Abstract
Preserved eggs are prone to lose water during storage, which causes the preserved eggs to shrink and have poor taste, bad flavor, and reduced quality. By studying a degradable coating agent and applying it to preserved eggs, we explored its effect on the quality of preserved eggs during storage. In this paper, the structure and performance of gelatin film (GF), gelatin–bacterial cellulose film (GBF), and gelatin–bacterial cellulose–MgO nanocomposite film (GBMF) were explored by adding bacterial cellulose (BC) and MgO nanoparticles to gelatin. The results showed that the BC solution increased the particle size and absolute value of the zeta potential. The cross-sectional microstructure of the film showed fewer and smaller pores. The water vapor permeability (WVP) decreased, and the elongation at break (EB) increased significantly. The addition of MgO nanoparticles increased the particle size and reduced the absolute value of the zeta potential. The cross section of the film became denser and more uniform by adding MgO nanoparticles, and the surface hydrophobicity of the film increased, and the EB decreased. After coating the preserved eggs with these films, the weight loss rate, the content of total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N), and the hardness were lower than that of uncoated preserved eggs. The pH of the uncoated preserved eggs also dropped faster than the coated preserved eggs. Moreover, the preserved egg coated with GBMF had the lowest weight loss rate and the highest sensory score. It can be seen that these three films had a certain preservation effect on preserved eggs, and the GBMF had the best preservation effect.
1. Introduction
Preserved egg is a traditional processed egg product in China, which not only has unique flavor, but also possesses high nutritional value and anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidation functions [1,2,3], and it is popular among consumers. At present, preserved eggs on the market are mostly sold in unpackaged form. However, the quality of unpackaged preserved eggs is prone to decline during storage, resulting in shrinkage, oxidative degradation of protein, and unpleasant smell. There are also businesses trying to vacuum-pack or pack preserved eggs in plastic bags to maintain their excellent quality. However, due to the increase in cost, on the one hand, and because the hard-to-degrade plastic is not environmentally friendly, on the other, preserved eggs are still stored and sold without packaging. Therefore, it is necessary to study coated materials that are safe and degradable to maintain the quality of preserved eggs during storage and sale. These coating materials can be extracted from various wastes, which not only improves the waste utilization rate but is also environmentally friendly [4].
Gelatin is composed of protein, which is the hydrolysate of collagen by acidic, alkali, enzymatic, etc., processes [5]. Gelatin is widely used in the food industry due to its good physical and chemical properties. Moreover, its excellent film-forming ability, transparency, and biodegradability [6] make it widely used for edible film, which has very promising application prospects. However, gelatin film (GF) is sensitive to moisture and has poor waterproof performance [7]. Therefore, it is usually combined with other materials to improve the moisture permeability and mechanical properties. Santos et al. [5] found that after adding cellulose whiskers into gelatin, the mechanical properties of the film were improved, and the water blocking performance was significantly improved. Kanmani et al. [8,9] showed that after adding zinc-containing nanoparticles, the UV barrier properties of the film were enhanced, the hydrophobicity and water barrier properties were improved, and the tensile strength (TS) was significantly improved. Bacterial cellulose (BC) is a kind of natural nanofiber polymer, which has more stable physical and chemical properties than ordinary cellulose. Its stable mechanical strength, non-toxicity, biodegradability, and other advantages [10,11] give it broad application prospects in the food packaging industry. Metal nanoparticles are widely used in film-forming materials due to their unique nanostructures and excellent physical and chemical properties, and research [12] has shown that the mechanical properties and humidity resistance properties of the gel-based film were significantly improved after blending with nanomaterials. However, research of metal nanoparticles mainly focuses on metal nanoparticles such as zinc and silver [8,13,14], and there are few studies on Mg nanoparticles. Moreover, there is little research on the blending of BC and MgO nanoparticles with gelatin.
Therefore, in this paper, after blending gelatin, BC, and MgO nanoparticles, the microstructure, mechanical properties, rheological properties, particle size, hydrophobicity, and water vapor permeability of the films were analyzed. At the same time, the gelatin-based films were used for the storage of preserved eggs, and the effects of the films on the pH, moisture content, texture characteristics, content of total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N), color, and sensory properties of preserved eggs were studied. This study is also expected to provide some theoretical bases for the use of BC and MgO nanoparticles in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Fresh duck eggs were purchased from Jiangxi Tianyun Agricultural Development Co., Ltd., Jiangxi, China (food grade) was obtained from Zhejiang Yinuo Biological Technology Co., Ltd., Zhejiang, China. BC was purchased from from Beijing Guanlan Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. Nano magnesium oxide was bought from Shanghai Maclin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. Other reagents were purchased from Xilong Science Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Dissolution of BC
The BC was dissolved according to the method of Qi et al. [15]. First, 4 g BC was dispersed in 48 g NaOH aqueous solution (14%), which was pre-cooled to 0 °C, and then stirred for 1 min. After that, 48 g urea aqueous solution (24%) pre-cooled to 0 °C was added to the previous solution and stirred vigorously for 2 min.
2.2.2. Preparation of Film Solutions and Films
The formulas of GF solution, gelatin–BC film (GBF) solution, gelatin–BC–MgO nanocomposite film (GBMF) solution were as follows: gelatin (20%, w/v), glycerin (3%, v/v); gelatin (20%, w/v), glycerin (3%, v/v), BC solution (5%, v/v); gelatin (20%, w/v), glycerin (3%, v/v), BC solution (5%, v/v), MgO (0.05%, w/v); respectively.
The above three mixed solution were boiled for 30 min, then homogenized in a homogenizer (T18, German IKA, Staufen, Germany) at 20,000 r/min for 20 min and finally at 600 w for 30 min using an ultrasonic instrument (100s, Deyi Life Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China). The prepared film solutions were vacuum-dried for 24 h, and the finished films were obtained.
