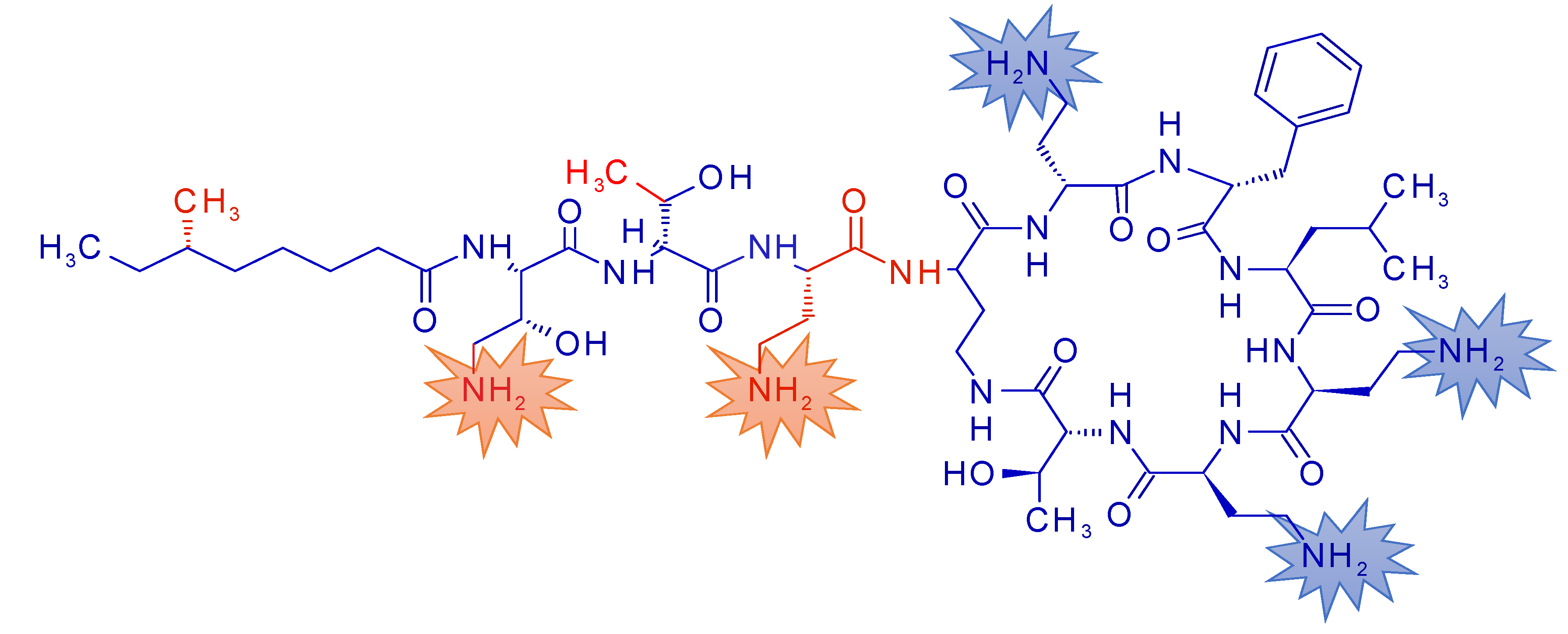
Excretion of the Polymyxin Derivative NAB739 in Murine Urine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Animals
2.3. Plasma and Urine Sample Analysis
3. Results
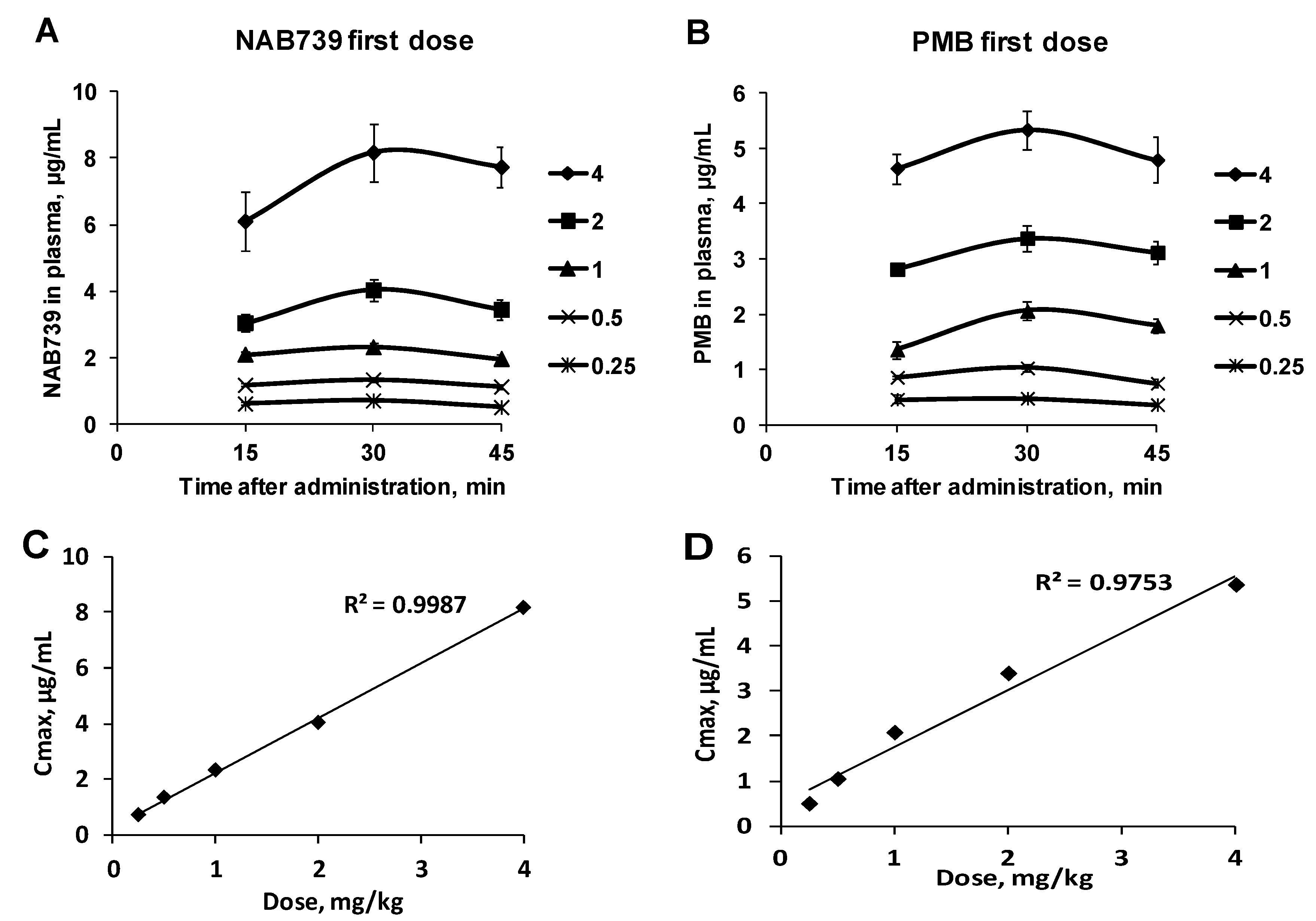
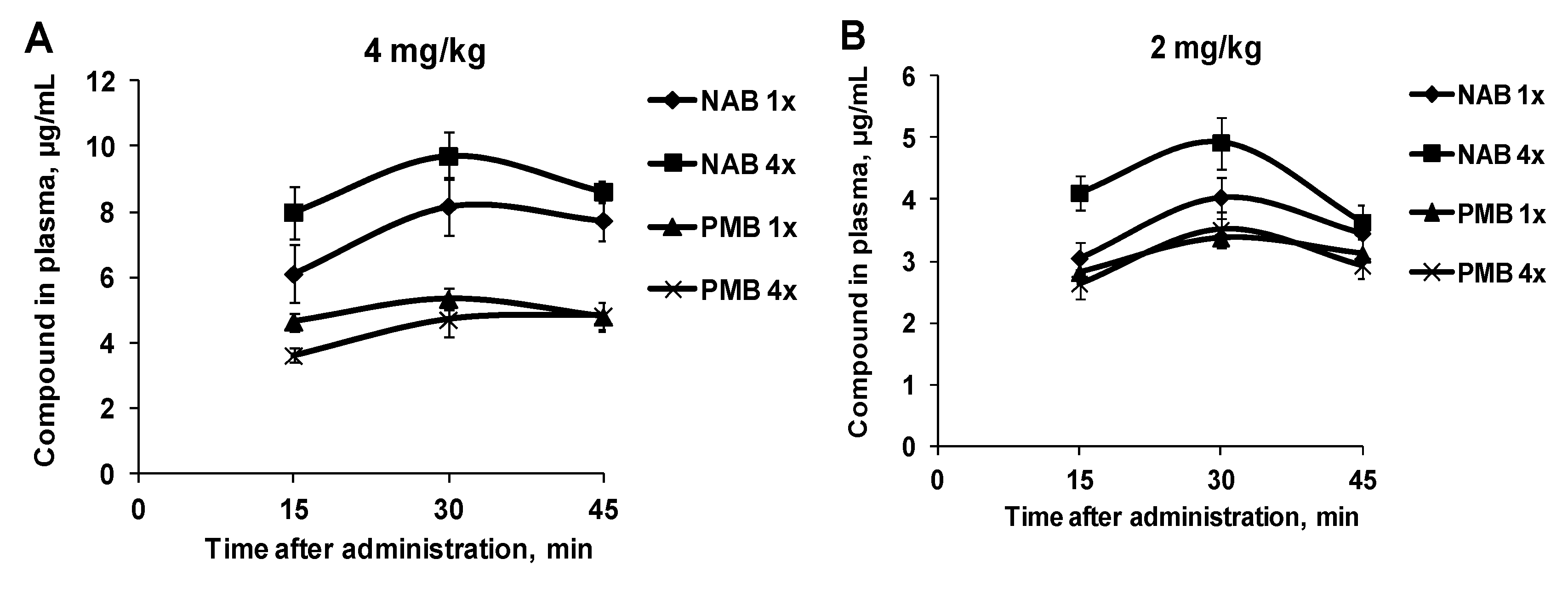
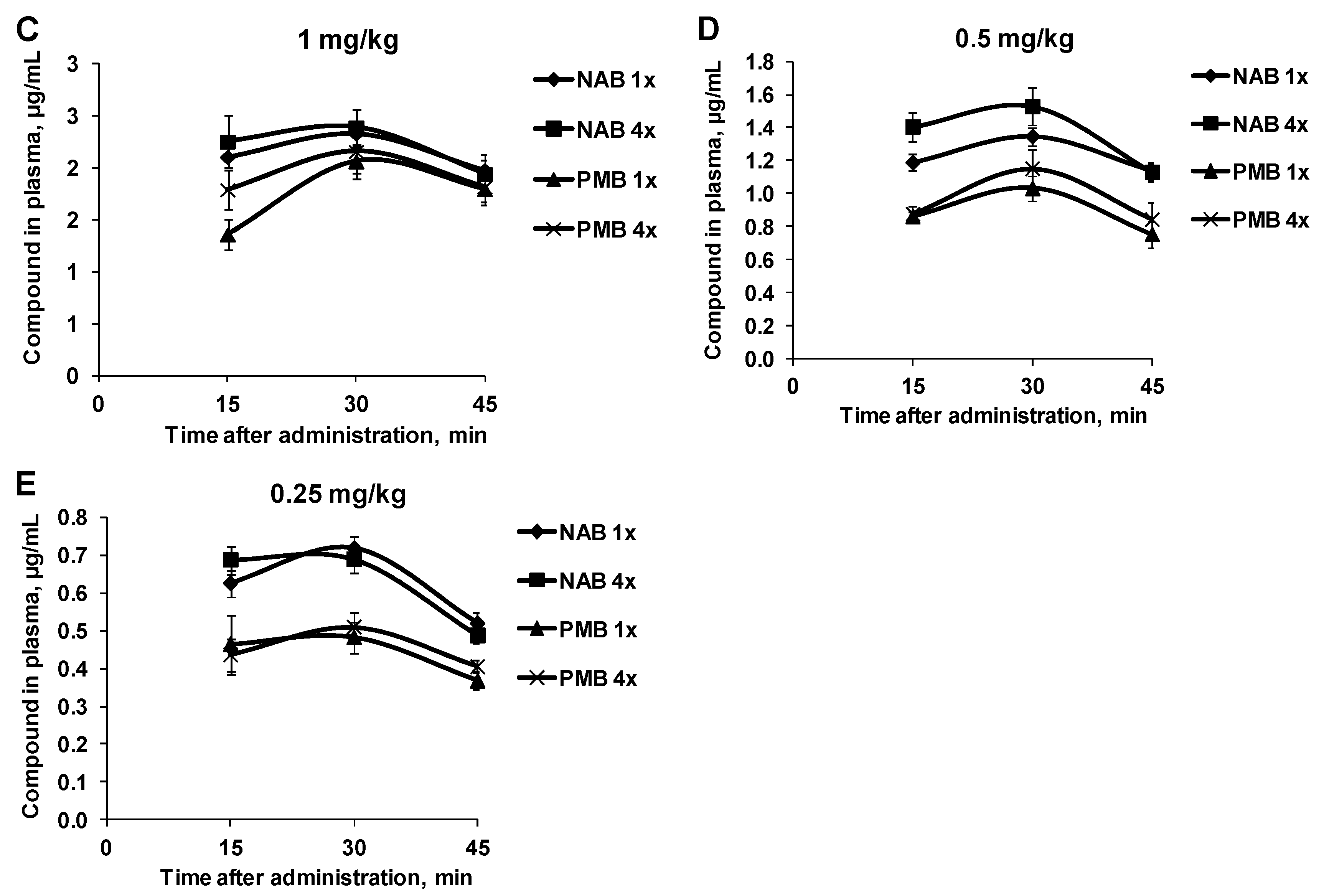
3.1. Pharmacokinetic Profiles of NAB739 and PMB
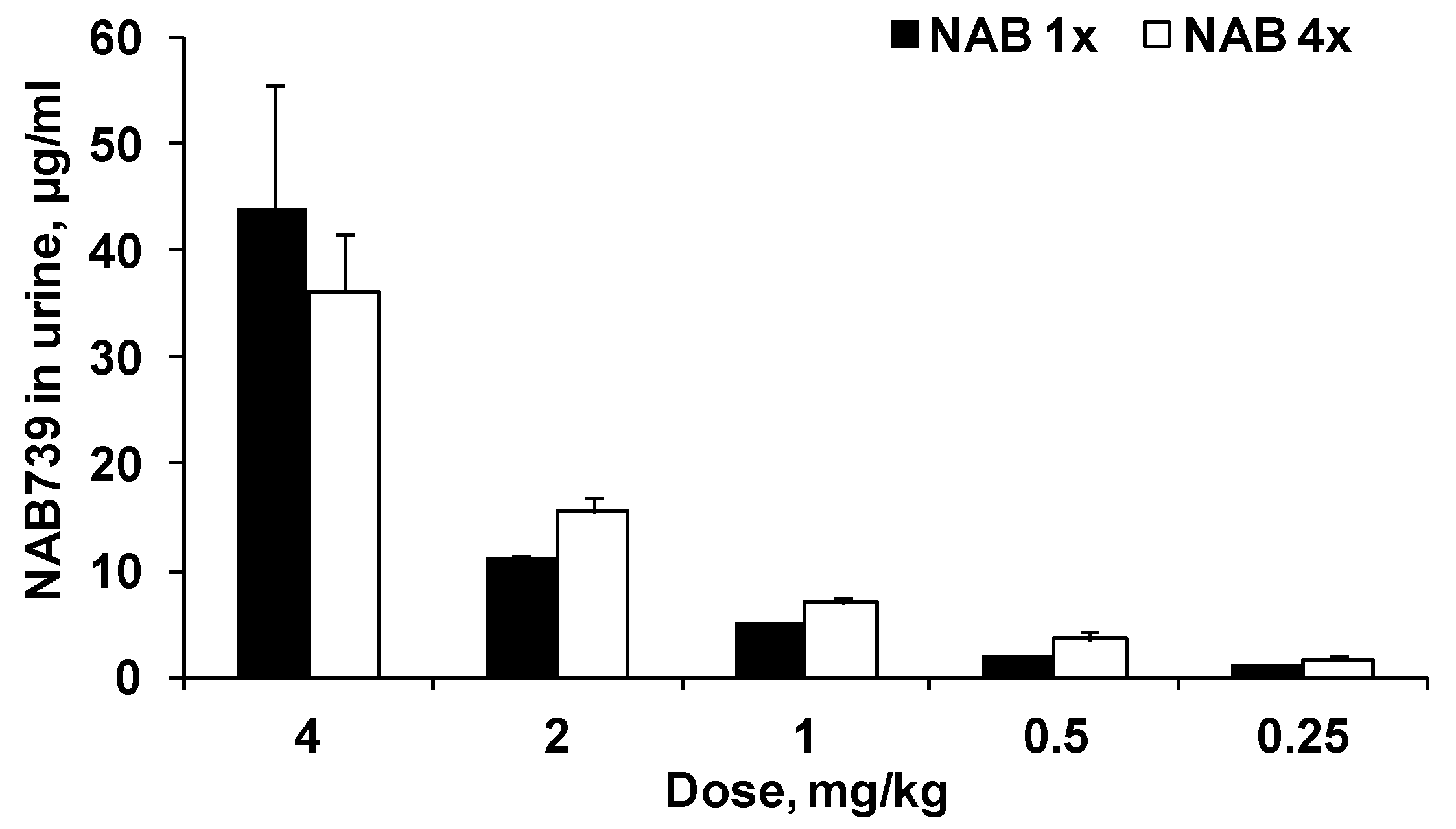
3.2. Urinary Elimination of NAB739 and PMB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fusco, A.; Coretti, L.; Savio, V.; Buommino, E.; Lembo, F.; Donnarumma, G. Biofilm formation and immunomodulatory activity of Proteus mirabilis clinically isolated strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Savio, V.; De Filippis, A.; Tufano, A.; Donnarumma, G. Induction of different apoptosis pathways by two Proteus mirabilis clinical isolates strains in prostatic epithelial cells. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, B.T.; Pogue, J.M.; Zavascki, A.P.; Paul, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Forrest, A.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Viscoli, C.; Giamarellou, H.; Karaiskos, I.; et al. International consensus guidelines for the optimal use of the polymyxins: Endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (ACCP), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), International Society for Anti-Infective Pharmacology (ISAP), Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), And Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP). Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 10–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Velkov, T.; Roberts, K.D. Discovery of novel polymyxin-like antibiotics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1145, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, W.; Lin, J.; Fang, S.; Qiu, J. Antibacterial mechanisms of polymyxin and bacterial resistance. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 679109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaara, M. Novel derivatives of polymyxins. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaara, M. New polymyxin derivatives that display improved efficacy in animal infection models as compared to polymyxin b and colistin. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavascki, A.P.; Goldani, L.Z.; Cao, G.; Superti, S.V.; Lutz, L.; Barth, A.L.; Ramos, F.; Boniatti, M.M.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous polymyxin b in critically ill patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2008, 47, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaara, M.; Vaara, T.; Vingsbo Lundberg, C. Polymyxin derivatives nab739 and nab815 are more effective than polymyxin b in murine Escherichia coli pyelonephritis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Group of National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (NC3Rs) Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The arrive guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.C.; Drummond, G.B.; McLachlan, E.M.; Kilkenny, C.; Wainwright, C.L. Guidelines for reporting experiments involving animals: The arrive guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaara, M.; Fox, J.; Loidl, G.; Siikanen, O.; Apajalahti, J.; Hansen, F.; Frimodt-Moller, N.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M.; Vaara, T. Novel polymyxin derivatives carrying only three positive charges are effective antibacterial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P.; Tulkens, P.M.; Denamur, S.; Vaara, T.; Vaara, M. Novel polymyxin derivatives are less cytotoxic than polymyxin b to renal proximal tubular cells. Peptides 2012, 35, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.M.; Dorfman, K. Hospital-Treated Gram-Negative Infections. Pharmacol Inf Dis, Decision Resources Group. Available