Abstract
Doping impurity into ZnO is an effective and powerful technique to tailor structures and enhance its optical properties. In this work, Zn1−xMgxO and Zn1−x−yMgxByO nanoparticles (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4; y = 0, 0.02, 0.04) were synthesized via one-pot method. It shows that the Mg and B dopants has great influence on crystallinity and surface morphology of ZnO nanoparticles, without changing the wurtzite structure of ZnO. The band structure study indicates that the competition of Conductive Band (CB) shift, Burstein–Moss (B-M) shift and Shrinkage effect will cause the band gap energy change in ZnO.
1. Introduction
As one of the third-generation wide band gap semiconductor materials, zinc oxide (ZnO) has attracted great attention in the field of optoelectronic functional materials due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, such as large exciton binding energy (60 meV), wide direct band gap energy (3.37 eV), low cost, and facile preparation [1,2,3,4]. In recent years, researchers have discovered that ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) have unique and superior structural, optical, electronic, and chemical properties compared to bulk ZnO materials [5,6]. Therefore, various methods for preparing ZnO NPs have been developed, such as co-precipitation, hydrothermal, combustion, spray pyrolysis, sol-gel, and high-temperature pyrolysis [7,8,9,10,11].
Doping impurity elements into the target lattice is an effective and powerful technique that can change the electronic structure and enhance electrical and optical properties [12]. Various elements (for example, Al, Ga, Mg, Mn) [13,14,15,16] have been used as donors to improve the optical, physical, and chemical properties of ZnO. Among them, Mg-doped ZnO NPs have attracted great attention; because the ionic radius between Mg2+ and Zn2+ is equivalent, doping Mg element will not cause huge lattice changes. Moreover, because of the large band gap of MgO, Mg doping can broaden the optical band gap of ZnO [17,18]. Jongchul Seo [19] synthesized Mg-doped ZnO (Zn1−xMgxO, where x = 0.000–0.010 M) nanoparticles via a co-precipitation method and showed an increase in the optical band gap from 3.32 to 3.51 eV with respect to the increase in the concentration of Mg doping. Riffat Sagheer [5] synthesized Zn1−xMgxO nanoparticles (x = 0–0.1, Δx = 0.02) via a co-precipitation method; the Eg of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles (3.080 eV) is greater than that of undoped ZnO nanoparticles (3.038 eV). XRD results confirmed that the synthesized nanoparticles are polycrystalline, which have a typical hexagonal wurtzite structure, and there are no other impurities or dopant phases in the ZnO crystal lattice. Charis Caroline [20] synthesized pure ZnO and Mg doped ZnO (Zn1−xMgxO; x = 0, 0.2, 0.4) by sol–gel method. The results show that the Eg increases from 3.16 to 3.24 eV with the Mg concentration from 0 to 0.4.
In addition, the group III elements are usually doped to increase the electrical properties of ZnO by increasing the carrier concentration [21]. Al is considered to be the best doping element to enhance optical and electrical properties [22]. B element is also used to investigate the transparent and electrically conductive of ZnO and found that the transmittance of B-doped ZnO thin films were obviously improved [23,24], but the optical band gap was decreased [21].
Although lots of research was carried out on the elements doping in ZnO, the effect of B-Mg co-doped was rarely seen. Therefore, in this work, pure ZnO, Mg-doped ZnO, and B-Mg co-doped ZnO NPs were synthesized by simple one-pot method. The effect of Mg and B doping on crystal structure, morphology, and the band structure of ZnO will be investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
For the present research work, Zn1−xMgxO and Zn1−x−yMgxByO nanoparticles (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4; y = 0, 0.02, 0.04) were synthesized via one-pot method. Here Zinc acetylacetonate (Zn(acac)2), Magnesium acetylacetonate (Mg(acac)2), Boric acid (H3BO3) were used as the Zn source, Mg source and B source, respectively. All the chemical ingredients were weighted in stoichiometric proportions for getting 10 mmol of final product. Then, a mixture of Zn(acac)2, Mg(acac)2, H3BO3, oleic acid (OA, 0.9 g), oleylamine (OAm, 2.50 g), and octadecene (ODE, 13.2 g) with specific composition was degassed at 120 °C for 30 min and heated to 280 °C in a closed beaker. The hot mixture was cooled to room temperature naturally in the air, and then, 30 mL of ethanol was added to precipitate the nanoparticles, the mixture solution was centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 5 min to get white precipitates. The precipitates were redispersed in 10 mL of n-hexane and washed with ethanol for three times. Finally, the precipitates were dried in hot air oven at 100 °C for 10 h. The dried precipitates were crushed to obtain desired nanoparticles.
