Asynchronous Synergistic Damage Effect of Atomic Oxygen and Space Micro Debris on Kapton Film
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
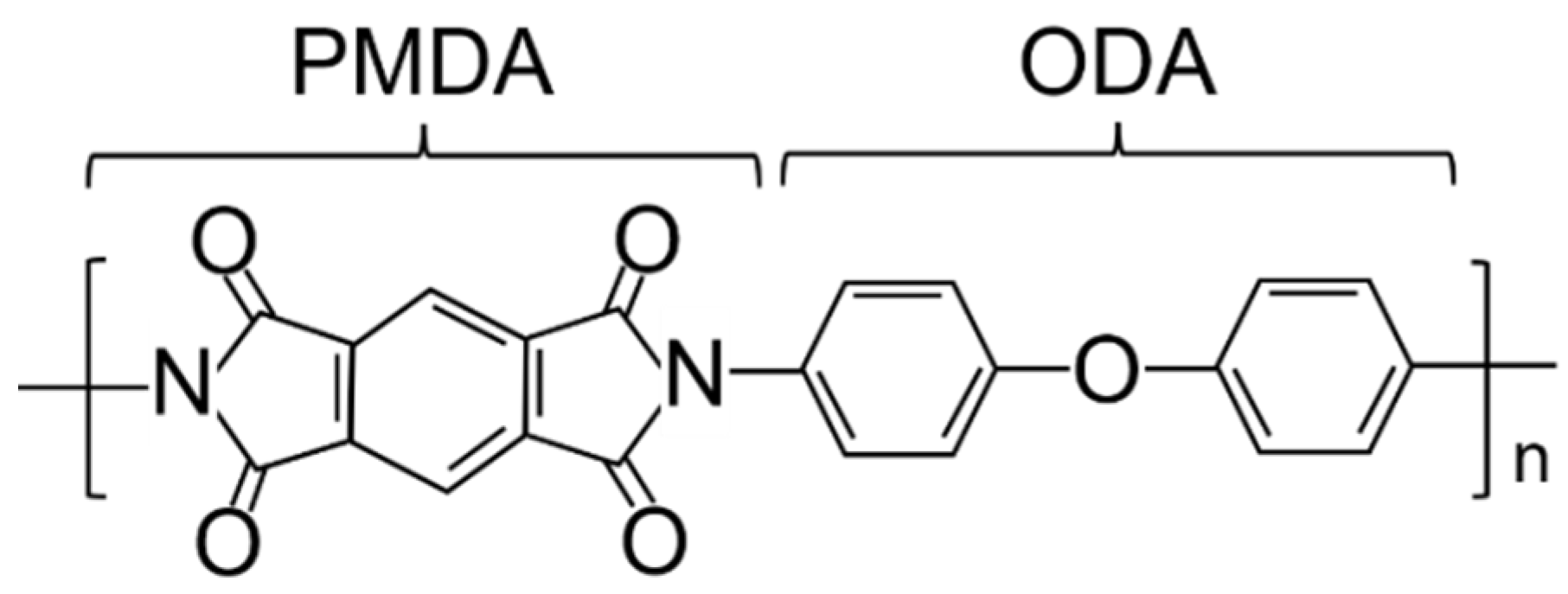
2.1. Materials
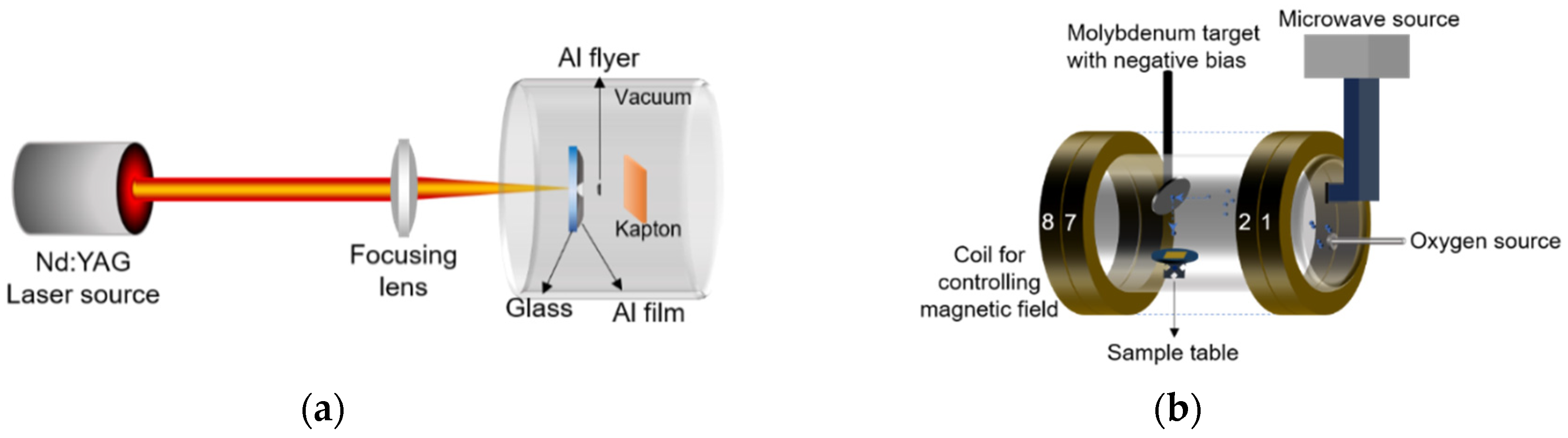
2.2. Ground Simulation Method of Atomic Oxygen and Micro Debris
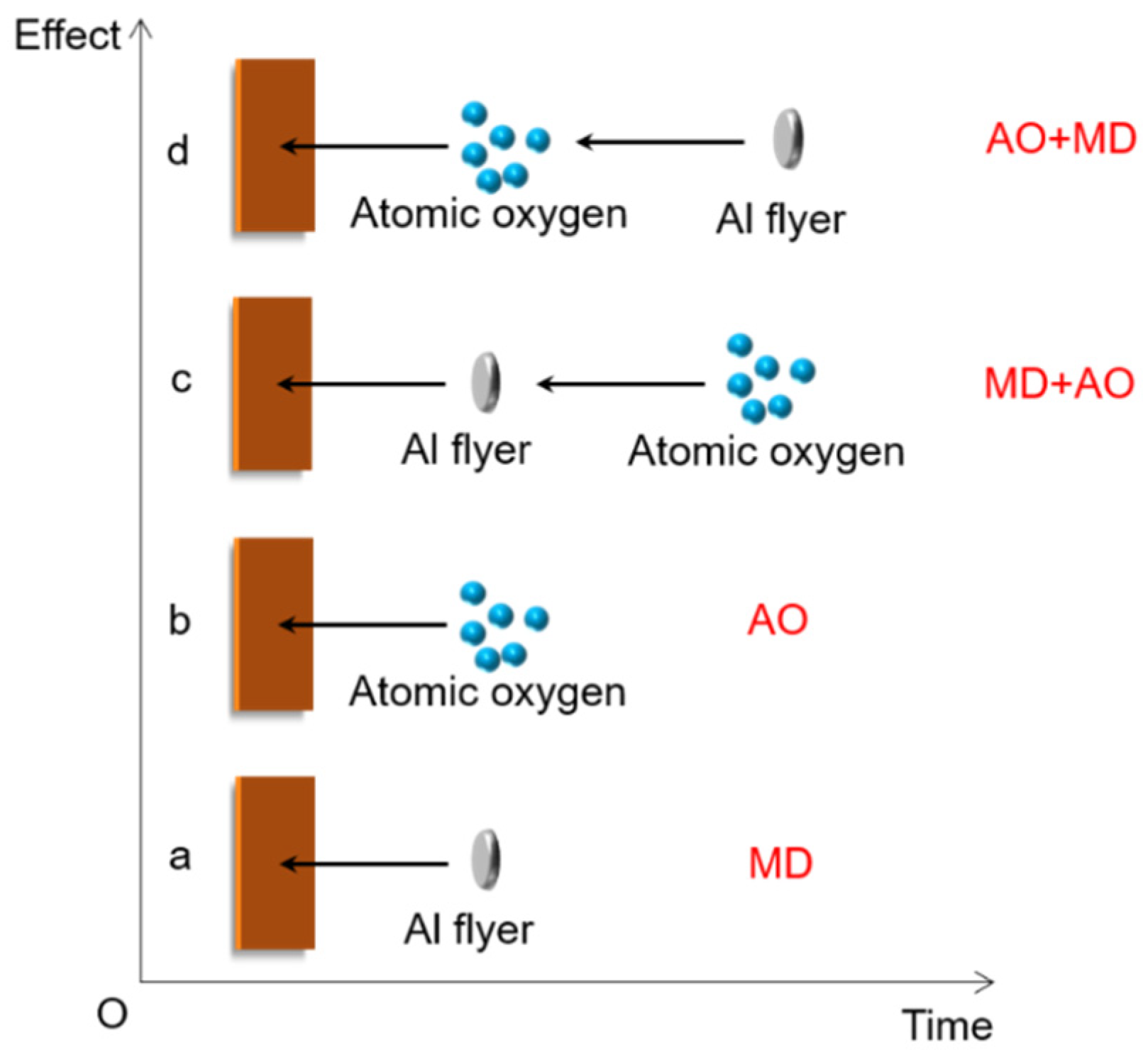
2.3. Development of Load Spectra
2.4. Material Performance Test and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
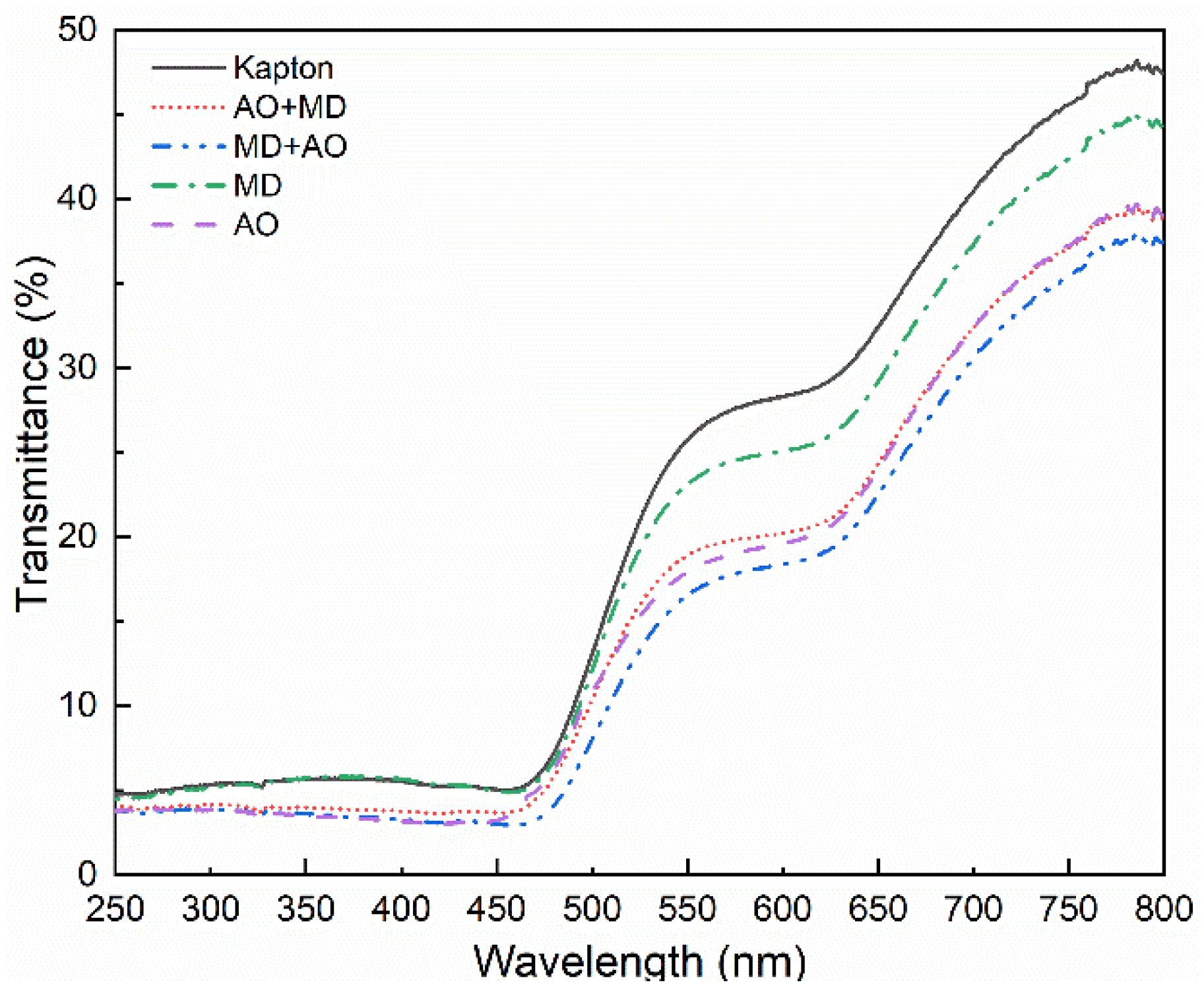
3.1. Optical Performance Analysis
3.2. Quality Change of Kapton Film
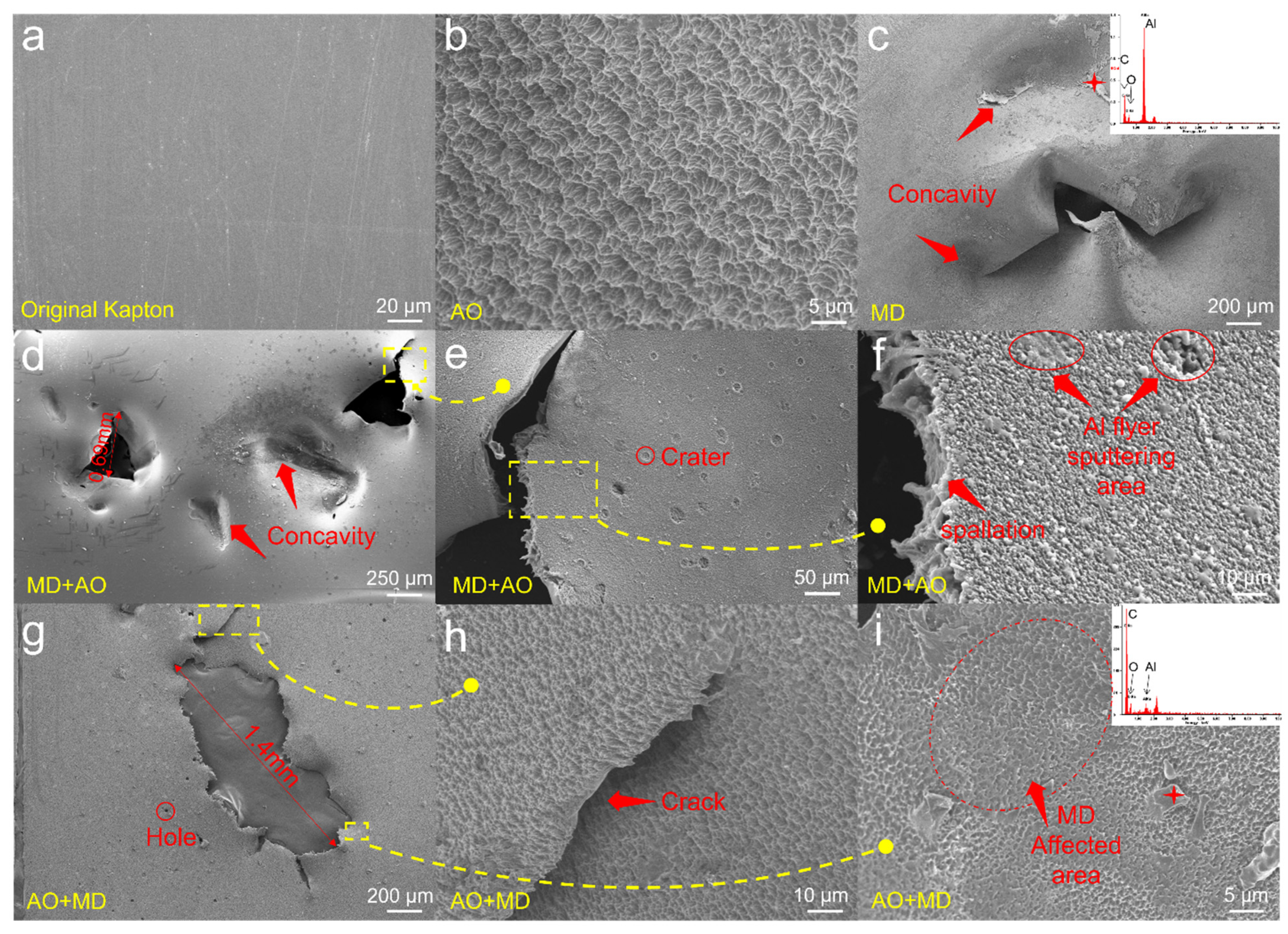
3.3. Microstructure Characterization
3.4. Infrared Spectrum Analysis
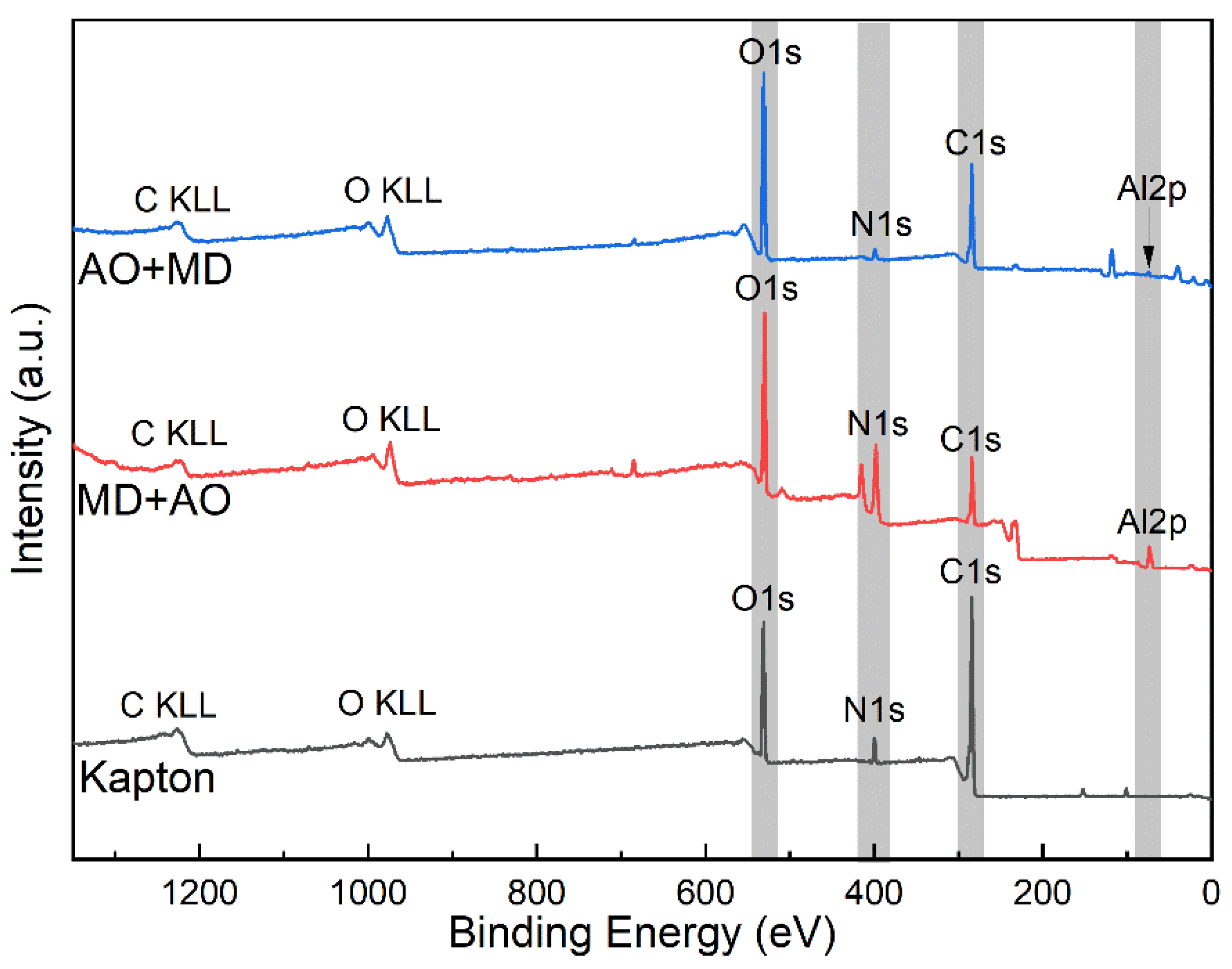
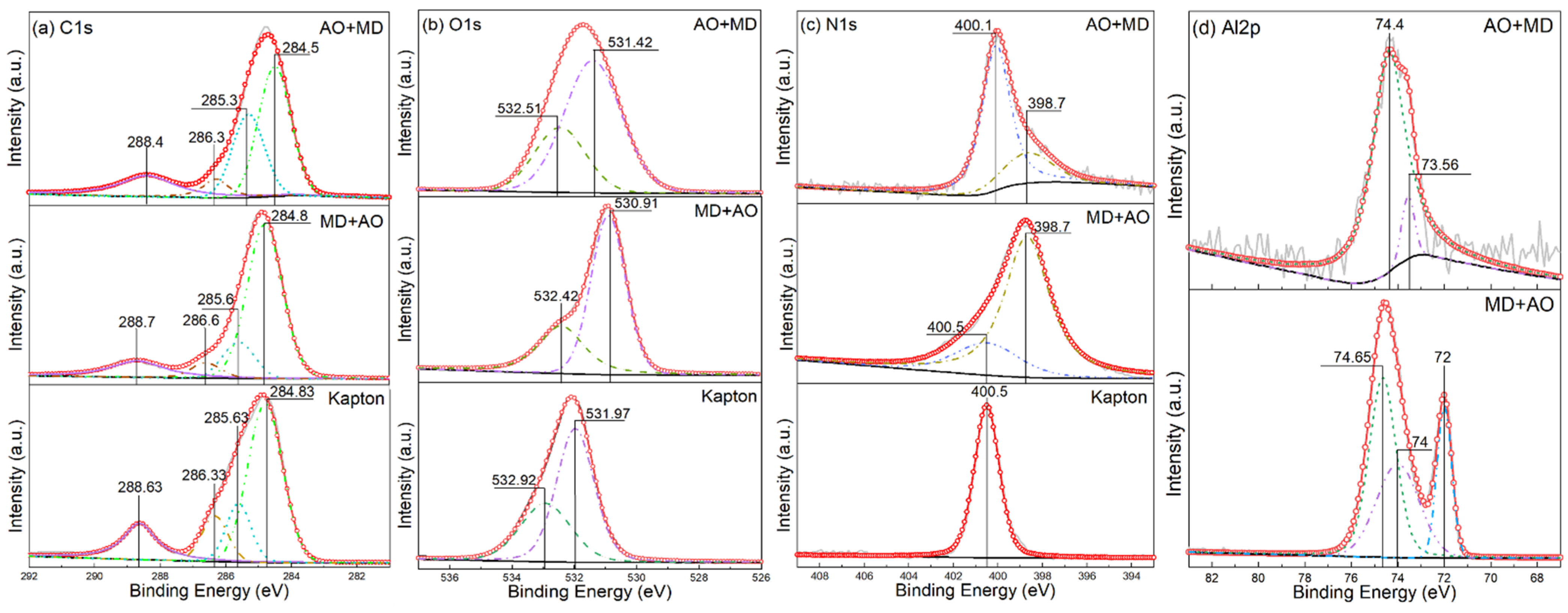
3.5. XPS Analysis
4. Conclusions
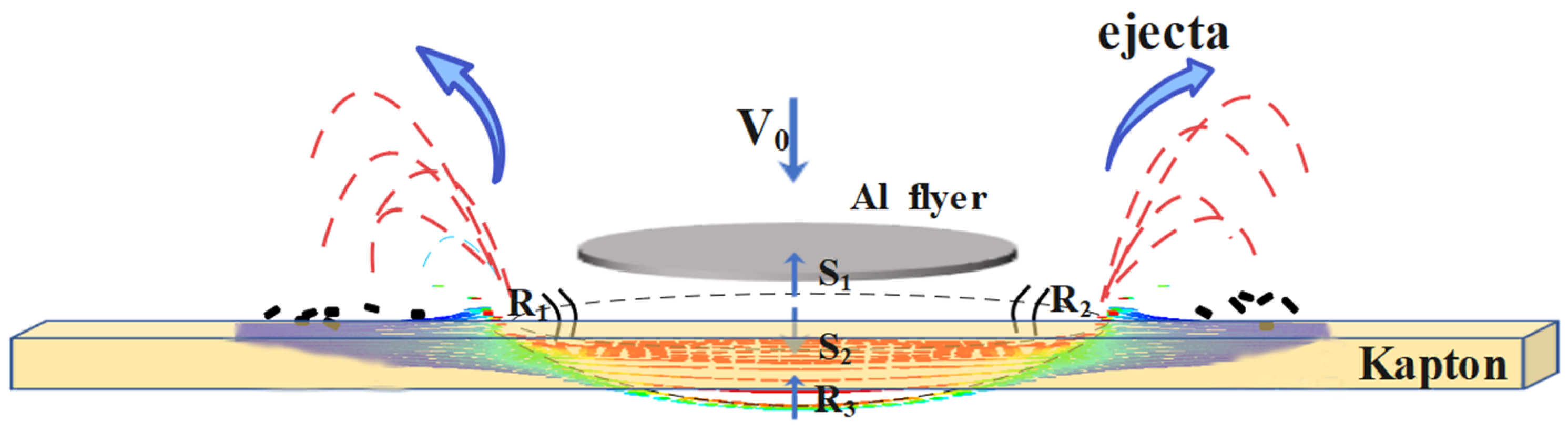
- After the asynchronous synergistic action of atomic oxygen and small debris, the Kapton film changed from brown yellow to light yellow; the gloss disappeared, and the transmittance decreased in the wavelength range of 600–800 nm. Under the condition of AO + MD load spectrum, the surface hole of Kapton film was larger than that under the MD + AO load spectrum, the residual aluminum particles formed by the reverse sputtering of Al particles produced during the impact process were less, the average transmittance of the film decreased slightly, and the weight loss of Kapton film was slightly more under the same atomic oxygen exposure time;
- Under the condition of MD + AO load spectrum, plastic tearing cracks, pits and holes appeared on the surface of Kapton film; under the condition of AO + MD load spectrum, the hole edge on the surface of Kapton film was straight, without obvious depression and tear characteristics. This