Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Wild Animals in Europe: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Staphylococcus aureus
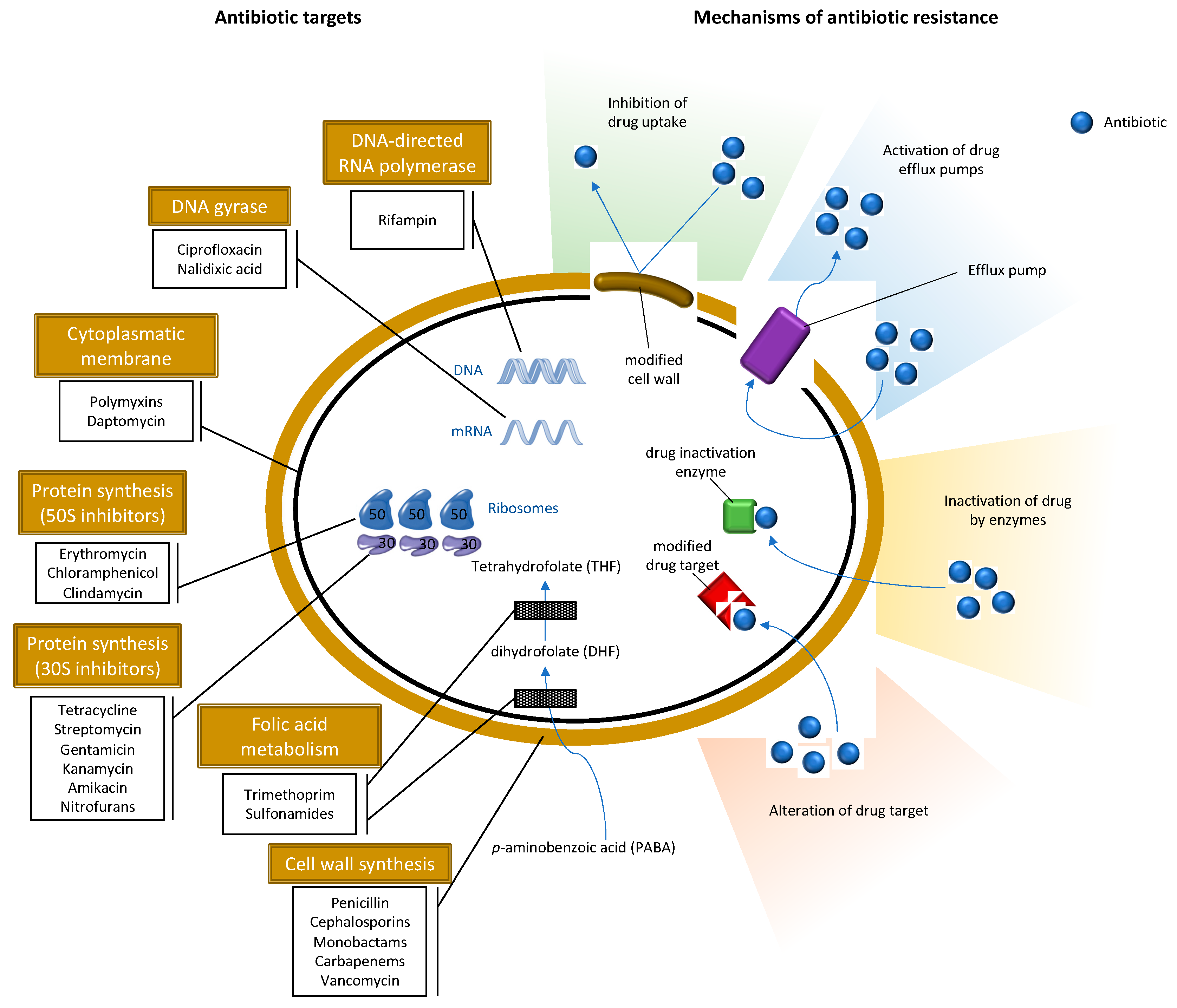
2.1. Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus
2.2. S. aureus Characterization by Molecular Typing
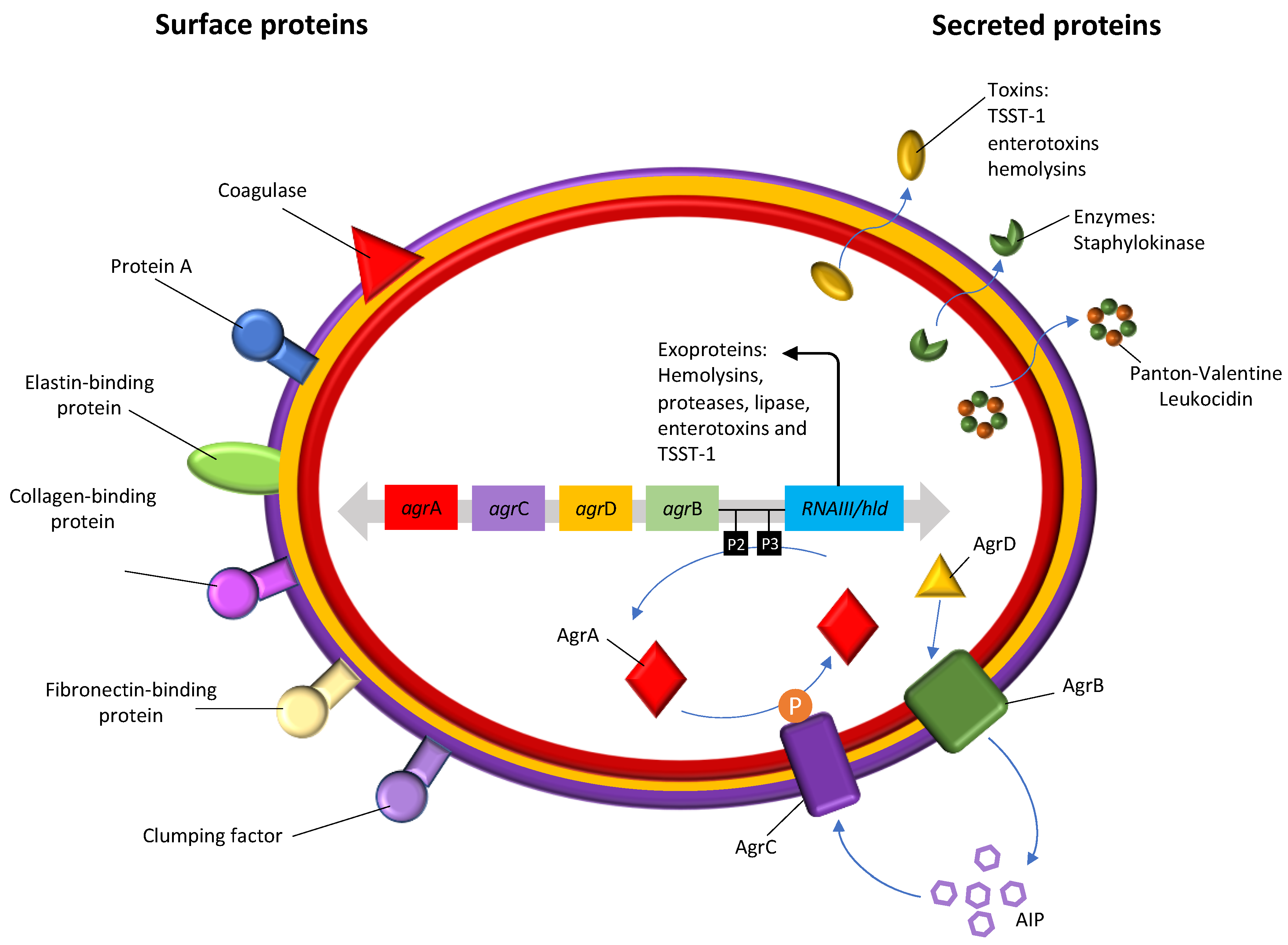
2.2.1. Accessory Gene Regulator (agr) Typing
2.2.2. spa Typing
2.2.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing
2.2.4. SCCmec Typing
3. Antibiotic Resistance in the Environment
S. aureus and MRSA in Wild Animals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ben-Haim, M.S.; Kanfi, Y.; Mitchell, S.J.; Maoz, N.; Vaughan, K.L.; Amariglio, N.; Lerrer, B.; de Cabo, R.; Rechavi, G.; Cohen, H.Y. Breaking the Ceiling of Human Maximal Life span. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2017, 73, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, S.B.; Hussain, M.A.; Nye, R.; Mehta, V.; Mamun, K.T.; Hossain, N. A Review on Antibiotic Resistance: Alarm Bells Are Ringing. Cureus 2017, 9, e1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Rigol, S. A brief history of antibiotics and select advances in their synthesis. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA, Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, V.; Almeida, F.; Carvalho, J.A.; Castro, A.P.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus EMRSA-15 clone as the predominant cause of diabetic foot ulcer infections in Portugal. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 39, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial resistance: Risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.M.; Wertheim, H.F.L.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bunnik, B.A.D.; Woolhouse, M.E.J. Modelling the impact of curtailing antibiotic usage in food animals on antibiotic resistance in humans. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 161067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, R.; Lucas, J.; Dahlberg, J.; Ramin, M.; Agenäs, S.; Bayat, A.-R.; Tapio, I.; Hammer, T.; Roslin, T. Compound- and context-dependent effects of antibiotics on greenhouse gas emissions from livestock. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 182049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igrejas, G.; Correia, S.; Silva, V.; Hébraud, M.; Caniça, M.; Torres, C.; Gomes, C.; Nogueira, F.; Poeta, P. Planning a One Health Case Study to Evaluate Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Its Economic Burden in Portugal. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinsstag, J.; Schelling, E.; Waltner-Toews, D.; Tanner, M. From “one medicine” to “one health” and systemic approaches to health and well-being. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 101, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 42, fux053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging Strategies to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, G.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Savini, V. Chapter 1-Staphylococcal Taxonomy. In Pet-To-Man Travelling Staphylococci; Savini, V., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–10. ISBN 978-0-12-813547-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Suo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jin, F.; Zhao, H.; Shi, C. Genetic and Virulent Difference Between Pigmented and Non-pigmented Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Tsubakishita, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakusabe, A.; Ohtsuka, M.; Hirotaki, S.; Kawakami, T.; Fukata, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Multiplex-PCR Method for Species Identification of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Miller, L.S. Host–pathogen interactions between the skin and Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, W.; Strommenger, B.; Stanek, C.; Cuny, C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in Humans and Animals, Central Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomer, L.