Abstract
Multi-element (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings were prepared through the magnetron sputtering of an equimolar CrHfNbTaTiVZr alloy target. This study determined the influences of N2-to-total (N2 + Ar) ratios (RN) on the composition, structure, mechanical properties, and electrical performance of the coatings. Coating thickness decreased from 898 nm to 128 nm with increasing RN from 0% to 100%. The alloy coating has bundles of fibrous structures with remarkable void boundaries. The coating changed from amorphous phase to face-centered cubic (FCC) phase with (111) preferred orientation, then to FCC phase with (200) preferred orientation, and finally to near-amorphous phase as RN increased from 0% to 100%. The microstructure of the nitride coatings transformed from a columnar structure with rough faceted tops and void boundaries into a dense and small structure with smooth domed tops. The grain size of the nitride coatings also decreased with RN. Accordingly, the electrical performance at high RN was poor. The nitride coating deposited at RN = 60% had the highest hardness of 16.6 GPa and the lowest friction coefficient of 0.52, owing to structural densification and grain refinement.
1. Introduction
Some conventional binary nitride coatings, such as TiN and CrN, have been extensively applied as protective layers that improve the surface hardness and friction characteristics and prolong the service life of materials [1]. In addition, they can also be adopted as a decorative layer for the underlying material and applied to heterojunction-based devices for electronics and solar power conversion [2,3,4]. However, with the rapid development of the machining industry, binary nitride coatings are no longer sufficient and are quickly replaced by complex ternary and quaternary nitrides. Solid solution strengthening and grain boundary hardening are the typical hardening mechanisms of these nitrides, and their application range can be further extended through appropriate composition design. Over the years, the development of ternary and quaternary nitrides seems to have reached its limit. Novel multi-element high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have been developed to meet the strict and diverse requirements in the future.
HEA coatings, which comprise at least five principal metal elements in near-equimolar ratios, have recently attracted extensive attention owing to their high hardness, excellent wear and corrosion resistance, and excellent thermal stability [5,6,7]. In 2004, Chen et al. completed the first study extending the multicomponent concept from alloys to compounds [8]. Attention has been given to HEA nitride coatings because they are chemically inert and harder than their corresponding metallic alloys. Since then, more than a hundred papers on high-entropy nitride coatings have been published. In accordance with the elements of HEAs, coatings can be split into two categories: strong nitride-forming metals, which have a negative enthalpy of formation (e.g., Cr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Ti, V, and Zr) [9,10,11], and non-nitride-forming metals, which have a positive enthalpy of formation (e.g., Co, Cu, Fe, and Ni) [12,13,14]. The sputter deposition technique has been extensively used in the production of HEA materials. HEA coating with various composition designs can be easily manipulated by combining different single target materials. HEA ceramic coatings, such as HEA nitride, carbide, and oxide coatings, can also be readily manufactured by introducing N2, C2H2, and O2 gases into the vacuum chamber, respectively [15,16]. The deposited coatings allow for a wide range of properties by tuning process parameters. High-entropy nitrides based on strong nitride-forming metals are prone to forming face-centered cubic (FCC) solid solutions and have high mechanical properties. However, the microstructure and physical properties of nitride coatings prepared by sputtering are remarkably affected by process parameters. Therefore, their relationships should be explored. Among these process parameters, N2-to-total (N2 + Ar) ratio (RN) strongly affects the physical properties of HEA nitride coatings. Sputtered HEA nitride coatings with different RN values have been developed. Chen et al. [17] fabricated (VAlTiCrMo)Nx coatings by tuning RN. The hardness of the coating attained up to around 5.6 GPa with increasing RN accompanied by a phase change from body-centered cubic (BCC) to FCC. Xing et al. [6] prepared (NbTiAlSiZr)Nx coatings by adjusting RN. These coatings are in the amorphous phase. The hardness of the coating reached the highest value of 12.4 GPa. Zhang et al. [14] investigated the effect of different RN values on (Al0.5CrFeNiTi0.25)Nx coatings. The introduction of nitrogen resulted in the transformation of the alloy coating in the amorphous phase into a nitride coating in the FCC phase. The nitride coating achieved a pronounced hardness of 21.45 GPa. Fieandt et al. [18] deposited (AlCrNbYZ)Nx coatings at various RN values. The alloy coating and the corresponding nitride coating have an amorphous phase with a minor cubic phase and FCC phase, respectively. The alloy coating has a low electrical resistivity of 223 μΩ·cm. The hardness of the nitride coating reached the maximum of 30 GPa. Feng et al. [19] explored the related properties of (CrTaNbMoV)Nx coatings under various RN values. They reported that the metal coating had an amorphous phase, and its nitrogen-containing coating revealed an FCC phase. The friction coefficient of the nitride coating was between 0.5 and 0.7, which was lower than that of the alloy coating (0.8). The nitride coating deposited at RN = 20% had a maximum hardness of 21.6 GPa. Cui et al. [20] fabricated (AlCrTiZrHf)Nx coatings by tuning RN. They found that the structure of the coating transforms from amorphous phase to FCC phase with increasing RN. The coating exhibited an excellent hardness of 33.1 GPa and a friction coefficient of 0.5 at the nitrogen content of 50%. Sha et al. [21] studied the influence of RN on the properties of (FeMnNiCoCr)Nx coatings. The primary FCC phase evolved to a BCC phase as RN increased. The nitride coating was composed of an FCC phase and had a superior hardness of 17 GPa. According to the findings of these recently published papers, the HEA nitride coating tends to form a single solid solution nitride phase based on the combined effect of high mixing entropy and high mutual solubility caused by many transition metal nitrides. Furthermore, the hardness value of the coatings published in different reports varied widely. The difference is caused by varying process parameters, including working pressure, substrate temperature, and substrate deviation, which have a remarkable impact on coating properties.
