Study on Size Effect in Indentation Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
3. Simulation and Validation
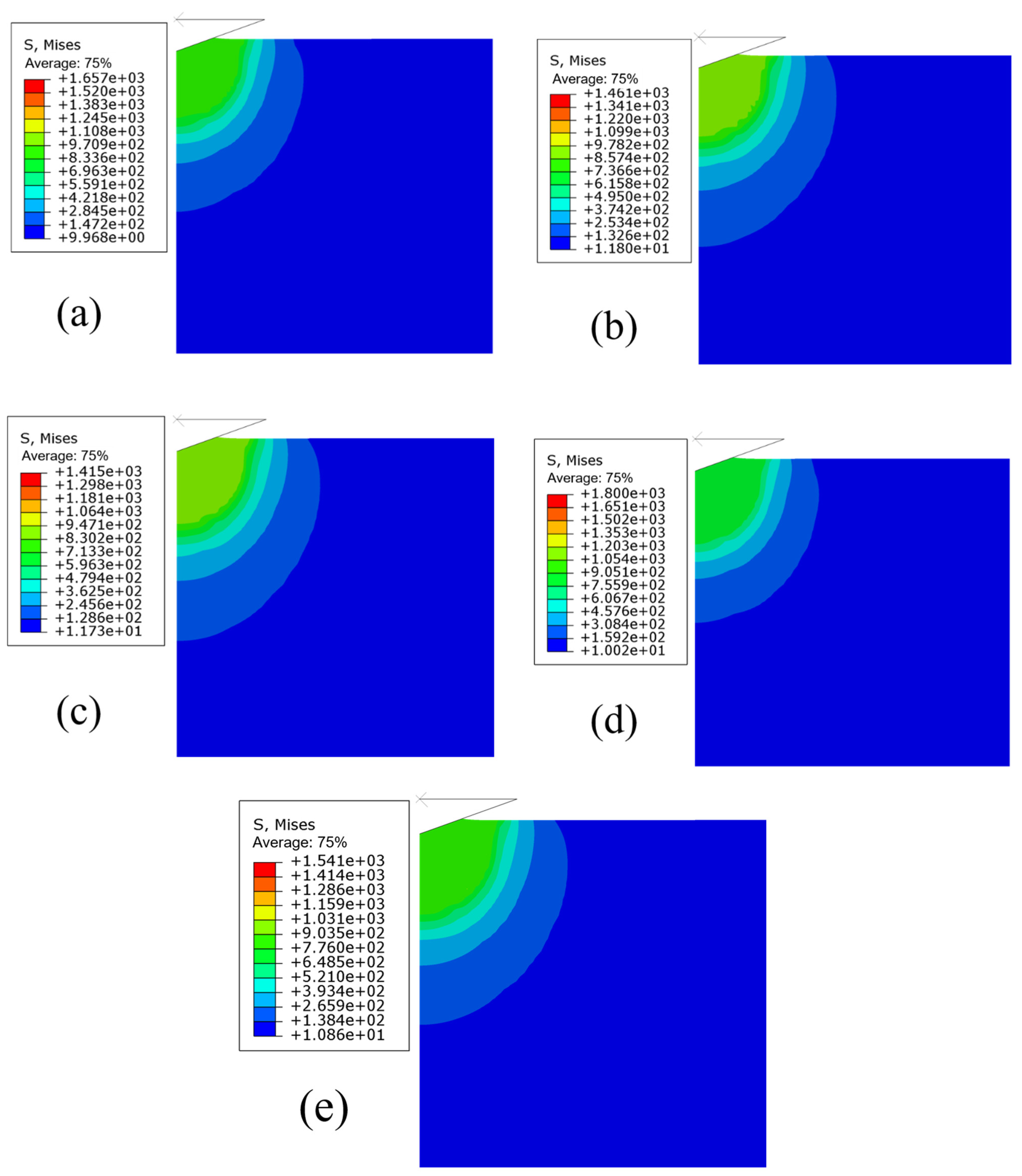
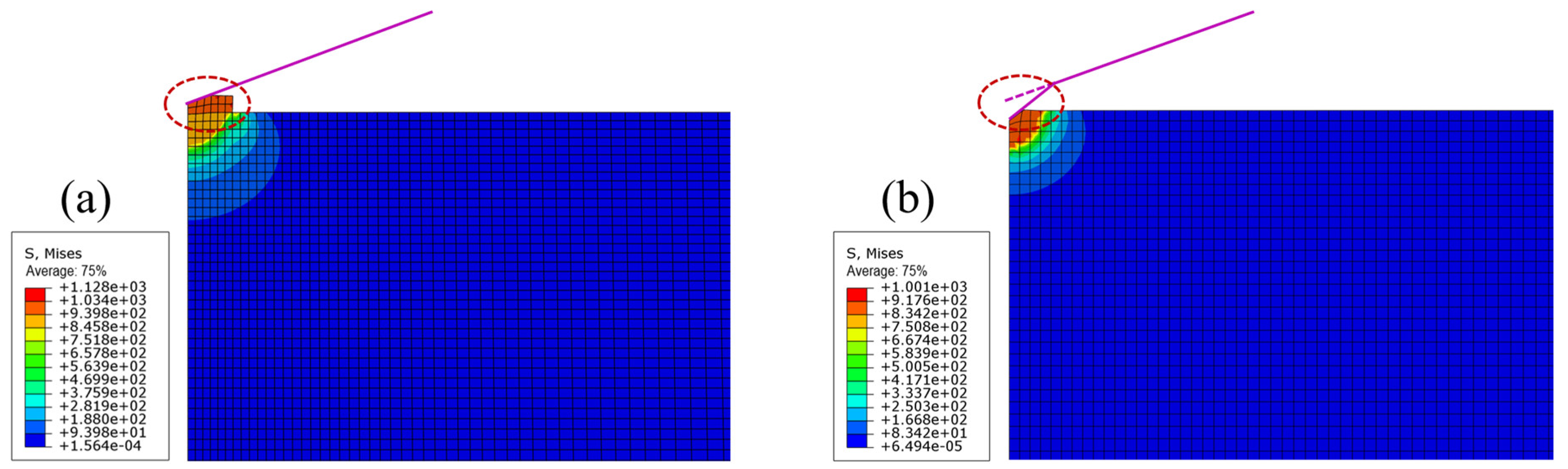
3.1. FEM of the Size Effect
