Understanding the Solid–Ice Interface Mechanism on the Hydrophobic Nano-Pillar Structure Epoxy Surface for Reducing Ice Adhesion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
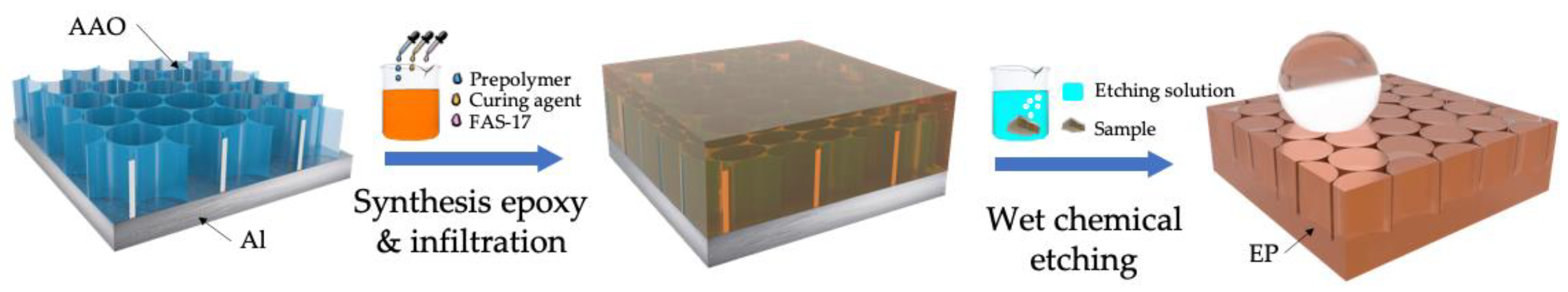
2.2. Sample Preparation Procedure
2.3. Surface Characterization
2.4. Non-Wettability Test
2.5. Ice Adhesion Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Morphologies
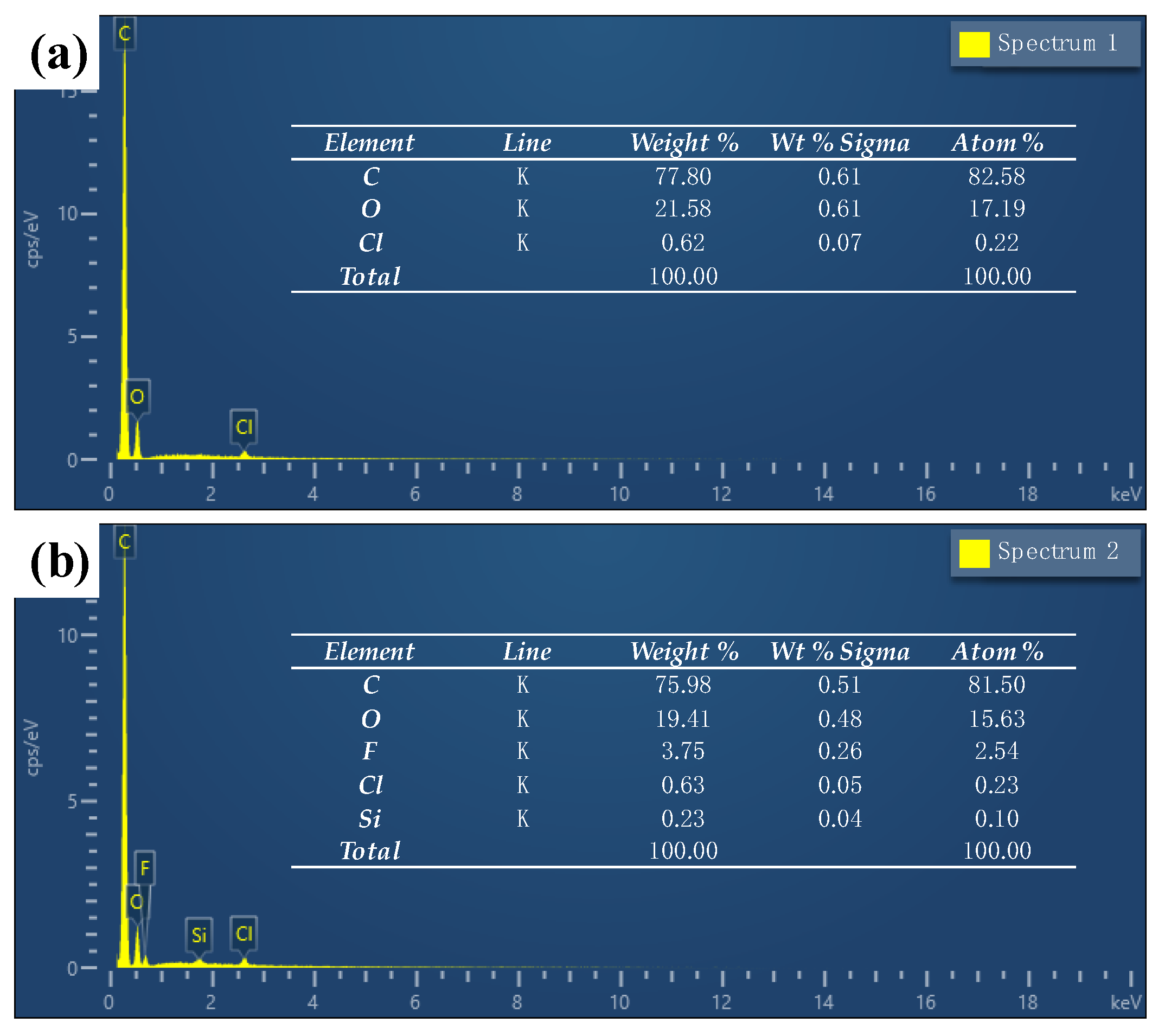
3.2. Characterization of Chemical Compositions
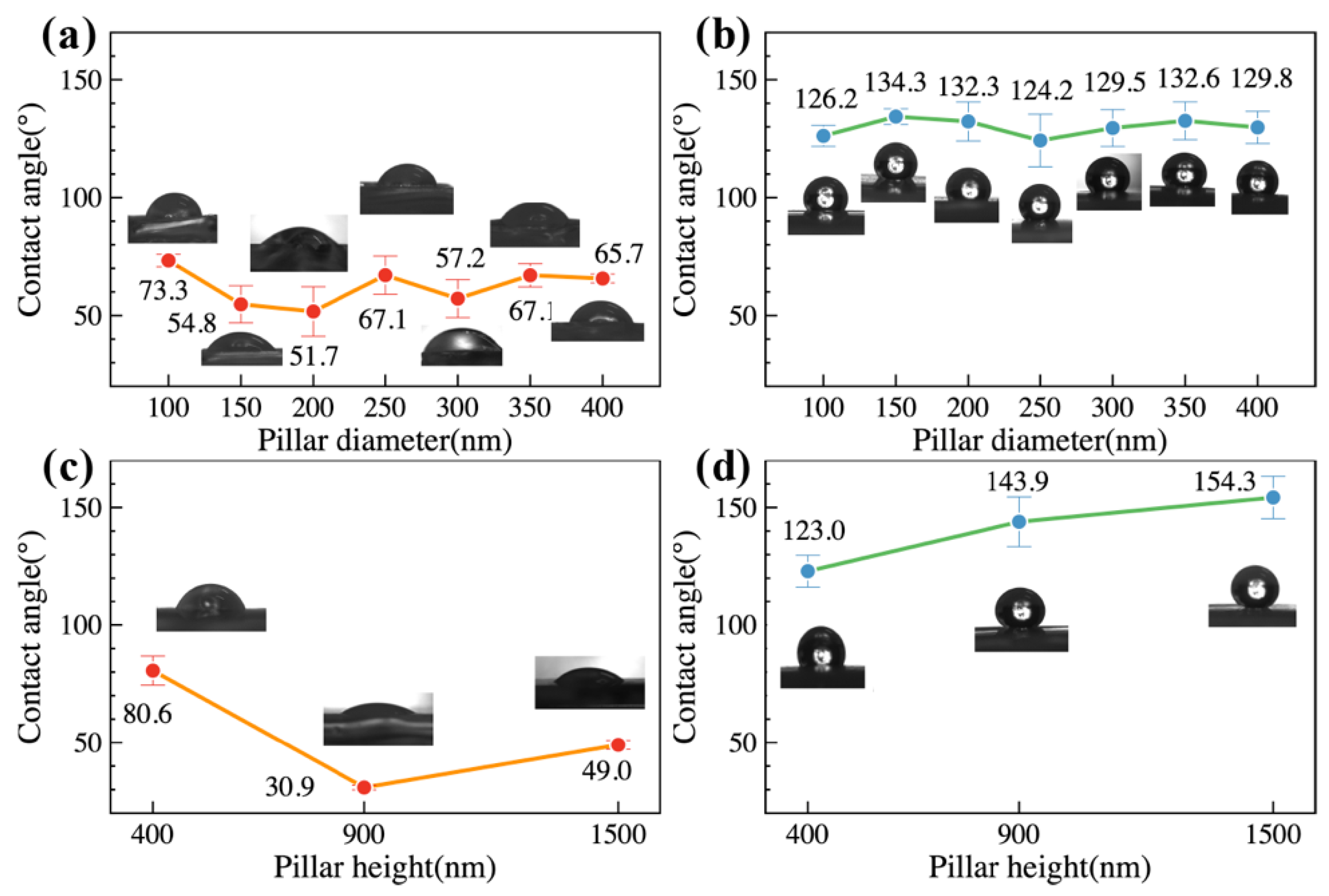
3.3. Static Water Repellency and Surface Energy
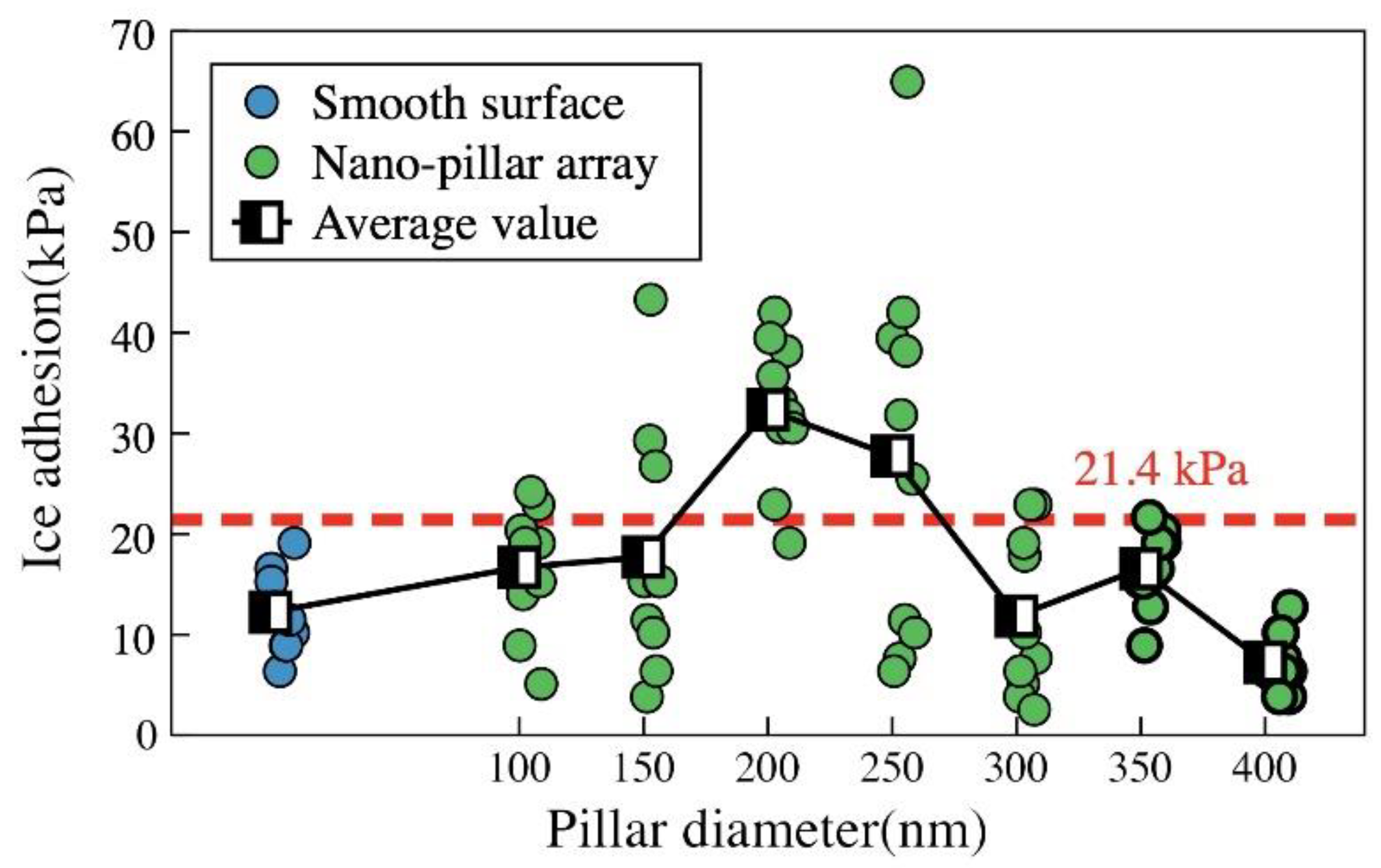
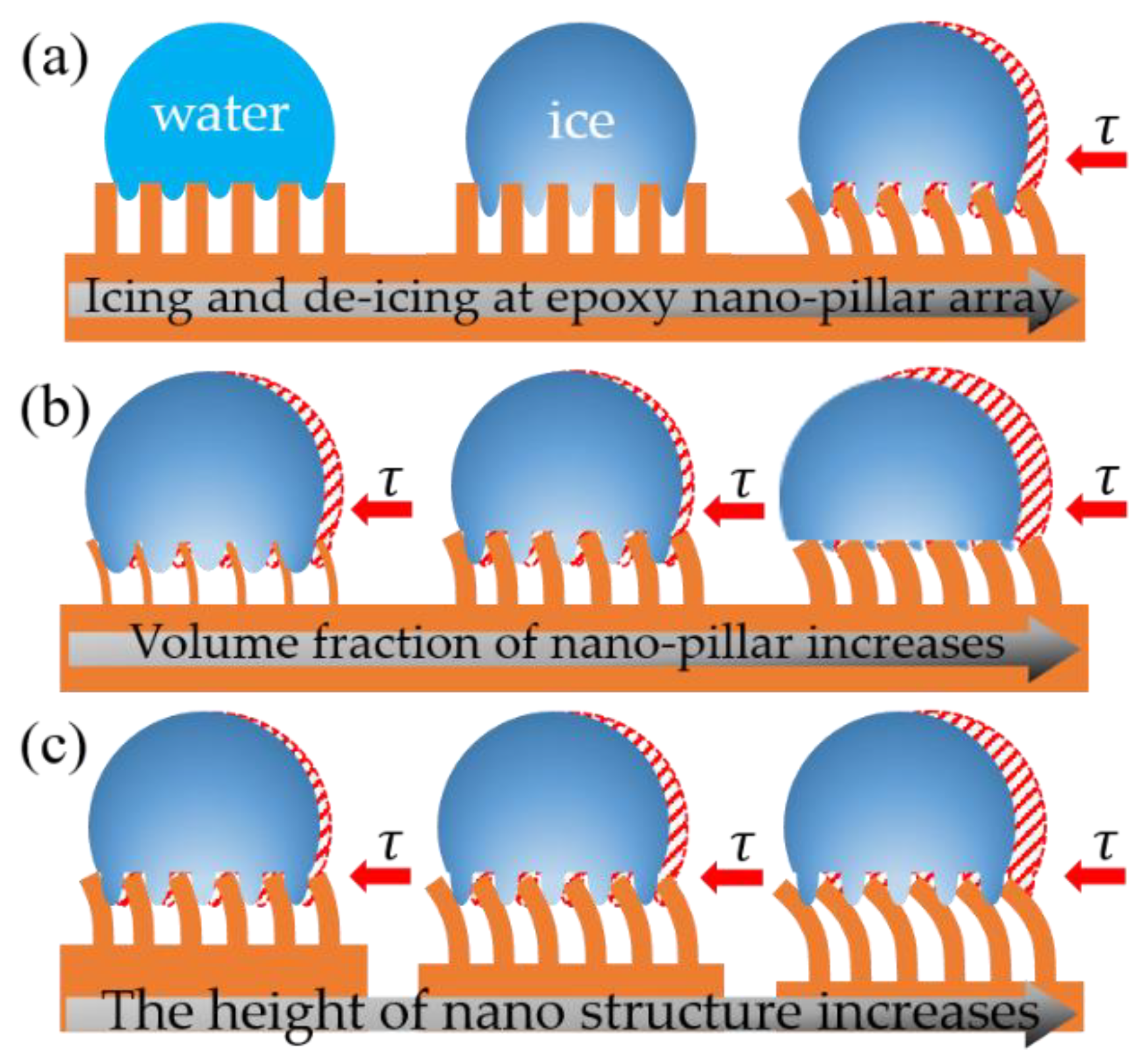
3.4. Ice Adhesion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tetteh:, E.; Loth, E. Reducing Static and Impact Ice Adhesion with a Self-Lubricating Icephobic Coating (SLIC). Coatings 2020, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Mulroney, A.T.; Gupta, M.C. Anti-icing epoxy resin surface modified by spray coating of PTFE Teflon particles for wind turbine blades. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Tao, J.; Zhu, C.; Lai, Y.; Chen, Z. Icephobic materials: Fundamentals, performance evaluation, and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 509–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Ryerson, C.C. Anti-icing and deicing techniques. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreder, M.J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Design of anti-icing surfaces: Smooth, textured or slippery? Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.H.; Li, Y.; Li, H.J.; Zhu, D.B. Super-hydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2010, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Q.; Hokkanen, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, F.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, S.