The present study attempted to understand the complex relationship between the microstructure and characteristics of high-entropy coatings. This high-entropy material is based on the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N system, which consists of seven nitride-forming metal elements. Although many different high-entropy nitride coatings have been reported, a general design rule is difficult to provide. Investigating new high-entropy nitrides is crucial to providing research support for industrial application. The constituting elements chosen for this study have the following aspects. Binary nitride coatings (e.g., HfN, TiN, ZrN) and ternary metal nitrides (e.g., TiHfN, TiZrN) are common hard protective coatings [1]. VN has a low friction coefficient owing to the formation of a lubricating oxide layer [22]. CrN exhibits good corrosion resistance and easily forms a dense oxide layer [23]. The incorporation of Nb and Ta can remarkably improve the thermal stability of coatings [24,25]. All the selected elements are strong nitride-forming elements and can easily react with nitrogen to form nitride. The mixing entropy in the septenary (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N system with different-sized atoms is very high and is expected to promote the mutual solubility of individual nitrides and favor the formation of nano-sized solid solution phases. These constituting elements have considerable implications for controlling their structures and properties. Exploring the tribological properties of the coatings is of particular importance because of the shortage of research on solid–solid composite lubrication. In this study, no external substrate heating or biasing was employed during deposition. RN was chosen as the controlling parameter because of its strong influence on nitrogen content in coatings and the kinetic energy of the sputtered species on the growing coating, which leads to drastic changes in the structure and properties of the coatings. This work discusses how the nitriding effect influences the mechanical and electrical performances of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings. Hardness and friction coefficient measurement can be used to evaluate the potential as a protective coating on cutting tools, dies, and molds. Electrical resistivity measurements are helpful in optimizing heterojunction-based electronics and solar energy conversion devices. The results can provide research support for industrial applications.
2. Experimental
The (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings were deposited on p-Si (100) wafers by the reactive magnetron sputtering method. The target size was 100 mm in diameter and 6 mm in thickness. The target was made with equiatomic amounts of Cr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Ti, V, and Zr elements (adjusted to 14.3 at.% for each element) by vacuum arc melting. The target melting procedure was repeated at least five times to guarantee chemical homogeneity. The Si wafer was chosen as the substrate to facilitate structural analyses, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JEOL JSM-6700F, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM 1200EX II, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) observations. Before deposition, the Si wafer was ultrasonically cleaned and rinsed with ethanol and distilled water. The vacuum in the sputtering chamber was pumped down to 2 × 10−4 Pa by utilizing a turbo pump. The deposition of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings was carried out in a mixture atmosphere of high-purity Ar and N2. The discharge power of the CrHfNbTaTiVZr alloy target was maintained at 200 W. The working distance from the target to the substrate was set at approximately 150 mm. The working pressure was 1 Pa, and the deposition time was 50 min for all the coatings. RN was varied from 0% to 100%. No external substrate heating or biasing was employed during deposition.
Electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA, PHI 500 VersaProbe, ULVAC-PHI, Inc., Chigasaki, Japan) with monochromatic AlKα radiation was used to determine the chemical composition of the coatings. X-ray diffractometry (XRD, MXP3, MAC Science Ltd., Yokohama, Japan) with monochromatic CuKα radiation was utilized to analyze the crystal structure of the coatings at a low glazing angle of incidence (θ = 1°). Furthermore, the average grain sizes of the coatings were estimated from the full width at half maximum using the Scherrer formula. Field-emission SEM (JEOL JSM-6700F) was employed for coating morphology observation and thickness measurements. The deposition rate was determined by dividing the thickness values by deposition time. Analytical TEM (JEM 1200EX II), coupled with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), was conducted to examine the microstructure. Atomic force microscopy was used to measure the surface roughness of the coatings. A TriboLab nanoindenter (Hysitron Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) equipped with a Berkovich diamond indenter tip was employed to evaluate mechanical properties. The applied load was controlled at 200 μN and the maximum penetration depth was below 1/10 of the film thickness to avoid interference with the substrate. The hardness and reduced modulus were derived from load–displacement curves using the Oliver and Pharr method. Five indentations were made for each sample. A tribometer (Anton Paar TRB3, Anton Paar Ltd., Graz, Austria) was used to evaluate the friction of the coatings. A 100Cr6 steel ball with a 6 mm diameter was used as the counterpart sliding on the rotating film. The applied normal load and sliding speed were 0.25 N and 0.01 m/s, respectively. The sliding distance was 5.0 mm. The four-point probe equipment was applied to quantify the electrical resistivity of the coatings.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the deposition rate of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The deposition rate of the film gradually decreased from 15.0 nm/min to 2.1 nm/min. The decrease in the deposition rate of the coatings can be interpreted in terms of three factors. (1) The poisoning of the target surface occurs during the reactive sputtering process. A higher RN promotes higher target poison, which results in a lower deposition rate. This occurrence is reasonable because the sputtering yield of the nitride is lower than that of the metal. (2) The ionization threshold of the N2 atom is remarkably higher than that of the Ar atom, which weakens the plasma and reduces the deposition rate [26,27].