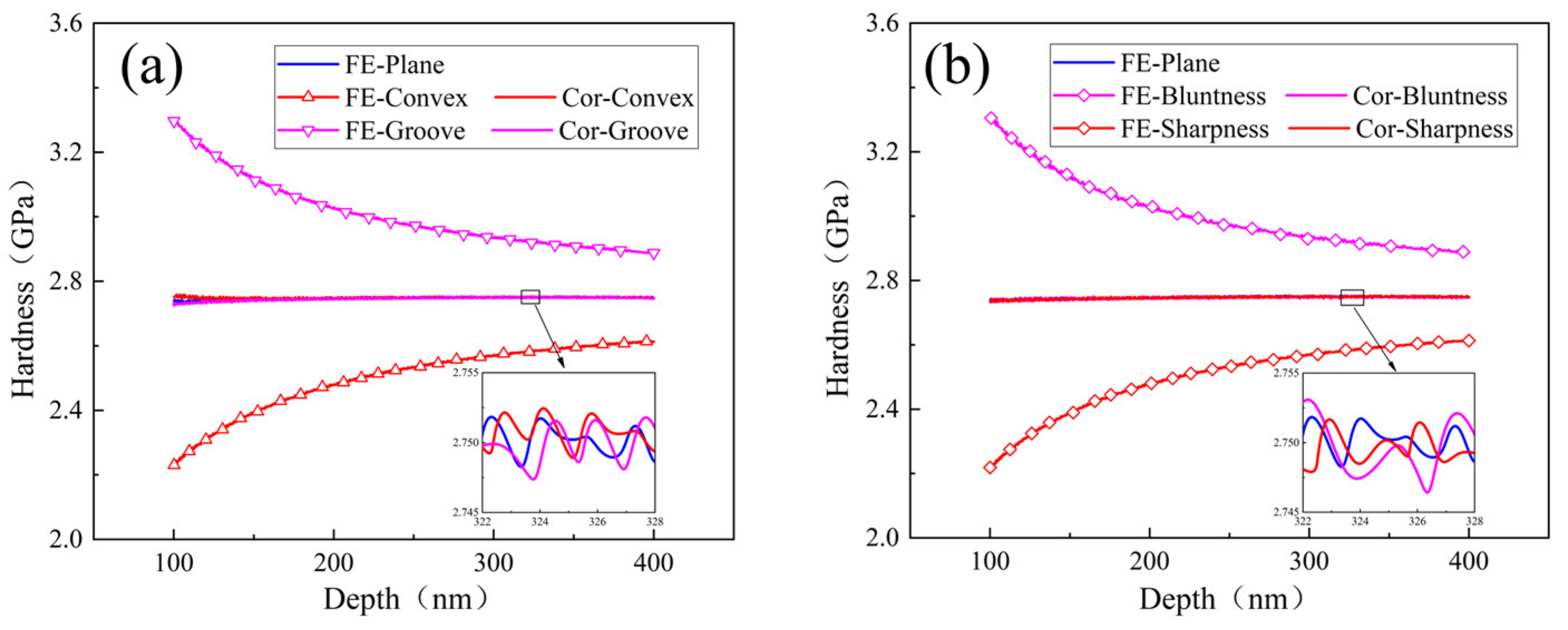
3.2. Comparison of Both Effects
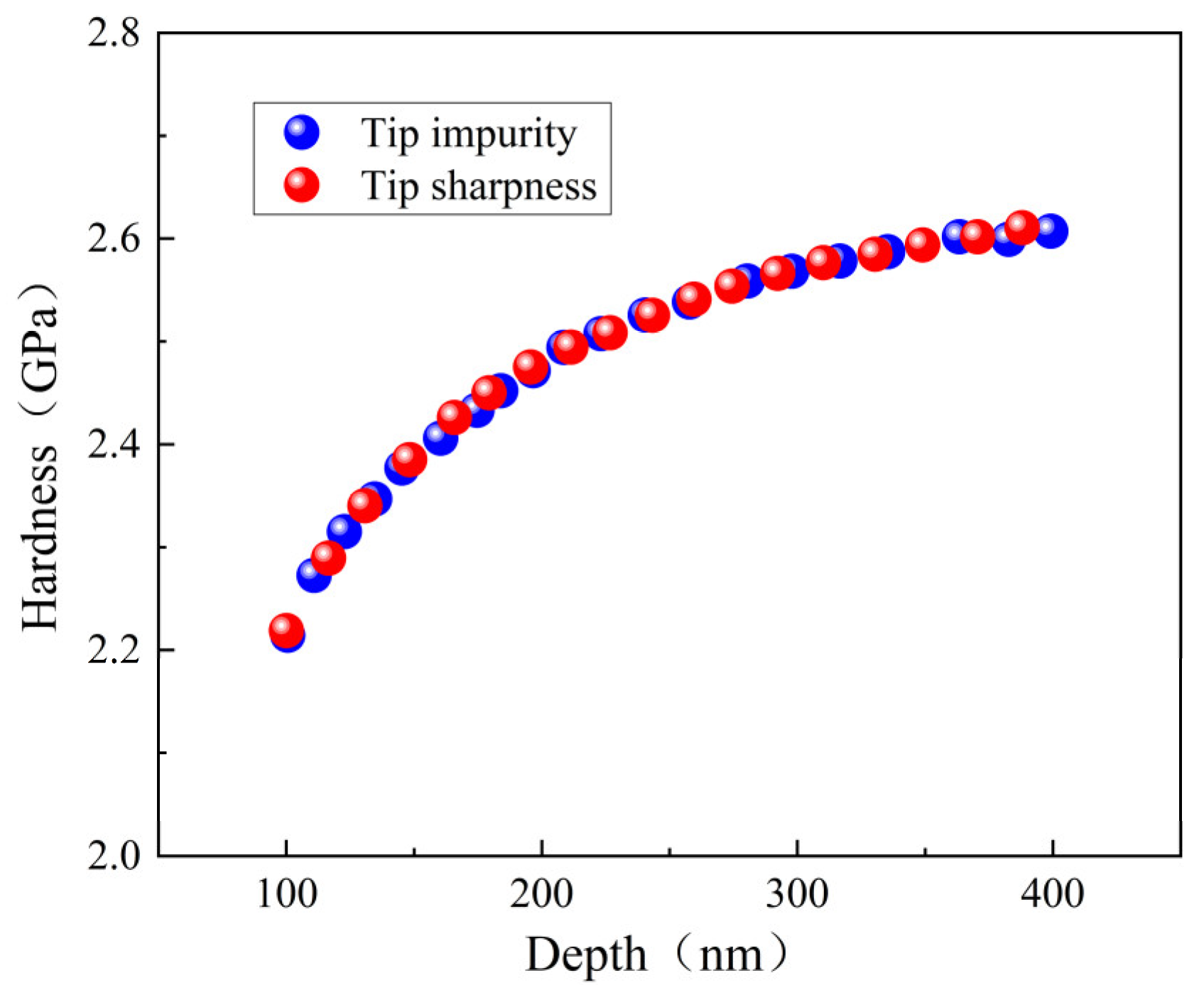
3.3. Experimental Comparison
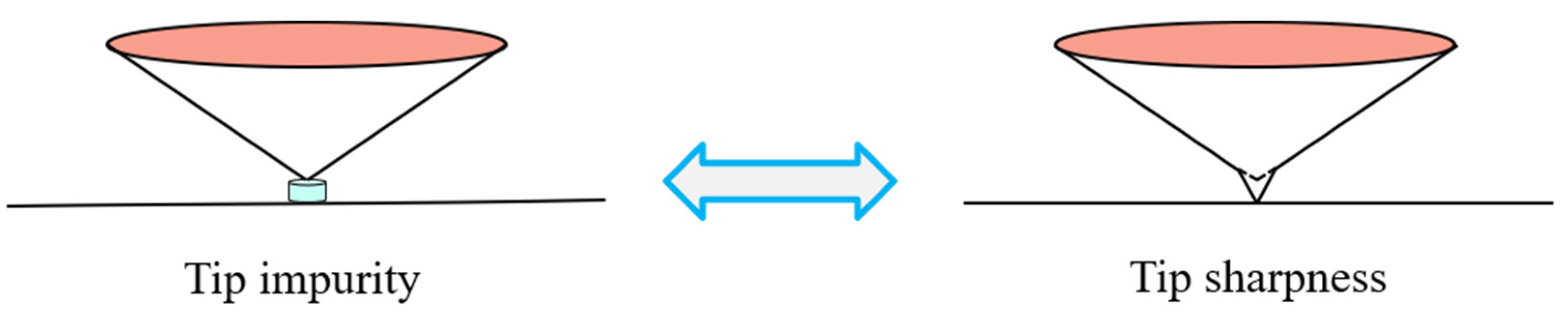
3.4. Elimination of ISE Based on External Factors
4. Conclusions
