Influence of Amidation on the Release Profiles of Insulin Drug from Chitosan-Based Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Methods
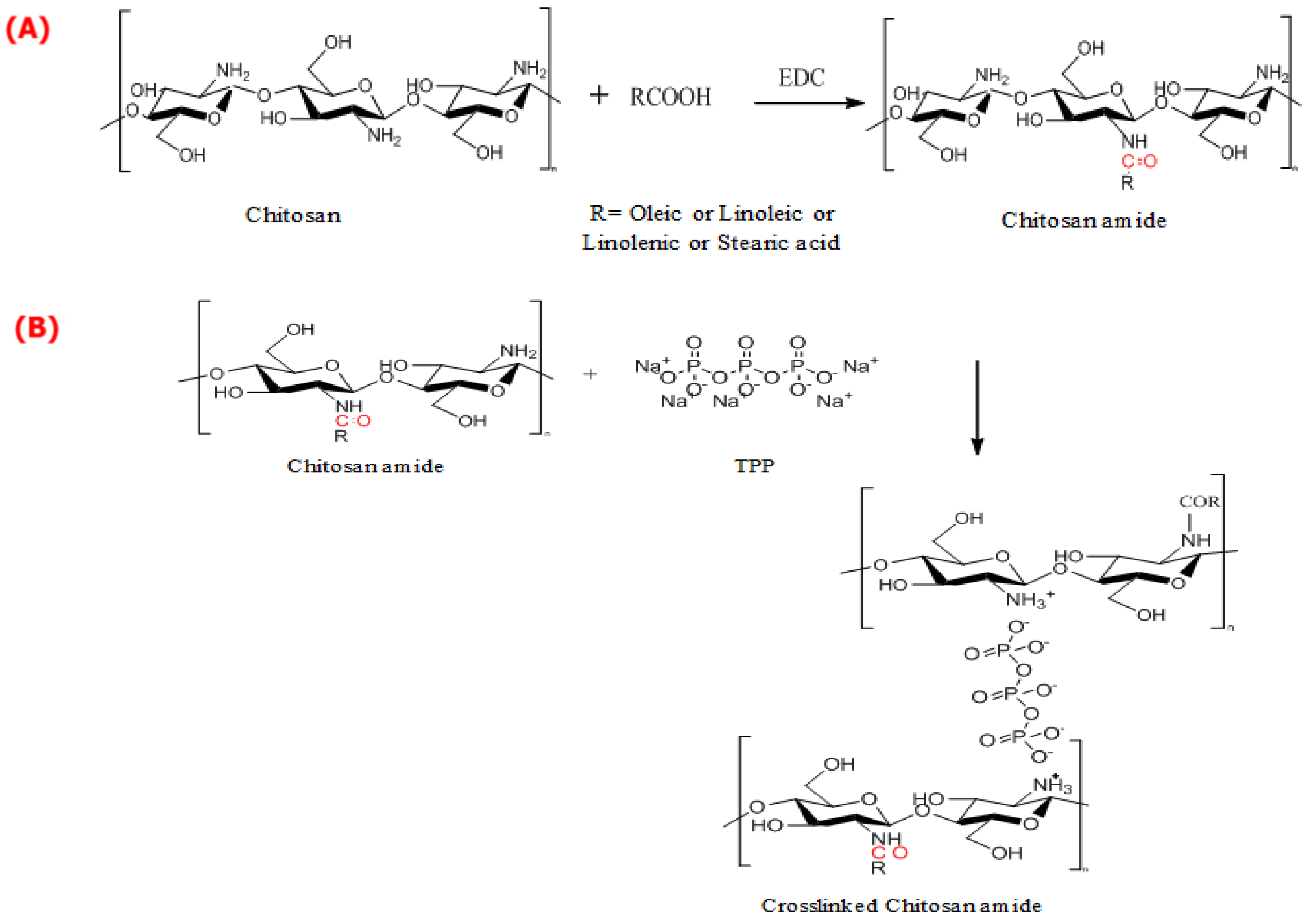
2.2. Synthesis of CS-Crosslinked Fatty Acid Amides
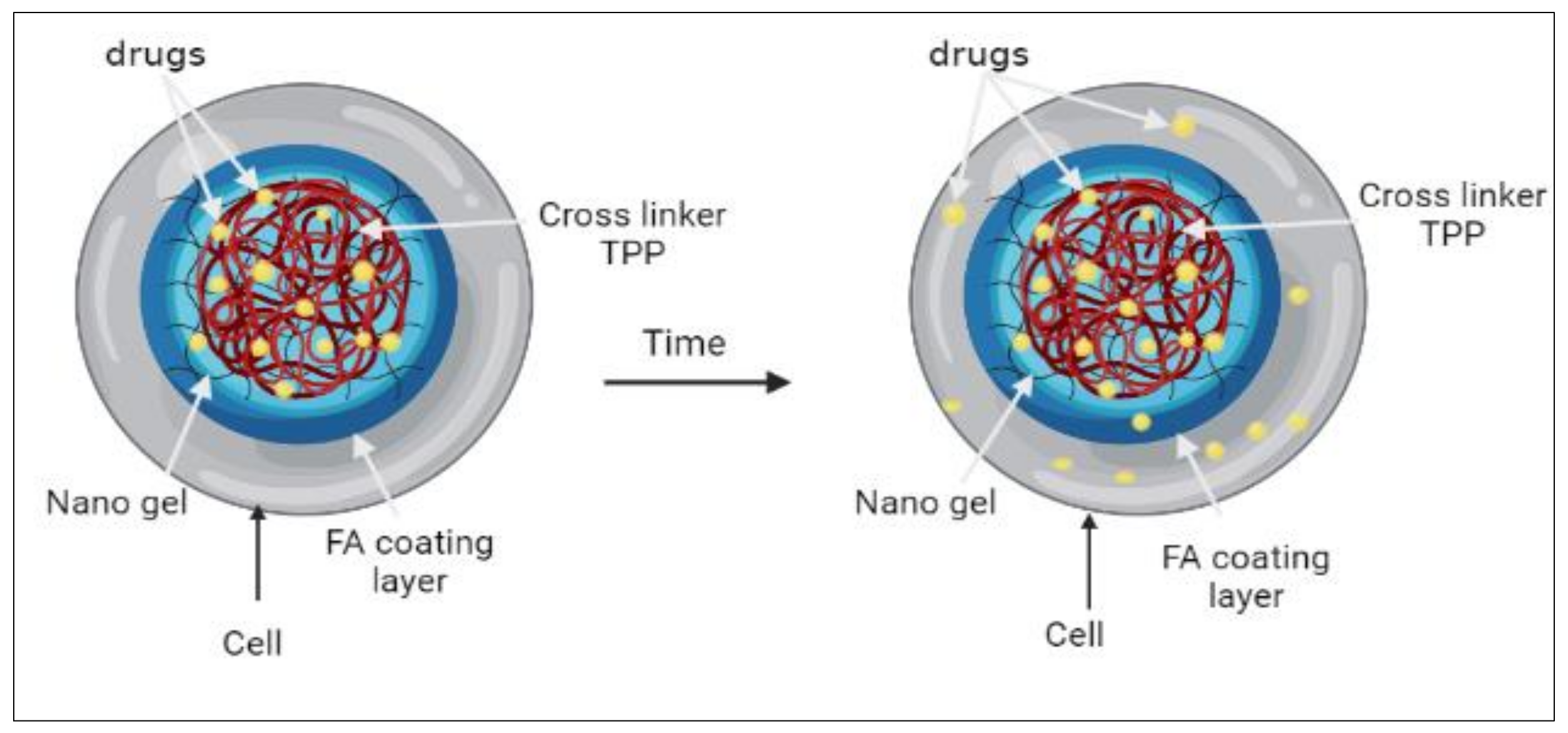
2.3. Studies of Insulin Drug Loading and Release
amount of insulin) × 100
2.4. Instrumental Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
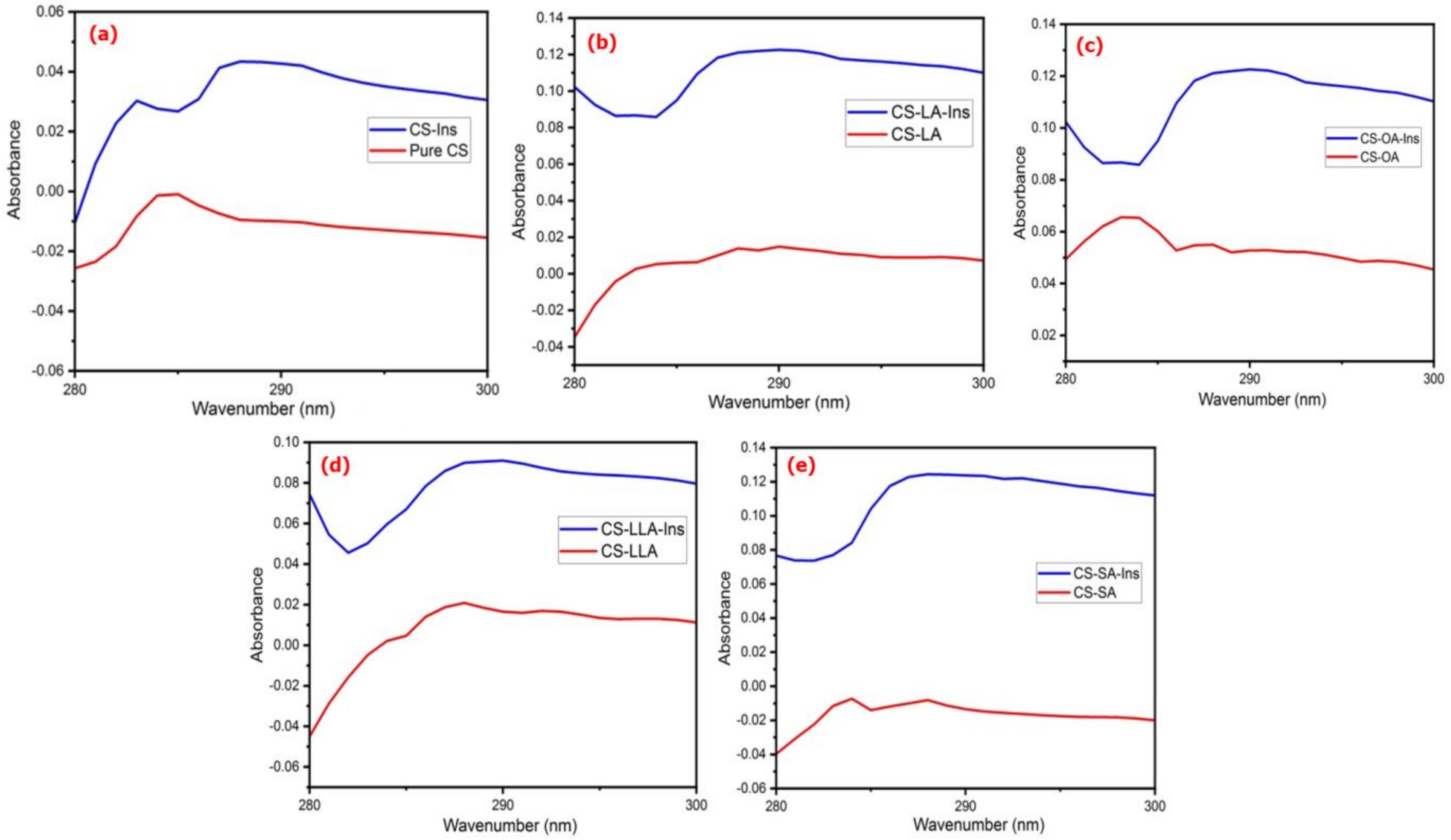
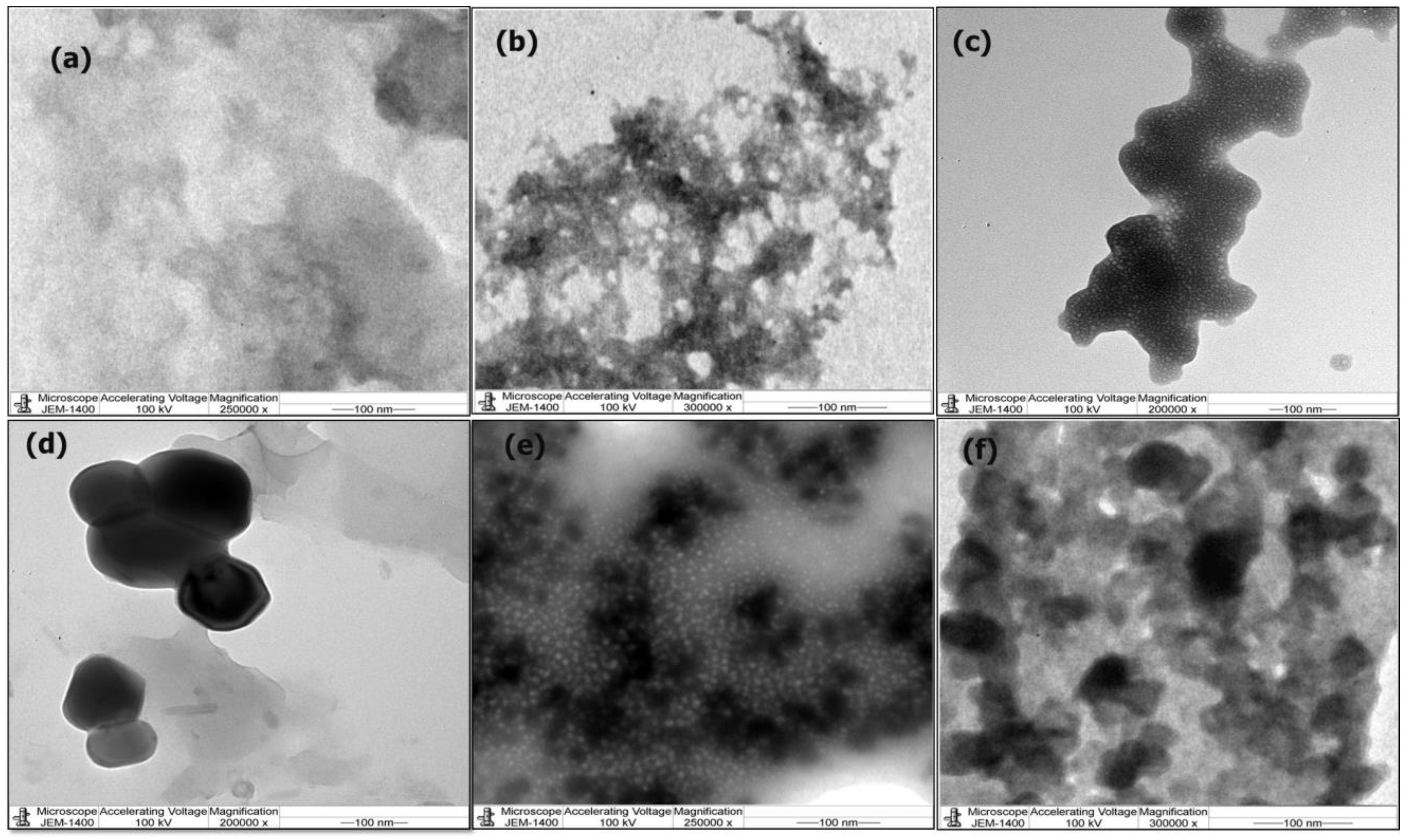
3.1. Physicochemical Analysis
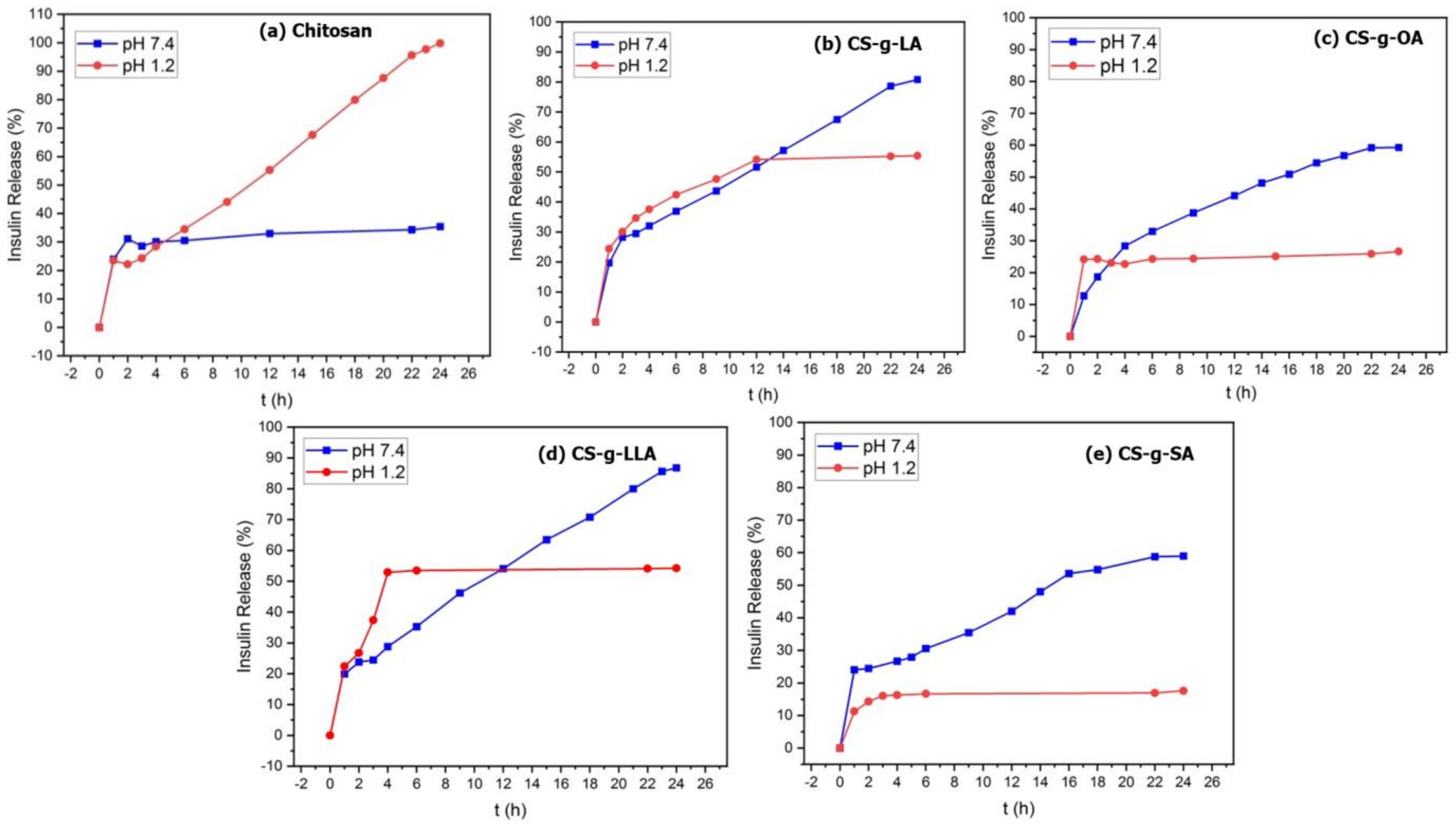
3.2. Insulin Drug Loading and Release Studies
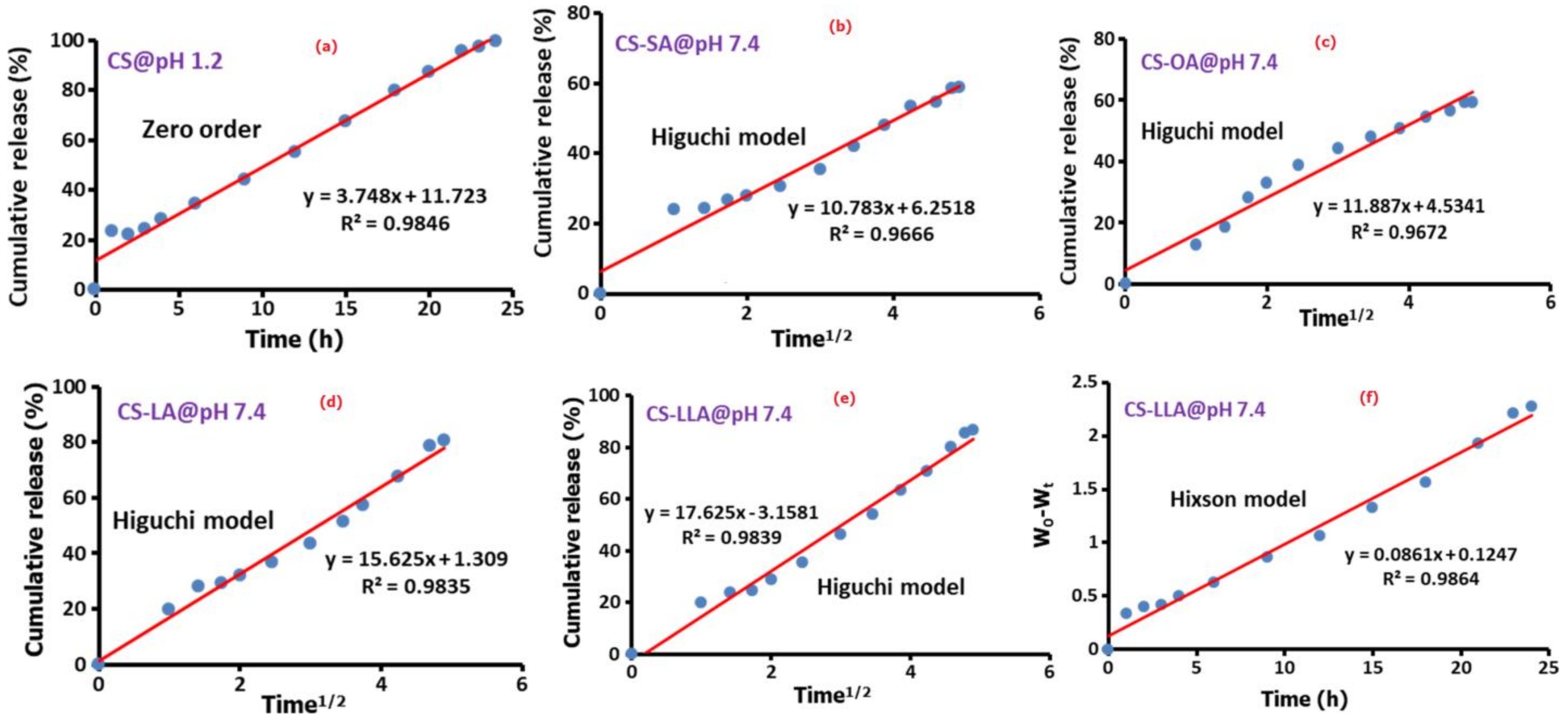
3.3. Drug Release Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Back, S.Y.; Song, J.G.; Han, H.K. Enhanced oral delivery of insulin via the colon-targeted nanocomposite system of organoclay/glycol chitosan/Eudragit® S100. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dağaşan, S. Insulin structure, function and diabetes models in animals. J. Exp. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 1, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, R. Introduction 1. In European Banking Law: The Banker-Customer Relationship, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.Y.; Al-Salami, H.; Dass, C.R. Formulation and characterisation of insulin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles capable of inducing glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells in vitro. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Jiang, T.; Di, J.; Tai, W.; Gu, Z. Emerging micro- and nanotechnology based synthetic approaches for insulin delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3595–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Das, D.; Dutta, P.; Kalita, J.; Wann, S.B.; Manna, P. Chitosan: A promising therapeutic agent and effective drug delivery system in managing diabetes mellitus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, M.; Vasiljevic, T. Can natural polymers assist in delivering insulin orally? Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, H. Chitosan-based self-assembled nanomaterials: Their application in drug delivery. View 2021, 2, 20200069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, D.N.; Prashanth, K.V.H.; Tharanathan, R.N. A review on potential anti-diabetic mechanisms of chitosan and its derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 3, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Santana, T.J.; Herrera-Méndez, C.H.; Rodríguez-Núñez, J.R. An overview of the chemical modifications of chitosan and their advantages. Green Mater. 2018, 6, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Sousa Victor, R.; Marcelo da Cunha Santos, A.; Viana de Sousa, B.; de Araújo Neves, G.; Navarro de Lima Santana, L.; Rodrigues Menezes, R. A review on Chitosan’s uses as biomaterial: Tissue engineering, drug delivery systems and cancer treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, R.; Omar, A.A.; Arunagiri, A.; Regupathi, I.; Thanabalan, M. Potential of chitosan and its derivatives for controlled drug release applications—A review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 642–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikušová, V.; Mikuš, P. Advances in chitosan-based nanoparticles for drug delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Singh, J. Synthesis and characterization of fatty acid grafted chitosan polymer and their nanomicelles for nonviral gene delivery applications. Bioconj. Chem. 2017, 28, 2772–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute, A.I.R.; Cardelle-cobas, A.; Montilla, A.; Olano, A.; Corzo, N. Synthesis, characterization and functional properties of galactosylated derivatives of chitosan through amide formation Ana I. Ruiz Matute. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M. Synthesis and characterization of an amphiphilic linoleic acid-g-quaternary chitosan with low toxicity. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, X.; Xu, G.; Yao, P. Fatty acid and quaternary ammonium modified chitosan nanoparticles for insulin delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Fray, M.; Niemczyk, A.; Pabin-Szafko, B. Chemical modification of chitosan with fatty acids. Prog. Chem. Appl. Chitin Its Deriv. 2012, 2012, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Ezzat, A.O. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by green method stabilized to synthetic human stomach fluid. Molecules 2014, 19, 6737–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elshaarani, T.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Fahad, S.; Ni, Z. Dextran-crosslinked glucose responsive nanogels with a self-regulated insulin release at physiological conditions. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 125, 109505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, T.H.H.; Eloy, J.O.; Ferreira, L.M.B.; Silva, I.C.D.; Pavan, F.R.; Gremião, M.P.D.; Chorilli, M. Insulin-loaded polymeric mucoadhesive nanoparticles: Development, characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manan, F.A.A.; Yusof, N.A.; Abdullah, J.; Mohammad, F.; Nurdin, A.; Yazan, L.S.; Khiste, S.K.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Drug release profiles of mitomycin c encapsulated quantum dots–chitosan nanocarrier system for the possible treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.C.; Silva, M.C.D.; Silva, H.N.D.; Albuquerque, D.; Gomes, A.A.R.; Silva, S.M.D.L.; Fook, M.V.L. Progress in the development of chitosan based insulin delivery systems: A systematic literature review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi Tahrir, F.; Ganji, F.; Mani, A.R.; Khodaverdi, E. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel for sustained release of insulin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yao, S.; Suo, D.; Ye, Y.; Pless, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jing, Y.; Gu, Z. Ultrasound-triggered noninvasive regulation of blood glucose levels using microgels integrated with insulin nanocapsules. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Nasim, F.; Mishra, R.; Bharti, R.P.; Kundu, P. Polyurethane-incorporated chitosan/alginate core–shell nano-particles for controlled oral insulin delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


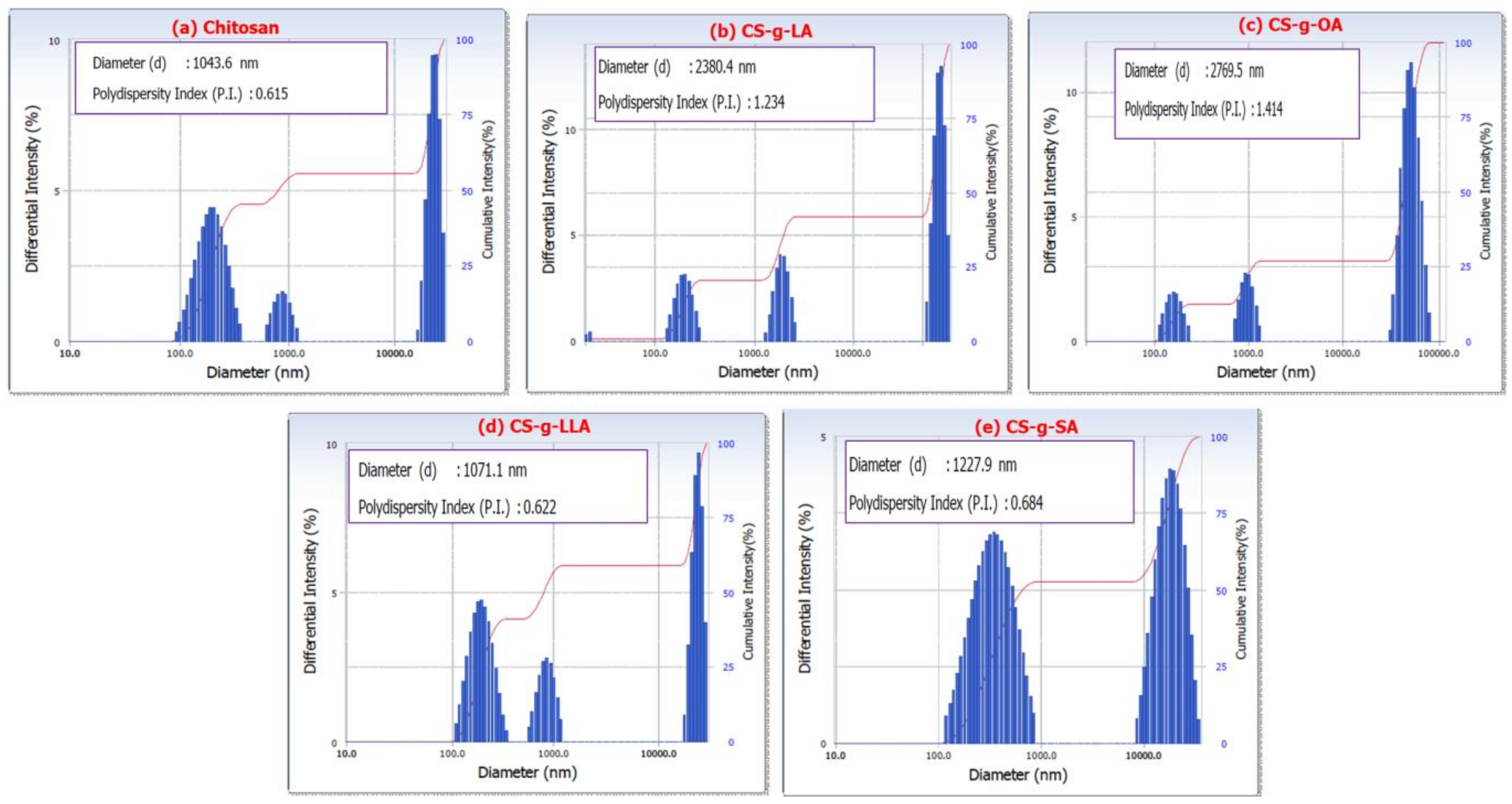
| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin | --- | --- | 0.64 |
| Pure CS | 1043 | 0.61 | 9.60 |
| CS-g-LA | 2380 | 1.23 | 32.1 |
| CS-g-OA | 2769 | 1.41 | 12.22 |
| CS-g-LLA | 1071 | 0.62 | 7.83 |
| CS-g-SA | 1227 | 0.68 | 1.30 |