-P.; Zhou, T.; Chang, Q.; He, B.; et al. Design of robust superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature 2020, 582, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neinhuis, W.B. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.-S.; Quan, Y.-Y.; Mao, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-L.; Lai, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Wei, K.; Li, H. Multifunctional superhydrophobic composite materials with remarkable mechanochemical robustness, stain repellency, oil-water separation and sound-absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedir, K.R.; Kannarpady, G.K.; Ryerson, C.; Biris, A.S. An outlook on tunable superhydrophobic nanostructural surfaces and their possible impact on ice mitigation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 112, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, G.; Tao, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, S.; Jin, M.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Anti-Icing Performance of Superhydrophobic Texture Surfaces Depending on Reference Environments. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Farzaneh, M.; Kulinich, S.A. Anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Liang, F.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, T.; Yi, B.; Tang, Y.; Lai, Y. A “PDMS-in-water” emulsion enables mechanochemically robust superhydrophobic surfaces with self-healing nature. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Lv, C.; Zhang, X. Freezing of sessile water droplets on surfaces with various roughness and wettability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 161609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Jing, R.N.; Ren, X.Y.; Gao, G.H. Fish-inspired anti-icing hydrogel sensors with low-temperature adhesion and toughness. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9373–9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, D.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J. Anti-icing Coating with an Aqueous Lubricating Layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6998–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Wong, T.S.; Alvarenga, J.; Kreder, M.J.; Adorno-Martinez, W.E.; Aizenberg, J. Liquid-Infused Nanostructured Surfaces with Extreme Anti-Ice and Anti-Frost Performance. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6569–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhuo, Y.; Hakonsen, V.; Ronneberg, S.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Epidermal Gland Inspired Self-Repairing Slippery Lubricant-Infused Porous Coatings with Durable Low Ice Adhesion. Coatings 2019, 9, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ibáñez-Ibáñez, P.F.; Håkonsen, V.; Wu, J.; Xu, K.; Zhuo, Y.; Luo, S.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Self-Deicing Electrolyte Hydrogel Surfaces with Pa-level Ice Adhesion and Durable Antifreezing/Antifrost Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 35572–35578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Jones, A.K.; Sikka, V.K.; Wu, J.; Gao, D. Anti-Icing Superhydrophobic Coatings. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12444–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, F.; Chiariello, A.; Dabkowski, D.; Corraro, G.; Marra, F.; Di Palma, L. Superhydrophobic Coatings as Anti-Icing Systems for Small Aircraft. Aerospace 2020, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.W.; Xiao, S.B.; Gao, H.J.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.L. Multiscale crack initiator promoted super-low ice adhesion surfaces. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6562–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, K.; Dhyani, A.; Thouless, M.D.; Tuteja, A. Low-interfacial toughness materials for effective large-scale deicing. Science 2019, 364, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Y.K.; Yang, M.T.; Desai, R.A.; Chen, C.S. Mechanical regulation of cell function with geometrically modulated elastomeric substrates. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Xiong, J.; Ge, M.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. A transparent superhydrophobic coating with mechanochemical robustness for anti-icing, photocatalysis and self-cleaning. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Jerca, V.V.; Hoogenboom, R. Bio-inspired Hydrogels as Multi-task Anti-icing Hydrogel Coatings. Chem 2020, 6, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, K.; Pakkanen, T.A. Superhydrophobic hierarchical three-level structures on 3D polypropylene surfaces. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-B.; Park, S.; Lim, H. Effects of morphology parameters on anti-icing performance in superhydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Shen, Y.; Luo, X.; Tao, J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y. A combination structure of microblock and nanohair fabricated by chemical etching for excellent water repellency and icephobicity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xie, X.; Xie, Y.; Tao, J.; Xu, Y. Statistically understanding the roles of nanostructure features in interfacial ice nucleation for enhancing icing delay performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Hejazi, V. Why Superhydrophobic Surfaces Are Not Always Icephobic. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8488–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulinich, S.A.; Farhadi, S.; Nose, K.; Du, X.W. Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Are They Really Ice-Repellent? Langmuir 2011, 27, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Song, Y. Superhydrophobic surface at low surface temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 093118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; He, M.; Li, K.Y.; Cui, D.P.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zeng, X.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, J.J.; Song, Y.L. Superhydrophobic surfaces cannot reduce ice adhesion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Q. Intelligent Icephobic Surface toward Self-Deicing Capability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkin, I.A.; Petrenko, V.F. Physical mechanisms responsible for ice adhesion. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 6267–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Minsky, H.K.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, K.; Turner, K.T.; Yang, S. Shear Adhesion of Tapered Nanopillar Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 11391–11397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Kim, G.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Minsky, H.; Turner, K.T.; Gianola, D.S.; Yang, S. Orthogonal Control of Stability and Tunable Dry Adhesion by Tailoring the Shape of Tapered Nanopillar Arrays. Adv. Mater. 2016, 27, 7788–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.T.; Wu, X.H.; Kumar, D.; Ho, J.W.C.; Kanhere, P.D.; Srikanth, N.; Liu, E.J.; Wilson, P.; Chen, Z. Development of Sol-Gel Icephobic Coatings: Effect of Surface Roughness and Surface Energy. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 20685–20692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, M.; Song, C.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, L. Icephobic/Anti-Icing Properties of Micro/Nanostructured Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Shen, Y.; Tao, J.; Xu, Y.; Jia, Z. Anti-icing performance of the superhydrophobic surface with micro-cubic array structures fabricated by plasma etching. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 586, 124180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberg, S.; Xiao, S.B.