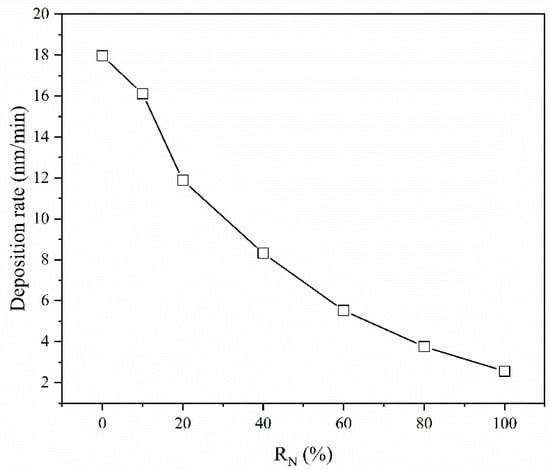
Figure 1.
Deposition rate of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 2 plots the ESCA element concentration in the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The elemental compositions of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings differed from the equiatomic target composition. The discrepancy in the composition of each element may be highly correlated with gas scattering, sputtering yield, and sputtering angle distribution [28]. The multiple overlap among different signals from these target constituents impedes the quantitative analysis of the coatings and affects the accuracy of the determination of the metal content of coatings. This unexpected compositional change has also been reported in other literature [29]. Therefore, the change in metal concentration in coatings will not be explored in this paper. The nitrogen content in coatings rose rapidly at first and then stabilized with the increase in RN. The coatings deposited at RN = 20% and above can be regarded as saturated nitride films. Among the target constituents, Cr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Ti, V, and Zr are all strong nitride formers based on the mixing enthalpy (ΔHmix) for target constituents and N element (ΔHmix values of −107, −218, −174, −173, −190, −143, and −233 kJ/mol, respectively). Thus, multicomponent nitrides based on strong nitride formers are prone to having high nitrogen contents when deposited at the same RN. Current research has started to provide the same insights [30].
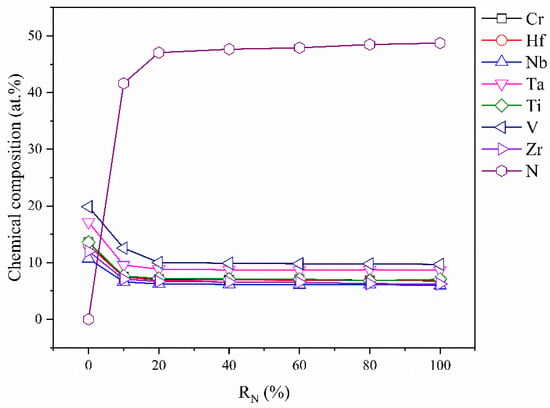
Figure 2.
