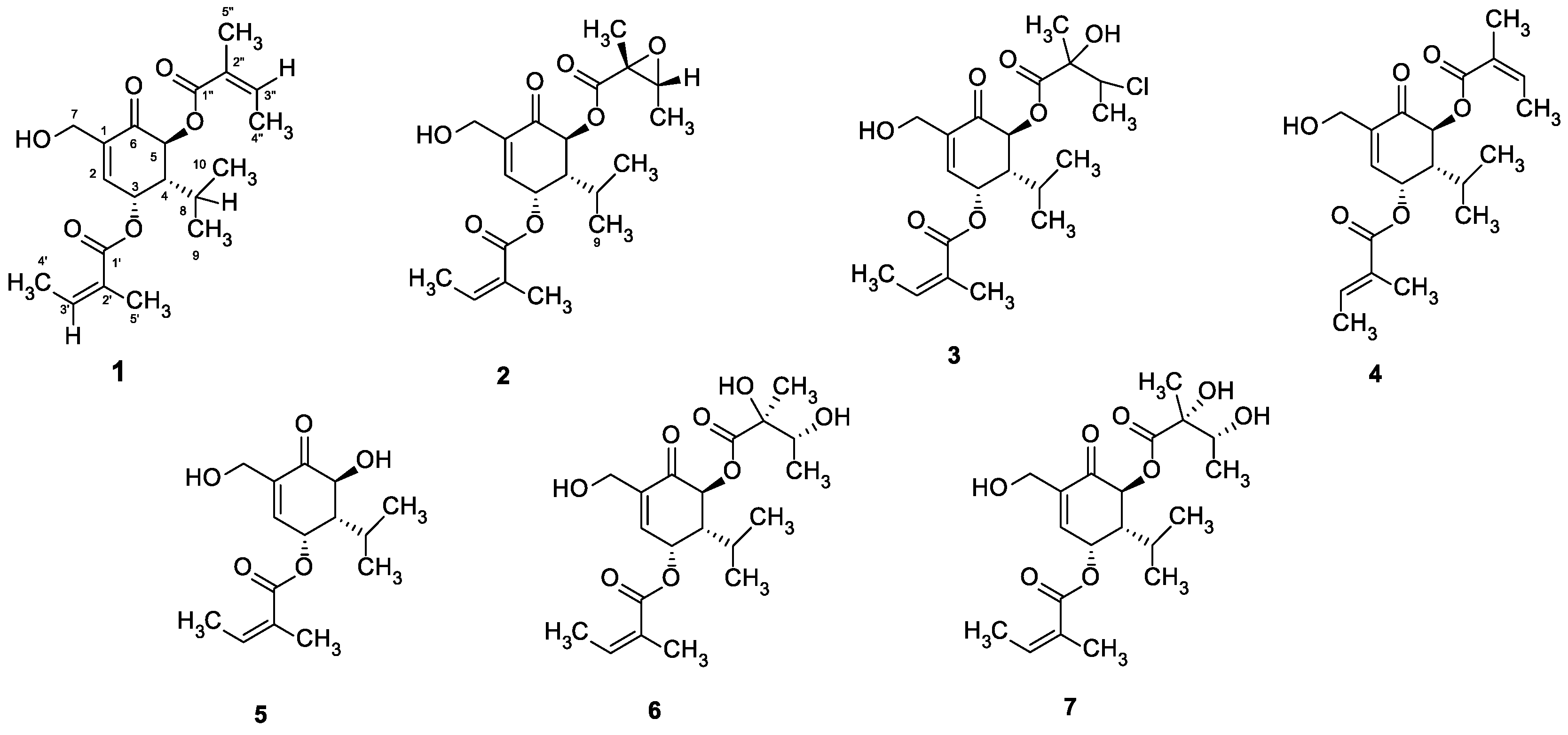
Antimicrobial and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Activity of Carvotacetones from Sphaeranthus africanus Against Mycobacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial and Resistance Modulatory Activity
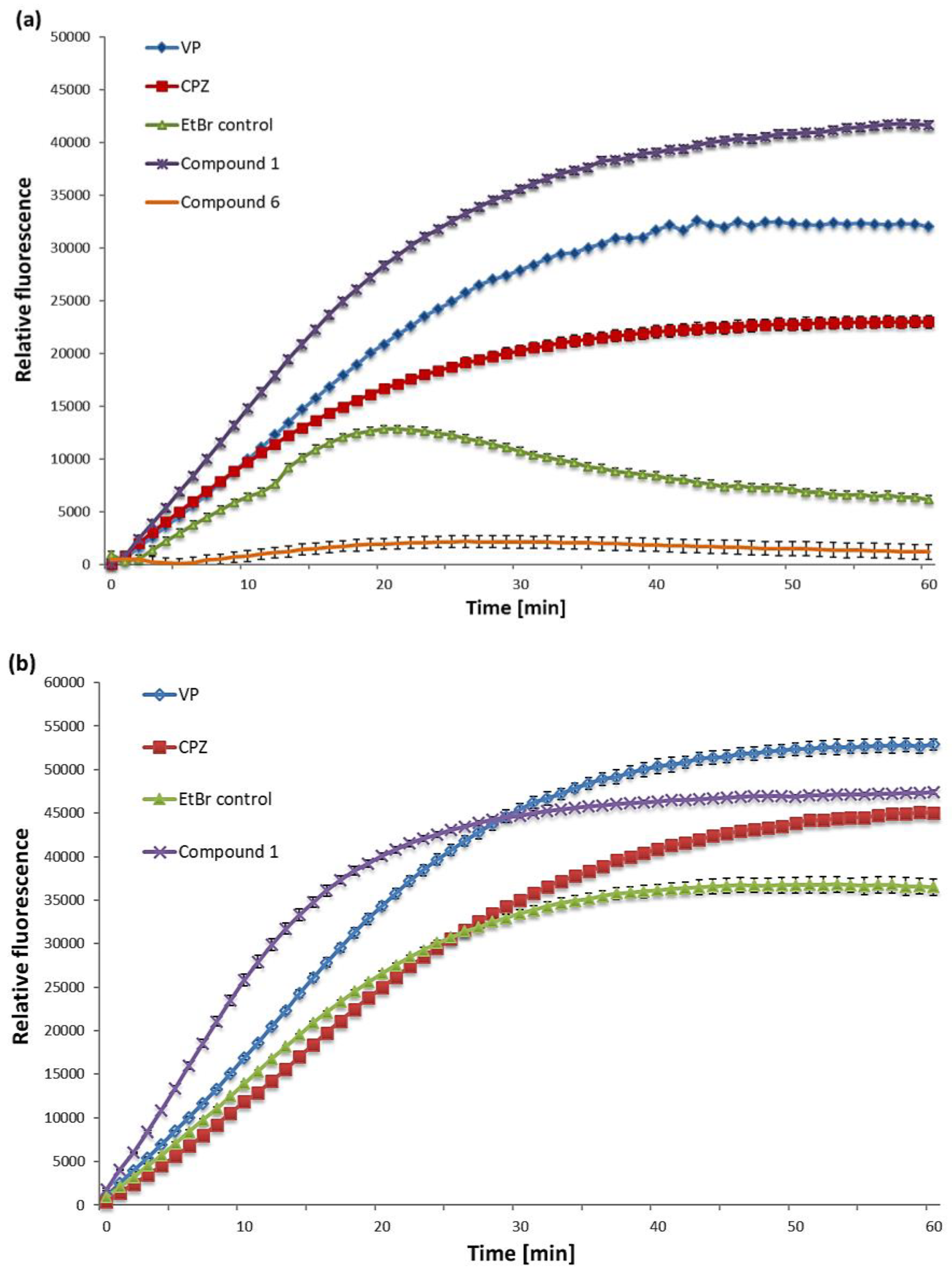
2.2. EtBr Accumulation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phytochemical Procedures
4.2. Plant Materials
4.3. Extractions and Isolations
4.4. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.5. MIC and Modulation Assays
4.6. EtBr Accumulation Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, S.J.; Payne, D.J.; Rappuoli, R.; De Gregorio, E. Technologies to address antimicrobial resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12887–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solnier, J.; Martin, L.; Bhakta, S.; Bucar, F. Flavonoids as novel efflux pump inhibitors and antimicrobials against both environmental and pathogenic intracellular mycobacterial species. Molecules 2020, 25, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2014, 6, PMC.S14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shriram, V.; Khare, T.; Bhagwat, R.; Shukla, R.; Kumar, V. Inhibiting bacterial drug efflux pumps via phyto-therapeutics to combat threatening antimicrobial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.; Piddock, L. The importance of efflux pumps in bacterial antibiotic resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Cravo, P.; Viveiros, M. Efflux pump inhibitors as a promising adjunct therapy against drug resistant tuberculosis: A new strategy to revisit mycobacterial targets and repurpose old drugs. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavri, M.; Piddock, L.J.; Gibbons, S. Bacterial efflux pump inhibitors from natural sources. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmasky, M.E. Strategies to prolong the useful life of existing antibiotics and help overcoming the antibiotic resistance crisis. In Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research-Anti Infectives; Atta-ur-Rhaman, Ed.; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, UAE, 2017; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, L.; Kristiansen, J.E.; Viveiros, M.; Atouguia, J. Activity of phenothiazines against antibiotic-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A review supporting further studies that may elucidate the potential use of thioridazine as anti-tuberculosis therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 47, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Viveiros, M.; Aínsa, J.A. Measuring efflux and permeability in mycobacteria. In Mycobacteria Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazaei, C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis and lipids: Insights into molecular mechanisms from persistence to virulence. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2018, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, P.K.; Amarh, V.; Cramer, P.; Arkaifie, G.B.; Blessie, E.J.; Fuseini, M.-S.; Carilo, I.; Yeboah, R.; Asare, L.; Robertson, B.D. Characterization of two new multidrug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium smegmatis: Tools for routine in vitro screening of novel anti-mycobacterial agents. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andries, K.; Verhasselt, P.; Guillemont, J.; Göhlmann, H.W.; Neefs, J.-M.; Winkler, H.; Van Gestel, J.; Timmerman, P.; Zhu, M.; Lee, E. A diarylquinoline drug active on the ATP synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 2005, 307, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, L. Effux pump inhibitors against nontuberculous mycobacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarnalatha, Y.; Krishnan, D.; Rajasekar, S.V. Antibacterial activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles from Sphaeranthus amaranthoides. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 594–596. [Google Scholar]
- Mumtaz, N.; Naqvi, S.B.S.; Asghar, M.A.; Asghar, M.A. Assessment of antimicrobial activity of Sphaeranthus indicus L. against highly resistant pathogens and its comparison with three different antibiotics. J. Dis. Glob. Health 2017, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ragasa, C.Y.; Tsai, P.-W.; Galvez, C.T.; Shen, C.-C. New carvotanacetone derivatives from Sphaeranthus africanus. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.; Pferschy-Wenzig, E.-M.; Kretschmer, N.; Kunert, O.; Huynh, L.; Bauer, R. Antiproliferative Carvotacetones from Sphaeranthus africanus. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.; Gao, X.; Kretschmer, N.; Pferschy-Wenzig, E.-M.; Raab, P.; Pirker, T.; Temml, V.; Schuster, D.; Kunert, O.; Huynh, L. Anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative compounds from Sphaeranthus africanus. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machumi, F.; Yenesew, A.; Midiwo, J.O.; Heydenreich, M.; Kleinpeter, E.; Tekwani, B.L.; Khan, S.I.; Walker, L.A.; Muhammad, I. Antiparasitic and anticancer carvotacetone derivatives of Sphaeranthus bullatus. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1934578X1200700902. [Google Scholar]
