Characterization of Five Novel Anti-MRSA Compounds Identified Using a Whole-Animal Caenorhabditis elegans/Galleria mellonella Sequential-Screening Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Compounds That Block the Ability of MRSA to Kill C. elegans
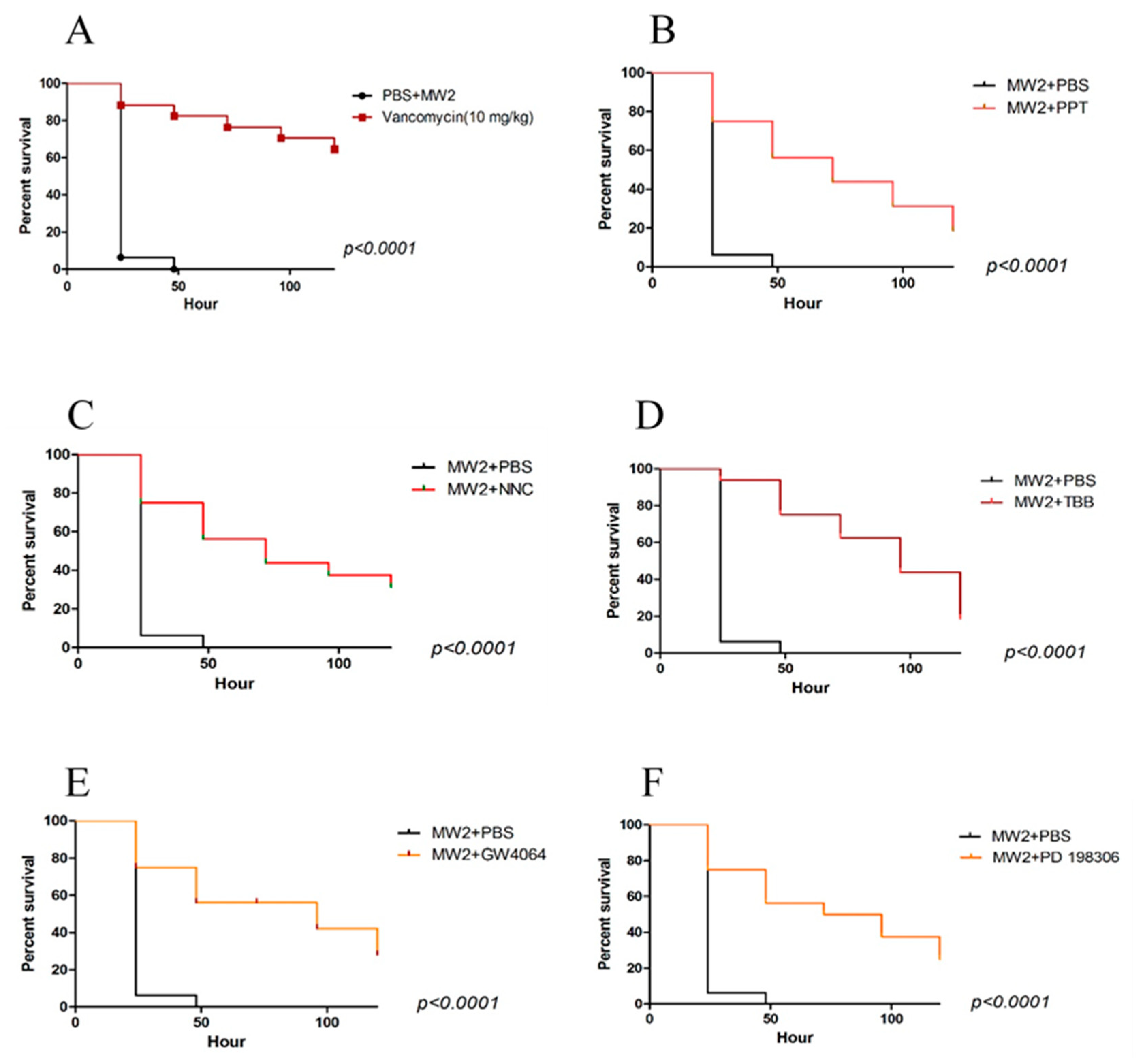
2.2. Galleria Mellonella Assays
2.3. Antibacterial Susceptibility
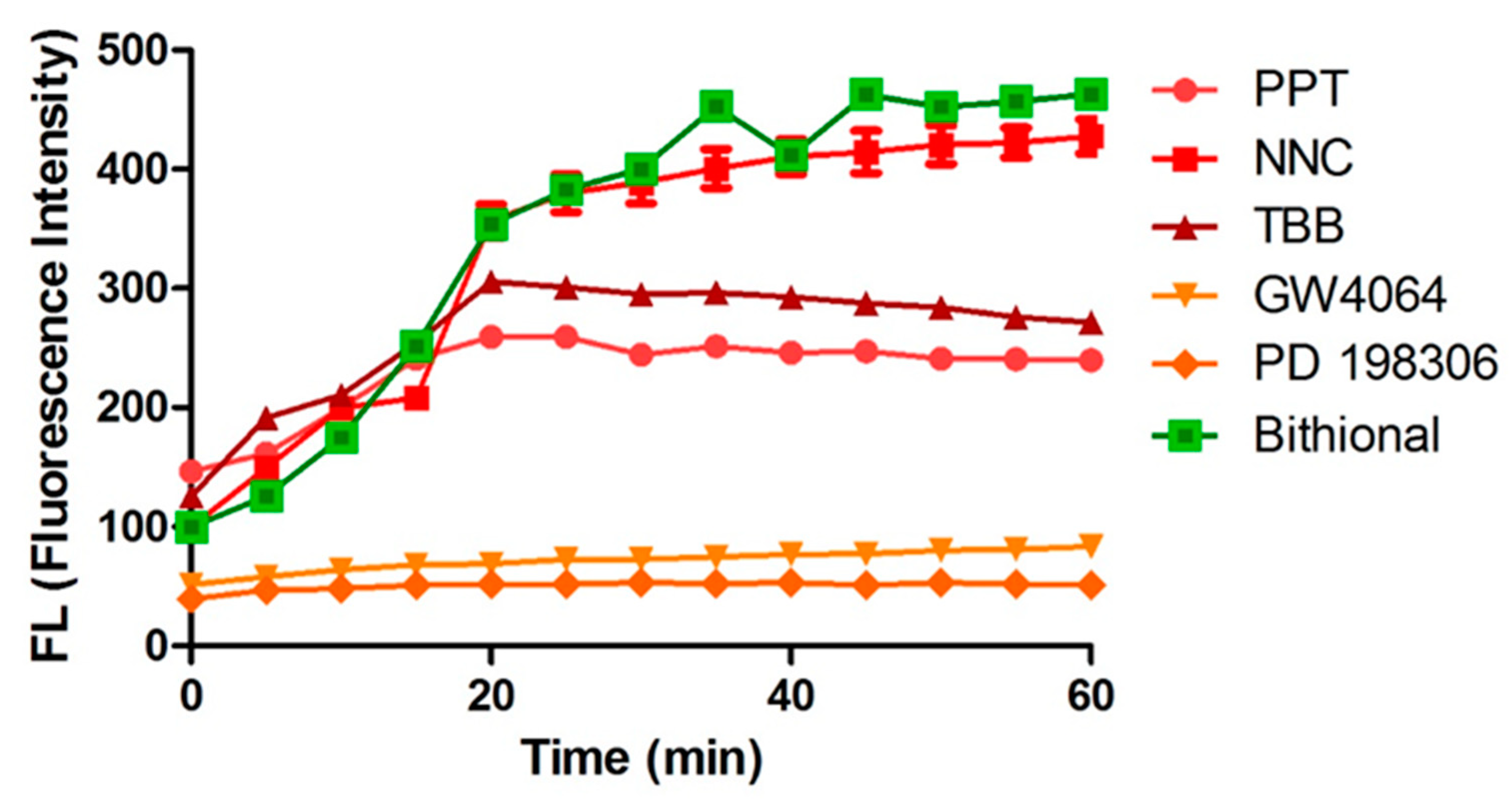
2.4. Membrane Permeabilization
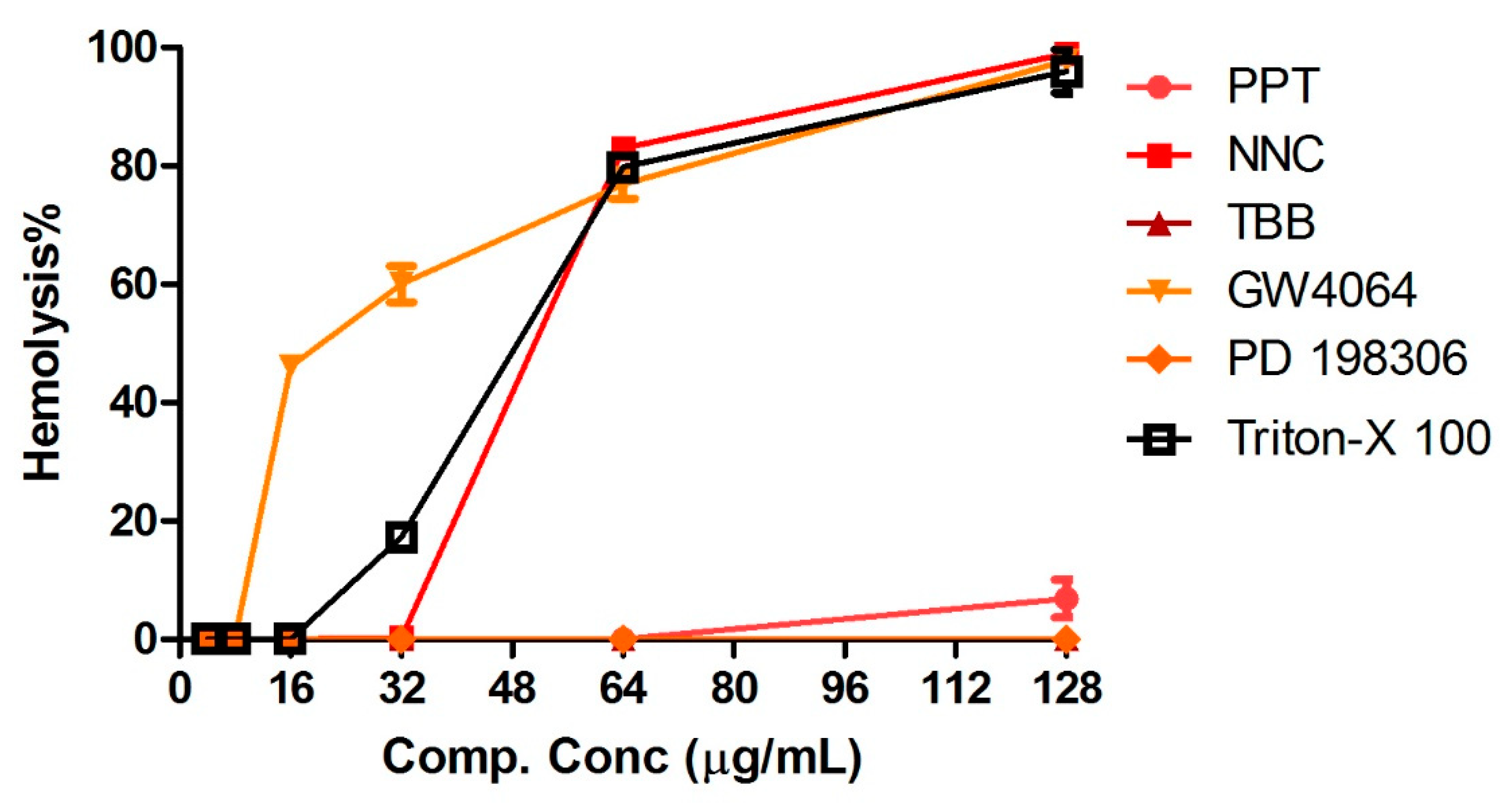
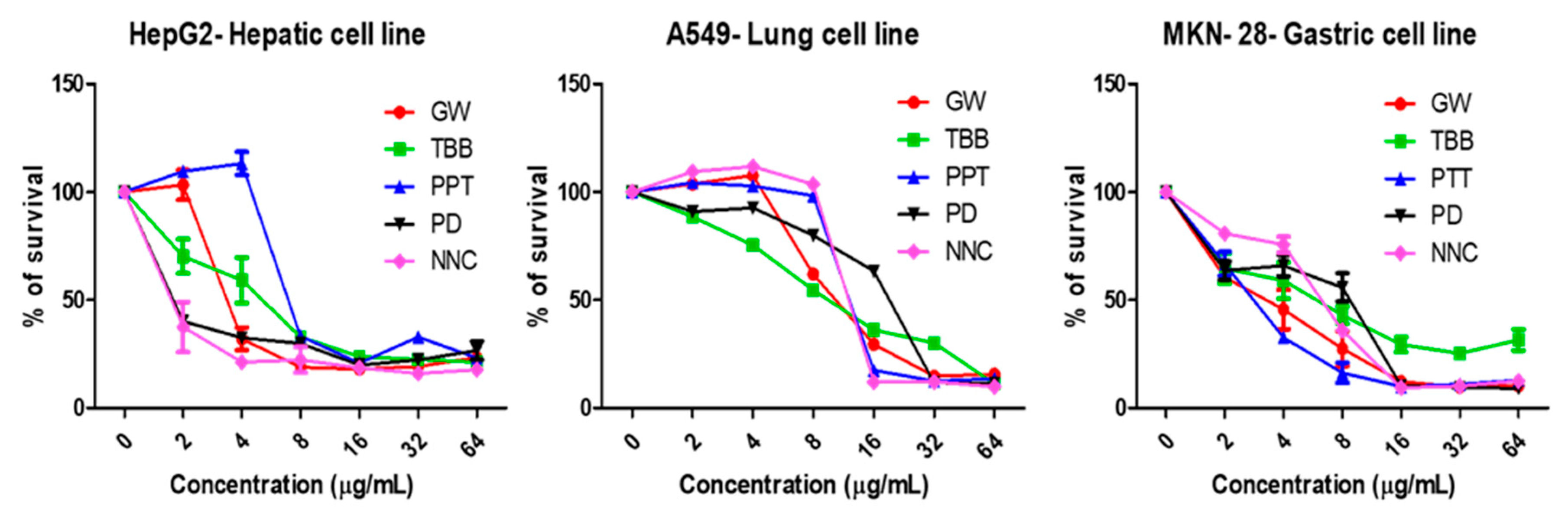
2.5. Human Red Blood Cell Hemolysis Assays and Cytotoxicity
2.6. Antibacterial Synergy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Hit Compounds
4.2. Galleria Mellonella Survival Assays
4.3. Antibacterial Susceptibility Assays
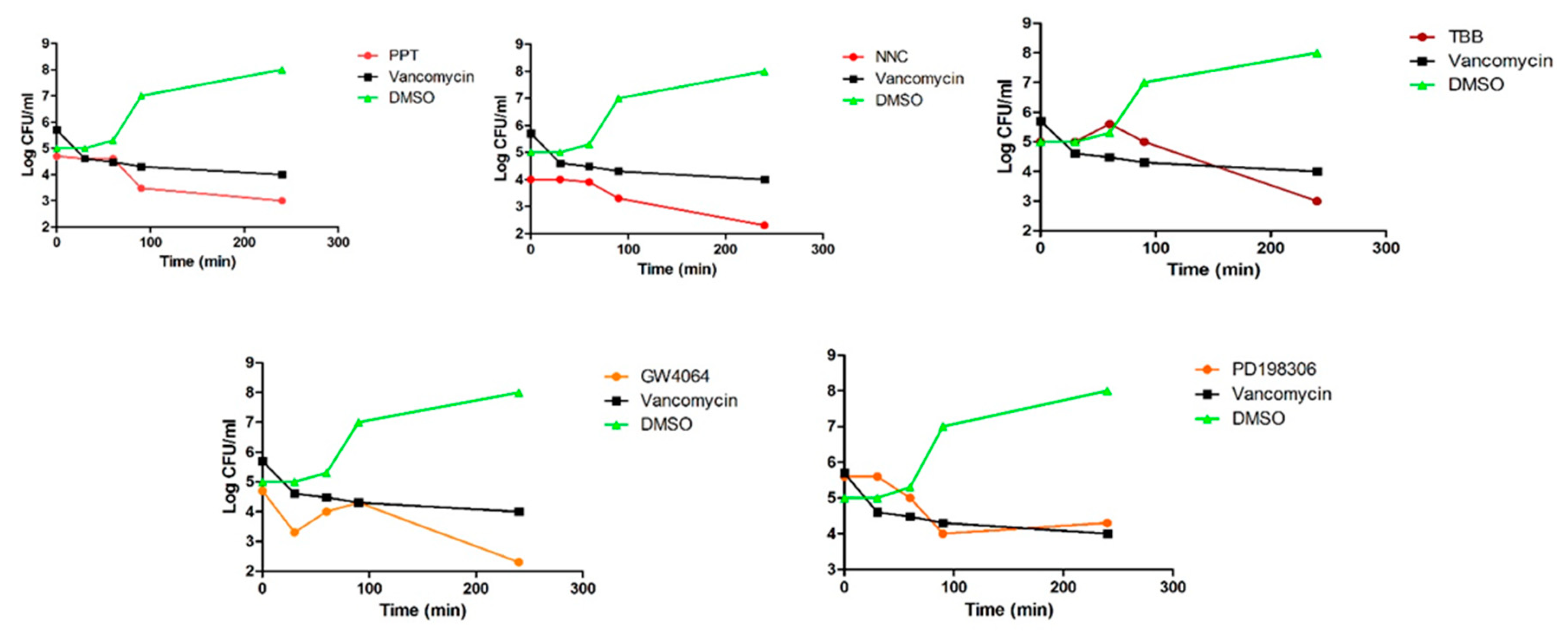
4.4. Time-To-Kill Assays
4.5. Membrane Permeabilization
4.6. Human Red Blood Cell (RBC) Hemolysis Assays
4.7. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.8. Checkboard Assays
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lowy, F.D. Antimicrobial resistance: The example of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okwu, M.U.; Olley, M.; Akpoka, A.O.; Izevbuwa, O.E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and anti-MRSA activities of extracts of some medicinal plants: A brief review. AIMS Microbiol. 2019, 5, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.O.; Baptiste, K.E. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci: A Review of Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms and Perspectives of Human and Animal Health. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewbank, J.J. Tackling both sides of the host-pathogen equation with Caenorhabditis elegans. Microbes. Infect. 2002, 4, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamuthiah, R.; Fuchs, B.B.; Jayamani, E.; Kim, Y.; Larkins-Ford, J.; Conery, A.; Ausubel, F.M.; Mylonakis, E. Whole animal automated platform for drug discovery against multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, T.I.; Ball, A.R.; Anklesaria, Z.; Casadei, G.; Lewis, K.; Ausubel, F.M. Identification of novel antimicrobials using a live-animal infection model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10414–10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirienko, N.V.; Kirienko, D.R.; Larkins-Ford, J.; Wahlby, C.; Ruvkun, G.; Ausubel, F.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa disrupts Caenorhabditis elegans iron homeostasis, causing a hypoxic response and death. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, A.; Krajangwong, S.; Crumlish, M.; Zadoks, R.N.; Walker, D. Galleria mellonella as an infection model for the multi-host pathogen Streptococcus agalactiae reflects hypervirulence of strains associated with human invasive disease. Virulence 2019, 10, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Zhu, W.; Hendricks, G.L.; Van Tyne, D.; Steele, A.D.; Keohane, C.E.; Fricke, N.; Conery, A.L.; Shen, S.; Pan, W.; et al. A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial persisters. Nature 2018, 556, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H.A.