Abstract
One of the methods of obtaining reduced graphene oxide (rGO) involves the oxidation of graphite to graphene oxide, which is then exfoliated and reduced. Each of these stages has a decisive influence on the properties of the produced nanoadditive, which determines its subsequent application. The process conditions which are examined during the oxidation stage are related to: The mixing time of the reactants before oxidation, sonication of the reaction mixture, and its composition. During reduction optimization, in turn, the form of the GO sample and the method of its purification, as well as the temperature at which this process took place, are examined. At each stage, the determined structural parameters of the produced materials (GO and rGO) are related to their morphology (SEM—scanning electron microscope), oxidation state (FTIR—Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, EDS—energy-dispersive spectrometer), structure defect (Raman spectroscopy), as well as the number of layers and crystalline structure (WAXS—wide-angle X-ray scattering). The obtained results show that the shorter mixing time of the reactants determines the formation of more oxygen functional groups. On the basis of the obtained results, the process conditions that enable the production of multilayer, well-exfoliated reduced graphene oxide, with only a slightly defected structure, are established.
1. Introduction
Although attempts to develop an effective method of obtaining graphene have been going on for many years, its mass production is still a major challenge [1,2]. The development of graphene production technology proceeds in two ways, and the main difference between the existing methods is the raw material from which it is produced. In bottom-up methods, carbon-containing chemical compounds, such as hydrocarbons or silicon carbide, are used as the starting material. Top-down methods, on the other hand, are based on the production of graphene from graphite [3,4,5]. One of the most promising ways to produce graphene from graphite is chemical exfoliation. In this method, in the initial phase, graphite is oxidized with strong oxidizing agents, which leads to the production of graphene oxide (GO). This product can be treated both as an end product, but also as an intermediate product from which the reduced graphene oxide is obtained by reduction. This process is currently regarded as one of the most promising methods of mass production of graphene (rGO—reduced graphene oxide) [6,7,8]. Depending on the oxidizing agents used, several paths leading to obtaining graphene oxide can be distinguished. The most popular oxidation processes include the methods described by Brodie (1859), Staudenmaier (1898), and Hummers (1958) [3,9]. In the graphite oxidation procedure described by Hummers and Offeman [10], the reaction mixture consisted of: Concentrated sulfuric acid, potassium permanganate, and sodium nitrate. The total oxidation reaction time was only a few hours, which was a great simplification compared to previous graphite oxidizing methods. Although this process has been widely used to this day, it also has its weaknesses, which have resulted in constant attempts to develop a new, safer, more efficient, and more ecological process for obtaining graphene oxide [11,12,13,14,15].
Marcano et al. [12] proposed an improved procedure, based on the Hummers method, that involves the use of KMnO4 and a mixture of sulfuric and phosphoric acid (H3PO4). As the authors assure, by introducing these modifications, it is possible to obtain well-oxidized graphene oxide with better hydrophilic properties. Although the method of GO production proposed by D.C. Marcano is more efficient than the classic Hummers method, the reaction requires the use of more reagents, and new reagents in the form of phosphoric acid are introduced, which may make it difficult to purify the graphene oxide. Guerrero-Contreras et al. [13] used the same reagents as the ones proposed by Hummers. They investigated the effect of different proportions of added oxidizing agents and different mixing times of the reagents on the properties of the obtained GO. The authors showed that by selecting these parameters, it is possible to obtain graphene oxide oxidized to a different degree. In 2016, another publication describing the modifications to the Hummers method appeared [14]. First of all, potassium ferrate was used as a new additional oxidizing agent. It has strong oxidizing properties, and at the same time, it is harmless to the environment, compared to other compounds used in various oxidation processes. The second oxidant (KMnO4) is added twice in this process, ensuring the formation of more oxygen functional groups in GO. It is also important that the volume of sulfuric acid has been significantly reduced compared to previous methods. This is particularly important from an ecological point of view and may make this method very competitive in the future.
To obtain rGO, it is necessary to reduce the previously prepared graphene oxide. This process can be carried out in many ways depending on the reducing agent used [16,17,18,19]. One of the methods is chemical reduction using such reducing agents as hydroquinone [20], NaBH4 [21], hydrazine and its derivatives [22,23]. There are also numerous attempts to carry out chemical reduction with the use of “environmentally-friendly” reducers, such as carrot root [24], tea [25], Lycium barbarum extract [26], or chrysanthemum extract [27]. However, a method that does not require the use of any additional compounds is thermal reduction. The reasons why it can be used in the mass production of graphene certainly include a relatively short process time, no compounds that could introduce heteroatomic impurities, and the lack of solvents that need to be removed after the reduction [28].
The most important parameter in thermal reduction is selecting the appropriate temperature, which will allow, to a large extent, the removal of oxygen functional groups. The first thermal reduction described in detail consisted of rapid heating of GO in an argon atmosphere to a temperature of 1050 °C [29]. In 2007, another publication by the same research group appeared in which they proposed a thermal reduction mechanism [30]. Based on the conducted experiments and theoretical calculations, they suggested that the minimum temperature required for the reduction and exfoliation of graphene oxide must exceed 550 °C. However, a process carried out continuously at such a high temperature generates high energy consumption [31]. For this reason, other solutions that would enable the implementation of the thermal reduction in milder conditions were sought.
As proved by Lv et al. [32], obtaining multilayer graphene by thermal reduction is possible even at 200 °C. To effectively remove oxygen functional groups and exfoliate the graphene layers at such a low temperature, they carried out the reduction process under reduced pressure. In high-temperature reduction, the exfoliation of the layers occurs as a result of the pressure generated by the release of gases. The use of a high vacuum (<1 Pa) causes it to act as an additional driving force that helps to expand the graphene layers. The vacuum used in this process, despite the low reduction temperature, resulted in a well-developed specific surface and high electrochemical capacity of the obtained graphene. H. Yang et al. [33] conducted a similar experiment in which they were able to obtain graphene with excellent electrical properties at a temperature of only ~150 °C.
The use of a high vacuum is not the only factor that may lower the reduction temperature of graphene oxide. Kaniyoor et al. [34] proved that conducting the process in the presence of hydrogen not only lowers down the reduction temperature (even to 200 °C), but also facilitates the exfoliation of graphene layers. As the authors suggest, the reduction mechanism in the presence of the gas is based on a rapid reaction of H2 with hydroxyl groups during which water vapor is formed. This reaction is highly exothermic and provides energy sufficient to overcome the weak van der Waals forces, thus ensuring effective exfoliation of the graphene layers.