- Pouny, I.; Vispé, S.; Marcourt, L.; Long, C.; Vandenberghe, I.; Aussagues, Y.; Raux, R.; Mutiso, P.B.C.; Massiot, G.; Sautel, F. Four new carvotanacetone derivatives from Sphaeranthus ukambensis, inhibitors of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.; Machado, D.; Couto, I.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Contribution of efflux activity to isoniazid resistance in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danquah, C.A.; Kakagianni, E.; Khondkar, P.; Maitra, A.; Rahman, M.; Evangelopoulos, D.; McHugh, T.D.; Stapleton, P.; Malkinson, J.; Bhakta, S. Analogues of disulfides from allium stipitatum demonstrate potent anti-tubercular activities through drug efflux pump and biofilm inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.; Ramos, J.; Couto, I.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Ethidium bromide transport across Mycobacterium smegmatis cell-wall: Correlation with antibiotic resistance. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viveiros, M.; Portugal, I.; Bettencourt, R.; Victor, T.C.; Jordaan, A.M.; Leandro, C.; Ordway, D.; Amaral, L. Isoniazid-induced transient high-level resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2804–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buroni, S.; Manina, G.; Guglierame, P.; Pasca, M.R.; Riccardi, G.; De Rossi, E. LfrR is a repressor that regulates expression of the efflux pump LfrA in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 4044–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.; Maitra, A.; McNerney, R.; Nair, M.; Gupta, A.; Coll, F.; Pain, A.; Bhakta, S.; Clark, T.G. The draft genome of Mycobacterium aurum, a potential model organism for investigating drugs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium leprae. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2015, 4, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Nyantakyi, S.A.; Li, M.; Gopal, P.; Aziz, D.B.; Yang, T.; Moreira, W.; Gengenbacher, M.; Dick, T.; Go, M.L. The mycobacterial membrane: A novel target space for anti-tubercular drugs. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, G.; Ruminiski, P.G.; Kumar, M.; Singh, K.; Hamzabegovic, F.; Hoft, D.F.; Eickhoff, C.S.; Selimovic, A.; Campbell, M.; Chibale, K. New verapamil analogs inhibit intracellular mycobacteria without affecting the functions of mycobacterium-specific T cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröblacher, B.; Kunert, O.; Bucar, F. Compounds of Alpinia katsumadai as potential efflux inhibitors in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2701–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockert, J.C.; Horobin, R.W.; Colombo, L.L.; Blázquez-Castro, A. Tetrazolium salts and formazan products in Cell Biology: Viability assessment, fluorescence imaging, and labeling perspectives. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelopoulos, D.; Bhakta, S. Rapid methods for testing inhibitors of mycobacterial growth. In Antibiotic Resistance Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, L.; Wagner, D.; Viveiros, M.; Sampaio, D.; Couto, I.; Vavra, M.; Kern, W.V.; Amaral, L. Thioridazine and chlorpromazine inhibition of ethidium bromide efflux in Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. (JAC) 2008, 61, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | MIC | MIC [c]Modulator+EtBr | MIC [c]Modulator+RIF | MF (EtBr) | MF (RIF) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | (μM) | (mg/L) | (mg/L) | |||
