Analysis of Iron Anchor Diseases Unearthed from Gudu Ruins in Xianyang City, Shaanxi Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
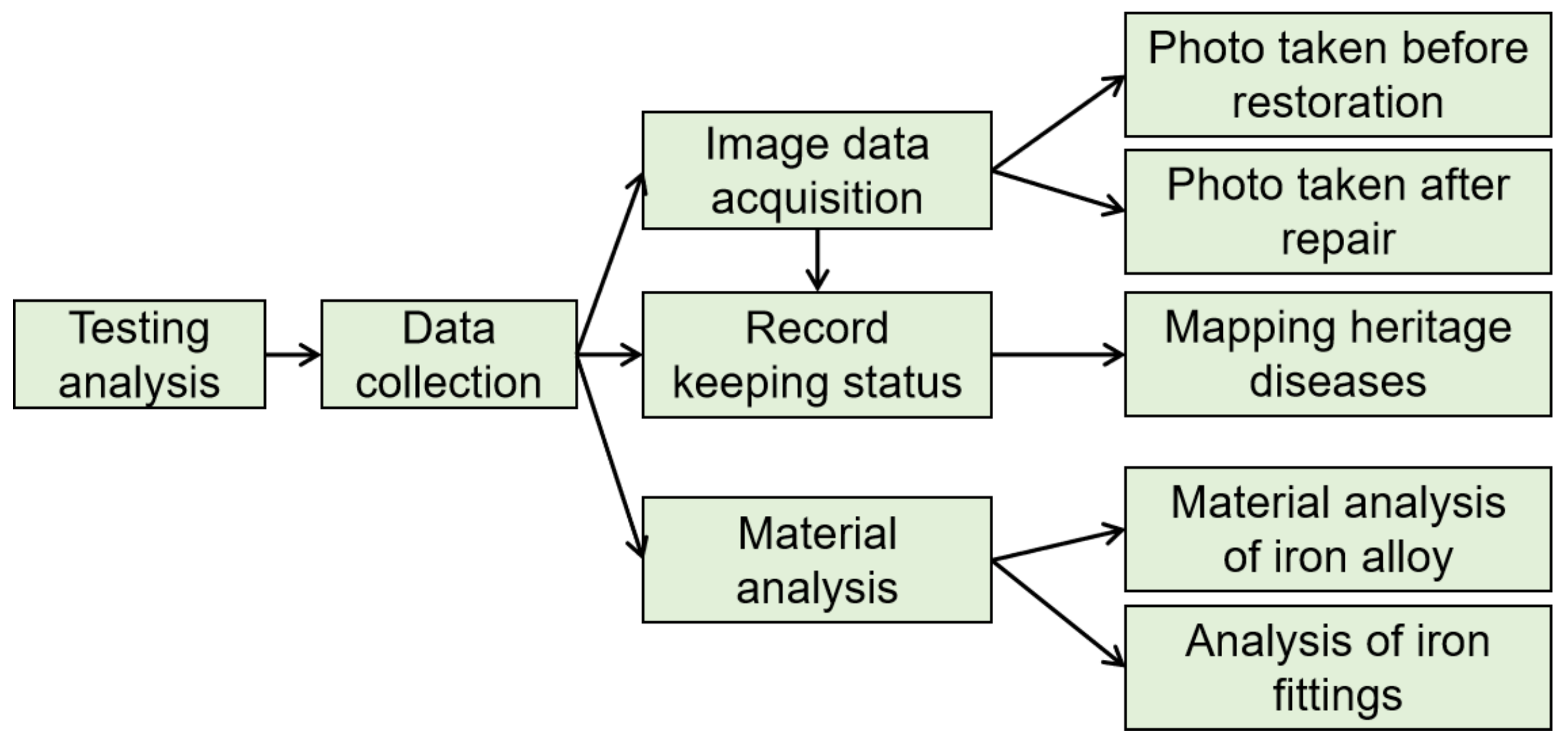
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
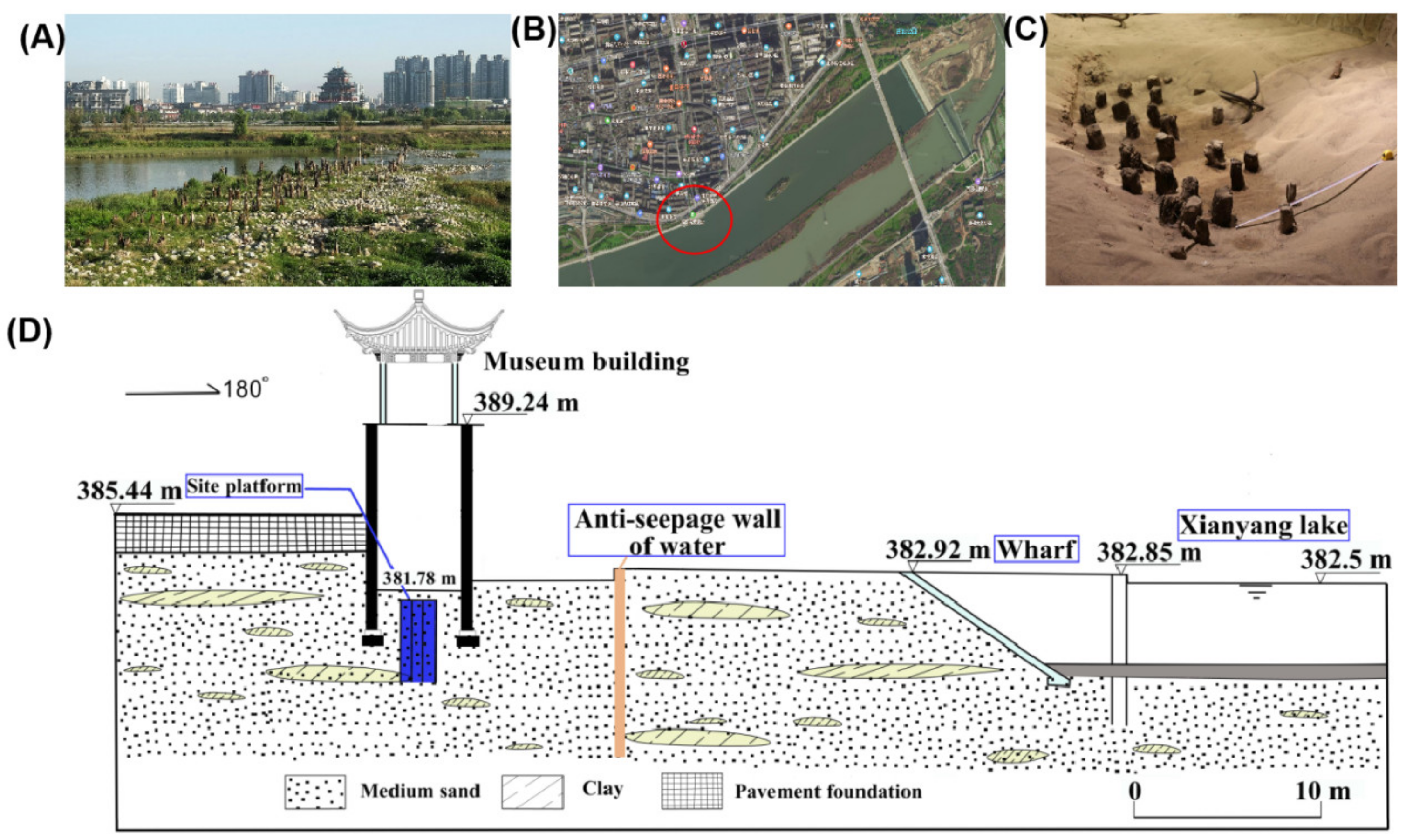
3.1. Investigation and Survey of the Occurrence Environment
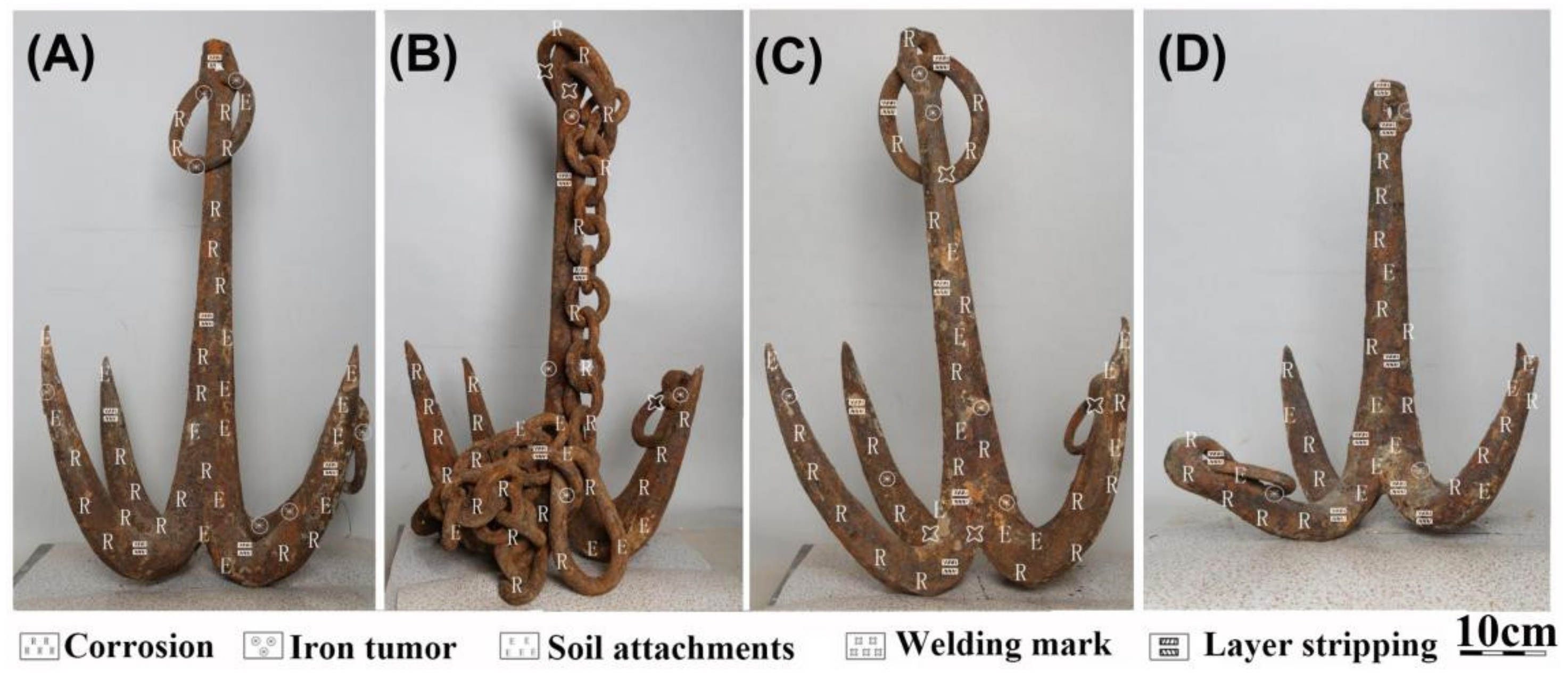
3.2. Preservation Status and Disease Type
3.3. Cast Iron Material Composition of Iron Anchor
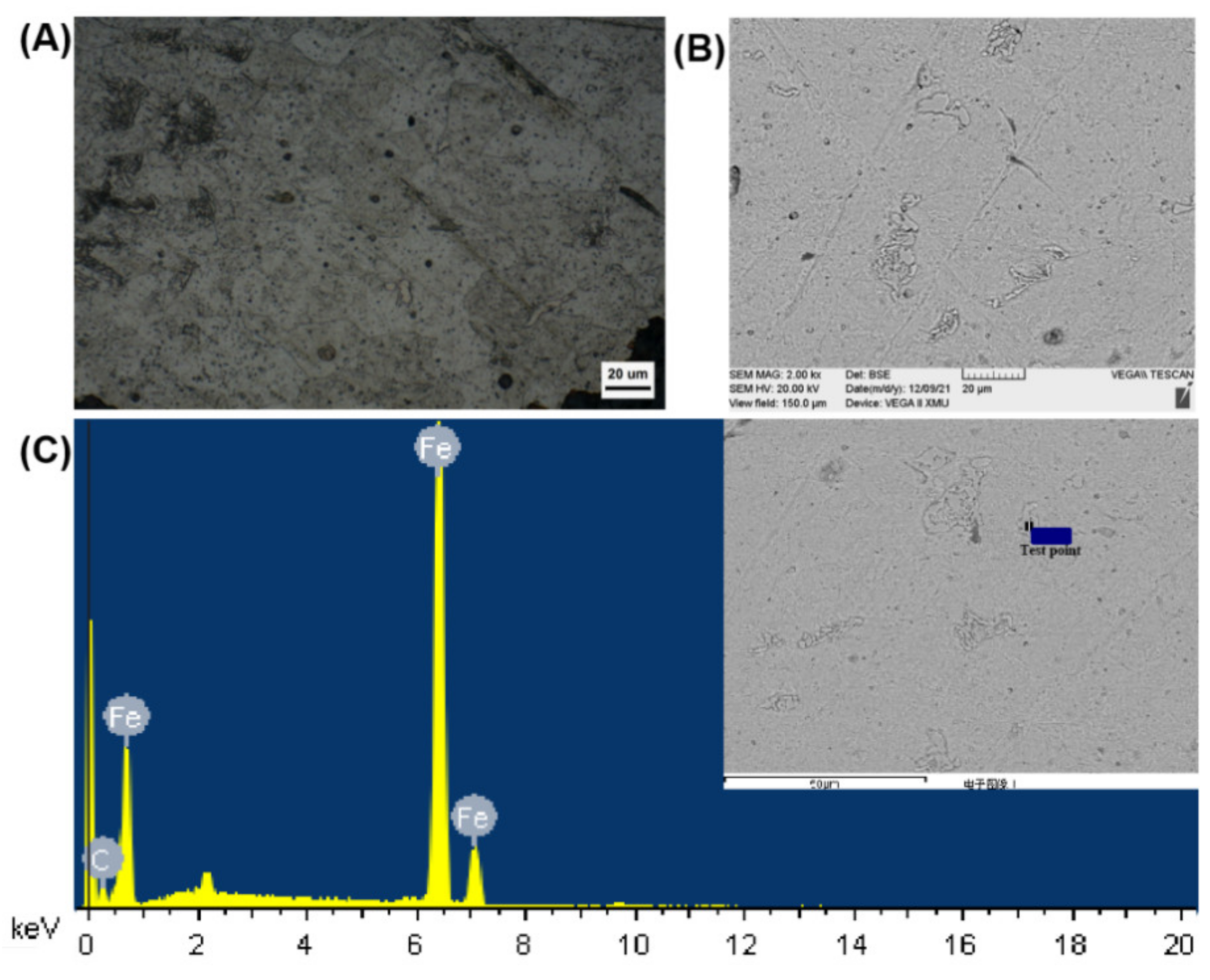
3.4. Corroded Microstructure
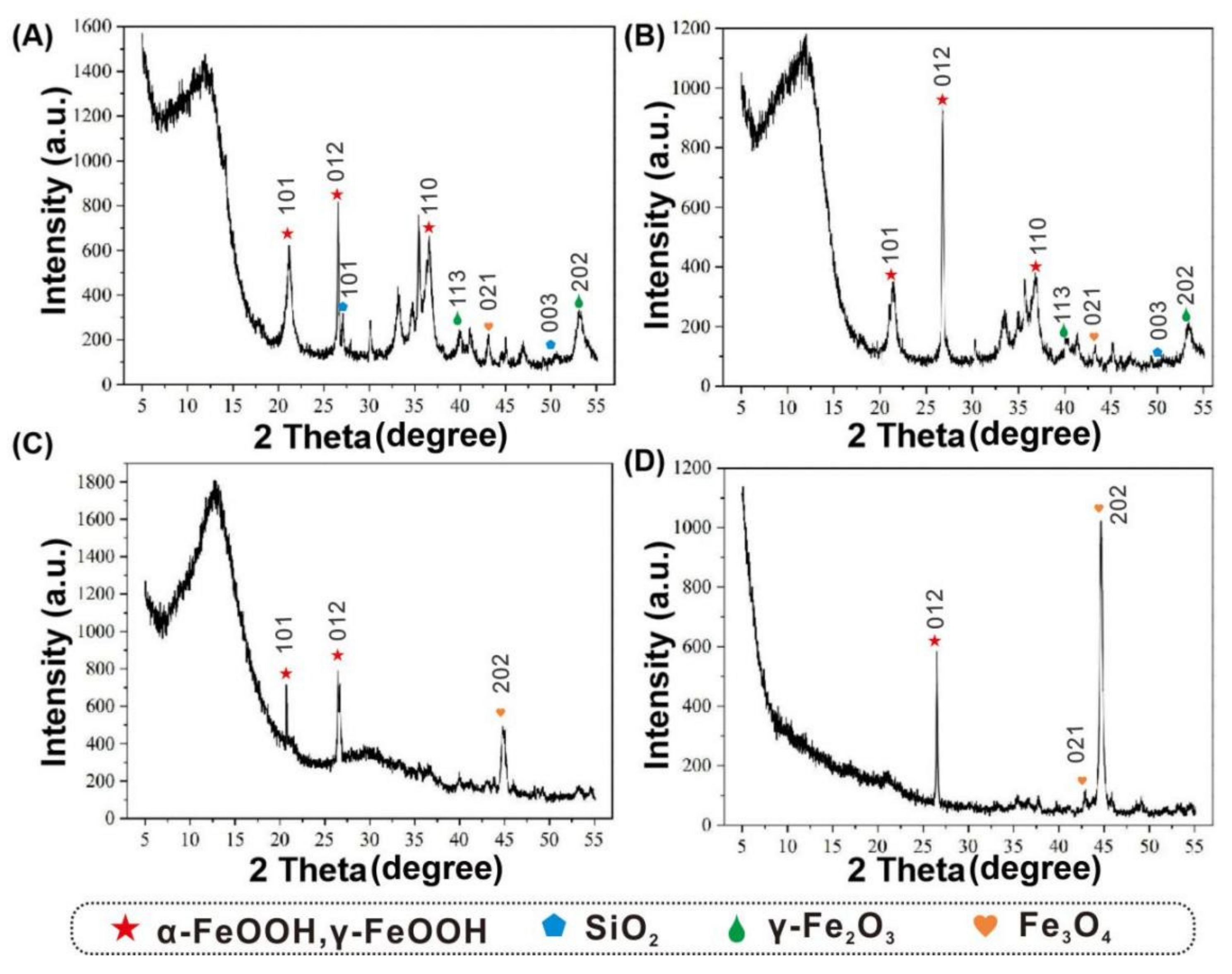
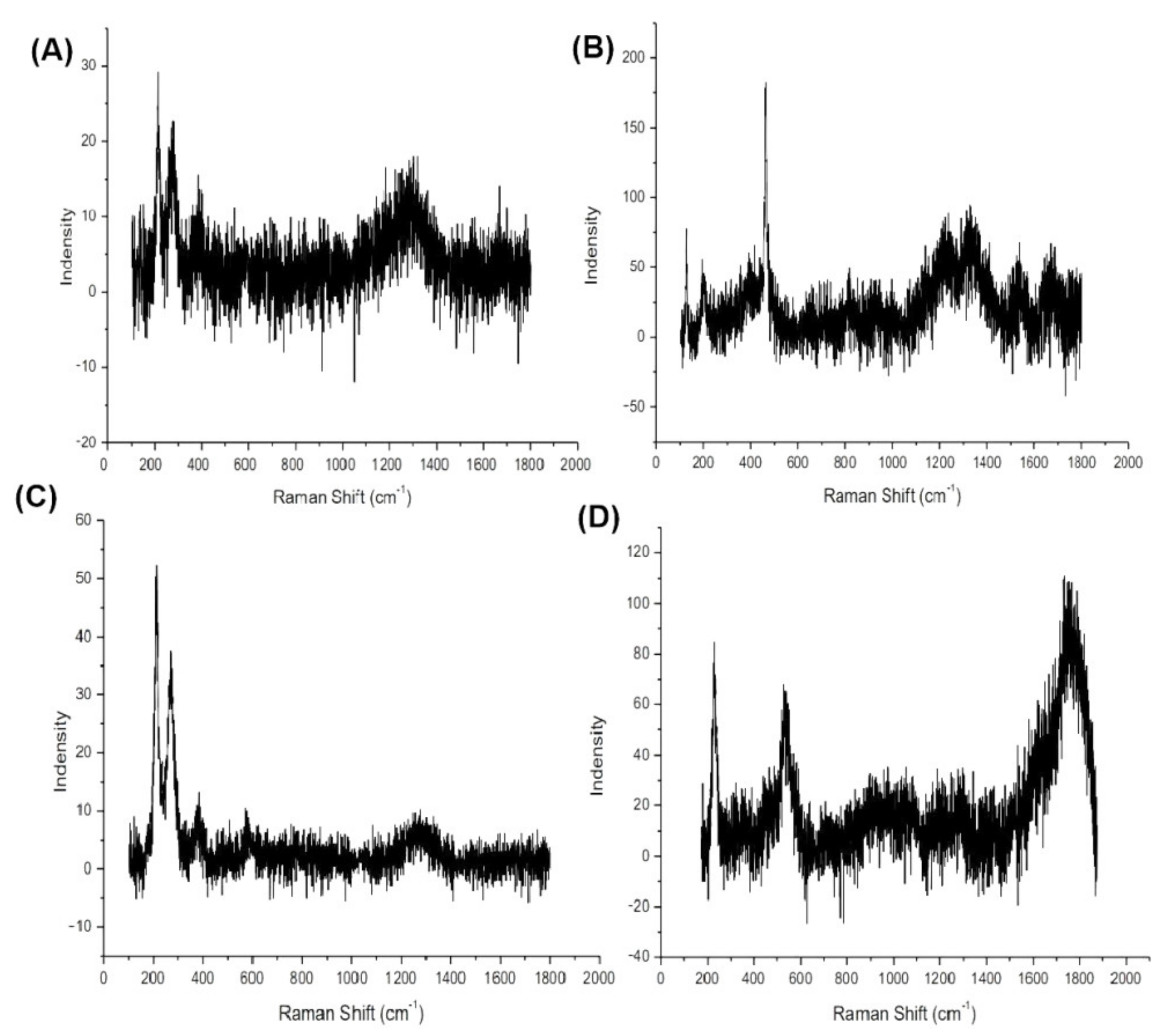
3.5. Corrosion Products
3.6. Chloride Ions in the Sample
3.7. Mechanism of Corrosion Evolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.G.; Zhu, X.; Guo, Q.; Liu, H. Structured-light based 3D reconstruction system for cultural relic packaging. Sensors 2018, 18, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, L.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ao, X.; Liao, D.; Gu, Y.; et al. Changes in soil microbial communities at Jinsha earthen site are associated with earthen site deterioration. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, F.; Huang, X.; Han, Y.; Jiang, N.; Cui, B.; Guo, Q.; Kong, M.; Song, L.; Pan, J. Analysis of microbial community in the archaeological ruins of Liangzhu city and study on protective materials. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gan, Q.; Ji, J.; Yao, N.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Qi, X.; Shi, J. Non-destructive identification of pigments printed on six imperial China engraved coiling dragon stamps. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhen, G.; Hao, X.; Tong, T.; Ni, F.; Wang, Z.; Jia, J.; Li, L.; Tong, H. Spectroscopic investigation and comprehensive analysis of the polychrome clay sculpture of hua yan temple of the liao dynasty. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 240, 118574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, A.; Thomas, P.; James, D.; David, B.; Geneste, J.-M.; Delannoy, J.-J.; Stuart, B. The characterisation of pigments used in X-ray rock art at dalakngalarr 1, central-western arnhem land. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmi, M.M.; Nurdini, N.; Maryanti, E.; Saiyasombat, C.; Setiawan, P.; Kadja, G.T.M. Ismunandar multi-analytical characterizations of prehistoric rock art pigments from karim cave, sangkulirang–mangkalihat site, east kalimantan, indonesia. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffino, C.; Guglielmi, V.; Faraone, S.; Vinaccia, A.; Bruni, S. Exploiting external reflection FTIR spectroscopy for the in-situ identification of pigments and binders in illuminated manuscripts. Brochantite and posnjakite as a case study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136 Pt B, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Teri, G.; Li, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Analysis of an ancient architectural painting from the jiangxue palace in the imperial museum, Beijing, China. Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.; Mphuthi, D.; Cukrowska, E.; Henshilwood, C.S.; van Niekerk, K.; Chimuka, L. Blombos cave: Middle stone age ochre differentiation through FTIR, ICP OES, ED XRF and XRD. Quat. Int. 2016, 404, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mai, B.; Fu, P.; Teri, G.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Multi-analytical research on the caisson painting of Dayu temple in Hancheng, Shaanxi, China. Coatings 2021, 11, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, F.; Burnstock, A.; Berg, K.; Miliani, C.; Brunetti, B.G.; Sgamellotti, A. A non-invasive XRF study supported by multivariate statistical analysis and reflectance FTIR to assess the composition of modern painting materials. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisegna, F.; Ambrosini, D.; Paoletti, D.; Sfarra, S.; Gugliermetti, F. A qualitative method for combining thermal imprints to emerging weak points of ancient wall structures by passive infrared thermography—A case study. J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, M. Chapter 5 hyperspectral imaging: A new technique for the non-invasive study of artworks. In Physical Techniques in the Study of Art, Archaeology and Cultural Heritage; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 199–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Laureti, S.; Malekmohammadi, H.; Sfarra, S.; Lanteri, L.; Colantonio, C.; Calabrò, G.; Pelosi, C. Surface and interface investigation of a 15th century wall painting using multispectral imaging and pulse-compression infrared thermography. Coatings 2021, 11, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.; Mas, N.; Cotte, P. Review of several optical non-destructive analyses of an easel painting. Complementarity and crosschecking of the results. J. Cult. Herit. 2011, 12, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Quantitative measurement of cast metal relics by pulsed thermal imaging. Quant. Infrared Thermogr. J. 2020, 5, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, D.; Paoletti, A.; Paoletti, D.; Sfarra, S. NDT methods in artwork corrosion monitoring. In O3A: Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology; SPIE: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoli, L.; Ning, T.; Sun, J.G.; Yong, L.; Liang, Q.; Fei, G.; Yi, H.; Guang, W.; Lichun, F. Evaluation of an ancient cast-iron Buddha head by step-heating infrared thermography. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 98, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, R.D.; Basilico, E.; Mingant, R.; Kittel, J.; Ropital, F.; Combrade, P.; Necib, S.; Deydier, V.; Crusset, D.; Marcelin, S. A study by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and surface analysis of corrosion product layers formed during CO2 corrosion of low alloy steel. Corros. Sci. 2020, 172, 108666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remazeilles, C.; Neff, D.; Bourdoiseau, J.A.; Sabot, R.; Jeannin, M.; Refait, P. Role of previously formed corrosion product layers on sulfide-assisted corrosion of iron archaeological artefacts in soil. Corros. Sci. 2017, 129, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samide, A.; Tutunaru, B.; Dobritescu, A.; Negrila, C. Study of the corrosion products formed on carbon steel surface in hydrochloric acid solution. J. Therm. Anal. 2012, 110, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H. The role of rusts in corrosion and corrosion protection of iron and steel. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novakova, A.A.; Gendler, T.S.; Manyurova, N.D.; Turishcheva, R.A. A mössbauer spectroscopy study of the corrosion products formed at an iron surface in soil. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, D.E.; Rimmer, M.B.; Emmerson, N.J. The influence of relative humidity and intrinsic chloride on post-excavation corrosion rates of archaeological wrought iron. Stud. Conserv. 2019, 64, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, W.; Keith, D.; Rodriguez, J. Less is more: Measure of chloride removal rate from wrought iron artifacts during electrolysis. Stud. Conserv. 2001, 46, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jiang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Tian, Y. Effects of chloride ions on corrosion of ductile iron and carbon steel in soil environments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Luo, S.X.; Sun, C. Effect of soil compositions on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of carbon steel in simulated soil solution. Mater. Werkst. 2010, 41, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Ai, Y.; Xiao, J.; Pan, D.; Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y. Impact of soil composition and electrochemistry on corrosion of rock-cut slope nets along railway Lines in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viereck, S.; Jovanovic, Z.R.; Haselbacher, A.; Steinfeld, A. Investigation of Na2SO4 removal from a supercritical aqueous solution in a dip-tube salt separator. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 133, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan-Reyes, C.; Fuentes-Aceituno, J.C.; Salinas-Rodríguez, A. The role of alkalizing agent on the manganese phosphating of a high strength steel part 1: The individual effect of naoh and NH4OH. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 291, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, G.; Che, C.; Zhang, B. Inhibitive effect of sodium molybdate on the corrosion behavior of galvanized steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.Y.; Yang, X.G.; Hou, B.R. Synthesis of polyaniline nanofiber and anticorrosion property of polyaniline–epoxy composite coating for q235 steel. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2012, 9, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Superhydrophobic oligoaniline-containing electroactive silica coating as pre-process coating for corrosion protection of carbon steel. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mai, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, M.; Cao, J. Analysis of Iron Anchor Diseases Unearthed from Gudu Ruins in Xianyang City, Shaanxi Province, China. Coatings 2022, 12, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12030381
Mai B, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Wang J, Li Y, Cao M, Cao J. Analysis of Iron Anchor Diseases Unearthed from Gudu Ruins in Xianyang City, Shaanxi Province, China. Coatings. 2022; 12(3):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12030381
Chicago/Turabian StyleMai, Bingjie, Youlu Chen, Ying Zhang, Yongsheng Huang, Juanli Wang, Yuhu Li, Ming Cao, and Jing Cao. 2022. "Analysis of Iron Anchor Diseases Unearthed from Gudu Ruins in Xianyang City, Shaanxi Province, China" Coatings 12, no. 3: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12030381
APA StyleMai, B., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Wang, J., Li, Y., Cao, M., & Cao, J. (2022). Analysis of Iron Anchor Diseases Unearthed from Gudu Ruins in Xianyang City, Shaanxi Province, China. Coatings, 12(3), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12030381