2.2.3. Determination of Film Solution Characteristics
Rheological Properties
The storage modulus G′ (Pa), loss modulus G′ (Pa), and viscosity J (Pa. s) of the film solutions were measured by a rheometer (HR-1, Waters, MA, USA). A parallel disc rotor was used for the test; the measurement temperature was 25 °C, the angular frequency was 1–100 rad/s, the strain was 1%, and the gap between the plates was 1 mm.
Particle Size and Zeta Potential
The prepared film solutions were diluted 100 times. The particle size was measured with a particle size analyzer (MS3000, Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvren, UK), and the zeta potential was tested with a potentiometer (Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malven, UK).
2.2.4. Determination of Film Properties
Microstructure
The microstructure of films was examined according to the method of Handa et al. [16] with slightly modification. The films were cut into the size of about 0.3 × 0.3 cm2. They were immersed in a glutaraldehyde fixative solution for fixation, and then rinsed with 0.1 M phosphate buffer. The prepared samples were dehydrated with ethanol and finally freeze-dried for 48 h with a vacuum freeze dryer (ALPHA14, Marin Christ, Osterode, Germany). The dried samples were sprayed with gold, and then an SEM (EVO 18, ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany) was used to observe the microstructure of the films.
Water Contact Angle
A surface tension meter (K100, KRUSS, Hamburg, Germany) was used to measure the water contact angle at 25 °C. Ultrapure water was dropped onto the surface of the film, and then the image was captured by a camera system [8].
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties were measured according to Chinese standard GB/T 1040.3-2006 [17]. The 120 × 20 mm2 film samples were used to test the elastic modulus (EM), TS, and elongation at break (EB) using an electronic universal testing machine (CTM2503, MTS Industry China Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The parameters were set as load 500 N, the initial clamping distance between the clamps was 40 mm, and the tensile speed was 10 mm/min. The experiment was repeated three times.
Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
The WVP was measured according to the method of Santos et al. [5] with slight modifications. Anhydrous calcium chloride (3 g), which was dried and crushed evenly, was put into a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask, and the mouth of the flask was quickly sealed with film. It was placed in a desiccator with a temperature of 25 °C and relative humidity (RH) of 83% to maintain a stable vapor pressure on both sides of the film, and it was weighed every 24 h for one week. Water vapor transmission was calculated by the change of the mass of the Erlenmeyer flask. The calculation formula of WVP (g mm/m2 d kPa) is as follows:
WVP = ∆m × L/(A × t × ∆p)
In the formula, ∆m stands for water vapor migration, g; L stands for film thickness, mm; A stands for film area, m2; t stands for measurement time, h; and ∆p represents the water vapor pressure difference between both sides of the film, kPa.
2.2.5. Determination of the Quality of Preserved Eggs
Pickling and Coating of Preserved Eggs
The fresh duck eggs were cleaned, checked, and graded before being placed in the picking solution, which was prepared by NaOH (4.5%, m/v), NaCl (4.0%, m/v), and CuSO4 (0.4%, m/v) [18]. The eggs were pickled at 25 °C for 40 days.
Mature preserved eggs were taken out and washed. Elastic preserved eggs were picked out and randomly divided into four groups. The four groups of preserved eggs were stored in a box with constant temperature (25 °C) and humidity (55% ± 5% RH). The preserved eggs without coating were used as the control group. The other three groups of preserved eggs were soaked in the GF solution, GBF solution, and GBMF solution for 20 s. After waiting for the preserved eggs of the coating groups to dry naturally, the above operation was repeated once to obtain three groups of preserved eggs coated with different films.
Weight Loss Rate
Ten preserved eggs were randomly picked and weighed every two weeks [19]. The calculation formula for weight loss rate is as follows:
The weight loss rate = (M1−M2)/M1 × 100%
In the formula, M1 represents the weight of preserved eggs before storage, g; and M2 represents the weight of preserved eggs after storage, g.
pH
The pH was determined according to the analytical method of Chinese standard GB/T 5009.47-2003 [20]. Five preserved eggs were washed and shelled, and then the preserved egg white and yolk were each added to water in a respective ratio of 2:1 to form a homogenate by using a homogenizer. About 15.00 g of homogenate (equivalent to 10.00 g sample) was diluted by water to a final volume of 150 mL and filtered with double-layer gauze. The pH of the filtrate was measured by a pH meter (PHS-25, Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Each sample was tested in parallel three times.
Texture Characteristics
The preserved egg white was cut into 1 cm3 cube blocks, and its hardness, springiness, and chewiness were measured by a texture analyzer (TA-XTPLUS, SMS, Surrey, UK). A P36 probe was used for the test; the compression ratio was 60%, the pre-test speed was 5.0 mm/s, and the test and post-test speeds were 2.0 mm/s. The experiment was performed 6 times.
TVB-N
The measurement of TVB-N was carried out by the trace diffusion method using Chinese standard GB 5009.228-2016 [21]. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
Color
A colorimeter (NS810, Shenzhen Threenh Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) was used to measure the color of preserved egg white and yolk. The egg white was cut into cubes with a height of 1 cm. A piece of white paper was placed on the bottom before the test. The surface color of the egg yolk was measured. The data was expressed as L* (brightness), a* (red/green), and b* (yellow/blue). The experiment was repeated 10 times.
Sensory Evaluation
A sensory evaluation table was set according to Chinese standard GB/T 5009.47-2003 [21] and GB 2749-2015 [22], as shown in Table 1. The samples were scored by 6 food professional researchers, with a full score of 15 and a corruption score of 0.

Table 1.
Sensory evaluation.