2.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
The crystal structure of all samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction with CuKa radiation (XRD, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). Analysis of surface features of all nanoparticles were carried out by using Sigma 500 Scanning electron microscope (SEM, Carl Zeiss AG, Jena, Germany) and Talos-F200s Transmission electron microscope(TEM, FEI, Waltham, MA, USA). Optical properties of the nanoparticles were explored by employing by a Scan UV spectrophotometer (UV-2700, Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan). The UV diffuse reflectance spectroscopy were recorded at room temperature ranging from 200 to 800 nm.
3. Results
3.1. XRD Analysis
To investigate the structural aspects of the ZnO, Mg doped ZnO and B-Mg doped ZnO nanoparticles, XRD patterns of all samples were listed and analyzed. The XRD patterns of Zn1−xMgxO nanoparticles with different doping concentrations (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) synthesized by the one-pot method are shown in Figure 1a,b. It can be seen from the patterns that the synthesized nanoparticles have sharp diffraction peaks, which indicates that the prepared nanoparticles have good crystallinity. The characteristic diffraction peaks indicate that the synthesized nanocrystals are ZnO with a wurtzite hexagonal structure (PDF# 80-0074). Moreover, no characteristic peak corresponding to the “Mg” element or its compound was detected, which indicates that “Mg” is a dopant, and no additional Mg related extrinsic phase exists in the ZnO matrix. For the wurtzite phase, calculate the lattice constants “a” and “c” of (100) and (002), respectively, as follows [25].
where λ is the wavelength of the incident X-ray (λ = 1.5406 Å), and θ is the Bragg angle. The influence of “Mg” atoms was investigated through the changes of peak positions of (100) and (002) planes, as in Figure 1b. Both peaks move to the lower 2θ value, as shown in the two circles in Figure 1b, indicating that the “Mg” atoms occupy the substitution lattice sites and interstitial sites [5]. However, the aspect ratio “c/a” listed in Table 1 is almost constant, which indicates that the dopant atoms are successfully combined with the ZnO host lattice without changing the crystal structure of the nanoparticles. In addition, according to Vegard’s law, a slight increase in the lattice parameters (“a” and “c”) of the ZnO lattice is noticed due to the high Mg doping concentration.
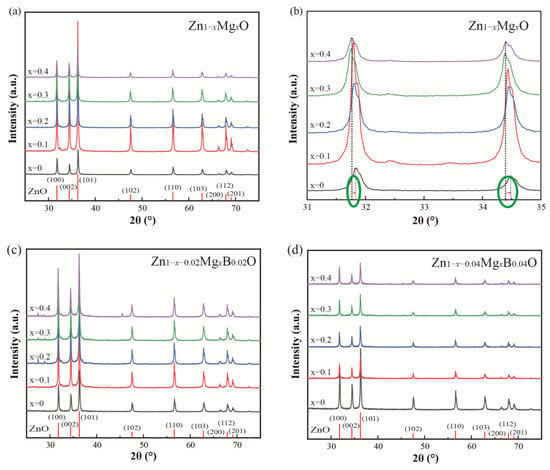
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of Zn1−x−yMgxByO. (a) Zn1−xMgxO; (b) enlarged XRD pattern of (100) and (002) plane of Zn1−xMgxO in (a); (c) Zn1−x−0.02MgxB0.02O; (d) Zn1−x−0.04MgxB0.04O.

Table 1.
Calculated parameters for nanoparticles.
Besides, the average crystallite size D was calculated from XRD peak of (101) by using the Debye–Scherrer equation, the dislocation density δ is defined as the length of dislocation lines per unit volume of the crystal, which is determined from the crystallite size D. We can also calculate the strain ε caused by the crystal defects and distortion [25].
where is the integral half width, K is a constant equal to 0.9. The calculated data are shown in Table 1. The crystal size of pure ZnO synthesized by one-pot method is only 38.9 nm, and it can be observed that the crystallite size increases while “Mg” atoms was doped, as shown in Table 1. Internal strain is generated in the parent ZnO system due to the difference between the ionic radii of Zn (0.057 nm) and Mg (0.060 nm). When the amount of doped Mg is small (x = 0.1), the doping atoms accelerate the diffusion rate in the Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles due to the small volume of Mg2+ ions, resulting in a larger crystal size. The reason may be due to the low Pauling electro-negativity (1.31) and the high reactivity of Mg [5]. However, as presented in Table 1, the crystal size D of the sample decreases as the doping concentration increases (x = 0.2, 0.3, 0.4) due to the influence of lattice strain and dislocation density [26].