Chemical compositions in (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 3a shows the XRD patterns of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. On the basis of the XRD analysis, the grain sizes and lattice parameter were determined (Figure 3b). The coatings deposited at RN = 0% exhibited an amorphous structure, as illustrated by the broad peaks. According to the literature, the large atomic size difference is considered the main factor for the formation of the amorphous structure [31]. The atomic size difference in an alloy is quantified by δ:
where , and ci and ri are the atomic percentage and atomic radius, respectively, of the i-th element. The numerical factor 100 was used to amplify the data for clarity. The (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings had high δ values up to 8.18, which led to severe lattice distortion and the formation of an amorphous structure. This result is consistent with previous studies on coatings, such as AlCrNbSiTiV (δ = 8.35) [32], AlCrTiVZr (δ = 5.90) [33], and AlCrTaTiZr (δ = 7.86) [34]. The diffraction peaks of (111), (200), (220), and (311), belonging to the FCC structure, are displayed. This result suggests that the metal elements formed metal nitrides after the introduction of nitrogen. CrN, HfN, NbN, TaN, TiN, VN, and ZrN had the same FCC structure that promotes FCC crystal structure formation. The mixing entropy increases slowly with the increase in nitrogen content [35]. However, the material with very high mixing entropy cannot overcome compounds with very large formation enthalpy, including borides, nitrides, and carbides, as well as oxidation [36]. The formation of nitrides in this study possibly resulted from the large formation enthalpy. Although high mixing entropy cannot limit nitride formation, it plays a decisive role in stabilizing a simple solid solution phase in an equiatomic mixture of CrN, HfN, NbN, TaN, TiN, VN, and ZrN. The cations randomly replace one sublattice, whereas nitrogen anions normally occupy the second sublattice [37]. That is, the single FCC solid solution for (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings is believed to be due to the thermodynamic stability related to its high mixing entropy, which enhances the mutual solubility of the target constituents and inhibits the formation of intermetallic compounds [19]. Figure 3c illustrates the texture coefficient evolution of the (111), (200), and (220) planes at various RN values. The texture coefficient of the hkl plane in an alloy is quantified by :
where is the measured intensity, N is the number of reflections. The (111) preferred orientation was detected in (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at RN = 10%. The (111) preferred orientation transformed into the (200) orientation as RN increased to 60%. Additionally, the diffraction peaks became broad, and their relative intensity decreased. The grain size decreased from 10.8 nm to 7.2 nm as RN increased from 10% to 60%. When RN was above 80%, the diffraction peaks became very broad and weak, which indicates that the coatings are near-amorphous. These results can be explained by kinetic constraints [38,39]. Metal adatoms form one and three nitrogen dangling bonds on the (100) and (111) surfaces, respectively. When sputtering deposition is performed at a low Ji/Jmetal flux ratio or RN, metal adatoms are likely to be trapped on adjacent (111) grains, which leads to the fast growth of (111) grains. As the Ji/JTi flux ratio or RN increases, metal adatoms on the (100) surface can form up to five dangling bonds, owing to the presence of a high amount of atomic reactive nitrogen, and result in the development of the (200) preferred orientation. Nitride coatings grown under high Ji/Jmetal flux ratio or RN have strong energetic discharge species colliding with the growing film, owing to the light mass of nitrogen, which causes a re-sputtering effect and consequently induces re-nucleation. As a result, coatings become poorly crystallized and even near-amorphous with increasing RN. RN also has a strong effect on the lattice parameter. The lattice parameter increased from 4.326 to 4.379 nm, which is within the range of solid solution from all constituted nitrides. The energetic bombardments at high RN may force the sputtered species to be embedded in the coating subsurface, which results in the creation of a strain field in the surrounding matrix and the increase in lattice parameter [29,32].
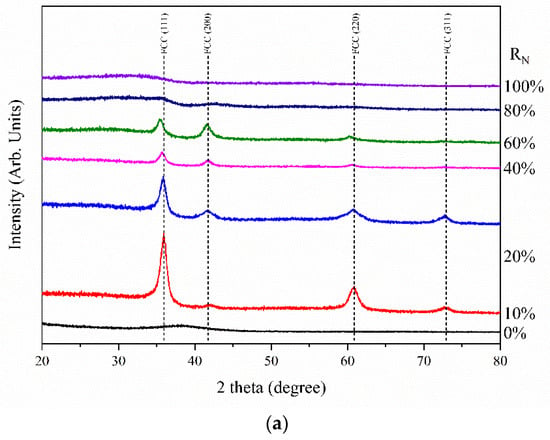
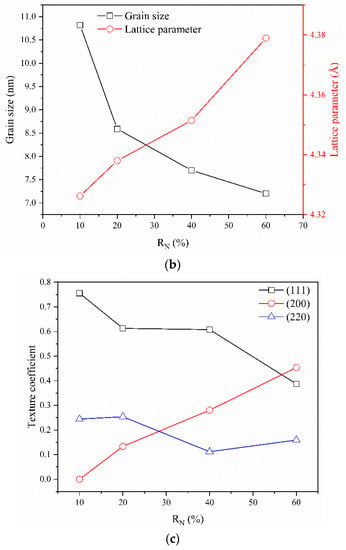
Figure 3.
(a) X-ray diffraction patterns of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN. (b) Grain and lattice parameter of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN. (c) Texture coefficient of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 4 shows the SEM images of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The surface roughness is revealed in Figure 5. The CrHfNbTaTiVZr alloy coatings deposited at RN = 0% exhibited a columnar structure with a cracked surface and a small roughness of 3.1 nm, which are related to high deposition pressure. Increasing RN to 10% yielded a sharp-faceted surface and a large roughness of 5.9 nm, which indicate crystalline development. As RN increased to 100%, the surface morphology transformed into a dome-like structure with a small roughness of 1.8 nm.
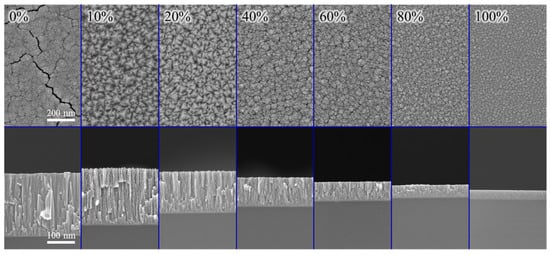
Figure 4.
