Influence of Phosphoric Acid on the Adhesion Strength between Rusted Steel and Epoxy Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adhesion Test
2.3. Characterization of Rust and Tannic Conversion Layer
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Concentrations of Phosphoric Acid on the Adhesion Strength
3.2. Mechanism of Adhesion Improvement
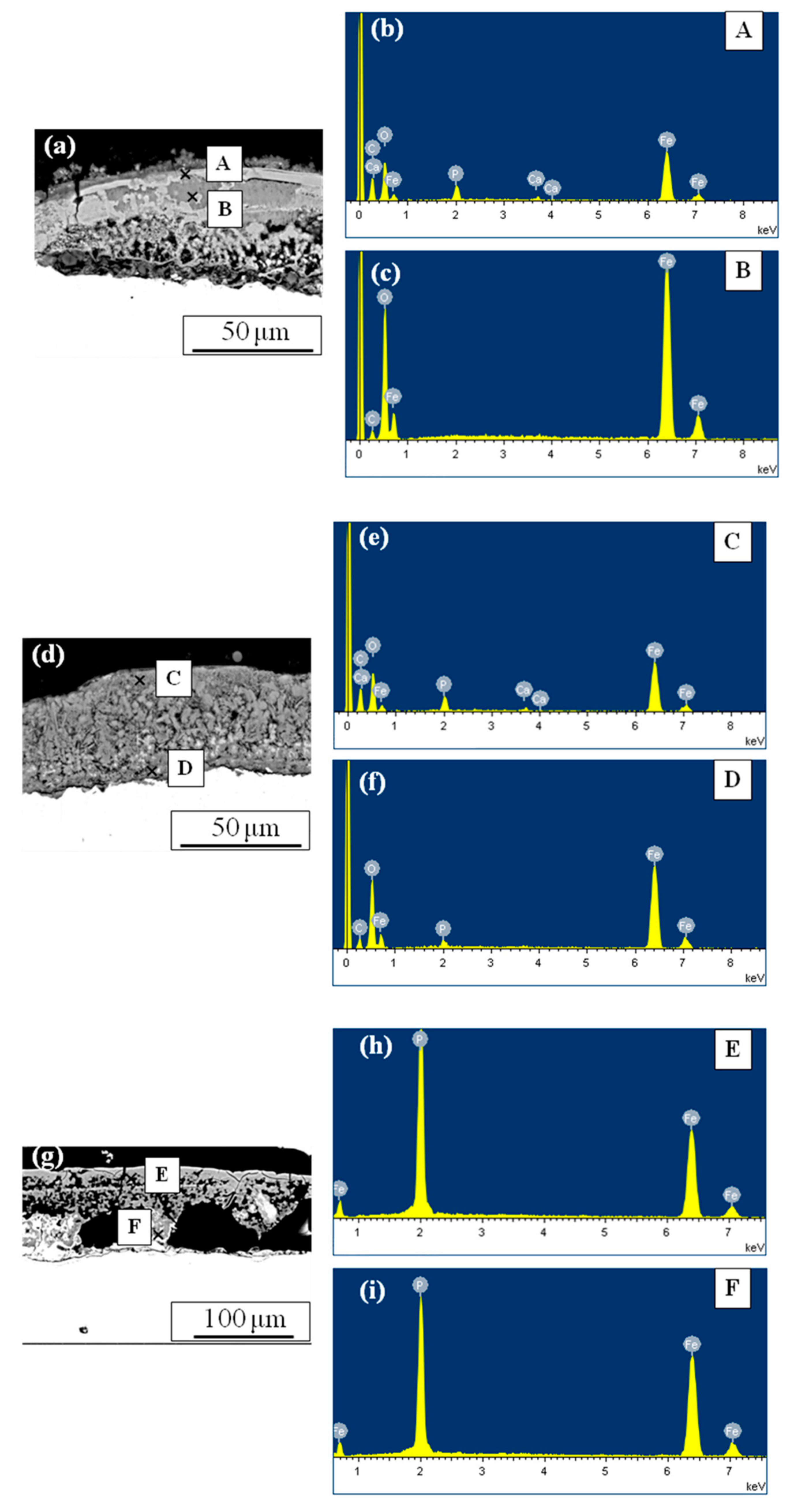
3.2.1. The Effect of Rust Composition
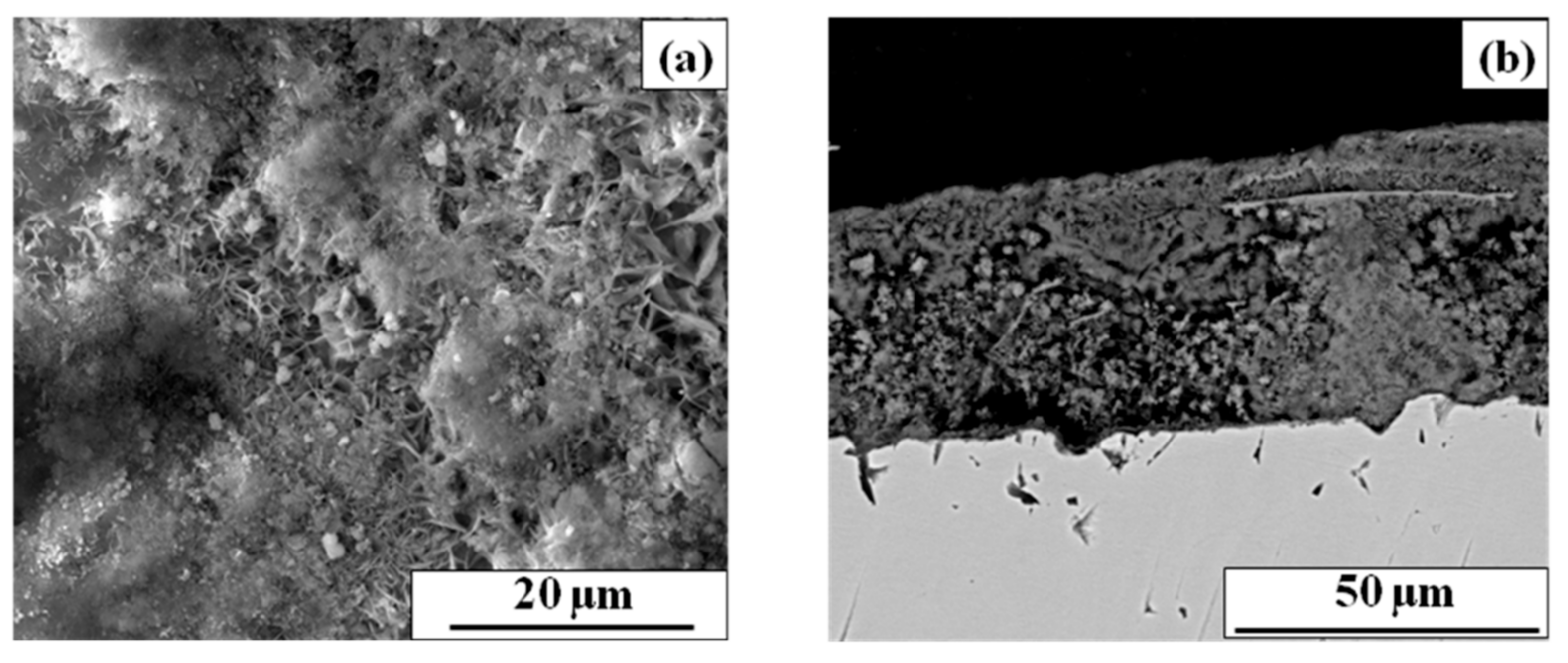
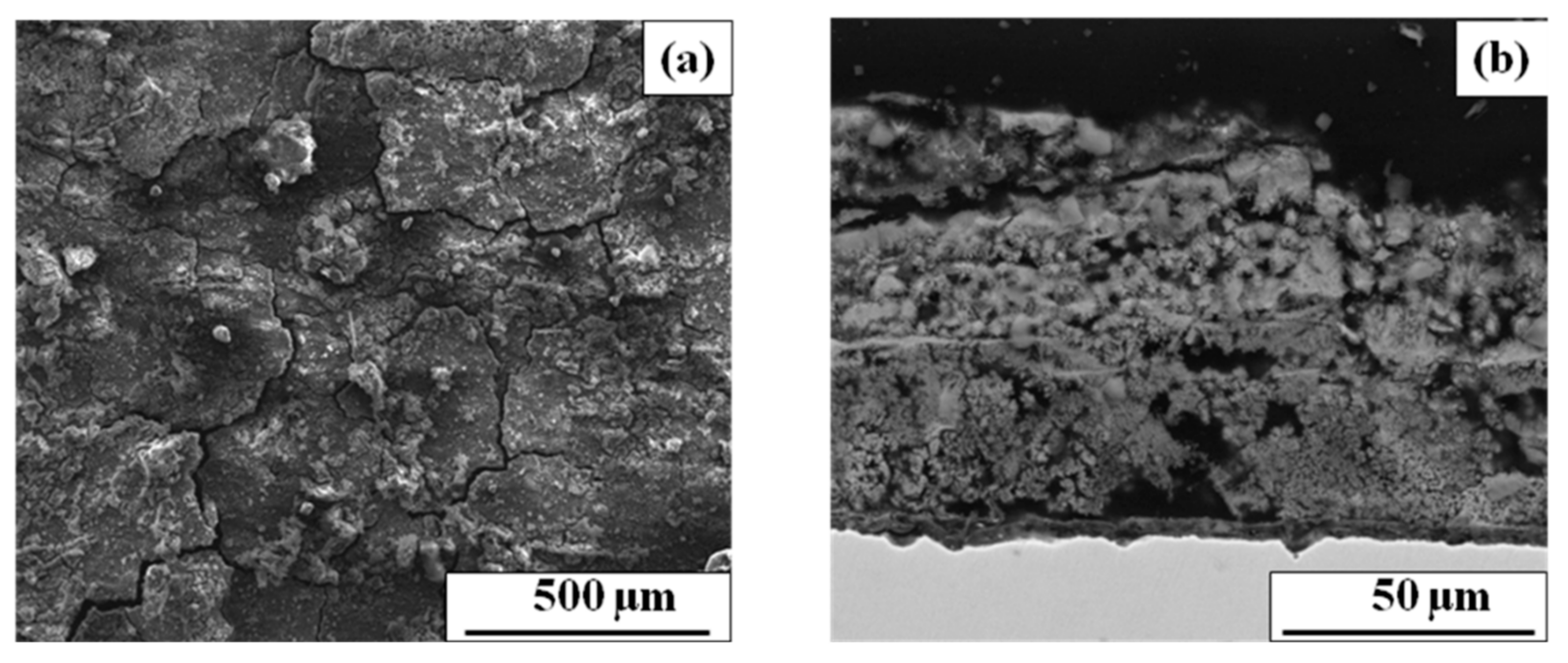
3.2.2. The Effect of Rust Morphology
3.2.3. Adhesion Strength Failure Analysis
3.2.4. Influence of pH and Phosphate Radical on Adhesion Strength
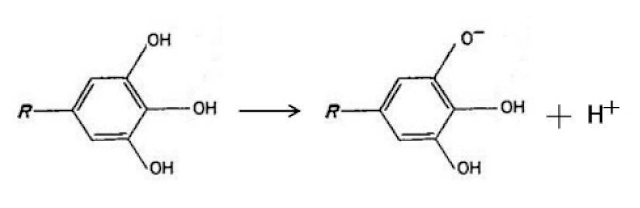

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croll, S. Surface roughness profile and its effect on coating adhesion and corrosion protection: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 148, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.D.D.; Bhattacharya, D. Performance and mechanism of action of self-priming organic coating on oxide covered steel surface. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 68, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, N.S.; del Amo, B.; Carbonari, O.R.; di Sarli, R.A.; Romagnoli, R. Painting rusted steel: The role of aluminum phosphosilicate. Corros. Sci. 2013, 74, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.; Pereira, D.; Figueiredo, M.O.; Lobo, V.M.M.; Morcillo, M. The influence of the interfacial conditions on rust conversion by phosphoric acid. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, L.M.; Margarit, I.C.P.; Mattos, O.R.; Cordoba-de-Torresi, S.I.; Fragata, F.L. Performance of rust converter based in phosphoric and tannic acids. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrazadan, S. The application of infrared spectroscopy to a study of phosphoric and tannic acids interactions with magnetite (Fe3O4), goethite (α-FeOOH) and lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH). Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1845–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazo, A.; Novoa, X.R.; Perez, C.; Puga, B. EIS study of the rust converter effectiveness under different conditions. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7565–7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S. Progress in rust converters. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ge, S.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z. Synthesis of 3,4,5-trihydroxy-2-[(hydroxyimino) methyl] benzoic acid as a novel rust converter. