Metallic Nanoparticle-Decorated Polydopamine Thin Films and Their Cell Proliferation Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of AgNPs and AuNPs
2.2. Preparation of PDA, PDA@AgNP, PDA@AuNP1, and PDA@AuNP2 Thin Films
2.3. Characterization of NPs and Thin Films
2.4. Cell Culture and Cell Adhesion to Thin Films
2.5. Cell Viability (MTT Assay)
3. Results and Discussion
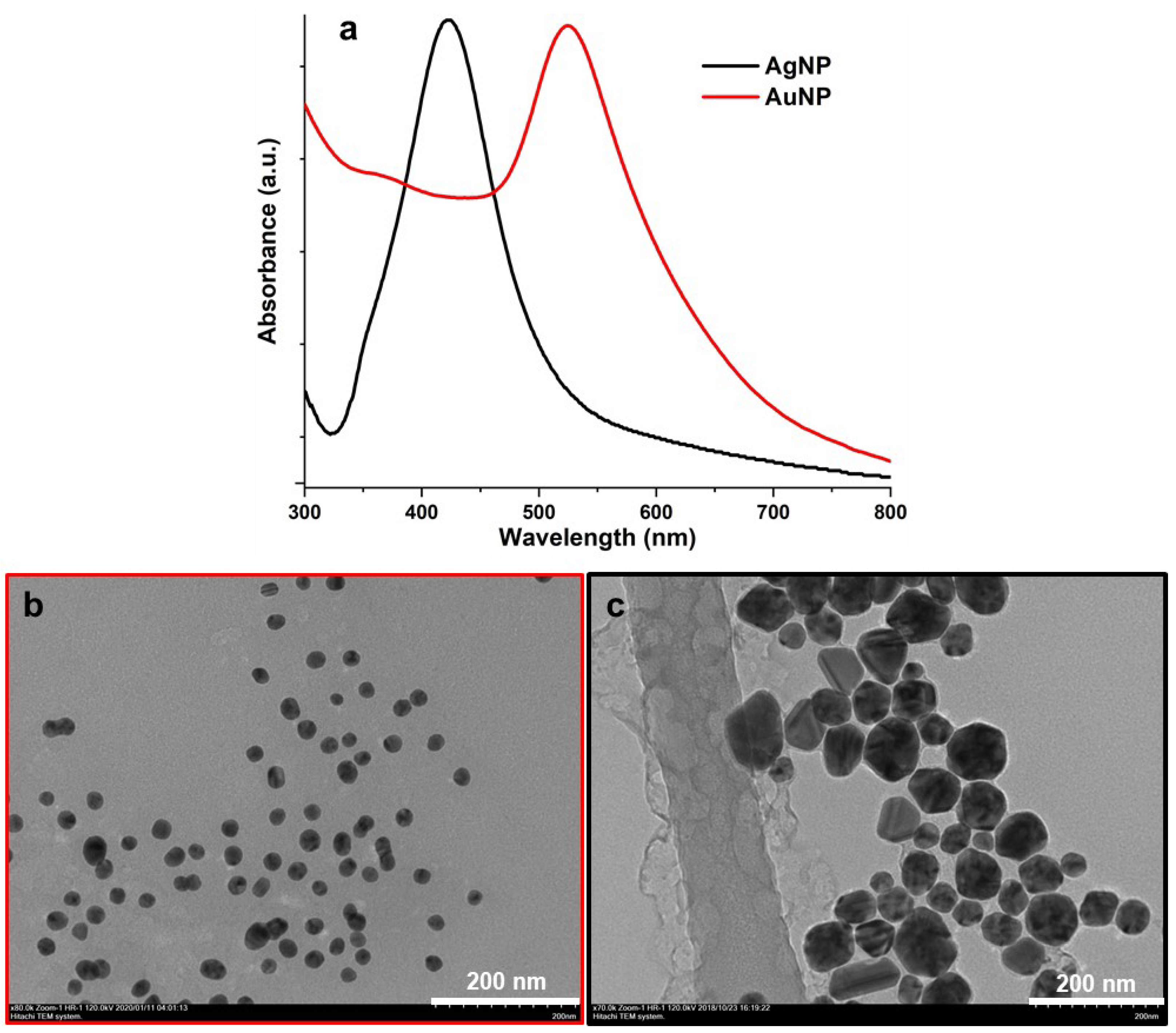
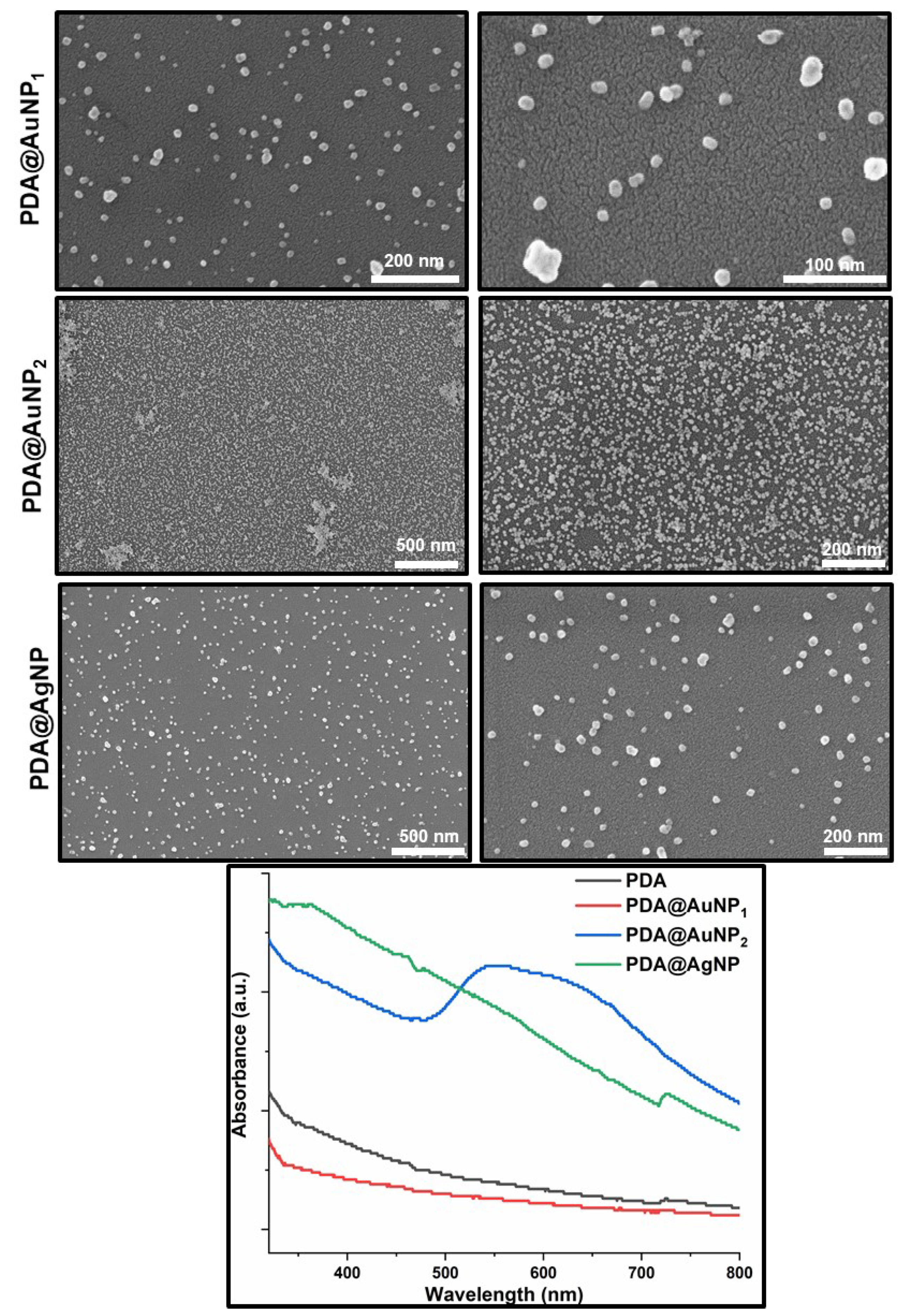
3.1. Characterization of NPs and Thin Films
3.2. Biocompatibility Testing of Thin Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Gong, L.; Xiang, L.; Du, Y.; Hu, W.; Zeng, H.; Xu, Z.-K. Deposition and adhesion of polydopamine on the surfaces of varying wettability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30943–30950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Lynge, M.; Schattling, P.; Städler, B. Recent developments in poly(dopamine)-based coatings for biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2725–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, A.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zelikin, A.N.; Tjipto, E.; Caruso, F. Self-polymerization of dopamine as a versatile and robust technique to prepare polymer capsules. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3042–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yan, Y.; Such, G.K.; Liang, K.; Ochs, C.J.; Postma, A.; Caruso, F. Immobilization and intracellular delivery of an anticancer drug using mussel-inspired polydopamine capsules. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-B.; Chen, W.-T.; Chien, H.-W.; Kuo, W.-H.; Wang, M.-J. Poly(dopamine) coating of scaffolds for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 4187–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Kung, K.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lee, T.-M.; Lui, T.-S. Engineering three-dimensional structures using bio-inspired dopamine and strontium on titanium for biomedical application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7927–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Bin Lee, Y.; Shin, H.; Um, S.H.; Kim, J.B.; Park, K.I.; Lee, H.; Cho, S.-W. Polydopamine-mediated surface modification of scaffold materials for human neural stem cell engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6952–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Bae, J.Y.; Koo, H.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Choi, W.S. A remote-controlled generation of gold@polydopamine (core@shell) nanoparticles via physical-chemical stimuli of polydopamine/gold composites. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.H.; Ryu, J.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, H.; Park, C.B. General functionalization route for cell adhesion on non-wetting surfaces. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, G.; Wang, K.; Wan, Q.; Tao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Recent developments in polydopamine: An emerging soft matter for surface modification and biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16819–16840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.H.; Park, C.B. Human endothelial cell growth on mussel-inspired nanofiber scaffold for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, C.B. Spatial control of cell adhesion and patterning through mussel-inspired surface modification by polydopamine. Langmuir 2010, 26, 15104–15108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Kim, K.Y.; Wook, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, K.D.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, H. Attenuation of thein vivotoxicity of biomaterials by polydopamine surface modification. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Jin, Q.; Ren, K.; Ji, J. Mussel-inspired polydopamine: A biocompatible and ultrastable coating for nanoparticlesin vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9384–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Qin, H.; Cheng, C.; Xia, Y.; He, C.; Nie, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C. Mussel-inspired self-coating at macro-interface with improved biocompatibility and bioactivity via dopamine grafted heparin-like polymers and heparin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 2, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebtsov, N.G.; Dykman, L.A. Optical properties and biomedical applications of plasmonic nanoparticles. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H. Biomedical applications of plasmon resonant metal nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2006, 1, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A. Biomedical applications of multifunctional plasmonic nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 5, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Gao, Z. Nanostructure-based electrical biosensors. Nano Today 2009, 4, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolková, B.; El Yamani, N.; Collins, A.R.; Gutleb, A.; Dusinska, M. Nanoparticles in food. Epigenetic changes induced by nanomaterials and possible impact on health. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 77, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, R.E.; Gouyau, J.; Lamouroux, E. Limitations of recent studies dealing with the antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles: Fact and opinion. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, E.; Milani, M.; Aval, S.F.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Nasrabadi, H.T.; Nikasa, P.; Joo, S.W.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; et al. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis methods, bio-applications and properties. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajnai, G.; Chiu, A.; Kan, T.; Cheng, C.