Influence of Different Acid on the Interfacial Compatibility between Rusted Steel and Water-Based Coating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
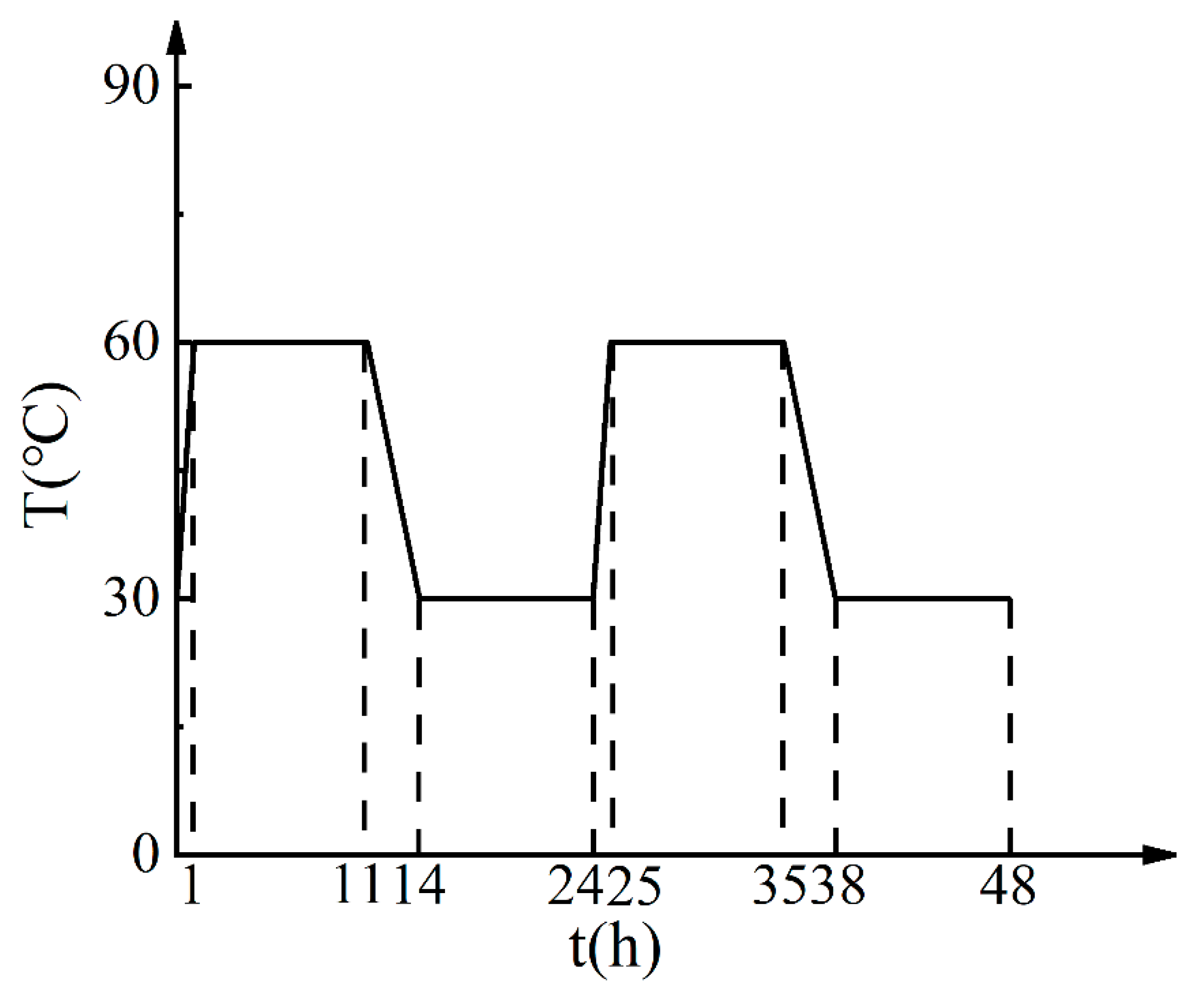
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
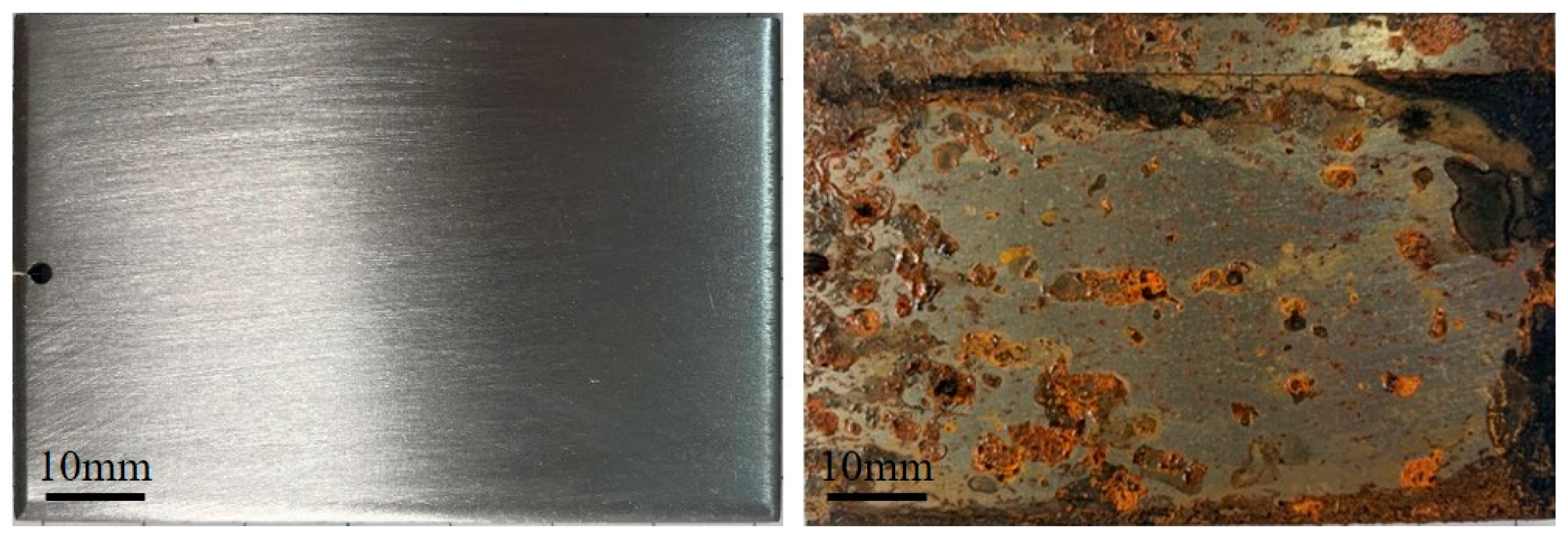
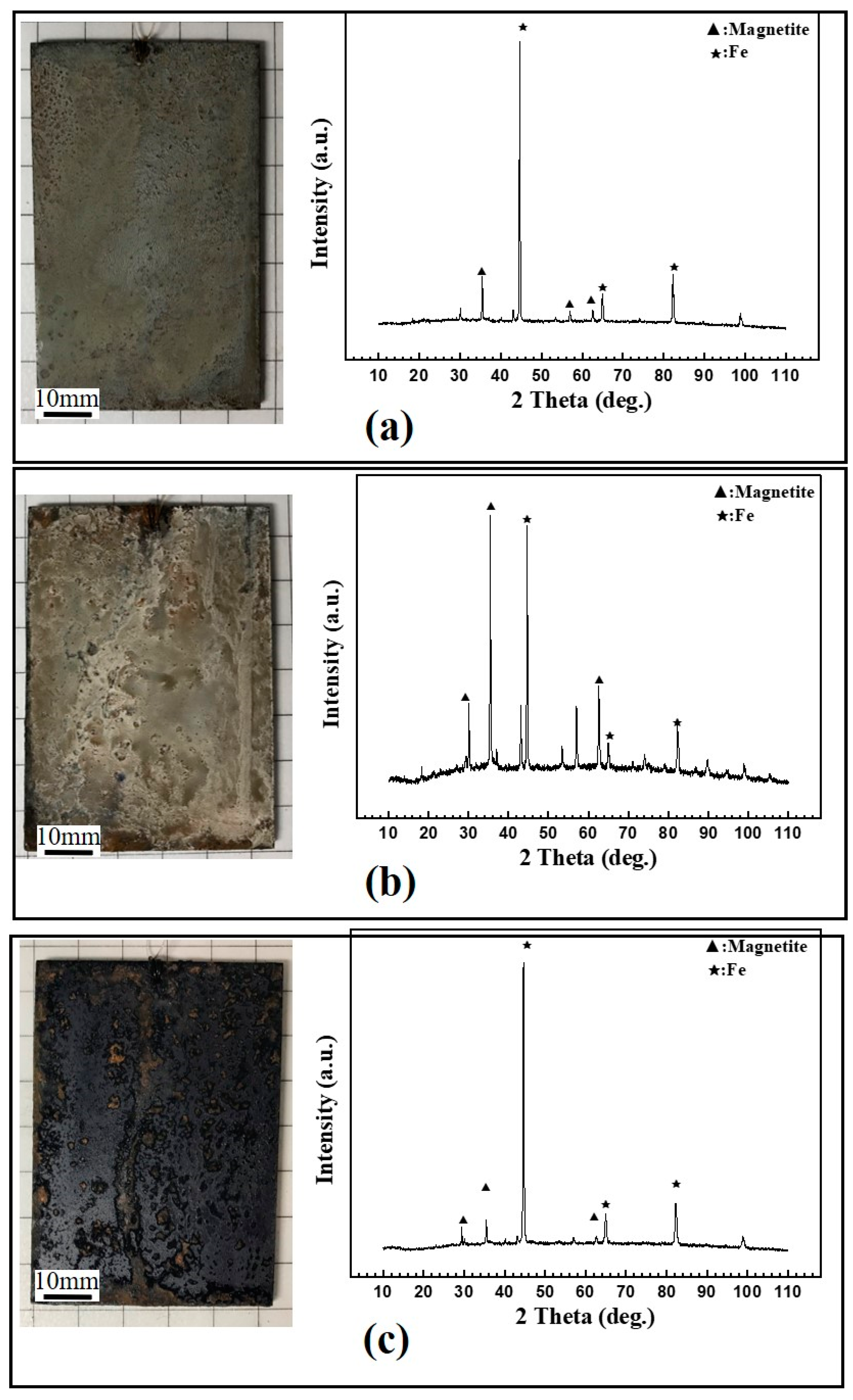
3.1. Effects of Different Acids on Damp-Heat Rust
3.2. The Interfacial Compatibility between Rusted Steel and Water-Based Coating
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.H. Correlation Between Steel Corrosion and Coating Wet Adhesion. Synth. Mater. Aging Appl. 2002, 31, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y. The influence of aluminum tri-polyphosphate on the protective behavior of Mg-rich epoxy coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 93, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Gao, J.; Shen, L.; Wan, H.; Li, X. The influence of aluminum tripolyphosphate on the protective behavior of an acrylic water-based paint applied to rusty steels. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 618971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D. The development of Zinc-Rich paints. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2004, 24, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, I.; Mestach, D.; Leiza, J.R.; Asua, J.M. Adhesion enhancement in waterborne acrylic latex binders synthesized with phosphate methacrylate monomers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 61, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Wan, H.; Tu, X.; Li, W. A better understanding of failure process of waterborne coating/metal interface evaluated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 142, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deflorian, F.; Fedrizzi, L. Adhesion characterization of protective organic coatings by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1999, 13, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, C.; Garcia, J.; Tornheim, A.P.; Sahore, R.; Bareño, J.; Liao, C.; Shkrob, I.A.; Iddir, H.H.; Abraham, D.P. Chemical “Pickling” of phosphite additives mitigates impedance rise in Li ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 9811–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Ansari, K.R.; Quraishi, M.A.; Obot, I.B. Pyranpyrazole derivatives as novel corrosion inhibitors for mild steel useful for industrial pickling process: Experimental and quantum chemical study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 52, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Novel diglycolic acid-based deep eutectic solvents and their applications as a rust remover. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, S.N.; del Amo, B.; Carbonari, R.O.; Di Sarli, A.R.; Romagnoli, R. Painting rusted steel: The role of aluminum phosphosilicate. Corros. Sci. 2013, 74, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumin, V.; Landolt, D. Effect of dispersion agent on the degradation of a water borne paint on steel studied by scanning acoustic microscopy and impedance. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Classification and Research Status of Tolerant Coating. Surf. Technol. 2018, 47, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Tu, W. Research progress of environment-friendly anti-rust coatings. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2008, 9. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HGJZ200809020.htm (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Vetere, V.F.; Deyá, M.C.; Romagnoli, R.; Del Amo, B. Calcium tripolyphosphate: An anticorrosive pigment for paint. J. Coat. Technol. 2001, 73, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, G.; Smeltzer, W.; Droguett, G. Comparison of steel anticorrosive protection formulated with natural tannins extracted from acacia and from pine bark. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.Y.; Shin, D.G.; Choi, D.S. Evaluation of the durability of mortar and concrete applied with inorganic coating material and surface treatment system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lv, H.; Fu, W.; Shi, S. Preparation and Performance of a New Waterborne Rust Converting Agent. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2018, 47, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.-M.; Chang, K.-C. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposite anticorrosive coatings. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S. Research and Application of a Highly Adaptable Anticorrosion Coating for Transmission Tower. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol. 2019, 31, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Fang, J.; Lian, B. Study on Preparation and Properties of High Performance Surface-Tolerant Epoxy Coating. Paint. Coat. Ind. 2019, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.D.N.; Bhattacharya, D. Performance and mechanism of action of self-priming organic coating on oxide covered steel surface. Prog. Org. Coat. 2010, 67, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ge, S.; Wang, J.; Du, H.; Song, K.; Fei, Z.; Shao, Q.; Guo, Z. Water-based Rust Converter and its Polymer Composites for Surface Anticorrosion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Yuan, P. Corrosion protection mechanism of aluminum triphosphate modified by organic acids as a rust converter. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

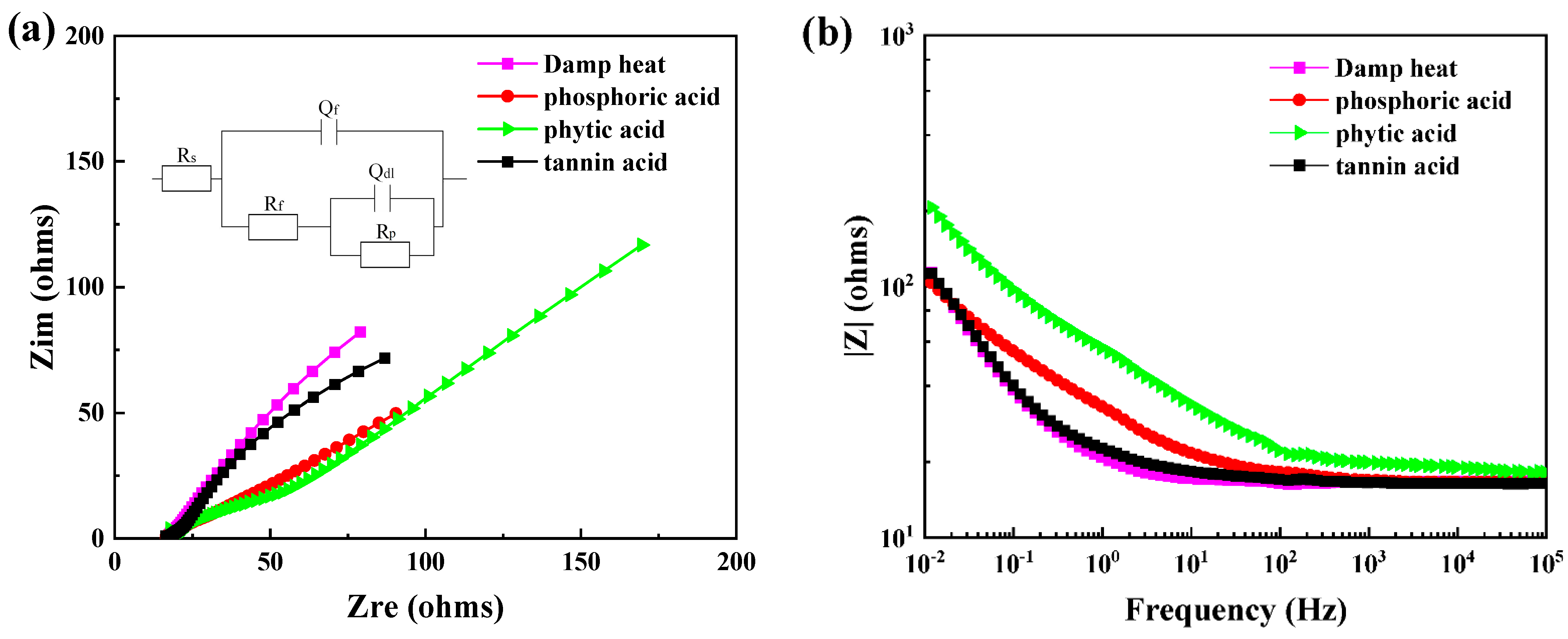
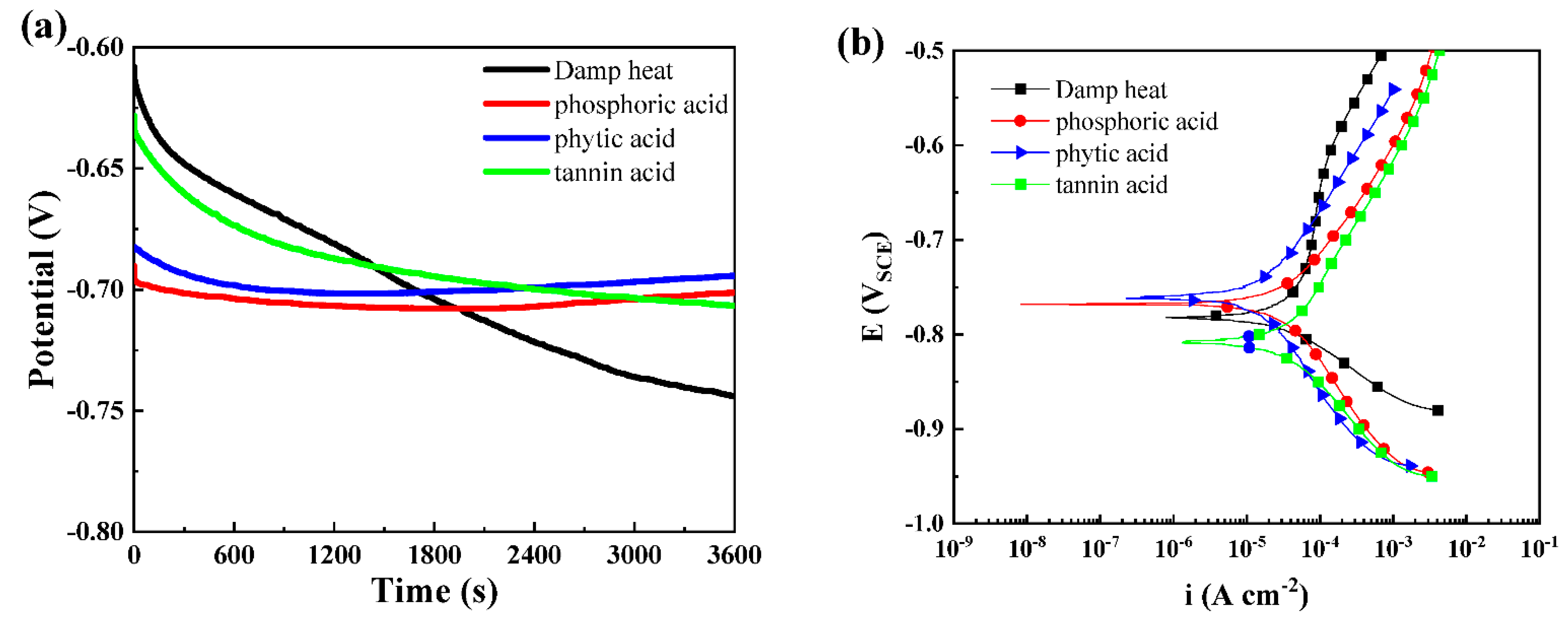
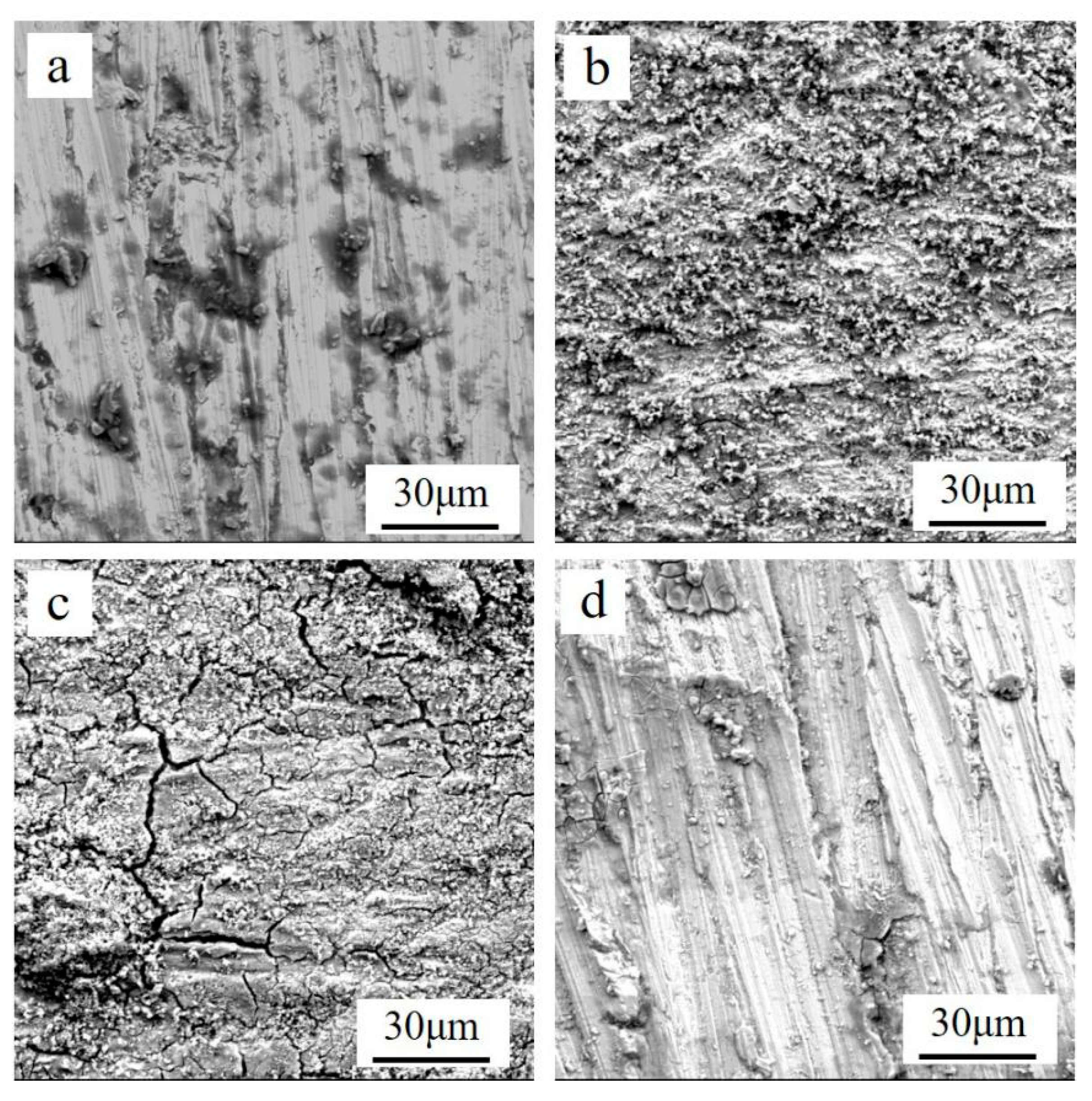
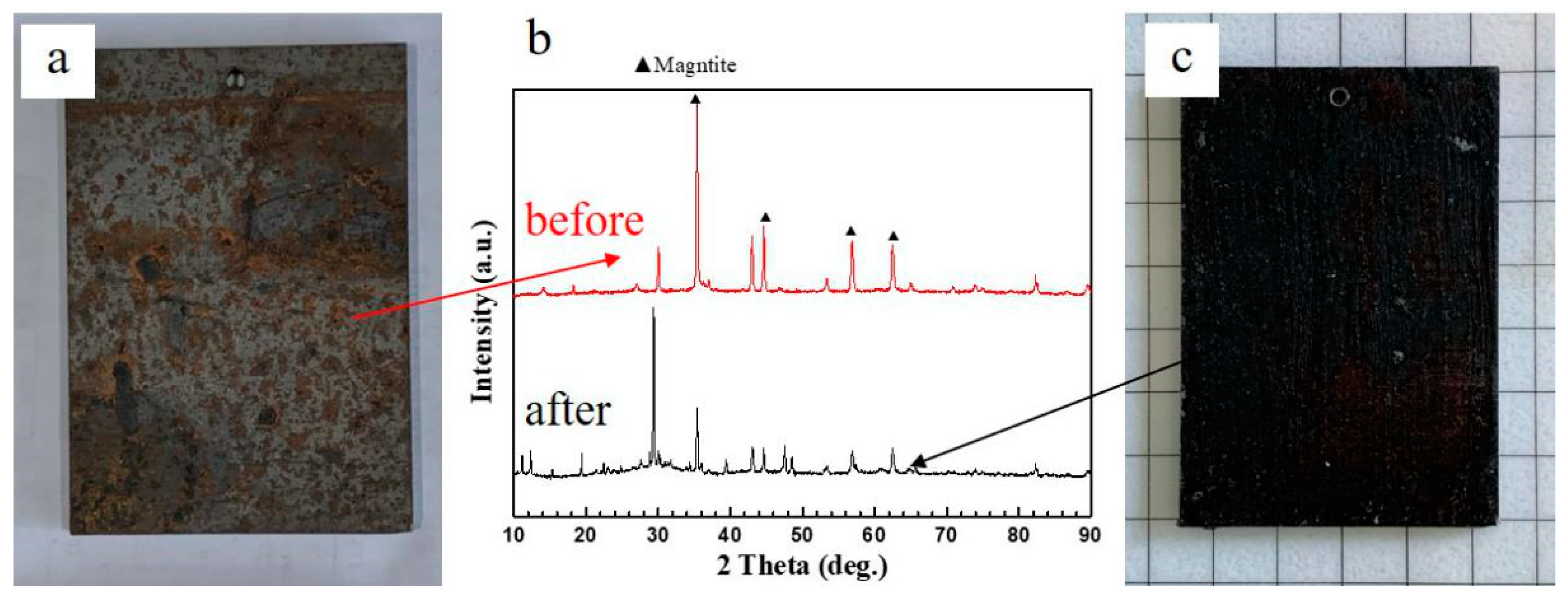
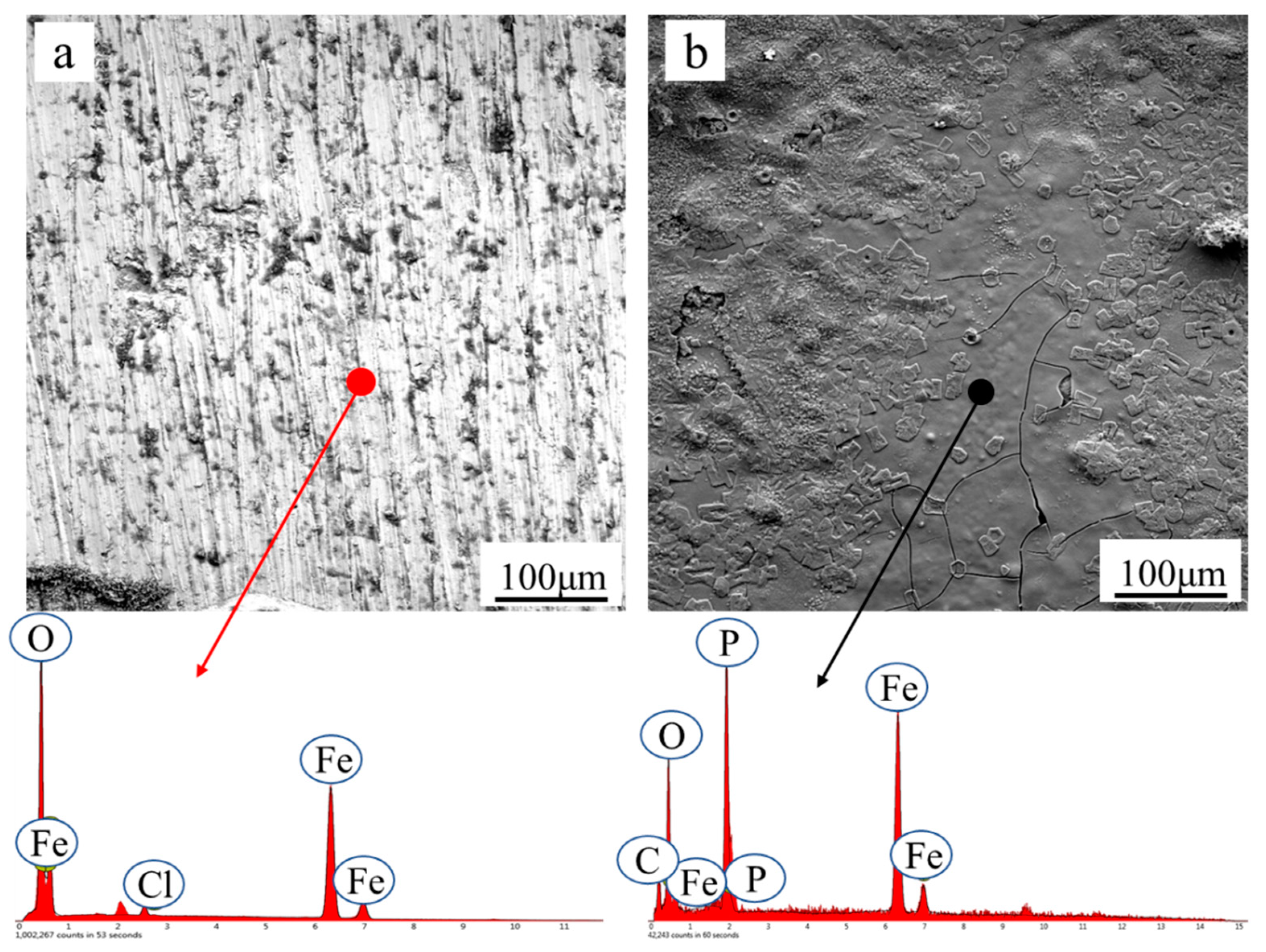
