Effects of the Size of Charged Nanoparticles on the Crystallinity of SiC Films Prepared by Hot Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
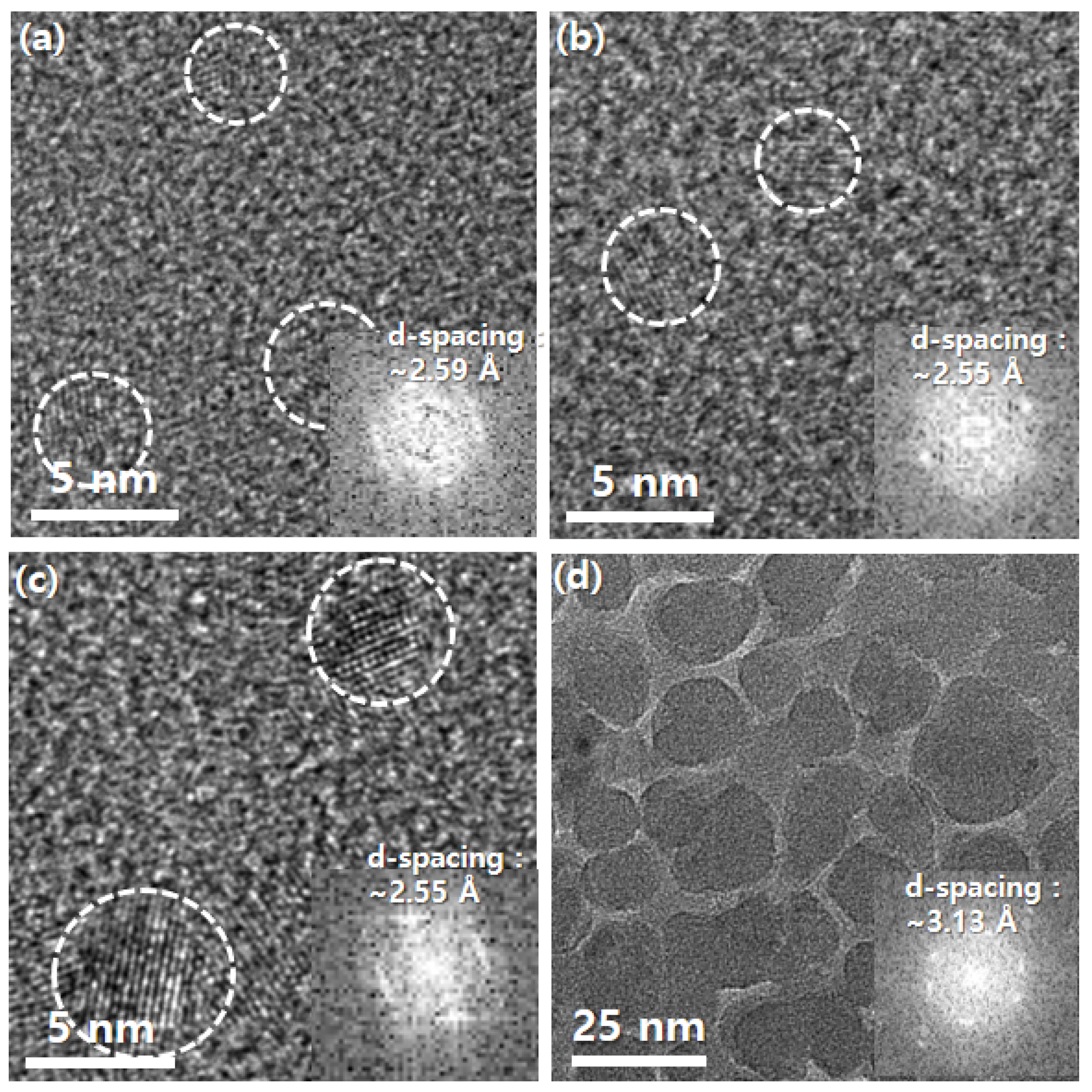
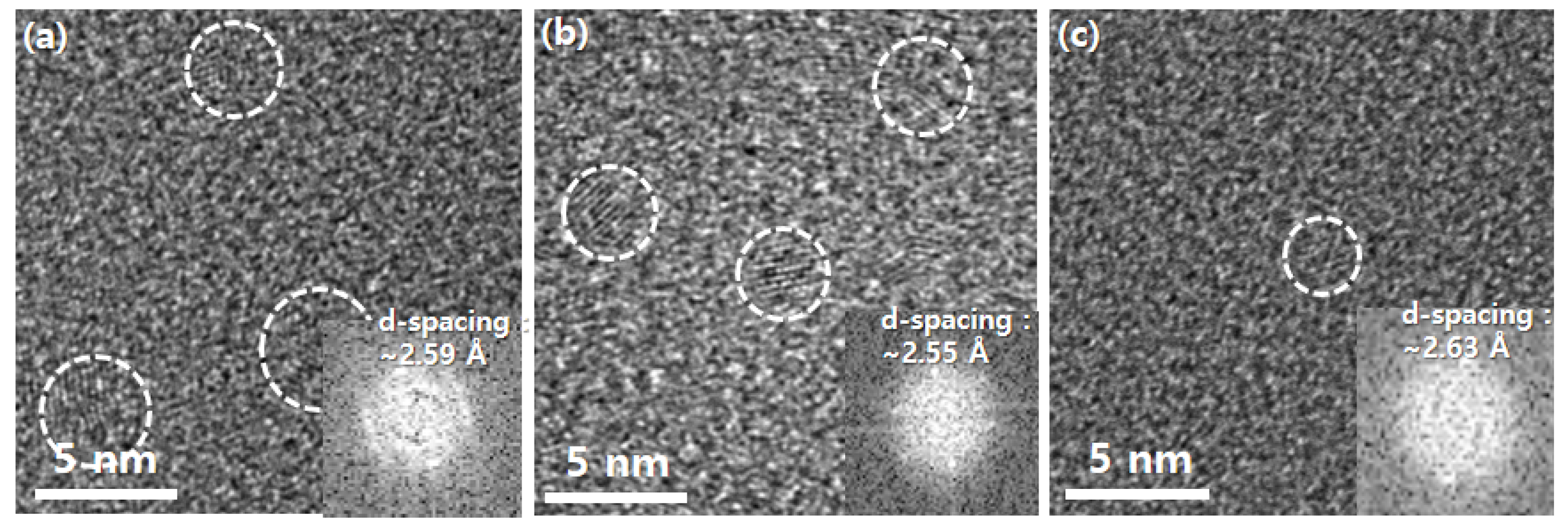
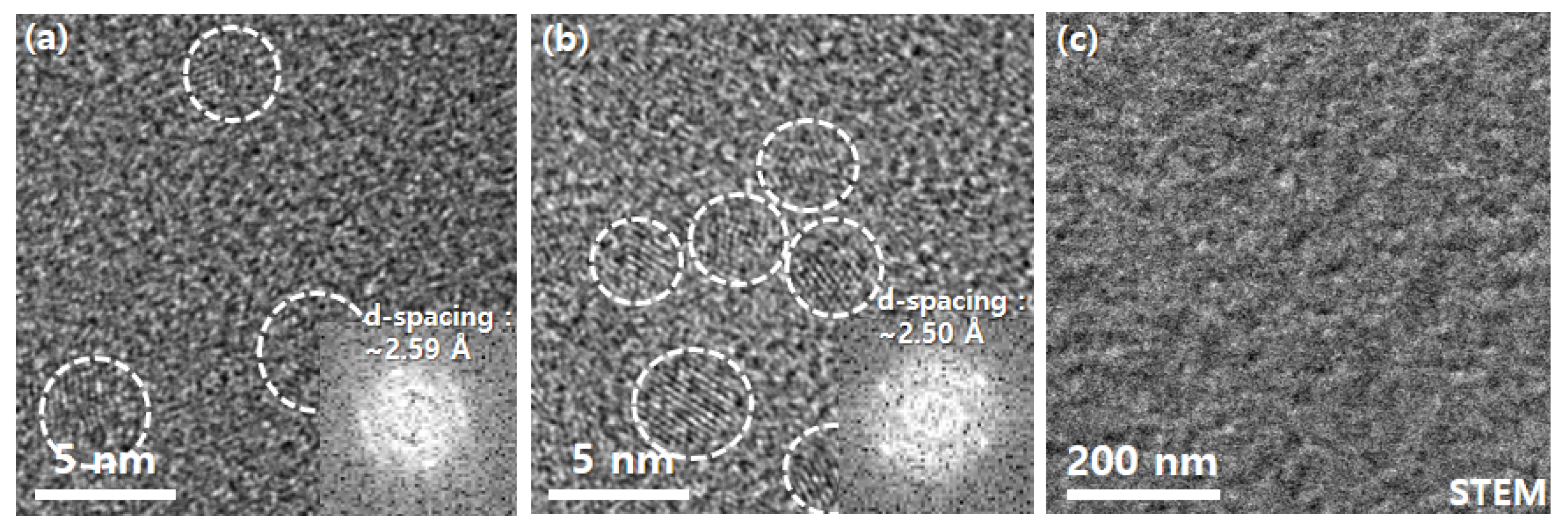
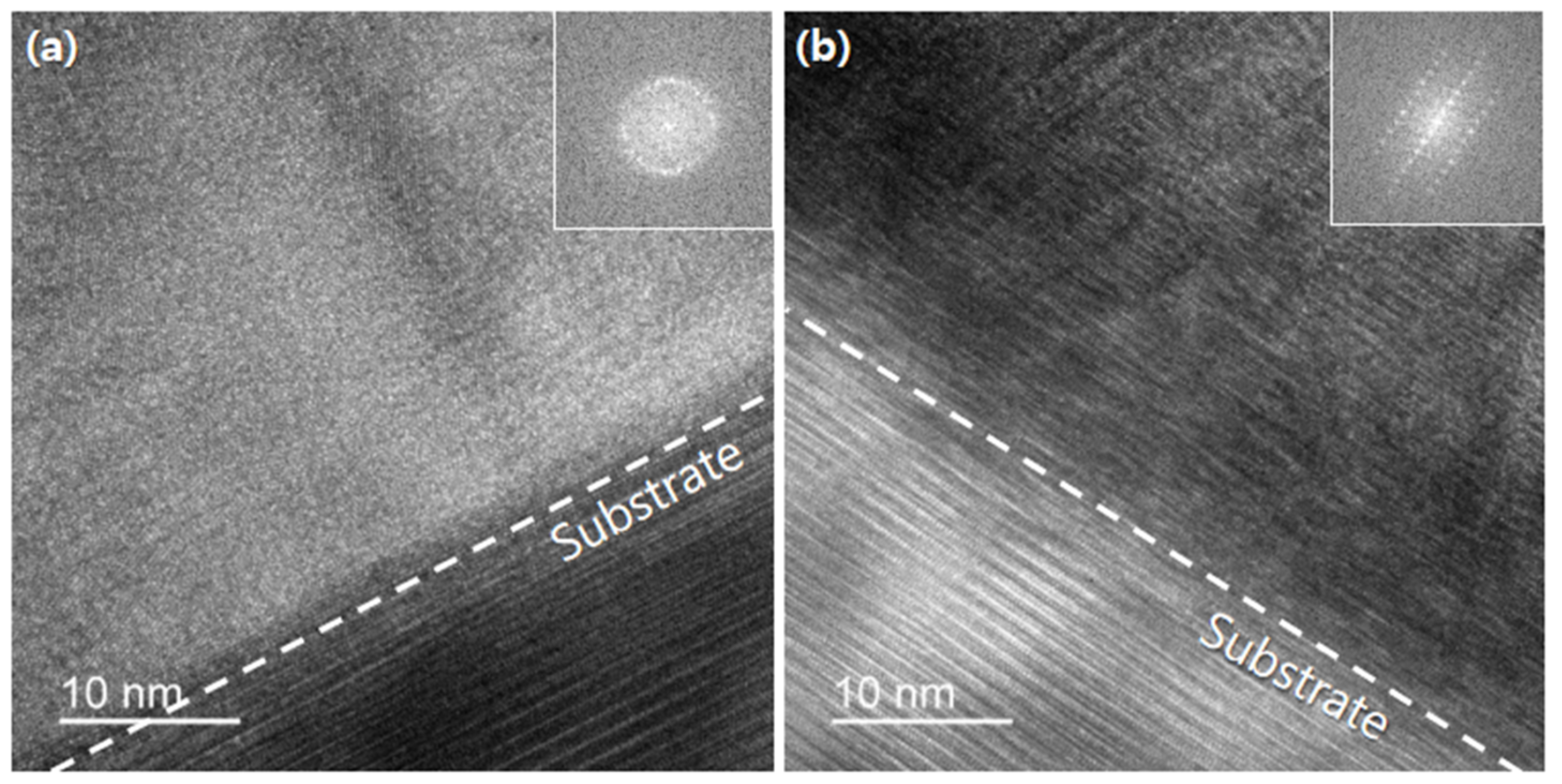
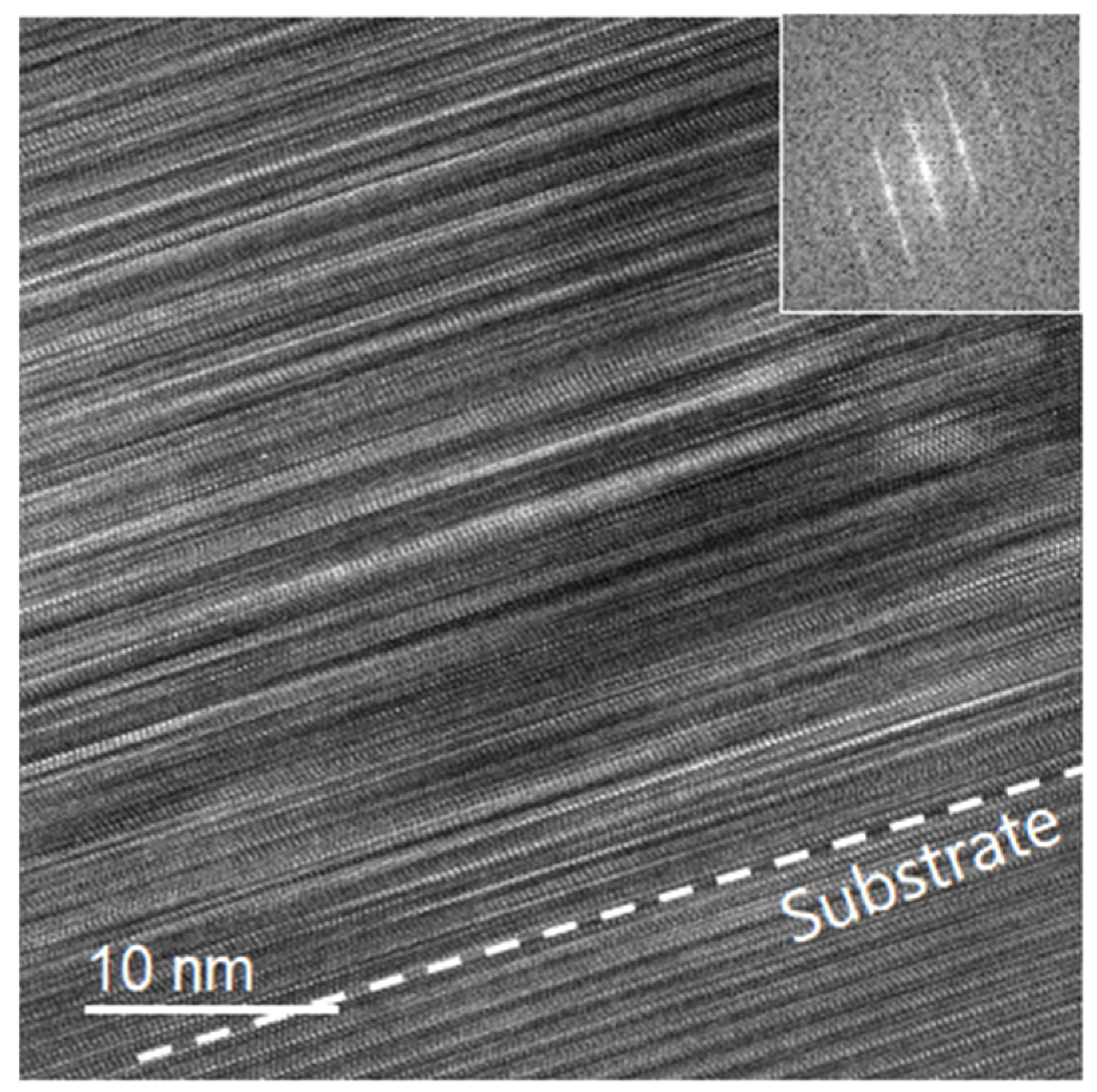
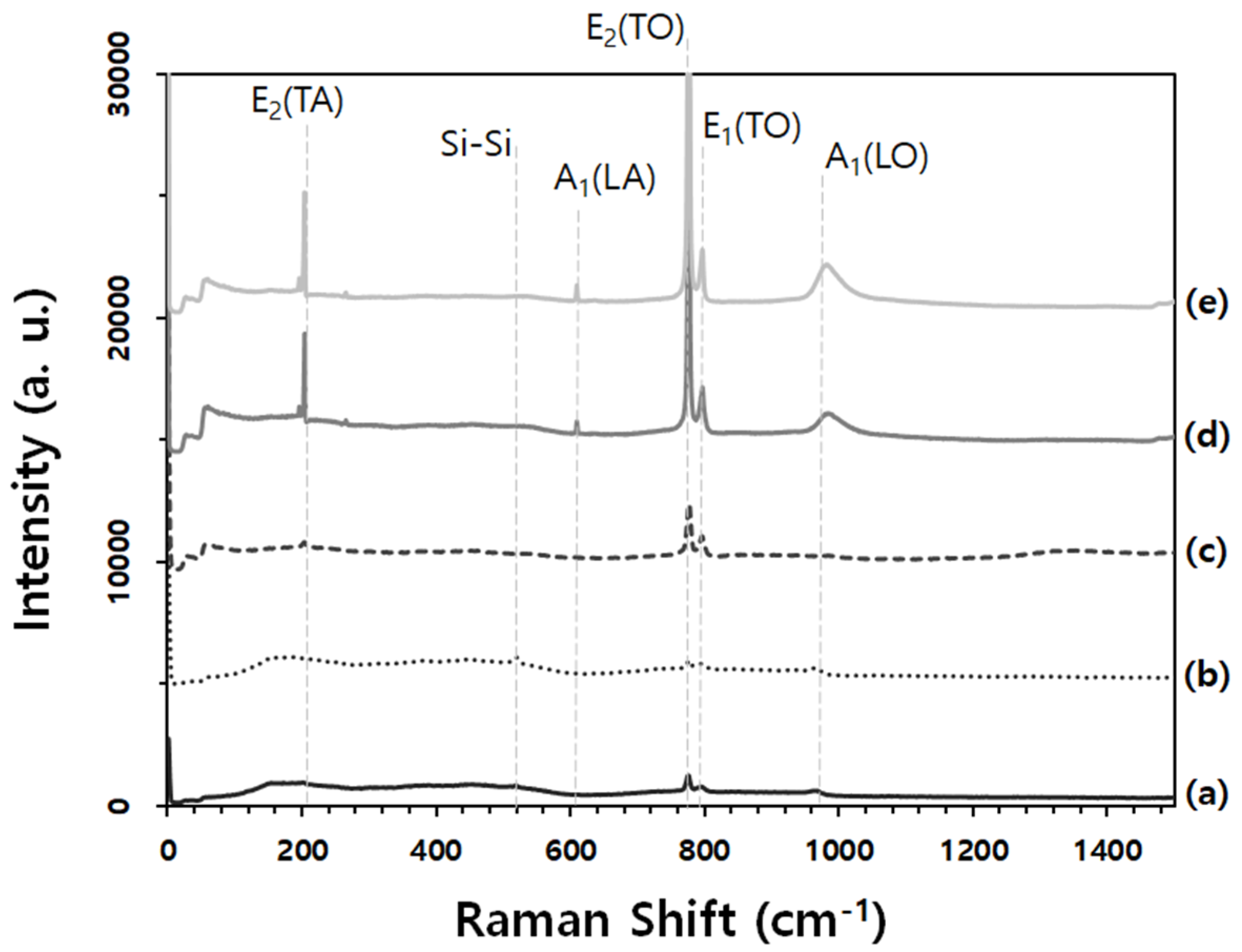
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cölfen, H.; Markus, A. Mesocrystals and Nonclassical Crystallization; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.-J.; Yu, S.-H. Recent advances in oriented attachment growth and synthesis of functional materials: Concept, evidence, mechanism, and future. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garscadden, A.; Ganguly, B.N.; Haaland, P.D.; Williams, J. Overview of growth and behaviour of clusters and particles in plasmas. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 1994, 3, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, E.; Stoffels, W.W.; Kroesen, G.M.W.; De Hoog, F.J. Dust formation and charging in an Ar/SiH4 radio-frequency discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1996, 14, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebauer, D.; Cölfen, H. Prenucleation clusters and non-classical nucleation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 564–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, N.-M.; Hahn, J.; Yoon, D. Charged cluster model in the low pressure synthesis of diamond. J. Cryst. Growth 1996, 162, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.