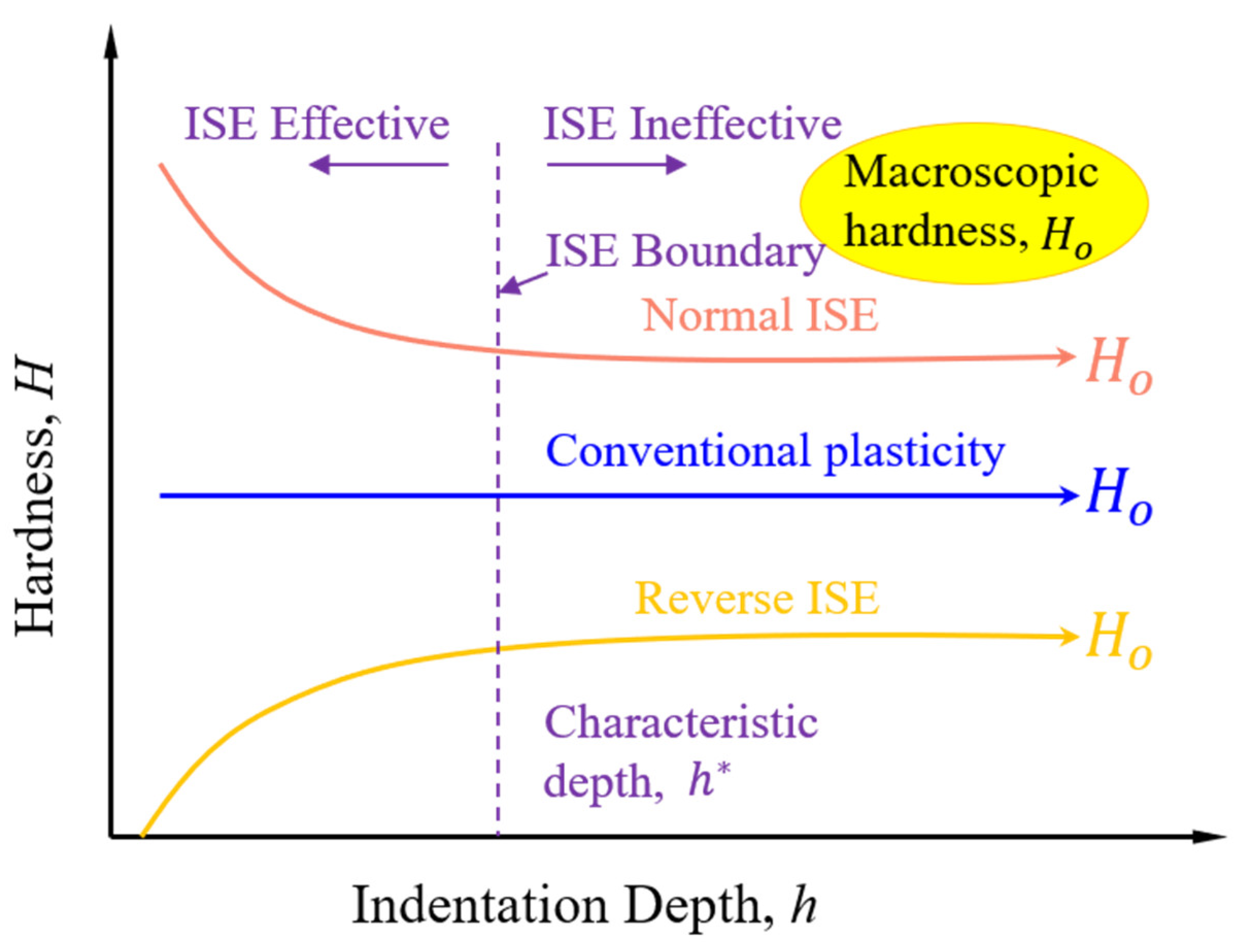
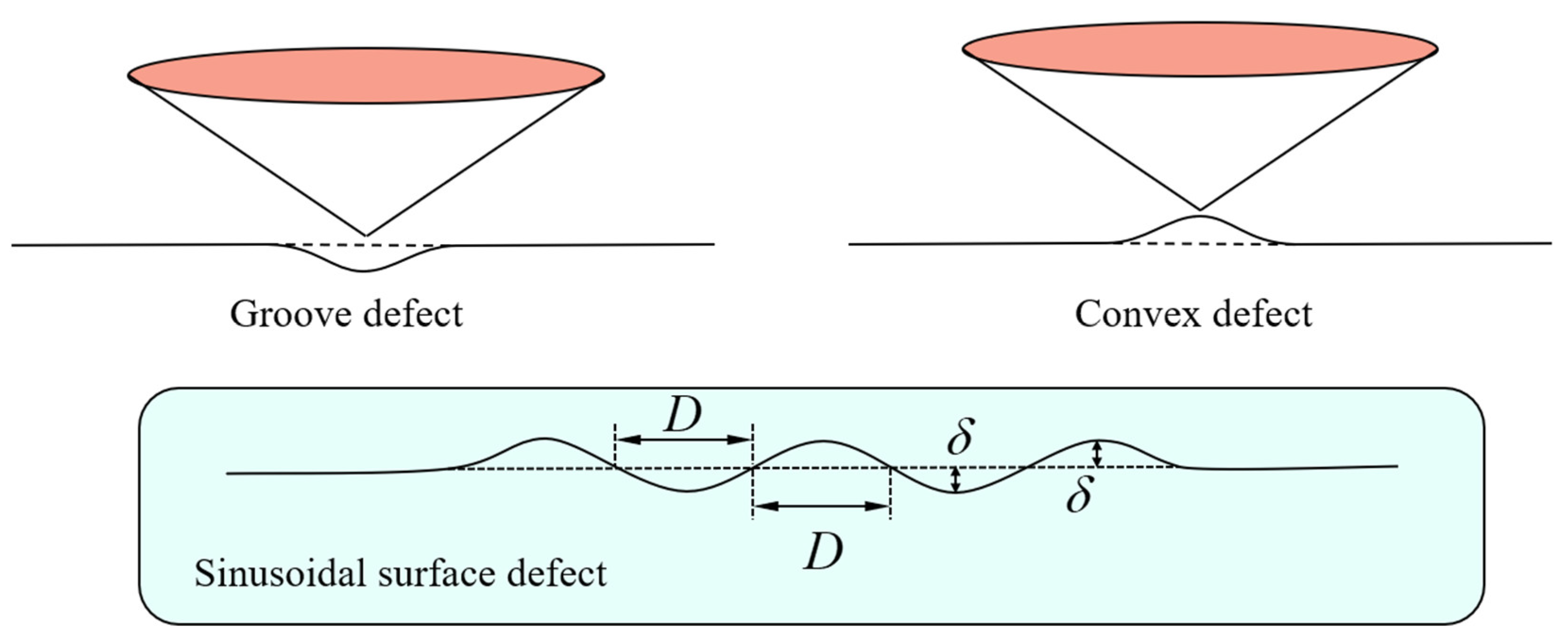
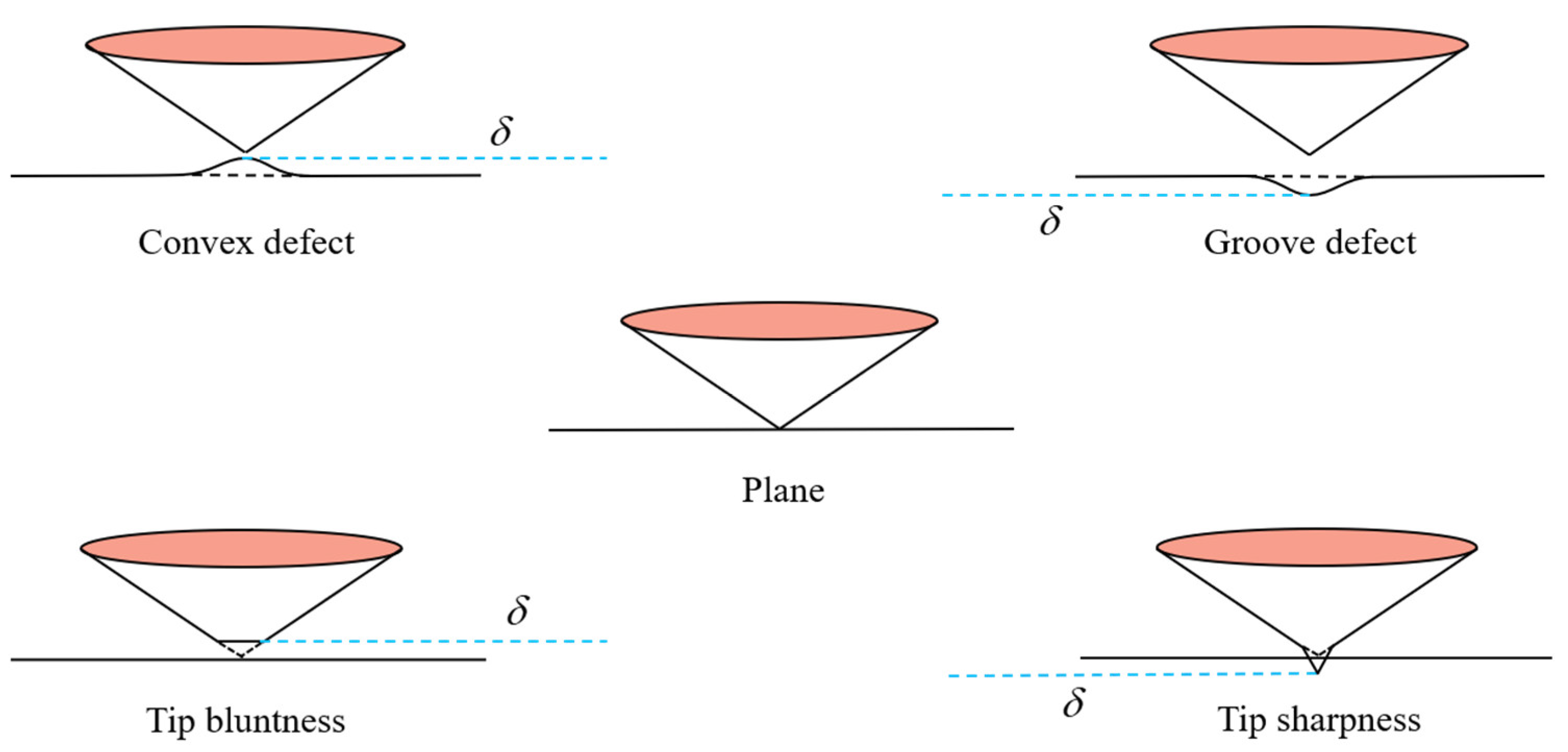
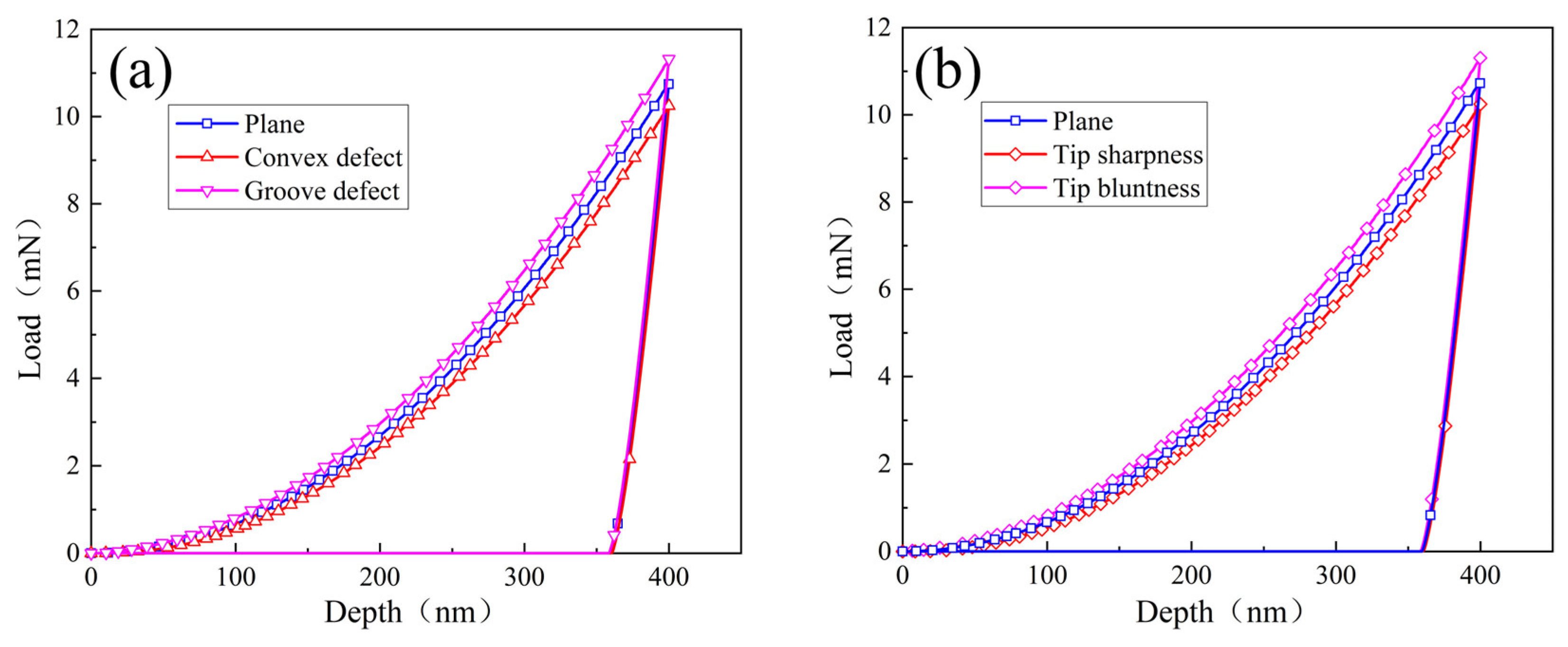
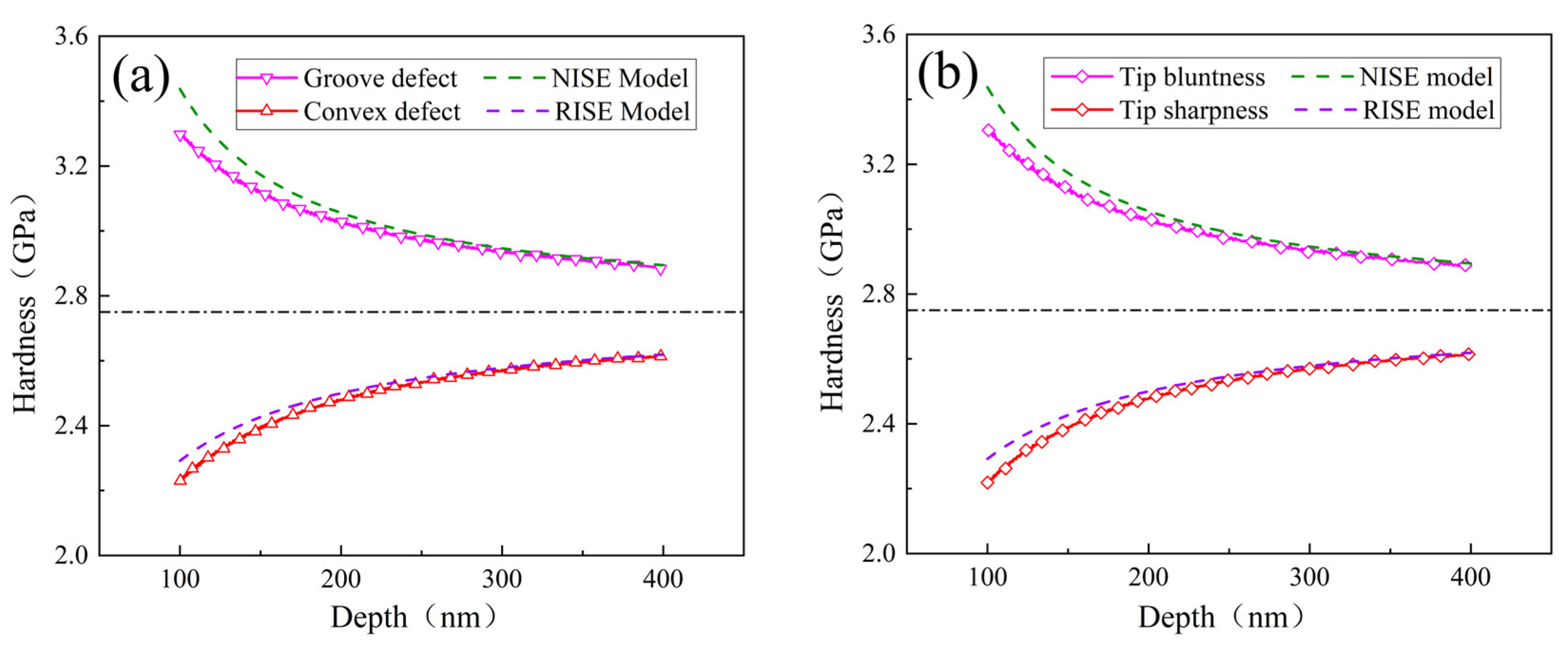
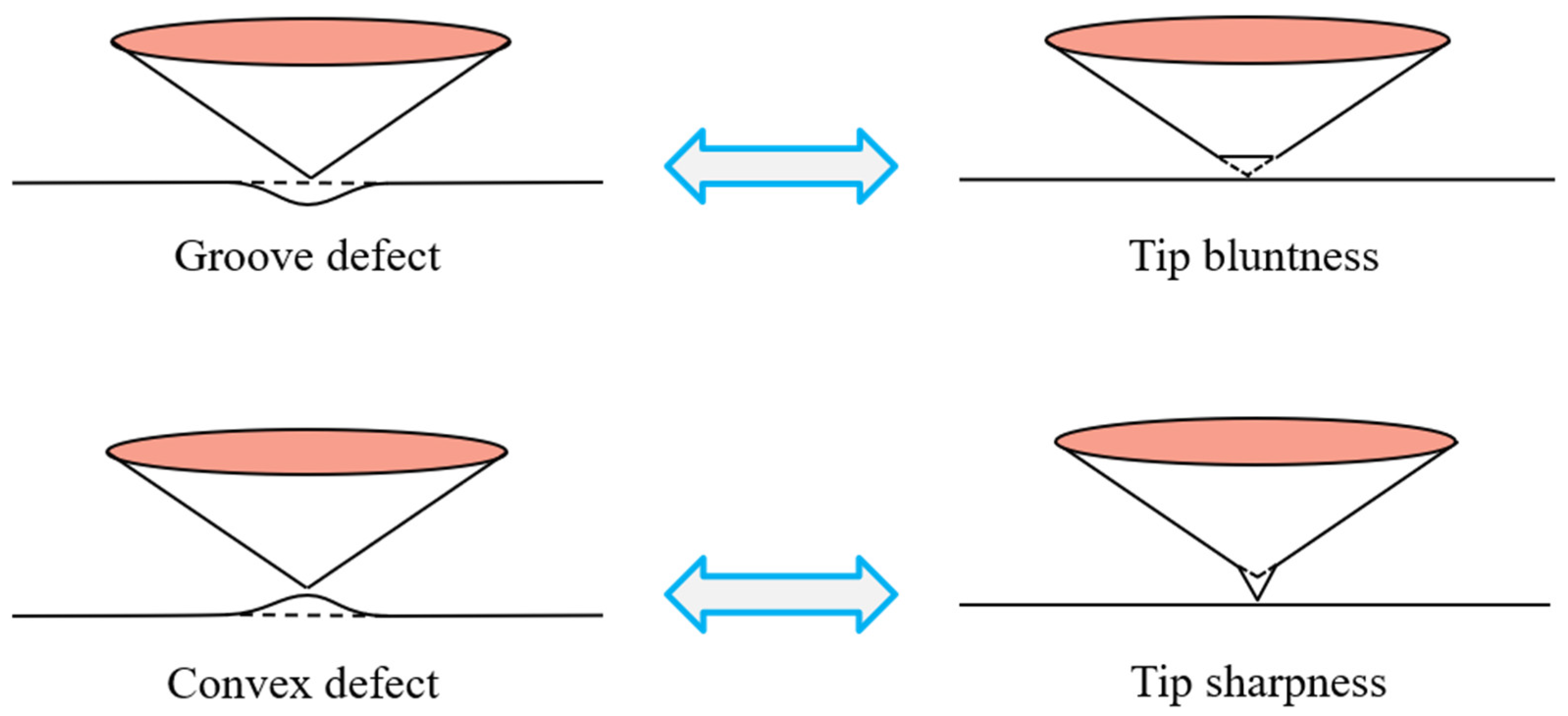
