Hydrothermal Deposition of ZnO Layer on Fe-Based Amorphous Fibres Used for the Preparation of Cold Sintered Fibre-Based Soft Magnetic Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterisation of the Amorphous Fibres
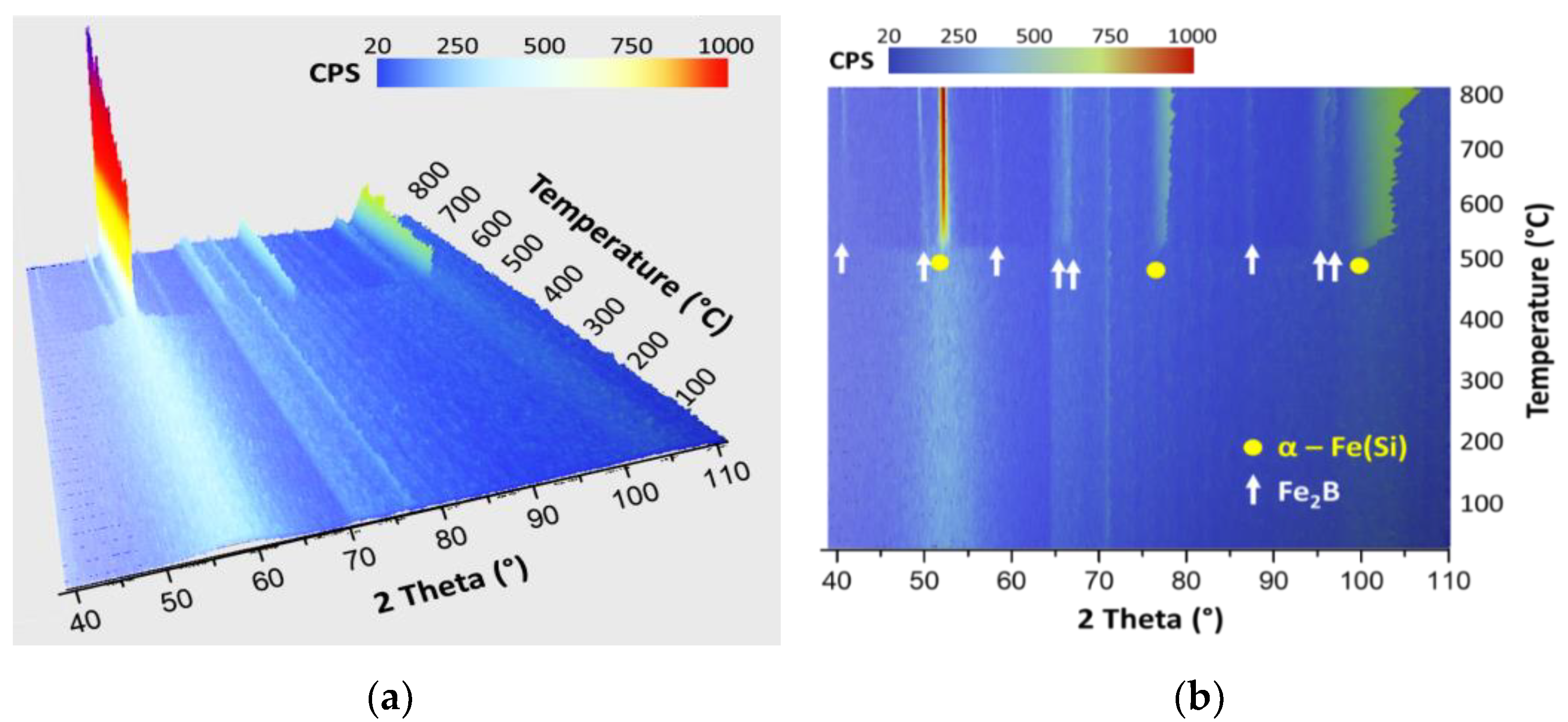
- The amorphous structure of the FeSiB fibres is stable up to the temperature of 500 °C. This is visible in the in-situ HT-XRD graph as a broad peak, from approximately 45° to 60° in 2 theta, which also has low intensity.
- The crystallisation of the amorphous fibres begins at 510 °C. As a result of fibres’ crystallisation, two new phases are formed almost simultaneously. The newly formed phases are (i) α-Fe(Si), a solid solution with a cubic crystal structure belonging to the space group Im-3m, space group number 229; and (ii) Fe2B, which is an iron boride compound with a tetragonal crystal structure belonging to the space group I4/mcm, space group number 140. The three principal peaks (the most intense) of α-Fe(Si) are situated at 52.9°, 78.1° and 100.7° and correspond, according to the JCPDS file no. 03-065-6323, to the following families of crystallographic planes: (110), (200) and (211). The peaks attributable to the Fe2B phase are situated at 41.3°, 50.3°, 53°, 58.9°, 66.8°, 67.9°, 88.8°, 96.6° and 98.2°. These correspond, according to the JCPDS file no. 00-036-1332, to the following families of crystallographic planes: (200), (002), (211), (112), (202), (310), (312), (213) and (411). As the temperature rises, peak intensities increase (Figure 3a), indicating the growth of the crystallinity of the phases. As a concluding remark, we can determine that the crystallisation of the fibres takes place at around 510 °C and the type of crystallisation is quasi-eutectic, consisting of the almost simultaneous formation (at a difference of only 10 °C) of the α-Fe(Si) and Fe2B phases. The first phase resulting from the crystallisation of the amorphous phase is α-Fe(Si). Also, the crystallisation of Fe2B at almost the same temperature as α-Fe(Si) excludes the application of any annealing to the fibres at temperatures above 510 °C, since the presence of Fe borides in any soft magnetic material induces a dramatic decrease in its soft magnetic properties (especially an increase in the coercive field) [29].
