Cytotoxicity and Antimycobacterial Properties of Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline Derivatives: Molecular Target Identification and Molecular Docking Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
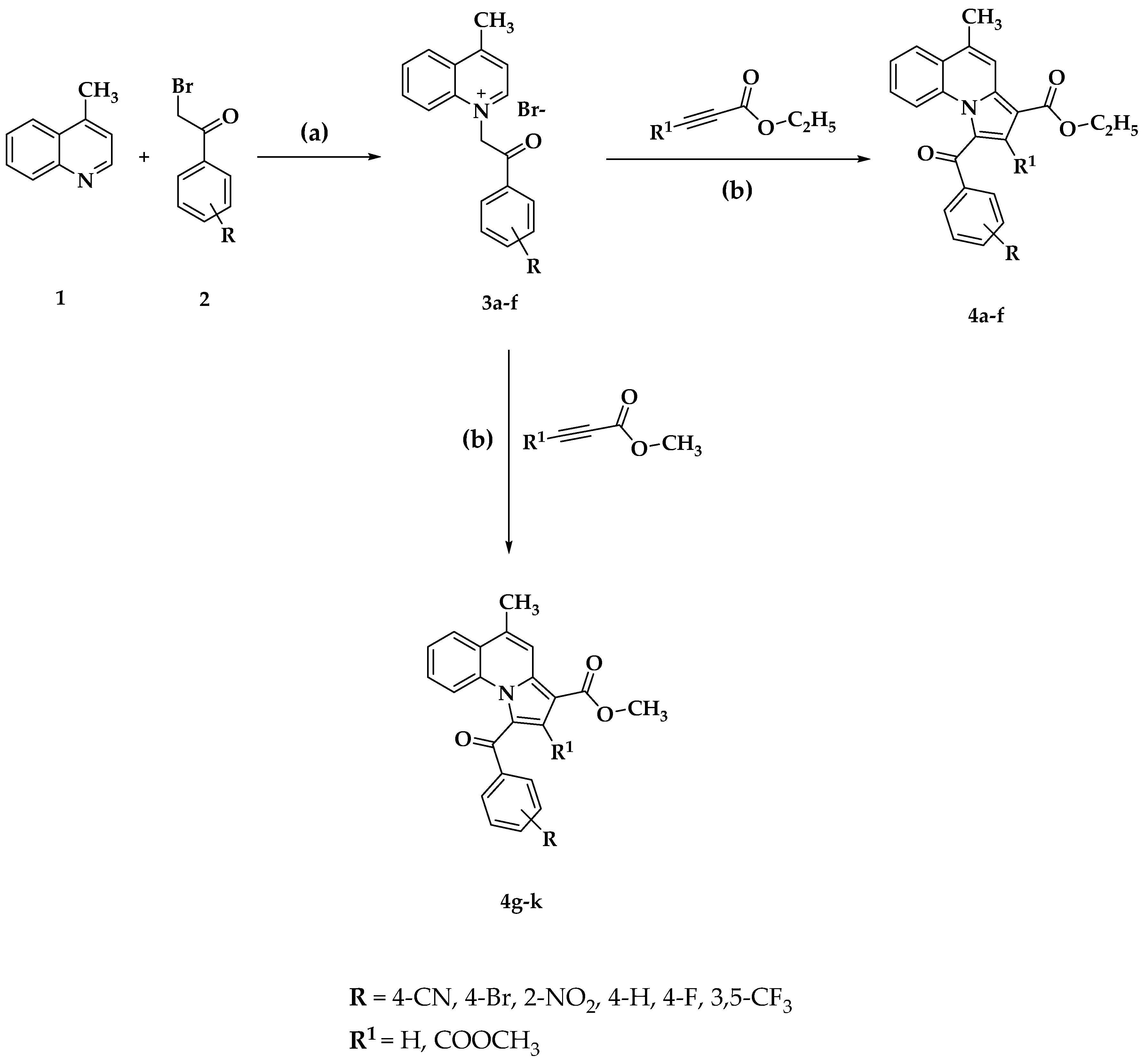
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Antitubercular Activity
2.3. Toxicity Studies
2.4. Computational Studies
2.4.1. Target Identification
2.4.2. ADME Analysis
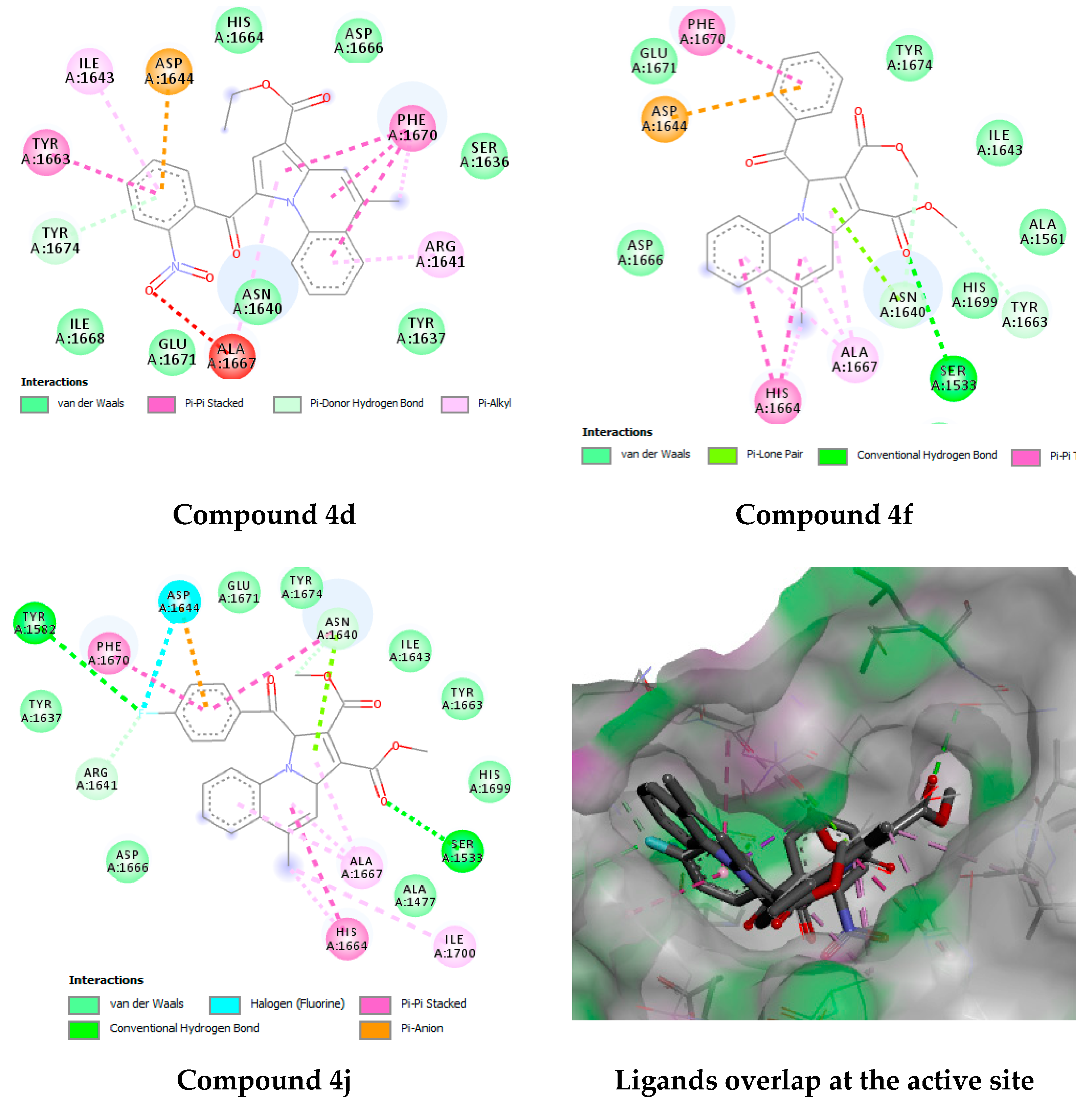
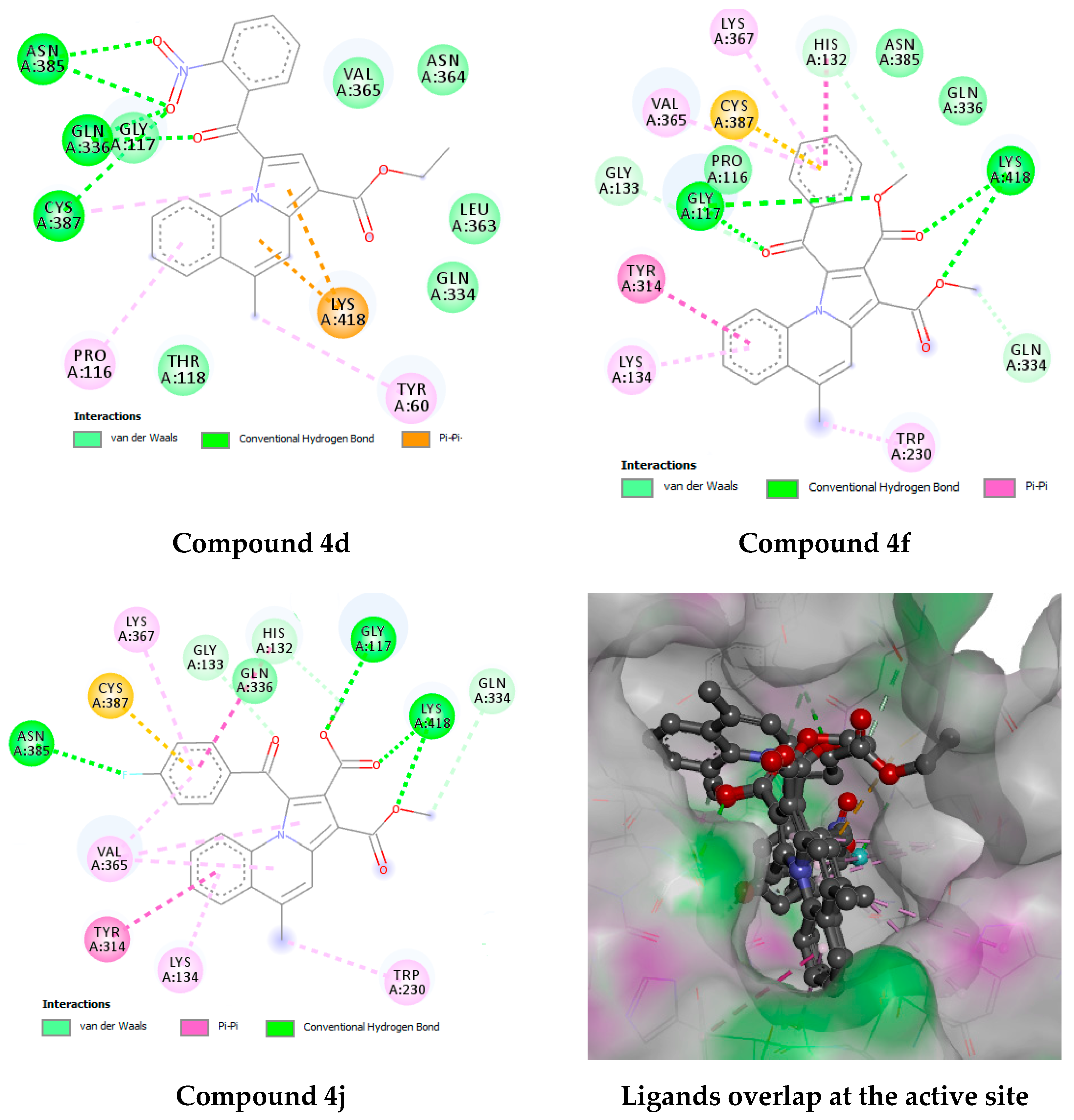
2.4.3. Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry of Compounds
3.2. Antitubercular Activity
3.2.1. Resazurin Microplate Assay
3.2.2. Determining Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
3.3. Safety Studies
3.4. Computational Studies
3.4.1. Target Identification
3.4.2. ADME Analysis
3.4.3. Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shruthi, T.; Eswaran, S.; Shivarudraiah, P.; Narayanan, S.; Subramanian, S. Synthesis, antituberculosis studies and biological evaluation of new quinoline derivatives carrying 1, 2, 4-oxadiazole moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambre, P.K.; Pissurlenkar, R.R.S.; Wavhale, R.D.; Shaikh, M.S.; Khedkar, V.M.; Wan, B.; Franzblau, S.G.; Coutinho, E.C. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 4-(substituted)phenyl-2-thioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-chromino[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-one and 4-(substituted)phenyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-chromino[4,3-d]pyrimidine-2,5-dione analogs as antitubercular agents. Med. Chem. Res. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, J.A.; Sotgiu, G.; Zumla, A.; Migliori, G.B. Best drug treatment for multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinal, M.A. The global situation of MDR-TB. Tuberculosis 2003, 83, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alveera, S.; Venugopala, K.N.; Khedr, M.A.; Pillay, M.; Nwaeze, K.U.; Coovadia, Y.; Shode, F.; Odhav, B. Antimycobacterial, docking and molecular dynamic studies of pentacyclic triterpenes from Buddleja saligna leaves. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Albericio, F.; Coovadia, Y.M.; Kruger, H.G.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Pillay, M.; Govender, T. Total synthesis of a depsidomycin analogue by convergent solid-phase peptide synthesis and macrolactonization strategy for antitubercular activity. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Nayak, S.K.; Pillay, M.; Prasanna, R.; Coovadia, Y.M.; Odhav, B. Synthesis and antitubercular activity of 2-(substituted phenyl/benzyl-amino)-6-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-(methoxycarbonyl)-4-methyl-3,6-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium chlorides. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Dharma Rao, G.B.; Bhandary, S.; Pillay, M.; Chopra, D.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; Alwassil, O.I.; Harsha, S.; Mlisana, K. Design, synthesis, and characterization of (1-(4-aryl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl, substituted phenyl-6-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-5-carboxylates against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 2681–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Pillay, M.; Bhandary, S.; Kandeel, M.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Morsy, M.A.; Chopra, D.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; et al. Synthesis and structural elucidation of novel benzothiazole derivatives as anti-tubercular agents: In-silico screening for possible target identification. Med. Chem. 2019, 15, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Pillay, M.; Abdallah, H.H.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Bhandary, S.; Chopra, D.; Attimarad, M.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Nair, A.B. Computational, crystallographic studies, cytotoxicity and anti-tubercular activity of substituted 7-methoxy-indolizine analogues. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Tratrat, C.; Pillay, M.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Bhandary, S.; Chopra, D.; Morsy, M.A.; Haroun, M.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; et al. Anti-tubercular activity of substituted 7-methyl and 7-formylindolizines and in silico study for prospective molecular target identification. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khedr, M.A.; Pillay, M.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Chopra, D.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; Alwassil, O.I.; Mlisana, K.; Odhav, B.; Venugopala, K.N. Molecular modeling studies and anti-TB activity of trisubstituted indolizine analogues; molecular docking and dynamic inputs. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 2163–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Tratrat, C.; Pillay, M.