is attributed to the fact that the film was eroded by atomic oxygen first, and the rough carpet shape was formed on the material surface, and the subsequent flyer impact became the crack source; at the same time, the atomic oxygen corrosion aging fracture strength of the surface material decreases.
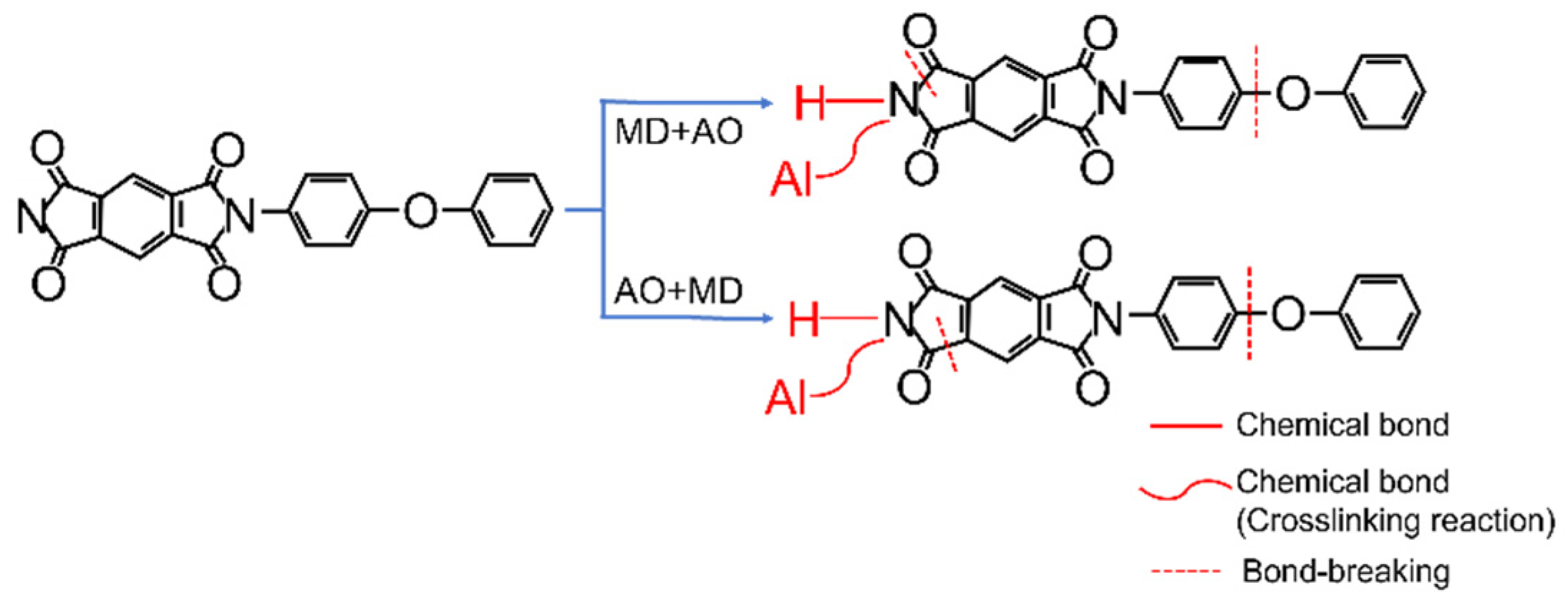
- Under the condition of MD + AO load spectrum, due to the adhesion of Al after the impact of micro debris, the subsequent atomic oxygen erosion of the film was reduced, so the C–C bond was not seriously damaged, and a considerable part of the residual aluminum flyer was oxidized to alumina by atomic oxygen. While the AO + MD loading spectrum test made the film first eroded by atomic oxygen, resulting in the reduction in the C–O bond and the C–C bond. The impact of micro debris had a great impact on the C–N bond. Hypervelocity impact leads to the thermal decomposition of the material, destroyed the C–N bond in the imide ring and generated N–H bond.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeritsyan, H.N.; Sahakyan, A.A.; Grigoryan, N.E.; Harutyunyan, V.V.; Arzumanyan, V.V.; Tsakanov, V.M.; Grigoryan, B.A.; Davtyan, H.D.; Dekhtiarov, V.S.; Rhodes, C.J.; et al. Space low earth orbit environment simulator for ground testing materials and devices. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 181, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, R.; Bolker, A.; Tsang, S.H.; Atar, N.; Verker, R.; Gouzman, I.; Hala, M.; Moshe, N.; Jones, A.; Grossman, E.; et al. POSS Enhanced 3D Graphene–Polyimide Film for Atomic Oxygen Endurance in Low Earth Orbit Space Environment. Polymer 2020, 191, 122270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, H.; Nakamura, T. Investigation of degradation mechanisms in mechanical properties of polyimide films exposed to a low earth orbit environment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, H.; Nakamura, T. Mechanical properties degradation of polyimide films irradiated by atomic oxygen. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.W.; Shen, Z.C.; Xiao, L. Study on Synergistic Effect of Space Environments on Spacecraft. Spacecr. Eng. 2013, 22, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.F.; Shao, Q.; Yue, H.H.; Yang, F. A Review of the Space Environment Effects on Spacecraft in Different Orbits. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93473–93488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-H.; Kim, C.-G. Low earth orbit space environment simulation and its effects on graphite/epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2006, 72, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Y.; Yang, D.Z.; Jiao, Z.K. Space Materials Manual–Physical State of Space Environment, 1st ed.; Aerospace Press: Beijing, China, 2012; Volume 1, pp. III–IV. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.M.; Zhang, L.; Yan, C.W. Synergic Effect of Atomic Oxygen and Vacuum Ultraviolet on Organic Coatings Degradation. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2007, 27, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, K.; Ohmae, N.; Tagawa, M. Effect of Relative Intensity of 5 eV Atomic Oxygen and 172 nm Vacuum Ultraviolet in the Synergism of Polyimide Erosion. High Perform. Polym. 2004, 16, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, H.; Miyazaki, E. Investigations into Synergistic Effects of Atomic Oxygen and Vacuum Ultraviolet. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2009, 469, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.Q.; Ren, G.H.; Tian, D.B.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Liu, C. Advances in research on low-orbit ultraviolet, charged particles, thermal cycling and atomic oxygen synergistic effects. Vacuum 2019, 56, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.W.; Song, L.M.; Wang, Z.H. A Study on Process Management and Control Technology of Asynchronous Coliaborative Simulation. J. Inn. Mong. Univ. Technol. 2007, 26, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, M.; Yokota, K. Atomic oxygen-induced polymer degradation phenomena in simulated LEO space environments: How do polymers react in a complicated space environment? Acta Astronaut. 2008, 62, 30203–30211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qiu, X.M.; Zhang, X.H.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Yang, J.H. Experimental investigation on the hypervelocity impact damage behavior of polyimide film. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 141, 103538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verker, R.; Grossman, E.; Gouzman, I.; Laikhtman, A.; Katz, S.; Freankel, M.; Maman, S.; Lempert, G.; Eliaz, N. Synergistic effect of simulated hypervelocity space debris and atomic oxygen on durability of POSS-polyimide nanocomposite. In Proceedings of the 10th Int. Symp. on Materials in Space Environment & the 8th Int. Conf. on Protection of Materials and Structures in a Space Environment—ISMSE/ICPMSE 2006, Collioure, France, 19–23 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.W.; Cai, M.H.; Han, J.W.; Huang, J.G.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Gao, Z.X.; Liu, D.Q. Research of Combined Effect of Small Space Debris and Atomic Oxygen. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2011, 31, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.F.