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2017, 10, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Fan, Z.B.; Li, X.G.; Jiang, B.; Yan, F.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.M. Improved anti-corrosion performance of epoxy zinc rich coating on rusted steel surface with aluminum triphosphate as rust converter. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 135, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, C.A.; Ocampo, L.M.; Arroyave, C.E. Possible improvements in the action of some rust converters. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, F.; Barrero, C.A.; Minotas, J.; Morales, A.L.; Greneche, J.M. Variable temperature mössbauer study of some rust converters. Hyperfine Interact. 2003, 148, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazo, A.; Novoa, X.R.; Perez, C.; Puga, B. The corrosion protection mechanism of rust converters: An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6156–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, G.; Smeltzer, W.; Droguett, G. Comparison of steel anticorrosive protection formulated with natural tannins extracted from acacia and from pine bark. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaén, J.A.; Araúz, E.Y.; Iglesias, J.; Delgado, Y. Reactivity of tannic acid with common corrosion products and its inflfluences on the hydrolysis of iron in alkaline solutions. Hyperfine Interact. 2003, 148, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.K.; Francis, R.A. The treatment of rusted steel with mimosa tannin. Corros. Sci. 1978, 18, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Bobrowicz, J. Sealing and anti-corrosive action of tannin rust converters. Corrosion 1993, 49, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.M.; Yuan, P.Y. Corrosion protection mechanism of aluminum triphosphate modified by organic acids as a rust converter. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.D.N.; Yadav, S. Role of tannic acid based rust converter on formation of passive film on zinc rich coating exposed in simulated concrete pore solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 1526–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, C.A.; Rios, J.F.; Morales, A.L.; Bohorquez, A.; Perez-Alcazar, G. On the analysis of the mössbauer spectra of the rust converted by tannic and phosphoric acids. Hyperfine Interact. 