2.2.6. Statistics and Analysis
Except for SEM, other data were expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD). The analysis of variance was performed by SPSS 25.0 software, and the significance of the data was tested by Duncan’s method. The significance level was p < 0.05. The research results were processed by Origin 2018 software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Properties of Film Solutions
3.1.1. Rheological Properties of the Film Solutions
The rheological properties of the three film solutions are shown in Figure 1. The viscosity of these films decreased (p < 0.05) with the increase of the angular frequency; especially when the angular frequency was in the range of 1–10 rad/s, the viscosity of each sample decreased rapidly and then stabilized. Under the same angular frequency, the composite film solutions had lower viscosity than that of the single GF solution, which indicated that the addition of BC reduced the viscosity of the GF solution. However, the addition of MgO nanoparticles seemed to have no effect on the viscosity of the GBF solution. There were obvious differences in the storage modulus and loss modulus between the GF solution and the other two film solutions. The storage modulus of the GF solution continuously increased (p < 0.05) with the increase of angular frequency and was always higher than the loss modulus. However, the storage modulus of the other two film solutions changed relatively smoothly (p > 0.05) and was lower than the loss modulus.
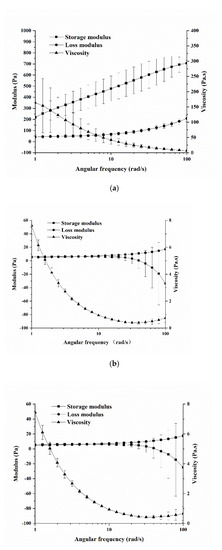
Figure 1.
Rheological properties of different film solutions: (a) GF; (b) GBF; (c) GBMF.
When the film solution was subjected to an external shearing force, the stable structure of the molecules was destroyed, which led to the increase of the free flow of molecules, resulting in the decrease of viscosity of the film [23]. When the shear rate increased to a certain extent, the molecular structure gradually became steady, and the molecular chain became fully oriented [24] at this time, which was why the viscosity value tended to be stable. It may be that the addition of BC solution changed the pH of the composite film solutions, resulting in a decrease in viscosity of the solutions. This may have increased the electrostatic repulsion in the solution, changing the structure of the proteins in gelatin, and reducing the expansion of the molecular chain [25], thereby reducing the viscosity of the composite film solutions. The storage modulus of the GF continuously increased and was always higher than the loss modulus, which means that the GF solution gradually formed an elastic protein gel network, the elasticity gradually increased, and the protein structure was more stable [26]. The addition of BC made it possible to change the molecular structure of gelatin, resulting in the weakening of the binding of gelatin–BC to water molecules and further reducing the ability to retain water molecules [9]. The gel properties of the film solution became weaker, so the storage modulus was greatly reduced. Moreover, the storage modulus became gradually lower than the loss modulus with the increase of angular frequency. This may be because the GBF solution did not have enough time to relieve the force through the intermolecular gap under the action of higher frequency oscillation, which directly caused the intermolecular force of the GBF solution to be further destroyed. This proved the existence of the interaction between gelatin and BC. It may be that gelatin and BC were connected by hydrogen bonds and other covalent bonds during the process of blending. The addition of MgO nanoparticles hardly changed the storage modulus and loss modulus of the film solution, indicating that the MgO nanoparticles at this concentration hardly affected the viscoelastic properties of the GBF solution.
3.1.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential of the Film Solutions
Table 2 shows the particle size and zeta potential of different film solutions. The particle size of the film solution greatly affects the mechanical properties of the film [27]. The addition of BC solution and MgO nanoparticles significantly increased (p < 0.05) the particle sizes of the film solutions. This might be due to the interaction between the BC and gelatin during the blending process, and the aggregation and adsorption characteristics of inorganic nanoparticles [8], since on the one hand, the MgO nanoparticles aggregated in the film solution. On the other hand, it might be because the MgO nanoparticles attached to the surface of the gelatin–BC molecules, which further increased the particle size of the film solution [8,28].

Table 2.
Particle size and absolute value of the zeta potential of different film solutions.
The absolute value of the potential was increased significantly (p < 0.05) by adding BC. However, with the addition of MgO nanoparticles, the absolute value of the potential of the film solution decreased significantly (p < 0.05). This was probably due to the presence of sodium hydroxide in the BC solution, which led to an increase in the concentration of OH– in the solution, and thus the absolute value of the potential increased. The decrease of the absolute value of the potential caused by MgO nanoparticles might also be related to the formation of MgO nanoparticle aggregates and the interaction between MgO nanoparticles and gelatin–BC [29]. When the polymer is mixed with the oxide system, the oxide surface adsorbs the polymer and changes the zeta potential of the polymer [30].
3.2. The Properties of Films
3.2.1. Microstructure of the Films
The cross-sectional microstructures of the three films are shown in Figure 2. On the cross-section of the GF, loose meshes of different sizes could be seen, and the surface was uneven and contained obvious particles. The pores in the GF may have been related to the composition and structure of the proteins. Studies have shown that certain animal proteins such as ovalbumin [31], bovine serum albumin [32], and whey protein [33] can combine with proteins in the form of non-covalent bonds, thus forming a fibrous mesh structure. The triple-helical structure of the protein in gelatin also mainly depends on non-covalent bonds, such as intramolecular hydrogen bonds [34,35], which might be the reason why the GF forms such a fibrous mesh structure.
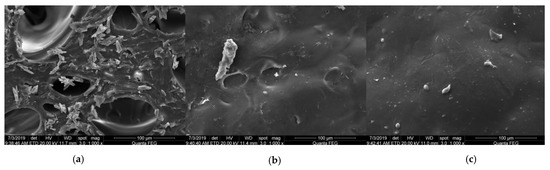
Figure 2.