-M.; Yoon, D.-Y.; Kim, D.-Y.; Hwang, N.-M. Effect of substrate materials in the low-pressure synthesis of diamond: Approach by theory of charged clusters. Z. Metallkd. 2005, 96, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, P.S.; Prawer, S.; Hoffman, A.; Manory, R.R.; Paterson PJ, K.; Stuart, S.A. Carbon diffusion in uncoated and titanium nitride coated iron substrates during microwave plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition of diamond. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 4643–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.-M.; Lee, D.-K. Charged nanoparticles in thin film and nanostructure growth by chemical vapour deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 3001–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.-M. Non-Classical Crystallization of Thin Films and Nanostructures in CVD and PVD Processes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, I.-D.; Park, C.-J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Hwang, N.-M. Effect of methane concentration on size of charged clusters in the hot filament diamond CVD process. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 223, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, K.-S.; Park, S.-W.; Hwang, N.-M. Non-classical crystallization of silicon thin films during hot wire chemical vapor deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 458, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.A.; Wang, F.F.; Costinett, D. Review of commercial GaN power devices and GaN-based converter design challenges. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 4, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.P. Wide bandgap semiconductor power devices for energy efficient systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 3rd Workshop on Wide Bandgap Power Devices and Applications, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2–4 November 2015; pp. 402–405. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, T.P. Progress in high voltage SiC and GaN power switching devices. In Silicon Carbide and Related Materials 2013: Selected, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Silicon Carbide and Related Materials (ICSCRM 2013), Miyazaki, Japan, 29 September–4 October 2013; Hajime, O., Hiroshi, H., Tsunenobu, K., Masahiro, Y., Heiji, W., Tomoaki, H., Hideharu, M., Tsuyoshi, F., Yasuhisa, S., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1077–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Millán, J.; Godignon, P.; Perpiñà, X.; Pérez-Tomás, A.; Rebollo, J. A survey of wide bandgap power semiconductor devices. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgener, R.H., II; Felix, R.L.; Renlund, G.M. Group II-VI Semiconductor Devices. U.S. Patent 7227196B2, 5 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- She, X.; Huang, A.Q.; Lucía, Ó.; Ozpineci, B. Review of silicon carbide power devices and their applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8193–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xun, Q.; Li, Z.; Du, S. Silicon carbide converters and MEMS devices for high-temperature power electronics: A critical review. Micromachines 2019, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benemanskaya, G.; Dementev, P.; Kukushkin, S.; Osipov, A.; Timoshnev, S. Carbon-based aromatic-like nanostructures on the vicinal SiC surfaces induced by Ba adsorption. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, M53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Du, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Zhou, L. A review of switching oscillations of wide bandgap semiconductor devices. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, Y.; Makino, E.; Sugiyama, N.; Kamata, I.; Hoshino, N.; Kojima, J.; Hara, K.; Tsuchida, H. Stable and high-speed SiC bulk growth without dendrites by the HTCVD method. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 448, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Suh, S.; Jeong, J.K.; Kim, H.J. Numerical study on the growth rate of silicon carbide single crystals in a high temperature chemical vapor deposition system. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 8344–8349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yang, M.; Lai, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, Q.; Tu, R.; Zhang, S.; Han, M.; Goto, T.; Zhang, L. Transparent highly oriented 3C-SiC bulks by halide laser CVD. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, A.; Bucio, T.D.; Oo, S.; Petra, R.; Khokhar, A.; Boden, S.A.; Gardes, F.; Reed, G.; Chong, H. Hot wire chemical vapor deposition for silicon photonics: An emerging industrial application opportunity. Thin Solid Films 2019, 676, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, S.; Tarazona, A.; Khokhar, A.; Petra, R.; Franz, Y.; Mashanovich, G.; Reed, G.; Peacock, A.; Chong, H. Hot-wire chemical vapour deposition low-loss a-Si: H waveguides for silicon photonic devices. Photonics Res. 2019, 7, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.R.; Morales, C.; Matsumoto, Y. Oxygen concentration effect on properties of SiOC thin films obtained by HWCVD. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control. (CCE), Mexico City, Mexico, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiyong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Xuewen, W.; Tianming, L.; Zhiming, C.; Shuixian, Z. Epitaxial monocrystalline SiC films grown on Si by HFCVD at 780 °C. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2000, 75, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Deng, Z.-H.; Wang, X.-W.; Yan, J.-F.; Ni, Y.-J. Epitaxial growth of SiC films at low temperature and its photoluminescence. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology, Shanghai, China, 23–26 October 2006; pp. 932–934. [Google Scholar]
