Abstract
The purpose of the present study is twofold: (i) to assess the salivary nickel, chromium, and iron concentrations and (ii) to characterize the surface microstructure of the typical commercially available Ni-containing metallic appliances during the first 12-week orthodontic treatment period. A total of 85 unstimulated saliva samples were collected from patients before treatment, after 2 days, and after 1, 4, and 12 weeks. Salivary ion concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy, and data were analyzed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS) software. The recorded mean metal concentrations were in the ranges of 132–175 µg/L for Ni, 171–192 µg/L for Cr, and 826–1023 µg/L for Fe. No statistically significant variations were observed between the different study times, and the null hypothesis (the concentrations of metallic ions in patients’ saliva did not significantly change after the placement of the orthodontic appliances) was accepted (p > 0.05). Mean salivary metallic ions were below toxic levels, and no adverse clinical reactions were registered. The intraoral surface degradation of the fixed components was corroborated by optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and energy dispersive spectrometry. Microstructural analysis after complete orthodontic procedure confirmed different corrosion types, from pitting to biocorrosion.
1. Introduction
Biocompatibility is the key property for materials employed in medical applications to assure that devices are safe for human usage. In orthodontics, fixed appliances are usually made of metallic alloys, such as Nitinol (47–52% Ni) and stainless-steel (SS, 8–12% Ni and 17–22% Cr) [1,2,3,4], due to their balanced set of properties, i.e., suitable mechanical properties (e.g., mechanical strength and/or elastic properties) and spontaneous passivation in corrosive environments [1,2]. Nevertheless, the oral cavity is an extreme environment for any metallic biomaterial [5]. The “mouth is the portal entry of the human body” [6]—an “open ecosystem” [7] in which variations of intraoral parameters are frequent and complex, leading to a unique corrosion-promoting human medium. A large number of factors—such as chemical composition; temperature and pH, influenced by diet, oral flora and its by-products; oral hygiene; and health and psychosomatic conditions of each individual [1,2,3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]—may contribute to this phenomenon.
Over the years, several and important in vitro and in vivo research studies have confirmed that metallic orthodontic appliances undergo several types of intraoral corrosion [1,2,3,12,15,16,17,18]. For instance, pitting corrosion is easily induced by the presence of fluorine and chlorine ions [13,19,20]; under low pH values [21,22,23], and fretting and crevice corrosion types can be found in the bracket/archwire contact surfaces, which are commonly tightened with ligatures (i.e., under load) [3,8,17,24,25,26]. The activity of biofilms—which quickly colonize bioalloy surfaces [27]—increase the corrosion susceptibility due to the generation of microgalvanic cells [8]. Moreover, a common orthodontic treatment consists of three sequential phases, the first of which—dental levelling and aligning—involves the simultaneous use of NiTi archwires and SS brackets and increases the risk of galvanic corrosion [1,18]. The end result of corrosion is metallic ion release into the oral cavity [1], such as Ni, Cr, Ti, Co, Mo, and Fe, which can be enhanced by the detrimental effects of the alloy usage (e.g., mechanical stress and fatigue) [3,28]. Several important consequences of this intraoral corrosion may arise and include enamel discoloration and demineralization, hypersensitivity, inflammatory reactions and local pain, and toxicity effects [1,3,25,29,30,31].
Among the metallic ions released into the oral cavity, nickel raises special health concerns and has been systematically studied [29,32,33,34,35], including in orthodontics [9,15,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. Nickel is a trace element in humans [33], and its participation in important cellular functions has been reported [9]. Its estimated average dietary intake ranges between 100 and 300 μg/day, possibly reaching 900 μg/day due to Ni-enriched foodstuff [2,33]. Nevertheless, no deficiency effects in humans have been reported [33]. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) considers inhaled nickel compounds as carcinogenic to humans (Group 1) and its metallic form a possible carcinogenic agent [29]. This transition metal is also a strong immunologic sensitizer, capable of triggering cytotoxic and mutagenic effects, and long-term exposure to a small amount can affect several cellular functions [15]. Moreover, emphasis has been given to Ni-induced genetic effects, including DNA damage and the inhibition of enzymes involved in DNA reparation [15,40]. Chromium is another well-known toxic element, linked to its hexavalent form, Cr (VI), which also exhibits mutagenic, cytotoxic, and carcinogenic effects in humans [15].
Nickel release from orthodontic components can accumulate in the oral mucosa cells [40,49] and decrease cellular viability [40], while systemic toxicity should not be ignored [49]. Ni also induces allergic reactions, as several intra- and extra-oral, subtle to severe symptoms have been reported: severe gingivitis without dental plaque, dermatitis, asthma, gingival hyperplasia, multiform erythema, and labial desquamation, among other symptoms [15,16,30,31,50]. Besides discomfort and pain, orthodontists may need to replace Ni-enriched components, interrupt the treatment, and refer the patient to an allergist or other specialist [50,51,52,53,54].
Despite all concerns, there is no scientific consensus on whether the short- or long-term nickel concentration increases are significant after placing the orthodontic appliances [9,10,11,36,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,55,56,57,58] and the real impact in human health [2,15,32,59]. Allergies in orthodontics are (fortunately) rare [31,60], but may be ineffectively diagnosed: subtle signs can be misinterpreted as mechanical injuries or bacterial-related [2,54,61,62]. Furthermore, while some researchers reported that salivary nickel leaching significantly increased after starting the orthodontic treatment [9,10,40,41,44,45,46,47,49,58], others found no significant oral concentration changes [11,36,48,55,56]. Consequently, further efforts must persist considering the quantification of released metallic ions into the saliva of orthodontic patients.
