Studying the Crucial Physical Characteristics Related to Surface Roughness and Magnetic Domain Structure in CoFeSm Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Structure Property and Grain Size Distribution
3.2. Composition Analysis
3.3. Surface Morphology and Roughness
3.4. Electrical Characteristics
3.5. Magnetic Properties
3.5.1. Magnetic Susceptibility
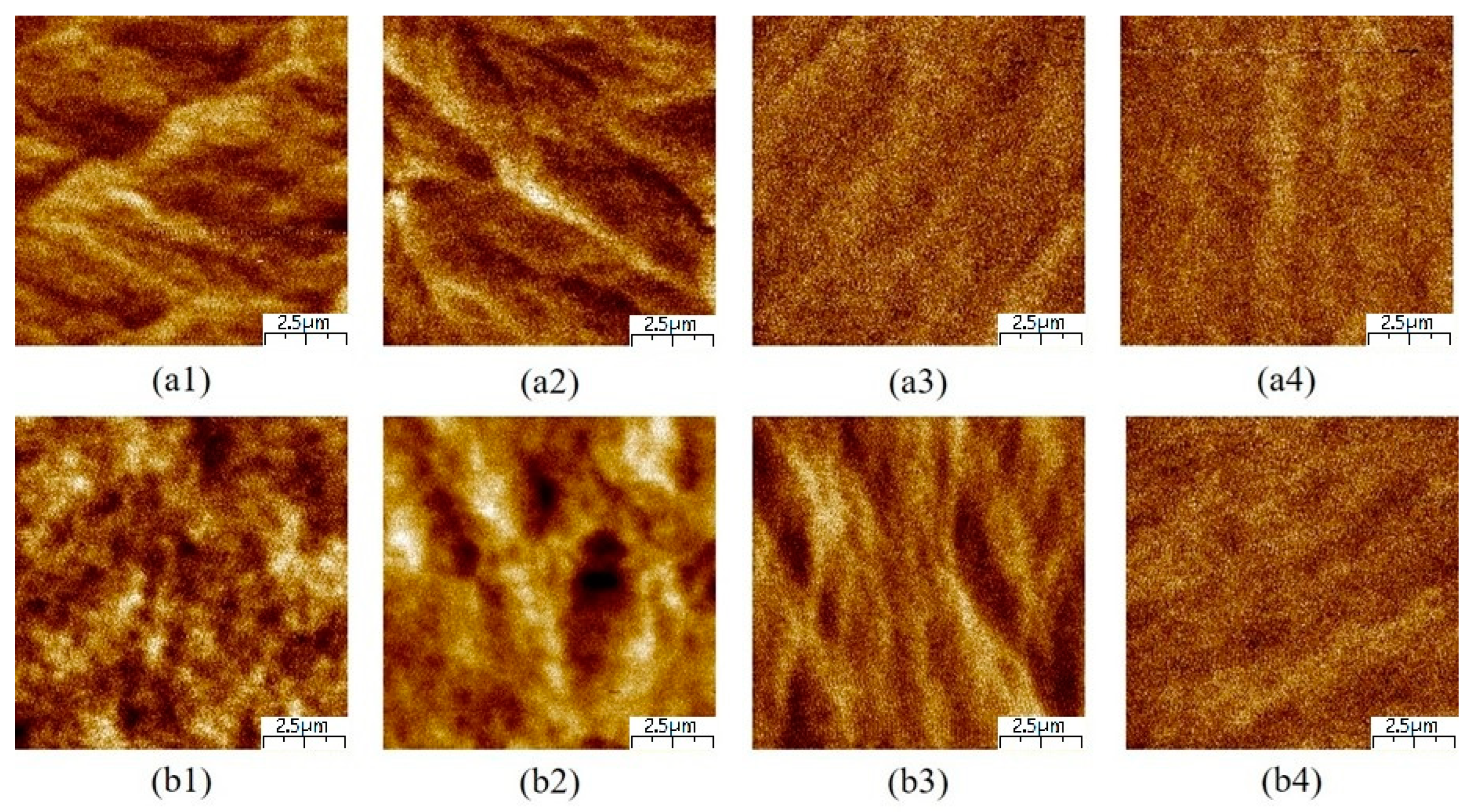
3.5.2. Magnetic Domain Structure
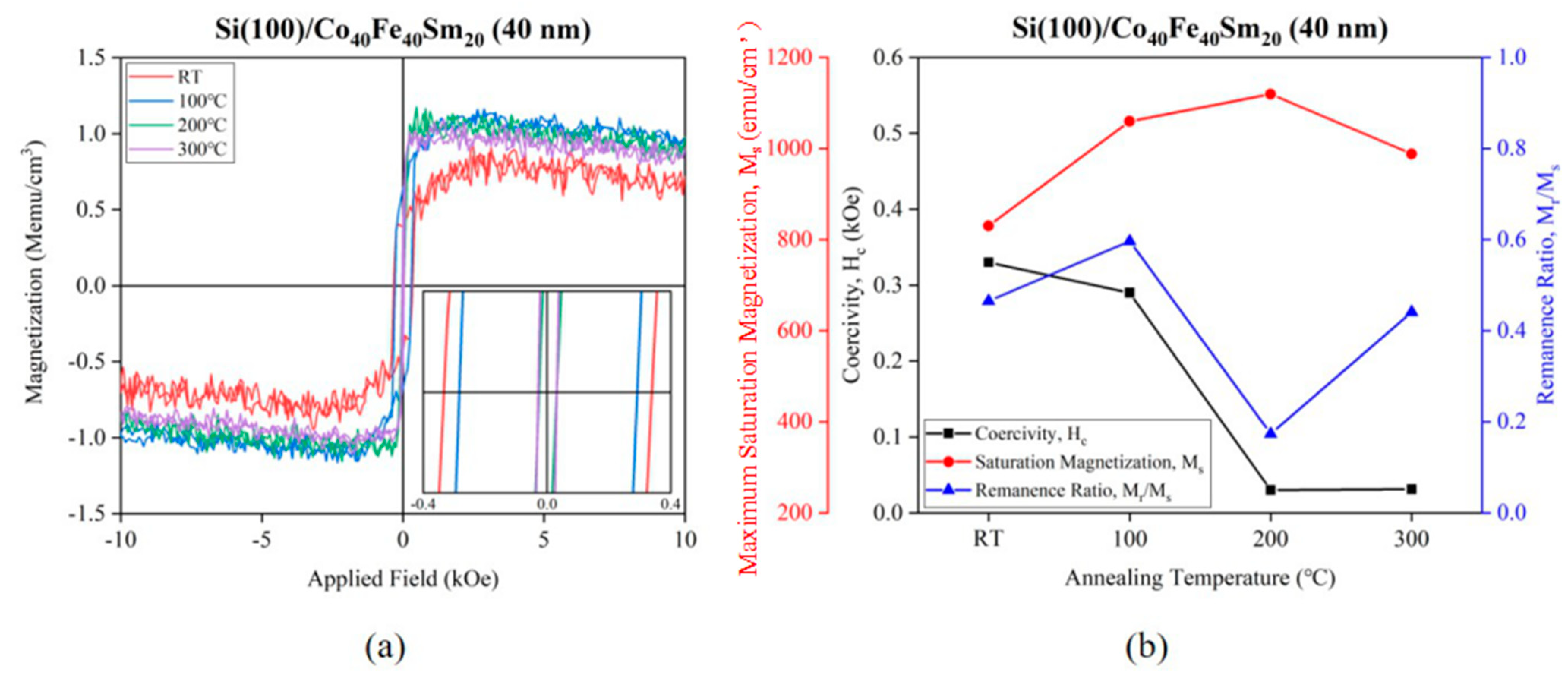
3.5.3. Hysteresis Loop
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seo, Y.; Kwen, K.W. High-density 1R/1W dual-port spin-transfer torque MRAM. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tey, M.S.V.; Chen, X.; Soumyanarayanan, A.; Ho, P. Chiral spin textures for next-generation memory and unconventional computing. CS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 5088–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.A.; Awschalom, D.D.; Buhrman, R.A.; Daughton, J.M.; Molnar, S.V.; Roukes, M.L.; Chtchelkanova, A.Y.; Treger, D.M. Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 2001, 294, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalu, E.E.; Bell, R.; Dupree, M. Improvement of the corrosion behavior of electrodeposited CoFeCu thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehriz, S.; Sohi, M.H.; Ebrahimi, S.A.S. Study of microstructure and magnetic properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline CoFeNiCu thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4757–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Gubbi, A.N.; Baker, I.; Robertson, L. Mechanical properties of soft magnetic FeCo alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 329–331, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijerina-Rosa, A.; Greneche, J.M.; Fuentes, A.F.