Abstract
The current paper investigates the effect of the heat treatment process on three grades of stainless steel alloys against the abrasive and the lubricant wear conditions, using 25 wt.% glucose solution for the industrial agriculture applications. The heat treatment process was carried out for one hour at 900 ± 10 °C, followed by quenching with monograde motor oil and tempering for more than two hours at 200 ± 10 °C. Several analyses were conducted to estimate the final mechanical, surface morphological and tribological properties for the studied materials, before and after the heat treatment process. The heat-treated martensitic stainless steel grade exhibited superior wear resistance and higher hydrophobicity compared to the other two heat-treated austenite stainless steel grades. Therefore, the mechanism of the heat treatment process, the chemical and physical nature of the parent material, and the viscosity of the selected lubricant all influence the final behaviour of the studied material against the applied operating conditions for the selected application.
1. Introduction
Stainless steel alloys are widely used as machine construction materials in industrial agriculture applications, including producing and refining sugar cane, beets, and other products containing high glucose solution concentrations. The quality and efficiency of the products are related to the machine-building materials made of different grades of stainless steel alloys. The market requires more qualified and moderated products [1,2] thus, several treatment methods are required to improve the machine used to manufacture stainless alloys to ensure the continuity and quality of the products. Further, the industry prefers available qualified material preparation and cheap material treatment methods. The nature of the elemental composition of the stainless steel alloy and the preparation method determine the final surface texture, mechanical, and tribological properties of the material. For example, adding chromium and nickel elements is very important for the standard austenitic stainless steel grades 304 and 316 to enhance their resistance against electrochemical corrosion, stabilize the austenitic phase, and prevent the transformation to any other unstable phases. However, most austenite stainless steel alloys are subjected to destructive attacks resulting from the hazardous interactions between their surface and the other surrounding liquids existing in their atmosphere. Accordingly, scientists developed stainless steel alloys, such as the martensitic type, to overcome such problems. Martensitic stainless steel alloys [3] are distinguished by their unique properties from the other austenite stainless steel grades. They are characterized by their ability to combine high tensile, good wear, and chemical corrosion resistance against aggressive solution environments.
All these properties are critical to overcoming the harsh surrounding environmental conditions that severely affect the quality of machines in the industry [4,5]. Consequently, Martensitic stainless steel alloys are used to construct seamless tubes in oil or gas industries, industrial knives, oil pipelines and pumps, or other parts of machines suitable for the petroleum or agriculture instrumental industries [6]. The tribological wear conditions, such as the applied load, the speed velocity and surface topography of the moving parts, and the abrasion resulting from the hard surface and lubricant, provide an estimate of the optimal friction coefficient and wear resistance of the material under investigation [7]. Moreover, the average surface roughness belonging to the examined material affects the material’s wear behaviour under lubricant conditions [8,9], and the adhesion contributes to the biocompatibility of the material [10]. According to Wenzel, Cassie and Baxter’s methods, there is a direct relationship between surface roughness and contact angle [11,12]. Numerous material treatment methods have been used to enhance the surface topography of stainless steel alloys, such as the femtosecond laser surface treatment [13] and radiofrequency plasma [14,15,16,17,18]. The rougher the surface, the more the contact angle or, the less the wettability between the lubricant and the examined material, resulting in a higher degree of hydrophobicity. The reduced wettability improves the electrochemical corrosion resistance of the material against the surrounding medium.
Moreover, the increased surface microhardness of the material enhances the material impedance against residual stresses and plastic deformation resulting during wear tests [19]. The heat treatment method is a well-known and inexpensive method of improving the properties of stainless steel alloys as a whole. It is a very important processing method due to its simplicity and environmentally friendly nature, and can improve the material’s chemical, physical, and mechanical properties.
The heat treatment performed under conditions, including treatment time and temperature for each step of the treatment process as austenitisation, tempering, and the cooling rate, are the main parameters controlling the properties affecting the final efficiency of the heat-treated stainless steel alloys [20]. The influence of post-heat treatment on the wear and corrosion resistance of martensitic stainless steel alloys against aggressive media and harsh tribological conditions has been discussed at high quenching and tempering temperatures. It has been concluded that increasing applied load enhances the worn volume loss of the investigated material according to the self-impedance of the studied material against plastic deformation. The heat treatment process could also produce better mechanical properties of the martensitic alloys that are recycled for industrial applications [5]. A further study has been carried out to determine the effect of tempering on the electrochemical corrosion properties of the Martensitic grade AISI4130, indicating that the heat treatment process leads to a decreased electrochemical corrosion current (IC) against 3.5% NaCl water saline solution. It also showed that the increased surface microhardness of the heat-treated material demonstrates the heat treatment process’ ability to improve the electrochemical corrosion and abrasive wear resistance of the material [21]. Previous studies discussed the advantage of the tempering process after quenching step on the mechanical properties of the heat-treated carbon steel. Tempering reduces material brittleness, leading to a better combination of hardness and toughness [22]. Several studies have shown the influence of the tribological system operating conditions, including the applied load, the sliding speed, the lubricant type, and the atmosphere temperature, on the final obtained friction and wear resistance of the investigated material [23]. The effect of the surface treatment process condition against several solutions (e.g., 3.5% NaCl, bi-distilled water, low ethanol and rapeseed oil) has been discussed. The study confirmed the deep relationship between the resultant treated material surface morphology, surface roughness and the final behaviour of the treated material wettability and corrosion resistance. The higher contact angles have been obtained with materials that have higher surface microhardness and are rougher [14,15,16,17,18]. Hence, the surface morphology of the treated material is a very important parameter affecting the quality of the material. Moreover, the time and temperature of the tempering treatment determine the surface microhardness of the heat-treated martensitic stainless steel grade. The lower tempering temperature leads to higher surface microhardness [24].