| 1 | 32 | 87.9 | 1 | 16 | 8 | 2 |
| 2 | 128 | 336.8 | 4 | - | 2 | - |
| 3 | 64 | 153.8 | 4 | - | 2 | - |
| 4 | 32 | 87.9 | 4 | - | 2 | - |
| 5 | 128 | 453.9 | 8 | - | 1 | - |
| 6 | 128 | 321.6 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 1 |
| 7 | 64 | 160.8 | 4 | - | 2 | - |
| EtBr | 8 | 20.3 | ||||
| RIF | 32 | 38.9 | ||||
| Substrate | MIC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. smegmatis mc2 155 | M. aurum ATCC 23366 | M. bovis BCG ATCC 35734 | ||||
| (mg/L) | (μM) | (mg/L) | (μM) | (mg/L) | (μM) | |
| 1 | 32 | 87.9 | 31.25 | 85.9 | 15.63 | 42.9 |
| 6 | 128 | 321.6 | 31.25 | 78.5 | 31.25 | 78.5 |
| Isoniazid | 4 | 29.2 | 0.5 | 3.6 | 0.1 | 0.7 |
| Verapamil | 250 | 550.7 | 250 | 550.7 | 320 [25] | 703.9 |
| Chlorpromazine | 25 | 78.6 | 20 | 62.9 | 20 [25] | 62.8 |
| EtBr | 8 | 20.3 | 1 | 2.5 | 0.5 [25] | 1.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, H.T.; Solnier, J.; Pferschy-Wenzig, E.-M.; Kunert, O.; Martin, L.; Bhakta, S.; Huynh, L.; Le, T.M.; Bauer, R.; Bucar, F. Antimicrobial and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Activity of Carvotacetones from Sphaeranthus africanus Against Mycobacteria. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070390
Tran HT, Solnier J, Pferschy-Wenzig E-M, Kunert O, Martin L, Bhakta S, Huynh L, Le TM, Bauer R, Bucar F. Antimicrobial and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Activity of Carvotacetones from Sphaeranthus africanus Against Mycobacteria. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(7):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070390
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Huyen Thi, Julia Solnier, Eva-Maria Pferschy-Wenzig, Olaf Kunert, Liam Martin, Sanjib Bhakta, Loi Huynh, Tri Minh Le, Rudolf Bauer, and Franz Bucar. 2020. "Antimicrobial and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Activity of Carvotacetones from Sphaeranthus africanus Against Mycobacteria" Antibiotics 9, no. 7: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070390
APA StyleTran, H. T., Solnier, J., Pferschy-Wenzig, E.-M., Kunert, O., Martin, L., Bhakta, S., Huynh, L., Le, T. M., Bauer, R., & Bucar, F. (2020). Antimicrobial and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Activity of Carvotacetones from Sphaeranthus africanus Against Mycobacteria. Antibiotics, 9(7), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9070390