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; Menéndez, J.L.; Rodríguez-González, F.J.; Montemayor, S.M. Partial substitution of cobalt by rare-earths (Gd or Sm) in cobalt ferrite: Effect on its microstructure and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22920–22929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Kayani, Z.N.; Hassan, A.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Managing the micro-structure and properties of Sm-ZnO thin films by tuning the contents of Sm. Phys. B Condes. Matter 2023, 662, 414964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Shah, J.; Kotnala, R.K. Magnetic and dielectric properties of rare earth substituted Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe1.95R0.05O4 (R = Pr, Sm and La) ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 210, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotibhawaris, T.; Luangvaranunt, T.; Jantaratana, P.; Boonyongmaneerat, Y. Effects of thermal annealing on microstructure and magnetic properties of electrodeposited Co-Fe alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 93, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, S.; Hibino, Y.; Bang, D.; Awano, H.; Kozeki, T.; Akamine, H.; Fujii, T.; Namazu, T.; Takenobu, T.; Koyama, T.; et al. Strain-induced reversible modulation of the magnetic anisotropy in perpendicularly magnetized metals deposited on a flexible substrate. Appl. Phys. Express 2016, 9, 043004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Zhukov, A.; González, J. Stress and/or field induced magnetic anisotropy in the amorphous Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si15.5B7 Alloy: Influence on the coercivity, saturation magnetostriction and magneto-impedance response. Phys. Status Solidi 2002, 194, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, P.C.; Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; Legarreta, L.G.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukov, A. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy enabling engineering of magnetic softness of Fe-rich amorphous microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 510, 166939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.L.D.; Zhukov, A.; Val, J.J.D.; González, J. Coercivity and induced magnetic anisotropy by stress and/or field annealing in Fe- and Co- based (Finemet-type) amorphous alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 294, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, P.C.; Blanco, J.M.; Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Churyukanova, M.; Taskaev, S.; Zhukov, A. Engineering of magnetic softness and domain wall dynamics of Fe-rich amorphous microwires by stress-induced magnetic anisotropy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1247. [Google Scholar]
- Novaković, M.; Popović, M.; Rajić, V. Study on the structural and magnetic properties of e-beam evaporated Co thin films annealed in vacuum. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 937, 168411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Jhou, T.