Figure 1c,d shows the XRD images of B-Mg co-doped ZnO nanoparticles with different B doping concentrations (y = 0.02, 0.04). Similar to Figure 1a, the addition of B element would not cause other additional peaks, indicating that B-Mg co-doping did not change the wurtzite structure of ZnO. However, the peak intensity decreases as the concentration of B increases, which indicates that the crystalline quality of the product is poor.
The differences between the crystallite size D of Zn1−xMgxO and the one of B codoped Zn1−xMgxO are presented in Figure 2a, to investigate the influence of B element. We have a medium D of 43.3 nm for Zn1−xMgxO sample, while in presence of B medium, D is 40.3 and 40.5 nm. It seems that the Mg concentration is less effective on the variation of D when samples are co-doped with B. The reason may be that the incorporation of B element increases the lattice strain and dislocation density of zinc oxide nanoparticles [26], as shown in Table 1 and Figure 2b,c.
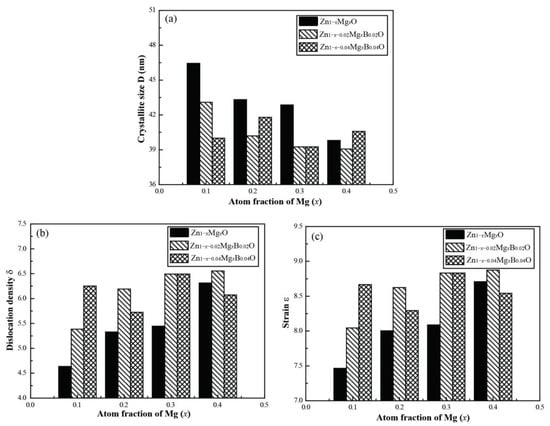
Figure 2.
Comparison of calculated parameters of Zn1−x−yMgxByO with different fraction of Mg. (a) crystallite size D; (b) dislocation density; (c) strain.
3.2. SEM and TEM Analysis
Using scanning electron microscope to study the effect of B and Mg doping on the surface morphology of ZnO nanoparticles, as presented in Figure 3. It can be observed that the pure ZnO synthesized by one-pot method has triangular and spherical grains and are seriously aggregated. When Mg doped in ZnO, as presented in Figure 3b–d, discal and hexagonal shapes appear, which means that the orientation of the sample is mostly perpendicular to the growth direction along the c-axis [27]. Besides, twinned crystal structures with a central vacant space in each twined building block have self-assembled. This phenomenon indicates that Mg element promotes the crystallization of ZnO. Comparing Figure 3d–f, it can be seen that with the addition of B element, the twin hexagonal crystal structure gradually disappears, and only a spherical structure exists in the Zn0.68Mg0.3B0.02O sample in Figure 3f. The B element reduces the crystallinity of ZnO, which is in agreement with the result of XRD.
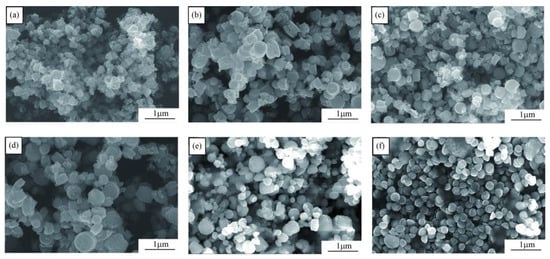
Figure 3.
SEM images of pure and doped ZnO nanoparticles. (a) Pure ZnO; (b) Zn0.9Mg0.1O; (c) Zn0.6Mg0.4O; (d) Zn0.7Mg0.3O; (e) Zn0.68Mg0.3B0.02O; (f) Zn0.66Mg0.3B0.04O.