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Characterization of the biological roles of the estrogen receptors, ERalpha and ERbeta, in estrogen target tissues in vivo through the use of an ERalpha-selective ligand. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 4172–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Keyser, B.M.; Tagmose, T.M.; Hansen, J.B.; Taylor, J.T.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, M.; Ragsdale, D.S.; Li, M. NNC 55-0396 [(1S,2S)-2-(2-(N-[(3-benzimidazol-2-yl)propyl]-N-methylamino)ethyl)-6-fluoro-1,2, 3,4-tetrahydro-1-isopropyl-2-naphtyl cyclopropanecarboxylate dihydrochloride]: A new selective inhibitor of T-type calcium channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, S.; Reddy, H.; Meggio, F.; Ruzzene, M.; Davies, S.P.; Donella-Deana, A.; Shugar, D.; Pinna, L.A. Selectivity of 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole, an ATP site-directed inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 (‘casein kinase-2′). FEBS Lett. 2001, 496, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, B.; van Harmelen, K.; Duran-Sandoval, D.; van Dijk, T.H.; Grefhorst, A.; Abdelkarim, M.; Caron, S.; Torpier, G.; Fruchart, J.C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. The farnesoid X receptor modulates adiposity and peripheral insulin sensitivity in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11039–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciruela, A.; Dixon, A.K.; Bramwell, S.; Gonzalez, M.I.; Pinnock, R.D.; Lee, K. Identification of MEK1 as a novel target for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, G.L. Bactericidal agents in the treatment of MRSA infections--the potential role of daptomycin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torella, J.P.; Chait, R.; Kishony, R. Optimal drug synergy in antimicrobial treatments. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Coote, P.J. Wax moth larva (Galleria mellonella): An in vivo model for assessing the efficacy of antistaphylococcal agents. J. Antimicrob Chemother 2011, 66, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascioferro, S.; Maggio, B.; Raffa, D.; Raimondi, M.V.; Cusimano, M.G.; Schillaci, D.; Manachini, B.; Plescia, F.; Daidone, G. Synthesis and biofilm formation reduction of pyrazole-4-carboxamide derivatives in some Staphylococcus aureus strains. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, P.R.; Parks, D.J.; Haffner, C.D.; Fivush, A.M.; Chandra, G.; Plunket, K.D.; Creech, K.L.; Moore, L.B.; Wilson, J.G.; Lewis, M.C.; et al. Identification of a chemical tool for the orphan nuclear receptor FXR. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 2971–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzene, M.; Brunati, A.M.; Sarno, S.; Marin, O.; Donella-Deana, A.; Pinna, L.A. Ser/Thr phosphorylation of hematopoietic specific protein 1 (HS1): Implication of protein kinase CK2. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannouli, M.; Palatucci, A.T.; Rubino, V.; Ruggiero, G.; Romano, M.; Triassi, M.; Ricci, V.; Zarrilli, R. Use of larvae of the wax moth Galleria mellonella as an in vivo model to study the virulence of Helicobacter pylori. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, G.; Derbentli, S. In vitro activity of daptomycin combinations with rifampicin, gentamicin, fosfomycin and fusidic acid against MRSA strains. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2017, 10, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwisai, T.; Hollingsworth, N.R.; Cowles, S.; Tharmalingam, N.; Mylonakis, E.; Fuchs, B.B.; Shukla, A. Repurposing niclosamide as a versatile antimicrobial surface coating against device-associated, hospital-acquired bacterial infections. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 045010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamuthiah, R.; Fuchs, B.B.; Conery, A.L.; Kim, W.; Jayamani, E.; Kwon, B.; Ausubel, F.M.; Mylonakis, E. Repurposing salicylanilide anthelmintic drugs to combat drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.J.; Qiu, S.; Zou, H.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Tang, C.; Saraswathi, P.; Verma, C.; Tan, D.T.; et al. Rapid bactericidal action of alpha-mangostin against MRSA as an outcome of membrane targeting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1828, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Zou, G.; Hari, T.P.A.; Wilt, I.K.; Zhu, W.; Galle, N.; Faizi, H.A.; Hendricks, G.L.; Tori, K.; Pan, W.; et al. A selective membrane-targeting repurposed antibiotic with activity against persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16529–16534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnansetyo, A.; Kamei, Y. MC21-A, a bactericidal antibiotic produced by a new marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica sp. nov. O-BC30(T), against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.H.; Park, M.; Woo, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Tharmalingam, N.; Seo, W.D.; Kim, J.B. Regulatory Effects of Black Rice Extract on Helicobacter pylori Infection-Induced Apoptosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorian, V. Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
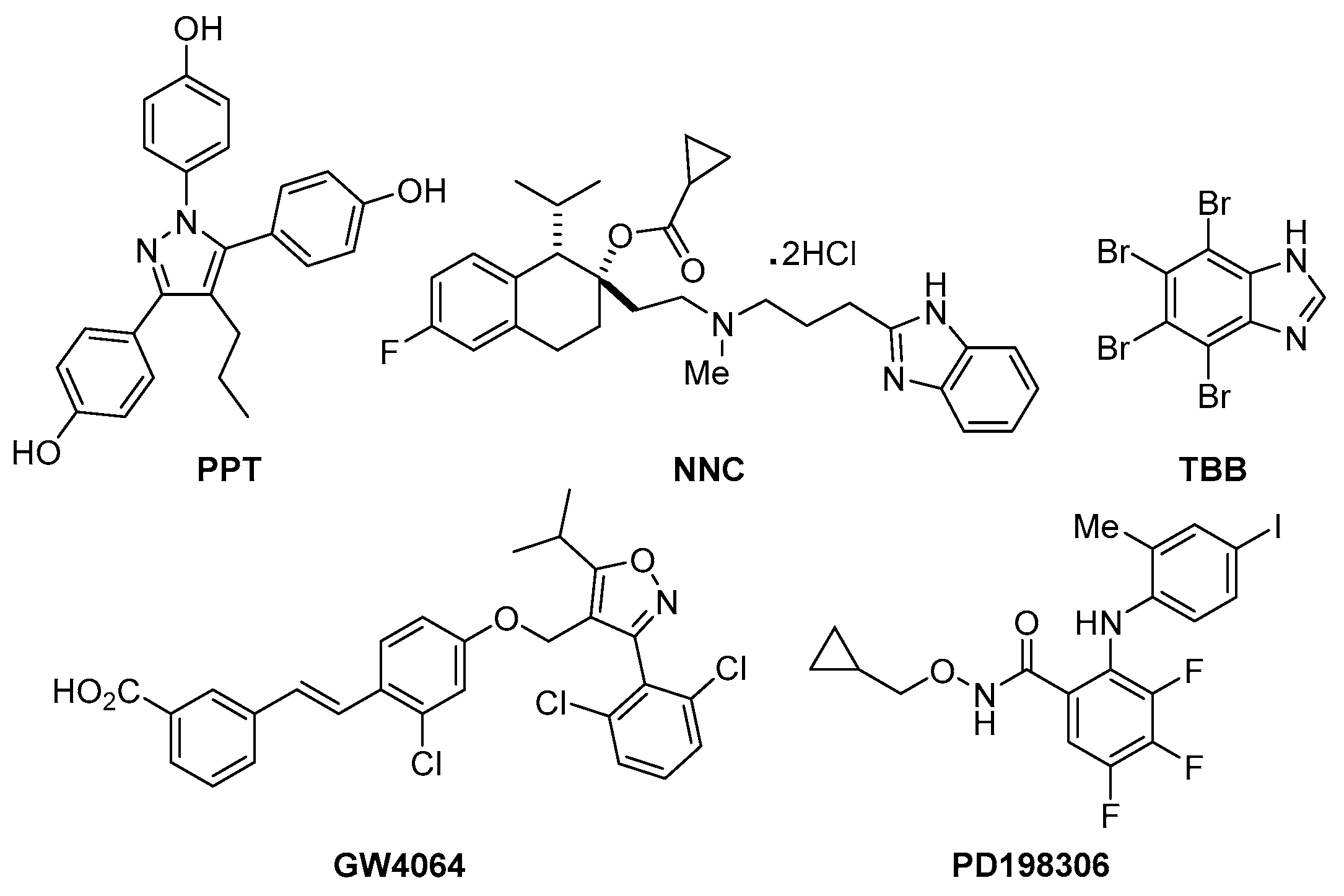
| Compounds | Chemical Name | Reported Bioactivity |
|---|---|---|
| PPT | 4,4′,4″-(4-Propyl-[1H]-pyrazole-1,3,5-triyl)trisphenol | Prevents ovariectomy-induced weight gain and loss of bone mineral density, and induces gene expression in the hypothalamus following systemic administration in vivo [10]. |
| NNC | (1S,2S)-2-[2-[[3-(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)propyl]methylamino]ethyl]-6-fluoro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-naphthalenyl cyclopropanecarboxylate dihydrochloride | Highly selective T-type calcium channel blocker. Displays IC50 values of 6.8 and >100 μM for inhibition of Cav3.1 T-type channels and HVA currents respectively in INS-1 cells [11]. |
| TBB | 4,5,6,7-Tetrabromobenzotriazole | Cell-permeable, selective inhibitor of casein kinase-2.Exhibits modest discrimination between CK2 subunits [12]. |
| GW4064 | 3-[2-[2-Chloro-4-[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-4-isoxazolyl]methoxy]phenyl]ethenyl]benzoic acid | Selective, non-steroidal farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist Shown to suppress autophagy in nutrient-deprived mouse hepatocytes [13]. |