| Sample | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | Equilibrium Time (h) | Drug Release (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.4 | pH 1.2 | |||
| Pure CS | 53.09 | 12 | 35.39 | 99.8 |
| CS-g-LA | 55.96 | 24 | 80.7 | 55.4 |
| CS-g-OA | 74.52 | 22 | 59.27 | 26.6 |
| CS-g-LLA | 83.38 | 24 | 86.7 | 54.2 |
| CS-g-SA | 71.65 | 22 | 58.9 | 17.5 |
| Sample | Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi Model | Korsmeyer-Peppas Model | Hixson Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.4 | pH 1.2 | pH 7.4 | pH 1.2 | pH 7.4 | pH 1.2 | pH 7.4 | pH 1.2 | pH 7.4 | pH 1.2 | |
| Pure CS-Insulin | 0.319 | 0.984 | 0.364 | 0.725 | 0.556 | 0.958 | 0.826 | 0.687 | 0.348 | 0.91 |
| CS-g-SA-Insulin | 0.889 | 0.263 | 0.953 | 0.326 | 0.966 | 0.508 | 0.835 | 0.314 | 0.936 | 0.274 |
| CS-g-OA-Insulin | 0.836 | 0.215 | 0.916 | 0.154 | 0.967 | 0.417 | 0.932 | 0.259 | 0.892 | 0.226 |
| CS-g-LA-Insulin | 0.942 | 0.622 | 0.972 | 0.727 | 0.983 | 0.869 | 0.591 | 0.441 | 0.976 | 0.696 |
| CS-g-LLA-Insulin | 0.972 | 0.426 | 0.969 | 0.472 | 0.983 | 0.667 | 0.654 | 0.404 | 0.986 | 0.452 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dahan, W.M.; Mohammad, F.; Ezzat, A.O.; Atta, A.M.; Al-Tilasi, H.H.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Influence of Amidation on the Release Profiles of Insulin Drug from Chitosan-Based Matrices. Coatings 2022, 12, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12040465
Dahan WM, Mohammad F, Ezzat AO, Atta AM, Al-Tilasi HH, Al-Lohedan HA. Influence of Amidation on the Release Profiles of Insulin Drug from Chitosan-Based Matrices. Coatings. 2022; 12(4):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12040465
Chicago/Turabian StyleDahan, Wasmia Mohammed, Faruq Mohammad, Abdelrahman O. Ezzat, Ayman M. Atta, Hissah Hamad Al-Tilasi, and Hamad A. Al-Lohedan. 2022. "Influence of Amidation on the Release Profiles of Insulin Drug from Chitosan-Based Matrices" Coatings 12, no. 4: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12040465
APA StyleDahan, W. M., Mohammad, F., Ezzat, A. O., Atta, A. M., Al-Tilasi, H. H., & Al-Lohedan, H. A. (2022). Influence of Amidation on the Release Profiles of Insulin Drug from Chitosan-Based Matrices. Coatings, 12(4), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12040465