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, T.H.; Chi, P.W. Impact of annealing on magnetic properties and structure of Co40Fe40W20 thin films on Si(100) Substrate. Materials 2021, 14, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Du, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y.; He, J. High magnetic field induced pillar growth and subsequent magnetic properties of the thermal evaporated Co thin films. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Phua, L.X.; Phuoc, N.N.; Ong, C.K. Influence of field-annealing on the microstructure, magnetic and microwave properties of electrodeposited Co0.3Fe0.7 films. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrizi, S.; Molaei, M.J.; Sohi, M.H. An investigation on magnetic properties and electrical resistivity of nanocrystalline CoFeNi thick films synthesized through stabilized bath. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 2547–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, M.; Alam, M.N.E.; Alameh, K.; Premchander, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Kotov, V.A.; Lee, Y.P. Annealing behaviour and crystal structure of RF-sputtered Bi-substituted dysprosium iron-garnet films having excess co-sputtered Bi-oxide content. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 075002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, J.; Lindblad, R.; Gorgoi, M.; Rensmo, H.; Jansson, U.; Lindblad, A. Understanding the effects of sputter damage in W–S thin films by HAXPES. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, J.O.; Mraz, S.; Primetzhofer, D.; Schneider, J.M. Correlative experimental and theoretical investigation of the angle-resolved composition evolution of thin films sputtered from a compound Mo2BC target. Coatings 2019, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, C. Thickness