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chai, L.H. The combined effect of space micro-debris and atomic oxygen on ITO/Kapton/Al film. Spacecr. Environ. Eng. 2016, 33, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouzman, I.; Grossman, E.; Verker, R.; Atar, N.; Bolker, A.; Eliaz, N. Advances in Polyimide-Based Materials for Space Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, C.W.; Qu, Q.; Li, M.S.; Cao, C.N. Effect of Atomic Oxygen on Spacecraft Materials and Its Protection II. Protection of Atomic Oxygen-Susceptible Materials. Mater. Rev. 2002, 16, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shit, S.C.; Shah, P.M. A Review on Silicone Rubber. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2013, 36, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.R.; Li, Z.H.; Shu, M.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.T.; Gao, Y. Surface treatment of 25-µm Kapton film by ammonia for improvement of TiO2 SiO2 coating’s adhesion. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.H.; Wei, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.H. Review on the Laser Technology Application in Space Environment Ground Simulation. Optoelectron. Technol. 2016, 33, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, S.W.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, Y.M. A Simulator for Producing of High Flux Atomic Oxygen Beam by Using ECR Plasma Source. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2004, 20, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Mu, H.; Shu, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y. Improved adhesion between SnO2/SiO2 coating and polyimide film and its applications to atomic oxygen protection. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.H.; Lei, X.F.; Xue, S.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.Y. Janus polyimide films with outstanding AO resistance, good optical transparency and high mechanical strength. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 535, 147654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, S.-Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Pan, Q.-Y.; Xu, G.S.; Yue, C.-Y. Improvements in transmittance, mechanical properties and thermal stability of silica–polyimide composite films by a novel sol–gel route. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.D.; Ma, G.Z.; Xu, B.S.; Xing, Z.G.; Li, G.L.; Zhang, S. The Erosion Effect of Kapton Film in a Groundbased Atomic Oxygen Irradiation Simulator. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2014, 29, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczala, D.M.; Brunsvold, A.L.; Minton, T.K. Erosion of Kapton® H by Hyperthermal Atomic Oxygen. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2006, 43, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.R. Effect of low earth orbit atomic oxygen on spacecraft materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, C.J.; Mcmillan, A.R. An Investigation of the Protection Afforded a Spacecraft by a Thin Shield. Aerosp. Sci. Meet. 1964, 2, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Tian, X.B.; Yang, S.Q.; Chu, P.K. A ground-based radio frequency inductively coupled plasma apparatus for atomic oxygen simulation in low Earth orbit. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 103301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Weiping, L.; Huicong, L.; Liqun, Z. Erosion of a Polyimide Material Exposed to Simulated Atomic Oxygen Environment. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2010, 23, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cui, W.F.; Zeng, X.W. Simulation investigations on debris cloud impact damage potential. Explos. Shock. Waves 2009, 29, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, D.; Xiong, R.; Shi, J.; Tian, F.Q.; Wang, X.; Lei, Q.Q. FTIR and Dielectric Studies of Electrical Aging in Polyimide under AC Voltage. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddaf, M.; Balasubramanian, C.; Alegaonkar, P.S.; Bhoraskar, V.N.; Mandle, A.B.; Ganeshan, V.; Bhoraskar, S.V. Surface interaction of polyimide with oxygen ECR plasma. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 222, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, G.B.; Sheng, L.S. Synthesis and Studies of Polyimide. Mater. Rev. 2008, 22, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, S.W.; Li, M.S.; Zhou, Y.C.; Tong, J.Y.; Sun, G. Investigation of Surface Reaction and Degradation Mechanism of Kapton during Atomic Oxygen Exposure. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.H.; Wang, D.; Liu, G.; Wei, Q. Atomic Oxygen Adaptability of Flexible Kapton/Al2O3 Composite Thin Films Prepared by Ion Exchange Method. Coatings 2019, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.C.; Ma, Z.L.; Dai, W.; Mu, Y.Q.; Bai, Y.; Ding, Y.G. Evolution Mechanism for Mechanical Property of Polyimide Film by Far Ultraviolet Irradiation. Surf. Technol. 2018, 47, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.J.; Shen, S.C.; Wang, J.B. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study of Polyimide Film by Ar Ion Bombardment. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Han, S.; Li, Q.M.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, G.Y. Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polyimide Pyrolysis Mechanism at High Temperature. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2016, 31, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, L.; Baird, R.; McCullen, E.; Auner, G.; Shreve, G. XPS analysis of aluminum nitride films deposited by plasma source molecular beam epitaxy. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, P.; Cadien, K. XPS analysis of AlN thin films deposited by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 315, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Surface Composition (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | Al | |
| Original Kapton | 75.18 | 19.18 | 5.64 | - |
| MD + AO Kapton | 45.66 | 32.58 | 3.62 | 18.15 |
| AO + MD Kapton | 47.32 | 48.95 | 0.15 | 3.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, P.; Wei, Q.; Hu, N.; Chen, X. Asynchronous Synergistic Damage Effect of Atomic Oxygen and Space Micro Debris on Kapton Film. Coatings 2022, 12, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020179
Tong P, Wei Q, Hu N, Chen X. Asynchronous Synergistic Damage Effect of Atomic Oxygen and Space Micro Debris on Kapton Film. Coatings. 2022; 12(2):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020179
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Peiyi, Qiang Wei, Ning Hu, and Xueguang Chen. 2022. "Asynchronous Synergistic Damage Effect of Atomic Oxygen and Space Micro Debris on Kapton Film" Coatings 12, no. 2: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020179
APA StyleTong, P., Wei, Q., Hu, N., & Chen, X. (2022). Asynchronous Synergistic Damage Effect of Atomic Oxygen and Space Micro Debris on Kapton Film. Coatings, 12(2), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12020179