In addition to temperature, which is a key element determining the removal of oxygen functional groups, other additional factors that will ensure appropriate reduction-exfoliation can also be used in this method. The use of microwave radiation or plasma treatment creates conditions that facilitate rapid heating, because graphene oxide can adsorb heat from these sources, quickly providing sufficient energy for the decomposition of oxygen functional groups [28].
As previously mentioned, through the action of the elevated temperature, oxygen functional groups are removed from the graphene oxide in the form of gaseous products that ensure the exfoliation of the graphene layers. If the pressure they generate is sufficiently high, then the thermal reduction can be rapid, and can take place in the form of micro-explosions. Such an approach to the process was presented in the articles by Qiu et al. [35] and Sun et al. [36], who compared the exfoliation of graphene oxide to the production of popcorn.
Detailed understanding of the oxidation and reduction processes obtains graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide is very important from both the academic and industrial point of view. Many parameters of the preparation process, i.e., reaction time, type of oxidizing agent, the proportion of reagents, size of graphite [13,37], affect the properties of resulting GO and rGO, which in turn determine their application. This paper presents the effect of the conditions applied under oxidation and reduction on the morphology, structure, and selected properties of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Based on our best knowledge, the parameters of the oxidation process analyzed in this paper have not been considered simultaneously. Furthermore, we have made an attempt to determine whether the structure of the previously obtained GO affects the process of thermal reduction and the structure of rGO.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The reagents employed during the oxidation, i.e., 98% H2SO4, KMnO4, 30% H2O2, 35–38% HCl and NaNO3 were supplied by Chempur S.A. (Piekary Śląskie, Poland) and used as received, without further purification. Graphite powder <20 μm was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Poznań, Poland).
2.2. Methods
Morphology of the samples was observed using the FEI Tecnai G2 20 X-TWIN transmission electron microscope (TEM, Hillsboro, OR, USA) and using the JEOL JSM 5500LV (Tokyo, Japan) scanning electron microscope (SEM). Before the images were obtained, all samples were coated with ~10 nm of gold at 30 mA using Leica EM ACE200 sputter coater (Wetzlar, Niemcy, Poland).
Phenom ProX scanning microscope equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS) was used to analyze the chemical composition of the obtained graphene oxides and reduced graphene oxides. The measurements were taken at a voltage of 15 kV. Three analyses were made for each sample and average values were calculated out of these.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) measurements were taken using Nicolet 6700 FT-IR spectrometer (Thermo Electron Corp., Madison, WI, USA) equipped with an MTEC model 300 photoacoustic accessory (MTEC Photoacoustics, Inc., Ames, IA, USA). The following measurement parameters were used: Resolution, 8 cm−1; spectral range, 500–4000 cm−1; deuterated triglycine sulfate (DTGS) detector; number of scans, 64. Data collection and post-processing were performed using OMNIC software (v. 8.0, Thermo Electron Corp, Madison, WI, USA).
The bulk density determination was performed on the basis of the BN-79/6048-02-06 [38] industry standard. The test consisted of placing a funnel on the tripod, under which the measuring cylinder of specific dimensions, previously weighed on the analytical balance, was placed. The distance from the lower edge of the outlet of the funnel to the upper edge of the cylinder was approximately 50 mm. The prepared sample was poured through the funnel into the measuring cylinder until a cone was formed above it. Using a smooth strip tool, the surface of the sample in the cylinder was leveled and then weighed on the analytical balance. For each obtained reduced graphene oxide, three tests were made from which the average bulk density values were calculated.
Wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) analyses were carried out using a URD 63 Seifert diffractometer (Rich. Seifert & Co. Röntgenwertk, Ahrensburg, Germany). CuKα radiation at an accelerating voltage of 40 kV and an anode current intensity of 30 mA was used. Measurements were performed in the range of angles from 5° to 55°, with increments of 0.1° for a range of 5°–38° and 0.05° for a range of 38.05°–55°. The d-spacings of samples were determined using Bragg’s Equation:
where n is an integer, λ is the wavelength, d is the interlayer spacing, and θ is the scattering angle. The number of layers was determined using the following equation:
where D is the size of crystallites, d is the interlayer distance, and N is the average number of sheets. The WAXS diffraction curves of the samples were deconvoluted using the WAXSFIT profile fitting program (v.2018) [39].
nλ = 2d × sin θ
N = D/d + 1
The thermal properties were characterized using a thermogravimeter (TGA Q500 V20.10 Build 36, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). The measurements were carried out at a temperature range of 30–800 °C and a heating rate of 20 °C/min in nitrogen gas (flow rate of 60 mL/min).
The Raman spectra of the samples were measured using Witec Raman Alpha M300+ (Ulm, Germany) with a 532 nm Nd-YAG laser for excitation, at 1 mW over 400 accumulations with an integration time of 2 s.
2.3. Preparation of Samples
2.3.1. Graphene Oxide
Graphene oxides were prepared using the method in which the following three parameters were changed: Mixing time of the reagents before adding the oxidizing agent, sonication of the reaction mixture before starting the oxidation process, and addition of sodium nitrate. The conditions under which individual samples were obtained are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Conditions for the graphite oxidation process.
Regardless of the method used to obtain graphene oxide, the proportions of the reactants remained the same and were the following: 30 g of graphite, 750 cm3 of sulfuric acid, 90 g of potassium permanganate, and in some cases, 15 g of sodium nitrate. A detailed description of the preparation of graphene oxides is provided in the Supplementary Materials (Part 1).