This work intends to contribute to this discussion. A 12-week treatment time was selected since this period usually matches the first of the three sequential orthodontic treatment phases: dental levelling and aligning. In this stage, orthodontists usually use NiTi archwires (%Ni > 50), which generate continuous loads remaining in the elastic regime during therapy, in addition to SS brackets and tubes (%Ni > 12), glued to the teeth and coupled to wires for control of tooth movement. In consequence, this is the phase in which a higher nickel content can be found inside the oral cavity. Therefore, the motivation of the study is to assess nickel, chromium, and iron salivary concentrations and to stablish the interrelationships with surface microstructural changes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Management
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB, Ethics Committee) of the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra (protocol code 129-CE-2017 and date of approval 18 December 2017). Seventeen unrelated Caucasian patients were randomly selected from the archives of the Institute of Orthodontics of the Dentistry Department of the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra, Portugal (Table 1): 11 females and six males, with an average weight of 65 ± 15 kg in the large age range of 12 to 46 years (mean 20 ± 8 years). All patients signed a written informed consent. The selection process was based on the following criteria: (i) no history of previous comprehensive orthodontic treatment (straight-wire technique); (ii) no systemic illness, meaningful health conditions or allergic reactions records; (iii) no metallic tooth restorations, such as amalgam filling or fixed prostheses; and (iv) followed by the same orthodontist. Patients were asked to avoid the consumption of Ni-rich food and drinks 2 h prior to sampling and were instructed to maintain their regular eating habits and oral hygiene in the meantime.

Table 1.
Main characteristics of the patients included in this study.
The fixed orthodontic appliances used in this study refer to an average of 10 brackets, two tubes or bands, and one archwire per patient, with a variable number of metallic ligatures. The main characteristics of these commercially available orthodontic components are summarized in Table 2, according to the manufacturers’ information.

Table 2.
Nominal chemical composition of the commercially available fixed orthodontic appliances used, according to the manufacturers.
2.2. Saliva Sampling
For saliva sampling, each patient was asked to swallow and rinse their mouths with distilled water for 20 s. Then, saliva was collected by direct spit (approximately 2–5 mL) into new and sterile polypropylene tubes without stimulation, that is, without additional tongue or cheek movements, or by chewing gum. Five samples were collected from each patient at the following times: prior to treatment (t0), and after two days (t1), one week (t2) four weeks (t3), and 12 weeks (t4) after placing the orthodontic appliances. Notice that the NiTi archwires were removed from four patients (P9, P11, P16, and P17) between t3 and t4 periods, Table 3. As a result, no 12-week (t4) sampling was performed. A total of 85 saliva samples were obtained and stored at −20 °C in a cold chamber before analysis.

Table 3.
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) ion concentrations of the 17 patients at the five time intervals: prior to treatment (t0) and after 2 days (t1), 1 week (t2), 4 weeks (t3), and 12 weeks (t4).
2.3. Samples Characterization and Statistical Analysis
The salivary concentrations of nickel, chromium, and iron were evaluated by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES,) using a PerkinElmer, Optima 8000 Series equipment (PerkinElemer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The detection limits were 5 μg/L for Ni and 10 μg/L for both Cr and Fe. Before ICP analysis, the patients’ saliva samples were subjected to a digestion process to eliminate chemical organic components, i.e., treated with 1 mL of H2SO4 per 0.5 mL of saliva. The resulting solutions were diluted at least 20 times with 0.5% HNO3. Three consecutive ICP measurements were conducted.
The statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS, version 24), at a significance level of p < 0.05. The mean and standard deviation of the metal ion concentrations as well as the descriptive statistic were determined using a linear mixed model. The null hypothesis tested in this investigation was that the concentrations of metallic ions in patients’ saliva do not significantly change after the placement of the orthodontic appliance.
The surface morphologies of the representative fixed orthodontic components were examined by optical microscopy (OM) and high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM–ZEISS Merlin Compact/VP Compact, Oberkochen, Germany). Both chemical composition and elemental distribution maps were obtained through energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS–coupled Oxford X-Max Instruments in the SEM system, Oxford Instruments, Oxford, UK). All retrieved components presented intense biofilm deposits and were ultrasonically cleaned (alcohol bath for 20 min) prior to analysis. The intraoral exposure was up to 22 weeks for the removable NiTi archwires and two years (treatment end) for both brackets and tubes. Additionally, the orthodontist was particularly vigilant to eventual manifestations of allergy symptoms.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Quantification of Ion Release
The intraoral evolutions of nickel, chromium, and iron concentrations, measured by ICP-OES-just prior to the clinical treatment with fixed orthodontic appliances (t0) and during the subsequent use up to 12 weeks, are presented in Table 3. The statistical analysis of the salivary metallic ion contents is summarized in Table 4, and the corresponding evolution, according to the 95% confidence interval, can be seen in Figure 1.

Table 4.
Descriptive statistics for the salivary metallic ion content (μg/L) at the time intervals. SD: Standard Deviation; CI: Confidence Interval.