| PD198306 | N-(Cyclopropylmethoxy)-3,4,5-trifluoro-2-[(4-iodo-2-methylphenyl)amino]-benzamide | Potent inhibitor of MEK1/2.Highly selective for MEK.Antihyperalgesic; blocks static allodynia in the streptozocin model of neuropathic pain [14]. |
| Compound | Z-Score |
|---|---|
| PPT | 5.54 |
| NNC | 5.83 |
| TBB | 3.16 |
| GW4064 | 3.28 |
| PD198306 | 3.43 |
| Compounds | MIC | MBC |
|---|---|---|
| PPT | 8 | 32 |
| NNC | 8 | >64 |
| TBB | 6 | >64 |
| GW4064 | 8 | >64 |
| PD198306 | 2 | >64 |
| Vancomycin | 1 | 8 |
| Clinical S. aureus Isolates and ESKAPE Pathogens | MIC (µg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPT | NNC | TBB | GW4064 | PD198306 | Vancomycin | |
| BF1 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| BF2 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| BF3 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| BF4 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| Enterococcus faecium | 8 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | 32 | >64 |
| Enterobactor aerogens | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 |
| Compounds | HepG2 | A549 | MKN-28 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPT | 8 | 16 | 8 |
| NNC | 2 | 16 | 8 |
| TBB | 8 | 16 | 16 |
| GW4064 | 4 | 16 | 8 |
| PD198306 | 2 | 16 | 16 |
| Compounds | Polymyxin B | Gentamycin | Erythromycin | Doxycycline | Oxacillin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPT | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| NNC | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 0.75 | 2.0 |
| TBB | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.625 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| GW4064 | 0.75 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.06 | 1.0 |