The current study set out to study the effect of the heat treatment process for 60 min at 900 ± 10 °C, followed by quenching with monograde motor oil and tempering for 120 min at 200 ± 10 °C, on three grades of stainless steel alloys used in industrial agriculture applications. Various analyses were performed to obtain the mechanical and tribological properties of each investigated stainless steel grade before and after the applied treatment process. For instance, the analyses involved surface microhardness, average surface roughness, surface wettability, and tribological wear under dry and lubricant conditions. The lubricant test was conducted in conjunction with the flow of a high viscous liquid material = 25 wt.% glucose solution, with a viscosity of 17.41 poise and pH = 5.57 at solution flow rate = 1.2027 mL/min.
2. Materials and Methods
The current study utilised two austenite stainless steel grades, S2 and S3, and Martensitic stainless steel grade S1. The spectrophotometer analyser type “Belec Vario Lab 2C at 20 KV” was used to determine the accurate chemical composition for these stainless steel grades. The obtained chemical composition and density for investigated materials are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The chemical composition and density for the investigated materials.
The investigated materials were cut from cylindrical stainless steel specimens measuring 12 mm in diameter and 2500 mm in length. Several steps were applied to prepare the samples for the heat treatment process. Firstly, all samples were cut carefully into equal thickness, which is 7 mm for each sample. After that, the grinding and polishing steps were performed using the silicon carbide paper sheets, starting from grade 60 to grade 4000, to achieve a shiny mirror surface for each sample. Finally, the digital Eumax ultrasonic cleaner was used to wash all samples clearly by immersing the selected polished samples into pure ethyl alcohol 99.9 wt.% for 25 min at 40 °C, to remove any residual precipitates before polishing and grinding steps.
The heat treatment process was applied at two stages. The first stage was to subject all the investigated samples to high temperature = 900 ± 5 °C, using the digital Muffle furnace Model: FHPX-12) made by the DAIHAN SCIENTIFIC CO for complete 60 min. All samples were then removed from the digital furnace red and hot and quenched carefully inside one litre of mono-grade motor oil, with a viscosity of 40 poise at room temperature for 10 min. At the second stage, all samples were washed carefully using hexane alcohol purity ≈ 99 wt.%, followed by ethyl alcohol purity 99 wt.%, to remove any unwanted precipitates over the surface of treated samples. Finally, all the investigated samples were exposed to another heat treatment step: tempering at a lower temperature 200 ± 10 °C for 120 min inside an oven type Fresh, and then left to cool freely to room temperature. Figure 1 represents the applied stages during the complete heat-treatment process.
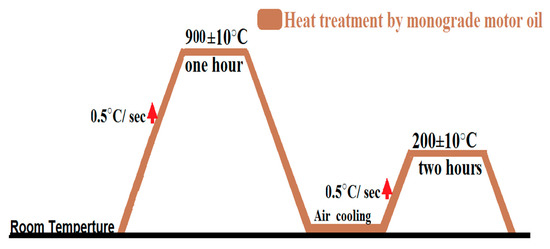
Figure 1.
The Schematic diagram for the heat-treatment mechanism.
Surface Characterisation, Mechanical and Tribological Analysis
The material surface characterisations have been applied using several instruments, involving the XRD instrument, optical microscope and scan electron microscope. The XRD analysis was applied using the JEOL diffractometer using a Cu-Kα target at an X-ray wavelength of λ = 1.54184 Å. The obtained data were recorded at the 2θ range from 30° to 90°. The surface microstructure, grain size, and the optical micrographs of the worn surfaces before and after the heat treatment processes were investigated using the Trinocular polarising microscope type (Fluoroscope-Polar T/R, made by Ray wild and the scanning electron microscopy instrument type VEGA3 TESCAN). A special etcher was prepared to characterise the studied material surface texture using a mixture of 1:9 mL nitric and ethanol acid. The mechanical and tribological analysis includes several measurements: surface microhardness, average surface roughness, surface wettability, abrasive and lubricant wear, and friction measurements.
The surface microhardness measurements were executed by the Matsuzawa Seki. Co. LTD at room temperature 27 ± 3 °C, and the test was performed at five different positions for each investigated sample surface at the Hv. 10 scale. The average surface roughness measurements were applied using the accredit Talysurf 50 instrument. Meanwhile, the wettability measurements, including contact angle and work of adhesion, were implemented by the Phoenix 300 device (S.E.O Co. Ltd., Hong Kong).
The tribological analyses, involving the specific abrasive wear rate, the specific lubricant wear rate, and friction coefficient measurements, were applied using the pin on disk tribometer, as shown in Figure 2 [25]. The test is applied by subjecting each investigated sample to a pressure = 0.5 MPA of an automobile hard grey cast iron disk moving at 7 m/s sliding speed for 18 min at room temperature 27 ± 3 °C. The abrasive dry wear conditions were executed by applying the test without any lubricant. The lubricant wear conditions were applied in conjunction with the flow of 25 wt.% glucose solution with viscosity 17.41 poise, pH = 5.57, and glucose flow rate 1.2027 mL/min. The PH parameter value of the lubricant was measured using a Jenway PH meter, and the viscosity was investigated using a viscometer type: first touch serial no 15.05TFO22 Lamy rheology instruments. It is very important to polish and clean the rotor disc friction area using 320 abrasive grid paper and pure acetone before the beginning of the wear test for the next investigated sample, to forbid any unwanted residues and achieve the best quality for the applied measurements.