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus Bloodstream Infections. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hal, S.J.; Jensen, S.O.; Vaska, V.L.; Espedido, B.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Gosbell, I.B. Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, E.D.; Sullivan, S.S.; Macesic, N.; Mehta, M.; Miko, B.A.; Nematollahi, S.; Shi, Q.; Lowy, F.D.; Uhlemann, A.-C. Reduced Mortality of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia in a Retrospective Cohort Study of 2139 Patients: 2007–2015. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldmann, O.; Medina, E. Staphylococcus aureus strategies to evade the host acquired immune response. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobel, M.; Pförtner, H.; Tuchscherr, L.; Völker, U.; Schmidt, F.; Kramko, N.; Schnittler, H.-J.; Fraunholz, M.J.; Löffler, B.; Peters, G.; et al. Post-invasion events after infection with Staphylococcus aureus are strongly dependent on both the host cell type and the infecting S. aureus strain. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollin, G.; Tan, X.; Tros, F.; Dupuis, M.; Nassif, X.; Charbit, A.; Coureuil, M. Intracellular Survival of Staphylococcus aureus in Endothelial Cells: A Matter of Growth or Persistence. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardiau, M.; Caplin, J.; Detilleux, J.; Graber, H.; Moroni, P.; Taminiau, B.; Mainil, J.G. Existence of two groups of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from bovine mastitis based on biofilm formation, intracellular survival, capsular profile and agr-typing. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 185, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehar, S.M.; Pillow, T.; Xu, M.; Staben, L.; Kajihara, K.K.; Vandlen, R.; DePalatis, L.; Raab, H.; Hazenbos, W.L.; Hiroshi Morisaki, J.; et al. Novel antibody–antibiotic conjugate eliminates intracellular S. aureus. Nature 2015, 527, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.L.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Coagulase-negative staphylococci as reservoirs of genes facilitating MRSA infection: Staphylococcal commensal species such as Staphylococcus epidermidis are being recognized as important sources of genes promoting MRSA colonization and virulence. Bioessays 2013, 35, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atshan, S.S.; Shamsudin, M.N.; Karunanidhi, A.; van Belkum, A.; Lung, L.T.T.; Sekawi, Z.; Nathan, J.J.; Ling, K.H.; Seng, J.S.C.; Ali, A.M.; et al. Quantitative PCR analysis of genes expressed during biofilm development of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 18, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Harper, L.; Shopsin, B.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis in diverse host environments. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darboe, S.; Dobreniecki, S.; Jarju, S.; Jallow, M.; Mohammed, N.I.; Wathuo, M.; Ceesay, B.; Tweed, S.; Basu Roy, R.; Okomo, U.; et al. Prevalence of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) and Antimicrobial Resistance in Community-Acquired Clinical Staphylococcus aureus in an Urban Gambian Hospital: A 11-Year Period Retrospective Pilot Study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenul, C.; Horswill, A.R. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuffs, S.W.; Herfst, C.A.; Baroja, M.L.; Podskalniy, V.A.; DeJong, E.N.; Coleman, C.E.M.; McCormick, J.K. Regulation of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 by the accessory gene regulator in Staphylococcus aureus is mediated by the repressor of toxins. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 112, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.; Borges, A.; Simões, M. Staphylococcus aureus Toxins and Their Molecular Activity in Infectious Diseases. Toxins 2018, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.; Yong, D.; Kim, J.M.; Song, Y.G. Accessory gene regulator group polymorphisms in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An association with clinical significance. Yonsei Med. J. 2007, 48, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlaes, D.M.; Projan, S.J. Antimicrobial Resistance versus the Discovery and Development of New Antimicrobials. In BT—Antimicrobial Drug Resistance: Mechanisms of Drug Resistance; Mayers, D.L., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 43–50. ISBN 978-1-59745-180-2. [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton, P.D.; Taylor, P.W. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: Mechanisms and modulation. Sci. Prog. 2002, 85, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishovitz, J.; Hermoso, J.A.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S. Penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubakishita, S.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Sasaki, T.; Hiramatsu, K. Origin and molecular evolution of the determinant of methicillin resistance in staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Hiramatsu, K.; Tomasz, A.; de Lencastre, H.; Perreten, V.; Holden, M.T.G.; Coleman, D.C.; Goering, R.; Giffard, P.M.; Skov, R.L.; et al. Guidelines for reporting novel mecA gene homologues. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4997–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadyen, A.C.; Fisher, E.A.; Costa, B.; Cullen, C.; Paterson, G.K. Genome analysis of methicillin resistance in Macrococcus caseolyticus from dairy cattle in England and Wales. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendener, S.; Cotting, K.; Perreten, V. Novel methicillin resistance gene mecD in clinical Macrococcus caseolyticus strains from bovine and canine sources. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; van Alen, S.; Idelevich, E.A.; Schleimer, N.; Seggewiß, J.; Mellmann, A.; Kaspar, U.; Peters, G. Plasmid-Encoded Transferable mecB-Mediated Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, E.M.; Paterson, G.K.; Holden, M.T.G.; Morgan, F.J.E.; Larsen, A.R.; Petersen, A.; Leroy, S.; De Vliegher, S.; Perreten, V.; Fox, L.K.; et al. A Staphylococcus xylosus isolate with a new mecC allotype. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małyszko, I.; Schwarz, S.; Hauschild, T. Detection of a new mecC allotype, mecC2, in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus saprophyticus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2003–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFadyen, A.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Drigo, I.; Parkhill, J.; Holmes, M.A.; Paterson, G.K. A mecC allotype, mecC3, in the CoNS Staphylococcus caeli, encoded within a variant SCCmec C. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, G.K.; Larsen, A.R.; Robb, A.; Edwards, G.E.; Pennycott, T.W.; Foster, G.; Mot, D.; Hermans, K.; Baert, K.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. The newly described mecA homologue, mecALGA251, is present in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a diverse range of host species. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Posautz, A.; Stalder, G.L.; Hoffmann, D.; Rosengarten, R.; Walzer, C. Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. carrying the mecC gene, isolated from wildlife. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2222–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Feßler, A.T.; Loncaric, I.; Wu, C.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Antimicrobial Resistance among Staphylococci of Animal Origin. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Gómez, P.; Alonso, C.A.; Camacho, M.C.; de la Puente, J.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Ramiro, Y.; Quevedo, M.A.; Blanco, J.M.; Zarazaga, M.; et al. Detection of MRSA of Lineages CC130-mecC and CC398-mecA and Staphylococcus delphini-lnu(A) in Magpies and Cinereous Vultures in Spain. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Alcalá, L.; Simón, C.; Gómez, P.; Mama, O.M.; Rezusta, A.