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.L. Nanoscale Correlations of Ice Adhesion Strength and Water Contact Angle. Coatings 2020, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojoudi, H.; McKinley, G.H.; Gleason, K.K. Linker-free grafting of fluorinated polymeric cross-linked network bilayers for durable reduction of ice adhesion. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jiang, C.Y.; Cao, X.B.; Chen, J.; Tian, W.; Yuan, W.Z. Reducing ice adhesion by hierarchical micro-nano-pillars. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Jang, H.; Chang, J.; Lee, K.-S.; Rip Kim, D. Fabrication of Micro-Patterned Aluminum Surfaces for Low Ice Adhesion Strength. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, Z.; Shen, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z. Understanding the Solid–Ice Interface Mechanism on the Hydrophobic Nano-Pillar Structure Epoxy Surface for Reducing Ice Adhesion. Coatings 2020, 10, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111043
Jia Z, Shen Y, Tao J, Zhang Y, Chen H, Lu Y, Wu Z. Understanding the Solid–Ice Interface Mechanism on the Hydrophobic Nano-Pillar Structure Epoxy Surface for Reducing Ice Adhesion. Coatings. 2020; 10(11):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111043
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Zhenfeng, Yizhou Shen, Jie Tao, Yu Zhang, Haifeng Chen, Yang Lu, and Zhengwei Wu. 2020. "Understanding the Solid–Ice Interface Mechanism on the Hydrophobic Nano-Pillar Structure Epoxy Surface for Reducing Ice Adhesion" Coatings 10, no. 11: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111043
APA StyleJia, Z., Shen, Y., Tao, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, H., Lu, Y., & Wu, Z. (2020). Understanding the Solid–Ice Interface Mechanism on the Hydrophobic Nano-Pillar Structure Epoxy Surface for Reducing Ice Adhesion. Coatings, 10(11), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10111043




