Corrosion Behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding in a Simulated Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
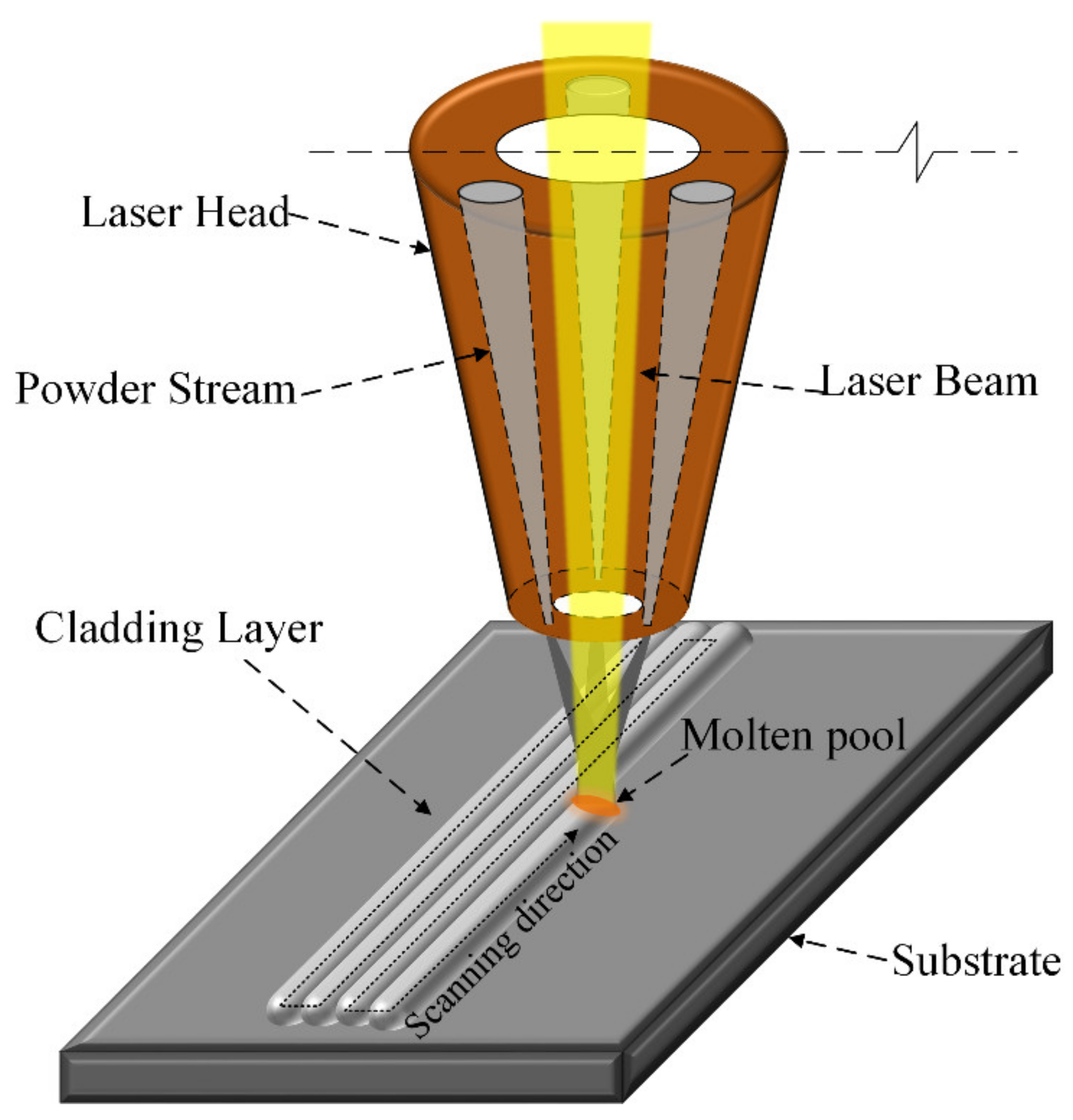
2.2. Laser Cladding Process
2.3. Characterization Method
2.4. Corrosion Experiment Method