2.3.2. Reduction of Graphene Oxides
The prepared graphene oxides (both those that have been neutralized and those that have been treated with hydrochloric acid) were thermally reduced by micro-explosion. For this purpose, 4 g of partially dried GO was placed in a thermal reduction chamber that was blown with an inert gas (nitrogen). The graphene oxide in the chamber was heated at a rate of approximately 30 °C/min, until micro-explosion occurred. The thermal reduction was carried out until the process ceased to take place in a rapid way (the maximum temperature of the process did not exceed 300 °C). For each of the obtained graphene oxides, the procedure described above was repeated five times, yielding rGO1–8 samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Graphene Oxide
The visual effect confirming obtaining graphene oxide during the oxidation reaction is the change in the color of the reaction mixture from grey to yellow-brown, which is related to the disturbance of the coupled electron systems π in the graphite structure. To assess the degree of graphite oxidation, however, it is necessary to perform tests to confirm the obtained chemical structure, e.g., using infrared spectroscopy. Accurate interpretation of GO FTIR spectra is difficult, due to the variety of functional groups that may be formed during oxidation. In the FTIR spectra, some characteristic band ranges for selected oxygen functional groups can be distinguished. Figure 1 presents the FTIR spectra for graphite and graphene oxides. For all GOs, the characteristic area is a wide band at the wavenumbers of 3700–2200 cm−1, which corresponds to the stretching vibrations in O–H bonds in hydroxyl groups [40]. The next band with its maximum at the wavenumber of ~1740 cm−1 comes from the stretching vibrations in the C=O bond occurring, among others, in aldehyde, ketone, carboxyl, and ester functional groups. A clear band in the range of 1680–1510 cm−1 indicates the presence of skeletal vibrations causing stretching of C=C double bonds in aromatic structures. For wavenumbers below 1500 cm−1 the so-called fingerprint region is present. For graphene oxides, it is precisely because of the possibility of the formation of many different oxygen groups that the overlapping of many bands is observed in this area. Among them, the ones that can certainly be distinguished are bands corresponding to: C–O stretching vibrations in carboxyl groups (~1420 cm−1); O-H scissor vibrations in the CO–H plane (~1410 cm−1); C–O stretching vibrations in epoxy groups (1250 cm−1); C–O stretching vibrations in the C–OH plane (~1070 cm−1); C-C stretching vibrations (~1070 cm−1); as well as C–O–C deformation vibrations in epoxy groups (~850 cm−1) [6,40].
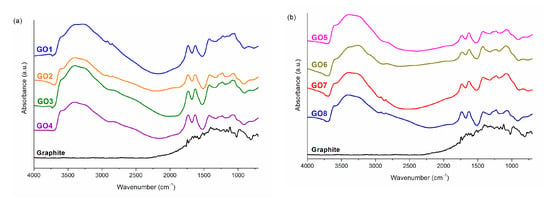
Figure 1.
(a) FTIR spectra of graphite and GO1–4; (b) FTIR spectra of graphite and GO5–8.
Comparing the FTIR spectra for graphite and for the obtained graphene oxides, it can be noticed that the application of the conditions described in Table 1 enabled effective oxidization of graphite to GO. This is evidenced by numerous bands derived from oxygen functional groups. To determine the influence of the methods of GO preparation on the degree of its oxidation, the ratio of the area of the absorption bands for two characteristic and distinct bands was calculated using the integration method. One of the bands is the band of vibrations that occur in carbonyl groups (C=O), while the other corresponds to skeletal vibrations (C=C). The determined values of are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
ratio calculated for obtained graphene oxides and C/O ratio in the obtained graphene oxides determined based EDS analysis.
As can be seen in Table 2, the use of different conditions in the preparation of GO results in samples that are oxidized to a different degree (taking into account the carbonyl groups). As shown by many studies, carbonyl groups (including aldehyde, ketone, carboxyl, and ester ones) are located at the edges of graphene layers, while hydroxyl and epoxy groups are placed in the plane of layers [18,41]. The differences in the calculated ratios may be related to the fact that the longer mixing of the reactants before the oxidation begins, results in better intercalation of H2SO4, which in turn may facilitate the formation of oxygen functional groups located in the plane of the layers. The penetration of sulfuric acid between the graphene layers in a shorter time, after adding the oxidant, probably results in the carbonyl groups on the edges of the layers being formed much easier than in the case of longer mixing. The result of this is the ratio being lower for the GO5–8 samples.
The obtained graphene oxides were also tested using EDS analysis to determine their atomic concentration (Table S1). The main elements identified for graphene oxides are carbon and oxygen. No sodium, nitrogen, manganese, and potassium was identified in any of the tested samples, though, which means that complete removal of sodium nitrate and unreacted potassium permanganate was possible during the purification. On the basis of the obtained results, the ratio of the atomic fraction of carbon to oxygen was calculated for all the prepared GO samples (Table 2). The lowest C/O ratio was calculated for GO1, GO3, and GO8, which means that these samples have the most oxygen atoms in their structure. GO6, on the other hand, turned out to be the least oxidized sample. As can be seen in Table 2, in the case of GO1–4 samples, the determined C/O ratio is lower than for other graphene oxides (GO1–4 have more oxygen atoms in their structure). The common feature of these samples is that before starting the oxidation process, the graphite was mixed with sulfuric acid for only 1 h, and not 24 h, as was the case with samples GO5–8. The obtained results are, therefore, a confirmation of infrared studies, which showed that GO1–4 have more stable oxygen functional groups.
Figure 2 shows Raman spectra for graphite and for graphene oxides obtained using various methods.
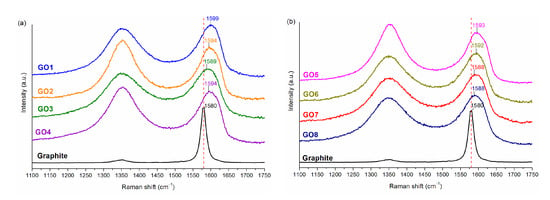
Figure 2.
(a) Raman spectra for graphite and for GO1–4; (b) Raman spectra for graphite and for GO5–8.
For graphite in the presented range (1100–1750 cm−1), two bands characteristic for carbon structures are visible: An intense G band (~1580 cm−1) and a low intensity D band (~1350 cm−1). Regardless of the oxidation method used, the D-band intensity of the GO samples increased significantly. The presence of this band is closely related to the disordering of the structure resulting from defects that may occur in the planes of the graphene layers. Oxidation of graphite causes the formation of oxygen functional groups both in the plane and at the edges of its layers, which contributes to the formation of defects resulting from the change in hybridization from sp2 into sp3 for some carbon atoms [42,43]. Moreover, in the G-band, differences resulting from the conducted oxidation process can be observed. The positions of this band for graphite and GO1–8 are shown in Figure 2. In the case of samples that were mixed for an hour prior to oxidation, the maximum of the G peak is shifted towards a higher wavenumber than in the case of the samples mixed for 24h. The research group of K. Krishnamoorthy et al. [44] proved that the position of the G band is shifted towards higher wavenumbers with the increase in the degree of oxidation. This would mean that the GO1–4 samples had more oxygen functional groups in their structure than the GO5–8 samples. These results confirm the previous conclusions drawn based on infrared spectroscopy and EDS analysis.