SEM images of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
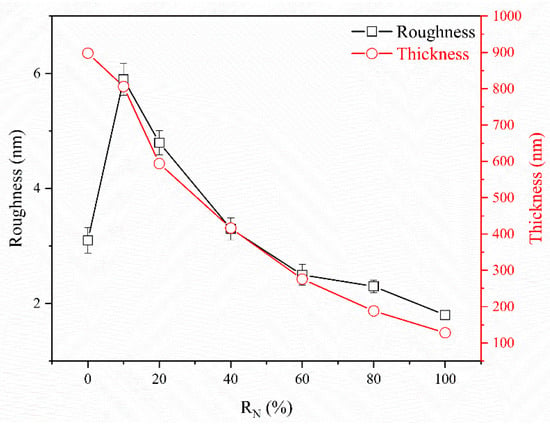
Figure 5.
Surface roughness and thickness of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the TEM images and the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns, respectively, for (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The CrHfNbTaTiVZr alloy coatings deposited at RN = 0% revealed a porous columnar structure. Each column consists of bundles of nanometer-sized fibers. The corresponding SAED patterns contain diffuse rings that can be assigned to an amorphous structure. This structure is consistent with the zone Ia structure of the Mahieu model [40]. The mean free path in the plasma is low at high deposition pressure. The sputtered particles undergo numerous collisions with the process gas before arriving at the surface of the growing film during deposition, which results in the loss of their kinetic energy. The coating structure has an amorphous appearance because the adatoms have not enough energy to develop large and compact crystals. An overhang structure can be formed by combining this with the shadow effect. Such a coating has an open-voided tapered fibrous structure with an amorphous phase and is classified as a zone Ia coating. When RN increased to 10%, the coating became a typical columnar structure with a highly faceted surface feature. The introduction of nitrogen increased the Ji/Jmetal flux ratio toward the substrate and thus enhanced the surface mobility of adatoms to expedite diffusion among planes. This occurrence induced a local crystal growth condition; thus, each crystal grew into dense and clearly faceted columns with a crystalline phase. The sharp FCC diffraction rings in the SAED pattern confirm the good crystallinity of the coating. However, the adatoms were still unable to overcome the existing diffusion barriers among grains. Local crystal growth exacerbates the shadow effect, resulting in deep cusps between columns and open-column boundaries. The microstructure changed from zone Ia to zone Ic. As RN increased to 100%, the surface became non-faceted and smooth without a visible void. The poor crystallinity feature can be identified through the broad FCC diffraction rings in the SAED pattern. The enhanced bombardment on the growing coating was large enough to interfere with column growth and drive re-nucleation, leading to structural densification and grain refinement. The voids between columns were completely filled, and a compact structure evolved. This structure can be considered a zone Ib coating. Notably, coating thickness is also a key determinant on the microstructure. A thin nitride coating is associated with small grain size and low surface roughness (Figure 4 and Figure 7) [41,42,43].
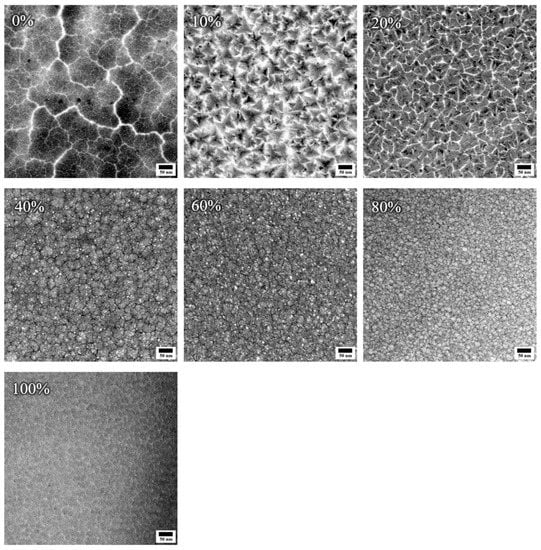
Figure 6.
TEM images of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
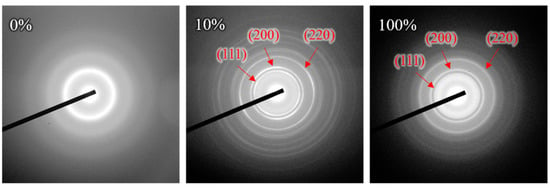
Figure 7.