Microstructure of different films: (a) GF; (b) GBF; (c) GBMF.
After adding the BC solution in gelatin, it could be clearly observed that the pores in the GF were buried, only slight depressions could be seen, and the surface was smoother. This indicated that there was a good interaction and compatibility between BC and gelatin. The possible reason is that the hydroxyl groups in BC combined with the carboxyl and amino groups in the gelatin molecular chain by hydrogen bonds and other covalent bonds [5]. At the same time, the BC molecules were evenly dispersed and arranged in the gelatin solution to make the structure of the composite film more compact.
There were no obvious bulges or depressions on the cross-section of the GBMF, and the film surface was denser and more uniform. However, due to the easy agglomeration of nanoparticles, particles and wrinkles could be clearly observed. This means that the MgO nanoparticles could better fill the pores of the film.
3.2.2. Water Contact Angle of the Films
The surface hydrophobicity of the film was evaluated by the contact angle between the film surface and water, and the hydrophobicity mainly depended on the surface morphology and chemical structure of the material [36]. The water contact angles of the three types of films are shown in Figure 3. The water contact angles of the films after adding BC and MgO nanoparticles were higher than those of GF, which increased from 81.15° ± 0.64° to 103.58° ± 6.02° and 104.5° ± 4.91°, respectively.

Figure 3.
Water contact angle of different films: (a) GF; (b) GBF; (c) GBMF.
The larger the water contact angle, the more hydrophobic the film surface. After adding the BC solution, the surface of the film changed from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. This was possibly because the BC reacted with gelatin, resulting in a decrease in the number of hydrophilic groups, and increased the surface hydrophobicity of the film. It has also been observed in another study [37] that the addition of cellulose nanoparticles can significantly improve the hydrophobic properties of the film. The addition of MgO nanoparticles slightly increased the water contact angle of the GBF, indicating that MgO nanoparticles also have the function of improving the surface hydrophobicity of the film. This is probably because MgO nanoparticles were distributed on the surface of the film, which hinders the contact between gelatin and water, resulting in an increase in the hydrophobic properties of the film. This has also been observed in another study [38], namely that ZnO nanoparticles have the effect of enhancing the hydrophobicity of the film.
3.2.3. Mechanical Properties of the Films
The mechanical properties of film material include EM, TS, and EB. The dispersion of the material matrix and the interaction between the matrixes are the main factors that determine the mechanical properties of polymer composites [8]. As shown in Table 3, the EM, TS, and EB of the GF were 50.11 ± 4.04 MPa, 3.20 ± 0.31 MPa, and 102.07% ± 4.81%, respectively. With the addition of BC solution, the EM and TS of the composite film decreased significantly (p < 0.05), and the EB increased significantly (p < 0.05). This might be due to the presence of urea and sodium hydroxide in the solvent used to dissolve the BC. Urea is a low molecular weight plasticizer similar to glycerol [38], which can reduce the brittleness of the film and improve the toughness of the film. It has been reported that the addition of plasticizers would change the mechanical properties of the film [39], and our results are similar to them. The presence of sodium hydroxide changed the pH of the films, which may have affected the stretch of the gelatin molecular chain to a certain extent. The degree of molecular chain extension of the protein base membrane is closely related to the mechanical properties of the film [9].

Table 3.
Mechanical properties and WVP of different films.
The EM and TS of the film did not change significantly (p > 0.05) after adding the MgO nanoparticles, but the EB was significantly reduced (p < 0.05), which indicated that the MgO nanoparticles reduced the toughness of the film and improved the brittleness of the film. This might be due to the poor dispersion of MgO nanoparticles in the film, resulting in the formation of nanoparticle agglomerates, which hindered the connection of hydrogen bonds and other covalent bonds in the film molecules, leading to the poor ductility of the film [8].
3.2.4. WVP of the Films
The WVP of packaging materials is very important for food, because water activity is usually one of the important factors that affect food safety and sensory quality. The WVP changes of the films are shown in Table 3. The WVP of the GF was 3.54 ± 0.10 g mm/m2 h kPa, which was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the other two composite films. This was mainly due to the hygroscopic properties of gelatin and glycerol [40].
With the addition of BC solution, the WVP of the film decreased significantly (p < 0.05) to 2.86 ± 0.09 g mm/m2 h kPa. This may have been related to the structure of the BC. Santos et al. [5] reported that after adding different concentrations of cellulose nanofibers to gelatin, the WVP of the film was significantly reduced, and it was attributed to the absence of amorphous areas of the cellulose whiskers and its dense hydrogen bond network. After adding BC to gelatin, the number and size of film pores were reduced (Figure 2), making it more difficult for water molecules to penetrate the film. The number and size of the pores of the film decreased (Figure 2), making it more difficult for water molecules to penetrate the film. The change of WVP of the film was not obvious (p > 0.05) after adding MgO nanoparticles. This was probably because the MgO nanoparticles were only combined with gelatin and BC through adsorption. However, this had no significant effect on the water vapor transmission rate of the film.
3.3. The Preservation Effect of Films on Preserved Eggs
3.3.1. The Changes in the Weight Loss Rate of Preserved Eggs
As shown in Figure 4, the weight loss rate of preserved eggs in each group increased significantly (p < 0.05) during storage, and there were significant differences (p < 0.05) between different groups. Among them, the weight loss rate of preserved eggs after coating was lower than that of the control group, and the weight loss rate of preserved eggs coated with GBMF was the lowest.