online: https://decisionresourcesgroup.com/report/246083-biopharma-hospital-treated-gram-negative-infections-2015/ (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. Available online: https://sentry-mvp.jmilabs.com (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Tyrrell, J.M.; Aboklaish, A.F.; Walsh, T.R.; Vaara, T.; Vaara, M. The polymyxin derivative nab739 is synergistic with several antibiotics against polymyxin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii. Peptides 2019, 112, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
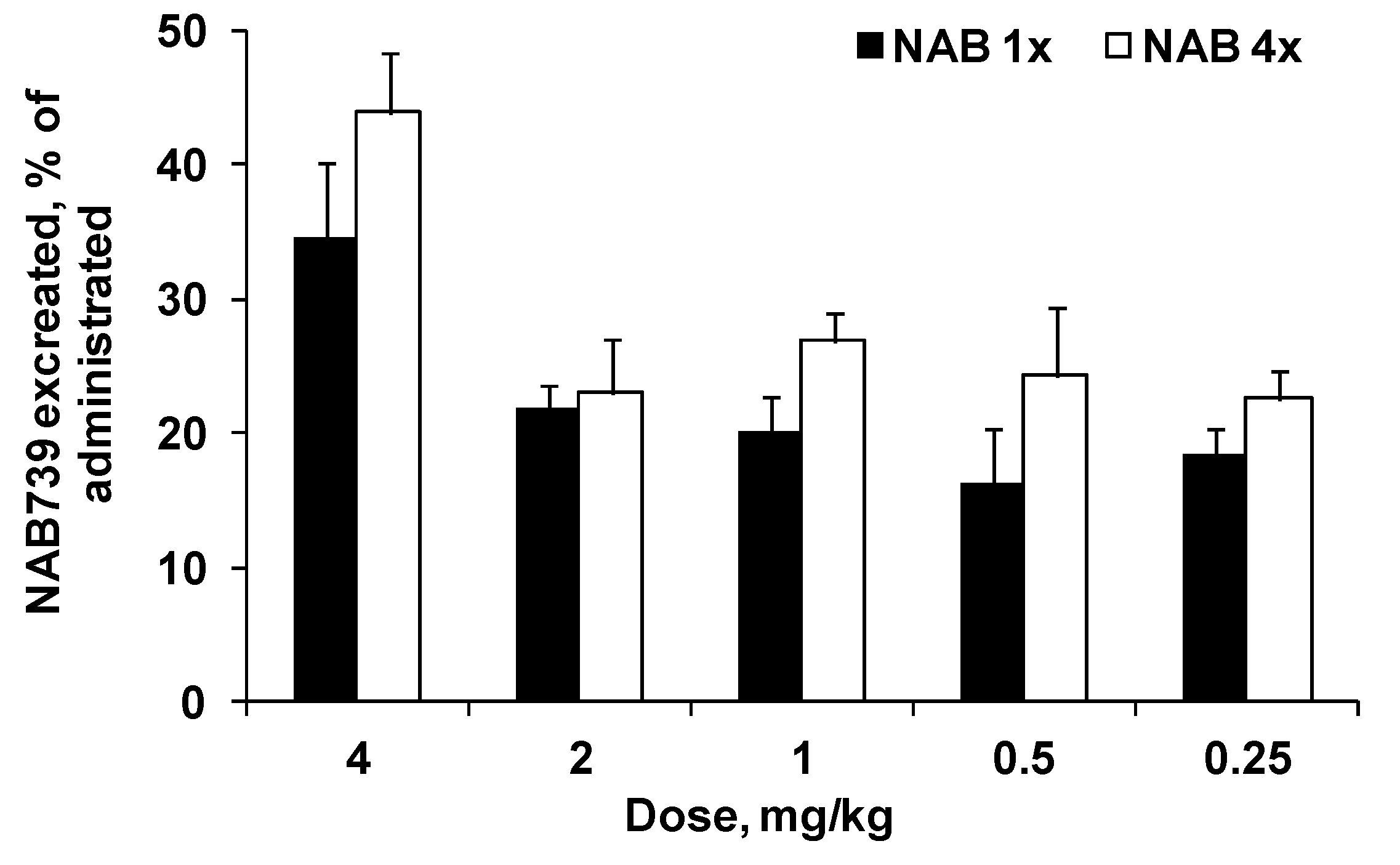
| Compound | MRM Transition | Cone Voltage, V | Collision Energy, eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAB739 | 359.66 > 425.19 | 30 | 8 |
| Exact mass 1076 Da | |||
| PMB *: | 301.86 > 101.02 | 30 | 12 |
| Polymyxin B1 | 402.12 > 101.02 | 30 | 15 |
| Exact mass 1202 Da | 602.50 > 101.02 | 30 | 30 |
| 298.36 > 101.02 | 30 | 10 | |