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus clones in wild mammals in Aragon, Spain, with detection of MRSA ST130-mecC in wild rabbits. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrero, M.C.; Valverde, A.; Fernández-Llario, P.; Díez-Guerrier, A.; Mateos, A.; Lavín, S.; Cantón, R.; Fernández-Garayzabal, J.-F.; Domínguez, L. Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecC gene in animals and urban wastewater, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepción Porrero, M.; Harrison, E.M.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F.; Paterson, G.K.; Díez-Guerrier, A.; Holmes, M.A.; Domínguez, L. Detection of mecC-Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in river water: A potential role for water in the environmental dissemination. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdács, M. The Continuing Threat of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Almeida, F.; Silva, A.; Correia, S.; Carvalho, J.A.; Castro, A.P.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Igrejas, G.; et al. First report of linezolid-resistant cfr-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in humans in Portugal. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswihi, S.S.; Udo, E.E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An update on the epidemiology, treatment options and infection control. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2018, 8, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateete, D.P.; Bwanga, F.; Seni, J.; Mayanja, R.; Kigozi, E.; Mujuni, B.; Ashaba, F.K.; Baluku, H.; Najjuka, C.F.; Källander, K.; et al. CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA coexist in community and hospital settings in Uganda. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.N.; Ocampo, A.M.; Vanegas, J.M.; Rodriguez, E.A.; Mediavilla, J.R.; Chen, L.; Muskus, C.E.; Vélez, L.A.; Rojas, C.; Restrepo, A.V.; et al. CC8 MRSA Strains Harboring SCCmec Type IVc are Predominant in Colombian Hospitals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantosti, A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus associated with animals and its relevance to human health. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among animals: Current overview. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevorkijan, B.K.; Petrovič, Ž.; Kocuvan, A.; Rupnik, M. MRSA diversity and the emergence of LA-MRSA in a large teaching hospital in Slovenia. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2019, 66, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petinaki, E.; Spiliopoulou, I. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among companion and food-chain animals: Impact of human contacts. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppitsch, W. Molecular typing of bacteria for epidemiological surveillance and outbreak investigation/Molekulare Typisierung von Bakterien für die epidemiologische Überwachung und Ausbruchsabklärung. Die Bodenkult. J. Land Manag. Food Environ. 2016, 67, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing: Its role in virulence and possibilities for its control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.L.; Novick, R.P.; Kreiswirth, B.; Kornblum, J.; Schlievert, P. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of an accessory gene regulator (agr) in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 4365–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, K.E.; Lee, E.; Benson, S.; Corrigan, R.; Cantera, M.; Shopsin, B.; Novick, R.P. agr function in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Microbiology 2008, 154, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Baldry, M.; Gless, B.H.; Bojer, M.S.; Espinosa-Gongora, C.; Baig, S.J.; Andersen, P.S.; Olsen, C.A.; Ingmer, H. Effect of Co-inhabiting Coagulase Negative Staphylococci on S. aureus agr Quorum Sensing, Host Factor Binding, and Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2212. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Li, S.R.; Jiang, B.; Hu, X.M.; Li, S. Therapeutic Targeting of the Staphylococcus aureus Accessory Gene Regulator (agr) System. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Weniger, T.; Harmsen, D.; Friedrich, A.W.; Witte, W. Assignment of Staphylococcus Isolates to Groups by spa Typing, SmaI Macrorestriction Analysis, and Multilocus Sequence Typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-F.; Xiao, M.; Liang, H.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Chen, G.-Y.; Meng, X.-Y.; Zou, G.-L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.-L.; et al. An improved MLVF method and its comparison with traditional MLVF, spa typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE for the typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallin, M.; Friedrich, A.W.; Struelens, M.J. spa Typing for Epidemiological Surveillance of Staphylococcus aureus. In BT—Molecular Epidemiology of Microorganisms: Methods and Protocols; Caugant, D.A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 189–202. ISBN 978-1-60327-999-4. [Google Scholar]
- Maiden, M.C.; Bygraves, J.A.; Feil, E.; Morelli, G.; Russell, J.E.; Urwin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zurth, K.; Caugant, D.A.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing: A portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3140–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deurenberg, R.H.; Vink, C.; Kalenic, S.; Friedrich, A.W.; Bruggeman, C.A.; Stobberingh, E.E. The molecular evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, H.F.; Deleo, F.R. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, S.; Chung, D.R.; Lindsay, J.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Kearns, A.M.; Westh, H.; MacKenzie, F.M. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Global epidemiology and harmonisation of typing methods. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IWG-SCC. Classification of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec): Guidelines for reporting novel SCCmec elements. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4961–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00020-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Jatzwauk, L.; Müller, E.; Nitschke, H.; Pfohl, K.; Slickers, P.; Reissig, A.; Ruppelt-Lorz, A.; Ehricht, R. Diversity of SCCmec Elements in Staphylococcus aureus as Observed in South-Eastern Germany. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, D.; Xue, H.; Zhao, X. Novel Type XII Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec Harboring a New Cassette Chromosome Recombinase, CcrC2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7597–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.; Johannesen, T.B.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Larsen, J.; Larsen, A.R.; Stegger, M. Novel SCCmec type XIII (9A) identified in an ST152 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 61, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, C.; Wieler, L.; Witte, W. Livestock-Associated MRSA: The Impact on Humans. Antibiotics 2015, 4, 521–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois, P.; Koessler, T.; Huyghe, A.; Harbarth, S.; Bento, M.; Lew, D.; Etienne, J.; Pittet, D.; Schrenzel, J. Rapid Staphylococcus aureus agr type determination by a novel multiplex real-time quantitative PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- O’Hara, F.P.; Suaya, J.A.; Ray, G.T.; Baxter, R.; Brown, M.L.; Mera, R.M.; Close, N.M.; Thomas, E.; Amrine-Madsen, H. spa Typing and Multilocus Sequence Typing Show Comparable Performance in a Macroepidemiologic Study of Staphylococcus aureus in the United States. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, T.C.; MacCannell, D.R. Chapter 9-Molecular Strain Typing and Characterisation of Toxigenic Clostridium difficile. In Current and Emerging Technologies for the Diagnosis of Microbial Infections; Sails, A., Tang, Y.-W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 42, pp. 329–357. ISBN 0580-9517. [Google Scholar]