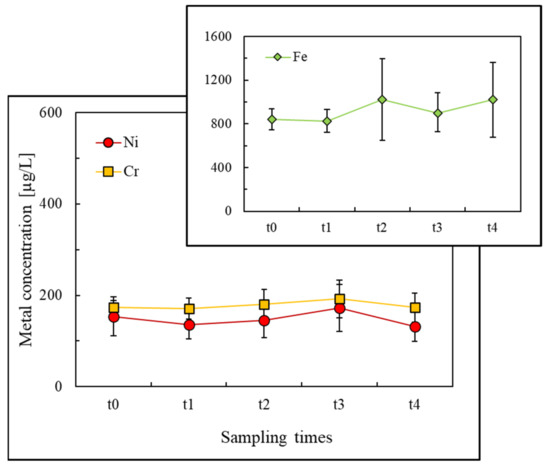
Figure 1.
Mean salivary Ni, Cr, and Fe concentrations during the fixed orthodontic treatment up to 12 weeks.
The mean baseline nickel content in saliva, before placing the appliances (t0), was 153.7 μg/L, and varied between 131.5 and 175.1 μg/L according to the treatment time (Table 4). The intraoral levels of chromium were similar to those of nickel, with an initial median concentration of 174.0 μg/L, and were between 171.4 and 192.4 μg/L during the treatment duration (Table 4). The highest metal concentration values were undoubtedly registered for iron: not only at the beginning of the fixed treatment (t0: 842.1 μg/L) but also throughout the entire treatment time, ranging between 825.9 and 1021.2 μg/L (Table 4).
The average and median nickel and chromium concentrations reported by other authors for similar time intervals showed large variations in comparison to the present study. Values between 0.4 and 670 μg/L for Ni have been assessed [9,36,37,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48], whereas chromium concentrations ranged from 0.3 to 2 mg/L [9,36,41,42,44,45,46,48]. Iron ions, to the authors’ knowledge, are rarely quantified. Only one study with an equivalent time interval (up to 60 days) was found in the literature, revealing an iron concentration range from 28.31 to 103.58 μg/L [45]. Those wide concentration ranges may be explained by dissimilar research methodologies, including unstimulated vs. stimulated saliva sampling, as well as distinct dietary habits of patients or even different grades of dental alloys and manufacturers [16,36,42,43].
As can be seen from the evolution of the mean salivary ion concentrations in Figure 1, the release process was more severe for iron and reached its maximum two days (t1) after placing the orthodontic appliances. After this period, the iron concentrations did not return to the initial level. For nickel and chromium release trends (Figure 1), a slight increase was detected, reaching a maximum four weeks after placing the orthodontic appliances (t3). Similar behaviour was reported by Agaoglu et al. [46], who observed a release peak one month after the orthodontic treatment started. Although differences between nickel and chromium concentrations diminished over the study period, the mean nickel concentrations were always the lowest. Similar behaviour was reported in other studies [9,42,44], and this occurrence may be attributed to nickel binding to salivary proteins, lowering its ionic form. Consequently, lower values have been measured by ICP-OES [42]. Changes in the individual salivary protein composition should therefore affect the nickel salivary concentration and its absorption/distribution in the human body.
The mean concentration trends assessed in this work (Figure 1) suggest that metallic release progression might be time dependent. One explanation is related to the formation of the outer oxide layer, Cr oxide–hydroxides for austenitic SS alloys (brackets and tubes), and Ti-based oxides for NiTi alloys (archwires). The effectiveness of corrosion resistance will be experienced after the formation of highly adherent passivation oxide films, reversing the upward metallic leaching trend. In the case of austenitic stainless-steel, both chromium and nickel impart corrosion resistance; chromium contributes to the spontaneous oxide layer formation, while nickel (8%–14%) makes more chromium accessible for passivation by competing to form salts [2]. NiTi alloys, due to the large titanium nominal composition (47%–52%) form several oxides, and their superior corrosion resistance when compared with SS alloys is attributed to the more stable titanium dioxide phase.
Unfortunately, passivation is an unstable phenomenon. The intraoral environment of the aqueous saliva medium with frequent variations in the chemical composition, temperature, and pH, affected by diet, oral microorganisms, hygiene, health [1,2,3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14], and even the psychosomatic conditions of each individual [11,45], contributes negatively to passivation. Therefore, corrosion reactions will continue to occur throughout the entire treatment, and the balance between the passive layer damage and its reconstitution will dictate the final corrosion resistance behaviour. In addition to the bioalloy aging process, the mechanical friction forces between the SS bracket/tube and the NiTi archwires may also increase the metallic ion concentrations in saliva.
Nevertheless, no statistically significant variations were observed in this study for metallic concentration values between the different periods, Table 4 and Figure 1, according to the linear mixed model. As a result, the null hypothesis tested in the present study—the concentrations of metal ions in patients’ saliva do not change significantly after the placement of the orthodontic appliance—was accepted (p > 0.05). A direct comparison between the values obtained in this study and those reported in other works is difficult, yet similar conclusions were obtained by other authors for equivalent [36,48] or long-term [11,55,56] study periods. Other studies, however, reported significant nickel salivary concentration increases: immediately after placing the fixed appliance [45,58] and after one day [45], one week [9,41,44,45], approximately one month [9,41,45,46], two months [45,47] or longer [9,10] treatment periods compared with before. Contradictory results can also be found in the literature for chromium concentrations over time [9,44,45,46].
