistance is a global problem–A UK perspective. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 36, 101136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, A. A review on bidirectional analogies between the photocatalysis and antibacterial properties of ZnO. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, C.R.; Dilarri, G.; Forsan, C.F.; Sapata, V.d.M.R.; Lopes, P.R.M.; de Moraes, P.B.; Montagnolli, R.N.; Ferreira, H.; Bidoia, E.D. Antibacterial action and target mechanisms of zinc oxide nanoparticles against bacterial pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Fathi, N.; Memar, M.Y.; Hosseiniyan Khatibi, S.M.; Khalilov, R.; Negahdari, R.; Zununi Vahed, S.; Maleki Dizaj, S. Anti-microbial activity of curcumin nanoformulations: New trends and future perspectives. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1926–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Arokia Vijaya Anand, M.; Ramachandran, V.; Karthikkumar, V.; Shalini, V.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Ernest, D. Biofabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Aspergillus niger, their antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticancer activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.; Rajanahalli, P.; Ahamed, M.; Rowe, J.J.; Hong, Y. ZnO nanoparticles induce apoptosis in human dermal fibroblasts via p53 and p38 pathways. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, G.R.K.S.; Tabrizi, M.H.; Ardalan, T.; Yadamani, S.; Safavi, E. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of anti-angiogenesis, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxicity properties. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Lee, K.E.; Vinayagam, R.; Kang, S.G. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Profiling of Pomegranate-pericarp Extract Functionalized-zinc Oxide Nanocomposite. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Wen, R.; Wei, D. Effects of the hydrophobicity of adsorbate on the adsorption of salicylic acid and 5-sulfosalicylic acid onto the hydrophobic-hydrophilic macroporous polydivinylbenzene/polymethylacrylethylenediamine IPN. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 421, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha Neto, A.C.; Maraschin, M.; Di Piero, R.M. Antifungal activity of salicylic acid against Penicillium expansum and its possible mechanisms of action. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, T.; Song, Y.; Feng, L.; Kear, P.J.; Riseh, R.S.; Sitohy, M.; Datla, R.; Ren, M. Salicylic acid fights against Fusarium wilt by inhibiting target of rapamycin signaling pathway in Fusarium oxysporum. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D.; Lan, X.; Huang, C.; Xin, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Du, G. A novel naturally occurring salicylic acid analogue acts as an anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB activity in RAW264. 7 macrophages. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Srivastava, N.; Rai, V.K.; Mishra, R.; Ajayakumar, P.V.; Yadav, N.P. A novel approach for dermal controlled release of salicylic acid for improved anti-inflammatory action: Combination of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance and response surface methodology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausina, P.; Branco, J.R.; Demaria, T.M.; Esteves, A.M.; Leandro, J.G.B.; Ochioni, A.C.; Mendonça, A.P.M.; Palhano, F.L.; Oliveira, M.F.; Abou-Kheir, W. Acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid present anticancer properties against melanoma by promoting nitric oxide-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, K.N.; Lim, P.Y.; Wan Ahmad Kammal, W.S.L.; Shamsudin, N. Efficacy and safety of Jessner’s solution peel in comparison with salicylic acid 30% peel in the management of patients with acne vulgaris and postacne hyperpigmentation with skin of color: A randomized, double-blinded, split-face, controlled trial. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Yatskayer, M.; Raab, S.; Oresajo, C. Tolerance and efficacy of a product containing ellagic and salicylic acids in reducing hyperpigmentation and dark spots in comparison with 4% hydroquinone. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.-J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of IκB kinase-β. Nature 1998, 396, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.K. Salicylates and their spectrum of activity. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. (Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents) 2007, 6, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.A.; Robertson, J.; Jumaily, A.A.; Ramos, M.V. Controlled Release of Sulfosalicylic Acid from Regenerated Cellulose/Functionalized Carbon Nanofibers/Polypyrrole Matrices. Int. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 4, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ye, W.; Qi, Y.; Ying, Y.; Xia, Z. Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Bacteria Through Antibiotics Delivery in Surface-Engineered Nano-Cargos: Recent Developments for Future Nano-Antibiotics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 696514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.J.; LaPlante, K.L. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A review. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2005, 25, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.; Castro, I.; Calabuig, E.; Salavert, M. Non-antibiotic treatment for infectious diseases. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2017, 1, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Czaplewski, L.; Bax, R.; Clokie, M.; Dawson, M.; Fairhead, H.; Fischetti, V.A.; Foster, S.; Gilmore, B.F.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Harper, D. Alternatives to antibiotics—A pipeline portfolio review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.D.; Brooks, A.E. Therapeutic strategies to combat antibiotic resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 78, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muflikhun, M.A.; Frommelt, M.C.; Farman, M.; Chua, A.Y.; Santos, G.N.C. Structures, mechanical properties and antibacterial activity of Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite materials synthesized via HVPG technique for coating application. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthiban, E.; Manivannan, N.; Ramanibai, R.; Mathivanan, N. Green synthesis of silver-nanoparticles from Annona reticulata leaves aqueous extract and its mosquito larvicidal and anti-microbial activity on human pathogens. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 21, e00297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthington, R.J.; Melander, C. Combination approaches to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. Nano-therapeutics: A revolution in infection control in post antibiotic era. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 2281–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ramachandran, V.; Murali, R.; Vinothkumar, V.; Raajasubramanian, D.; Kanagalakshimi, A. Biogenic Metal Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Properties. In Nanotechnological Approaches in Food Microbiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- Aldalbahi, A.; Alterary, S.; Ali Abdullrahman Almoghim, R.; Awad, M.A.; Aldosari, N.S.; Fahad Alghannam, S.; Nasser Alabdan, A.; Alharbi, S.; Ali Mohammed Alateeq, B.; Abdulrahman Al Mohsen, A. Greener synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characterization and multifaceted applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Ullah, N.; Haroon, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Optical, morphological and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Papaver somniferum L. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29541–29548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Lin, K.; Li, Y.; Dang, M.; Jiang, L. Synthesis of biocompatible zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles and their neuroprotective effect of 6-OHDA induced neural damage in SH-SY 5Y cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundrarajan, M.; Ambika, S.; Bharathi, K. Plant-extract mediated synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pongamia pinnata and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rehman, W.; Khan, M.M.; Qureshi, M.T.; Gul, A.; Haq, S.; Ullah, R.; Rab, A.; Menaa, F. Phytogenic fabrication of ZnO and gold decorated ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Tang, M. Review of the effects of manufactured nanoparticles on mammalian target organs. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, P.R.; Jayaseelan, C.; Mary, R.R.; Mathivanan, D.; Suseem, S.R. Acaricidal, pediculicidal and larvicidal activity of synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using Momordica charantia leaf extract against blood feeding parasites. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 181, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapriya, M.; Sharmili, S.A.; Baskar, R.; Balaji, R.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Alanzi, K.F.; Vaseeharan, B. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cynara scolymus leaves: Enhanced hemolytic, antimicrobial, antiproliferative, and photocatalytic activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mumtaz, S.; Li, C.-H.; Hussain, I.; Rotello, V.M. Combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria using nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Santhoshkumar, M.; Lee, K.E.; David, E.; Kang, S.G. Bioengineered gold nanoparticles using Cynodon dactylon extract and its cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Abbes, N.; Jing, X.; Zhang, L. A review of the green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and their prospects for application in antibacterial textiles. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2021, 16, 15589250211046242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Ameen, F.; Rizvi, A.; Ali, K.; Sonbol, H.; Zaidi, A.; Khan, M.S.; Musarrat, J. Destruction of cell topography, morphology, membrane, inhibition of respiration, biofilm formation, and bioactive molecule production by nanoparticles of Ag, ZnO, CuO, TiO2, and Al2O3 toward beneficial soil bacteria. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7861–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Serov, D.A.; Rebezov, M.B.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. A Mini Review of Antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 641481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnwal, A.; Kumar, G.; Pant, G.; Hossain, K.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B. Perspectives on Usage of Functional Nanomaterials in Antimicrobial Therapy for Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13492–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte, J.; Abreu, A.C.; Borges, A.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. Antimicrobial activity of selected phytochemicals against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus and their biofilms. Pathogens 2014, 3, 473–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Elliott, A.G.; Kavanagh, A.M.; Ramu, S.; Cooper, M.A. In vitro antimicrobial activity of acne drugs against skin-associated bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Elumalai, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Sangwan, R.S. Nano silver particle synthesis using Swertia paniculata herbal extract and its antimicrobial activity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Li, W.; Shen, X.; Perez-Aguilar, J.M.; Chong, Y.; Gao, X.; Chai, Z.; Chen, C.; Ge, C.; Zhou, R. Differential Pd-nanocrystal facets demonstrate distinct antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthupandy, M.; Rajivgandhi, G.; Muneeswaran, T.; Song, J.-M.; Manoharan, N. Biologically synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as nanoantibiotics against ESBLs producing gram negative bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, A. Advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for cosmetic applications. In Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Smijs, T.G.; Pavel, S. Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreens: Focus on their safety and effectiveness. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2011, 4, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, R.; Peskar, B.A. Anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin and sodium salicylate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 447, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirich, E.G.; Longauer, J.K.; Kirkwood, A.H. Dermatopharmacology of salicylic acid. Dermatology 1975, 151, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, B.; Kristensen, O. Topical salicylic acid interferes with UVB therapy for psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1991, 71, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bair, W.B.; Hart, N.; Einspahr, J.; Liu, G.; Dong, Z.; Alberts, D.; Bowden, G.T. Inhibitory effects of sodium salicylate and acetylsalicylic acid on UVB-induced mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2002, 11, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar]


| ZnO NPs | SA | 5-SSA | SA-ZnO NPs | 5-SSA-ZnO NPs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group | Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group | Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group | Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group | Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group |
| 3380 | O-H | 3230 | O-H | 3022 | C-H | 3403 | O-H | 3400 | O-H |
| 1382 | C-H | 2999 | C-H | 1657 | C=C | 1599 | -N-O | 1606 | C=C |
| 903 | =C-H | 1653 | C=O | 1607 | C=C | 1484 | O-H | 1470 | C-H |
| 693 | =C-H | 1607 | C=C | 1478 | O-H | 1466 | C-H | 1242 | C-OH |
| - | - | 1441 | O-H | 1438 | COO | 1393 | C-H | 1089 | C-O |
| - | - | 1291 | C-O | 1118 | C-O | 1249 | C-N | 1032 | C-O |
| - | - | 1205 | C-O | 1023 | S=O | 1141 | C-OH | 670 | C=C |
| - | - | 1151 | C-OH | 715 | C-H | 755 | C=C | 558 | Zn-C |
| - | - | 886 | C-H | 655 | C=C | 655 | C=C | 900 | Zn-O |
| - | - | 688 | =C-H | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | - | 560 | Zn-C | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | - | 780 | Zn-O | - | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.G.; Lee, K.E.; Singh, M.; Vinayagam, R. Salicylic-Zinc Nanocomposites with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Coatings 2023, 13, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050941
Kang SG, Lee KE, Singh M, Vinayagam R. Salicylic-Zinc Nanocomposites with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Coatings. 2023; 13(5):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050941
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sang Gu, Kyung Eun Lee, Mahendra Singh, and Ramachandran Vinayagam. 2023. "Salicylic-Zinc Nanocomposites with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity" Coatings 13, no. 5: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050941
APA StyleKang, S. G., Lee, K. E., Singh, M., & Vinayagam, R. (2023). Salicylic-Zinc Nanocomposites with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Coatings, 13(5), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050941