The typical transmission electronic microscopy (TEM) images of pure ZnO, Zn0.7Mg0.3O, Zn0.68Mg0.3B0.02O, and Zn0.66Mg0.3B0.04O nanoparticles are presented in Figure 4. Pure ZnO nanoparticles with an average particle size of 20–50 nm are agglomerated. The well-resolved interfringe distance of 2.89 Å corresponds to the (100) lattice planes of ZnO. In the Zn0.7Mg0.3O sample, discal-shaped particles showing good crystallinity are observed, which is consistent with the SEM results. After doping B ions, only spherical structures are present in Figure 4c,d. In addition, the lattice resolved images in Figure 4b–d all show that the lattice spacing is 2.85 Å, which can correspond to the (100) plane of ZnO, confirming that B-Mg co-doping did not change the structure of wurtzite zinc oxide.
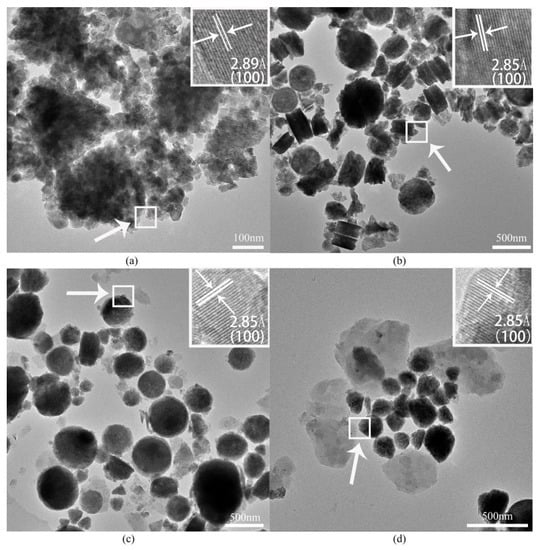
Figure 4.
Typical transmission electronic microscopy (TEM) images of (a) pure ZnO, (b) Zn0.7Mg0.3O, (c) Zn0.68Mg0.3B0.02O, and (d) Zn0.66Mg0.3B0.04O nanoparticles.
3.3. UV–VIS Analysis
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy was used to study and analyze the optical properties of pure and B-Mg co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Figure 5 presents the UV diffuse reflectance spectra of pure and Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles with different Mg concentrations. It can be observed that there is a blue shift of the reflection peak between 370 and 400 nm. This is a phenomenon in which the band gap of a semiconductor increases, that is, the absorption is pushed to higher energy due to an increase in the population in the conduction band. On further observation, as shown in the enlarged image in Figure 5a, compared with pure ZnO, Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles have higher reflectance, which is due to the increase in Eg.
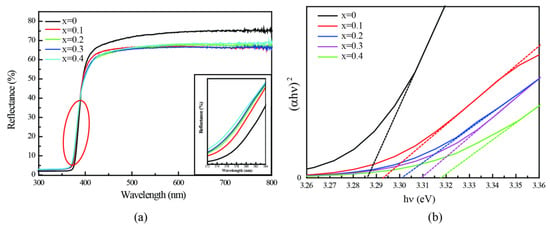
Figure 5.
(a) UV reflectance spectra of Zn1−xMgxO nanoparticles; the inset is the enlarged figure in the red circle; (b) Tauc plots for determination of optical band gap energy of Zn1−xMgxO nanoparticles.
The optical bandgap energy was calculated by the Kubelka–Munk equation [28], as follows.
where R is the reflectance. F(R) is the absorption coefficient (α) in Tauc equation [28]:
We estimate the Eg by extrapolating the linear plot of the Tauc equation, as presented in Figure 5b. It can be observed that the Eg values increased from 3.286 eV to 3.318 eV for undoped ZnO and Zn0.6Mg0.4O nanoparticles. It is because of the conduction band shift (CB shift) owing to the wider Eg of MgO (7.7 eV), as presented in Figure 6b. In addition, the Eg of Zn1−xMgxO nanoparticles increase gradually with the increase of the Mg dopants. The reason may be due to the Burstein–Moss shift (B-M shift) caused by more electrons generated by substituting Mg2+ ions in ZnO. The schematic showing effect of CB shift and B-M shift is presented in Figure 6c.
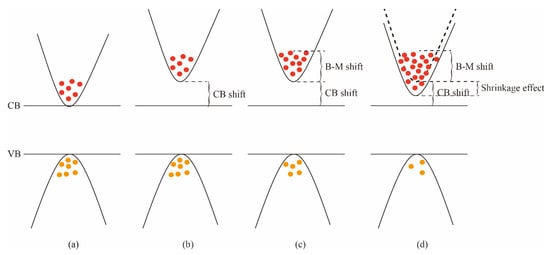
Figure 6.