SAD patterns of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 8 shows the hardness and modulus of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The CrHfNbTaTiVZr alloy coating exhibited a hardness and a modulus of 8.1 and 166.9 GPa, respectively. The hardness and modulus slightly increased to 5.4 and 121.4 GPa at RN = 10%, respectively. The high hardness can be attributed to the formation of multiple strong nitrides. However, the magnitude of hardness increase in this study was extremely small. This finding can be ascribed to the deep cusps between columns and open-column boundaries. As RN increased, the hardness and modulus increased initially and reached the maximum values of 16.6 and 246.2 GPa, respectively, at RN = 60%. The primary reason is the markedly reduced density of voids existing between the column structures, which enhances the hardness effectively. The second reason is the grain refinement that impedes dislocation motion during plastic deformation. The coating deposited at RN = 60% had the maximum hardness, which can be attributed to its denser columnar structure and smaller grain size than other coatings. Further increasing RN to 100% slightly decreased the hardness and elastic modulus to 14.0 and 218.3 GPa, respectively. The formation of an amorphous structure at high RN is usually associated with low hardness. Dislocations cannot be defined in an amorphous material. A deformation mechanism, such as grain boundary sliding, was proposed to appear at very fine grain sizes approaching the amorphous state and lead to the softening of materials [44].
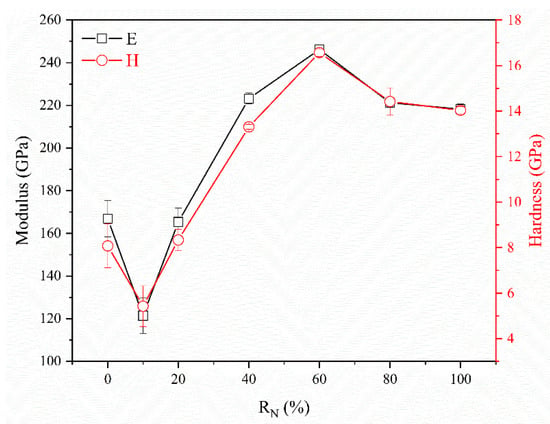
Figure 8.
Modulus and hardness of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 9 shows the friction coefficient, H/E, and H3/E2 ratios of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The friction coefficient of the CrHfNbTaTiVZr alloy coating was 0.65. With the introduction of nitrogen, the coating was nitrided and exhibited an increased friction coefficient of 0.67. The friction coefficient initially decreased and then increased with increasing RN. The friction coefficient of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coating reached the lowest value of 0.52 at RN = 60% and then increased to 0.64 at RN = 100%. The variation in friction coefficient is related to surface roughness and mechanical properties. The low surface roughness can reduce frictional resistance. However, in this study, (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings do not follow the same trend of reduced friction coefficient with surface roughness. According to Leyland and Mayrhofer, H/E represents the elastic strain to failure, and H3/E2 represents the resistance to plastic deformation [45,46]. These values can be calculated to assess the relevance of coatings for tribological applications. High H/E and H3/E2 values indicate improved tribological properties. Figure 9 clearly demonstrates that the friction coefficient, H/E, and H3/E2 present a similar variation tendency with RN. Notably, a very sharp increase in friction coefficient was observed in the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at the RN values of 40% and 50% even though they have low surface roughness and high H/E and H3/E2 values. The thinness of the coating may be responsible for this abnormal phenomenon [47].
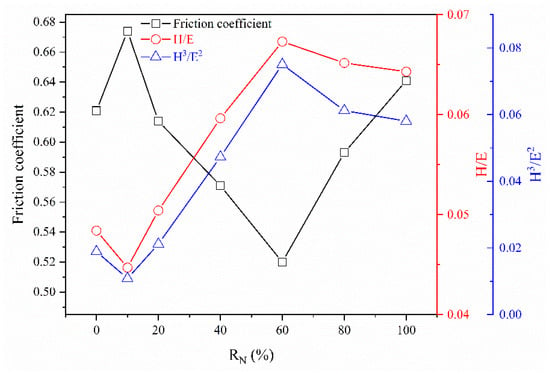
Figure 9.
Friction coefficient, H/E, and H3/E2 of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
Figure 10 shows the electrical resistance of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN values. The electrical resistance remarkably increases from 201 Ω·cm to 456410 Ω·cm by increasing RN to 100%. Notably, the increase in electrical resistivity was stronger when RN was below 20%. This phenomenon can be attributed to the enhanced covalent or ionic character in the metal–N bonding with increasing nitrogen content [48]. The nitrogen content of the coatings became stable at RN above 20% as shown in Figure 2. The decrease in electrical resistivity at RN > 20% is triggered by the grain boundary scattering caused by the small grain size, as shown in Figure 3c.
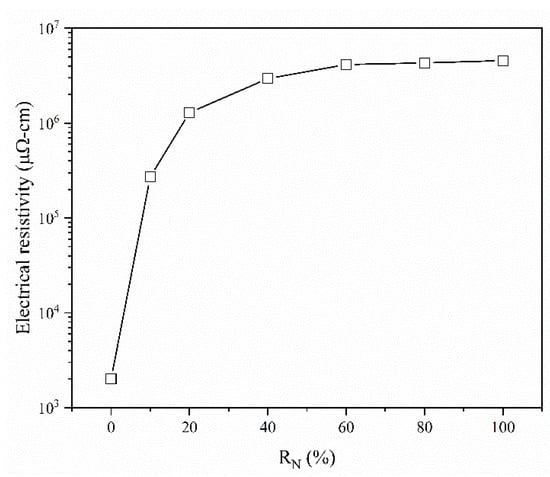
Figure 10.