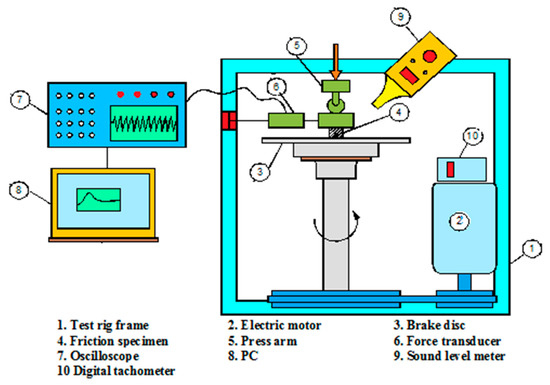
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram for the pin on the disk tribological system [25].
3. Results
3.1. XRD and Structural Analysis
Figure 3 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns at the 2θ range from 30° to 90° for all the studied stainless steel grades, where part (A) represents the untreated S1, S2 and S3 samples and part (B) displays the heat-treated samples OS1, OS2 and OS3. Although all the selected materials are mostly stainless steel alloys with comparable densities, the diffraction patterns produced for each sample are not unique. S1 is a Martensitic stainless steel grade characterised by a base-centred cubic structure with reflection planes (110), (200) and (211) [6], whereas S2 and S3 are austenite stainless steel grades defined by a face-centred cubic structure with reflection planes (111), (200) and (220). Furthermore, S1 prefers the alpha (110) direction planes; however, S2 and S3 choose the gamma (111) direction planes [14,15,16,17,18,26].
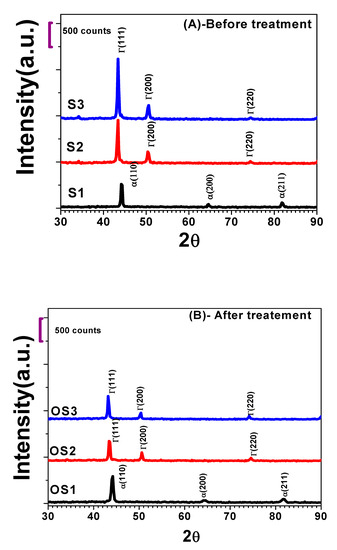
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction analysis for the stainless steel grades (A) before and (B) after the heat treatment process.
Several parameters obtained from the XRD analysis demonstrate the influence of the heat treatment process on the selected stainless steel grades, including texture coefficient, full width half maximum (FWHM), and crystallite size [14,15,16,17,18,27] (Table 2). The texture coefficient is obtained by dividing (the intensity of preferred orientation) by (the summation of the other whole peak intensities existing in the crystal), and the crystallite size is defined by the Williamson–Hall plot equation.

Table 2.
Texture coefficient, FWHM and Crystallite size obtained by XRD analysis.
Figure 4 shows the obtained optical surface microstructure for the investigated stainless steel alloys using the Trinocular polarizing microscope type (Fluoroscope-Polar T/R, made by Ray wild) at the magnification 20×. Meanwhile, Figure 5 represents a higher magnification scale = 1K× using the scanning electron microscopy instrument type VEGA3 TESCAN) to show the obtained the grain size for both of the martensitic and austenitic samples S1 and S3, before and after the heat treatment process.
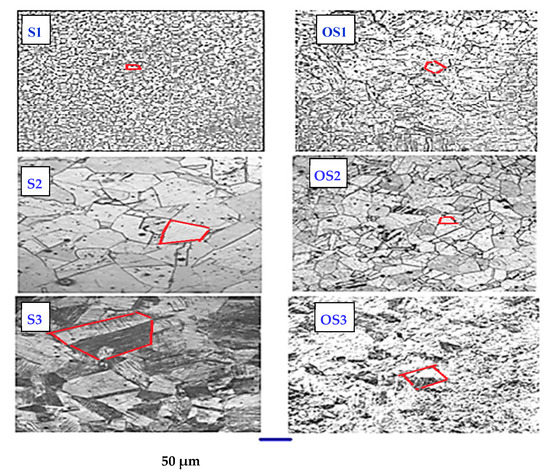
Figure 4.
Optical microstructure for investigated materials, before and after the heat-treatment process magnification 20×.
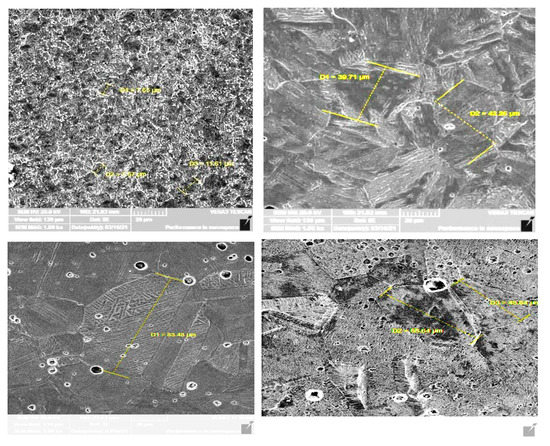
Figure 5.
Scan electron microscope magnification 1K× for the Martensitic and austenite stainless steel grades S1 and S3 before and after the heat-treatment process.
