Salvage Bacteriophage Therapy for a Chronic MRSA Prosthetic Joint Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
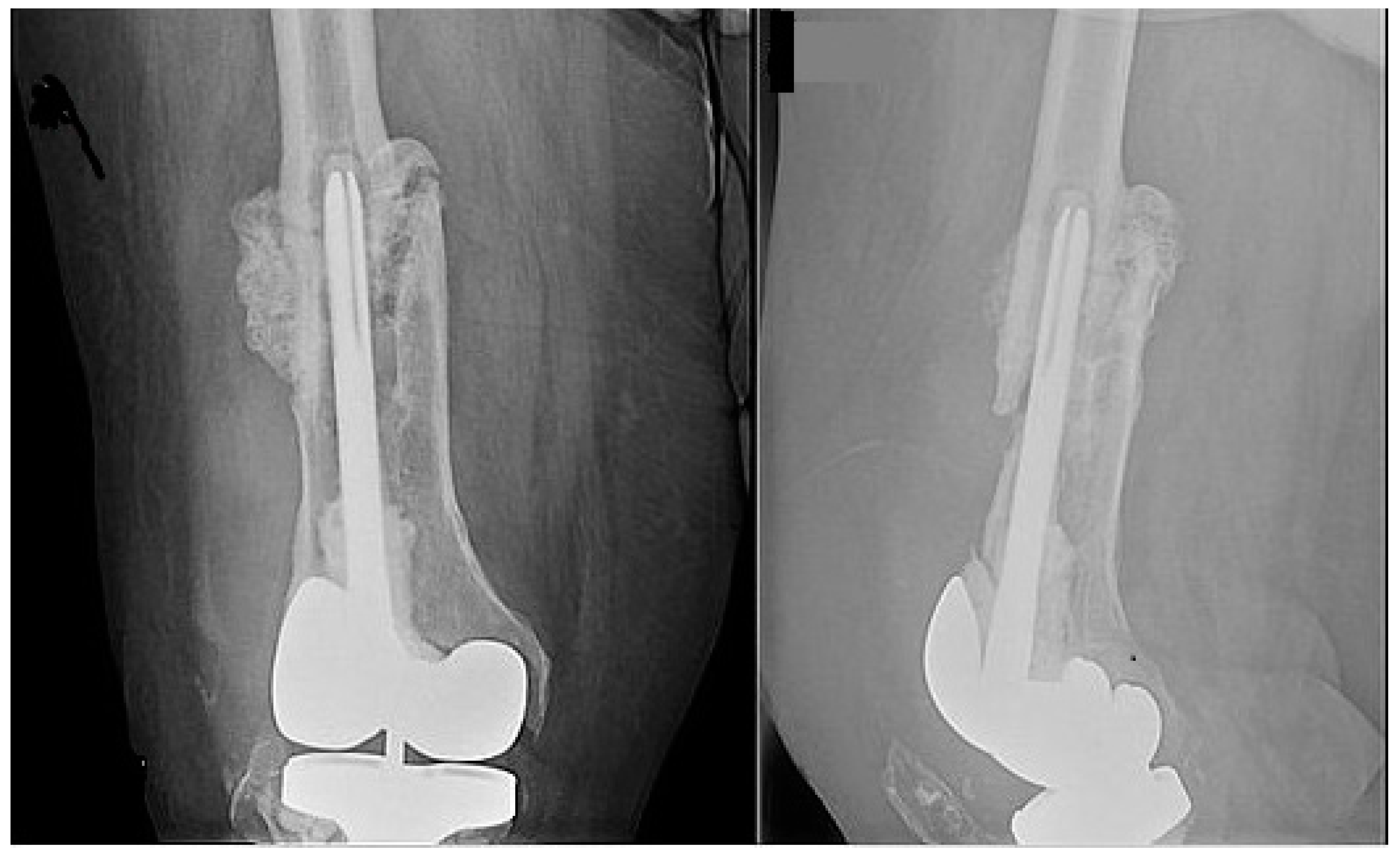
2. Case
3. Methods
3.1. Bacterial Isolation
3.2. Bacteriophage Screening Using the Host Range Quick Test (HRQT)
3.3. Phage Amplification and Purification
3.4. Repurification, Final Therapy Formulation, and Quality Control Testing
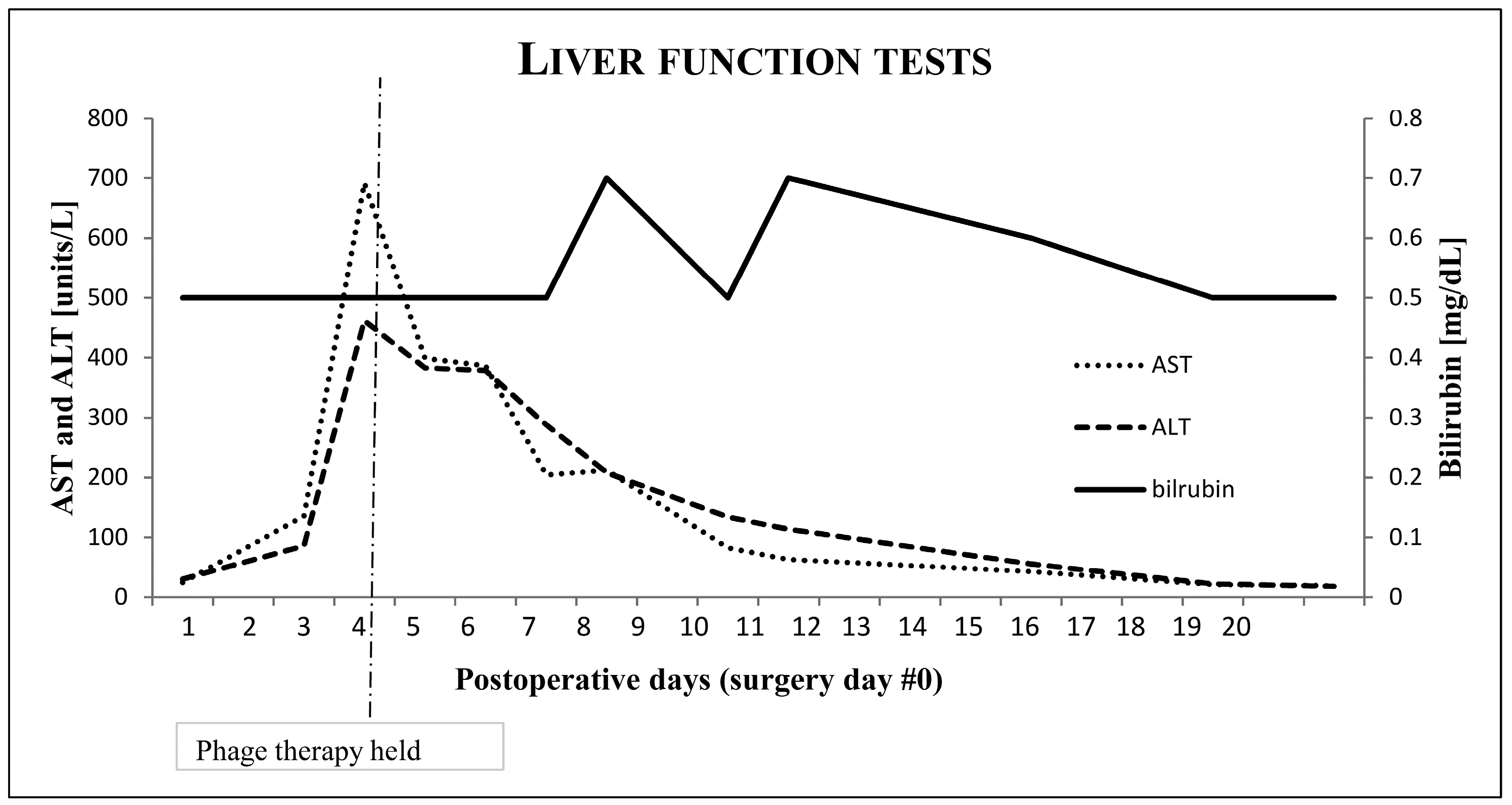
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurtz, S.M.; Lau, E.; Watson, H.; Schmier, J.; Parvizi, J. Economic Burden of Periprosthetic Joint Infection in the United States. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 61–65.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsuhara, K.; Shelton, T.J.; Meehan, J.P.; Lum, Z.C. Mortality During Total Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S337–S342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, T.-F.C.; O’Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, K. Targeting Enterococcus faecalis Biofilms with Phage Therapy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2696–2705. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, S.A.; Drilling, A.; Morales, S.; Cornet, M.E.; Woodworth, B.A.; Fokkens, W.J.; Psaltis, A.J.; Vreugde, S.; Wormald, P.J. Activity of Bacteriophages in Removing Biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, C.; Colak, M.; Yilmaz, B.C.; Ersoz, G.; Kutateladze, M.; Gozlugol, M. Bacteriophage Therapy in Implant-Related Infections. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2013, 95, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K. Code of Federal Regulations; Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, April 2019; pp. 381–384.