Finally, dietary studies conducted in different countries estimate a daily nickel intake of 100–300 μg/day from food and drinking water. In addition, consumption of Ni-enriched foodstuffs (e.g., processed food) may increase this value up to 900 μg/day [2,33]. Concerning chromium, an average daily intake of 50–280 μg/day has been estimated [2]. Iron is an essential element and is consumed daily in large quantities in the human diet; iron does not represent a risk to human health [32,45]. Thus, the actual ion release quantification during the dental levelling and aligning stage (the first 12 weeks of an orthodontic treatment) can be considered negligible from a toxicological perspective, despite the low number of patients included in the sample. No patients showed allergy symptoms.
3.2. Surface Appliance Characterization
As expected, the microstructural analysis, by SEM, EDS, and OM, of the fixed appliances corroborated the oral metallic leaching, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7.

Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs of the NiTi archwires: (a) patient P12–13 weeks; (b) patient P3–22 weeks of intraoral use.
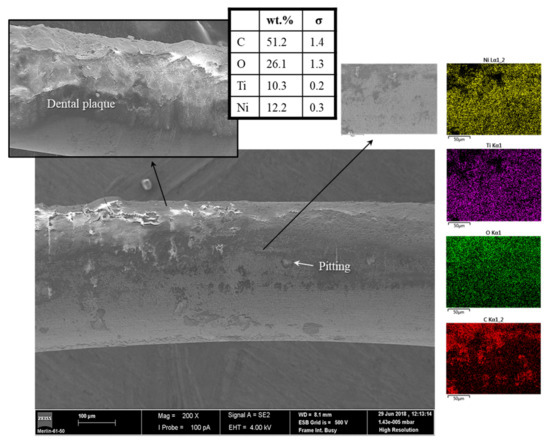
Figure 3.
SEM micrographs and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) elemental distribution maps of the NiTi archwire from patient P8–17 weeks of intraoral use.
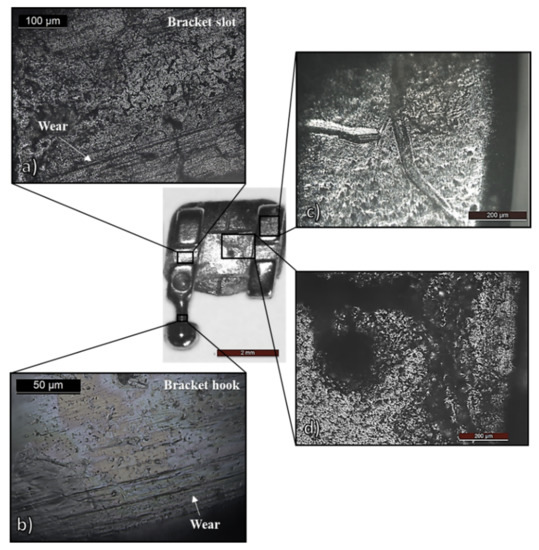
Figure 4.
SS bracket after two years of intraoral use: optical microscopy (OM) micrographs showing (a,b) fretting corrosion; (c) deformation tracks by archwires manipulation; (d) biofilm-covered pitting corrosion.
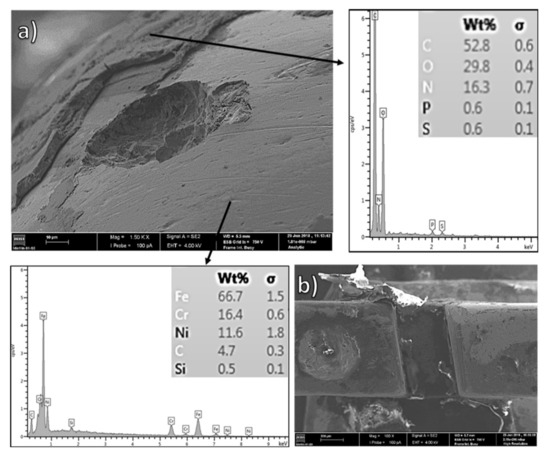
Figure 5.
SS bracket after two years of intraoral use: SEM and OM micrographs coupled to EDS chemical compositions of the two distinct zones–stainless steel and biofilm-adherent surfaces. (a) pitting morphology underneath a biofilm layer, (b) biofilm accumulation.
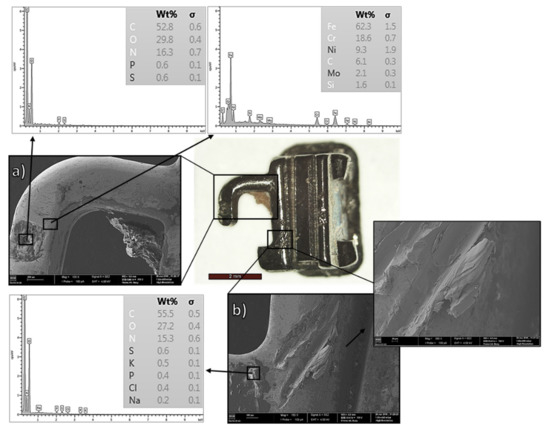
Figure 6.
SS tube after two years of intraoral use: SEM and OM micrographs coupled with EDS chemical composition: (a) cavity filled with organic material; (b) wear track coupled with debris.
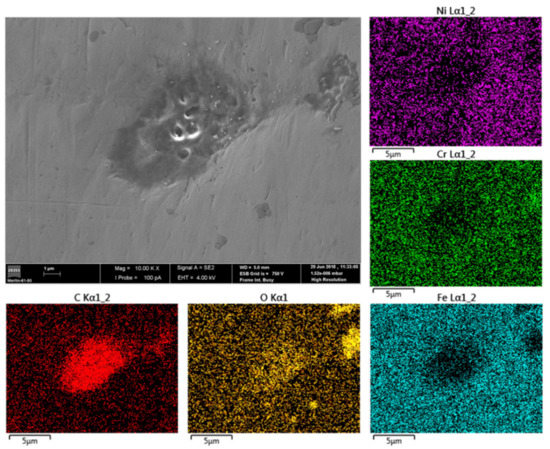

Figure 7.