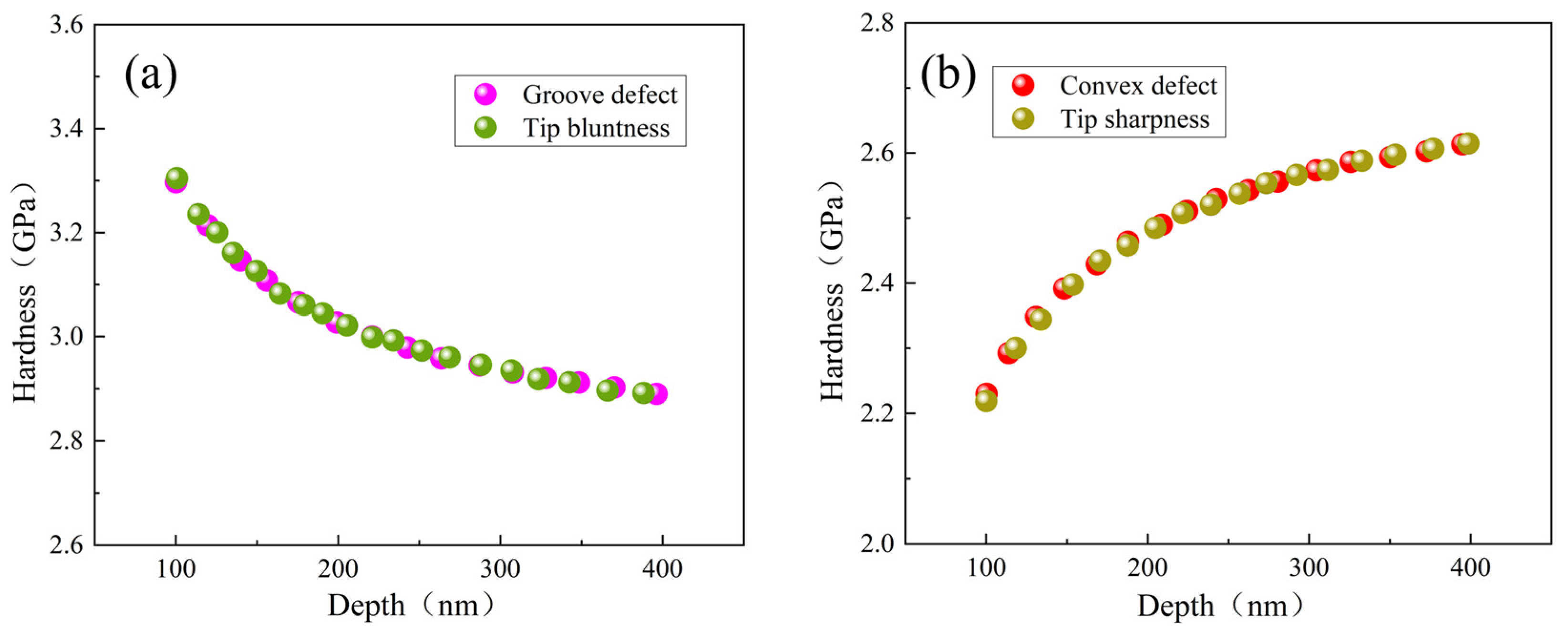
- Surface defects and indenter tip irregularity can lead to the emergence of the ISE. To be specific, both groove defect and tip bluntness can result in a normal ISE that is