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Al-Attraqchi, O.H.A.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; Alwassil, O.I.; Nair, A.B.; Sreeharsha, N. In silico design and synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidinones and tetrahydropyrimidinethiones as potential thymidylate kinase inhibitors exerting anti-TB activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.-M.; Hu, H.-W.; Xu, J.-H. Regioselective synthesis of 3-acylindolizines and benzo- analogues via 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of N-ylides with maleic anhydride. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandeep, C.; Venugopala, K.N.; Mohammed, A.K.; Mahesh, A.; Basavaraj, P.; Rashmi, S.K.; Rashmi, V.; Odhav, B. Review on chemistry of natural and synthetic indolizines with their chemical and pharmacological properties. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 8, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Uppar, V.; Mudnakudu-Nagaraju, K.K.; Basarikattia, A.I.; Chougala, M.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Mohan, M.K.; Banuprakashe, G.; Venugopala, K.N.; Ningegowda, R.; Padmashali, B. Microwave induced synthesis, and pharmacological properties of novel 1- benzoyl-4-bromopyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline-3-carboxylate analogues. Chem. Data Collect. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, R.D.; Pavey, D.E.; Benslay, D.N. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of some 2,2-dimethyl-1,2-dihydroquinolines. J. Med. Chem. 1973, 16, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, D.; Blouin, M.; Brideau, C.; Chan, C.-C.; Desmarais, S.; Ethier, D.; Falgueyret, J.-P.; Friesen, R.W.; Girard, M.; Girard, Y.; et al. Quinolines as potent 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors: Synthesis and biological profile of L-746,530. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppar, V.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Venugopala, K.N.; Deb, P.K.; Kar, S.; Alwassil, O.I.; Gleiser, R.M.; Garcia, D.; Odhav, B.; Mohan, M.K.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline derivatives for their larvicidal activity against Anopheles arabiensis. Struct. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, M.; Rizzi, G.; Bacchi, A.; Carcelli, M.; Rogolino, D.; Pala, N.; Sanchez, T.W.; Taheri, L.; Dayam, R.; Neamati, N. Design and synthesis of novel dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acids as HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2925–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Carreiras, M.C.; Leon, R.; de los Rios, C.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; Iriepa, I.; Moraleda, I.; Galvez, E.; Garcia, M.; et al. Synthesis and biological assessment of diversely substituted furo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-amine and pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinolin-4-amine derivatives, as novel tacrine analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 6119–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, E.; Laessig, K. FDA Approval of Bedaquiline—The benefit–risk balance for drug-resistant Tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Feng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, N.; Kan, Y. Copper acetate monohydrate: A cheap but efficient oxidant for synthesizing multi-substituted indolizines from pyridinium ylides and electron deficient alkenes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8637–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An open-source program for chemistry aware data visualization and analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, P.K.; Mailavaram, R.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Kaki, V.R.; Kaur, R.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.-N.; Akkinepally, R.R. Synthesis, adenosine receptor binding and molecular modelling studies of novel thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, P.K.; Ahmad, J.; Dina, E.-R.; Tan, Y.H.; Nasr, E.M.; Pichika, M.R. Molecular docking studies and comparative binding mode analysis of FDA approved HIV protease inhibitors. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 6227–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; El-Rabie, D.; Ahmad, J.; Nalaiya, J.A.P.; Siong, L.C.; Kulasekar, A.L.K.; Pichika, M.R. In silico binding mode analysis (molecular docking studies), and ADME prediction of some novel inhibitors of aurora kinase a in clinical trials. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 6221–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Morcillo, N.; Lemus, D.; Montoro, E.; Telles, M.A.; Simboli, N.; Pontino, M.; Porras, T.; Leon, C.; Velasco, M.; et al. Multicenter study of MTT and resazurin assays for testing susceptibility to first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2005, 9, 901–906. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikuni, O.; Mayumi, T.; Kenichi, S. Inhibitory activity of quinolones against DNA gyrase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 47, 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook, G.; Reggiards, Z.; Tigertt, W.D. Automable radiometric detection of growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in selective media. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1977, 115, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Mossman, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinger, J.M.; Schuster, D.; Danzl, B.; Schwaiger, S.; Markt, P.; Schmidtke, M.; Gertsch, J.; Raduner, S.; Wolber, G.; Langer, T. In silico target fishing for rationalized ligand discovery exemplified on constituents of Ruta graveolens. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, J.L.; Bender, A.; Davies, J.W. In silico target fishing: Predicting biological targets from chemical structure. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2006, 3, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Luo, C.; Luo, X.; Zheng, M.; Chen, K.; Jiang, H. In Silico target fishing: Addressing a “Big Data” problem by ligand-based similarity rankings with data fusion. J. Cheminformatics 2014, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Korff, M.; Freyss, J.; Sander, T. Flexophore, a new versatile 3D pharmacophore descriptor that considers molecular flexibility. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2008, 48, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.K.; Al-Attraqchi, O.; Al-Qattan, M.N.; Raghu Prasad, M.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 19—Applications of Computers in Pharmaceutical Product Formulation. In Dosage Form Design Parameters; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollastri, M.P. Overview on the Rule of Five. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2010, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.K. The contribution of P-glycoprotein to pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 39, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M. Importance of P-glycoprotein for drug disposition in humans. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 33, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H. CYP induction-mediated drug interactions: In vitro assessment and clinical implications. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1089–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.T.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, A.; Parai, M.K.; Shetty, N.; Wallis, D.; Woolhiser, L.; Hastings, C.; Dutta, N.K.; Galaviz, S.; Dhakal, R.C.; Shrestha, R.; et al. Development of a Novel Lead that Targets M. tuberculosis Polyketide Synthase 13. Cell 2017, 170, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiebel, J.; Krimmer, S.G.; Rower, K.; Knorlein, A.; Wang, X.; Park, A.Y.; Stieler, M.; Ehrmann, F.R.; Fu, K.; Radeva, N.; et al. High-Throughput Crystallography: Reliable and Efficient Identification of Fragment Hits. Structure 2016, 24, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

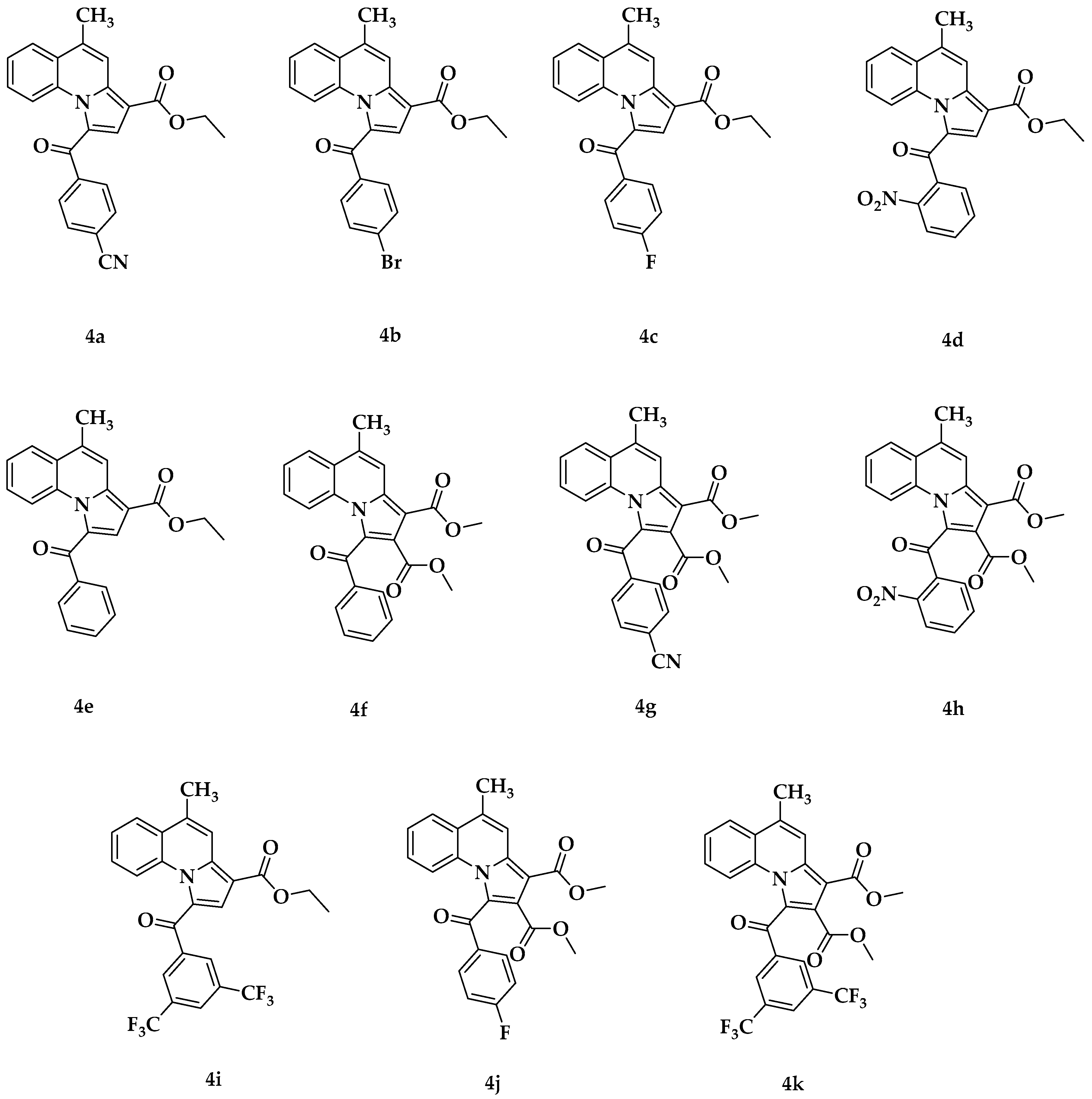

| Compound Code | MIC (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| H37Rv * | MDR-MTB ** | |
| 4a | 64 | NA |
| 4b | 32 | NA |
| 4c | 32 | NA |
| 4d | 8 | NA |
| 4e | 20 | NA |
| 4f | 16 | 64 |
| 4g | 32 | NA |
| 4h | 128 | NA |
| 4i | 128 | NA |
| 4j | 8 | 16 |
| 4k | 32 | 32 |
| Compound Code | cLogP1 | Rotatable Bonds | GI Absorption | BBB Permeable | P-gp Binding | CYP Inhibition | Lipinski Violations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A2 | 2D6 | 34A | |||||||
| 4a | 4.320 | 5 | High | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | 0 |
| 4b | 5.209 | 5 | High | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 1 |
| 4c | 4.585 | 5 | High | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 0 |
| 4d | 3.563 | 6 | High | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | 0 |
| 4e | 4.484 | 5 | High | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | 0 |
| 4f | 3.991 | 6 | High | Yes | No | No | No | No | 0 |
| 4g | 3.827 | 6 | High | No | No | No | No | Yes | 0 |
| 4h | 3.069 | 7 | High | No | No | No | No | Yes | 0 |
| 4i | 6.181 | 7 | Low | No | Yes | No | No | No | 1 |
| 4j | 4.092 | 6 | High | No | No | No | No | No | 0 |
| 4k | 5.688 | 8 | Low | No | No | Yes | No | No | 2 |
| Comp. Code | Experimental MIC (µg/mL) | Docking Free Energy | Experimental MIC (µg/mL) | Docking Free Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H37Rv * | Pks13 | MDR-MTB | DprE1 | |
| 4a | 64 | −10.91 (10.05 nM) | NA | −7.89 (1.63 µM) |
| 4b | 32 | −9.73 (73.15 nM) | NA | −8.10 (1.15 µM) |
| 4c | 32 | −11.18 (6.35 nM) | NA | −7.88 (1.67 µM) |