SS tube after two years of intraoral use: surface SEM micrograph and the corresponding EDS elemental distribution maps.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the NiTi archwires used in the dental levelling and aligning stage of patients P12, P8, and P3 for 13, 17, and 22 weeks, respectively. All wires revealed clear signs of intraoral usage, including pitting corrosion (Figure 3), wear tracks (Figure 2), and high accumulation of highly adherent dental plaque despite the previous cleaning process with ultrasound. The EDS elemental distribution maps of the wire from patient P8, Figure 3, corroborated the notorious presence of organic material (carbon and oxygen contents of 51 and 26 wt.%, respectively) on its surface: oral biofilms. Notice that the detected Ni/Ti ratio of approximately 1.2, by EDS, matches the alloy chemical composition (Table 2–with expected ratio of approximately 1–1.5).
The oral cavity is ideal for the inevitable proliferation of microorganisms. In biofilms, bacteria and other microorganisms (fungi and viruses) are embedded in an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) [63]. This EPS matrix provides not only structural stability but also antimicrobial tolerance and resistance against the host immune system. In fact, a grown (mature) biofilm is advantageous to its inhabitants by providing nutrients to and protecting both aerobic and anaerobic colonizers—even against drugs, antimicrobial factors from saliva, and phagocytic cells [7,64,65]. However, the extremely complex EPS chemical composition [63] can negatively impact the performance of metallic alloys, increasing the treatment time or even causing its failure.
Mystkowska et al. [8] suggested three main mechanisms for biologically induced pitting corrosion based on the formation of microgalvanic cells with different oxygenation degrees due to the presence of biofilms. Briefly, one of the reported mechanism states that the functional groups of the EPS produced by microbes bind metallic ions with different affinities along the surface. Consequently, a heterogenic distribution of metallic ions appears along the surface, and the metallic substrate below regions with high affinity will function as the anode. Moreover, the microbiological activity of dental plaques releases several by-products into the saliva, altering the chemical composition and oxygenation reaction and the pH values of the oral cavity. As a result, localized corrosion will occur, i.e., pitting, as observed in Figure 3.
Intimately related to the microbiologically induced corrosion phenomenon is wear corrosion, which also promotes metallic ion release into the oral cavity [3,8]. Wear corrosion occurs due to the relative movement of two surfaces under load (fretting) and contributes to the degradation of the material [1,2,3]. During orthodontic treatment, the surfaces of both archwires and bracket slots experience loads due to the use of metallic or polymeric ligatures. The small displacements caused the wear tracks observed in (Figure 2), as a result of fretting corrosion, which disrupt the passive films and consequently decrease corrosion resistance [1,2,3]. If food and/or biofilm are present between the sliding surfaces, the wear rate is likely to increase due to roughness increases and microgalvanic cell generation [8].
In this work, the in vivo release of titanium was not quantified. However, the presence of detachments/cracks/inclusions in the passive titanium oxide layer (Figure 3)—which can be masked by the presence of biofilm—would suggest a much higher nickel release than that of the bracket/tube appliances (SS alloy), in accordance with the NiTi alloy composition. Indeed, NiTi materials are a nearly equiatomic alloy of Ni and Ti, whereas a maximum of 13 wt.% Ni is present in the austenitic composition SS alloys (Table 2). Moreover, the presence of dissimilar alloys (SS and NiTi) enhances the corrosion extension, by galvanic corrosion, and therefore increases the metallic oral content, which was not registered in this study.
According to the microbiologically induced corrosion process described above, it is also credible to assume an uptake of metallic ions by oral microorganisms. In fact, Fors and colleagues [37] reported biofilm formation with a very high nickel content on metallic surfaces in comparison to dental plaque on teeth surfaces during an orthodontic treatment. These phenomena may lower the nickel/chromium salivary concentrations and thus validate the ICP results obtained in the present work. Moreover, although oral corrosion may continue, this metal uptake by microorganisms prevent the increase–decrease concentration curve profile.
This hypothesis was also suggested by other authors, which is closely related to the plaque thickness increase due to the greater difficulty in maintaining proper oral hygiene during orthodontic treatment [3,8,11,16,37,45,56]. Indeed, other studies state that the surface of SS brackets is quickly colonized by biofilms as early as 24 h after placing the orthodontic appliances [27].
As expected, these results are in line with those obtained for the SS bracket and tube components after two years of orthodontic treatment, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7, presenting clear signs of in vivo usage.
Firstly, wear tracks related to fretting corrosion were observed in the bracket slot, Figure 4a, which contacts the archwire under load—the counterpart region of the surfaces observed in Figure 2. Wear tracks were also found on the brackets’ “hooks”, Figure 4b, in which metallic ligatures were anchored during the orthodontic treatment. Furthermore, orthodontists manipulate the appliances with metallic tools (placement, tightening, removal), which also damage the surface, e.g., the plastic deformation “tracks” displayed in Figure 4c. A more severe and deeper plastic deformation morphology was found on the tube surface, as can be seen in Figure 6b, due to handling. Even the masticatory process itself may cause surface “scratches” and “notching” [3], and, in consequence, passive film or biofilm disruption [8].