manifested as an increase in hardness with decreasing depth. Both convex defect and tip sharpness can result in a reverse ISE that is manifested as a decrease in hardness with decreasing depth.
- The ISE based on surface defect was compared with that based on tip irregularity. The groove defect can be equivalently expressed as tip bluntness and the convex defect can be equivalently expressed as tip sharpness.
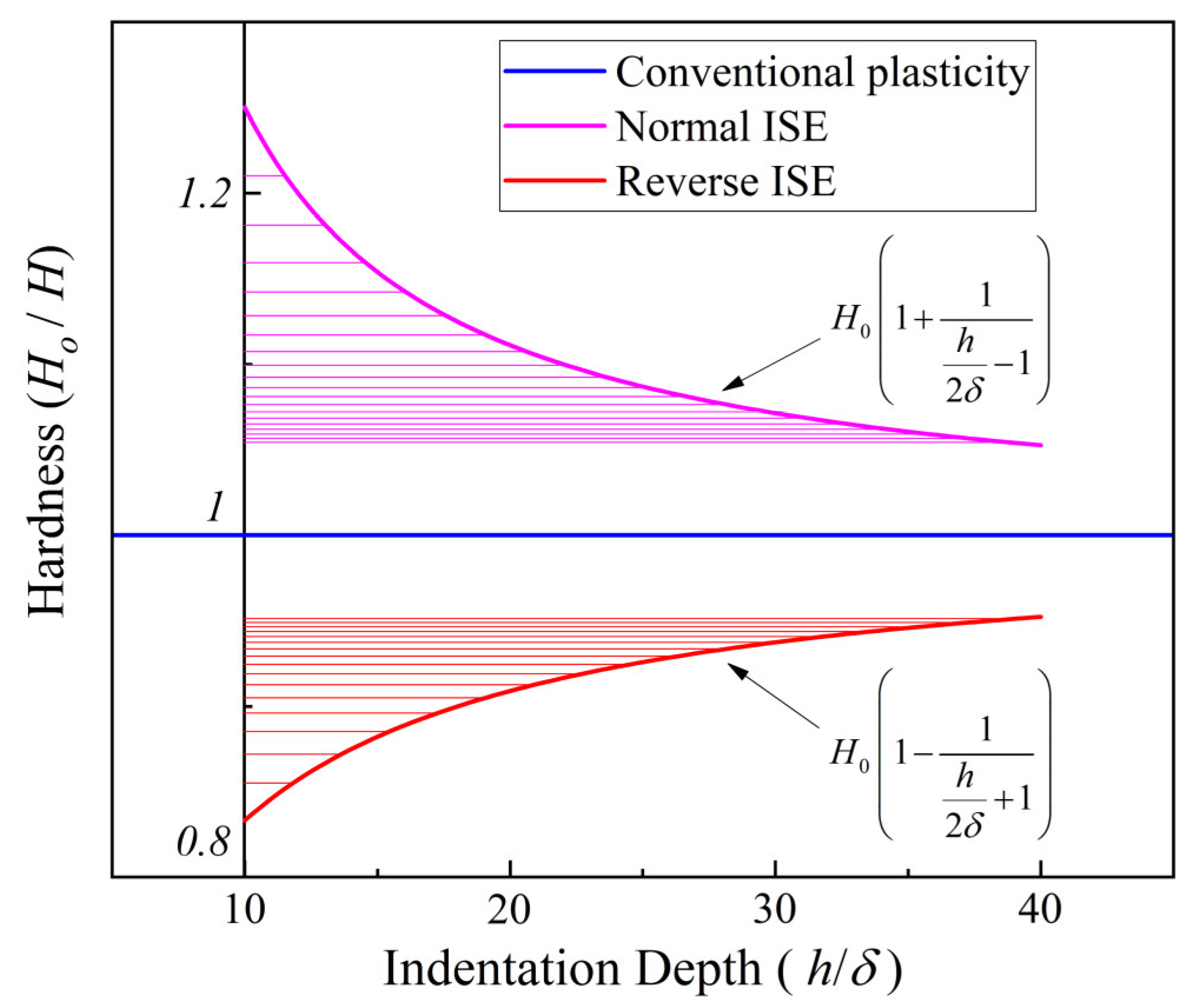