dependence of surface roughness and magnetic properties of FeNiCr thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 333, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, S.R.; Kar, J.P. Effect on electrical properties of CuI thin film prepared by a spin coating technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 76, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojier, K.; Savaloni, H. A study on the dependence of DC electrical properties and nanostructure of Cu thin films on film thickness. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2013, 3, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, W.J.; Guerra, Y.; Garcia, P.; Hernández, E.P. Saturation magnetization as a function of temperature in Zn doped YIG nanoparticles. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2022, 138, 115054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chang, Z.G. Low-frequency alternative-current magnetic susceptibility of amorphous and nanocrystalline Co60Fe20B20 films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Chang, Y.H.; Liu, W.J.; Liang, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wu, T.H. Effect of low-frequency AC magnetic susceptibility of Ru/Co60Fe20V20 and Ta/Co60Fe20V20 films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 465, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porthun, S.; Abelmann, L.; Lodder, C. Magnetic force microscopy of thin film media for high density magnetic recording. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1998, 182, 238–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göddenhenrich, T.; Lemke, H.; Hartmann, U.; Heiden, C. Magnetic force microscopy of domain wall stray fields on single crystal iron whiskers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1990, 56, 2578–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerts, J.; Vandezande, S.; Temst, K.; Haesendonck, C.V. Surface roughness effects on the magnetization reversal of polycrystalline Fe/Ag thin films. Solid State Commun. 2004, 131, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gamache, R.; Wang, G.C.; Lu, T.M.; Palasantzas, G.; Hosson, J.T.M.D. Effect of surface roughness on magnetic domain wall thickness, domain size, and coercivity. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyachkin, A.S.; Komogortsev, S.V. Power-law behavior of coercivity in nanocrystalline magnetic alloys with grain-size distribution. Scr. Mater. 2018, 152, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.L.; Ma, Y.Q.; Ma, Q.; Zheng, G.H.; Dai, Z.X.; Wu, M.Z.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.Q.; Chen, X.S. One-step hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of high magnetization CoFe2O4/Co0.7Fe0.3 nanocomposite permanent magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeaux, C.A.; Kulkarni, V.; Chang, W.S.; Neumann, O.; Cao, Y.; Brinson, B.; Orozco, C.A.; Chen, C.W.; Morosan, E.; Link, S.; et al. Impurity-induced plasmon damping in individual cobalt-doped hollow Au nanoshells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14056–14061. [Google Scholar]
- Jud, E.; Gauckler, L.J. The Effect of Cobalt Oxide Addition on the Conductivity of Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95. J. Electroceramics 2005, 15, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
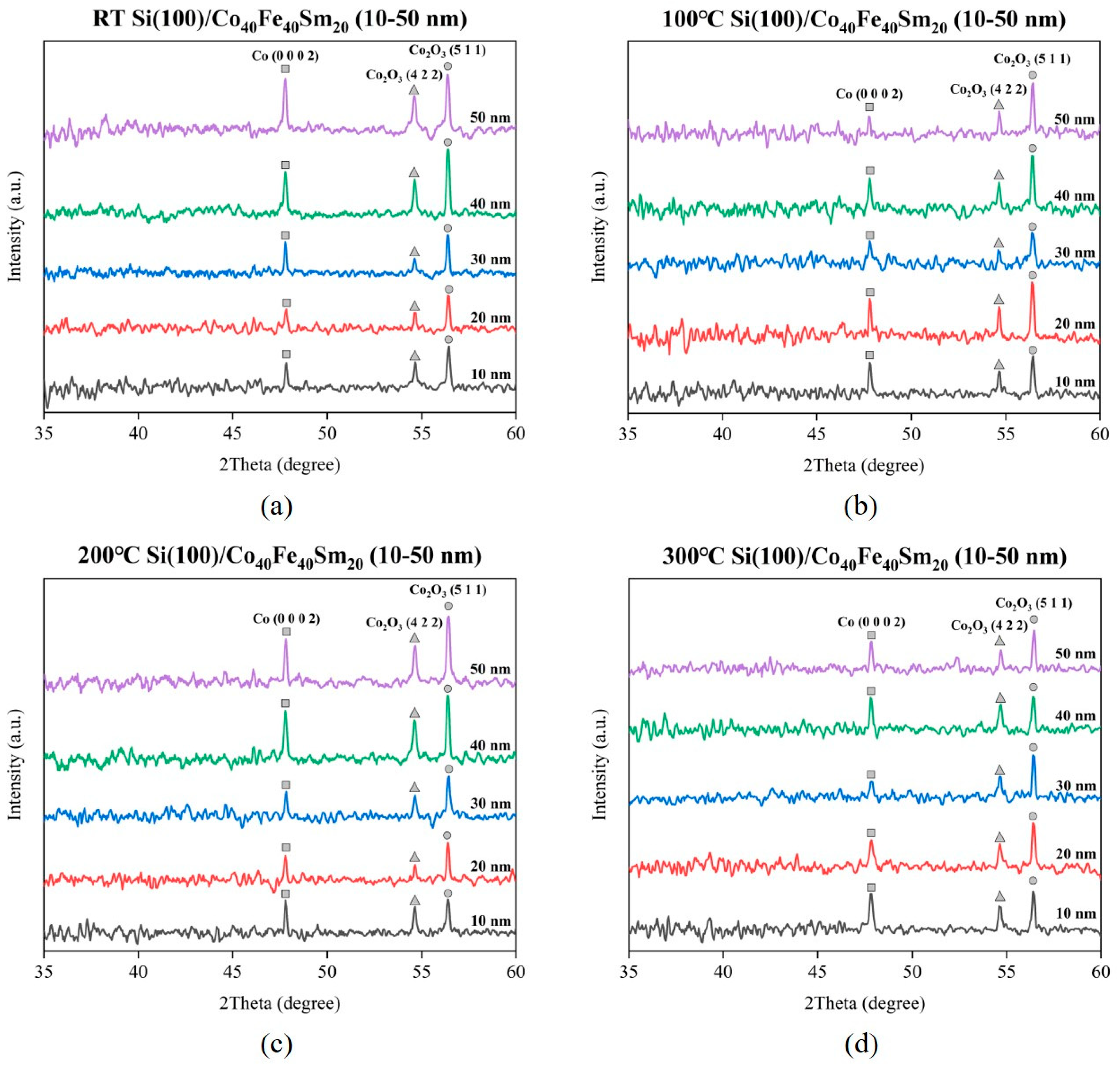