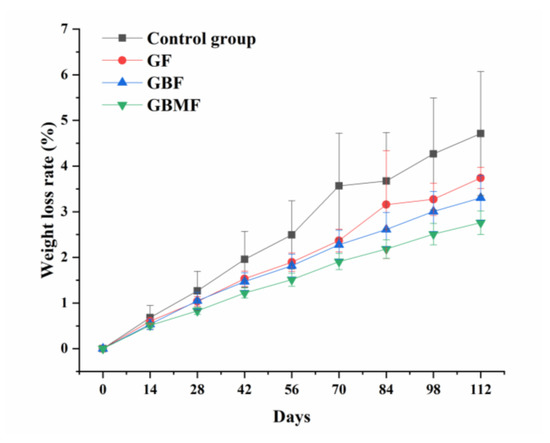
Figure 4.
Changes in the weight loss rate of preserved eggs coated with different films.
In the process of pickling fresh duck eggs into preserved eggs, the original structures of eggshell and eggshell membrane are destroyed by strong alkali. Therefore, the water and some volatile components in preserved eggs will continue to escape from the pores of the damaged eggshell. With the extension of storage time, biochemical reactions such as oxidative degradation continue to occur inside the preserved eggs, leading to an increase in volatile components, which is also the reason for the increase in the weight loss rate of preserved eggs.
Compared with the control group, the increasing trend of the weight loss rate of preserved eggs of the coating groups decreased to varying degrees, which shows that these films can effectively prevent the loss of moisture and other volatile substances in preserved eggs. Combined with the above analysis of the film, it can be seen that the preserved eggs coated with gelatin solution had the highest moisture permeability (Table 3), so the water in preserved eggs was more likely to penetrate the film and eggshell, resulting in more water loss in preserved eggs. In addition, the GF was more hydrophilic (Figure 3) and easier to be wetted by water. The microstructure of the GBMF was denser (Figure 2), and the film had a better ability to prevent water vapor penetration (Table 3), so the weight loss rate of preserved eggs coated with GBMF was the smallest. The smaller the pores of the films coated on the preserved egg shell were, the tighter the molecular structure was of the film, and thus less water in the preserved eggs could escape, which led to the difference in the weight loss rate of preserved eggs coated with different films.
3.3.2. The Changes in the pH of Preserved Eggs
As shown in Figure 5, the pH of preserved egg white and yolk showed a downward trend (p < 0.05) during storage. The pH of each coating group was significantly different (p < 0.05) from that of the control group, and it was basically higher than that of the control group during the entire storage process. However, there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) among the coating groups.
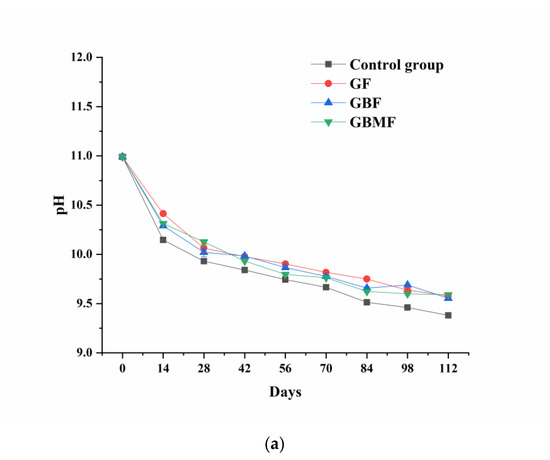
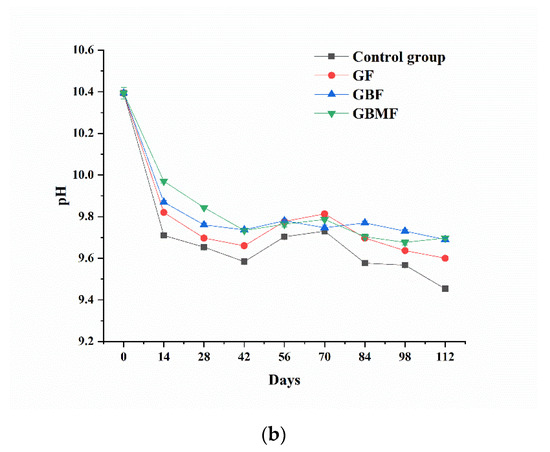
Figure 5.
Changes of the pH of preserved egg white (a) and yolk (b) coated with different films.
During the curing process of preserved eggs, a series of reactions such as oxidation, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, and Strecker degradation lead to the production of alcohols, aromatic compounds, and heterocyclic compounds in the preserved eggs [41,42]. Some volatile basic nitrogen-containing substances might escape from the preserved eggs through the pores of the egg shell with the extension of storage time and eventually lead to a decrease in pH. At the same time, these substances are also an important part of the unique flavor of preserved eggs [43].
After the preserved eggs were coated, the pores on the eggshell were blocked, which could reduce the escape of volatile basic nitrogen-containing substances inside the preserved eggs, and the decrease in pH was also delayed. Compared with the control group, the films could better prevent the exchange of substances between the inside and outside of preserved eggs and inhibit the oxidation of preserved eggs, resulting in less volatile alkaline nitrogen-containing substances.
3.3.3. The Changes of Textural Characteristics of Preserved Eggs
The texture characteristics largely reflect the sensory characteristics of food. The increase in hardness and chewiness represents the loss of water in the food, which lead to the drying of the surface of food and the deterioration of food sensory quality. The changes in texture characteristics of preserved egg white in all groups are shown in Figure 6. The change trends of hardness, springiness, and chewiness of all groups were consistent. Among them, hardness and chewiness of preserved eggs in each group showed an upward trend (p < 0.05) during storage, and the springiness remained basically unchanged (p > 0.05). The hardness and chewiness of the three coating groups were significantly lower (p < 0.05) than those of the control group, but there were no significant differences (p > 0.05) in the hardness and chewiness between the three coating groups.