3. Results and Discussion
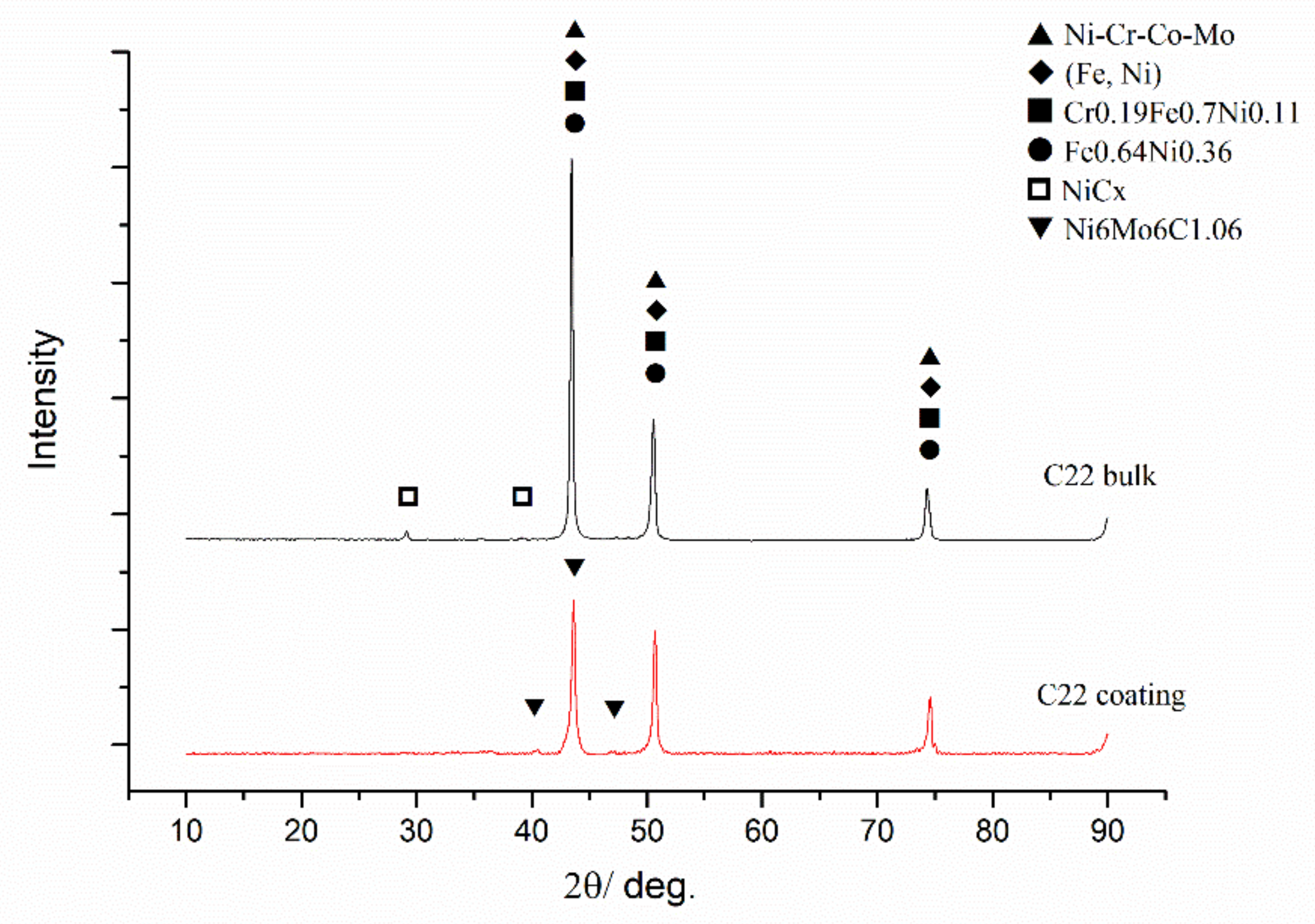
3.1. XRD Analysis
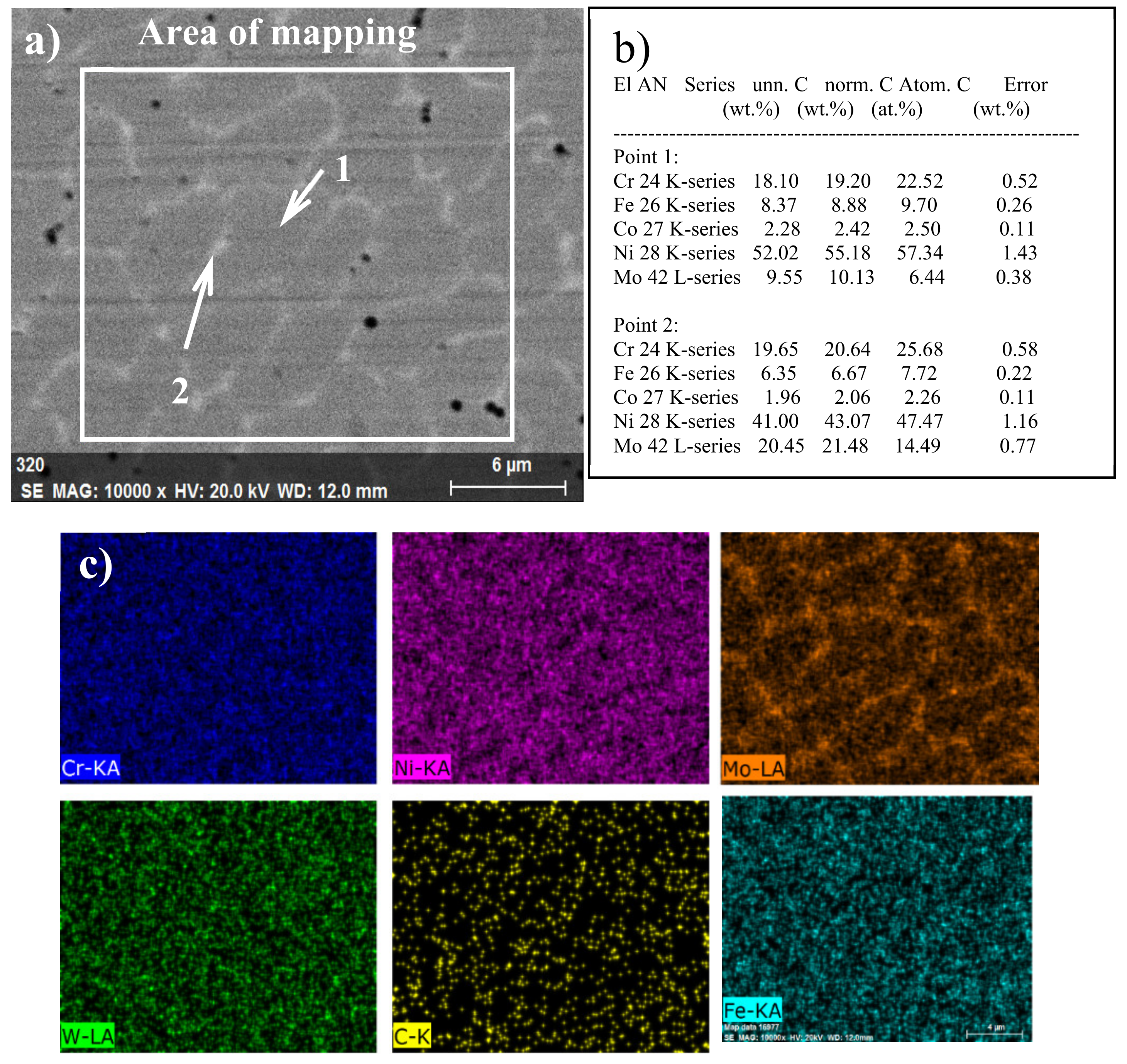
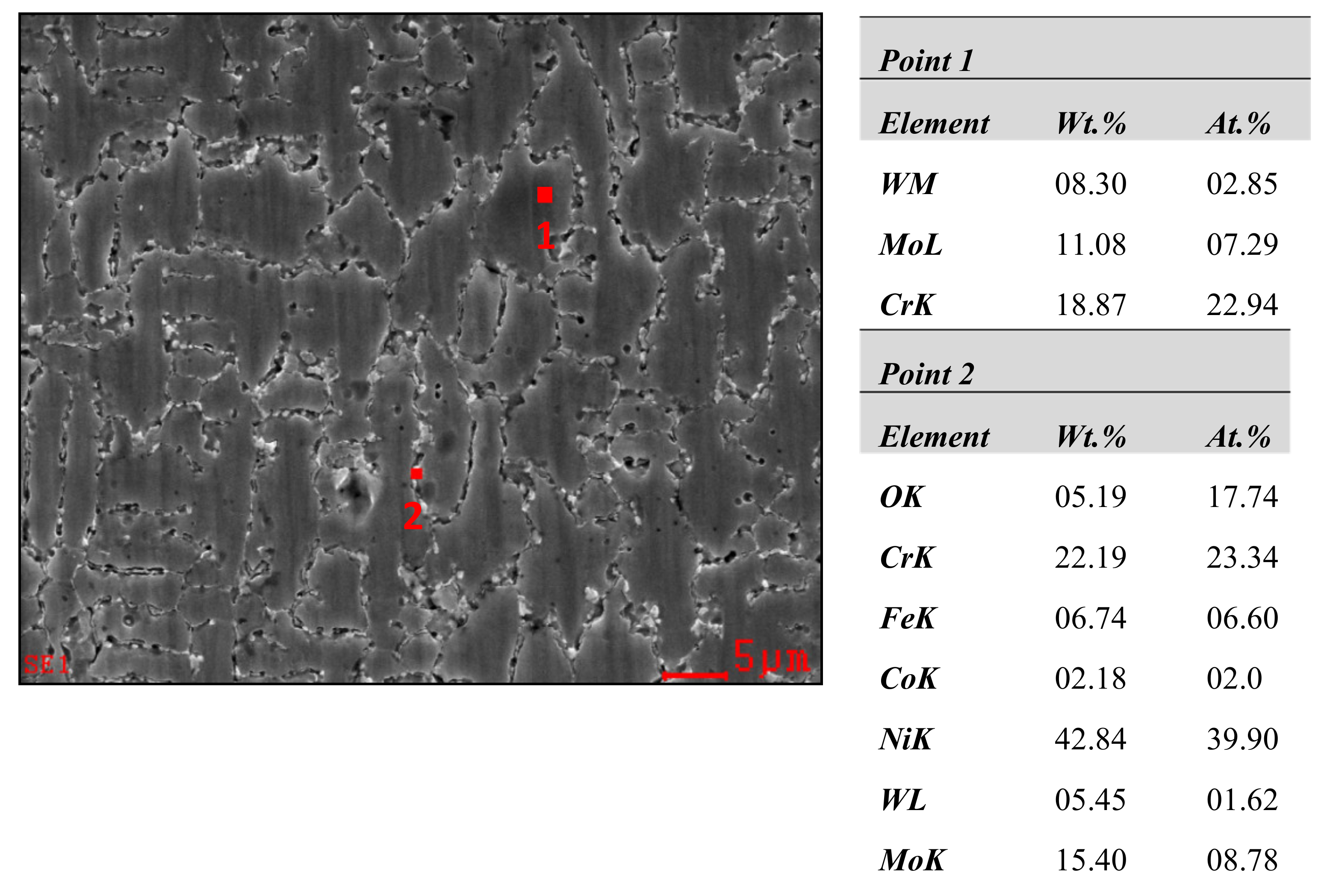
3.2. SEM and EDS Analysis
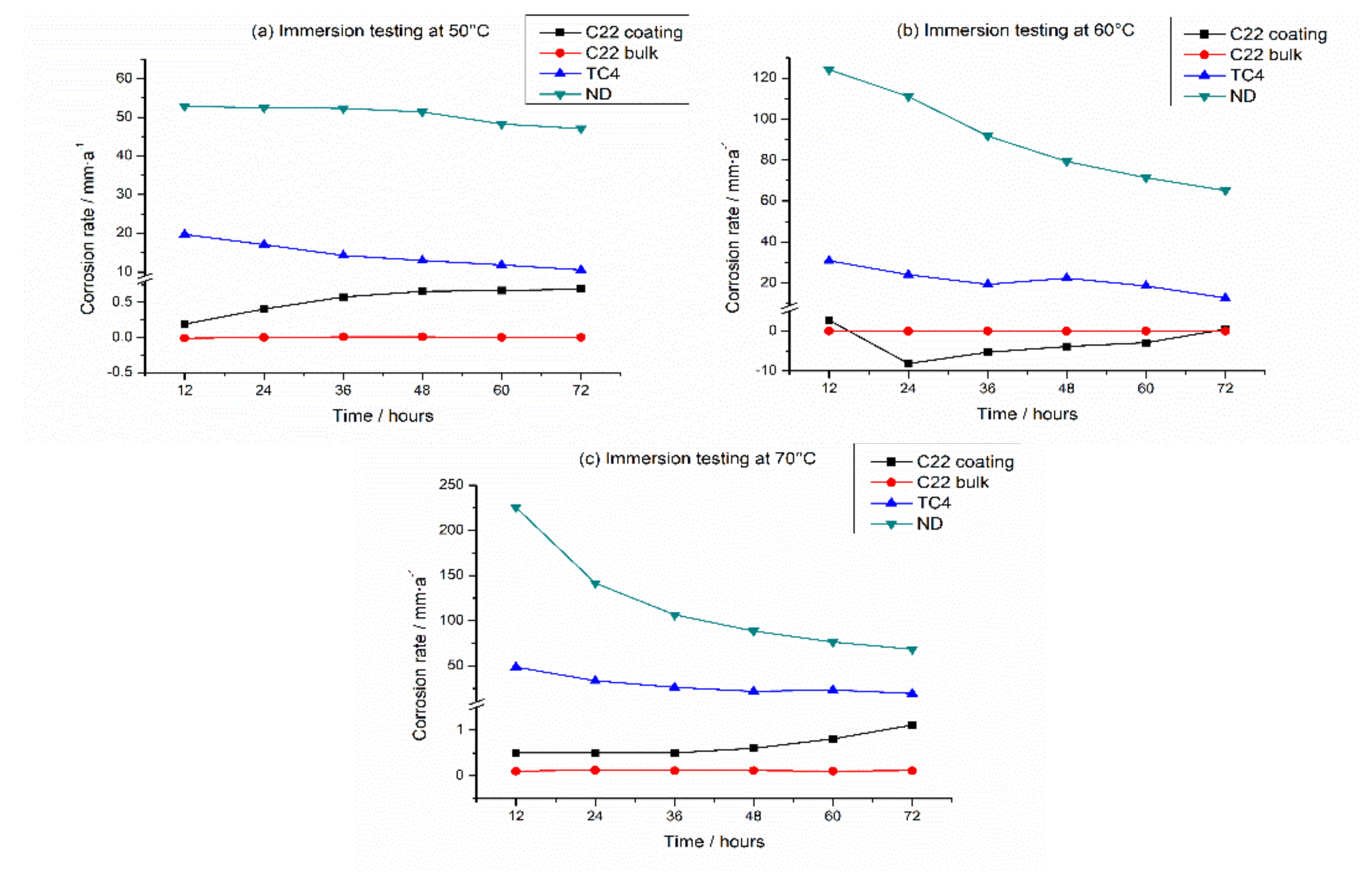
3.3. Corrosion Rate Analysis
3.4. Corrosion Morphology and Analysis
4. Conclusions
- A Hastelloy C22 coating fabricated by coaxial laser cladding technology is composed of a γ-Ni solid solution and carbide Ni6Mo6C1.06, essentially similar to the cast Hastelloy C22 bulk.
- The microstructure of the C22 coating mainly contains eutectic and dentrite, and the distribution of solidification from the bottom to the top is cellular, columnar, and equiaxed. These characteristics are similar to Ni–Cr–Mo coatings fabricated by powder presetting laser cladding.
- The corrosion resistance of the C22 coating in a simulated sulfuric acid dew point corrosion environment is very close to that of C22 bulk, and approximate 20 times that of titanium alloy TC4 and 160 times that of corrosion-resistant steel ND. The increase in temperature obviously aggravates the corrosion of the four specimens.