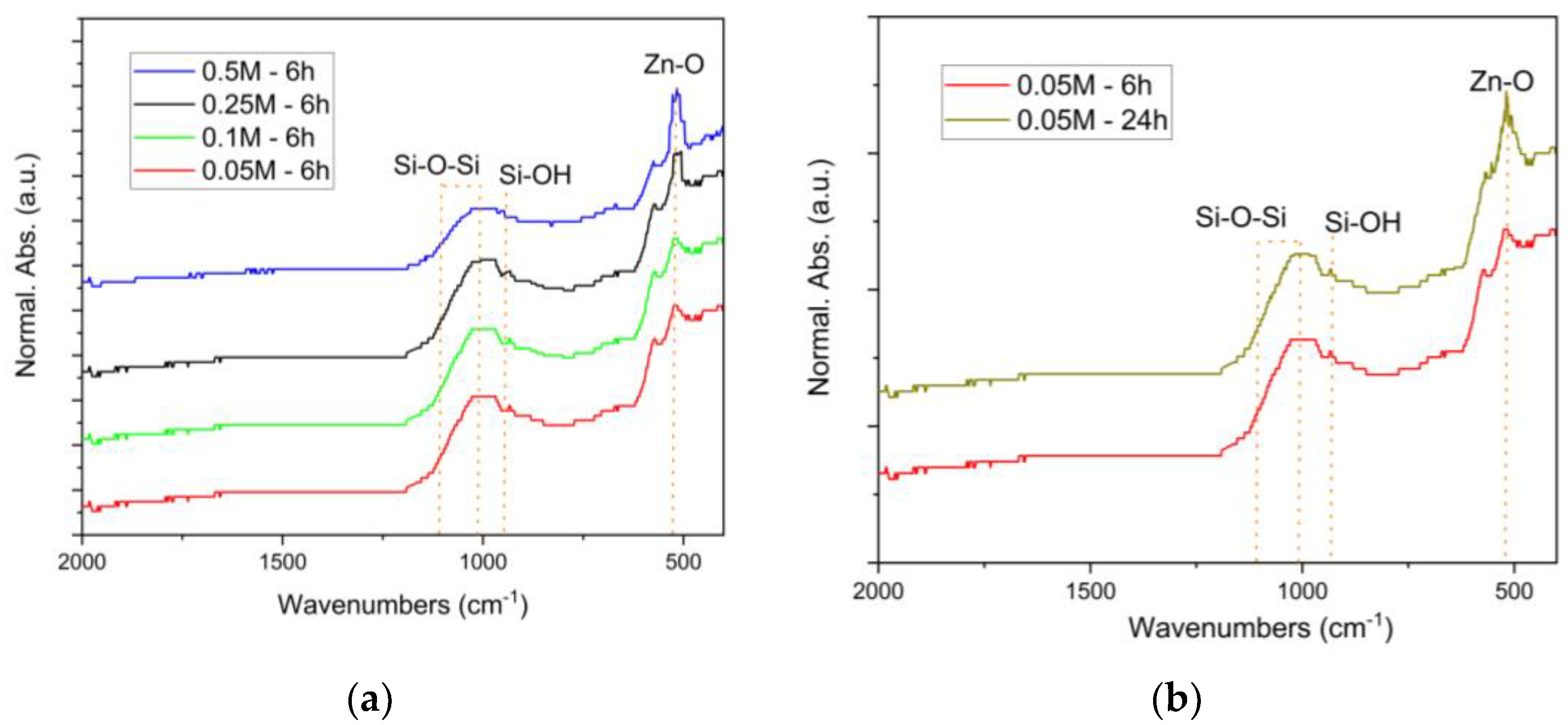
3.2. Characterisation of the ZnO-Coated Amorphous Fibres
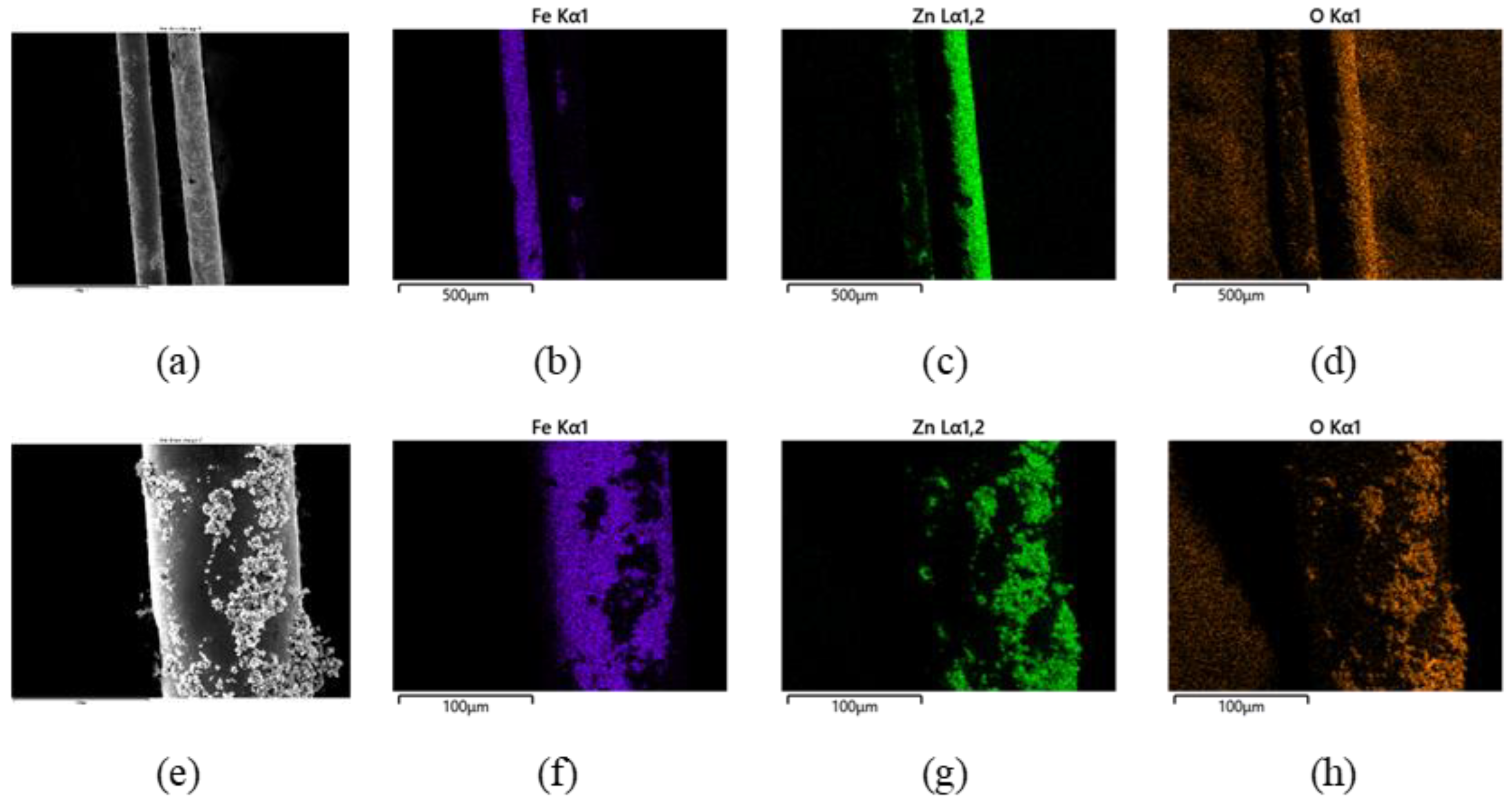
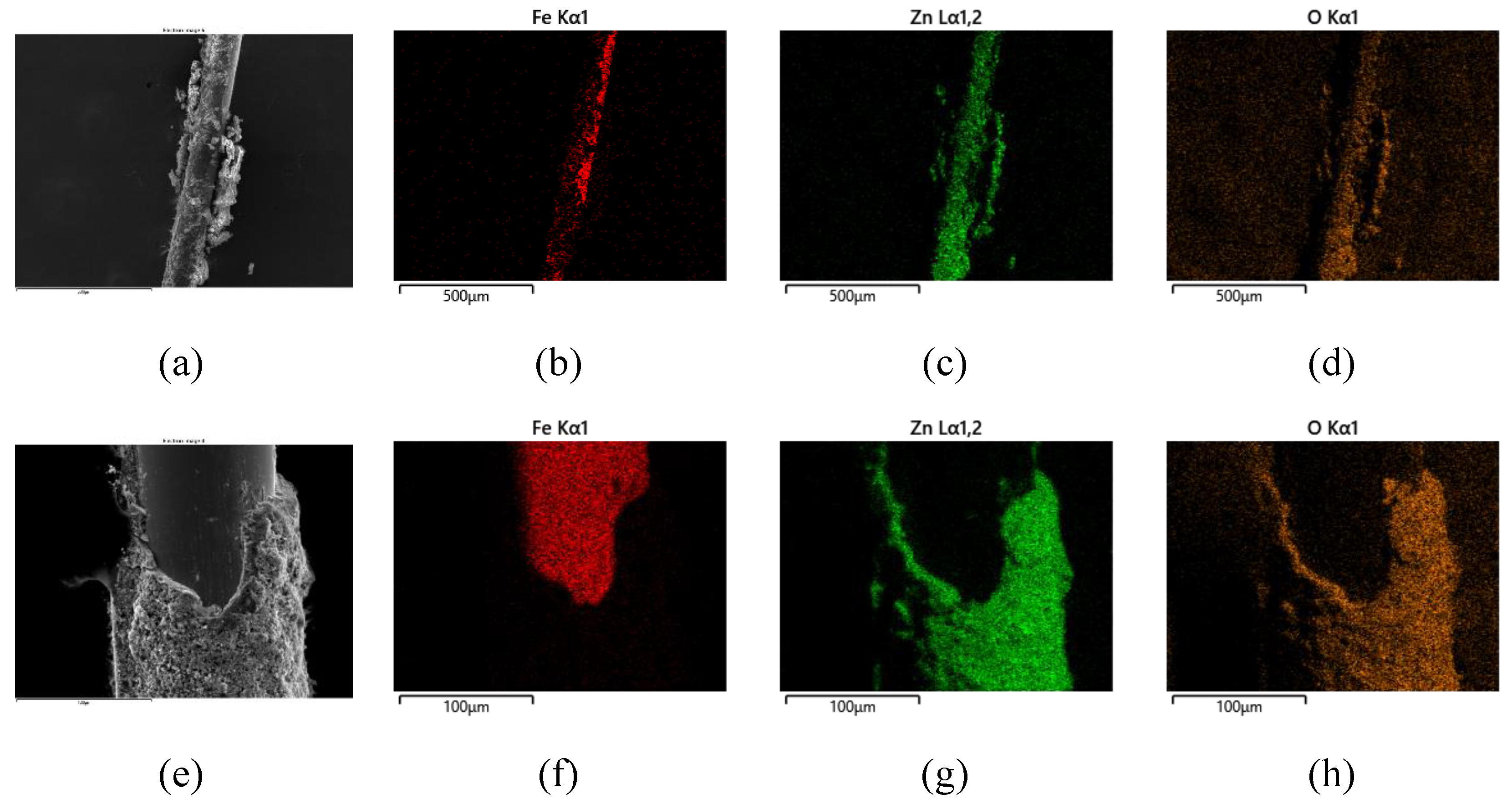
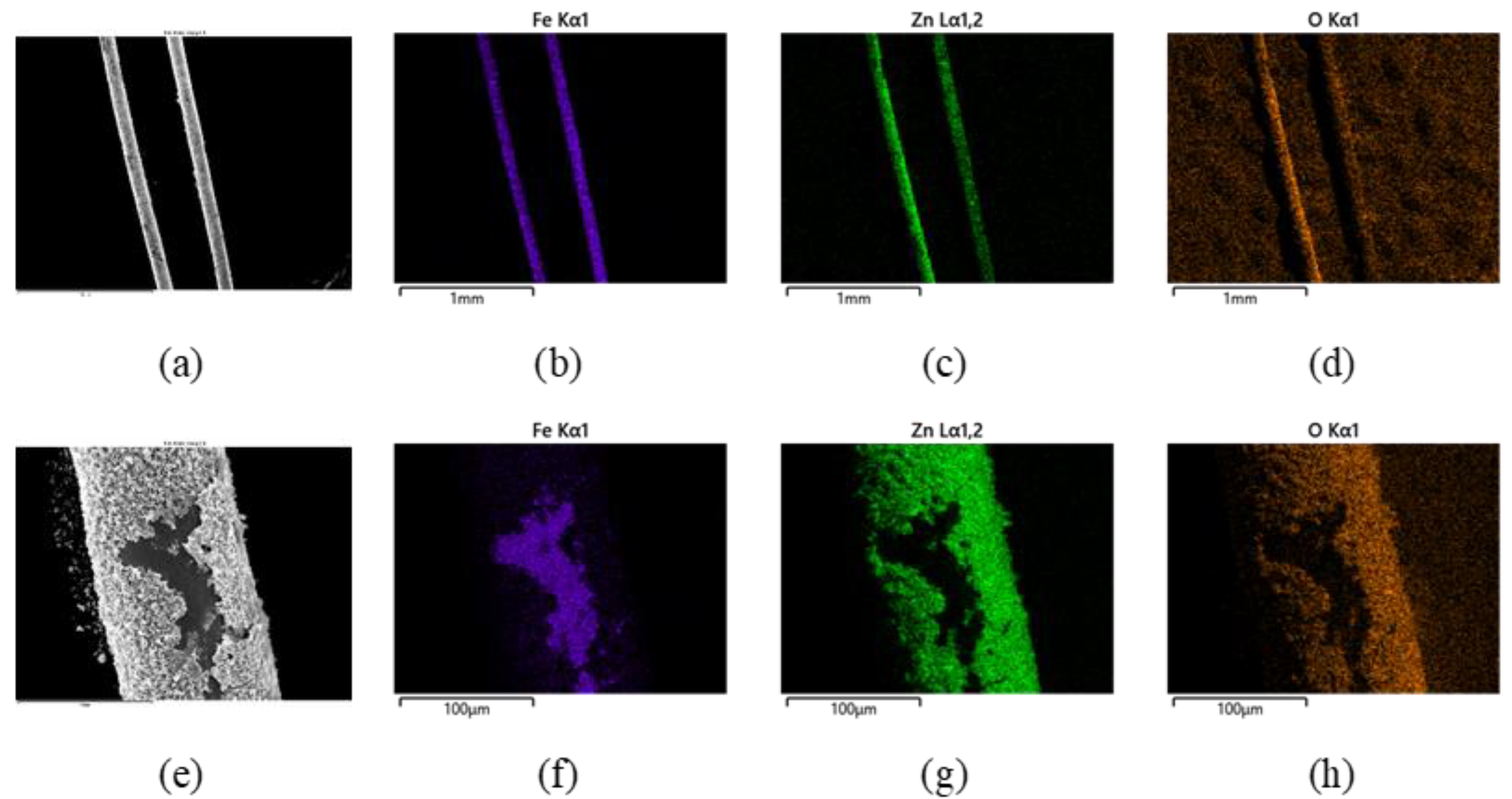
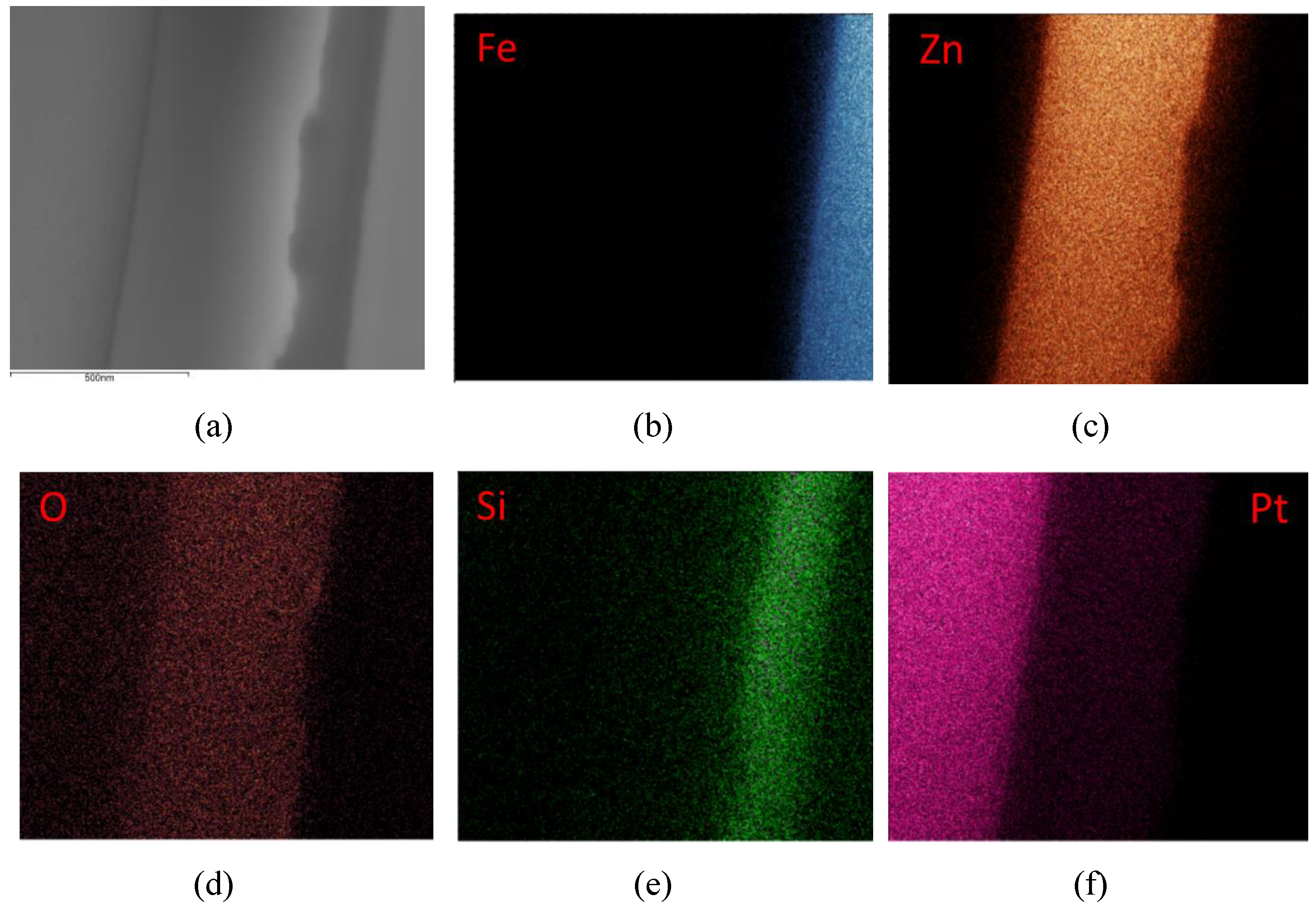
3.3. Electron Microscopy Investigations (SEM, TEM, EDX) of the Deposited Layer
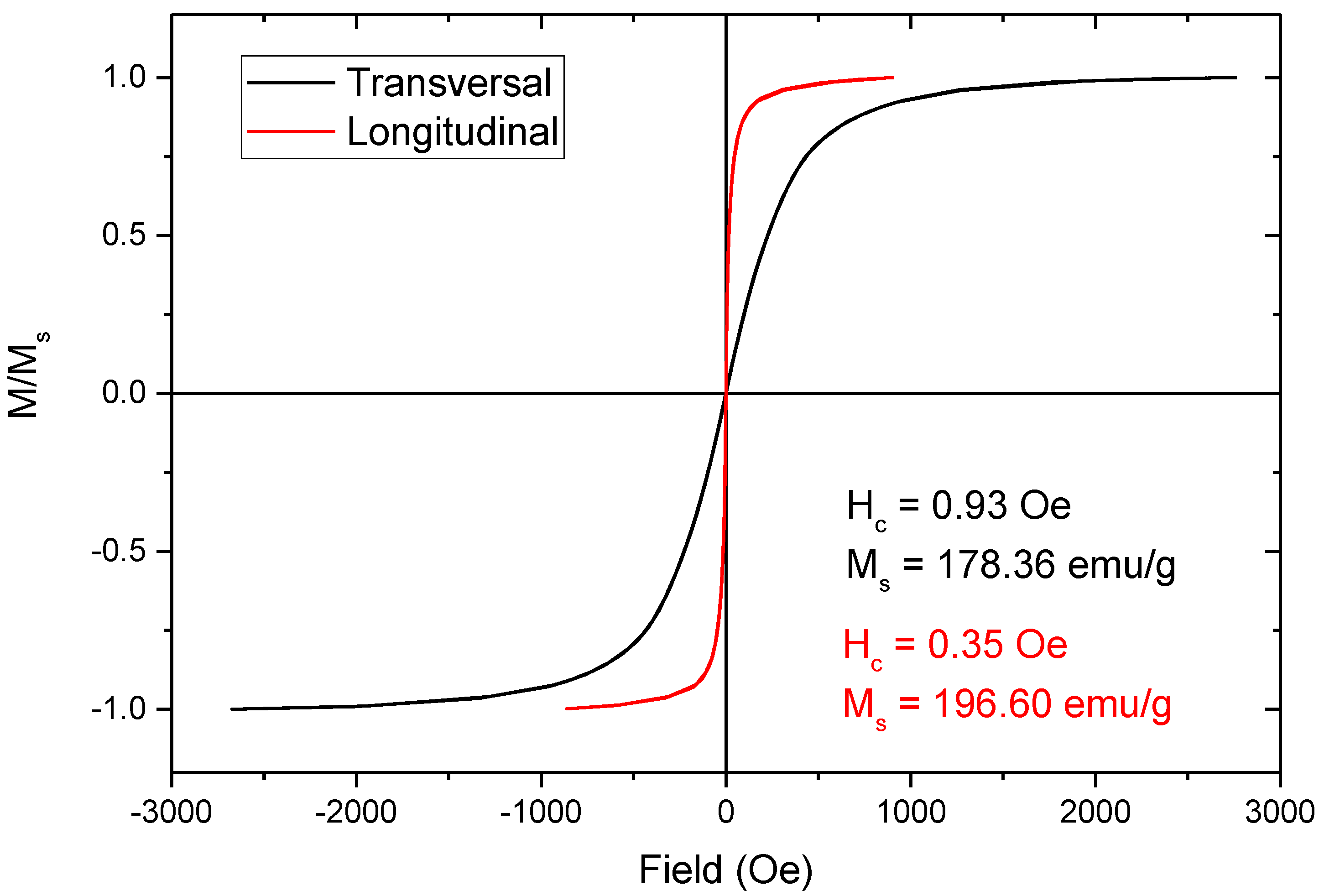
3.4. Magnetic Properties of the Coated Fibres
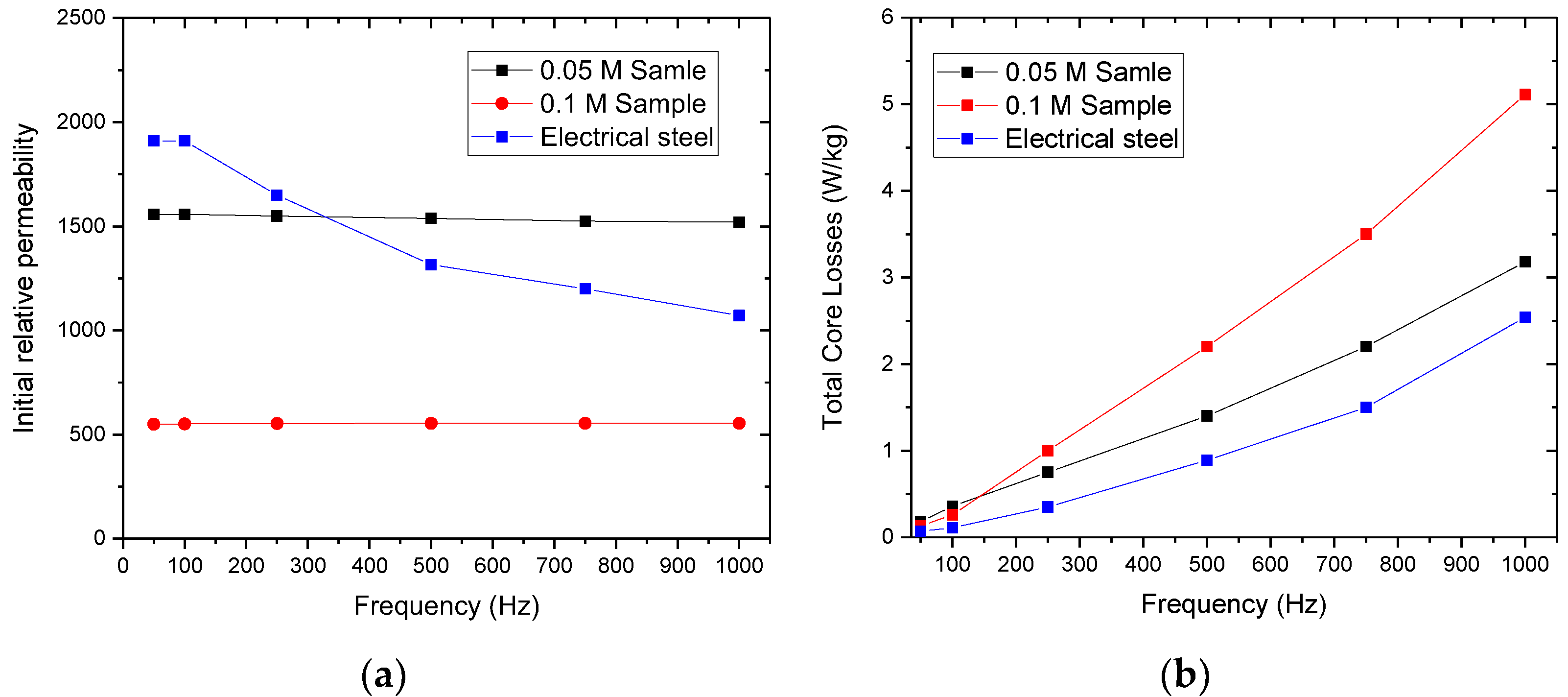
3.5. DC and AC Characteristics of the Cold Sintered Fibre-Based Soft Magnetic Composites
4. Conclusions
- (i)
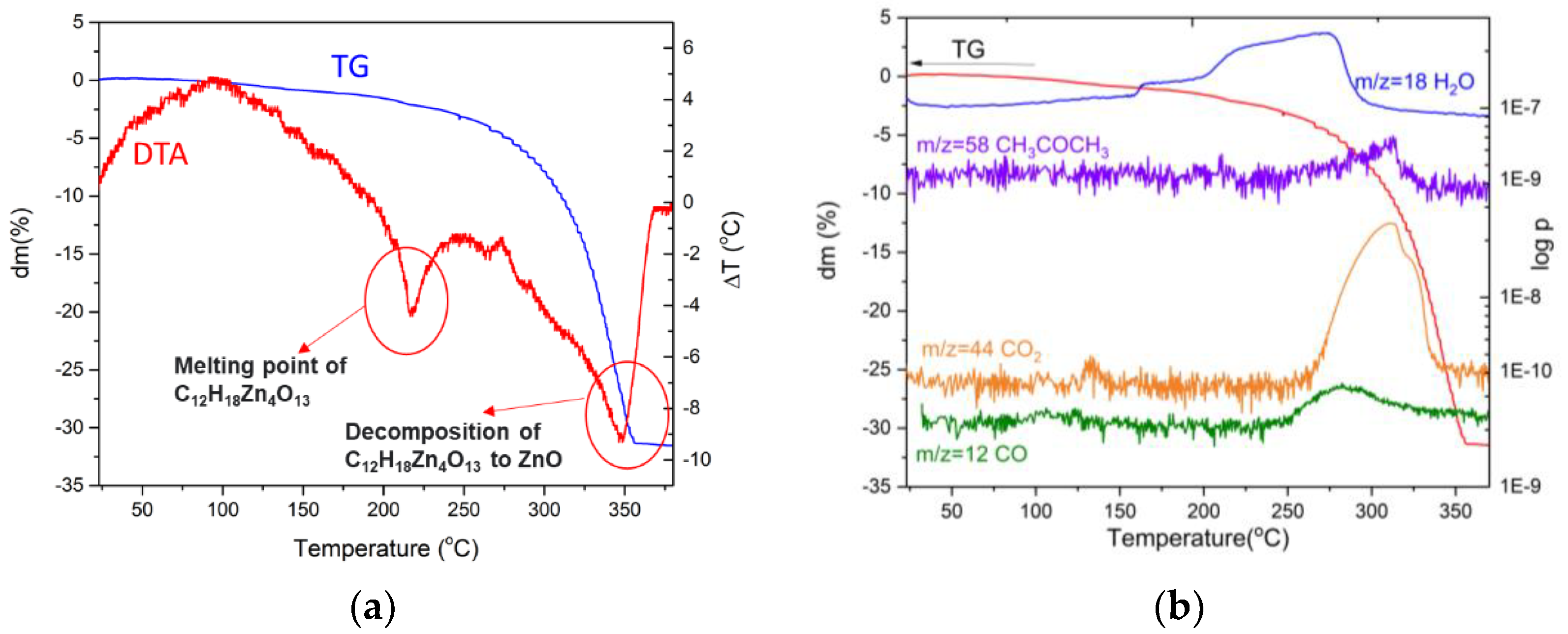
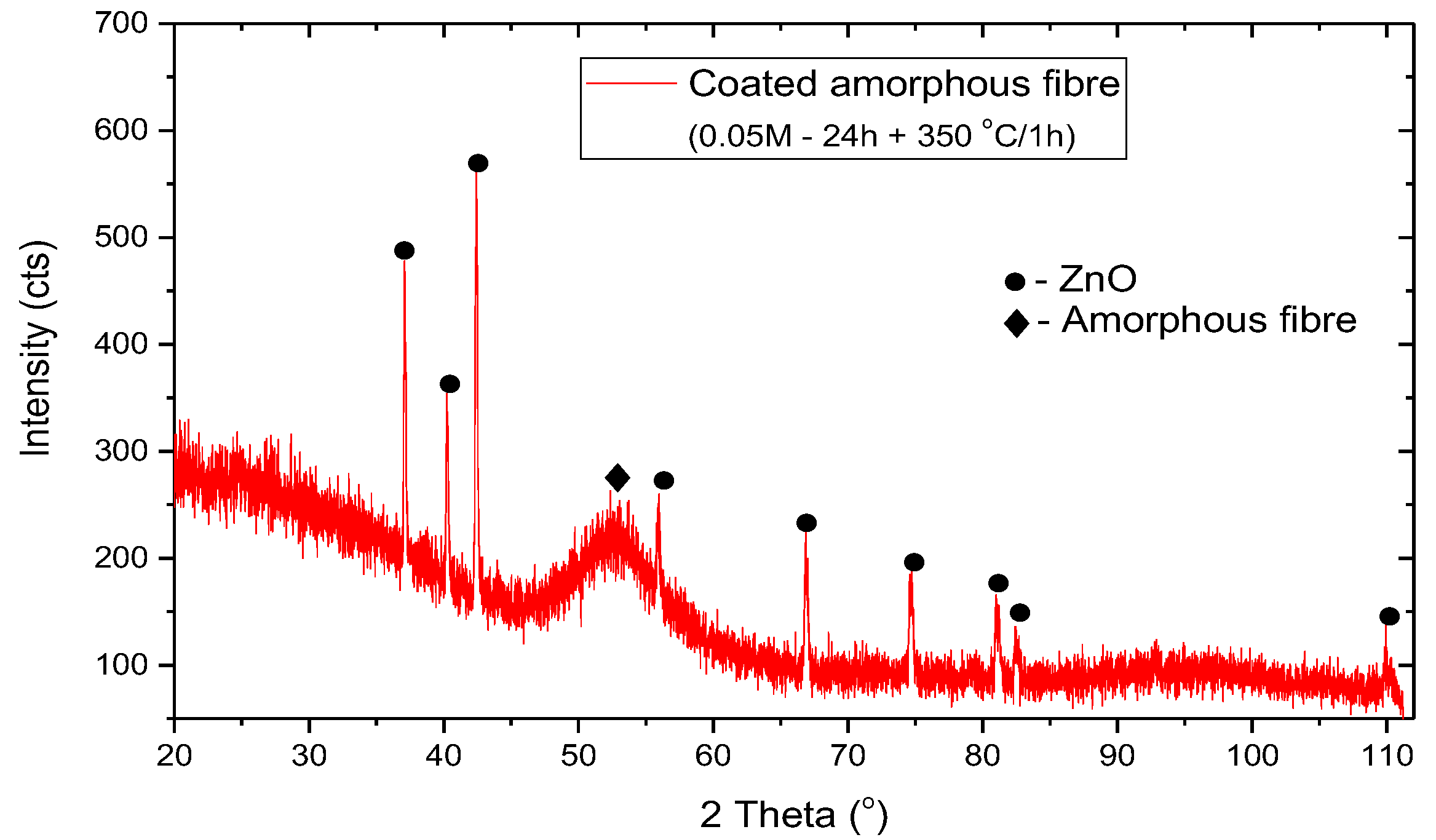
- The decomposition of the Zn acetate starts at about 260 °C and ends at about 350 °C as proved by DTA-TG-MS analysis. As the result of the thermally decomposed precursor solution, the fibres are covered with a layer of ZnO as proved by XRD investigation.
- (ii)
- Hydrothermal deposition for 6 h using a precursor of 0.5 M and 0.25 M leads to a thick and brittle ZnO layer with low adherence to the fibres. The most promising coatings were obtained when the concentration of the precursor solution was reduced to 0.1 M (deposition duration of 6 h) and 0.05 M (deposition duration of 24 h).
- (iii)
- According to the TEM image and the EDX analysis, the thickness of the SiO2 layer is 150–200 nm and the ZnO layer has a thickness of 450–500 nm for the 0.05 M sample.
- (iv)
- The saturation magnetisation of the coated fibres decreases as the concentration of the precursor and the deposition duration increase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Périgo, E.A.; Weidenfeller, B.; Kollár, P.; Füzer, J. Past, present, and future of soft magnetic composites. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 031301-37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, K.J.; Taheri, M. Soft magnetic composites: Recent advancements in the technology. Met. Powder Rep. 2017, 72, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveyra, J.M.; Ferrara, E.; Huber, D.L.; Monson, T.C. Soft magnetic materials for a sustainable and electrified world. Science 2018, 362, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, H.; Janghorban, K. Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 189, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błyskun, P.; Kowalczyk, M.; Łukaszewicz, G.; Cieślak, G.; Ferenc, J.; Zackiewicz, P.; Kolano-Burian, A. Influence of particles size fraction on magnetic properties of soft magnetic composites prepared from a soft magnetic nanocrystalline powder with no synthetic oxide layer. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 272, 115357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghtin, M.; Taghvaei, A.H.; Hashemi, B.; Janghorban, K. Effect of heat treatment on magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites with Al2O3 insulation coating produced by sol–gel method. J. Alloy Compd. 2013, 58, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, A.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, C.; Gao, X. Magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites with SiO2 coating obtained by reverse microemulsion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Che, S. In-situ formation of Fe3O4 and ZrO2 coated Fe-based soft magnetic composites by hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaei, A.H.; Ebrahimi, A.; Ghaffari, M.; Janghorban, K. Magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites with MgO coating obtained by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaei, A.H.; Shokrollahi, H.; Janghorban, K. Properties of iron-based soft magnetic composite with iron phosphate–silane insulation coating. J. Alloy Compd. 