| PD198306 | 1.0 | 0.625 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 0.75 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khader, R.; Tharmalingam, N.; Mishra, B.; Felix, L.; Ausubel, F.M.; Kelso, M.J.; Mylonakis, E. Characterization of Five Novel Anti-MRSA Compounds Identified Using a Whole-Animal Caenorhabditis elegans/Galleria mellonella Sequential-Screening Approach. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080449
Khader R, Tharmalingam N, Mishra B, Felix L, Ausubel FM, Kelso MJ, Mylonakis E. Characterization of Five Novel Anti-MRSA Compounds Identified Using a Whole-Animal Caenorhabditis elegans/Galleria mellonella Sequential-Screening Approach. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(8):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080449
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhader, Rajamohammed, Nagendran Tharmalingam, Biswajit Mishra, LewisOscar Felix, Frederick M. Ausubel, Michael J. Kelso, and Eleftherios Mylonakis. 2020. "Characterization of Five Novel Anti-MRSA Compounds Identified Using a Whole-Animal Caenorhabditis elegans/Galleria mellonella Sequential-Screening Approach" Antibiotics 9, no. 8: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080449
APA StyleKhader, R., Tharmalingam, N., Mishra, B., Felix, L., Ausubel, F. M., Kelso, M. J., & Mylonakis, E. (2020). Characterization of Five Novel Anti-MRSA Compounds Identified Using a Whole-Animal Caenorhabditis elegans/Galleria mellonella Sequential-Screening Approach. Antibiotics, 9(8), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080449