On the diffraction patterns in Figure 3, the results for graphite and graphene oxides obtained by various methods are presented.
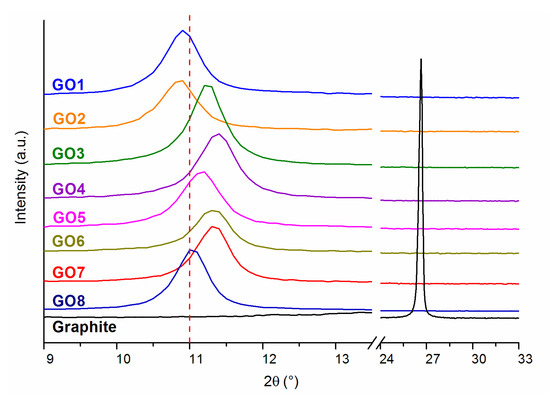
Figure 3.
WAXS patterns for graphite and for graphene oxides obtained using various methods.
Graphite is characterized by an ordered crystalline structure, which is described in the X-ray diffraction pattern by a sharp peak appearing at the scattering angle 2θ = 26.5°, while the distance between the graphene layers is 0.33 nm. The oxidation process disrupted this structure, causing the peak to shift to 2θ in the range of 10.85° to 11.38°, depending on the oxidation conditions applied. Based on Bragg’s law, for individual graphene oxides, interplanar distances were determined, the values of which are presented in Table 3. The shift of the peak towards lower values of the scattering angle 2θ proves a very good exfoliation that occurred as a result of the appearance of oxygen functional groups between the graphene layers in GO [45].

Table 3.
Data obtained from X-ray examinations of the size of crystallites, the number of graphene layers in graphite and graphene oxides, as well as the distance between them.
The consequence of the oxidation process is also a change in the size of the crystallites. The use of a strong oxidant, as well as sonication in some cases, resulted in a significant reduction in the size of crystallites, which is also shown in Table 3. Among the obtained graphene oxides, the largest crystallites, and thus, the largest number of graphene layers, were observed for GO3 and GO8. During the oxidation of these samples, neither sonication nor the addition of NaNO3 was used, which probably contributed to this result.
Following the exfoliation, the number of layers in the obtained graphene oxides, compared to graphite, was significantly reduced, as calculated from the following relationship [46]. Data in Table 3 show that the oxidation reaction, regardless of the conditions, resulted in an approximately five-fold reduction in layers compared to the original graphite. GO5 was determined to have the lowest number of layers. This sample, prior to the addition of the oxidizing agent, was mixed for 24 h, and then it was obtained using both sonication and NaNO3 addition. The simultaneous application of all these parameters resulted in the greatest exfoliation of this sample.
3.2. Reduced Graphene Oxide
During the preparation of the rGO, the thermal reduction was not carried out at a strictly defined temperature, but the effort was made to reduce each sample by micro-explosion. Figure 4a shows a diagram of the initial reduction temperatures for individual graphene oxides, i.e., the temperatures at which this process began to take place rapidly.
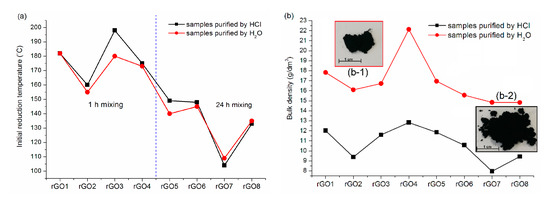
Figure 4.
(a) Diagram of the initial reduction temperatures for individual graphene oxides; (b) diagram of the bulk density determined for graphene oxides neutralized or purified with hydrochloric acid; (b-1) picture of rGO purified by H2O; (b-2) picture of rGO purified by HCl.
In all cases, regardless of whether the GO sample was neutralized or purified with hydrochloric acid, the reduction started below 200 °C. As previously mentioned, the phenomenon of micro-explosions is related primarily to the removal of oxygen functional groups from graphene planes, which generate sufficiently high pressure. The thermogravimetric analysis carried out for graphene oxide shows that in the temperature range of 120–350 °C, there is a rapid loss of mass, which is attributed to the release of less stable oxygen functional groups [47]. The fact that the reduction of the prepared GO happened at the lower end of this range may be related to the form of the samples that were reduced. It should be remembered that GO1–8 contained up to 70% of water, which probably caused the adsorbed water, heated rapidly, to contribute significantly to the violent process flow. For comparison, a reduction of the completely dried GO sample was also performed. Although, in this case, the reduction also took place using micro-explosions, there were some differences between the two processes. The reduction of dried graphene oxide started at a much lower temperature than for the samples in the form of a paste. The phenomenon of micro-explosions was already observed at 100 °C, and the whole process lasted only a few minutes, during which the temperature increased only to 150 °C. Another difference, visible after the reduction was completed, was the form in which the samples were obtained. In the case of rGO prepared from wet graphene oxide, a black, “fluffy” powder was obtained, while in the case of dried GO, some graphene was in the form of a powder and some in the form of hard lumps (Figures S1 and S2). This means that the thermal reduction of partially dried graphene oxide obtain a homogeneous sample in the form of a powder, while a higher temperature causes more efficient removal of oxygen functional groups.
Analyzing the data presented in Figure 4a, it can also be noticed that the initial reduction temperatures of samples, both neutralized and treated with hydrochloric acid, are similar for individual graphene oxides. This means that HCl did not act as an additional factor that significantly influenced the thermal reduction temperature. Nevertheless, its use during the production process significantly simplifies and shortens the step associated with the purification of graphene oxide. Typically, after obtaining graphene oxide, unwanted ions present in the reaction mixture are removed by neutralization with distilled water in the process of filtration or centrifugation. However, these processes are very time-consuming because the produced GO increases its volume and forms a stable colloidal system when the mixture is neutralized. For this reason, the time required for filtration or centrifugation is extended. The use of hydrochloric acid during the purification of graphene oxide disturbs the stability of the water dispersion formed. As a result, as unwanted ions are removed, GO retains its original volume and the ability to sediment rapidly at all times. By introducing this relatively inexpensive reagent into the purification, the process is greatly simplified, and the time needed to remove impurities is reduced.