Electrical resistivity of (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings deposited at various RN.
4. Conclusions
(CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N films were deposited at different RN values by reactive radiofrequency magnetron sputtering using an equimolar CrHfNbTaTiVZr target. The microstructures, mechanical performance, and electrical characteristics of the coatings were studied. The following conclusions were drawn:
- The deposition rate of the coatings gradually decreased with increasing RN. The nitrogen content of the (CrHfNbTaTiVZr)N coatings quickly increased initially and then became stable with increasing RN.
- The coatings deposited at RN = 0% had bundles of fibrous structures with an amorphous phase. A high density of cracks and voids was detected. At RN = 10%, the structure was transformed into a heavily open-voided columnar structure with an FCC phase. Moreover, the (111) orientation was preferred because it had the highest growth rate. When RN was further increased to 60%, the energetic bombardment at high RN caused grain refinement and lattice expansion. The structure gradually transformed into a compact and dense columnar structure. Moreover, high RN created a high amount of atomic reactive nitrogen, which led to the development of the (200) preferred orientation. The further increase in RN changed the structure into an amorphous-like phase because of excessive energetic bombardment.
- When RN = 0%, the coating had a cracked surface with a small roughness of 3.1 nm. Increasing the RN to 10% made the surface faceted and have a high roughness of 5.9 nm. Further increasing the RN to 100% formed a very smooth, dome-shaped surface with a roughness of 1.8 nm.
- The maximum hardness and modulus values were 16.6 and 246.2 GPa, respectively, which were obtained in the coating deposited at RN = 60%. This result was explained by structural densification and grain refinement.
- The coating obtained at RN = 60% exhibited the highest H/E and H3/E2 ratios and a decreased friction coefficient of 0.52.
- The poor electrical performance at high RN could be attributed to the enhanced metal–N bonding and small grain size.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, D.-C.T.; investigation, D.-C.T.; data curation, D.-C.T. and E.-C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.-C.T.; writing—review and editing, Z.-C.C. and F.-S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Grant No. NSC100-2221-E-005-034-MY3.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported in part by the Core Facility Center of the National Cheng Kung University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Toth, L.E. Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Brus, V.V. Open-circuit analysis of thin film heterojunction solar cells. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovan, M.M.; Brus, V.V.; Maryanchuk, P.D. Electrical and photoelectric properties of anisotype n-TiN/p-Si heterojunctions. Semiconductors 2013, 47, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovan, M.N.; Brus, V.V.; Maistruk, E.V.; Maryanchuk, P.D. Electrical and optical properties of TiN thin films. Inorg. Mater. 2014, 50, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, M.; Jiang, C.; Qiao, B.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J. Thermal stability of AlCrTaTiZrMo-nitride high entropy film as a diffusion barrier for Cu metallization. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Jin, P.; Zhang, Y. Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of NbTiAlSiZrNx High-Entropy Films Prepared by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Entropy 2019, 21, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Pelenovich, V.; Liu, Y.; Ke, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Ma, G.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Effect of bias voltages on microstructure and properties of (TiVCrNbSiTaBY)N high entropy alloy nitride coatings deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2022, 195, 110710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Shun, T.T.; Yeh, J.W.; Wong, M.S. Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 188–189, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.-C.; Chang, Z.-C.; Kuo, L.-Y.; Lin, T.-J.; Lin, T.-N.; Shiao, M.-H.; Shieu, F.-S. Oxidation resistance and structural evolution of (TiVCrZrHf)N coatings. Thin Solid Film. 2013, 544, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braic, V.; Vladescu, A.; Balaceanu, M.; Luculescu, C.R.; Braic, M. Nanostructured multi-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C hard coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 211, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, K.; Riekehr, L.; Fritze, S.; Lewin, E. Multicomponent Hf-Nb-Ti-V-Zr nitride coatings by reactive magnetron sputter deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedoncker, R.; Djemia, P.; Radnóczi, G.; Tétard, F.; Belliard, L.; Abadias, G.; Martin, N.; Depla, D. Reactive sputter deposition of CoCrCuFeNi in nitrogen/argon mixtures. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 769, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Lv, S.J.; Zhao, R.F.; Liu, Z.X.; Guan, S.K. Effect of sputtering parameters on (AlCrMnMoNiZr)N films. Surf. Eng. 2014, 30, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.-H.; Liao, W.-B.; Zhao, K. Effects of Nitrogen Content on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of (Al0.5CrFeNiTi0.25)Nx High-Entropy Films by Reactive Sputtering. Entropy 2018, 20, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Padamata, S.K.; Yasinskiy, A.; Yanov, V.; Saevarsdottir, G. Magnetron Sputtering High-Entropy Alloy Coatings: A Mini-Review. Metals 2022, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.H.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, W.R.; Zhang, Y. A brief review of high-entropy films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Cai, Z.; Pu, J.; Lu, Z.; Chen, S.; Zheng, S.; Zeng, C. Effects of nitriding on the microstructure and properties of VAlTiCrMo high-entropy alloy coatings by sputtering technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 153836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Fieandt, K.; Riekehr, L.; Osinger, B.; Fritze, S. Erik Lewin, Influence of N content on structure and mechanical properties of multi-component Al-Cr-Nb-Y-Zr based thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 389, 125614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wan, Z. Chemical state, structure and mechanical properties of multi-element (CrTaNbMoV)Nx films by reactive magnetron sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 121991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Li, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, K.; Ma, F.; Chen, X.; Feng, R.; Liaw, P.K. Effects of nitrogen content on microstructures and mechanical properties of (AlCrTiZrHf)N high-entropy alloy nitride films. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 834, 155063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, C.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, Z.; Munroe, P. FeMnNiCoCr-based high entropy alloy coatings: Effect of nitrogen additions on microstructural development, mechanical properties and tribological performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-K.; Baik, Y.-J. Increase of hardness and oxidation resistance of VN coating by nanoscale multilayered structurization with AlN. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2528–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, R.; Kumar, N.; Dash, S.; Arivuoli, D.; Tyagi, A.K. Wear mechanism of CrN/NbN superlattice coating sliding against various counterbodies. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2013, 41, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Chen, D.J.; Wu, F.B. Microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of sputtering TaN coating by controlling RF input power. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 303, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontalvo, G.A.; Terziyska, V.; Mitterer, C. High-temperature tribological behaviour of sputtered NbNx thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.S.; Pichilingi, M. Sputtering in a glow discharge ion source-pressure dependence: Theory and experiment. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1994, 27, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Mao, D.; Hopwood, J. Ionized physical vapor deposition of titanium nitride: A global plasma model. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 4040–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohring, M. Chapter 3—Thin-Film Evaporation Processes. In Materials Science of Thin Films, 2nd ed.; Ohring, M., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 95–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Z.-C. Structure and properties of duodenary (TiVCrZrNbMoHfTaWAlSi)N coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 220, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, E. Multi-component and high-entropy nitride coatings—A promising field in need of a novel approach. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 160901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C.T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.-K.; Yeh, J.-W. Effects of nitrogen content on structure and mechanical properties of multi-element (AlCrNbSiTiV)N coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Sui, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hao, J. Tailoring the microstructure, mechanical and tribocorrosion performance of (CrNbTiAlV)Nx high-entropy nitride films by controlling nitrogen flow. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 107, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-H.; Lin, S.-J.; Yeh, J.-W.; Chang, S.-Y. Preparation and characterization of AlCrTaTiZr multi-element nitride coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 3275–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Miller, J.D.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C. Accelerated exploration of multi-principal element alloys with solid solution phases. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J.; Chin, T.-S.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chen, S.-K.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chou, S.-Y. Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2533–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, C.M.; Sachet, E.; Borman, T.; Moballegh, A.; Dickey, E.C.; Hou, D.; Jones, J.L.; Curtarolo, S.; Maria, J.-P. Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greene, J.E.; Sundgren, J.-E.; Hultman, L.; Petrov, I.; Bergstrom, D.B. Development of preferred orientation in polycrystalline TiN layers grown by ultrahigh vacuum reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 2928–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultman, L.; Sundgren, J.-E.; Greene, J.E.; Bergstrom, D.B.; Petrov, I. High-flux low-energy (≂20 eV) N+2 ion irradiation during TiN deposition by reactive magnetron sputtering: Effects on microstructure and preferred orientation. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 5395–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depla, D.; Mahieu, S.; Greene, J.E. Chapter 5—Sputter Deposition Processes. In Handbook of Deposition Technologies for Films and Coatings, 3rd ed.; Martin, P.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 253–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Yan, S.Q.; Zhao, R.F.; Liu, Z.X. Structure and properties of (AlCrMoNiTi)Nx and (AlCrMoZrTi)Nx films by reactive RF sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.-C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-R.; Liang, S.-C.; Shieu, F.-S. Effect of nitrogen flow ratios on the structure and mechanical properties of (TiVCrZrY)N coatings prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.-C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-R.; Jung, D.-R.; Shieu, F.-S. Effect of nitrogen flow ratios on the microstructure and properties of (TiVCr)N coatings by reactive magnetic sputtering. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2011, 269, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.W.; Fougere, G.E. Mechanical properties of nanophase metals. Nanostruct. Mater. 1995, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyland, A.; Matthews, A. On the significance of the H/E ratio in wear control: A nanocomposite coating approach to optimised tribological behaviour. Wear 2000, 246, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayrhofer, P.H.; Mitterer, C.; Musil, J. Structure–property relationships in single- and dual-phase nanocrystalline hard coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174–175, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Z. Structure and mechanical properties of multi-element (AlCrMnMoNiZr)Nx coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 560, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.-C.; Chang, Z.-C.; Kuo, B.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, E.-C.; Shieu, F.-S. Structural, electro-optical, and mechanical properties of reactively sputtered (TiZrHf)N coatings. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14257–14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).