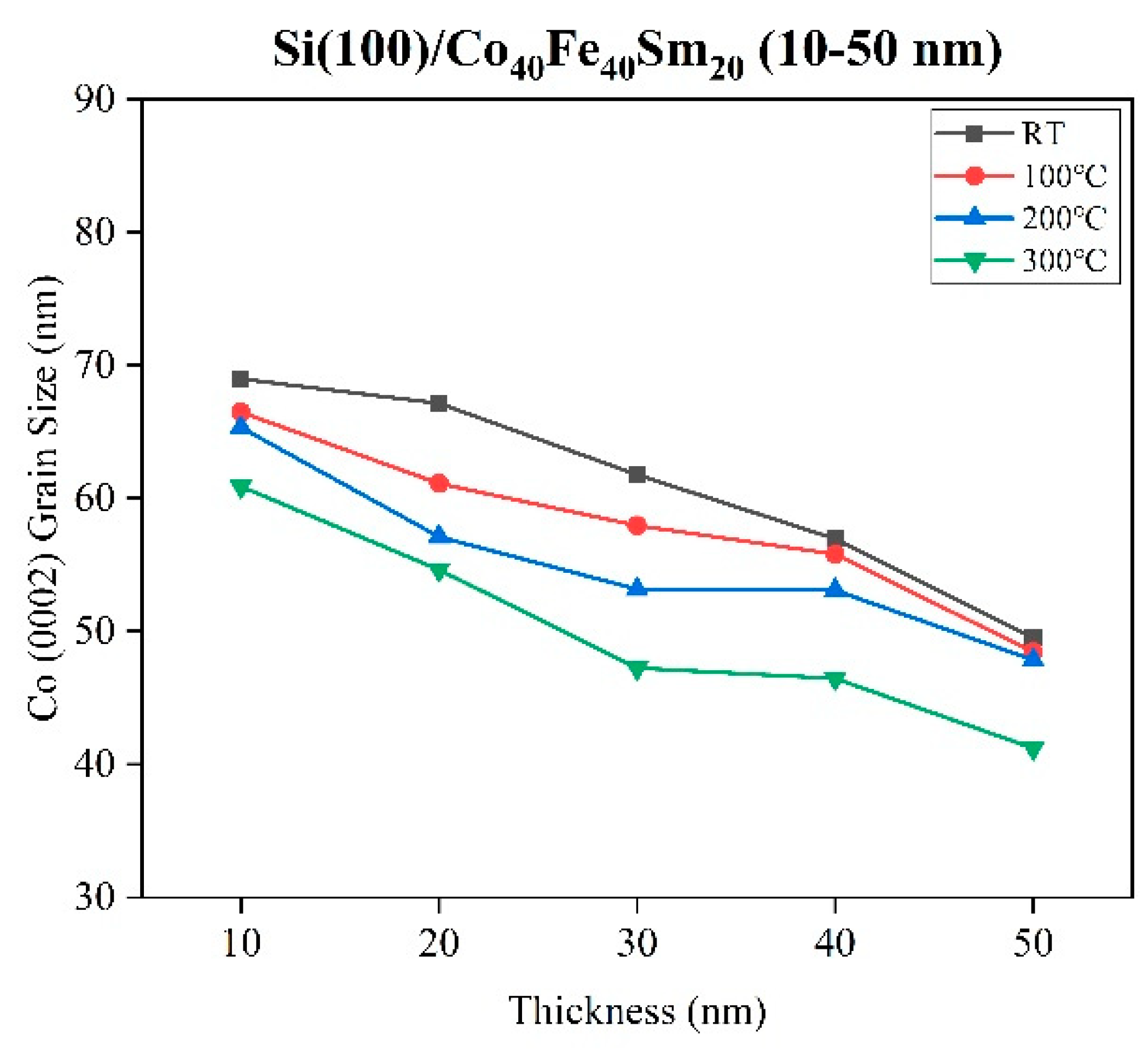
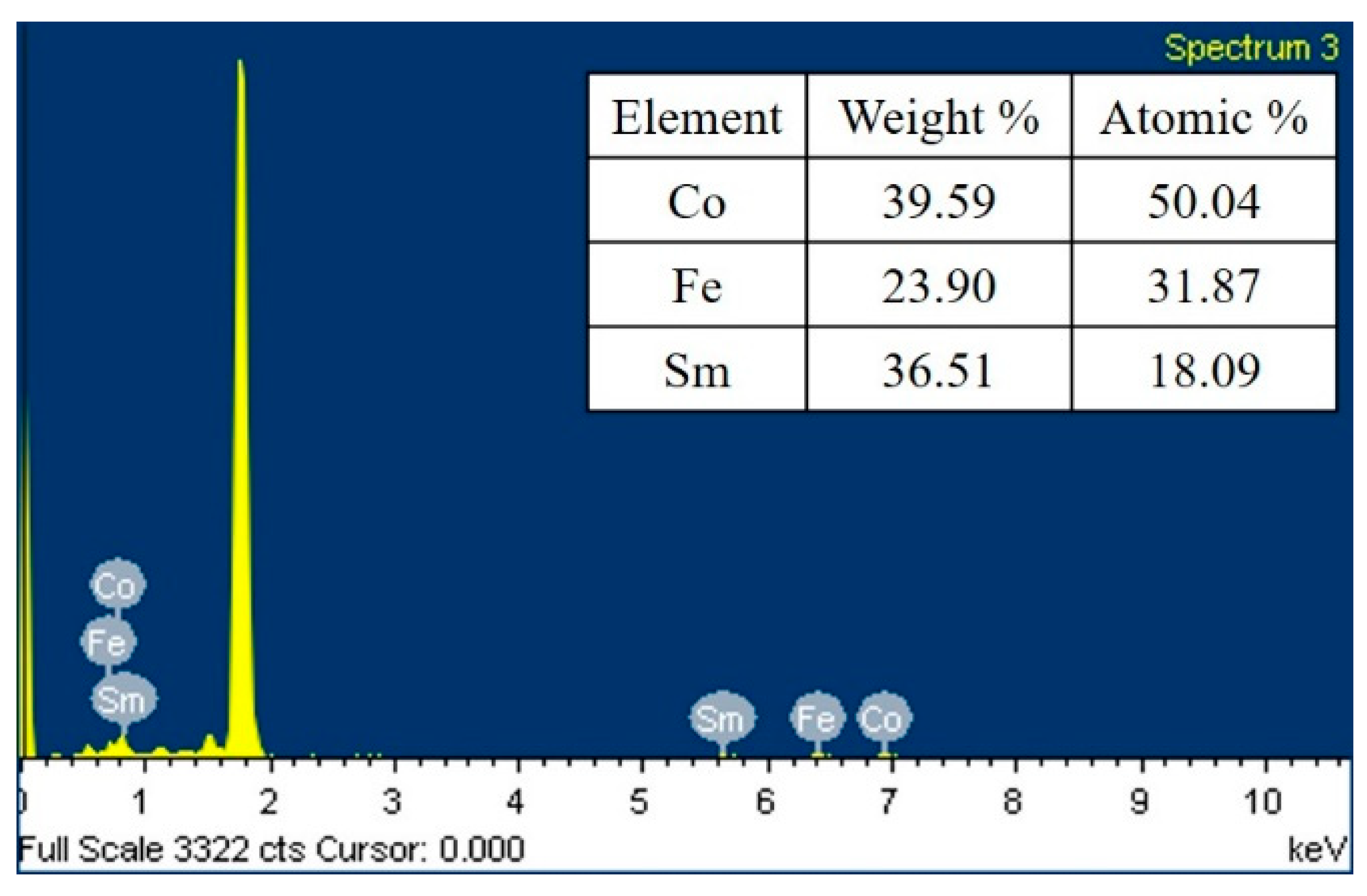
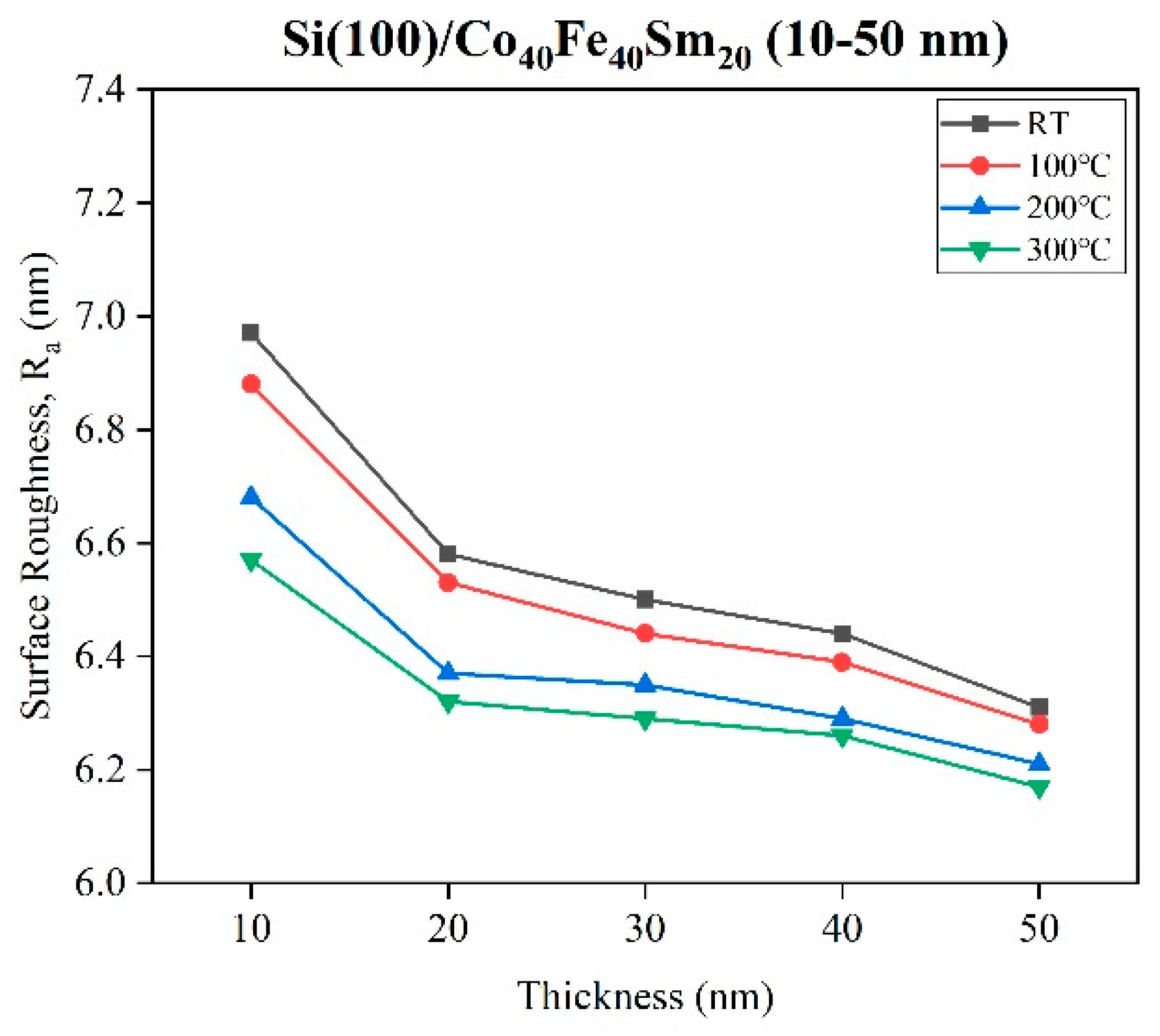
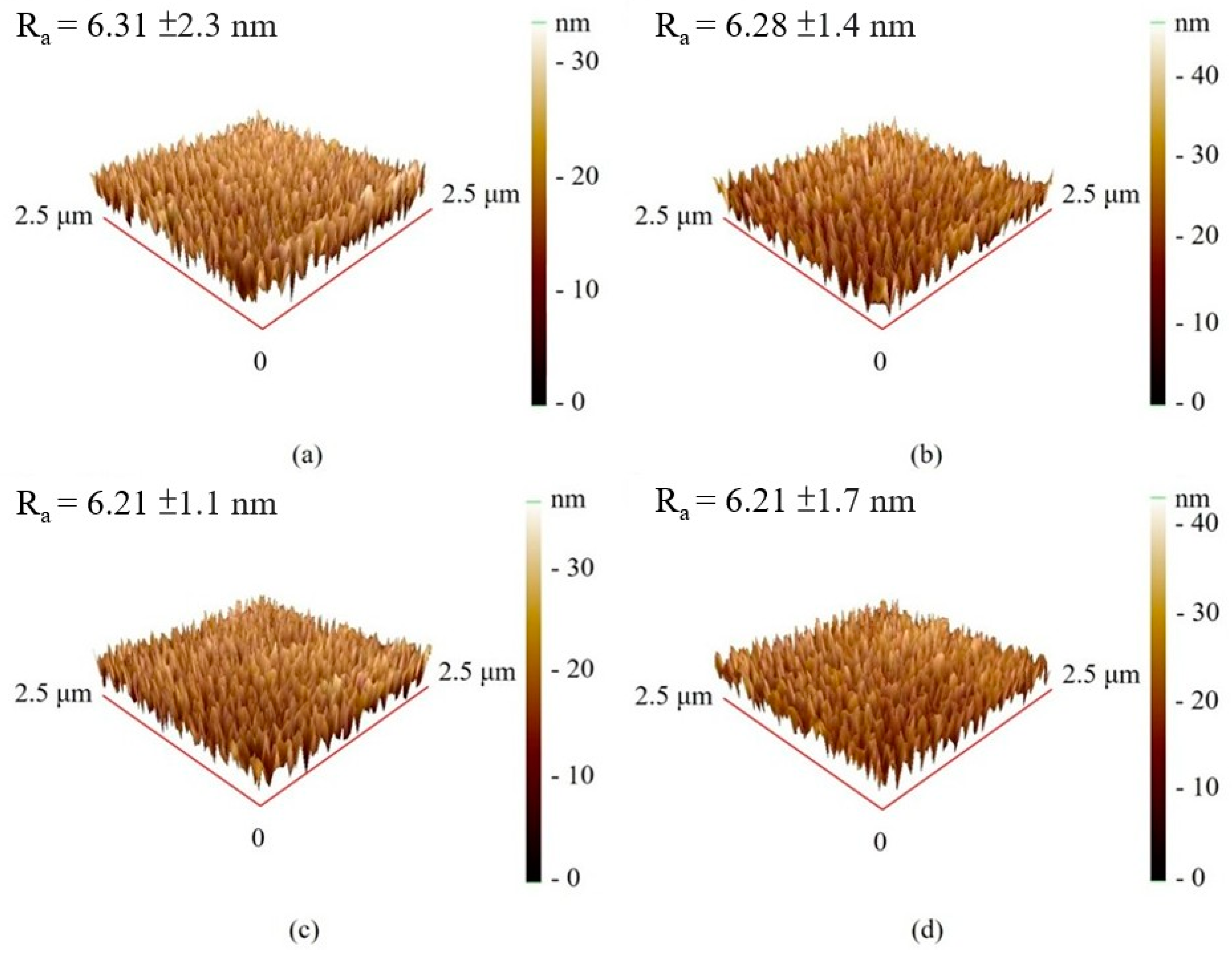
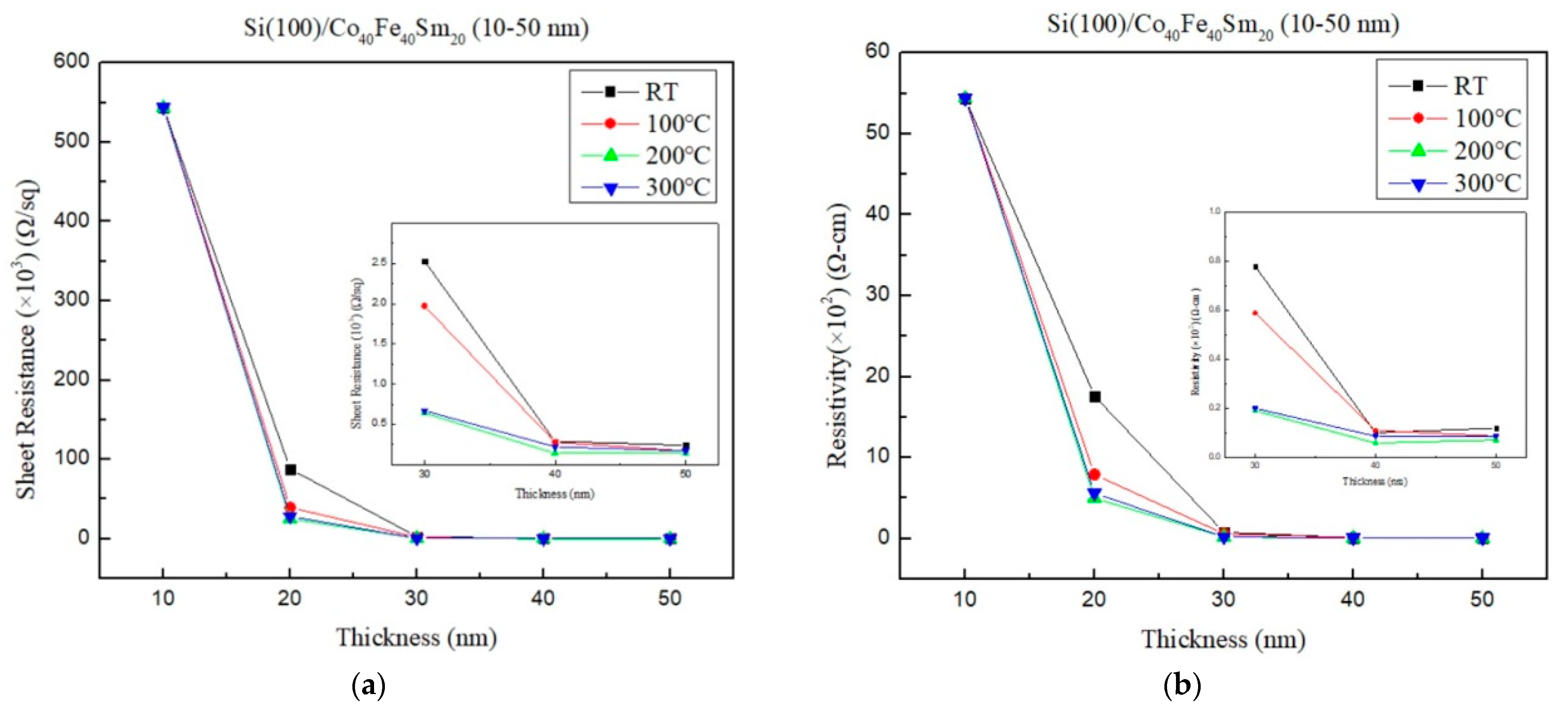
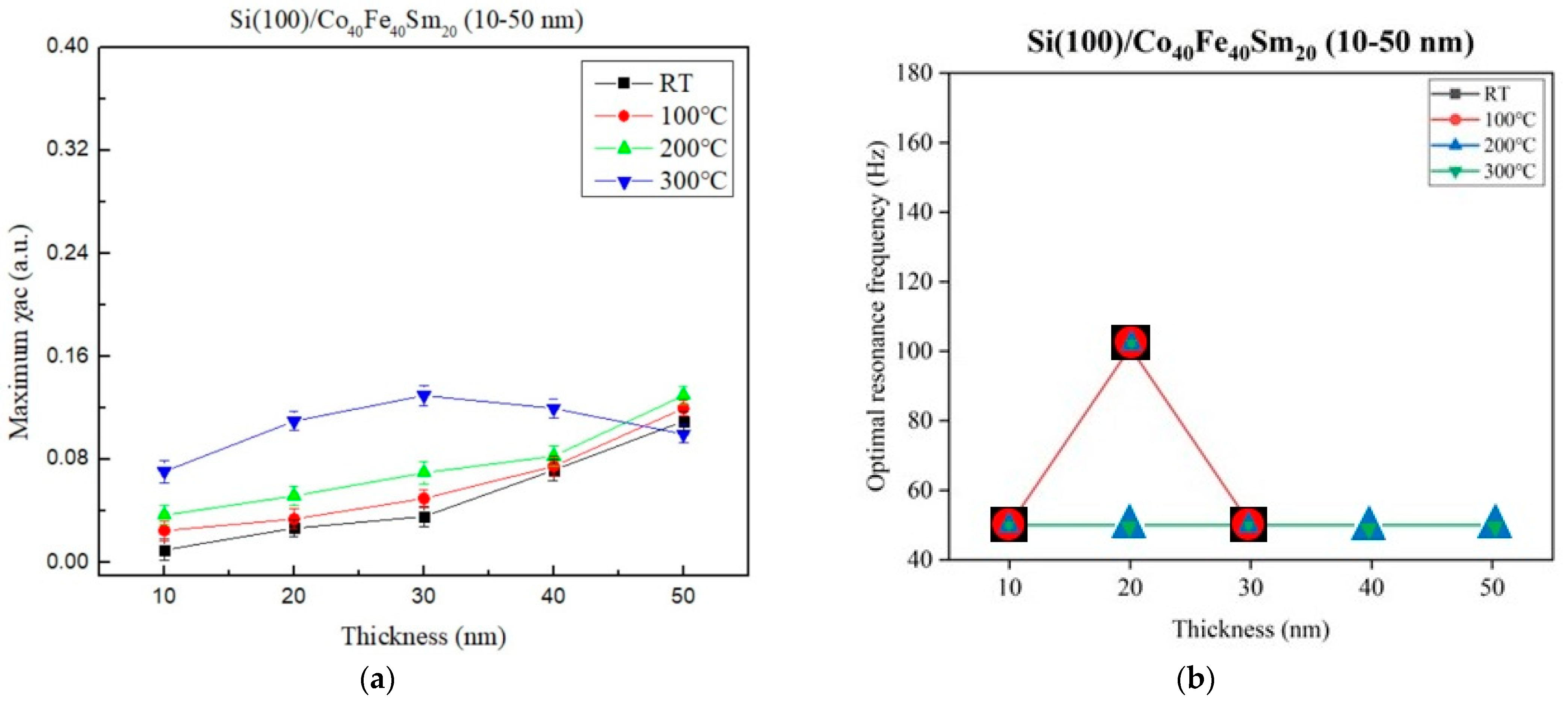
| Ta (°C) | Thickness (nm) | D (nm) | Ra (nm) | Rs (kΩ/sq) | ρ (×10−2 Ω-cm) | Maximum χac (a.u.) | Optimal Resonance Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT | 10 | 68.96 | 6.97 | 543.9 | 54.4 | 0.010 | 50 |
| 20 | 67.13 | 6.58 | 87.90 | 17.6 | 0.027 | 100 | |
| 30 | 61.76 | 6.50 | 2.53 | 0.78 | 0.036 | 50 | |
| 40 | 56.95 | 6.44 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.072 | 50 | |
| 50 | 49.50 | 6.31 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.110 | 50 | |
| 100 | 10 | 66.47 | 6.88 | 543.9 | 54.4 | 0.025 | 50 |
| 20 | 61.10 | 6.53 | 39.36 | 7.87 | 0.034 | 100 | |
| 30 | 57.94 | 6.44 | 1.97 | 0.59 | 0.050 | 50 | |
| 40 | 55.79 | 6.39 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.075 | 50 | |
| 50 | 48.44 | 6.28 | 0.17 | 0.086 | 0.120 | 50 | |
| 200 | 10 | 65.32 | 6.68 | 543.9 | 54.4 | 0.037 | 50 |
| 20 | 57.10 | 6.37 | 25.03 | 5.00 | 0.052 | 50 | |
| 30 | 53.15 | 6.35 | 0.64 | 0.19 | 0.070 | 50 | |
| 40 | 53.08 | 6.29 | 0.14 | 0.058 | 0.083 | 50 | |
| 50 | 47.85 | 6.21 | 0.14 | 0.071 | 0.130 | 50 | |
| 300 | 10 | 60.89 | 6.57 | 543.9 | 54.4 | 0.071 | 50 |
| 20 | 54.62 | 6.32 | 28.05 | 5.61 | 0.110 | 50 | |
| 30 | 47.23 | 6.29 | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.130 | 50 | |
| 40 | 46.46 | 6.26 | 0.22 | 0.086 | 0.120 | 50 | |
| 50 | 41.21 | 6.17 | 0.17 | 0.086 | 0.100 | 50 |
| Ta (°C) | Hc (kOe) | Ms (emu/cm3) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT | 0.330 | 830.29 | 0.47 |