Conducting thermal reduction using micro-explosion resulted in obtaining rGO in the form of light and fluffy powder. For this reason, it was decided to determine the bulk density, the results being presented in Figure 4b. Initially, the bulk density was determined for the graphite from which rGO was obtained. The value for this material was 241 g/dm3, which is fifteen times more than for the reduced forms. As shown in Figure 4b, acid-treated samples have 1.5 times lower bulk density than samples treated with water only. Although the acid used did not significantly affect the temperature at which the micro-explosion took place, it plays a significant role in forming graphene with a more fluffy structure. When heating a GO sample that has not been neutralized, acid is not removed as quickly as water. This causes an increase in pressure between the layers, which is generated not only by the removed oxygen functional groups, but also by the released hydrogen chloride. In this case, it acts as an additional driving force aiding the exfoliation of the reduced sample [31]. Due to the results discussed above, the further part of the research concerns only rGO purified with HCl.
The reduction in the bulk density of graphene in relation to graphite may result, among others, from changes in morphology that can be observed with a scanning electron microscope. During the production of rGO in the oxidation-reduction process, at each stage, the layers in the starting material, i.e., graphite, are exfoliated. Figure 5a shows that it is a coarse-grained agglomerate powder which, as we know, consists of many graphene layers. Figure 5b displayed the smooth surface of GO with wrinkles and folded regions. These observations could be accounted for by the formation of oxygen-containing functional groups and various GO structural defects [48]. Due to the reduction by micro-explosion, the obtained rGO has a completely different morphology. The reduced graphene oxide, shown in Figure 5c,d, has a porous structure. The gases released during thermal reduction caused exfoliation accompanied by the formation of pores between the graphene layers [49]. However, the use of different conditions during the oxidation and reduction processes did not cause significant differences in the morphology of individual rGO samples. Nevertheless, in all cases, it was possible to obtain a porous product.
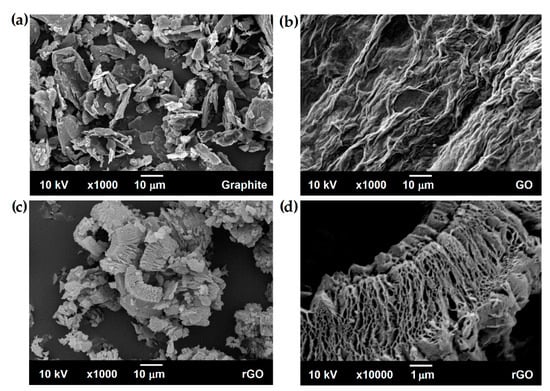
Figure 5.
SEM images: (a) graphite; (b) graphene oxide; (c,d) reduced graphene oxide.
Figure 6 shows an example of a diffractogram for graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. As a result of the thermal reduction, the peak characteristic of GO, which is located at 2θ ≅ 11° disappears, while a wide peak of low intensity appears at 2θ ≅ 24°. This shift is related to the reduction of the interplanar distance in the obtained reduced graphene oxide from ~0.8 nm (for GO) to ~0.37 nm, which occurred due to the removal of oxygen functional groups [50]. The wide rGO peak proves that much fewer crystalline regions can be observed in this structure than in graphite or even in graphene oxide [51]. This is because the reduction does not restore the graphite structure, and the random and disordered restoration of the layered structure results in the presence of much smaller crystallites.
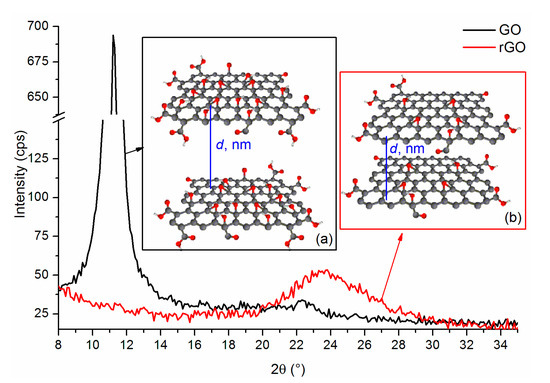
Figure 6.
WAXS patterns for (a) graphene oxide and for (b) reduced graphene oxide.
The process of thermal reduction of graphene oxides prepared using various methods contributed to obtaining rGO with crystallites of much smaller sizes (Table 4). The smallest sizes of crystallites were obtained for rGO3, the oxide of which was obtained without the use of sonication and addition of NaNO3. As shown in Figure 4a, the reduction of this sample started at the highest temperature among all graphene oxides. A micro-explosion at a temperature close to 200 °C probably contributed to such a significant, as much as 10-fold, reduction in the size of crystallites in the obtained reduced graphene oxide. The opposite situation can be observed for rGO7, in the case of which the presence of the largest crystallites may also be related to the reduction temperature. If the micro-explosion occurs at too low a temperature, it may lead to the formation of an insufficient amount of gas that could ensure effective exfoliation. Then, the crystalline regions present in the graphene oxide structure are not exfoliated to the appropriate degree, which in turn leads to obtaining reduced graphene oxide with a greater number of layers. Therefore, to confirm the effective exfoliation of the obtained rGOs, the number of layers for each of the samples was calculated. The layered nature of rGOs was also confirmed by TEM and HRTEM (high-resolution TEM) images (Figure S3).The rGO with the highest number of layers was the one whose oxide was obtained using Method 7, which, as explained earlier, may be due to a too low reduction temperature.

Table 4.
Data obtained from X-ray examinations of the size of crystallites, the number of graphene layers in rGO, as well as the distance between them.
Figure 7a shows the FTIR spectra for graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxides. For rGOs obtained in thermal reduction, as compared to the GO spectrum, almost complete disappearance of two characteristic bands is observed, one of which comes from hydroxyl groups (2200–3700 cm−1), while the other one is assigned to vibrations in epoxy groups (at wavenumbers below 1500 cm−1). Obviously, the rGO spectrum shows distinct bands corresponding to vibrations of single and double carbon-carbon bonds present in carbon rings (for the wavenumbers 1070 cm−1 for C–C and 1600 cm−1 for C=C, respectively). Despite the reduction, apart from the bands mentioned above, there are also absorption bands attributed to vibrations occurring in carboxyl (~1290 cm−1) and carbonyl (~1748 cm−1) groups.