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chang, J. Trends of gold nanoparticle-based drug delivery system in cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2014, 6, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Schacht, E. Biopolymer-based hydrogels as scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: A review. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1387–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutolf, M.; Hubbell, J. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.M.; George, J.H. Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science 2005, 310, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Filová, E.; Parizek, M.; Ruml, T.; Švorčík, V. Modulation of cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation on materials designed for body implants. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 739–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, M.J.; Gadegaard, N.; Oreffo, R.O.C. Harnessing nanotopography and integrin–matrix interactions to influence stem cell fate. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, M.J.P.; Richards, R.G.; Dalby, M.J. Nanotopographical modification: A regulator of cellular function through focal adhesions. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A. The employment of a conformal polydopamine thin layer reduces the cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Turk. J. Zool. 2020, 44, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M. Silver-nanoparticle-decorated gold nanorod arrays via bioinspired polydopamine coating as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) platforms. Coatings 2019, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Yilmaz, M. Bimetallic core–shell nanoparticles of gold and silver via bioinspired polydopamine layer as surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) platform. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M. 3-D and plasmonic nanoparticle decorated catalytic system via bio-inspired polydopamine coating: Cigar filter case study. Hacet. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 46, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakirci, G.; Yilmaz, M.; Babur, E.; Ozden, D.; Demirel, G. Understanding the effect of polydopamine coating on catalytic reduction reactions. Catal. Commun. 2017, 91, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, B.; Yilmaz, M.; Turk, M.; Kocum, I.C.; Pişkin, E. Antenna-type radiofrequency generator in nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48427–48434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Bakirci, G.; Erdogan, H.; Tamer, U.; Demirel, G. The fabrication of plasmonic nanoparticle-containing multilayer films via a bio-inspired polydopamine coating. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 12638–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Senlik, E.; Bişkin, E.; Yavuz, M.S.; Tamer, U.; Demirel, G. Combining 3-D plasmonic gold nanorod arrays with colloidal nanoparticles as a versatile concept for reliable, sensitive, and selective molecular detection by SERS. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5563–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.S.; Yilmaz, M.; Babur, E.; Ozdemir, B.; Erdogan, H.; Tamer, U.; Demirel, G. Large area uniform deposition of silver nanoparticles through bio-inspired polydopamine coating on silicon nanowire arrays for practical SERS applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4894–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazario, E.; Sanchez-Marcos, J.; Menendez, N.; Herrasti, P.; García-Hernández, M.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A. One-pot electrochemical synthesis of polydopamine coated magnetite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 48353–48361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangmeister, R.A.; Morris, T.A.; Tarlov, M.J. Characterization of polydopamine thin films deposited at short times by autoxidation of dopamine. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8619–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureshkumar, M.; Siswanto, D.Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-K.; Wang, M.-J. Antibacterial and biocompatible surfaces based on dopamine autooxidized silver nanoparticles. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Huang, L.-Y.; Shen, T.-L.; Yeh, J.A. Cell adhesion, morphology and biochemistry on nano-topographic oxidized silicon surfaces. Eur. Cell Mater. 2010, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, A.A.; Ahmad, M.R. A review of cell adhesion studies for biomedical and biological applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18149–18184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffi, C.; Shi, Z.; Kong, C.H.; Wang, W. In vitro findings of titanium functionalized with estradiol via polydopamine adlayer. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Sui, J. One-step deposition of antibacterial Ag@PDA hybrid films on an NiTi alloy. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29263–29272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aysin, F.; Yilmaz, A.; Yilmaz, M. Metallic Nanoparticle-Decorated Polydopamine Thin Films and Their Cell Proliferation Characteristics. Coatings 2020, 10, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090802
Aysin F, Yilmaz A, Yilmaz M. Metallic Nanoparticle-Decorated Polydopamine Thin Films and Their Cell Proliferation Characteristics. Coatings. 2020; 10(9):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090802
Chicago/Turabian StyleAysin, Ferhunde, Asli Yilmaz, and Mehmet Yilmaz. 2020. "Metallic Nanoparticle-Decorated Polydopamine Thin Films and Their Cell Proliferation Characteristics" Coatings 10, no. 9: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090802
APA StyleAysin, F., Yilmaz, A., & Yilmaz, M. (2020). Metallic Nanoparticle-Decorated Polydopamine Thin Films and Their Cell Proliferation Characteristics. Coatings, 10(9), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090802