3.2. Mechanical and Tribological Characterisation
Table 3 illustrates the impact of the heat treatment process on the surface microhardness, average surface roughness, and wettability measurements [14,15,16,17,18] against a liquid drop of 25 wt.% glucose solution based on the Sessile Drop method for all the investigated materials, before and after the heat treatment process.

Table 3.
Surface microhardness, average surface roughness, and wettability for the stainless steel grades, before and after the heat-treatment process.
The wettability behaviour for the contact angle between the liquid drop of 25 wt.% glucose solution and the surface of the stainless steel alloys before and after the heat treatment process is summarised in Figure 6.
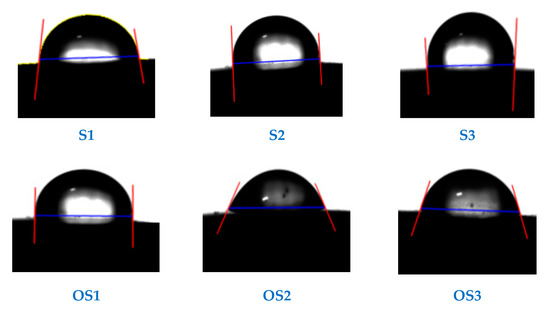
Figure 6.
Contact angle measurements for a liquid drop 25 wt.% glucose solution poured on the surface of the stainless steel grades, before and after the heat treatment process.
The tribological wear and friction coefficient analysis, for all the investigated stainless steel alloys before and after the heat treatment process, was performed against abrasive and lubricant wear conditions. Several parameters are obtained from this analysis to scrutinise the wear behaviour for each analysed sample, like the mean friction coefficient and the specific wear rate.
Figure 7A–C represents the friction coefficient behaviour COF for the analysed materials S1, S2, and S3, before and after the heat treatment process, as a function of distance per meter. The test time was fixed to be 18 min at a total sliding velocity of seven m/s to achieve a final total sliding distance = 7000 m. The test was conducted under two distinct conditions: abrasive wear without any solution and lubricant wear in the presence of 25 wt.% glucose solution with a viscosity of 17.41 poise, pH = 5.57, and solution flow rate at 1.2027 mL/min. Figure 8 depicts the obtained optical micrographs of the worn surfaces for all the investigated stainless steel grades against abrasive and lubricant wear conditions. The specific wear rate is calculated by the following equation:
where the : is the difference of weight per gram of the investigated samples before and after applying the wear test, is the applied friction force per Newton, is the density of investigated sample per (g/cm3), V is the sliding speed per (m/s), and t is the duration time of test per second.
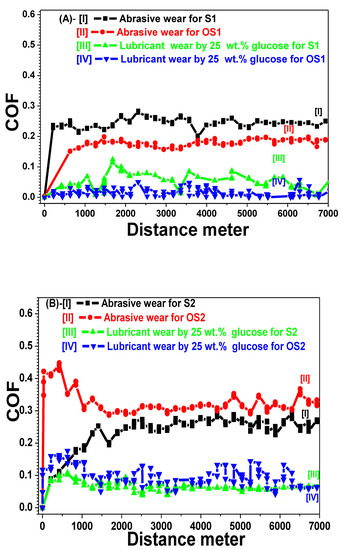
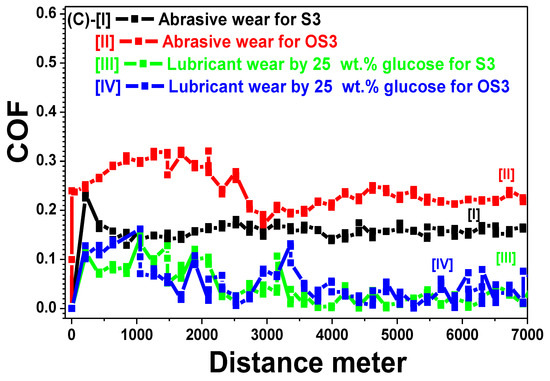
Figure 7.
Friction coefficient (COF) as a function of distance for the stainless steel grades, before and after the heat treatment process against abrasive and lubricant wear conditions by 25 wt.% glucose solution.
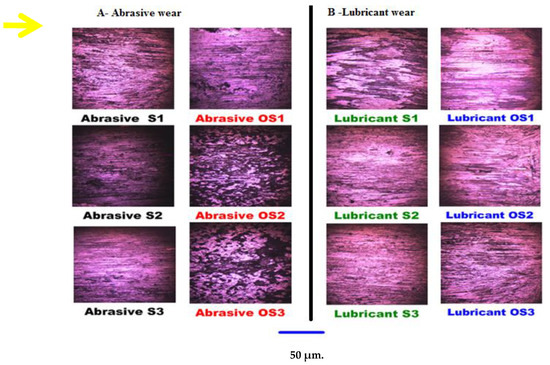
Figure 8.
The optical micrograph images of the worn surfaces in the sliding direction of friction for the investigated samples against abrasive and lubricant wear conditions.
Furthermore, Figure 9 and Table 4 summarise the corresponding mean friction coefficient COF and specific wear rate values for the stainless steel grades, before and after the heat treatment process against dry and lubricant wear conditions.