- Chongtrakool, P.; Ito, T.; Ma, X.X.; Kondo, Y.; Trakulsomboon, S.; Tiensasitorn, C.; Jamklang, M.; Chavalit, T.; Song, J.-H.; Hiramatsu, K. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated in 11 Asian countries: A proposal for a new nomenclature for SCCmec elements. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Rude, T.H.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Pulse Field Gel Electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1373, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Raval, I.H. Chapter 32-Pathogenic Microbial Genetic Diversity with Reference to Health. In Microbial Diversity in the Genomic Era; Das, S., Dash, H.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 559–577. ISBN 978-0-12-814849-5. [Google Scholar]
- Noller, A.C.; McEllistrem, M.C.; Pacheco, A.G.F.; Boxrud, D.J.; Harrison, L.H. Multilocus variable-number tandem repeat analysis distinguishes outbreak and sporadic Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5389–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, T.L.; Barer, M.R. 3-Classification, identification and typing of micro-organisms. In Medical Microbiology, 18th ed.; Greenwood, D., Barer, M., Slack, R., Irving, W., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2012; pp. 24–38. ISBN 978-0-7020-4089-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bumgarner, R. Overview of DNA microarrays: Types, applications, and their future. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2013, 22, Unit-22.1. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelbary, M.M.H.; Basset, P.; Blanc, D.S.; Feil, E.J. 24-The Evolution and Dynamics of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. In Genetics and Evolution of Infectious Disease, 2nd ed.; Tibayrenc, M., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 553–572. ISBN 978-0-12-799942-5. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.E.; Kaleta, E.J.; Arora, A.; Wolk, D.M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry: A fundamental shift in the routine practice of clinical microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 547–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, P.M.; Loureiro, L.; Matos, A.J.F. Transfer of multidrug-resistant bacteria between intermingled ecological niches: The interface between humans, animals and the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, A.; Coyne, S.; Berendonk, T. Origin and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance: The Common Mechanisms of Emergence and Spread in Water Bodies. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Carvalho, I.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Soil Antibiotics and Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Affecting Wildlife. In Antibiotics and Antibiotics Resistance Genes in Soils; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 51, pp. 313–325. [Google Scholar]
- Hocquet, D.; Muller, A.; Bertrand, X. What happens in hospitals does not stay in hospitals: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in hospital wastewater systems. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 93, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, I.; Williams-Nguyen, J.; Hwang, H.; Sargeant, J.M.; Nault, A.J.; Singer, R.S. Systematic Review: Impact of point sources on antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the natural environment. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, e162–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, P.; Casado, C.; Sáenz, Y.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Estepa, V.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Diversity of species and antimicrobial resistance determinants of staphylococci in superficial waters in Spain. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrero, M.; Valverde, A.; Mateos, A.; Cantón, R.; Gortázar, C.