2003, 148, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Suwalski, J. Use of Mössbauer spectroscopy to study reaction products of polyphenols and iron compounds. Corrosion 1994, 50, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaén, J.A.; González, L.; Vargas, A.; Olave, G. Gallic acid, ellagic acid and pyrogallol reaction with metallic iron. Hyperfine Interact. 2003, 148, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, A.N.; Tripathi, R.P.; Dhoot, K. The effect of phosphoric acid on rust studied by mössbauer spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 1990, 30, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhao, X. High performance rust converter with a formula based on poly phosphoric acid and tannic acid. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 150, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, G.; Smeltzer, W.; Droguett, G. Use of tannin anticorrosive reaction primer to improve traditional coating systems. Corrosion 1994, 50, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Ge, S.S.; Wang, J.X.; Du, H.Y.; Song, K.N.; Fei, Z.Y.; Shao, Q.; Guo, Z.H. Water-based rust converter and its polymer composites for surface anticorrosion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.A.; Rocca, E.; Steinmetz, J.; Kassim, M.J. Inhibitive action of mangrove tannins and phosphoric acid on pre-rusted steel via electrochemical methods. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.T.; Zhang, B.; Lei, B.; Li, Y. Enhancement the adhesion between epoxy coating and rusted structural steel by tannic acid treatment. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2014, 27, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8501-1. Preparation of Steel Substrates before Application Of Paints and Related Products—Visual Assessment Cleanliness—Part 1: Rust Grades and Preparation Grades of Uncoated Steel Substrates and Of Steel Substrates after Overall Removal of Previous Coatings; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- ASTM B117-95. Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996; Volume 03.02.
- ISO 2808. Paints and Varnishes-Determination of Film Thickness, Classication; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- ISO 4624-2002. Paints and Varnishes—Pull-Off Test for Adhesion; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Díaz, I.; Chico, B.; de la Fuente, D.; Simancas, J.; Vega, J.M.; Morcillo, M. Corrosion resistance of new epoxy–siloxane hybrid coatings: A laboratory study. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 69, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.; Kuban, B.; Razvan, A. The application of infrared spectroscopy to the study of atmospheric rust systems—I. Standard spectra and illustrative applications to identify rust phases in natural atmospheric corrosion products. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.; de Saldana, E.G.; Jaen, J.A. On the tannic acid Interaction with metallic iron. Hyperfine Interact. 2001, 134, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J. Application of infrared spectroscopy for investigation of rust phase component conversion by agents containing oak tannin and phosphoric acid. Corrosion 1991, 47, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.C.; Mcenaney, B. The inflfluence of dissolved oxygen concentration on the corrosion of grey cast iron in water at 50 °C. Corros. Sci. 1979, 19, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Lu, M.S.; Huang, H.M.; Chang, F.C. Chemical reactions, thermal and mechanical properties of epoxy—Polycarbonate blends cured with aromatic amines. J. Polym. Res. 1996, 3, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.T. Precipitation and dissolution of iron and manganese oxides. Environ. Catal. 2005, 1, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.H. Studies on mathematical models of wet adhesion and lifetime prediction of organic coating/steel by grey system theory. Materials 2017, 10, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Element | C | S | P | Mn | Si | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 0.176 | 0.023 | 0.019 | 0.570 | 0.233 | 0.033 | Balance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Lei, B.; Guo, X. Influence of Phosphoric Acid on the Adhesion Strength between Rusted Steel and Epoxy Coating. Coatings 2021, 11, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020246
Li Y, Lei B, Guo X. Influence of Phosphoric Acid on the Adhesion Strength between Rusted Steel and Epoxy Coating. Coatings. 2021; 11(2):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020246
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yang, Bing Lei, and Xuqiang Guo. 2021. "Influence of Phosphoric Acid on the Adhesion Strength between Rusted Steel and Epoxy Coating" Coatings 11, no. 2: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020246
APA StyleLi, Y., Lei, B., & Guo, X. (2021). Influence of Phosphoric Acid on the Adhesion Strength between Rusted Steel and Epoxy Coating. Coatings, 11(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11020246






