Secondary Antibiotic Resistance, Correlation between Genotypic and Phenotypic Methods and Treatment in Helicobacter pylori Infected Patients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic Data of Patients
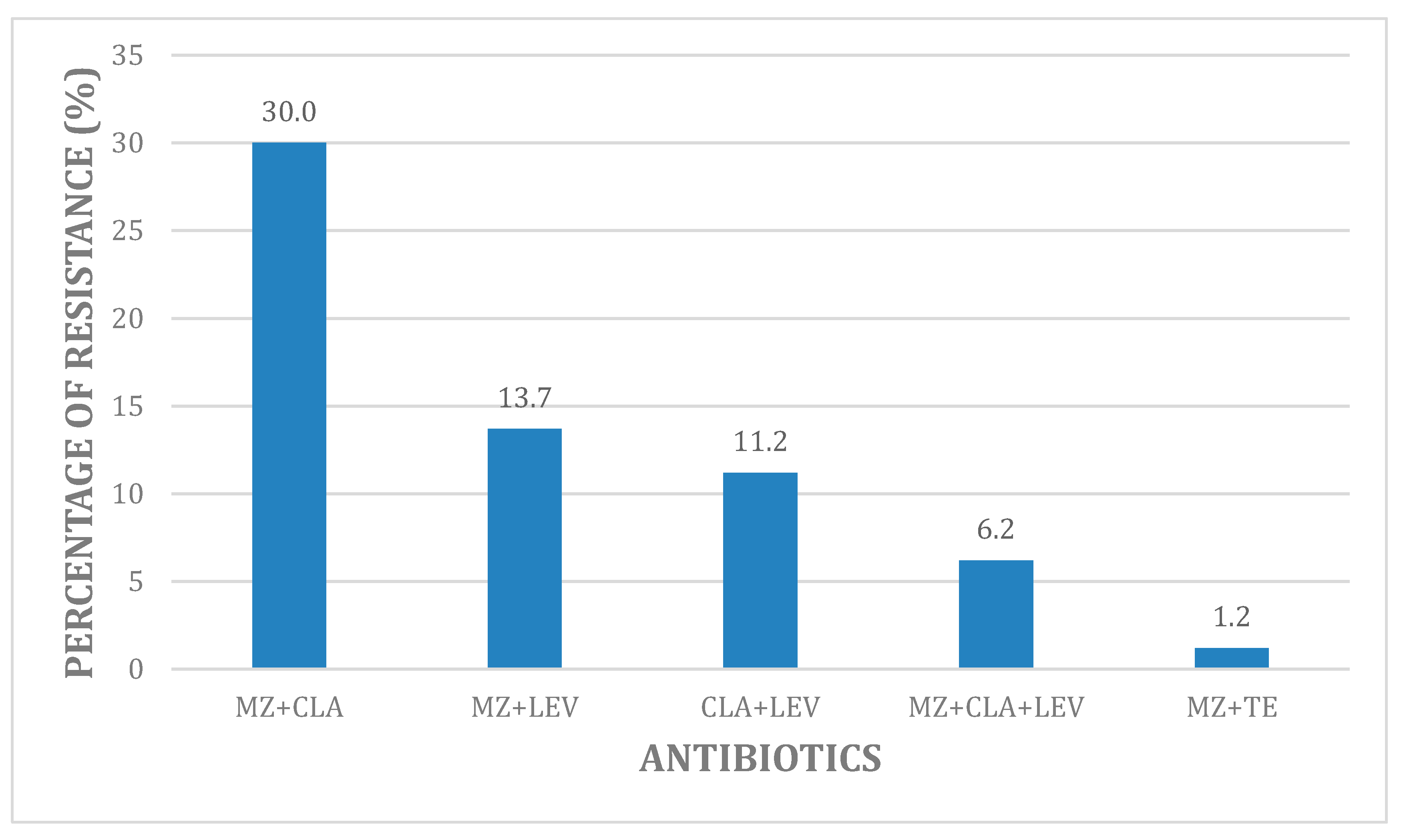
2.2. Overall Phenotypic Hp Antibiotic Resistance
2.3. Genetic Resistance to Clarithromycin and Levofloxacin: Correlation with In Vitro Phenotypic Method
2.4. Eradication Rate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients Selection
4.2. Culture and E-Test Susceptibility
4.3. Genotyping Susceptibility Method
4.4. Therapy
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Consent for Publication
Data Availability
References
- Atherton, J.C.; Peek, R.M.; Tham, K.T.; Cover, T.L.; Blasér, M.J. Clinical and pathological importance of heterogeneity in vacA, the vacuolating cytotoxin gene of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Zeng, Z.R.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, J.M.; Du, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.B.; Xu, S.P.; et al. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Chinese patients: A multiregion prospective 7-year study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 780.e5–780.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nahar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Khan, R.; Ahmad, M.M.; Datta, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dhar, S.C.; Sarker, S.A.; Douglas, E.; Berg, E.; et al. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated in Bangladesh. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 4856–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorini, G.; Zullo, A.; Saracino, I.M.; Pavoni, M.; Vaira, D. Antibiotic resistance pattern of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated in Italy during 2010–2016. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitessa, V.; Monno, R.; Panarese, A.; Cuppone, R.; Burattini, O.; Marangi, S.; Curlo, M.; Fumarola, L.; Petrosillo, A.; Parisi, A.; et al. Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori Strains Isolated in Bari, Southern Italy, in 2017–2018 by Phenotypic and Genotyping Methods. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thung, I.; Aramin, H.; Vavinskaya, V.; Gupta, S.; Park, J.Y.; Crowe, S.E.; Valasek, M.A. Review article: The global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selgrad, M.; Meissle, J.; Bornschein, J.; Kandulski, A.; Langner, C.; Varbanova, M.; Wex, T.; Tammer, I.; Schlüter, D.; Malfertheiner, P. Antibiotic susceptibility of Helicobacter pylori in central Germany and its relationship with the number of eradication therapies. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluemel, H.; Goelz, B.; Goldman, J.; Gruger, J.; Hamel, H.; Loley, K.; Ludolph, T.; Meyer, J.; Miehlke, S.; Mohr, A.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Germany, 2015–2018. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, T.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group and Consensus panel. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wueppenhorst, N.; Stueger, H.P.; Kist, M.; Glocker, E.O. High secondary resistance to quinolones in German Helicobacter pylori clinical isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Versalovic, J.; Shortridge, D.; Kibler, K.; Griffy, M.V.; Beyer, J.; Flamm, R.K.; Tanaka, S.K.; Graham, D.Y.; Go, M.F. Mutations in 23S rRNA are associated with clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 10.0. 2020. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_10.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Balakrishna, J.P.; Filatov, A. Coccoid Forms of Helicobacter pylori Causing Active Gastritis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 140, A101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanizaj, T.F.; Katicic, M.; Skurla, B.; Ticak, M.; Plecko, V.; Kalenic, S. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy success regarding different treatment period based on clarithromycin or metronidazole triple-therapy regimens. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretz, A.; Paritsky, M.; Nasser, O.; Brodsky, D.; Glyatman, T.; Segal, S.; On, V. Resistance of Helicobacter pylori to tetracycline, amoxicillin, clarithromycin and metronidazole in Israel children and adults. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotaslou, R.; Leylabadlo, H.E.; Asl, Y.M. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A recent literature review. World J. Methodol. 2015, 5, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Yin, Z.; Lu, N.H. Recent progress of Helicobacter pylori treatment. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2020, 133, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Cheng, H.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Zheng, X. The evolution of Helicobacter pylori antibiotics resistance over 10 years in Beijing, China. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ke, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, C.; Yang, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Chinese children: A multicenter retrospective study over 7 years. Helicobacter 2017, 22, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiki, N.; Omata, F.; Uemura, M.; Suzuki, S.; Ishii, N.; Iizuka, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Fujita, Y.; Katsurahara, M.; Imoto, I.; et al. Annual change of primary resistance to clarithromycin among Helicobacter pylori isolates from 1996 through 2008 in Japan. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.I.; Jeong, S.H.; Chung, J.W.; Park, D.K.; Kim, K.O.; Kwon, K.A.; Kim, Y.J.; So, S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; et al. Rifabutin and Furazolidone Could Be the Candidates of the Rescue Regimen for Antibiotic-Resistant, H. pylori in Korea. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 9351801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouihat, N.; Burucoa, C.; Benkirane, A.; Seddik, H.; Sentissi, S.; Al Bouzidi, A.; Elouennas, M.; Benouda, A. Helicobacter pylori primary antibiotic resistance in 2015 in Morocco: A phenotypic and genotypic prospective and multicenter study. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, S.; Reddy, R.; Alsarraj, A.; El-Serag, H.B.; Graham, D.Y. Antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori among male United States veterans. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitui, M.; Patel, A.; Leos, N.K.; Doern, C.D.; Park, J.Y. Novel Helicobacter pylori sequencing test identifies high rate of clarithromycin resistance. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saracino, I.M.; Zullo, A.; Holton, J.; Castelli, V.; Fiorini, G.; Zaccaro, C.; Ridola, L.; Ricci, C.; Gatta, L.; Vaira, D.; et al. High prevalence of primary antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori isolates in Italy. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2012, 21, 363–365. [Google Scholar]