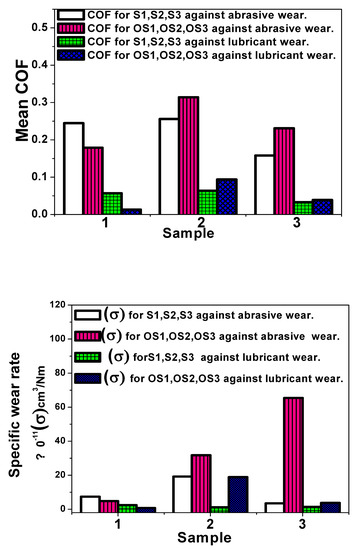
Figure 9.
The mean friction coefficient COF and the specific abrasive wear rate values under abrasive and lubricant wear conditions for the stainless steel grades, before and after the heat treatment process.

Table 4.
The tribological results against abrasive and lubricant wear conditions for the stainless steel grades, before and after heat-treatment process.
4. Discussion
4.1. XRD and Structural Analysis
According to the XRD analysis and optical microstructure (Figure 3B and Figure 4), the heat treatment process for 60 min at high temperature 900 ± 10 °C, followed by quenching with mono-grade motor oil and tempering for another more 120 min at 200 ± 10 °C, lowered the diffraction pattern intensity and the crystallite size of OS2 and OS3 austenite stainless steel samples, due to the formation of the retained austenite phase. In contrast, the same heat treatment conditions increased the diffraction pattern intensity and the crystallite size of the OS1 martensitic stainless steel sample, because of forming the hardened martensitic phase.
It can be seen from Table 2 that the texture coefficient and crystallite sizes of the alpha (110) preferred planes in the OS1 heat-treated martensitic sample are larger than those in the untreated S1 sample. On the other hand, the texture coefficient and crystallite size of the gamma (111) preferred planes in OS2 and OS3 heat-treated austenite samples are smaller than those in the untreated S2, S3 samples. The FWHM was decreased for the OS1 following the heat treatment process and increased for the OS2, and OS3 treated samples. It can be concluded that the heat treatment process for the Martensitic sample Sl led to the formation of the hardened martensitic phase, which is harder and more crystalline than the other retained austenitic phase initiated for the austenite stainless steel OS2 and OS3 samples after the heat treatment process. As illustrated in Figure 3, sample S1 has a predominantly bcc martensitic microstructure, with an average grain size of ≈8 µm, whereas the heat treatment process increased the grain size of the heat-treated grade OS1 to ≈42 µm due to the formation of the new tempered and more crystalline hardened martensitic phase, which is known for its high mechanical resistance, tensile nature, and toughness [7]. Meanwhile, the grain size of the untreated austenite sample S3 was ≈83.48µm, which was reduced to ≈58.64 µm for heat-treated samples OS3, owing to the formation of the weak and retained austenite phase after the heat treatment process.
4.2. Mechanical and Tribological Characterization
4.2.1. Surface Microhardness
The obtained surface microhardness measurements indicated that both the heat-treated austenite stainless steel samples OS2 and OS3 have lower surface microhardness values compared to the untreated austenite stainless steel samples S2 and S3, due to the newly formed weak retained austenite phase. Nonetheless, the Martensitic heat-treated sample OS1 has a higher surface microhardness than the untreated sample S1. The increased surface microhardness of the OS1 sample is directly related to the initiation of a new hardened martensitic phase, owing to the heat treatment parameters applied, including the time, temperature, and parent phase of the bulk treated material [24,28]. Several previous studies reported the advantage of tempering after quenching step on the mechanical properties of the heat-treated carbon steel, because it decreases brittleness, leading to a better combination between hardness and toughness [22,29]. Meanwhile, an opposite behaviour was recorded for both the heat-treated austenite stainless steel samples OS2, OS3 at the same heat treatment process, owing to the formation of the weak retained austenite phase [30].
4.2.2. Surface Roughness and Wettability
The average surface roughnesses for heat-treated austenite stainless steel grades OS2 and OS3 have lower values compared to the untreated austenite stainless steel samples S2, S3. Meanwhile, the heat-treated sample OS1 has a higher average surface roughness following the heat treatment process compared to the untreated martensitic sample S1. Moreover, the wettability characteristics of the investigated materials include both contact angle and work of adhesion for a drop of 25 wt.% glucose solution. As shown from Figure 6 and Table 3, the obtained contact angles (°) and work of adhesion (mN/m) measurements for both of the heat-treated austenite stainless steel samples OS2 and OS3 are inversely related compared to those of the untreated samples. According to the previously mentioned status of the OS2 and OS3 samples, it can be concluded that decreasing the average surface roughness reduces the degree of the contact angle between the liquid drop of glucose solution and the examined material surface. As a result, the glucose liquid spreads on the heat-treated austenite materials surface, increasing the degree of adhesion between the glucose liquid and the investigated material surface. Accordingly, the heat-treated austenitic samples OS2 and OS3 become more hydrophilic and softer than the untreated austenite samples S1 and S2. However, a rougher surface, a higher contact angle and a lower work of adhesion are obtained for the heat-treated martensitic sample compared to the untreated one. Consequently, the heat-treated sample OS1 is more hydrophobic and rougher than the untreated martensitic sample S1. These results match those of previous studies that used the Wenzel and Cecil wettability calculation methods [11,31].
Furthermore, the average surface roughness of investigated material is directly proportional to the contact angle, and inversely proportional to the obtained work of adhesion. Thus, the hydrophobic or hydrophilic nature of the resulting material is controlled basically by the final chemical, physical microstructure, and average surface roughness of the investigated material, which all contribute to the whole treatment process. Moreover, several previous investigations have established a strong correlation between the obtained parameters, such as surface microhardness, friction coefficient, and the material surface topography characterisation of the investigated material, including roughness and wettability [14,15,16,17,18]. The previous techniques could increase the surface roughness of treated stainless steel alloys and transfer their surface microstructure from a hydrophilic morphology into a hydrophobic nature [14,15,16,17,18,32,33].