| 4d | 8 | −11.40 (4.38 nM) | NA | −9.38 (133.64 nM) |
| 4e | 20 | −9.44 (119.83 nM) | NA | −7.76 (2.05 µM) |
| 4f | 16 | −9.16 (191.47 nM) | 64 | −8.33 (782.97 nM) |
| 4g | 32 | −10.40(23.84 nM) | NA | −7.33 (4.22 µM) |
| 4h | 128 | −10.43 (22.68 nM) | NA | −7.30 (4.48 µM) |
| 4i | 128 | −9.39 (131.39 nM) | NA | −7.13 (5.96 µM) |
| 4j | 8 | −9.54 (101.68 nM) | 16 | −8.31 (810.31 nM) |
| 4k | 32 | −9.10 (212.01 nM) | 32 | −7.19 (5.40 µM) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venugopala, K.N.; Uppar, V.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Abdallah, H.H.; Pillay, M.; Deb, P.K.; Morsy, M.A.; Aldhubiab, B.E.; Attimarad, M.; Nair, A.B.; et al. Cytotoxicity and Antimycobacterial Properties of Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline Derivatives: Molecular Target Identification and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050233
Venugopala KN, Uppar V, Chandrashekharappa S, Abdallah HH, Pillay M, Deb PK, Morsy MA, Aldhubiab BE, Attimarad M, Nair AB, et al. Cytotoxicity and Antimycobacterial Properties of Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline Derivatives: Molecular Target Identification and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(5):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050233
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenugopala, Katharigatta N., Vijayakumar Uppar, Sandeep Chandrashekharappa, Hassan H. Abdallah, Melendhran Pillay, Pran Kishore Deb, Mohamed A. Morsy, Bandar E. Aldhubiab, Mahesh Attimarad, Anroop B. Nair, and et al. 2020. "Cytotoxicity and Antimycobacterial Properties of Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline Derivatives: Molecular Target Identification and Molecular Docking Studies" Antibiotics 9, no. 5: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050233
APA StyleVenugopala, K. N., Uppar, V., Chandrashekharappa, S., Abdallah, H. H., Pillay, M., Deb, P. K., Morsy, M. A., Aldhubiab, B. E., Attimarad, M., Nair, A. B., Sreeharsha, N., Tratrat, C., Yousef Jaber, A., Venugopala, R., Mailavaram, R. P., Al-Jaidi, B. A., Kandeel, M., Haroun, M., & Padmashali, B. (2020). Cytotoxicity and Antimycobacterial Properties of Pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinoline Derivatives: Molecular Target Identification and Molecular Docking Studies. Antibiotics, 9(5), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050233