- The corrosion behavior of the C22 coating is intergranular corrosion. The segregation of molybdenum, chromium containing corrosion products, and smaller anode micro-batteries leads to the more severe corrosion compared to that of C22 bulk. The ion diffusion process is the dominant influence factor of the corrosion rate.
- In consideration of the similar performance and the lower cost compared to those of a whole C22 alloy application, the laser cladding C22 coating is a potential technology for preventing sulfuric acid dew point corrosion in low-temperature devices in coal-fired boilers, such as FDG systems and backend ductworks.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, D.M.; Kieffer, J.K.; Trewella, R.J.; Wummer, C.J.; Mathay, W.L. Determining corrosivity of flue gas condensate. Power Eng. 1984, 88, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.R. Dewpoint Corrosion; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Huijbregts, W.M.M.; Leferink, R.G.I. Latest advances in the understanding of acid dewpoint corrosion: Corrosion and stress corrosion cracking in combustion gas condensates. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2004, 51, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M. Problems existing in operation of wet limestone/gypsum desulfuration system in luohuang power plant and analysis. Therm. Power Gener. 2004, 7, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Z. Analysis of low temperature corrosion in coal-fired boiler. Ind. Boil. 2001, 6, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, D.; Kear, R.W. The corrosion of a steel surface by condensed films of sulphuric acid. J. Appl. Chem. 2007, 1, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworowski, R.J.; Mack, S.S. Evaluation of Methods for Measurement of SO3/H2SO4 in Flue Gas. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1979, 29, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, R.T. The kinetics of SO3 formation in oil-fired boilers. J. Inst. Energy 1982, 55, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadori, A. Estimation of combustion flue gas acid dew point during heat recovery and efficiency gain. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Sun, F.Z.; Shi, Y.T.; Li, F.; Ma, L. Experimental study and mechanism analysis on low temperature corrosion of coal fired boiler heating surface. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 80, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.M.; Kieffer, J.K.; Trewella, R.J.; Wummer, C.J.; Mathay, W.L. Flue Gas Condensate Sampling and Analysis Study; NACE: Houston, TX, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, L. Corrosion in flue gas desulfurization plants and other low temperature equipment. Mater. Corros. 1992, 43, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOHURD. GB 50051-2013: Code for Design of Chimneys; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Saidur, R.; Ahamed, J.U.; Masjuki, H.H. Energy, exergy and economic analysis of industrial boilers. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, H.T.; Rosenberg, H.S. Technical aspects of lime/limestone scrubbers for coal-fired power plants: Part II: Instrumentation and technology. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1980, 30, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Jozewicz, W. Flue gas desulfurization: The state of the art. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 1676–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.T.; Oh, O.Y.; Chang, S.Y. Analysis of degradation of a super-austenitic stainless steel for flue gas desulfurization system after a fire accident. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2008, 15, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangchen, M.; Jin, C.; Kunling, J.; Lan, M.; Sijie, Z.; Kai, W. Environmental influence and countermeasures for high humidity flue gas discharging from power plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makansi, J. Anticipate corrosion problems. Power 1984, 128, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordzilowski, J.; Darowicki, K. Anti-corrosion protection of chimneys and flue gas ducts. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1998, 45, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.Y.; Chen, H.; Liang, Z.Y.; Zhao, Q.X. Experimental study on corrosion of steels for flue gas reheaters in a coal-fired power plant. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 115, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Chen, H.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, Q. Deposition and corrosion characteristics of liquid-solid droplets on tubular corrosion probes in desulfurized flue gas. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 90, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, Z.G. Corrosion evaluation of one wet desulfurization equipment—Flue gas desulfurization unit. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radway, J.E.; Exley, L.M. A practical review of the cause and control of cold end corrosion and acidic stack emissions in oil-fired boilers. In Proceedings of the Winter Meeting of the ASME, Houston, TX, USA, 30 November–5 December 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, V. Cold end corrosion: Causes and cures. Hydrocarb. Process. 1989, 68, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, V. Solve waste-fuel boiler corrosion problems in procurement. Power Eng. 1991, 95, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pendrous, R. Corrosion resistance of FGD ductwork materials. Process Eng. 1989, 70, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.K.; Koch, G.H.; Ross, R.W. Corrosion performance of duplex and austenitic stainless steels in simulated fgd environments. In International Corrosion Conference Series, v 1996-March; NACE: Houston, TX, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cerny, M.X.; Peacock, D.K. Application and performance of titanium linings in FGD ductwork and stacks. Mater. Corros. 