- Yasui, K.; Eto, J.; Narita, Y.; Takata, M.; Akahane, T. Low-temperature heteroepitaxial growth of SiC on (100) Si using hot-mesh chemical vapor deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hens, P.; Brow, R.; Robinson, H.; Cromar, M.; Van Zeghbroeck, B. Epitaxial growth of cubic silicon carbide on silicon using hot filament chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 2017, 635, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zeghbroeck, B.; Robinson, H.; Brow, R.R. Hot filament CVD growth of 4H-SiC epitaxial layers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Silicon Carbide and Related Materials 2017, Washington, DC, USA, 17–22 September 2017; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, K.-S.; Hwang, N.-M. Generation of charged SiC nanoparticles during HWCVD process. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2020, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Yu, B.D.; Kim, D.-Y.; Hwang, N.-M. Effects of cluster size and substrate temperature on the homoepitaxial deposition of Au clusters. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 242, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, P.M.; Edwards, A.G.; Feigerle, C.S.; Shaw, R.W.; Coffey, D.W.; Heatherly, L.J.; Clausing, R.E.; Robinson, L.; Glasgow, D.C. Filament metal contamination and Raman spectra of hot filament chemical vapor deposited diamond films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 8, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Yang, S.M.; Kim, C.S.; Hwang, N.M. Effect of bias applied to hot wires on generation of positive and negative charges during silicon hot-wire chemical vapor deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 17011–17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H. Atom clusters—New applications of high-voltage electron microscopy “micro-laboratory” to materials science. Ultramicroscopy 1991, 39, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H. The magic size and the magic number of atom clusters. Sci. Technol. 1995, 7, 9–20. [Google Scholar]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kwon, J.-H.; Hwang, N.-M. Effects of the Size of Charged Nanoparticles on the Crystallinity of SiC Films Prepared by Hot Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition. Coatings 2020, 10, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10080726
Kim D, Kim D-Y, Kwon J-H, Hwang N-M. Effects of the Size of Charged Nanoparticles on the Crystallinity of SiC Films Prepared by Hot Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition. Coatings. 2020; 10(8):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10080726
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Daseul, Du-Yun Kim, Ji-Hye Kwon, and Nong-Moon Hwang. 2020. "Effects of the Size of Charged Nanoparticles on the Crystallinity of SiC Films Prepared by Hot Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition" Coatings 10, no. 8: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10080726
APA StyleKim, D., Kim, D.-Y., Kwon, J.-H., & Hwang, N.-M. (2020). Effects of the Size of Charged Nanoparticles on the Crystallinity of SiC Films Prepared by Hot Wire Chemical Vapor Deposition. Coatings, 10(8), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10080726