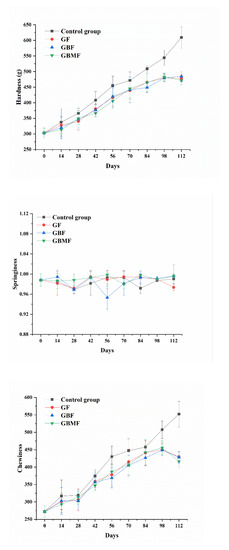
Figure 6.
Changes of texture characteristics of preserved egg white coated with different films.
The increase in hardness and chewiness of preserved eggs during storage can be explained from two aspects. On the one hand, the pH of the preserved egg white gradually decreased (Figure 5), so that the net charge content of the protein molecules decreased, the electrostatic repulsion between the proteins became smaller, and the protein molecular network became tighter. Finally, the formed egg white gel had a higher hardness and a more stable structure [44]. On the other hand, the gradual loss of water in preserved eggs during storage made the charged structures or hydrophilic groups that originally combined with water combine with each other, enhancing the structure of the gel [45].
The hardness and chewiness of the coated preserved eggs were lower than those of the control group, which may be because the pH of the control group dropped faster (Figure 5), and the preserved egg white lost more water, resulting in a denser structure of the gel and greater hardness and chewiness. The films could slow down the decrease of pH and the loss of water, so the hardness and chewiness of the film groups were smaller. Although the microstructure (Figure 2), hydrophobic strength (Figure 3), and WVP (Table 3) of the three kinds of films were different, they had little effect on the hardness and chewiness of preserved eggs. This might also be related to the insignificant difference in pH (Figure 5) between preserved eggs in the film coating groups analyzed above.
3.3.4. The Changes in the Content of TVB-N in Preserved Eggs
As shown in Figure 7, the TVB-N content of preserved egg white and yolk of each group gradually increased (p < 0.05) over time. In addition, the TVB-N content of egg white and yolk in the control group was obviously higher (p < 0.05) than those of three coating groups after the sixth week. However, the differences in TVB-N content of the three coating groups were not significant (p > 0.05).
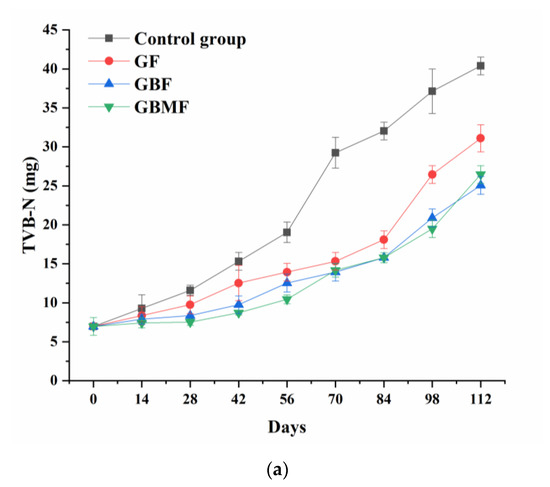
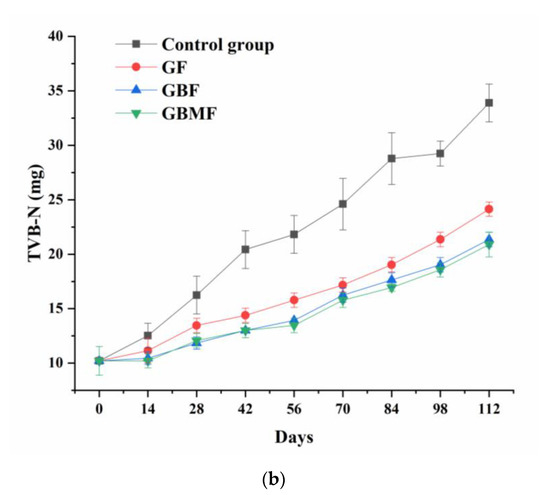
Figure 7.
Changes in the TVB-N content of preserved egg white (a) and yolk (b) coated with different films.
During the curing process of preserved eggs, most of the proteins degrade into small molecular weight peptides and even amino acids because of the strong alkali [46]. As a result, preserved egg white is more easily decomposed into basic nitrogen-containing substances such as ammonia and amines. Therefore, the TVB-N of freshly marinated preserved eggs was also higher.
The TVB-N content of the control group was higher than that of the coating groups, possibly because the pH of the control group decreased faster. As a result, the activity of protease in preserved eggs was enhanced, the rate of decomposing proteins was increased, and more basic nitrogen-containing substances were produced. The difference between the coating groups was not significant, indicating that these three films have no significant impact on the TVB-N content in preserved eggs, and the main influencing factors might be temperature and pH.
3.3.5. The Changes in the Color of Preserved Eggs
The color changes of preserved egg white and yolk are shown in Table 4 and Table 5. The value of L* and b* of preserved egg white in each group showed a significant decrease (p < 0.05) during storage, indicating that the brightness of egg white became darker, and the yellow color gradually disappeared. The value of a* of preserved egg white in each group increased notably (p < 0.05) within 0–14 days, which indicated that the color changed to red, but then the changes were relatively stable. After 114 days of storage, we found that the value of a* of the preserved egg white in the control group was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that of the preserved egg at the beginning of storage, which means that the color of the preserved egg white in the control group changed to red. In general, the yellowness of each preserved egg white disappeared during storage, the color gradually darkened, and the degree of darkening of the control group was lower than that of the coating groups.

Table 4.
Changes in the color of the preserved egg white coated with different films.

Table 5.
Changes in the color of the preserved egg yolk coated with different films.