Indeed, pronounced, highly adherent biofilm layers observed by OM (Figure 4d) were confirmed by SEM–EDS analysis. As can be seen in Figure 5 and Figure 6, the EDS results confirmed the presence of organic material, mainly composed of carbon (more than 50 wt.%), oxygen, and nitrogen. Notice the accumulation of biofilm inside the component’s cavity, Figure 5b and Figure 6a. Further observation revealed evident pitting corrosion morphologies underneath the removed biofilm layers, as shown in Figure 5a for the bracket clinically used for two years. As described previously for NiTi archwires, the microorganisms can promote the corrosion of metallic surfaces underneath the biofilm layers (microbiologically induced corrosion) through the generation of microgalvanic cells [8]. Certain anaerobic bacteria found in the mouth can also reduce sulfates (sulfate-reducing bacteria) and release by-products (such as H2, H2S, and FeS) that induce strong local cathodes and gradually destroy the metallic surface [8,66]. The evident pitting corrosion morphologies, well documented in Figure 5a, are likely a consequence of microbiologically induced corrosion.
Notwithstanding the clear evidence of corrosion of orthodontic appliances, the metallic ion concentrations obtained in this work are nontoxic, largely inferior to the doses obtained from the human diet. The absence of notorious changes during the treatment—especially for nickel—shows the complexity of the intraoral environment, possibly with metal binding to proteins and uptake by biofilms. Nevertheless, the effect of local concentrations of metallic ions is still not well understood in orthodontics [15], and the authors of a recent study [49] encouraged further research on the bioaccumulation and bioconcentration of nickel ions in the oral cavity, suggesting that their presence may present a real threat to the tissues even at sub-toxic concentrations. Since the oral metal release from fixed appliances, due to corrosion processes, should be treated as a chronic exposure to toxic agents, it would be of great interest and a scientific challenge to investigate the accumulation at specific sites in the human body as well, particularly in mouth tissues.
Analogous to this study, most in vivo investigations face an unavoidable limitation, that is, the lack of continuous monitoring of metal ion concentrations in saliva [37,44]—the major obstacle in determining the levels of ions released in vivo [58]. The use of a biomarker that does not allow us to monitor chronic exposure to trace elements (e.g., metal ions) may cause a cumulative data failure. Further investigation should persist since local or systemic, subtle to severe symptoms of allergic reactions to metals in this medical field may in fact occur, typically in hypersensitive individuals [3,30,31,57], especially for nickel [50,51,52,53,67].
4. Conclusions
The present in vivo study for multiple-phase orthodontic alloys during the dental levelling and aligning phase allowed us to conclude the following:
- Nickel, chromium, and iron concentrations in patients’ saliva did not significantly change during the first 12 weeks of the orthodontic treatment;
- Pitting and fretting types of corrosion were identified, in addition to that promoted by the highly adherent biofilm layers, i.e., biocorrosion.
Although these results might support the safety of orthodontic treatments in the long-term, further investigation must persist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.L.; methodology, C.S.L. and S.A.P.; software, A.R.M. and S.A.P.; validation, A.R.M. and S.A.P.; formal analysis, A.F. and A.R.M.; investigation, A.F., A.R.M. and S.A.P.; resources, C.S.L. and S.A.P.; data curation, A.F. and A.R.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F. and A.R.M.; writing—review and editing, C.S.L. and S.A.P.; visualization, A.F. and A.R.M.; supervision, C.S.L. and S.A.P.; project administration, C.S.L. and S.A.P.; funding acquisition, A.F. and C.S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is sponsored by national funds through FCT–Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia and through the PhD Grant SFRH/BD/143905/2019 attributed to A.F.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki [68] and was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB, Ethics Committee) the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra (protocol code 129-CE-2017 and date of approval 18/12/2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research is sponsored by FEDER funds through the program COMPETE–Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade and by national funds through FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, UIDB/00285/2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chaturvedi, T.P.; Upadhayay, S.N. An overview of orthodontic material degradation in oral cavity. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2010, 21, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, K.; Sernetz, F.; Dymock, D.; Sandy, J.R.; Ireland, A.J. Corrosion of orthodontic appliances-should we care? Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, T.; Athanasiou, A.E. In Vivo Aging of Orthodontic Alloys: Implications for Corrosion Potential, Nickel Release, and Biocompatibility. Angle Orthod. 2002, 72, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.W.; Sarver, D.M.; Ackerman, J.L. Contemporary orthodontic appliances. In Contemporary Orthodontics; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 347–389. ISBN 978032308317. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, D.C. Metal corrosion in the human body: The ultimate bio-corrosion scenario. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2008, 17, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthamuthu, S.; Rajasekar, A.; Sathiyanarayanan, S.; Muthukumar, N.; Palaniswamy, N. Electrochemical behaviour of microbes on orthodontic wires. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 988–996. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, H.F.; Hassell, T.M. Biofilm—Plaque Formation on Tooth and Root Surfaces. In Color Atlas of Dental Hygene-Periodontology; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 24. ISBN 9783131417619. [Google Scholar]