Schematic showing effect of doping on ZnO band structure. (a) Band structure of pure ZnO; (b) CB shift of band structure during doping; (c) both CB shift and B-M shift of band structure when the carrier concentration C < CMott; (d) CB shift, B-M shift, and shrinkage effect of band structure when the carrier concentration C > CMott.
The influence of the B element on the Eg is also studied. The calculated Eg of pure and doped ZnO nanoparticles are presented in Figure 7. Different from Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles, the Eg of B-Mg co-doped ZnO increases first and then decreases while the doping amount of Mg element gradually increases. A small number of carriers induced by doping will cause Burstein–Moss shift, broadening Eg, as shown in Figure 6c. However, when the concentration of carriers is higher than the critical concentration of Mott transition (CMott), Urbach tail will cause the shrinkage of energy gap [29], which is shown in Figure 6d. It is known that the replacement of B3+ atom with host Zn2+ atom generates a large amount of carrier, and excessive carrier concentration results in the decreasing of Eg (Shrinkage effect).
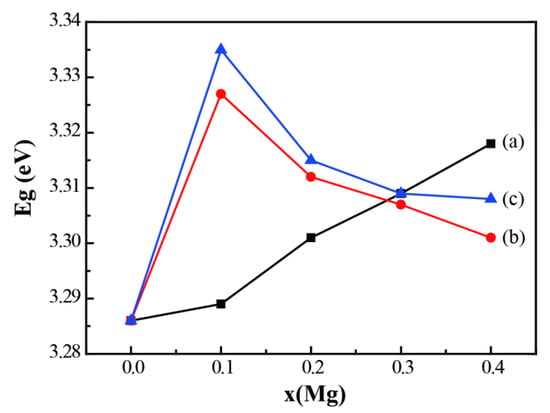
Figure 7.
Band gap energy Eg of pure and doped ZnO nanoparticles. (a) Zn1−xMgxO; (b) Zn1−0.02−xMgxB0.02O; (c) Zn1−0.04−xMgxB0.04O.
4. Conclusions
The pure and doped ZnO nanoparticles were successfully synthesized by a simple one-pot method. XRD results show that both Mg and B are incorporated into the ZnO lattice without changing the original wurtzite structure of ZnO. By introducing Mg element into ZnO nanoparticles, the lattice parameter is increased. However, the B element increases the lattice strain and dislocation density, thereby decreasing the crystallite size. Combined with the analysis of the microstructure, it can be seen that Mg ions promote the crystallization of ZnO, while B ions make the crystallinity worse. The influence of doping Mg and B on the band structure is also investigated. The results show that the Eg of ZnO nanoparticles increase with doping Mg, while that of B-Mg co-doped ZnO increases first and then decreases due to the competition of CB shift, Burstein–Moss shift and Shrinkage effect.
Author Contributions
Y.L. (Yongli Li): methodology, formal analysis, and data curation. Y.L. (Yuechan Li): conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft preparation. A.X.: writing—review and editing, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China Joint Fund for Cross-strait Scientific and Technological Cooperation (No. U2005212), Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2020J02049), Major Project of Science and technology of Xiamen City (Nos. 3502ZCQ20201001, 3502Z20201003), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2019J01873), open fund of Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Materials and Applications, Xiamen University of Technology (No. fma2020009), and Pandengketi of Xiamen University of Technology (No. XPDKQ20002).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yogamalar, N.R.; Bose, A.C. Absorption-emission of hydrothermally grown Al: ZnO nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 8493–8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Kant, K.M.; Anita, D.; Thirupathiah, S.; Rama, N.; Tiwari, B.; Kottaisamy, M.; Rao, M.S.R. Structure, microstructure and physical properties of ZnO based materials in various forms: Bulk, thin film and nano. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 6312–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Wang, C.; Park, W. ZnO nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S22–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Singh, P.; Kumar, V. Synthesis and characterization of pure ZnO and La-doped ZnO (Zn0.98La0.02O) films via novel sol-gel screen-printing method. Optik 2018, 158, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagheer, R.; Khalil, M.; Abbas, V.; Kayani, Z.N.; Tariq, U. Effect of Mg doping on structural, morphological, optical and thermal properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Optik 2020, 200, 163428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golic, D.L.; Brankovic, G.; Nesic, M.P.; Vojisavljevic, K.; Recnikn, A.; Daneu, N.; Bernik, S.; Scepanovic, M.; Poleti, D.; Brankovic, Z. Structural charecterization of self-assembled ZnO nanoparticles obtained by the sol–gel method from Zn(CH3COO)2 2H2O. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 395603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoufi, D. Synthesis and microstructural properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitthichai, S.; Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Influence of Mg dopant on photocatalytic properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 125, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshmipriya, V.; Radha, K.P. Synthesis, structural, vibrational, thermal studies of Mg doped ZnO nanoparticles using chemical precipitation method. Int. J. Multidiscip. Educ. Res. 2016, 1, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Aneesh, P.M.; Vanaja, K.A.; Jayaraj, M.K. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6639, 66390J. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.S.; Kumar, V.R.; Suvarna, R.P. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles by solution combustion method: DC conductivity studies. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2017, 5, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhu, L.S.; Cao, W.S.; Li, P.D.; Zhan, Z.L.; Chen, Z.H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J. Defect-related optical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via low temperature hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtaran, S. Al doped ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrohysis technique: Influence of different annealing time. Opt. Mater. 2021, 114, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.C.; Hwang, S.M.; Choi, J.H.; Kwon, Y.H.; Cho, H.K.; Kim, S.W.; Lim, J.H.; Joo, J. Effects of In or Ga doping on the growth behavior and optical properties of ZnO nanorods fabricated by hydrothermal process. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2013, 210, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinet, G.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, M.; Anshul, A. Structural and optical properties of Mg modified ZnO nanoparticles: An X-ray peak broadening analysis. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 125, 114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, N.A.; Fauzia, V.; Iwan, S.; Roza, L.; Umar, A.A.; Budi, S. Mn-doping-induced photocatalytic activity enhancement of ZnO nanorods prepared on glass substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtomo, A.; Kawasaki, M.; Koida, T.; Masubuchi, K.; Koinuma, H. MgxZn1−xO as II-VI widegap semiconductor alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, A.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Zeng, H. Lattice restraint induced ultra-large bandgap widening of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8969–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, G.; Seo, J. Influence of Mg doping on the structural, morphological, optical, thermal, and visible-light responsive antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priscilla, S.J.; Daniel, R.; Dhakshayani, Y.; Caroline, S.C.; Sivaji, K. Effect of magnesium dopant on the structural, morphological and electrical properties of ZnO nanoparticles by sol–gel method. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurma, T. Effect of boron doping concentration on structural optical electrical properties of nanostructured ZnO films. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1189, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pon, V.D.; Wilson, K.S.J.; Hariprasad, K.; Ganesh, V.; Ali, H.E.; Algarni, H.; Yahia, I.S. Enhancement of optoelectronic properties of ZnO thin films by Al doping for photodetector applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 2021, 151, 106790. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, S.; Feitknecht, L.; Schluchter, R.; Kroll, U.; Sauvain, E.V.; Shah, A. Rough ZnO layers by LP-CVD process and their effect in improving performances of amorphous and microcrystalline silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fay, S.; Steinhauser, J.; Nicolay, S.; Ballif, C. Polycrystalline ZnO: B grown by LPCVD as TCO for thin film silicon solar cells. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 2961–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, P.; Thomas, S. Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2014, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mimouni, R.; Kamoun, O.; Yumak, A.; Mhamdi, A.; Boubaker, K.; Petkova, P.; Amlouk, M. Effect of Mn content on structural, optical, opto-thermal and electrical properties of ZnO: Mn sprayed thin films compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Chatterjee, S. Structure-directing property and growth mechanism induced by capping agents in nanostructured ZnO during hydrothermal sysnthesis—A systematic review. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 22, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohar, R.S.; Sugihartono, I.; Fauzia, V.; Umar, A.A. Dependence of optical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanorods on Al dopant. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 19, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, H.S.; Li, B.; Feng, B.X.; He, Y.Y.; Chen, C. Effect on optical band-gap of transparent and conductive CdIn2O4 thin film due to defects-induced Burstein-moss and band-gap narrowing characteristics. Acta Phys. Sin. 2005, 54, 842–847. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).