- Henry, M.; Biswas, B.; Vincent, L.; Mokashi, V.; Schuch, R.; A Bishop-Lilly, K.; Sozhamannan, S. Development of a high throughput assay for indirectly measuring phage growth using the OmniLogTM system. Bacteriophage 2012, 2, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrella, L.A.; Quinones, J.; Henry, M.; Hannah, R.M.; Pope, R.K.; Hamilton, T.; Teneza-Mora, N.; Hall, E.; Biswajit, B. Characterization of novel Staphylococcus aureus lytic phage and defining their combinatorial virulence using the OmniLog® system. Bacteriophage 2016, 6, e1219440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, T.; Leboucher, G.; Fevre, C.; Herry, Y.; Conrad, A.; Josse, J.; Batailler, C.; Chidiac, C.; Medina, M.; Lustig, S.; et al. Salvage Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention (“DAIR”) With Local Injection of a Selected Cocktail of Bacteriophages: Is It an Option for an Elderly Patient With Relapsing Staphylococcus aureus Prosthetic-Joint Infection? Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkhilaishvili, T.; Winkler, T.; Müller, M.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Bacteriophages as Adjuvant to Antibiotics for the Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 64, 00924–01019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onesa, J. Bacteriophage application for difficult-to-treat musculoskeletal infections: Development of a standard multidisciplinary treatment protocol. Viruses 2019, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhr, J.W.; Weissman, G. Intracellular distribution and degradation of bacteriophage in mammalian tissues. J. Immunol. 1965, 94, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inchley, C. The actvity of mouse Kupffer cells following intravenous injection of T4 bacteriophage. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1969, 5, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kazankov, K.; Jørgensen, S.M.D.; Thomsen, K.L.; Møller, H.J.; Vilstrup, H.; George, J.; Schuppan, D.; Grønbæk, H. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phage ID | Lot Number | Titer (PFU/mL) | Endotoxin (EU/dose) | Host Cell Protein (ng/mL) | USP <71> Sterility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaGR51Φ1 | eIND19092601 | 2.7 × 109 | <1 | <10 | PASSED |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doub, J.B.; Ng, V.Y.; Johnson, A.J.; Slomka, M.; Fackler, J.; Horne, B.; Brownstein, M.J.; Henry, M.; Malagon, F.; Biswas, B. Salvage Bacteriophage Therapy for a Chronic MRSA Prosthetic Joint Infection. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050241
Doub JB, Ng VY, Johnson AJ, Slomka M, Fackler J, Horne B, Brownstein MJ, Henry M, Malagon F, Biswas B. Salvage Bacteriophage Therapy for a Chronic MRSA Prosthetic Joint Infection. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(5):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050241
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoub, James B., Vincent Y. Ng, Aaron J. Johnson, Magdalena Slomka, Joseph Fackler, Bri’Anna Horne, Michael J. Brownstein, Matthew Henry, Francisco Malagon, and Biswajit Biswas. 2020. "Salvage Bacteriophage Therapy for a Chronic MRSA Prosthetic Joint Infection" Antibiotics 9, no. 5: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050241
APA StyleDoub, J. B., Ng, V. Y., Johnson, A. J., Slomka, M., Fackler, J., Horne, B., Brownstein, M. J., Henry, M., Malagon, F., & Biswas, B. (2020). Salvage Bacteriophage Therapy for a Chronic MRSA Prosthetic Joint Infection. Antibiotics, 9(5), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050241