- Mystkowska, J.; Niemirowicz-Laskowska, K.; Łysik, D.; Tokajuk, G.; Dąbrowski, J.R.; Bucki, R. The role of oral cavity biofilm on metallic biomaterial surface destruction–corrosion and friction aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.; Tikku, T.; Khanna, R.; Maurya, R.P.; Verma, G.; Murthy, R.C. Release of nickel and chromium ions in the saliva of patients with fixed orthodontic appliance: An in-vivo study. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 6, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, F.; Jafari, A.; Amini, P.; Sepasi, S. Metal ion release from fixed orthodontic appliances—An in vivo study. Eur. J. Orthod. 2012, 34, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, F.; Rakhshan, V.; Mesgarzadeh, N. Effects of long-term fixed orthodontic treatment on salivary nickel and chromium levels: A 1-Year prospective cohort study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 150, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhashemi, A.; Jahangiri, S.; Kharrazifard, M. Release of nickel and chromium ions from orthodontic wires following the use of teeth whitening mouthwashes. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitra, P.; Prashantha, G.S.; Rao, A. Effect of fluoride agents on surface characteristics of NiTi wires. An ex vivo investigation. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2020, 10, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.E.; Lyons, K.M.; Kieser, J.A.; Waddell, N.J. Diurnal variation of intraoral pH and temperature. BDJ Open 2017, 3, 17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Cameán, A.; Jos, Á.; Mellado-García, P.; Iglesias-Linares, A.; Solano, E.; Cameán, A.M. In vitro and in vivo evidence of the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of metal ions released by orthodontic appliances: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 86–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulewicz, M.; Chojnacka, K. Trace Metal Release from Orthodontic Appliances by In Vivo Studies: A Systematic Literature Review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 137, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fróis, A.; Evaristo, M.; Santos, A.C.; Louro, C.S. Salivary pH Effect on Orthodontic Appliances: In Vitro Study of the SS/DLC System. Coatings 2021, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polychronis, G.; Al Jabbari, Y.S.; Eliades, T.; Zinelis, S. Galvanic coupling of steel and gold alloy lingual brackets with orthodontic wires: Is corrosion a concern? Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Han, E.; Ke, W. Influence of fluoride and chloride on corrosion behavior of NiTi orthodontic wires. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.M.; Ponces, M.J.; Lopes, J.D.; Vasconcelos, M.; Pollmann, M.C.F. Orthodontic wires and its corrosion—The specific case of stainless steel and beta-titanium. J. Dent. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.-T.; Huang, T.-H. Variations in surface characteristics and corrosion behaviour of metal brackets and wires in different electrolyte solutions. Eur. J. Orthod. 2010, 32, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, Y.S.; Odnevall Wallinder, I. Metal release from stainless steel in biological environments: A review. Biointerphases 2016, 11, 018901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhta, M.; Pavlin, D.; Slaj, M.; Varga, S.; Lapter-Varga, M.; Slaj, M. Type of archwire and level of acidity: Effects on the release of metal ions from orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daems, J.; Celis, J.-P.; Willems, G. Morphological characterization of as-received and in vivo orthodontic stainless steel archwires. Eur. J. Orthod. 2009, 31, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifakakis, I.; Eliades, T. Adverse reactions to orthodontic materials. Aust. Dent. J. 2017, 62, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, S.; Aliaga-Del Castillo, A.; Pinzan, A.; Sakoda, K.; Bellini-Pereira, S.; Janson, G. Orthodontic brackets friction changes after clinical use: A systematic review. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e482–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velliyagounder, K.; Ardeshna, A.; Koo, J.; Rhee, M.; Fine, D.H. The Microflora Diversity and Profiles in Dental Plaque Biofilms on Brackets and Tooth Surfaces of Orthodontic Patients. J. Indian Orthod. Soc. 2019, 53, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Yen, C.C.; Kao, C.T. Comparison of ion release from new and recycled orthodontic brackets. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2001, 120, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Nickel and nickel compounds. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2011, 100C, 169–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukoor, K.M.; Shaj, F.; Shabeer, N.N.; Jayarajan, J. Nickel Allergies in Orthodontic Treatment. Int. J. Prev. Clin. Dent. Res. 2016, 3, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Upadhyay, U.; Tandon, R.; Kumar, S. Nickel Allergy and Orthodontics. Asian J. Oral Health Allied Sci. 2011, 1, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Malta, 2011; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44584/9789241548151_eng.pdf;jsessionid=3072B3854FD2BCDDE00E3442198A1CED?sequence=1 (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Cempel, M.; Nikel, G. Nickel: A review of its sources and environmental toxicology. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Eliaz, N. Corrosion of Metallic Biomaterials: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocadereli, L.; Ataç, A.; Kale, S.; Özer, D. Salivary Nickel and Chromium in Patients with Fixed Orthodontic Appliances. Angle Orthod. 2000, 70, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fors, R.; Persson, M. Nickel in dental plaque and saliva in patients with and without orthodontic appliances. Eur. J. Orthod. 2006, 28, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olms, C.; Yahiaoui-Doktor, M.; Remmerbach, T.W. Contact allergies to dental materials. Swiss Dent. J. 2019, 129, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg, N.B.; Pelletier, J.L.; Jacob, S.E.; Schneider, L.C.; Cohen, B.; Horii, K.A.; Kristal, C.L.; Maguiness, S.M.; Tollefson, M.M.; Weinstein, M.G.; et al. Nickel allergic contact dermatitis: Identification, treatment, and prevention. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20200628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, H.S.; Selim, E.M.N.; Kamel Eid, F.H.; Tawfik, W.A.; Al-Ashkar, E.A.; Mostafa, Y.A. Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and metal release in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances: A longitudinal in-vivo study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 140, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.P.; Sehgal, V.; Pradhan, K.L.; Chandna, A.; Gupta, R. Estimation of nickel and chromium in saliva of patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. World J. Orthod. 2008, 9, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, R.S.; Khanna, B.; Pasha, A.; Vinay, K.; Narayan, A.; Chaitra, K. Evaluation of Nickel and Chromium Ion Release During Fixed Orthodontic Treatment Using Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer: An In Vivo Study. J. Int. Oral Health 2015, 7, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Petoumeno, E.; Arndt, M.; Keilig, L.; Reimann, S.; Hoederath, H.; Eliades, T.; Jäger, A.; Bourauel, C. Nickel concentration in the saliva of patients with nickel-titanium orthodontic appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.; Kailasam, V.; Padmanabhan, S.; Chitharanjan, A.B. In-vivo evaluation of salivary nickel and chromium levels in conventional and self-ligating brackets. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2011, 140, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.M.; De Menezes, L.M. Nickel, chromium and iron levels in the saliva of patients with simulated fixed orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aǧaoǧlu, G.; Arun, T.; Izgü, B.; Yarat, A. Nickel and Chromium Levels in the Saliva and Serum of Patients with Fixed Orthodontic Appliances. Angle Orthod. 2001, 71, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masjedi, M.; Niknam, O.; Haghighat Jahromi, N.; Javidi, P.; Rakhshan, V. Effects of Fixed Orthodontic Treatment Using Conventional, Copper-Included, and Epoxy-Coated Nickel-Titanium Archwires on Salivary Nickel Levels: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 174, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassaei, S.; Dadfarnia, S.; Ahadian, H.; Moradi, F. Nickel and chromium levels in the saliva of patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. Orthodontics 2013, 14, e76–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Ibáñez, R.; Lara-Carrillo, E.; Morales-Luckie, R.A.; Romero-Guzmán, E.T.; Toral-Rizo, V.H.; Ramírez-Cardona, M.; García-Hernández, V.; Medina-Solís, C.E. Evaluation of the release of nickel and titanium under orthodontic treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, C.L.; Vincent, S.K.; Barker, B.F. Allergic reaction to orthodontic wire: Report of case. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1989, 118, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, J.; Ahing, S.I.; Karaiskos, N.E.; Wiltshire, W.A. Nickel allergy and orthodontics, a review and report of two cases. Br. Dent. J. 2008, 204, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokitha, O.E.; Chatzistavrou, E. A severe reaction to Ni-containing orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrnrooth, M.; Kerosuo, H. Face and Neck Dermatitis from a Stainless Steel Orthodontic Appliance. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 1194–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.; Reichle, R.; Bauer, R.R.; Schopf, P.M. Allergies Induced by Orthodontic Alloys: Incidence and Impact on Treatment. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2004, 65, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliades, T.; Trapalis, C.; Eliades, G.; Katsavrias, E. Salivary metal levels of orthodontic patients: A novel methodological and analytical approach. Eur. J. Orthod. 2003, 25, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, F.; Borzabadi Farahani, A.; Jafari, A.; Rabbani, M. In vivo study of metal content of oral mucosa cells in patients with and without fixed orthodontic appliances. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2008, 11, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petoumeno, E.; Kislyuk, M.; Hoederath, H.; Keilig, L.; Bourauel, C.; Jäger, A. Corrosion Susceptibility and Nickel Release of Nickel Titanium Wires during Clinical Application. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2008, 69, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ousehal, L.; Lazrak, L. Change in nickel levels in the saliva of patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. Int. Orthod. 2012, 10, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Bracho, M.G.; Takahashi, C.S.; Castillo, W.O.; Saraiva, M.C.P.; Küchler, E.C.; Matsumoto, M.A.N.; Ferreira, J.T.L.; Nelson-Filho, P.; Romano, F.L. Genotoxic effects in oral mucosal cells caused by the use of orthodontic fixed appliances in patients after short and long periods of treatment. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setcos, J.C.; Babaei-Mahani, A.; di Silvio, L.; Mjör, I.A.; Wilson, N.H.F. The safety of nickel containing dental alloys. Dent. Mater. 2006, 22, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, P.E.; Benson, P.E. Potential Hazards of Orthodontic Treatment—What Your Patient Should Know. Dent. Update 2002, 29, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gursoy, U.K.; Sokucu, O.; Uitto, V.J.; Aydin, A.; Demirer, S.; Toker, H.; Erdem, O.; Sayal, A. The role of nickel accumulation and epithelial cell proliferation in orthodontic treatment-induced gingival overgrowth. Eur. J. Orthod. 2007, 29, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karygianni, L.; Ren, Z.; Koo, H.; Thurnheer, T. Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasvand Zarasvand, K.; Rai, V.R. Microorganisms: Induction and inhibition of corrosion in metals. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 87, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, P.D.; Head, D.A.; Devine, D.A. Dental plaque as a biofilm and a microbial community—Implications for treatment. J. Oral Biosci. 2015, 57, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyzer, G.; Stams, A.J.M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendl, B.; Wiltsche, H.; Lankmayr, E.; Winsauer, H.; Walter, A.; Muchitsch, A.; Jakse, N.; Wendl, M.; Wendl, T. Metal release profiles of orthodontic bands, brackets, and wires: An in vitro study. J. Orofac. Orthop./Fortschr. Der Kieferorthopädie 2017, 78, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Medical Association Inc. (VMA) WMA Declaration Of Helsinki—Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/ (accessed on 11 April 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).