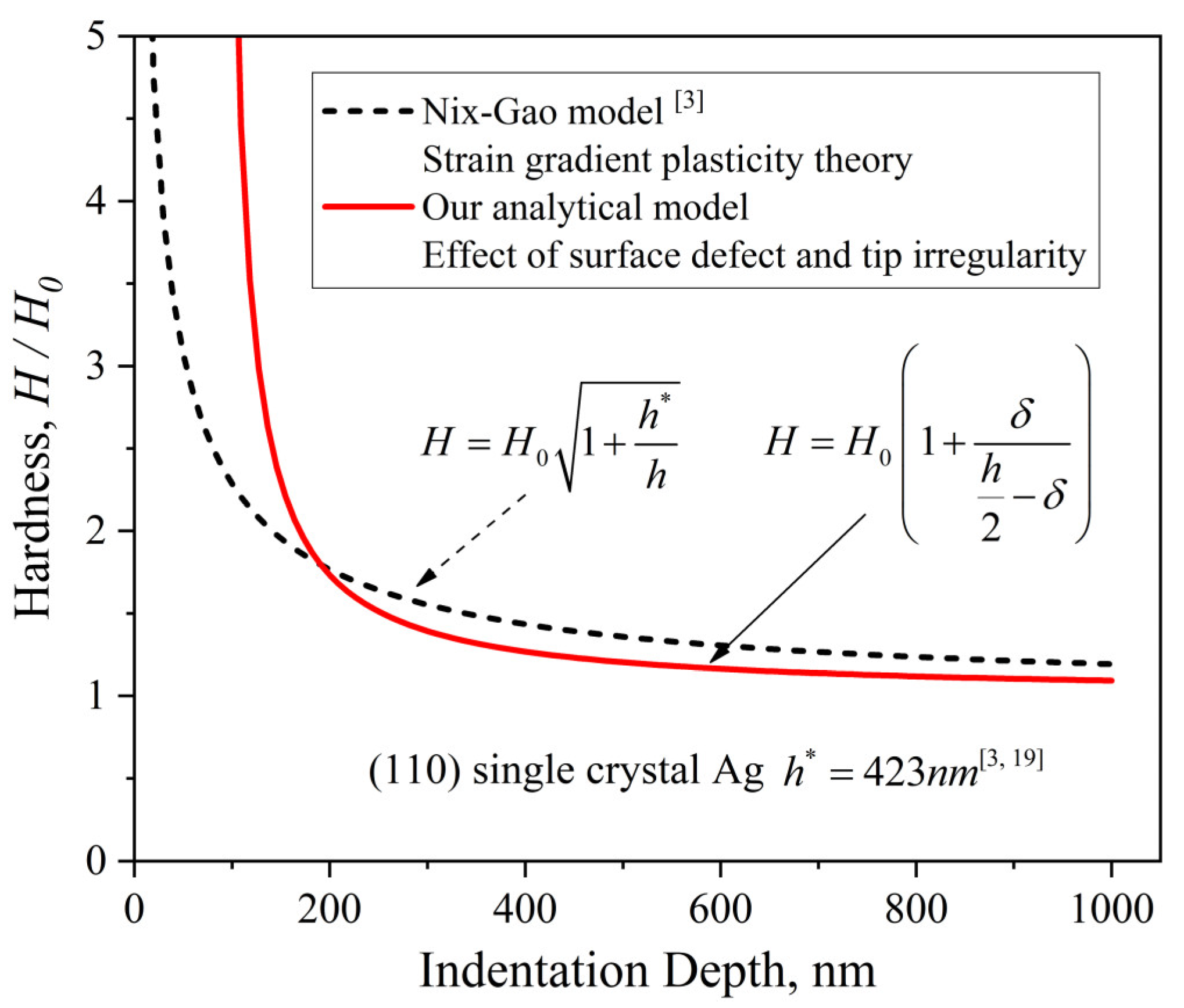
- The developed analytical model revealed the hardness–depth-dependent relationships of both the normal ISE and the reverse ISE. To be specific, the normal ISE is expressed as and the reverse ISE is expressed as .