4.2.3. Tribological Wear Properties against Abrasive and Lubricant Wear Conditions
When discussing the tribological wear properties, we start first with the abrasive wear condition for all the investigated grades before and after the heat treatment process, as depicted in Figure 7A–C, where curves I and II represent the COF behaviour for the untreated and treated samples, respectively.
Figure 7A-I represents the COFS1 behaviour versus distance for the martensitic sample S1. The obtained curve is not smooth along with the whole distance, where there is a slight drop at the COFS1 value = 0.1876 at a distance of 3780 m. On the other hand, Figure 7A-II illustrates the COFOS1 curve for the heat-treated martensitic OS1 sample. A smoother curve and much lower values for the COFOS1 were noticed compared to the COFS1 curve I of the untreated sample S1 at the same abrasive wear conditions.
Figure 7B-I displays the COFS2 behaviour for the untreated austenitic sample S2 and Figure 7B-II represents the COFOS2 behaviour for the heat-treated austenitic sample OS2. The B–II curve exhibits a sharper increase in the COFOS2 behaviour until it reached COFOS2 = 0.289, distance = 1682 m, at which point the curve started a quitter smother movement, until [COFOS2 = 0.3084, distance = 4410 m]. It then resumed its former high fluctuating COFOS2 behaviour until the curve ended. The COFOS2 values are higher than the COFS2 ones.
Figure 7C-I shows the COFS3 behaviour for the other untreated austenitic sample S3 and Figure 7C-II depicts the COFOS3 curve for the OS3 sample after the heat treatment. A sharp continuous increase was found at the beginning of the (C—II) curve compared to the untreated sample, until it reached COFOS3 = 0.1814 and distance = 2941 m, and it then started to decrease. The COFOS3 values for heat-treated sample OS3 are also higher than the untreated COFS3 state.
Figure 8A represents the obtained optical micrographs of the worn surfaces for all studied samples against abrasive wear conditions without lubricant. The wear test damaged and corroded the surface of all investigated samples. Furthermore, all the worn surfaces are accompanied by some metal transfer aligned in the direction of rotation resulting from the sliding motion of the contact surfaces (i.e., sample and brake disk) [34,35].
According to Figure 9, it can be concluded that the heat treatment process improved the friction coefficient behaviour and specific wear resistance for the heat-treated martensitic sample OS1, where the specific wear rate decreased after heat treatment. Meanwhile, the heat treatment process has a detrimental influence on the wear resistance of the other two austenitic samples, where both OS2 and OS3 samples achieved higher specific wear rates following the heat treatment process. Moreover, the specific wear rate varies from one sample to the other depending on its surface microhardness; for instance, lower worn volumes are obtained against harder surfaces. These results match the previous surface microhardness measurements and the Bowden and Tabor theory [36].
Secondly, the lubricant wear condition against the flow of 25 wt.% glucose solution is depicted in Figure 7A-III. The COFLS1 curve decreased sharply compared to the former abrasive conditions COFS1 for the same material, due to the viscous lubricant of 25 wt.% glucose solution flowing at a rate of 1.2027 mL/min. However, there are several zigzag fluctuations in the COFLS1 behaviour, showing the instability of this Martensitic grade against lubricant. These fluctuation drops occurred at (COFLS1 = 0.113, distance = 1682 m), (COFLS1 = 0.0842, distance = 3572 m), (COFLS1 = 0.087, distance = 4623 m) and (COFLS1 = 0.0652, distance = 5582 m). Figure 7A-IV reveals the COFLOS1 behaviour for the heat-treated sample OS1 against lubricant wear conditions. The fluctuations at the COFLOS1 curve were diminished or disappeared compared to the untreated sample COFLS1.
Figure 7B-III shows the COFLS2 behaviour against lubricant for the austenitic untreated sample S2, which is quieter and smoother than the curve III COFLS1 for the untreated martensitic sample S1. Figure 7B-IV indicated an increase and more fluctuation in the COFLOS2 behaviour for the heat-treated sample OS2.
The COFLS3 behaviour for the other untreated austenitic sample S3 is shown in Figure 7C-III, IV represents the COFLOS3 curve for the OS3 sample after heat treatment. A sharp continuous increase was noticed at the beginning of the COFLOS3 curve compared to the untreated sample until reaching COFLOS3 = 0.1814 and distance = 2941 m, and it then started to decrease. Nevertheless, the COFLOS3 values are higher than those obtained for the untreated sample S3.
According to the optical micrographs for the investigated samples against lubricant wear conditions using 25 wt.% glucose solution (Figure 8B), the amount of metal transfer and worn volume loss were significantly reduced for all the examined samples compared to the abrasive dry wear conditions because of the viscous glucose solution, which worked as an inhibitor cutting fluid [37]. Additionally, as illustrated in Figure 9 and Table 3, the same behaviour occurred for the mean COF and the specific lubricant wear. After the heat treatment process, the heat-treated Martensitic sample OS1 attained a lowered specific wear rate. On the other hand, the second and third austenitic heat-treated samples, OS2 and OS3, demonstrated enhanced specific wear rates, respectively.