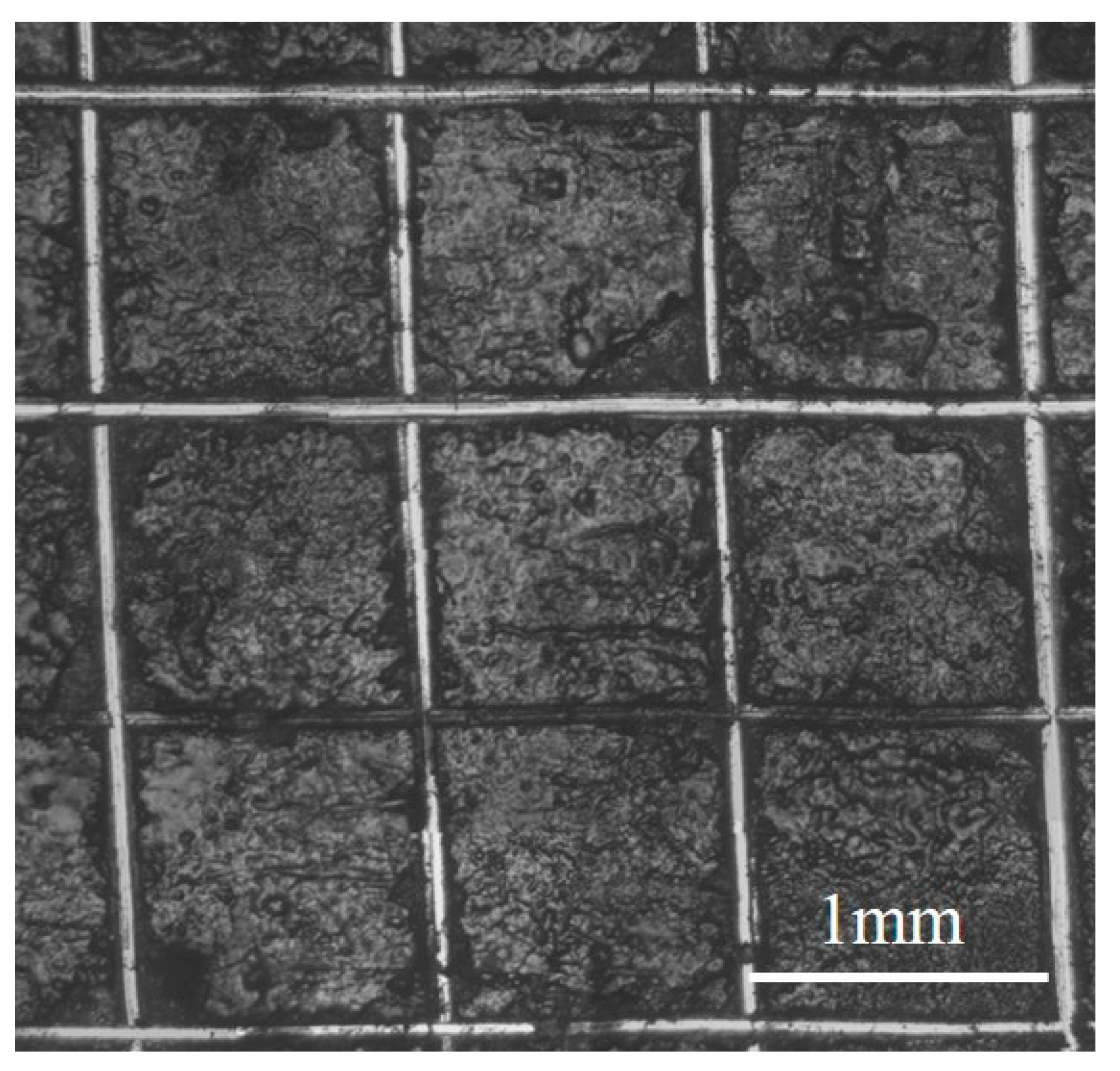
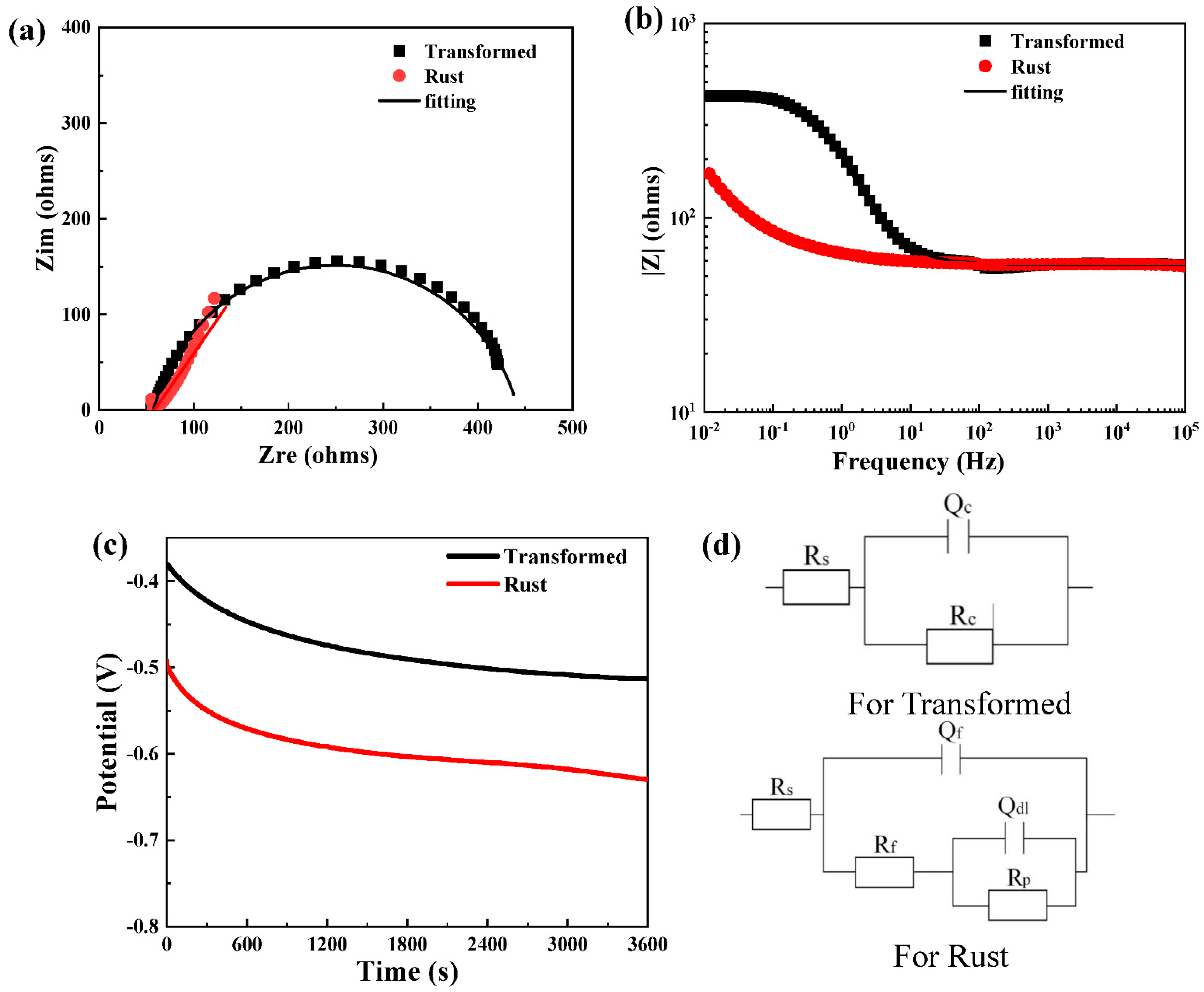
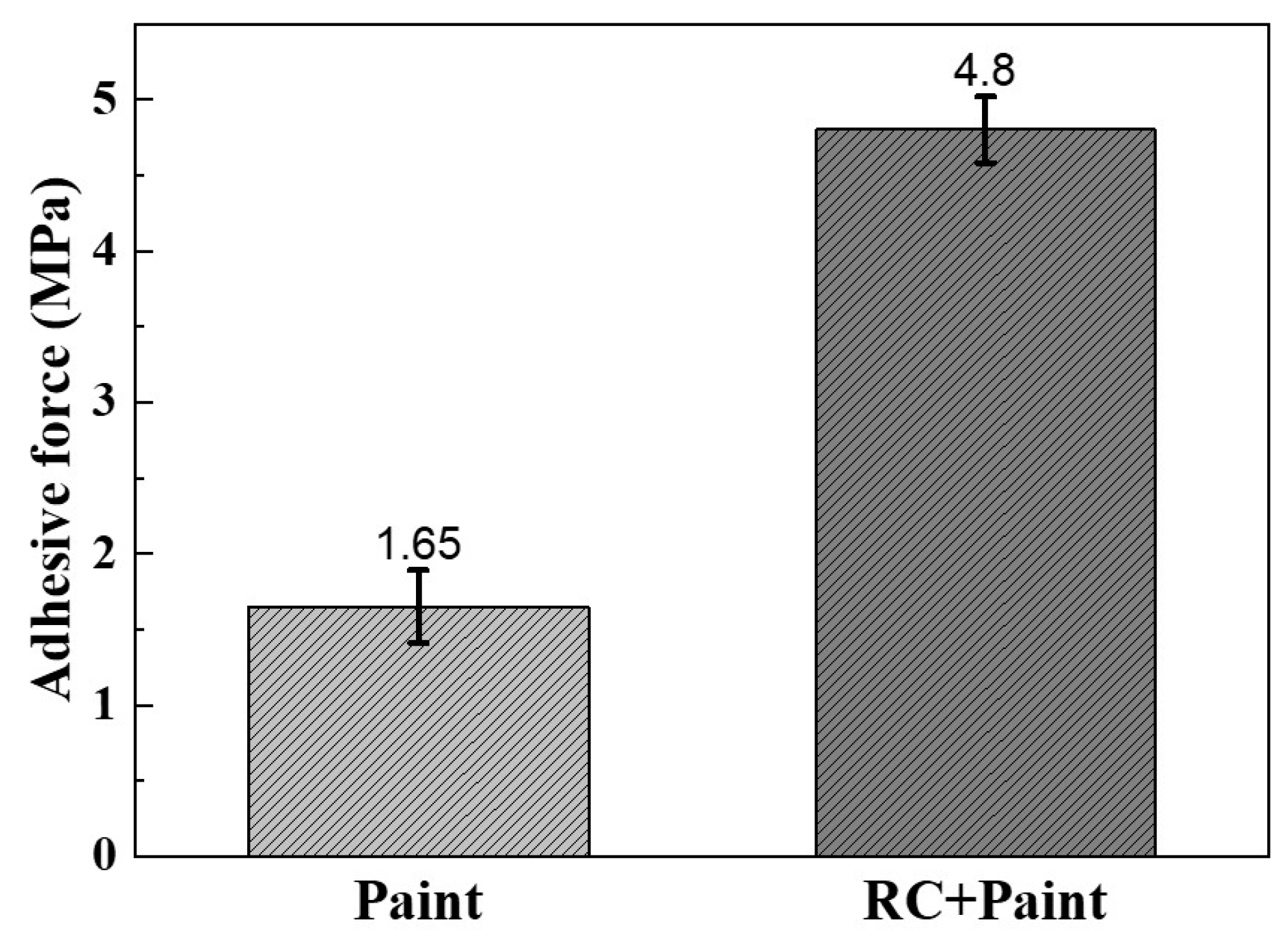
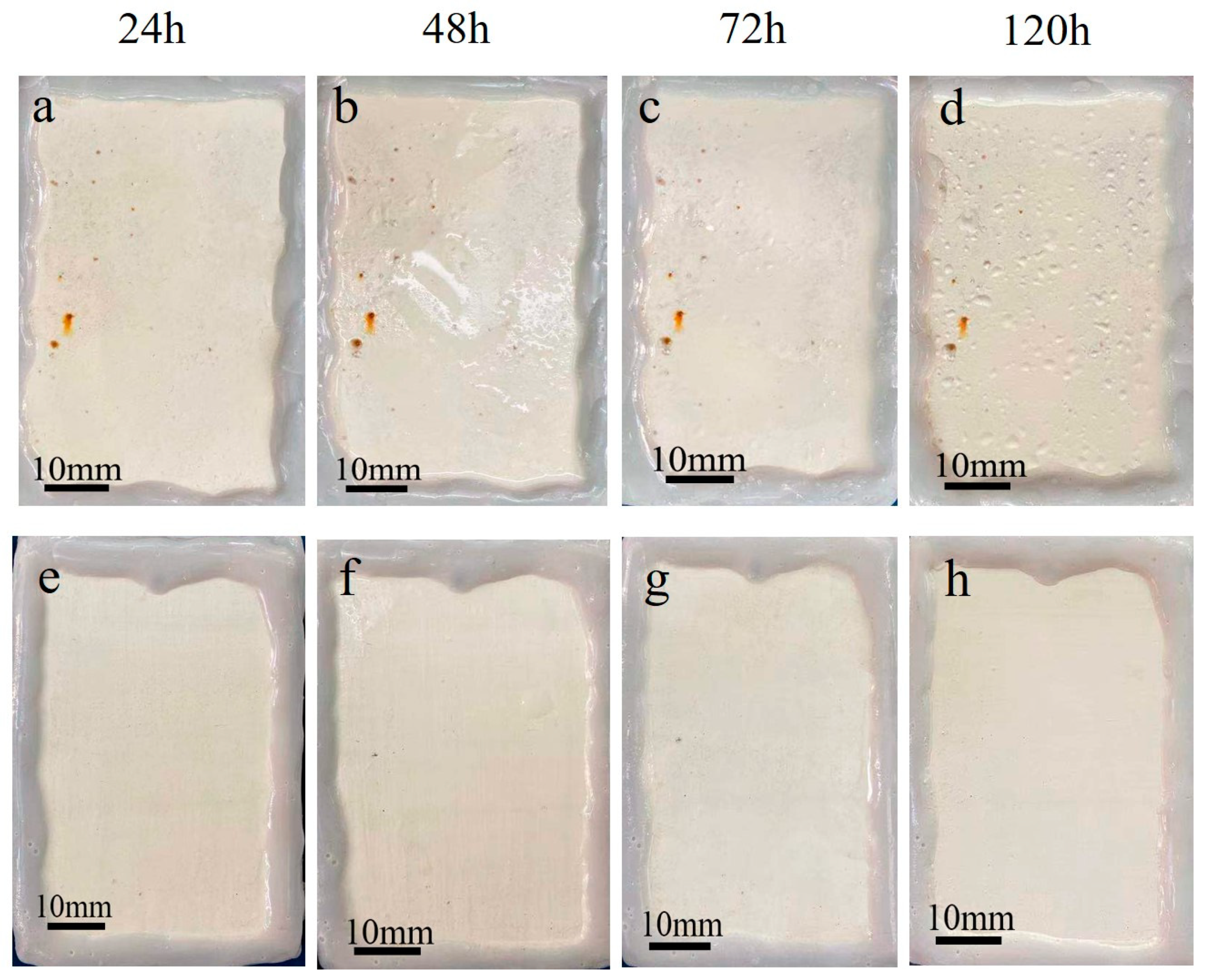
| Module Value in Low Frequency (ohms) | Corrosion Potential (mV) | Corrosion Current Density (10−5 A/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damp-heat | 114.00 ± 21.31 | −782.00 ± 56.21 | 2.48 ± 0.62 |
| Phosphoric acid | 103.20 ± 16.42 | −767.50 ± 32.36 | 1.64 ± 0.46 |
| Phytic acid | 205.90 ± 32.26 | −759.30 ± 43.23 | 0.76 ± 0.21 |
| Tannic acid | 112.60 ± 13.69 | −808.10 ± 51.61 | 2.80 ± 0.56 |
| Element | O | Fe | Cl | P | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 25.82 | 73.00 | 1.17 | 0 | 0 |
| After | 12.87 | 61.25 | 0 | 13.54 | 12.33 |
| Module Value in Low Frequency (ohms) | |
|---|---|
| before | 168.6 ± 36 |
| after | 424.2 ± 55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L. Influence of Different Acid on the Interfacial Compatibility between Rusted Steel and Water-Based Coating. Coatings 2021, 11, 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111412
Li W, Jiang Y, Liu D, Zhu J, Xie Y, Liu L. Influence of Different Acid on the Interfacial Compatibility between Rusted Steel and Water-Based Coating. Coatings. 2021; 11(11):1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111412
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenbo, Yue Jiang, Dingguo Liu, Jiran Zhu, Yi Xie, and Lanlan Liu. 2021. "Influence of Different Acid on the Interfacial Compatibility between Rusted Steel and Water-Based Coating" Coatings 11, no. 11: 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111412
APA StyleLi, W., Jiang, Y., Liu, D., Zhu, J., Xie, Y., & Liu, L. (2021). Influence of Different Acid on the Interfacial Compatibility between Rusted Steel and Water-Based Coating. Coatings, 11(11), 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111412