2009, 481, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Che, S.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Ying, Y. The preparation and magnetic performance of the iron-based soft magnetic composites with the Fe@Fe3O4 powder of in situ surface oxidation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 454, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, K.J.; Taheri, M.L. NiZnCu-ferrite coated iron powder for soft magnetic composite applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 463, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zheng, H.; Lei, J.; Qiao, L.; Ying, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, W.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Structure and magnetic properties of Fe-based soft magnetic composites with an Li-Al-O insulation layer obtained by hydrothermal synthesis. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 816, 152617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Feng, S.; Jiang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, R.; An, Y.; Wang, J. Intergranular insulating reduced iron powder-carbonyl iron powder/SiO2-Al2O3 soft magnetic composites with high saturation magnetic flux density and low core loss. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, J.; Zou, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhou, B.; Yu, R. High-strength and corrosion-resistant Fe/Al2SiO5 soft magnetic composites fabricated by a nanoscale solid-reaction coating method. J. Alloy Compd. 2022, 912, 165174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamţu, B.V.; Belea, A.; Popa, F.; Ware, E.; Marinca, T.F.; Vintiloiu, I.; Badea, C.; Pszola, M.; Nasui, M. Properties of soft magnetic composites based on Fe fibres coated with SiO2 by hydrothermal method. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 826, 154222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.A.; Guo, J.; Baker, A.; Lanagan, M.; Guo, H. Cold Sintering Ceramics and Composites. U.S. Patent 2017/0088471 A1, 30 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grasso, S.; Biesuz, M.; Zoli, L.; Taveri, G.; Duff, A.I.; Ke, D.; Jiang, A.; Reece, M.J. A review of cold sintering processes. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2020, 119, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galotta, A.; Sglavo, V.M. The cold sintering process: A review on processing features, densification mechanisms and perspectives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Floyd, R.; Lowum, S.; Maria, J.-P.; de Beauvoir, T.H.; Seo, J.-H.; Randall, C.A. Cold Sintering: Progress, Challenges, and Future Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2019, 49, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Floyd, R.; Lowum, S.; Cabral, M.; Dickey, E.; Maria, J.-P. Mechanism studies of hydrothermal cold sintering of zinc oxide at near room temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 4459–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, S.; Guo, H.; Guo, J.; Baker, A.L.; Wang, K.; Shiratsuyu, K.; Randall, C.A. Cold sintering and co-firing of a multilayer device with thermoelectric materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 3488–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamţu, B.V.; Opriş, A.; Pszola, P.; Popa, F.; Marinca, T.F.; Vlad, N.; Chicinaş, I. Preparation and characterisation of soft magnetic composites based on Fe fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamţu, B.V.; Irimie, A.; Popa, F.; Gabor, M.S.; Marinca, T.F.; Chicinaş, I. Soft magnetic composites based on oriented short Fe fibres coated with polymer. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 840, 155731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamţu, B.V.; Pszola, M.; Vermeşan, H.; Stoian, G.; Grigoraş, M.; Opriş, A.; Cotojman, L.; Marinca, T.F.; Lupu, N.; Chicinaş, I. Preparation and characterisation of Fe/Fe3O4 fibres based soft magnetic composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamţu, B.V.; Pszola, M.; Opriş, A.; Popa, F.; Marinca, T.F.; Chicinaş, I. Influence of fibres diameter on the AC and DC magnetic characteristics of Fe/Fe3O4 fibres based soft magnetic composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Li, Y.-Y. Synthesis of ZnO nanowires by thermal decomposition of zinc acetate dihydrate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazumi, S. Magnetostatic Phenomena. In Physics of Ferromagnetism, 2nd ed.; Birman, J., Edwards, S.F., Friend, R., Llewellyn Smith, C.H., Rees, M., Sherrington., D., Veneziano, G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Alleg, S.; Kartout, S.; Ibrir, M.; Azzaza, S.; Fenineche, N.E.; Suñol, J.J. Magnetic, structural and thermal properties of the Finemet-type powders prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraguay, F.D.; Estrada, W.L.; Acosta, D.R.N.; Andrade, E.; Miki-Yoshida, M. Growth, structure and optical characterization of high quality ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Film. 1999, 350, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor-Tejedor, M.I.; Paredes, L.; Anderson, M.A. Evaluation of ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy as an “in Situ” Tool for Following the Hydrolysis and Condensation of Alkoxysilanes under Rich H2O Conditions. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 3410–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P. Infrared spectroscopy of sol–gel derived silica-based films: A spectra-microstructure overview. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 316, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, G.; Asif, M.H.; Zainelabdin, A.; Zaman, S.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Influence of pH, precursor concentration, growth time, and temperature on the morphology of ZnO nanostructures grown by the hydrothermal method. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 269692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Enhancement of ZnO nanorods properties using modified chemical bath deposition method: Effect of precursor concentration. Crystals 2020, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamţu, B.V.; Nasui, M.; Marinca, T.F.; Popa, F.; Chicinaş, I. Soft magnetic composites based on hybrid coated Fe-Si nanocrystalline powders. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 330, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Mechanical Behaviour. In Bulk Metallic Glasses, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 361–458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Dong, Y.; Chi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, L.; Gong, M.; Huang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X. Fe-based amorphous soft magnetic composites with SiO2 insulation coatings: A study on coatings thickness, microstructure and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13449–13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type of FSMCs | DC Magnetic Properties | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bs | Hc | µrmax | ||
| (T) | (A/m) | - | ||
| Fe fibres with polymer (1 wt% Araldite) | 1.52 | 353 | 893 | [23] |
| Fe fibres coated with SiO2 (200 nm) | 1.39 | 367 | 797 | [16] |
| Fe fibres coated with SiO2 (200 nm) + 1 wt% Araldite | 1.26 | 353 | 733 | [16] |
| Short Fe fibres + polymer (1 wt% Araldite) | 1.28 | 421 | 506 | [24] |