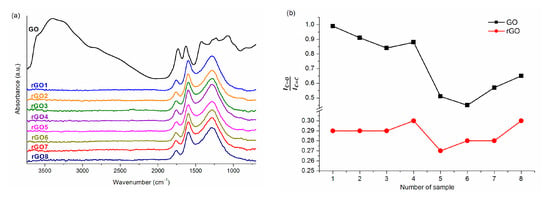
Figure 7.
(a) FTIR spectrum for graphene oxide and rGO1–8; (b) The ratio of the area of the carbonyl group bands to the double bond bands between carbon atoms in aromatic rings calculated using the integration method for graphene oxides and reduced graphene oxides.
During thermal reduction, not all oxygen functional groups are removed with the same ease. The extent to which GO is reduced depends not only on how many oxygen groups the oxide initially had, but also on what kind of groups they were. It is known that hydroxyl and epoxy groups are less stable and easier to remove than carbonyl or carboxyl groups [52]. This is perfectly visible in this case as well. Despite the thermal reduction, the spectrum still shows bands at ~1740 cm−1 and ~1290 cm−1, precisely corresponding to the carbonyl and carboxyl groups. For the rGO1–8 spectra, only slight differences can be observed between the individual samples. However, the degree of removal of the more stable oxygen functional groups (for carbonyl groups) discussed above was investigated. For this purpose, as for GO, the ratio of the area of bands was calculated using the integration method. Figure 7b presents all calculated values for both GO and rGO obtained. The thermal reduction resulted in a decrease in the calculated ratios in the studied samples. Regardless of their values before the reduction process, as a result of the process, they remained the same in virtually all rGO samples. Although different reduction temperatures were used for individual graphene oxides, it turned out that they are sufficient to partially remove, among others, carbonyl groups. On the other hand, the use of low-temperature thermal reduction does not allow the complete removal of the more stable oxygen functional groups, because ratio is approximately 0.29. It should also be remembered that the data presented in Figure 7b relate to the ratio calculated for C=O and C=C. Bands derived from C–O stretching vibrations in carboxyl groups (also referred to as stable functional groups) have been omitted from the considerations, due to the presence of this band in the fingerprint region where the overlapping of many other functional groups is observed.
EDS analysis was also performed for the reduced graphene oxides. The elements that make up the rGO structure include, obviously, carbon and oxygen, the atomic share of carbon in the tested samples being over 80%. The analyzed materials also did not contain atoms of chlorine, which was added in the graphene oxide purification process. Thus, hydrochloric acid is not only an important factor facilitating the removal of unwanted ions, but also is not a source of contamination in the obtained rGO. This means that the conditions both before and during low-temperature thermal reduction enabled the production of reduced graphene oxide devoid of any unnecessary elements. Table 5 shows the values of the atomic ratios of carbon to oxygen as calculated for all reduced graphene oxides.

Table 5.
The atomic ratios of carbon to oxygen for all reduced graphene oxides.
The reduced graphene oxides obtained using methods 1–4 are characterized by a slightly higher C/O ratio, which suggests that these samples were better reduced than the others (rGO5–8). Although their oxides had more oxygen atoms in their structure, the reduction process resulted in more effective removal of oxygen functional groups (Table S2). This phenomenon is certainly related to the temperature at which the reduction was carried out. As shown in Figure 4a, the mean initial process temperature for the GO1–4 samples was higher than for the GO5–8 samples. This difference evidently reduced graphene oxides obtained using methods 1–4 to have fewer oxygen atoms in their structure.
Figure 8 presents TGA curves for graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. In the case of rGO, the pronounced three-stage weight loss characteristic of graphene oxide is not observed. The first weight loss up to ~100 °C, which is attributed to the removal of adsorbed water, practically does not occur for rGO. Moreover, in the temperature range of 120–350 °C, when a large and rapid GO weight loss occurs, the TGA curve for reduced graphene oxide changes slightly, and the sample loses only a few percent of its weight. However, when analyzing the curve in the entire temperature range, it is visible that the thermally reduced graphene oxide still contains more stable oxygen functional groups, the loss of which is visible only above 500 °C.
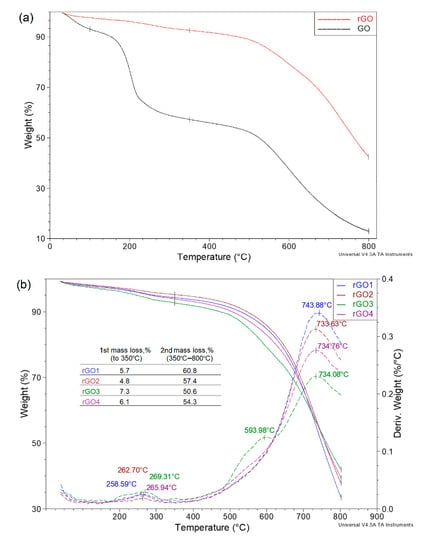
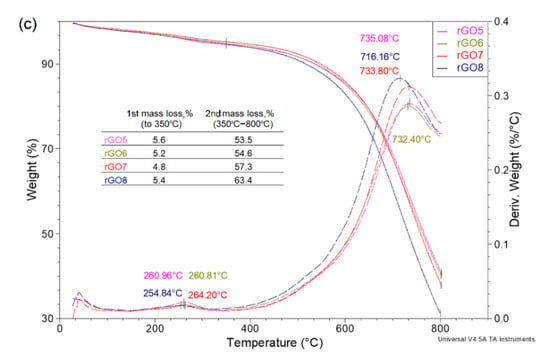
Figure 8.
(a) TGA curves for graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide; (b) TGA curves for rGO1–4; (c) TGA curves for rGO5–8.
Comparing the TGA curves of the rGO1–8 samples, it can be seen that in almost all cases, these curves follow a similar course (Figure 8b,c). The first weight loss, which was observed at ~270 °C, is related to the removal of less stable oxygen functional groups and is less than 8%. This means that low-temperature thermal reduction almost completely removed the hydroxyl and epoxy groups. The presented thermograms clearly show that, in fact, up to 500 °C, they obtained rGO samples are thermally stable. As demonstrated by the previously presented results, low-temperature thermal reduction does not ensure complete removal of oxygen functional groups, and their presence was also confirmed by thermogravimetric analysis. Above 700 °C, there is a rapid weight loss, which is comparable for most samples and amounts to approximately 60% of the weight.