The color change of preserved eggs is mainly related to the Maillard reaction. The high pH and the existence of glucose in the preserved eggs make them more prone to Maillard reactions [44]. The Maillard reaction causes the production of brown or even black melanoid, which results in darker color of preserved eggs. During storage, the degree of color change in the control group was less than that in the three coating groups, indicating that the degree of Maillard reaction in the preserved eggs was lower. This may have been due to the lower pH of the control group (Figure 5), resulting in less electrostatic repulsion between proteins and tighter binding between proteins molecules [44]; thus, the number of amino groups that could participate in the Maillard reaction also decreased. On the other hand, the decrease of pH also reduced the reactivity of amino and carbonyl compounds [47], reducing the extent of the Maillard reaction. At the same time, the loss of water also led to the accumulation of pigment substances. The control group lost more water, which resulted in more pigment accumulation and a darker color [45].
3.3.6. The Changes in Sensory Evaluation of Preserved Eggs
As shown in Figure 8, the sensory score of preserved eggs in each group gradually decreased (p < 0.05) during storage, and the sensory quality of preserved eggs in different groups was significantly different (p < 0.05). The fastest decrease was shown in the sensory score of the control group, and the slowest decline occurred in preserved eggs coated with GBMF.
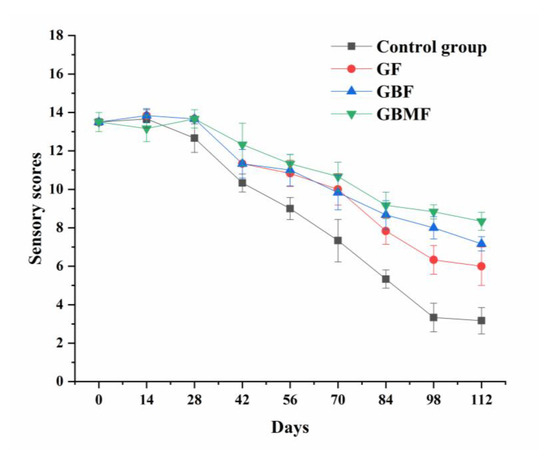
Figure 8.
Changes of the sensory score of preserved eggs coated with different films.
The increase in weight loss rate (Figure 4) increased the hardness of the preserved egg white (Figure 6) during the storage process, which eventually caused the shrinkage of preserved eggs. The Maillard reaction made the color of preserved egg darker due to the accumulation of pigment (Table 4). The degradation of protein and the oxidation of fatty acids led to a musty odor, which reduced the sensory score of preserved eggs. The coating on the preserved egg shell could block the pores of preserved egg shell to a certain extent, effectively reducing the drying shrinkage of preserved eggs caused by water loss or the exchange of other substances inside and outside, so as to ensure the integrity of preserved eggs. On the other hand, the films could inhibit the entry of external oxygen to avoid oxidation of fat in preserved eggs; at the same time, they could reduce the Maillard reaction induced by oxygen to a certain extent, and they ultimately reduced the generation of preserved musty odor and the deepening of the color.
4. Conclusions
The addition of BC and MgO nanoparticles gave the film a more compact microstructure. It also enhanced the surface hydrophobicity of the film and improved the mechanical properties and WVP. After these three kinds of film were applied to the preserved eggs, it was found that all three films could reduce the quality loss and TVB-N content of preserved eggs during storage, and effectively maintain the hardness of preserved egg white and ensure the sensory quality of preserved eggs. Among them, the GBMF had the best preserved egg quality, which may be attributed to the dense composite structure and good water vapor barrier properties of the film.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T. and Y.Z.; Data curation, Y.W.; Formal analysis, Y.W.; Funding acquisition, Y.T. and Y.Z.; Investigation, Y.W.; Project administration, Y.T. and Y.Z.; Validation, Y.T. and Y.Z.; Writing—original draft, Y.W.; Writing—review and editing, W.L., Y.T., and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [the National Natural Science Foundation of China] grant No. [31871832, 31760439 and 32060551].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31871832, 31760439, and 32060551).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ma, M. Egg and Egg Product Processing; In Chinese; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, N.; Yao, Y.; Xu, M.; Du, H.Y.; Tu, Y.G. The anti-inflammatory activity of peptides from simulated gastrointestinal digestion of preserved egg white in DSS-induced mouse colitis. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 6444–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, M.; Du, H.; Wu, N.; Tu, Y. Isolation and identification of peptides from simulated gastrointestinal digestion of preserved egg white and their anti-inflammatory activity in TNF-α-induced Caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 63, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Al-Asmar, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Roviello, V.; Esposito, M.; Mariniello, L. Preparation and characterization of bioplastics from grass pea flour cast in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Coatings 2018, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.M.; Filho, M.D.S.M.S.; Caceres, C.A.; Rosa, M.D.F.; Morais, J.P.S.; Pinto, A.M.; Azeredo, H.M. Fish gelatin films as affected by cellulose whiskers and sonication. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, A.D.T.; Balbinot, E.; Weber, C.I.; Tonial, I.B.; Machado-Lunkes, A. Fish Gelatin: Characteristics, Functional Properties, Applications and Future Potentials. Food Eng. Rev. 2014, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, P.J.D.A.; Menegalli, F.; Hubinger, M.; Roques, M. Mechanical, water vapor barrier and thermal properties of gelatin based edible films. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Zou, L.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Hydrophobic Ethylcellulose/Gelatin Nanofibers Containing Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9498–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.-W. Physical, mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin based active nanocomposite films containing AgNPs and nanoclay. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Phillips, G.O.; Yang, G. Utilization of bacterial cellulose in food. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.I.; Lee, S.E.; Yang, H.; Jin, Y.-H.; Park, C.-S.; Park, Y.S. Toxicologic evaluation of bacterial synthesized cellulose in endothelial cells and animals. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia, P.J.; Otoni, C.G. Nanotechnology and Edible Films for Food Packaging Applications, Bio-based Materials for Food Packaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Pakseresht, S.; Alogaili, A.W.M.; Akbulut, H.; Placha, D.; Pazdziora, E.; Klushina, D.; Konvičková, Z.; Kratošová, G.; Holešová, S.; Martynková, G.S. Silver/Chitosan Antimicrobial Nanocomposites Coating for Medical Devices: Comparison of Nanofiller Effect Prepared via Chemical Reduction and Biosynthesis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 2938–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunati, E.; Peltzer, M.A.; Armentano, I.; Jiménez, A.; Kenny, J.M. Combined effects of cellulose nanocrystals and silver nanoparticles on the barrier and migration properties of PLA nano-biocomposites. J. Food Eng. 2013, 118, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liebert, T.; Heinze, T. The dissolution of cellulose in NaOH-based aqueous system by two-step process. Cellulose 2011, 18, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, A.; Takahashi, K.; Kuroda, N.; Froning, G.W. Heat-induced Egg White Gels as Affected by pH. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Standard. GB 1040.3-2006, Plastics-Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 3: Test Conditions for Film and Sheets; The Standard Press of PR China: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.-G.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Du, H.-Y. Simultaneous Determination of 20 Inorganic Elements in Preserved Egg Prepared with Different Metal Ions by ICP-AES. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 6, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xue, H.; Xiong, C.; Li, J.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effects of temperature on quality of preserved eggs during storage. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3144–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Standard. GB/T 5009.47-2003, Analytical Methods for Hygienic Standards of Eggs and Egg Products; The Standard Press of PR China: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Standard. GB 5009.228-2016 Determination of Volatile Basic Nitrogen in Food; The Standard Press of PR China: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Standard. GB 2749-2015, Eggs and Egg Products; The Standard Press of PR China: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Oromiehie, A. Rheological and structural characterisation of film-forming solutions and biodegradable edible film made from kefiran as affected by various plasticizer types. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Luo, Z. Effect of glutamic acid on rheological properties of tapioca starch paste. Food Sci. 2012, 33, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Han, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, R.; et al. Effect of the interaction between myofibrillar protein and heat-induced soy protein isolates on gel properties. CyTA J. Food 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Malik, H.N.; Singhal, D.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Malakar, D.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Electrospun polycaprolactone/ZnO nanocomposite membranes as biomaterials with antibacterial and cell adhesion properties. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atares, L.; Bonilla, J.; Chiralt, A. Characterization of sodium caseinate-based edible films incorporated with cinnamon or ginger essential oils. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Go, M.-R.; Bae, S.-H.; Choi, S.-J. ZnO Interactions with Biomatrices: Effect of Particle Size on ZnO-Protein Corona. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusiak, J.; Grządka, E.; Bastrzyk, A. Stability, adsorption and electrokinetic properties of the chitosan/silica system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 554, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagis, L.M.C.; Veerman, C.; Ganzevles, R.; Ramaekers, M.; Bolder, S.G.; Van Der Linden, E. Mesoscopic structure and viscoelastic properties of β-lactoglobulin gels at low pH and low ionic strength. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, C.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Heck, J.; Van Der Linden, E. Mesostructure of fibrillar bovine serum albumin gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2003, 31, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, M.; Van De Velde, F.; Stijnman, A.; Van De Pijpekamp, A.; Visschers, R.W. Structure and rheological properties of acid-induced egg white protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.K.; Brodsky, B.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Ramshaw, J.A. Structural consequences of D-amino acids in collagen triple-helical peptides. Biopolymers 1999, 49, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Colby, R.H.; Lusignan, C.P.; Whitesides, T.H. Kinetics of Triple Helix Formation in Semidilute Gelatin Solutions. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9999–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natu, M.V.; De Sousa, H.C.; Gil, M.H. Effects of drug solubility, state and loading on controlled release in bicomponent electrospun fibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Alboofetileh, M.; Rezaei, M.; Behrooz, R. Comparing physico-mechanical and thermal properties of alginate nanocomposite films reinforced with organic and/or inorganic nanofillers. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, S.; Brabu, B.; Thiruvadigal, D.J.; Gopalakrishnan, C.; Natarajan, T. Optical, bactericidal and water repellent properties of electrospun nano-composite membranes of cellulose acetate and ZnO. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J. Gelatin and its application in science and technology. Gelatin Sci. Technol. 2009, 29, 28–49. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, M.; Motamedzadegan, A. The Effect of Plasticizers on Mechanical Properties and Water Vapor Permeability of Gelatin-Based Edible Films Containing Clay Nanoparticles. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2015, 5, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, G.A.; Lourenço, R.V.; Bittante, A.M.Q.B.; Sobral, P.J.D.A. Physical and morphological properties of nanocomposite films based on gelatin and Laponite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Tu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. Changes in gel characteristics of egg white under strong alkali treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, A.; Chen, M.; Ockerman, H.W.; Chen, J. Effect of different alkali treatments on the chemical composition, physical properties, and microstructure of pidan white. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 52, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, M.; Du, H.; Tu, Y. Relationship between protein structure changes and in vitro digestion of preserved egg white during pickling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasen, P.; Benjakul, S. Effects of green tea and chinese tea on the composition and physical properties of pidan white. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2011, 35, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasen, P.; Benjakul, S. Chemical composition, physical properties and microstructure of pidan white as affected by different divalent and monovalent cations. J. Food Biochem. 2011, 35, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Shao, Y.; Tu, Y. Changes of microstructure characteristics and intermolecular interactions of preserved egg white gel during pickling. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Benjakul, S. Effect of glucose treatment on texture and colour of pidan white during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 51, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).