| Fe fibres coated with Fe3O4 (0–514 nm) | 1.49 | 366 | 886 | [25] |
| Fe fibres coated with Fe3O4 (210–920 nm) | 1.43 | 389 | 798 | [25] |
| Fe fibres coated with Fe3O4 (309 nm–1.70 µm) | 1.35 | 398 | 719 | [25] |
| Fe77.5Si7.5B15 coated with ZnO (0.05 M sample) | 0.45 | 40.9 | 2180 | This work |
| Fe77.5Si7.5B15 coated with ZnO (0.1 M sample) | 0.41 | 101 | 820 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neamţu, B.V.; Popa, F.; Ware, E.; Marinca, T.F.; Gabor, M.S.; Piglesan, F.P.; Nasui, M. Hydrothermal Deposition of ZnO Layer on Fe-Based Amorphous Fibres Used for the Preparation of Cold Sintered Fibre-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Coatings 2022, 12, 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101527
Neamţu BV, Popa F, Ware E, Marinca TF, Gabor MS, Piglesan FP, Nasui M. Hydrothermal Deposition of ZnO Layer on Fe-Based Amorphous Fibres Used for the Preparation of Cold Sintered Fibre-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Coatings. 2022; 12(10):1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101527
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeamţu, Bogdan Viorel, Florin Popa, Ecaterina Ware, Traian Florin Marinca, Mihai Sebastian Gabor, Florin Pop Piglesan, and Mircea Nasui. 2022. "Hydrothermal Deposition of ZnO Layer on Fe-Based Amorphous Fibres Used for the Preparation of Cold Sintered Fibre-Based Soft Magnetic Composites" Coatings 12, no. 10: 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101527
APA StyleNeamţu, B. V., Popa, F., Ware, E., Marinca, T. F., Gabor, M. S., Piglesan, F. P., & Nasui, M. (2022). Hydrothermal Deposition of ZnO Layer on Fe-Based Amorphous Fibres Used for the Preparation of Cold Sintered Fibre-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Coatings, 12(10), 1527. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101527