According to the results, it can be concluded that the average surface roughness of the material, wettability, which comes from the interaction between the poured saline and the two contact solid surfaces moving relatively by each other, and surface microhardness could all contribute to the final material surface properties.
Moreover, the heat treatment process initiated the retained austenite phase in the case of the austenitic samples, S2 and S3, decreasing the crystallinity. Furthermore, the mechanical and tribological analyses indicate that both heat-treated austenitic samples have softer surfaces compared to the untreated samples. On the other hand, we found that the heat-treated martensitic stainless steel grade has increased grain size and crystallinity, leading to higher surface microhardness and a rougher surface than the untreated sample.
These results exhibited stable and smooth COFOS1, LOS1 for the heat-treated Martensitic grade OS1 against dry and lubricant conditions, confirming the improvement of specific wear resistance of the heat-treated martensitic grade. Meanwhile, increased and unstable fluctuated COFOS2, LOS2 and COFOS3, LOS3 curves are found for both the heat-treated austenite stainless steel samples, OS2 and OS3, under dry and lubricant wear conditions, leading to deteriorated wear resistance of the material. The main factors affecting abrasive wear conditions are the relative surface microhardness and speed of the two moving parts (brake disk and examined specimen).
In the case of lubricant wear by 25 wt.% glucose solution, another factor is added to the whole wear process: the high viscosity of the fluid 17.4 poise. Since it has a higher viscosity than water (≈1 poise) and flows by a speed flow rate of ≈1.2027 mL/min, the glucose lubricant is pushed to adhere strongly to the surface of the examined material, acting as an inhibitor between the two moving surfaces (pin disk and examined material). The final specific wear rate against lubricant is lower than the final abrasive wear rate. The rougher surfaces have less adhesion, respell lubricant solution, more hydrophobic, and have lower specific lubricant wear rate and friction coefficient, and vice versa was found for the opposite condition.
5. Conclusions
The effect of the heat treatment process on the three grades of stainless steel alloys against both of the abrasive and lubricant wear conditions using 25 wt.% glucose solution was examined for industrial applications. The mechanical and tribological characterisation revealed an increase in the surface microhardness and roughness, as well as a decrease in wear rate and friction coefficient for the heat-treated martensitic sample, due to the formation of the hardened Martensitic phase for the heat-treated Martensitic stainless steel grade S1. Meanwhile, the heat-treated austenite samples exhibited lower surface microhardness and surface roughness, and a higher wear rate and friction coefficient, owing to the production of the weak retained austenite phase for the heat-treated stainless steel grades S2 and S3. Finally, the interaction of any material against abrasive and lubricant wear conditions depends greatly on its surface morphology, wettability, and nature of the utilised lubricant material.
Author Contributions
S.A.A.-S. (Conceptualization, methodology, resources, project administration, Investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, review and editing), H.M.A.H. (Investigation, data curation, review and editing) and A.A.M. (Conceptualization, project administration, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation and review and editing). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| S1: | The first martensitic stainless steel grade. |
| S2: | The second austenite stainless steel grade. |
| S3: | The third austenite stainless steel grade. |
| OS1: | The first heat-treated martensitic stainless steel grade. |
| OS2: | The second heat-treated austenite stainless steel grade. |
| OS3: | The third heat-treated austenite stainless steel grade. |
| : | Specific wear rate. |
| COF: | Coefficient of friction. |
| COFS: | The COF behaviour for the untreated sample against abrasive wear conditions. |
| COFOS: | The COF behaviour for the heat-treated sample against abrasive wear conditions. |
| COFLS: | The COF behaviour for the untreated sample against lubricant wear conditions. |
| COFLOS: | The COF behaviour for the heat-treated sample against lubricant wear conditions. |
| ƠS: | The specific wear rate for the untreated sample against abrasive wear conditions. |
| ơOS: | The specific wear rate for the heat-treated sample against abrasive wear conditions. |
| ơLS: | The specific wear rate for the untreated sample against lubricant wear conditions. |
| ơLOS: | The specific wear rate for the heat-treated sample against lubricant wear conditions. |
References
- Singh, A.; Ansari, K.R.; Alanazi, A.K.; Quraishi, M.A.; Banerjee, P. Biological macromolecule as an eco-friendly high temperature corrosion inhibitor for P110 steel under sweet environment in NACE brine ID196: Experimental and computational approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 345, 117866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajobi, M.A.; Loto, T.R.; Oluwole, O.O. Austenitic 316L Stainless Steel; Corrosion and Organic Inhibitor: A Review. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch SZ, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 886, pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burja, J.; Šuler, B.; Češnjaj, M.; Nagode, A. Effect of Intercritical Annealing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 0.1C-13Cr-3Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnot, M.; Nogueira, R.P.; Roche, V.; Berthomé, G.; Chauveau, E.; Estevez, R.; Mantel, M. Sulfide stress corrosion study of a super martensitic stainless steel in H2S sour environments: Metallic sulfides formation and hydrogen embrittlement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 394, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliardouh, N.E.; Tlili, S.; Oulabbas, A.; Ramoul, C.E.; Meddah, S.; Kaleli, H. Investigation on dry sliding wear performance and corrosion resistance of 13Cr5Ni2Mo supermartensitic stainless steel. Tribol. Ind. 2021, 43, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramoul, C.E.; Ghelloudj, O.; Gharbi, A.; Tlili, S.; Beliardouh, N.E.; Chouchane, T. Plastic deformation effect on wear and corrosion resistance of super martensitic stainless steel. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2021, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.P.; Calderon-Hernandez, J.W.; Magnabosco, R.; Hincapie-Latino, D.; Alonso-Falleiros, N. Effect of niobium on phase transformations, mechanical properties and corrosion of supermartensitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perfermance 2017, 26, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, D.; Ehl, T.; De Boer, G.N.; Hewson, R.W.; Thompson, H.M.; Gao, L.; Toropov, V.V. Two-scale EHL: Three-dimensional topography in tilted-pad bearings. Tribol. Int. 2014, 79, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudeep, U.; Tandon, N.; Pandey, R.K. Performance of lubricated rolling/sliding concentrated contacts with surface textures: A review. J. Tribol. 2015, 137, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Recum, A.F.; Shannon, C.E.; Cannon, C.E.; Long, K.J.; van Kooten, T.G.; Meyle, J. Surface roughness, porosity, and texture as modifiers of cellular adhesion. Tissue Eng. 1996, 2, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizi-Bandoki, P.; Benayoun, S.; Valette, S.; Beaugiraud, B.; Audouard, E. Modifications of roughness and wettability properties of metals induced by femtosecond laser treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgioli, F.; Galvanetto, E.; Bacci, T. Effects of surface modification by means of low-temperature plasma nitriding on wetting and corrosion behavior of austenitic stainless steel. Coatings 2020, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Kameesy, S.U.; El-Hossary, F.M.; Eissa, M.M.; Abd El-Moula, A.A.; Al-Shelkamy, S.A. Enhancing the capability of plasma treated austenite stainless steels as thermal reactor materials. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kameesy, S.U.; El-Hossary, F.M.; Eissa, M.M.; Abd El-Moula, A.A.; Al-Shelkamy, S.A.; Saeed, A. Radiation shielding, mechanical and tribological properties of treated AISI304L using H2/N2 rf plasma. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 1253, p. 012034. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hossary, F.M.; El-Kameesy, S.U.; Eissa, M.M.; Abd El-Moula, A.A.; Al-Shelkamy, S.A. Influence of Rf plasma carbonitriding on AISI304L, SSMn6Ni and SSMn10Ni for nuclear applications. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 096596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Eissa, M.; El-Hossary, F.; EL-Kameesy, S.; Elmoula, A. Mechanical and gamma ray attenuation properties of N316L steel treated by rf plasma as a nuclear material. Arab. J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2019, 52, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.T.; Liu, D.X.; Han, D. Improvement of corrosion and wear resistances of AISI 420 martensitic stainless steel using plasma nitriding at low temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Li, D.; Li, Y.Y.S. Microstructure evolution and orientation relationship of reverted austenite in 13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel During the Tempering Process. Materials 2019, 12, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosayebi, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Dehghanian, C. Tempering kinetics and corrosion resistance of quenched and tempered AISI 4130 medium carbon steel. Mater. Corros. 2021, 92, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.A.; Inam, A.; Farooq, A. Mechanical and corrosion properties of medium carbon low alloy steel after cyclic quenching and tempering heat–treatments. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 016553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Yu, J.; Elkady, O.A.; Saleh, B. Studies on the effect of applied load, sliding speed and temperature on the wear behavior of M50 steel reinforced with Al2O3 and/or graphene nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Mirzadeh, H.; Dehghanian, C. Effects of spheroidization heat treatment and intercritical annealing on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of medium carbon dual phase steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 257, 123721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Barakat, W.S.; YAMohamed, A.; AAlsaleh, N.; Elkady, O.A. The development of WC-based composite tools for friction stir welding of high-softening-temperature materials. Metals 2021, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, S.; Lenger, H.; Siller, I. M303 HIGH HARD—A corrosion resistant plastic mould steel with higher hardness. BHM Berg-und Hüttenmännische Monatshefte 2010, 155, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakkani, M.F.; Sedky; Hassan, H.A.; Saddik, M.S.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Al-Shelkamy, S.A. Bioengineering, characterization, and biological activities of C@Cu2O@Cu nanocomposite based-mediated the Vicia faba seeds aqueous extract. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1998–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, Z.; Mirzadeh, H. Spheroidization heat treatment and intercritical annealing of low carbon steel. J. Min. Metall. B Metall. 2019, 55, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.T.; Li, Z.D.; Yang, C.F.; Xie, S.K.; Yong, Q.L. Cleavage fracture and microstructural effects on the toughness of a medium carbon pearlitic steel for high-speed railway wheel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 761, 138036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essoussi, H.; Elmouhri, S.; Ettaqi, S.; Essadiqi, E. Heat treatment effect on mechanical properties of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 32, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, S.T.; Saibel, E. Surface roughness effect on slider bearing lubrication. ASLE Trans. 1967, 10, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.T.; Oh, K.; Singh, P.M.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Wettability control of stainless steel surfaces via evolution of intrinsic grain structures. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 5196–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.T.; Oh, K.; Singh, P.M.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Hydrophobicity and improved localized corrosion resistance of grain boundary etched stainless steel in chloride-containing environment. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, C61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, W. Theoretical and experimental exploration on the micro asperity contact load ratios and lubrication regimes transition for water-lubricated stern tube bearing. Tribol. Int. 2021, 164, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, W. An investigation on the lubrication characteristics of floatingring bearing with consideration of multi-coupling factors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 162, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D. Friction and wear-developments over the last fifty years. IMechE 1987, 245, 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Li, D.Y. Experimental studies on tribological properties of pseudoelastic TiNi alloy with comparison to stainless steel 304. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).