The reduced graphene oxides were examined using Raman spectroscopy. As shown in Table 6, for rGO, the G-band is shifted towards lower wavenumbers (redshift) compared to the position recorded for the GO. Such a shift is described in the literature as “graphitic self-healing” and indicates partial restoration of the graphite structure [53]. However, the changes taking place during the oxidation and reduction reactions preclude the G-bands for graphite and rGO from overlapping completely. In addition, a distinct D-band is still visible for the reduced graphene oxides; the half-width and intensity of the band is as high or even higher than that for GO. The consequence of the D-band increase is obviously a change in ratio, the calculated values of which for all GO and rGO samples are presented in Table 6. The ratio of the intensity of D/G bands is a measure of the defects present on graphene structure. For most rGO samples, ratio exceeds 2, and this value is much higher than for GO1–8. This is because during the reduction, among others, carbon dioxide is removed, which causes the formation of further defects and vacancy defects in the graphene structure [54]. The smallest difference between graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide occurred in the case of the sample obtained using Method 3.

Table 6.
Raman shift G band and ratio for graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide.
4. Conclusions
The paper presents the effect of the oxidation and reduction process conditions on the structure and selected properties of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide.
In the oxidation process, the following conditions were checked: The reagents mixing time before adding the oxidizing agent, sonicating of the reaction mixture before starting the oxidation, and adding sodium nitrate. On the basis of the obtained results, it can be concluded that the graphene oxides in which the reactants were mixed for an hour before the oxidation started (GO1–4) had more oxygen atoms in their structure. Moreover, it can be specified that the oxygen present in these samples was present mainly in the form of carbonyl groups, which are usually located at the edges of the graphene layers. Furthermore, on the basis of the obtained results, no influence of NaNO3 and sonication on the degree of oxidation of GO samples was observed.
The observations made during the thermal reduction, as well as the comparison of the obtained rGOs, conclude that the water content in the reduced samples significantly affects the form of the final product. When the reduced graphene oxide was in the form of a paste containing up to 70% water, a homogeneous material in the form of fluffy powder was obtained. In addition, samples that contained up to 70% water were reduced by means of micro-explosions at higher temperatures, which resulted in more effective removal of oxygen functional groups. The use of hydrochloric acid not only facilitated the purification process of graphene oxide, but also conditioned the obtaining of rGO samples in the form of light powder with much lower bulk density. Graphene oxides that had more oxygen atoms in their structure (GO1–4) were reduced at a higher temperature, which in turn resulted in a more effective reduction of the corresponding rGOs.
The conclusion of X-ray studies is that the structural properties of reduced graphene oxides, such as the size of crystallites, were primarily influenced by the temperature at which the reduction took place. The smallest size of crystallites was determined in the rGO3 sample, for which the initial reduction temperature was the highest among all prepared reduced graphene oxides.
Of all the produced reduced graphene oxides, the rGO3 sample is certainly a noteworthy one. Graphene oxide prepared using Method 3 was characterized by a large size of crystallites and a high degree of oxidation. This sample was characterized by the greatest change in the supermolecular structure as a result of the thermal reduction. The micro-explosion, starting at a temperature close to 200 °C, resulted in a 10-fold reduction in the size of the crystallites in this sample. As a result of the efficient exfoliation of GO3 to rGO3, it was possible to reduce the number of layers from 23 to 6. What is important, however, is that despite such significant structural changes, the rGO3 sample was the least defected one, as evidenced by the results of Raman spectroscopy. Our previous research shows that the fewer defects present in the rGO structure, the better its electrical properties [46]. Moreover, Method 3 has a simplified procedure: Short mixing time, without sonication and NaNO3, which is important from an industrial point of view.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6412/11/2/166/s1, Figure S1: (a) Fluffy powder of reduced graphene oxide obtained from wet graphene oxide (top view); (b) lumps of reduced graphene oxide obtained from dried graphene oxide (top view), Figure S2: (a) Fluffy powder of reduced graphene oxide obtained from wet graphene oxide (front view); (b) lumps of reduced graphene oxide obtained from dried graphene oxide (front view), Figure S3: (a) TEM image and (b) HRTEM image of reduced graphene oxide (rGO3), Table S1: Elemental composition of graphene oxide samples, Table S2: Elemental composition of reduced graphene oxide samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.; methodology, M.S., C.Ś., and W.B.; validation, M.S.; investigation, M.S., C.Ś., and W.B.; resources, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, C.Ś., W.B., and R.F.; visualization, M.S.; supervision, R.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Novoselov, K.S.; Fal’Ko, V.I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P.R.; Schwab, M.G.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raccichini, R.; Varzi, A.; Passerini, S.; Scrosati, B. The role of graphene for electrochemical energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, D.P. Graphene oxide: Strategies for synthesis, reduction and frontier applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64993–65011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, T.; Wang, Y.; Hahn, Y.B. Graphene and its derivatives for solar cells application. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.T.; LaChance, A.M.; Zeng, S.; Liu, B.; Sun, L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide and their nanocomposites. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frogley, M.D.; Wang, C.; Cinque, G.; Barber, A.H. Polarised infrared microspectroscopy of edge-oriented graphene oxide papers. Vib. Spectrosc. 2014, 75, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadipelli, S.; Guo, Z.X. Graphene-based materials: Synthesis and gas sorption, storage and separation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 69, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.U.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C. Preliminary comparison of different reduction methods of graphene oxide. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.K.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, S.; Kim, S.; Yoon, D.H.; Yang, W.S. Facile synthesis of graphene oxide in a Couette-Taylor flow reactor. Carbon N. Y. 2015, 83, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of Graphitic Oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 208, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yao, B.; Li, C.; Shi, G. An improved Hummers method for eco-friendly synthesis of graphene oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 64, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Contreras, J.; Caballero-Briones, F. Graphene oxide powders with different oxidation degree, prepared by synthesis variations of the Hummers method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 153, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, B.; Bulin, C.; Li, R.; Xing, R. High-efficient synthesis of graphene oxide based on improved hummers method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Qiblawey, H.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.; Al-Ghouti, M. Synthesis of graphene oxides particle of high oxidation degree using a modified Hummers method. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 23997–24007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabchinskii, M.K.; Dideikin, A.T.