| Polymyxin B2 | 301.44 > 101.02 | 30 | 15 |
| Exact mass 1188 Da | 595.42 > 101.02 | 30 | 30 |
| Validation Parameter | Performance Criteria | Obtained Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAB739 | PMB | ||
| Plasma | |||
| Selectivity | Response for the analyte in matrix blank ≤ 20% of LOQ | 2.3% | 10% |
| Linearity | R2 ≥ 0.985 | R2 0.9998 | R2 0.9998 |
| 0.008–17.2 μg/mL | 0.007–15.7 μg/mL | ||
| Limit of quantification | Set at concentration level where S/N ≥ 10 | 0.008 μg/mL | 0.007 μg/mL |
| (S/N ≥ 40) | (S/N ≥ 10)) | ||
| Urine | |||
| Selectivity | Response for analyte in matrix blank ≤ 20% of LOQ | 3.8% | 10% |
| Linearity | R2 ≥ 0.985 | R2 0.9996 | R2 0.998 |
| 0.07–17.2 μg/mL | 0.58–15.7 μg/mL | ||
| Limit of quantification | Set at concentration level where S/N ≥ 10 | 0.07 μg/mL | 0.58 μg/mL |
| (S/N ≥ 20) | (S/N ≥ 10)) | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaara, M.; Vaara, T.; Kuka, J.; Sevostjanovs, E.; Grinberga, S.; Dambrova, M.; Liepinsh, E. Excretion of the Polymyxin Derivative NAB739 in Murine Urine. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040143
Vaara M, Vaara T, Kuka J, Sevostjanovs E, Grinberga S, Dambrova M, Liepinsh E. Excretion of the Polymyxin Derivative NAB739 in Murine Urine. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(4):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040143
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaara, Martti, Timo Vaara, Janis Kuka, Eduards Sevostjanovs, Solveiga Grinberga, Maija Dambrova, and Edgars Liepinsh. 2020. "Excretion of the Polymyxin Derivative NAB739 in Murine Urine" Antibiotics 9, no. 4: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040143
APA StyleVaara, M., Vaara, T., Kuka, J., Sevostjanovs, E., Grinberga, S., Dambrova, M., & Liepinsh, E. (2020). Excretion of the Polymyxin Derivative NAB739 in Murine Urine. Antibiotics, 9(4), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040143