- Rhie, S.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Shin, T.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.G. Discovery of a novel mutation in DNA gyrase and changes in the fluoroquinolone resistace of Helicobacter pylori over a 14-year period: Single centre study in Korea. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrits, M.M.; Van der Wouden, E.J.; Bax, D.A.; Van Zwet, A.A.; Van Vliet, A.H.M.; De Jong, A.; Kusters, J.G.; Thijs, J.C.; Kuipers, E.J. Role of the rdxA and frxA genes in oxygen dependent metronidazole resistance of Helicobacter pylori. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, J.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Perez-Perez, G.; Madrazo-De la Garza, A.; Dehesa, M.; González-Valencia, G.; Muñoz, O. Increasing multidrug resistance in Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from children and adults in Mexico. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2677–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khademi, F.; Poursina, F.; Hosseini, E.; Akbari, M.; Safaei, H.G. Helicobacter pylori in Iran: A systematic review on the antibiotic resistance. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, A.; Bosch, A.; Bettiol, M.; Nossa González, D.L.; Erben, M.F.; Lamberti, Y. Novel Guanidine Compound against Multidrug-Resistant Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Bacterial Species. Molecules 2018, 23, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chimenti, F.; Bizzarri, B.; Bolasco, A.; Secci, D.; Chimenti, P.; Carradori, S.; Granese, A.; Rivanera, D.; Lilli, D.; Scaltrito, M.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro selective anti-Helicobacter pylori activityofN-substituted-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-3-carboxamides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makipour, K.; Friedenberg, F.K. The potential role of N-acetylcysteine for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, H.; Shiotani, A.; Katsumata, R.; Fujita, M.; Nakato, R.; Murao, T.; Ishii, M.; Kamada, T.; Haruma, K.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori eradication with proton pump inhibitors or potassium-competitive acid blockers: The effect of clarithromycin resistance. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 3215–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binyamin, D.; Pastukh, N.; On, A.; Paritsky, M.; Peretz, A. Phenotypic and genotypic correlationas expressed in Helicobacter pylori resistance to clarithromycin and fuoroquinolones. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jyh, M.L.; Chang, C.Y.; Sheng, W.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, M.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Hung, H.W.; Chian, H.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, M.S. Genotypic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori Strains Correlates with Susceptibility Test and Treatment Outcomes after Levofloxacin- and Clarithromycin-Based Therapies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, N.; Nam, R.H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.S.; Jung, H.C. GenoType HelicoDR test in the determination of antimicrobial resistance of Helicobacter pylori in Korea. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Wu, M.S. Rational Helicobacter pylori therapy: Evidence-based medicine rather than medicine-based evidence. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uotani, T.; Graham, D.Y. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori using the rapid urease test. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkic, A.; Vucovic, J.; Cindro, P.V.; Pisac, V.P.; Tonkic, M. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. A short review. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2017, 10, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascellino, M.T.; Oliva, A.; De Angelis, M.; Pontone, S.; Porowska, B. Helicobacter pylori infection: Antibiotic resistance and eradication rate in patients with gastritis showing previous treatment failures. New Microbiol. 2018, 41, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Miendje Deyi, V.Y.; Burette, A.; Bentatou, Z.; Maaroufi, Y.; Bontems, P.; Lepage, P.; Reynders, M. Practical use of GenoType® HelicoDR, a molecular test for Helicobacter pylori detection and susceptibility testing. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursi, A.; Di Mario, F.; Franceschi, M.; De Bastiani, R.; Elisei, W.; Baldassarre, G.; Ferronato, A.; Grillo, S.; Landi, S.; Zamparella, M.; et al. New bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori: A first Italian experience in clinical practice. Helicobacter 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisber, J.P.; Pajares, J.M. Review article: 13 C-urea breath test in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection—A critical review. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capurso, G.; Martino, G.; Grossi, C.; Delle Fave, D. Hypersecretory duodenal ulcer and Helicobacter pylori infection: A four-year follow-up study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2000, 32, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Long, X.; Ji, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, D.; Gao, H.; Xu, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Randomized controlled trial: Susceptibility-guided therapy versus empiric bismuth quadruple therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibiotics | MIC Values (µg/mL) | Resistant Strains (n, %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC Breakpoints | MIC50 | MIC90 | MIC Ranges | |||
| ≤S | R | |||||
| Metronidazole | 8 | 8 | 9–32 | 128 | ≤1–256 | 50 (61.6) |
| Clarithromycin | 0.25 | 0.5 | ≤8 | 64 | ≤0.12–128 | 28 (35) |
| Levofloxacin | 1 | 1 | ≤0.25 | 16 | ≤0.12–32 | 12 (15) |
| Tetracycline | 1 | 1 | ≤0.25 | ≤1 | ≤0.12–≤8 | 2 (2.5) |
| Amoxicillin | 0.12 | 0.12 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12–≤1 | 1 (1.2) |
| Clarithromycin (CLA) Resistance (n = 80) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PCR | E-Test | 0.417 | |
| Resistance rate, n (%) | 34 (42.5) | 28 (35) | |
| 23S rRNA genes | |||
| −A 2143G | 24 | 20 (MIC 4–128 µg/mL) | |
| −WT + A 2143G | 10 * | 8 (MIC >0.5–≤4 µg/mL) | |
| Levofloxacin (LEV) Resistance (n = 80) | p-Value | ||
| PCR | E-Test | 0.036 | |
| Resistance rate, n (%) | 24 (30) | 12 (15) | |
| gyrA mutations | |||
| −Codon N87 K | 18 | 8 (MIC 4–32 µg/mL) | |
| −Codon D91 G | 6 | 4 (MIC >1–≤4 µg/mL) | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mascellino, M.T.; Oliva, A.; Miele, M.C.; De Angelis, M.; Bruno, G.; Severi, C. Secondary Antibiotic Resistance, Correlation between Genotypic and Phenotypic Methods and Treatment in Helicobacter pylori Infected Patients: A Retrospective Study. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090549
Mascellino MT, Oliva A, Miele MC, De Angelis M, Bruno G, Severi C. Secondary Antibiotic Resistance, Correlation between Genotypic and Phenotypic Methods and Treatment in Helicobacter pylori Infected Patients: A Retrospective Study. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(9):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090549
Chicago/Turabian StyleMascellino, Maria Teresa, Alessandra Oliva, Maria Claudia Miele, Massimiliano De Angelis, Giovanni Bruno, and Carola Severi. 2020. "Secondary Antibiotic Resistance, Correlation between Genotypic and Phenotypic Methods and Treatment in Helicobacter pylori Infected Patients: A Retrospective Study" Antibiotics 9, no. 9: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090549
APA StyleMascellino, M. T., Oliva, A., Miele, M. C., De Angelis, M., Bruno, G., & Severi, C. (2020). Secondary Antibiotic Resistance, Correlation between Genotypic and Phenotypic Methods and Treatment in Helicobacter pylori Infected Patients: A Retrospective Study. Antibiotics, 9(9), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090549