| 100 | 0.290 | 1059.82 | 0.60 |
| 200 | 0.030 | 1119.44 | 0.17 |
| 300 | 0.031 | 988.19 | 0.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fern, C.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chiang, C.-C.; Lai, J.-X.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chen, W.-G.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, S.-H.; Lin, K.-W. Studying the Crucial Physical Characteristics Related to Surface Roughness and Magnetic Domain Structure in CoFeSm Thin Films. Coatings 2023, 13, 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13111961
Fern C-L, Liu W-J, Chang Y-H, Chiang C-C, Lai J-X, Chen Y-T, Chen W-G, Wu T-H, Lin S-H, Lin K-W. Studying the Crucial Physical Characteristics Related to Surface Roughness and Magnetic Domain Structure in CoFeSm Thin Films. Coatings. 2023; 13(11):1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13111961
Chicago/Turabian StyleFern, Chi-Lon, Wen-Jen Liu, Yung-Huang Chang, Chia-Chin Chiang, Jian-Xin Lai, Yuan-Tsung Chen, Wei-Guan Chen, Te-Ho Wu, Shih-Hung Lin, and Ko-Wei Lin. 2023. "Studying the Crucial Physical Characteristics Related to Surface Roughness and Magnetic Domain Structure in CoFeSm Thin Films" Coatings 13, no. 11: 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13111961
APA StyleFern, C.-L., Liu, W.-J., Chang, Y.-H., Chiang, C.-C., Lai, J.-X., Chen, Y.-T., Chen, W.-G., Wu, T.-H., Lin, S.-H., & Lin, K.-W. (2023). Studying the Crucial Physical Characteristics Related to Surface Roughness and Magnetic Domain Structure in CoFeSm Thin Films. Coatings, 13(11), 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13111961








