Measurement of Ion Energy Distribution and Deposition of Ti Thin Films Using ABPPS Technology on Glass Substrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
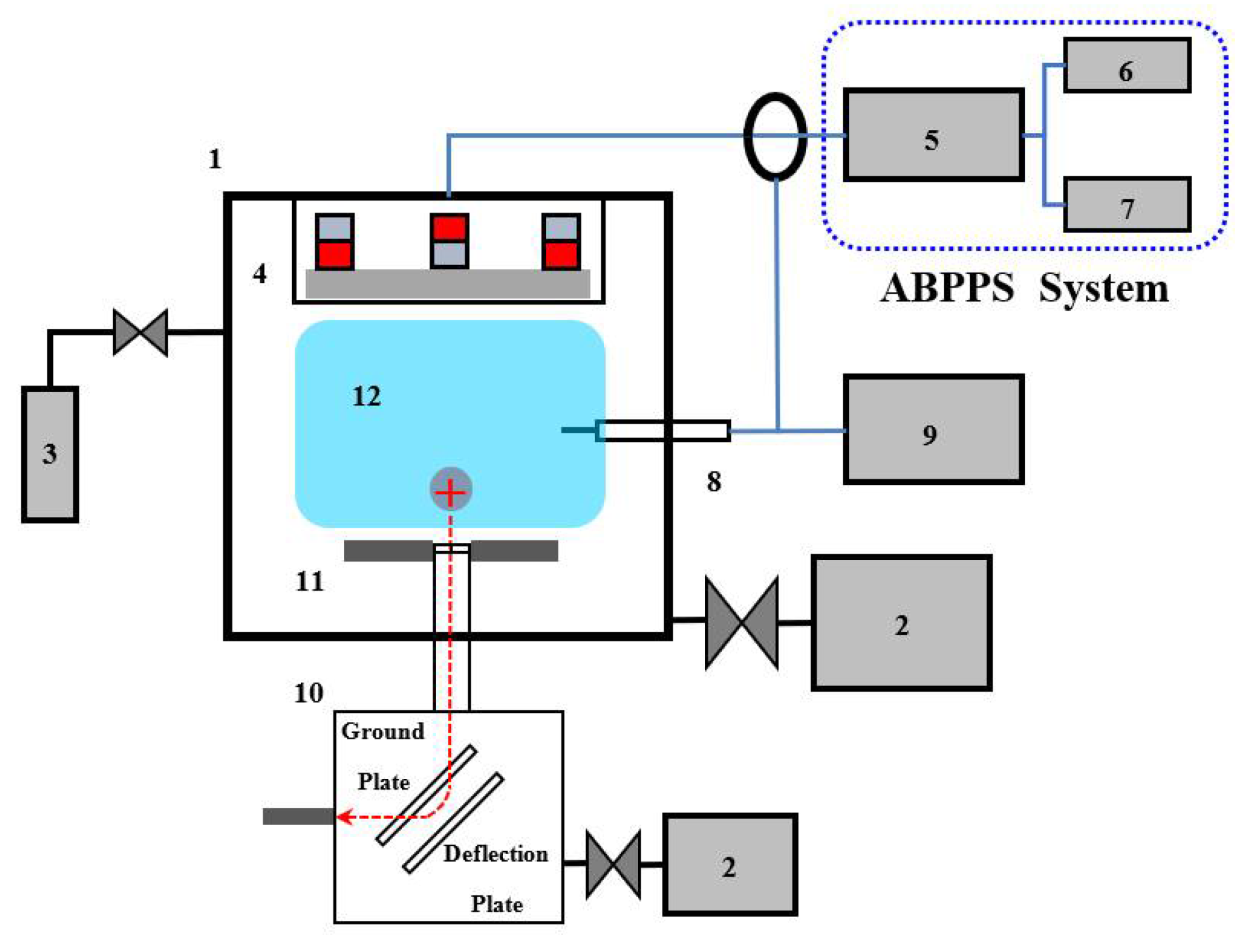
2. Experimental Details
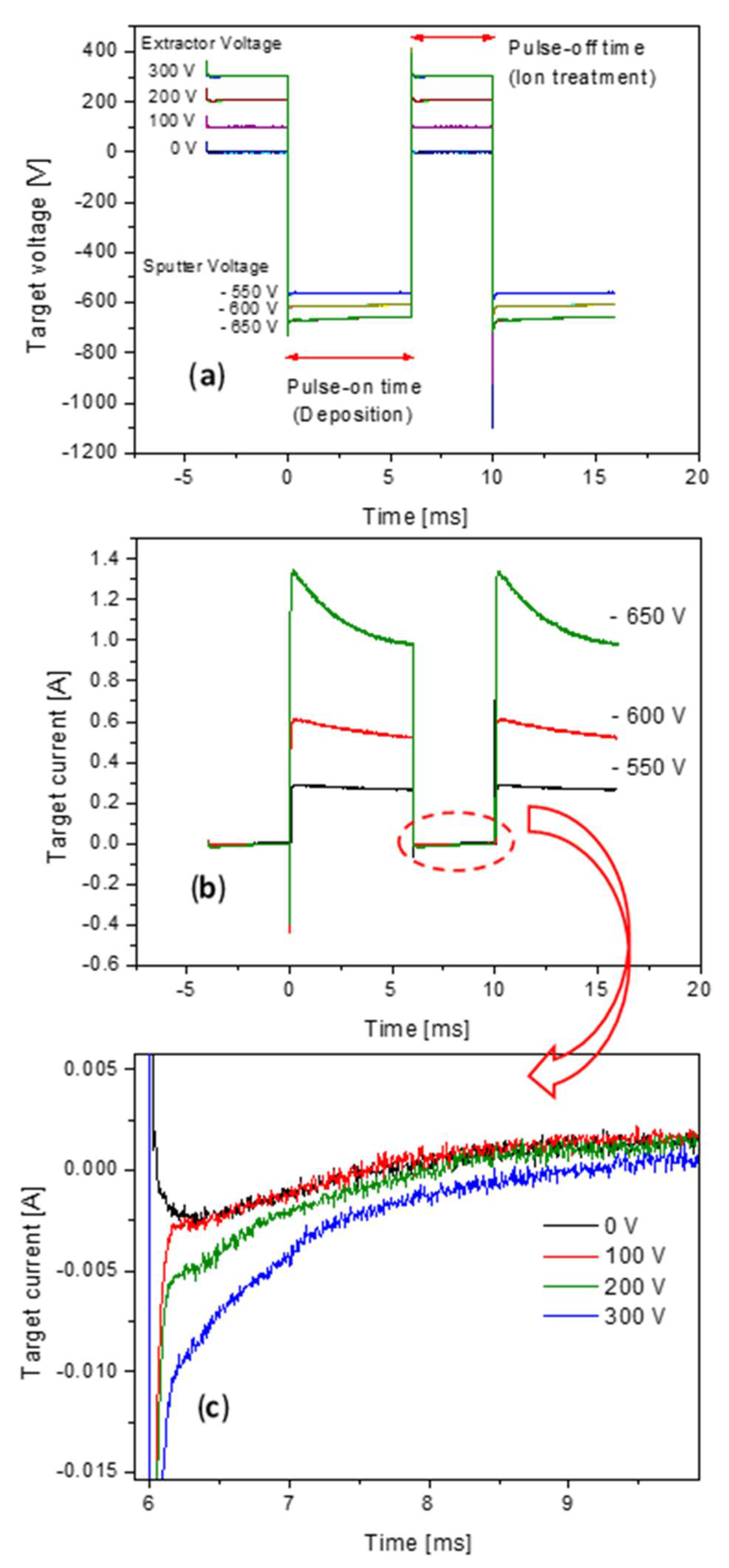
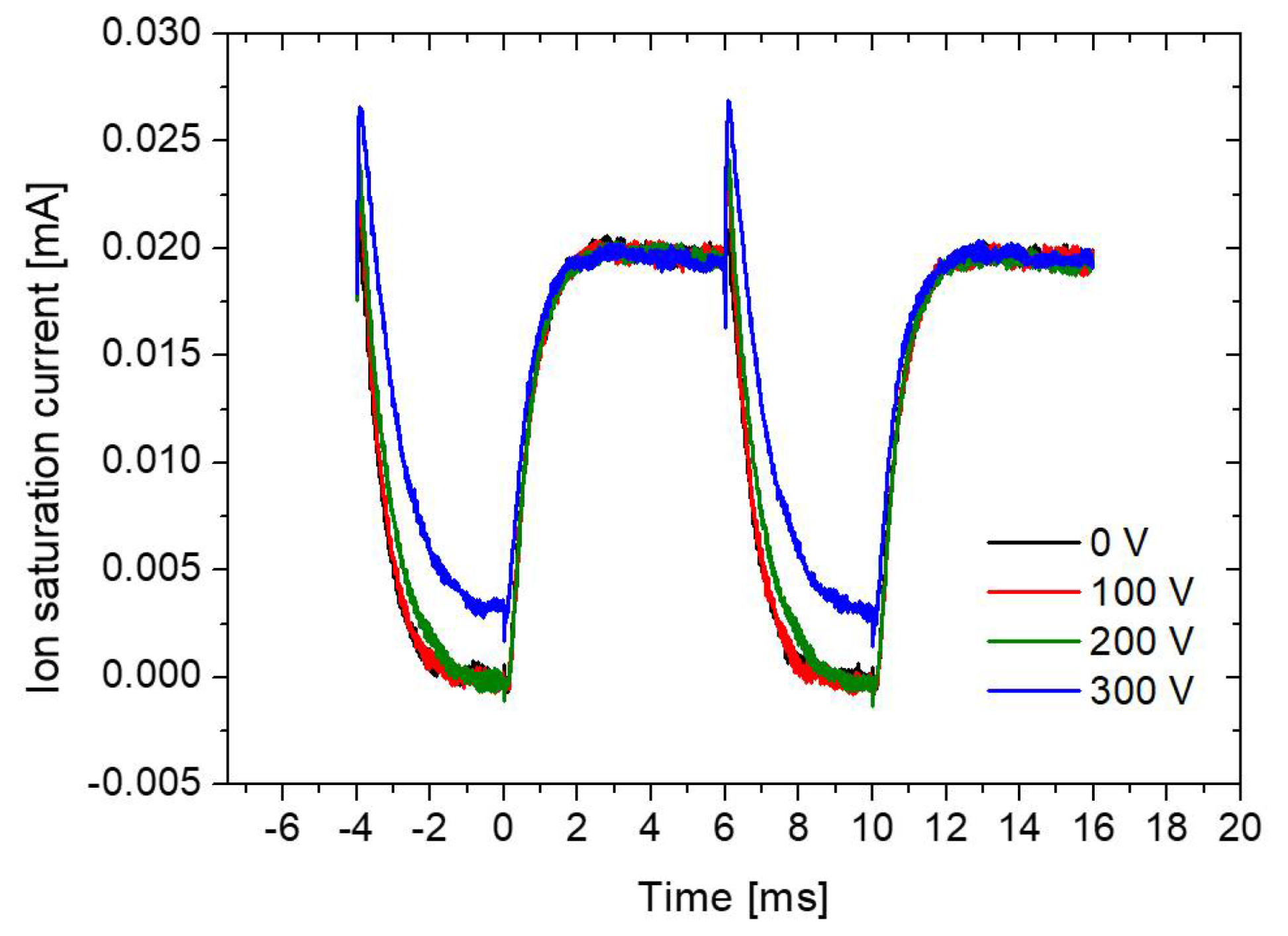
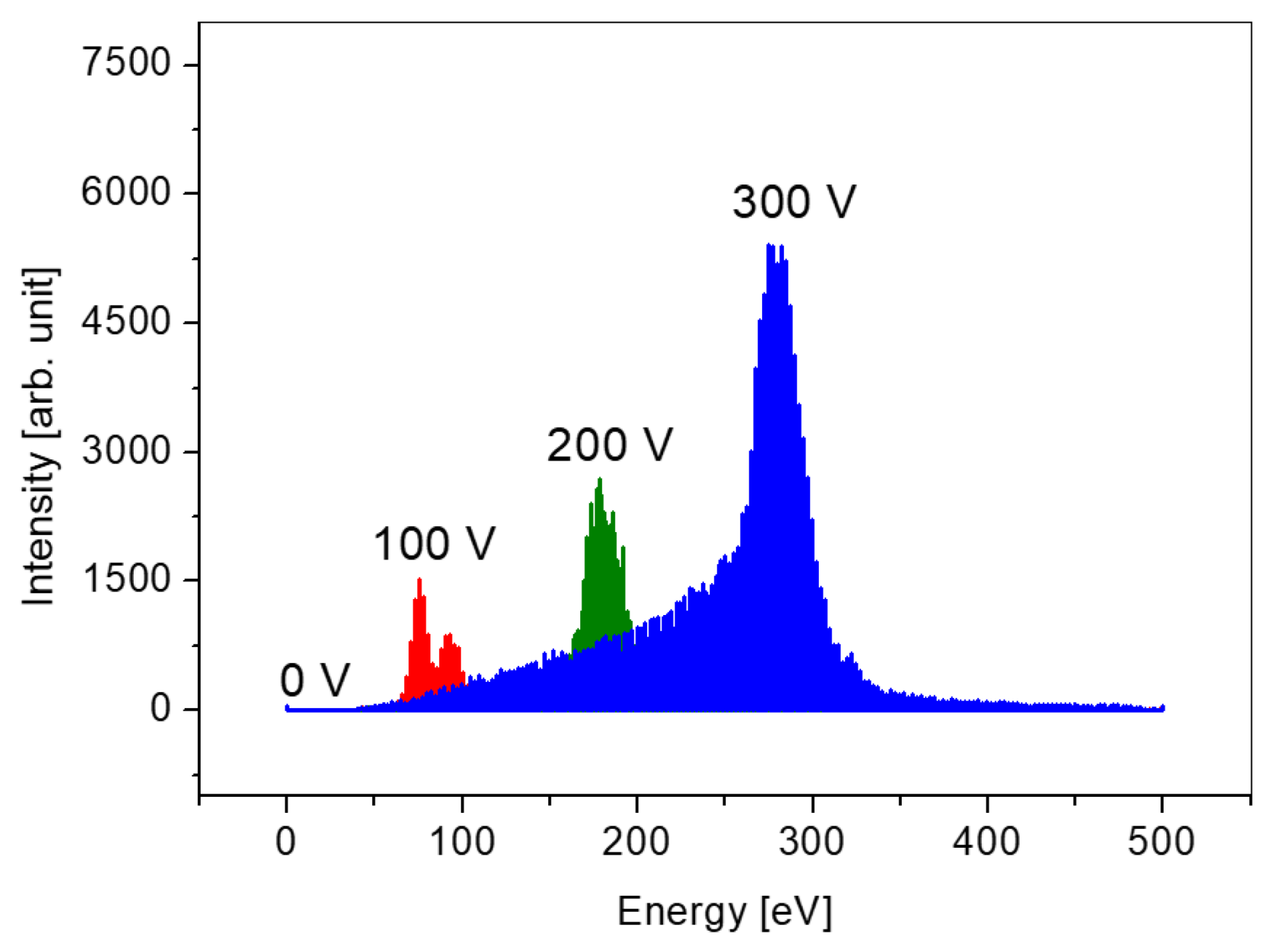
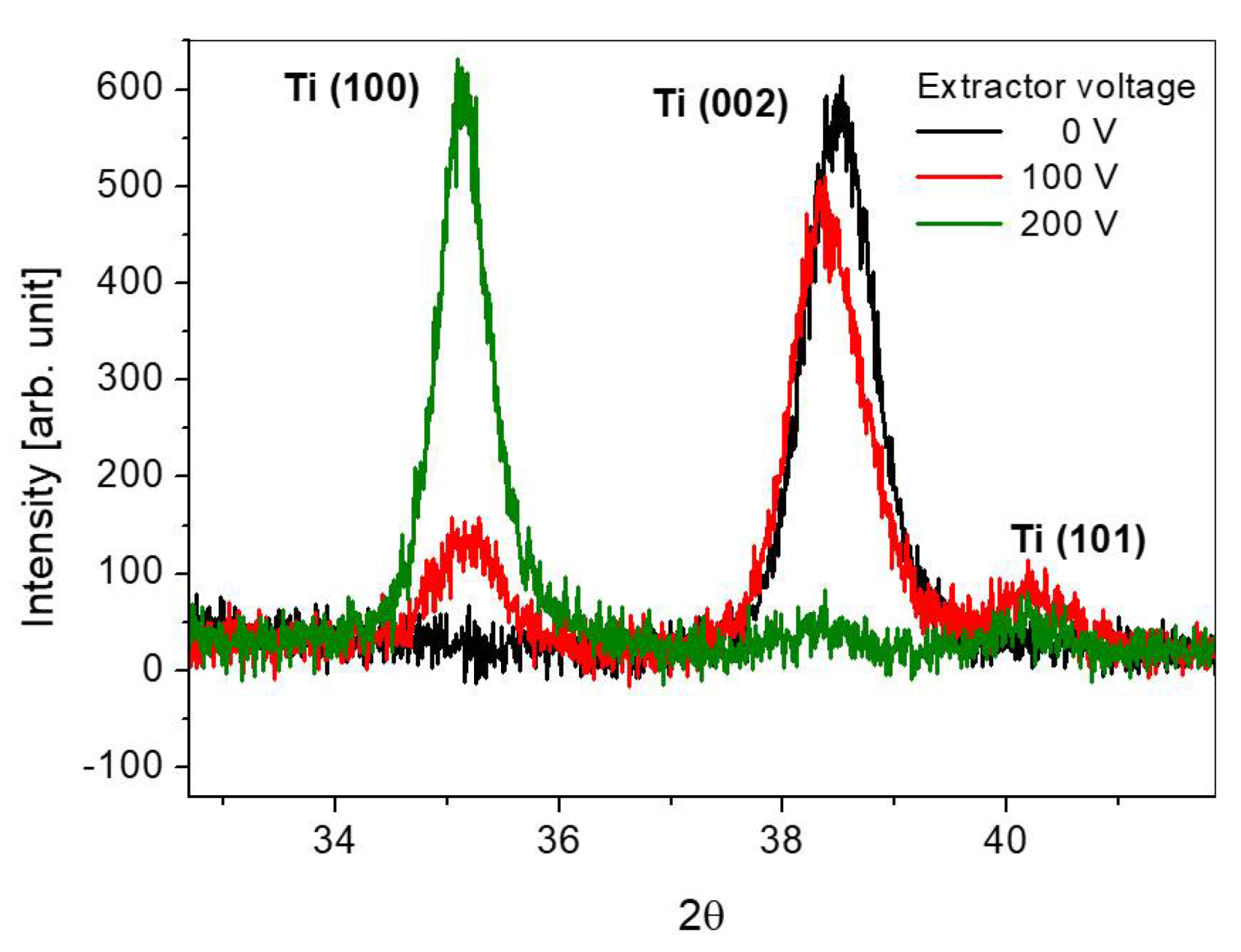
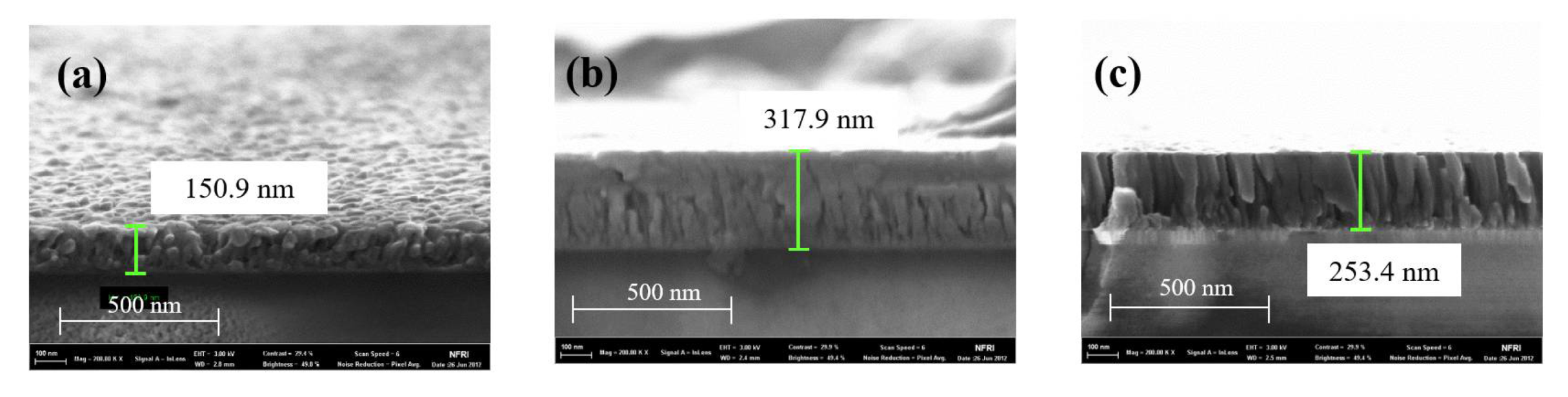
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schiller, S.; Goedicke, K.; Reschke, J.; Kirchhoff, V.; Schneider, S.; Milde, F. Pulsed magnetron sputter technology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1993, 61, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Arnell, R.D. Magnetron sputtering: A review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 2000, 56, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Moore, J.J.; Mishra, B.; Sproul, W.D.; Rees, J.A. Examination of the pulsing phenomena in pulsed-closed field unbalanced magnetron sputtering (P-CFUBMS) of Cr–Al–N thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4640–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Moore, J.J.; Mishra, B.; Pinkas, M.; Sproul, W.D.; Rees, J.A. Effect of asynchronous pulsing parameters on the structure and properties of CrAlN films deposited by pulsed closed field unbalanced magnetron sputtering (P-CFUBMS). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 1418–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Henderson, P.S.; Arnell, R.D.; Roche, G.A.; Carter, D. Reactive pulsed magnetron sputtering process for alumina films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2000, 18, 2890–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, J. Asymmetric bipolar pulsed DC: The enabling technology for reactive PVD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 98, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.W.; Bäcker, H.; Aranda-Gonzalvo, Y.; Kelly, P.J.; Arnell, R.D. The distribution of ion energies at the substrate in an asymmetric bi-polar pulsed DC magnetron discharge. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2002, 11, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.Y. Asymmetric bipolar pulsed DC sputtered nanocrystalline VN coatings for electrode materials in lithium battery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, L.Q.; He, Z.J.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.F.; Liu, A.; Wang, B.Y. Deposition of dense and smooth Ti films using ECR plasma-assisted magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 3356–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanizam; Soufhwee, H.A.R.; Anuar, K.A.R.; Nizam, A.R.M.; Mohamad, N. The effect of pulse DC and DC substrate bias during in situ cleaning PVD process on surface roughness. Procedia Eng. 2013, 53, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Shum, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.K.Y. Effect of bias voltage on the properties of CeO2−x coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 326, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišina, M.; Bradley, J.W.; Bäcker, H.; Aranda-Gonzalvo, Y.; Karkari, S.K.; Forder, D. Investigation of the pulsed magnetron discharge by time- and energy-resolved mass spectrometry. Vacuum 2003, 68, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Moore, J.J.; Rees, J.A. Electrostatic quadrupole plasma mass spectrometer and Langmuir probe measurements of mid-frequency pulsed DC magnetron discharges. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barshilia, H.C.; Rajam, K.S. Reactive sputtering of hard nitride coatings using asymmetric-bipolar pulsed DC generator. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, R.R.; Haas, J.M.; Gallimore, A.D. Development of a 45-degree parallel-plate electrostatic energy analyzer for hall thruster plume studies: Preliminary Data, IEPC-99-113. In Proceedings of the 26th International Electric Propulsion Conference, Kitakyushu, Japan, 17–21 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood, J.; Guarnieri, C.R.; Whitehair, S.J.; Cuomo, J.J. Langmuir probe measurements of a radio frequency induction plasma. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1993, 11, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Bremmell, K.E.; Griesser, H.J. Molecular-level removal of proteinaceous contamination from model surfaces and biomedical device materials by air plasma treatment. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 76, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpilowski, K.; Rymuszka, D. Surface properties of glass plates activated by air, oxygen, nitrogen and argon plasma. Glass Phys. Chem. 2016, 42, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Shimizu, H. Control of crystal orientation of Ti thin films by sputtering. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 44, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyachandran, Y.L.; Karunagaran, B.; Narayandass, S.K.; Mangalaraj, D.; Jenkins, T.E.; Martin, P.J. Properties of titanium thin films deposited by dc magnetron sputtering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 431, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-H.; Cho, S.-J.; Jung, C.-K.; Bae, I.-S.; Boo, J.-H.; Kim, S. The structural and mechanical properties of Ti films fabricated by using RF magnetron sputtering. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2007, 51, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Tay, B.K.; Lau, S.P.; Shi, X.; Tan, H.S. Influence of substrate bias on the microstructure and internal stress in Cu films deposited by filtered cathodic vacuum arc. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2001, 19, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, E.; Kikuchi, N. Mechanisms of the structural modification of Ti films by pulsed direct current and inductively coupled plasma-assisted pulsed direct current sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2017, 634, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Gas | Ar |
| Operating pressure (Pa) | 0.133 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 100 |
| Duty ratio (%) | 60 |
| Sputter voltage (V) | −550, −600, −650 |
| Extractor voltage (V) | 0, 100, 200, 300 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Base pressure (Pa) | 1.33 × 10−4 |
| Gas | Ar |
| Operating pressure (Pa) | 0.479 |
| Distance between target and substrate (mm) | 100 mm |
| Modulator frequency (kHz) | 15 |
| Modulator duty cycle (%) | 60 |
| Sputter voltage (V) | (−) 600 |
| Extractor voltage (V) | 0, 100, 200 |
| Substrate | Glass |
| Substrate temperature | Room temp. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-C.; Kim, Y.-W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, J.-B.; Kim, J.-S.; Han, D.-S. Measurement of Ion Energy Distribution and Deposition of Ti Thin Films Using ABPPS Technology on Glass Substrate. Coatings 2021, 11, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11080904
Kim D-C, Kim Y-W, Kim Y-H, Park J-B, Kim J-S, Han D-S. Measurement of Ion Energy Distribution and Deposition of Ti Thin Films Using ABPPS Technology on Glass Substrate. Coatings. 2021; 11(8):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11080904
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dae-Chul, Young-Woo Kim, Yong-Hyun Kim, Jong-Bae Park, Jong-Sik Kim, and Duk-Sun Han. 2021. "Measurement of Ion Energy Distribution and Deposition of Ti Thin Films Using ABPPS Technology on Glass Substrate" Coatings 11, no. 8: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11080904
APA StyleKim, D.-C., Kim, Y.-W., Kim, Y.-H., Park, J.-B., Kim, J.-S., & Han, D.-S. (2021). Measurement of Ion Energy Distribution and Deposition of Ti Thin Films Using ABPPS Technology on Glass Substrate. Coatings, 11(8), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11080904