- The effect of both external factors on the ISE is uniformly equivalent to a depth deviation δ. The ISE based on δ is eliminated and the deviation of measured hardness is corrected. The core idea of this method is based on the calibration of depth deviation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.D.; Gao, H. Indentation size effects in crystalline materials: A law for strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, M.R.; Hutchinson, J.W. The mechanics of size-dependent indentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 2049–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmustafa, A.; Eastman, J.; Rittner, M.; Weertman, J.; Stone, D. Indentation size effect: Large grained aluminum versus nanocrystalline aluminum-zirconium alloys. Scr. Mater. 2000, 43, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, K.; Franke, O.; Böhner, A.; Göken, M. Indentation size effect in Ni–Fe solid solutions. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 6825–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, K.; Backes, B.; Franke, O.; Göken, M. Indentation size effect in metallic materials: Modeling strength from pop-in to macroscopic hardness using geometrically necessary dislocations. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Higgins, W.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Pharr, G.M.; Xie, K.Y. Exploring the origins of the indentation size effect at submicron scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025657118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-I.; Yoo, B.-G.; Kim, Y.-J.; Oh, J.-H.; Choi, I.-C.; Bei, H. Indentation size effect in bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Volz, T.; Weygand, S.M.; Schwaiger, R. The indentation size effect of single-crystalline tungsten revisited. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Nix, W.D. Indentation size effect in MgO. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lu, C.; Tieu, A.K. Crystal plasticity finite element method modelling of indentation size effect. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 54, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Asempah, I.; Li, X.; Zang, S.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Ding, J.; Jin, L. Indentation size effect in aqueous electrophoretic deposition zirconia dental ceramic. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhl, F.; Huth, S.; Theisen, W. Detection of the indentation-size-effect (ISE) and surface hardening by analysis of the loading curvature C. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 84, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Gwak, E.-J.; Ahn, S.-M.; Jang, J.-I.; Han, H.N.; Kim, J.-Y. Indentation size effect in nanoporous gold. Acta Mater. 2017, 138, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathavate, V.S.; Kumar, B.P.; Singh, I.; Prasad, K.E. Analysis of indentation size effect (ISE) in nanoindentation hardness in polycrystalline PMN-PT piezoceramics with different domain configurations. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 11870–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.M.; Herbert, E.G.; Gao, Y. The indentation size effect: A critical examination of experimental observations and mechanistic interpretations. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2010, 40, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, N.; Muller, G.; Ashby, M.F.; Hutchinson, J.W. Strain gradient plasticity: Theory and experiment. Acta Metall. Mater. 1994, 42, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Clarke, D.R. Size dependent hardness of silver single crystals. J. Mater. Res. 1995, 10, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K.; Surowska, B.; Błaziak, P. Analysis of the indentation size effect in the microhardness measurement of some cobalt-based alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 77, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Gong, J.; Miao, H. On the description of indentation size effect in hardness testing for ceramics: Analysis of the nanoindentation data. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Huang, Y.; Nix, W.; Hutchinson, J. Mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity—I. Theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1999, 47, 1239–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gao, H.; Nix, W.; Hutchinson, J. Mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity—II. Analysis. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2000, 48, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qu, S.; Hwang, K.; Li, M.; Gao, H. A conventional theory of mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity. Int. J. Plast. 2004, 20, 753–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Gao, H.; Nix, W.; Xia, Z. A study of microindentation hardness tests by mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 15, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hwang, K.; Nix, W.; Pharr, G.; Feng, G. A model of size effects in nano-indentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2006, 54, 1668–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Huang, Y.; Pharr, G.; Hwang, K. The indentation size effect in the spherical indentation of iridium: A study via the conventional theory of mechanism-based strain gradient plasticity. Int. J. Plast. 2006, 22, 1265–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K. On the reverse indentation size effect and microhardness measurement of solids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2000, 63, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslić, M.; Orešković, L.; Rede, V.; Maksimović, V. Indentation Size Effect of Composite A356+ 6% FA Subjected to ECAP. Metals 2022, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, L.; Yi, X.; Gao, H.; Duan, H. Model of nanoindentation size effect incorporating the role of elastic deformation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 126, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Qiu, J.; Wang, H.; Su, B. Indentation Size Effect Model of Ti6Al4V Alloy by Combining the Macroscopic Power-Law Constitutive Relation and Strain Gradient Theory. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmustafa, A.; Stone, D. Nanoindentation and the indentation size effect: Kinetics of deformation and strain gradient plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2003, 51, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rub, R.K.A.; Voyiadjis, G.Z. Analytical and experimental determination of the material intrinsic length scale of strain gradient plasticity theory from micro-and nano-indentation experiments. Int. J. Plast. 2004, 20, 1139–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.-B.; Lee, H.-K.; Park, H.-C. Effect of grain size on the indentation hardness for polycrystalline materials by the modified strain gradient theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 2719–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Duan, H. Modelling nano-indentation of ion-irradiated FCC single crystals by strain-gradient crystal plasticity theory. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 116, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerberich, W.; Tymiak, N.; Grunlan, J.; Horstemeyer, M.; Baskes, M. Interpretations of indentation size effects. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 69, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Long, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Indentation depth dependence of the mechanical strength of Ni films. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 043512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ngan, A. Depth dependence of hardness in copper single crystals measured by nanoindentation. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manika, I.; Maniks, J. Size effects in micro-and nanoscale indentation. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Long, B. Numerical Study on the Regression Method to Eliminate the Influence of Surface Morphology on Indentation Hardness of Thin Films. Coatings 2022, 12, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.-Y.; Meng, G.-H.; Chen, L.; Li, G.-R.; Liu, M.-J.; Zhang, W.-X.; Zhao, L.-N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.-D.; Wan, C.-L. Progress in ceramic materials and structure design toward advanced thermal barrier coatings. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 985–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W. Thickness effects on the delamination energy release rate of thermal barrier coating subjected to thermo-mechanical loads. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2022, 254, 111937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.-G.; Su, J.-J.; Feng, X.-Q. Effect of surface roughness on nanoindentation test of thin films. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 4965–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kang, S.-K.; Lee, J.-J.; Jang, J.-I.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kwon, D. Influence of surface-roughness on indentation size effect. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 3555–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.G.; Starink, M.J.; Gao, N. The influence of indenter tip rounding on the indentation size effect. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3690–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swadener, J.; George, E.; Pharr, G. The correlation of the indentation size effect measured with indenters of various shapes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Diebels, S. Modelling and parameter re-identification of nanoindentation of soft polymers taking into account effects of surface roughness. Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 64, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Proudhon, H. Finite element analysis of frictionless contact between a sinusoidal asperity and a rigid plane: Elastic and initially plastic deformations. Mech. Mater. 2014, 77, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudharshan Phani, P.; Oliver, W.; Pharr, G. Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by load and depth sensing indentation: Improvements to the technique based on continuous stiffness measurement. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2137–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Dao, M.; Kumar, P.; Ramamurty, U.; Karniadakis, G.E.; Suresh, S. Extraction of mechanical properties of materials through deep learning from instrumented indentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7052–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, I.N. The relation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric Boussinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1965, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Slaughter, W.S.; Li, M.; Mao, S.X. Material-length-scale-controlled nanoindentation size effects due to strain-gradient plasticity. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4461–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Sangal, S.; Basu, S. Finite element studies on indentation size effect using a higher order strain gradient theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M. The role of friction to the indentation size effect in amorphous and crystallized Pd-based alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 3072–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Matsuoka, S.; Nagashima, N. Determination of fatigue mesoscopic mechanical properties of an austenitic stainless steel using depth-sensing indentation (DSI) technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, N.; Cox, J. The micro-hardness of metals at very low loads. Philos. Mag. 1970, 22, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. A continuum damage model for ductile fracture of weld heat affected zone. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1991, 40, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-J. Unified CDM model and local criterion for ductile fracture—I. Unified CDM model for ductile fracture. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1992, 42, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Young’s Modulus | Poisson’s Ratio | Yield Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA2 | 108 GPa | 0.34 | 0.88 GPa |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, J. Study on Size Effect in Indentation Tests. Coatings 2022, 12, 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121962
Li X, Zhang W, Dong Z, Wang Z, Li D, Zhang J. Study on Size Effect in Indentation Tests. Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121962
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaozhen, Weixu Zhang, Zhelin Dong, Zhiguo Wang, Dingjun Li, and Jianpu Zhang. 2022. "Study on Size Effect in Indentation Tests" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121962
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, W., Dong, Z., Wang, Z., Li, D., & Zhang, J. (2022). Study on Size Effect in Indentation Tests. Coatings, 12(12), 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121962