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Baidakova, M.V.; Shnitov, V.V.; Roth, F.; Konyakhin, S.V.; Besedina, N.A.; Pavlov, S.I.; Kuricyn, R.A.; et al. Facile reduction of graphene oxide suspensions and films using glass wafers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evlashin, S.; Dyakonov, P.; Khmelnitsky, R.; Dagesyan, S.; Klokov, A.; Sharkov, A.; Timashev, P.; Minaeva, S.; Maslakov, K.; Svyakhovskiy, S.; et al. Controllable laser reduction of graphene oxide films for photoelectronic applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 28880–28887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.K.; Pumera, M. Chemical reduction of graphene oxide: A synthetic chemistry viewpoint. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.W.; Lai, C.W.; Abd Hamid, S.B. Controllable electrochemical synthesis of reduced graphene oxide thin-film constructed as efficient photoanode in dye-sensitized solar cells. Materials 2016, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Park, J.; Gou, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Yao, J. Facile synthesis and characterization of graphene nanosheets. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8192–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, K.K.; Benayad, A.; Yoon, S.M.; Park, H.K.; Jung, I.S.; Jin, M.H.; Jeong, H.K.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Efficient reduction of graphite oxide by sodium borohydride and its effect on electrical conductance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Piner, R.D.; Chen, X.; Wu, N.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Stable aqueous dispersions of graphitic nanoplatelets via the reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide in the presence of poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate). J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.B.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. A green approach for the reduction of graphene oxide by wild carrot root. Carbon N. Y. 2012, 50, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.X.; Yin, J. Facile synthesis of soluble graphene via a green reduction of graphene oxide in tea solution and its biocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Green reduction of graphene oxide via Lycium barbarum extract. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 246, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Li, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H. Chrysanthemum extract assisted green reduction of graphene oxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 183, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lv, W.; Xie, X.; Tang, D.; Liu, C.; Yang, Q.H. Towards low temperature thermal exfoliation of graphite oxide for graphene production. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 62, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniepp, H.C.; Li, J.; Mcallister, M.J.; Sai, H.; Herrera-alonso, M.; Adamson, D.H.; Prud, R.K.; Car, R.; Saville, D.A.; Aksay, I.A. Functionalized single graphene sheets derived from splitting graphite oxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 8535–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcallister, M.J.; Li, J.; Adamson, D.H.; Schniepp, H.C.; Abdala, A.A.; Liu, J.; Herrera-alonso, O.M.; Milius, D.L.; Car, R.; Prud, R.K.; et al. Single sheet functionalized graphene by oxidation and thermal expansion of graphite. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Lu, D.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, W. Synthesis of graphene by low-temperature exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide under ambient atmosphere. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Tang, D.M.; He, Y.B.; You, C.H.; Shi, Z.Q.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, C.M.; Hou, P.X.; Liu, C.; Yang, Q.H. Low-temperature exfoliated graphenes: Vacuum-promoted exfoliation and electrochemical energy storage. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3730–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Kannappan, S.; Pandian, A.S.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lu, W. Nanoporous graphene materials by lowerature vacuum-assisted thermal process for electrochemical energy storage. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniyoor, A.; Baby, T.T.; Ramaprabhu, S. Graphene synthesis via hydrogen induced low temperature exfoliation of graphite oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8467–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Guo, F.; Hurt, R.; Külaots, I. Explosive thermal reduction of graphene oxide-based materials: Mechanism and safety implications. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 72, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zheng, L.; Zhan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, L. Actuation triggered exfoliation of graphene oxide at low temperature for electrochemical capacitor applications. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 68, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas, C.; Álvarez, P.; Blanco, C.; Santamaría, R.; Granda, M.; Ares, P.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.; Menéndez, R. The effect of the parent graphite on the structure of graphene oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2012, 50, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BN-79/6048-02-06 Sadza–Metody Badań–Oznaczenie Gęstości Nasypowej; Wydawnictwa Normalizacyjne: Warsaw, Poland, 1980.
- Rabiej, M. Application of the particle swarm optimization method for the analysis of wide-angle X-ray diffraction curves of semicrystalline polymers. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, T.; Berkesi, O.; Dékány, I. DRIFT study of deuterium-exchanged graphite oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2005, 43, 3186–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Kumar, N.; Panda, K.; Kanan, V.; Joshi, S.; Visoly-Fisher, I. Role of oxygen functional groups in reduced graphene oxide for lubrication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K.S.; Roth, S.; et al. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, L.M.; Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Raman spectroscopy in graphene. Phys. Rep. 2009, 473, 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.; Kim, S.J. The chemical and structural analysis of graphene oxide with different degrees of oxidation. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 53, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas, C.; Álvarez, P.; Blanco, C.; Santamaría, R.; Granda, M.; Gutiérrez, M.D.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.; Menéndez, R. Critical temperatures in the synthesis of graphene-like materials by thermal exfoliation-reduction of graphite oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 52, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieradzka, M.; Ślusarczyk, C.; Fryczkowski, R.; Janicki, J. Insight into the effect of graphite grain sizes on the morphology, structure and electrical properties of reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 7059–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryczkowska, B.; Sieradzka, M.; Sarna, E.; Fryczkowski, R.; Janicki, J. Influence of a graphene oxide additive and the conditions of membrane formation on the morphology and separative properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaashani, R.; Najjar, A.; Zakaria, Y.; Mansour, S.; Atieh, M.A. XPS and structural studies of high quality graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide prepared by different chemical oxidation methods. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Mehmood, A.; Ha, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Chung, K.Y. Reduced graphene oxide as a stable and high-capacity cathode material for Na-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, K.K.H.; Huang, H.H.; Joshi, R.K.; Yoshimura, M. Chemical reduction of graphene oxide using green reductants. Carbon N. Y. 2017, 119, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Q.; Yin, R.; Liu, F.; Chen, H. Characterization of graphite oxide after heat treatment. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.D.; Jeong, H.M. Graphene prepared by thermal reduction-exfoliation of graphite oxide: Effect of raw graphite particle size on the properties of graphite oxide and graphene. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudin, K.N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H.C.; Prud’homme, R.K.; Aksay, I.A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, L.; Ran, Q. Supercapacitors based on low-temperature partially exfoliated and reduced graphite oxide. J. Power Sources 2012, 212, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).