1992, 43, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.; Rajeswari, S. Evaluation of mercaptoazoles as corrosion inhibitors in simulated sulphur dioxide scrubber environments. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1995, 42, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CICIND. Model Code for Steel Chimneys, Revision 1—1990, Amendment A—2002; CICIND (International Committee on Industrial Construction): Zurich, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, S.D.; Covino, B.S. ASM Handbook Vol. 13c: Corrosion: Environments and Industries; ASM International: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, L.; Ni, H.; Hao, W.; Man, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Influence of temperature on the electrochemical and passivation behavior of 2507 super duplex stainless steel in simulated desulfurized flue gas condensates. Corros. Sci. 2017, 118, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asphahani, A.I.; Nicholas, A.F.; Silence, W.L.; Meyer, T.H. High performance alloys for solving severe corrosion problems in flue gas desulfurization systems. Mater. Corros. 1989, 40, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshio, T.; Katsuo, S. Corrosion-resistant Ni-Cr-Mo alloys in hot concentrated sulphuric acid with active carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1995, 198, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darowicki, K.; Krakowiak, S. Durability evaluation of Ni-Cr-Mo super alloys in a simulated scrubbed flue gas environment. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 1999, 46, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkheiner, R.; Remer, V. Corrosion-resistant alloys for flue gas desulfurization installations. Chem. Pet. Eng. 1993, 29, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al’tpeter, E.; Kirkheiner, R.; Rokel, M.; Uait, F. Corrosion resistance of alloys in sulfuric acid at various concentrations and temperatures. Chem. Pet. Eng. 1995, 31, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanger, G.; Rameau, J.J. Behaviour of Hastelloy C22 steel in sulphate solutions at pH 3 and low temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 2097–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.; Rajeswari, S. Evaluation of high Ni-Cr-Mo alloys for the construction of sulfur dioxide scrubber plants. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1996, 5, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haemers, T.A.M.; Rickerby, D.G.; Lanza, F.; Geiger, F.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Laser Cladding of Stainless Steel with Hastelloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2001, 3, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.; Timms, N.; Bryden, B.; Pashby, I. High power diode laser cladding. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2003, 138, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Yao, Y. Characteristics of cobalt-based alloy coating on tool steel prepared by powder feeding laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2007, 39, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Characterization of dilution action in laser-induction hybrid cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2011, 43, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidouci, A.; Pelletier, J.M.; Ducoin, F.; Dezert, D.; el Guerjouma, R. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of laser coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 123, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, J.N. Nd: YAG laser cladding of marine propeller with hastelloy C-22. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 2004, 79, 1583–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Bai, S.L.; de Liu, Z. Microstructures, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Hastelloy C22 coating produced by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Bai, S.L.; de Liu, Z. Corrosion behavior of Hastelloy C22 coating produced by laser cladding in static and cavitation acid solution. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2014, 24, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Bai, S.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; de Liu, Z. Effect of mechanical polishing on corrosion behavior of Hastelloy C22 coating prepared by high power diode laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 303, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Bai, S.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; de Liu, Z. Improvement of Ni-Cr-Mo coating performance by laser cladding combined re-melting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 308, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bai, S.L. The anti-corrosion behavior under multi-factor impingement of Hastelloy C22 coating prepared by multilayer laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 437, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bai, S.L.; Ge, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.Y. Erosion-corrosion behavior and electrochemical performance of Hastelloy C22 coatings under impingement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 456, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.D.; Li, C.C.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, C. High temperature corrosion behaviors of 20G steel, Hastelloy C22 alloy and C22 laser coating under reducing atmosphere with H2S. Coatings 2020, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, M.A.; Shannon, G.J.; Steen, W.M. Laser generating metallic components. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 July–1 August 1997; Volume 3092, pp. 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, J.; Dutta, D.; Kikuchi, N.; Ghosh, A. Closed loop direct metal deposition: Art to Part. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2000, 34, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, U.; Ocelík, V.; de Hosson, J.T.M. Analysis of coaxial laser cladding processing conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 197, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.D.; Partes, K.; Seefeld, T.; Vollertsen, F. Comparison of coaxial and off-axis nozzle configurations in one step process laser cladding on aluminum substrate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, J. Effect of yttrium on the corrosion behaviour of 09CrCuSb alloy in concentrated sulphuric acid. Corros. Sci. 2013, 69, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Zhao, Q.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, Z.C.; Tao, W.Q. Mechanism research on coupling effect between dew point corrosion and ash deposition. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 54, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Designation: G1-03 (Reapproved 2017), Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Designation: G31-12a, Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moskovits, P. Low-Temperature Boiler Corrosion and Deposits—A Literature Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1959, 51, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, F.G.; Silence, W.L.; Wright, D. Predicting the corrosivity of an operating FGD system. Power Eng. 1994, 98, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Sun, F.L.; Lv, S.J.; Li, X.G. A new steel with good low-temperature sulfuric acid dew point corrosion resistance. Mater. Corros. 2012, 63, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.z.; de Liu, Z.; Li, H.c.; Wang, Y.t.; Li, B. Investigations on the behavior of laser cladding Ni-Cr-Mo alloy coating on TP347H stainless steel tube in HCl rich environment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 232, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J. A comparative study on the high temperature corrosion of TP347H stainless steel, C22 alloy and laser-cladding C22 coating in molten chloride salts. Corros. Sci. 2014, 83, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, L. Effects of powder concentration distribution on fabrication of thin-wall parts in coaxial laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2005, 37, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mi, G.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, P.; Shao, X.; Wang, C. Morphologies, microstructures and properties of TiC particle reinforced Inconel 625 coatings obtained by laser cladding with wire. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Shi, C.; Zhou, S.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L.C. Enhanced corrosion and wear resistance properties of carbon fiber reinforced Ni-based composite coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A. Performance of corrosion-resistant alloys in concentrated acids. Acta Metall. Sin. 2017, 30, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorhe, D.D.; Raja, K.S.; Namjoshi, S.A.; Radmilovic, V.; Tolly, A.; Jones, D.A. Electrochemical methods to detect susceptibility of Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy 22 to intergranular corrosion. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2005, 36, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Chou, J.M.; Hsieh, R.I.; Lee, J.L. Corrosion behaviour of vacuum induction-melted Ni-based alloy in sulphuric acid. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Ni | Cr | Mo | Mn | Fe | Si | Co | V | W | Ti | Al | Cu | Sb | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C22 powders | Bal. | 21.3 | 13.2 | - | 2.93 | - | 2.0 | - | 3.0 | - | - | - | - | 0.08 |
| C22 bulk | Bal. | 20.0 | 13.8 | 0.45 | 5.0 | 0.08 | 1.83 | 0.3 | 3.2 | - | - | - | - | 0.001 |
| TC4 | - | - | - | - | 0.3 | 0.15 | - | 3.8 | - | Bal. | 6.1 | - | - | - |
| ND | - | 0.92 | 0.089 | 0.43 | Bal. | 0.28 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.38 | 0.08 | - |
| Q235 | - | - | - | 0.08 | Bal. | 0.37 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.16 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, C. Corrosion Behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding in a Simulated Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion Environment. Coatings 2020, 10, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090849
Zheng C, Liu Z, Chen S, Liu C. Corrosion Behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding in a Simulated Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion Environment. Coatings. 2020; 10(9):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090849
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Chao, Zongde Liu, Shanshan Chen, and Congcong Liu. 2020. "Corrosion Behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding in a Simulated Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion Environment" Coatings 10, no. 9: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090849
APA StyleZheng, C., Liu, Z., Chen, S., & Liu, C. (2020). Corrosion Behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo Alloy Coating Fabricated by Laser Cladding in a Simulated Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion Environment. Coatings, 10(9), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090849