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.-F.; Domínguez, L. Staphylococcus aureus Genetic Lineages Found in Urban Effluents and River Water. Int. J. Water Wastewater Treat. 2016, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lepuschitz, S.; Mach, R.; Springer, B.; Allerberger, F.; Ruppitsch, W. Draft Genome Sequence of a Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 Isolate from a River Sample. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01166-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendonk, T.U.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Cytryn, E.; Walsh, F.; Bürgmann, H.; Sørum, H.; Norström, M.; Pons, M.-N.; et al. Tackling antibiotic resistance: The environmental framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, J.; Friese, A.; Klees, S.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Fetsch, A.; Rösler, U.; Hartung, J. LA-MRSA contamination of air and soil surfaces in the vicinity of pig barns: A longitudinal study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friese, A.; Schulz, J.; Hoehle, L.; Fetsch, A.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Hartung, J.; Roesler, U. Occurrence of MRSA in air and housing environment of pig barns. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agersø, Y.; Vigre, H.; Cavaco, L.M.; Josefsen, M.H. Comparison of air samples, nasal swabs, ear-skin swabs and environmental dust samples for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in pig herds. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclaux, F.G.; Sakwinska, O.; Charrière, N.; Semaani, E.; Oppliger, A. Concentration of Airborne Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA and MSSA), Total Bacteria, and Endotoxins in Pig Farms. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2013, 57, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gillings, M. Evolutionary consequences of antibiotic use for the resistome, mobilome and microbial pangenome. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. Antibiotic resistance in the environment: A link to the clinic? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.; Wright, G. The antibiotic resistance “mobilome”: Searching for the link between environment and clinic. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, C.M.; Gocayne, J.D.; White, O.; Adams, M.D.; Clayton, R.A.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Bult, C.J.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Sutton, G.; Kelley, J.M.; et al. The Minimal Gene Complement of Mycoplasma genitalium. Science 1995, 270, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; McGrann, K.M.; Hughes, D.W.; Wright, G.D. Sampling the antibiotic resistome. Science 2006, 311, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Ellabaan, M.M.H.; Charusanti, P.; Munck, C.; Blin, K.; Tong, Y.; Weber, T.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Lee, S.Y. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes from antibiotic producers to pathogens. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, E.M.H.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Cross, P.; Feil, E.J.; Gaze, W.H.; Hawkey, P.M.; Johnson-Rollings, A.S.; Jones, D.L.; Lee, N.M.; Otten, W.; et al. The role of the natural environment in the emergence of antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L.; Dalsgaard, A. Occurrence and fate of antibiotic resistant bacteria in sewage. Environ. Proj. 2002, 722, 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S.O.; Lyon, B.R. Genetics of antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, B.; Persson, L.; Ekström, K.; Unnerstad, H.E.; Uhlhorn, H.; Börjesson, S. High occurrence of mecC-MRSA in wild hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Sweden. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.; Silva, N.; Manageiro, V.; Ramos, S.; Coelho, A.; Gonçalves, D.; Caniça, M.; Torres, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. First report on MRSA CC398 recovered from wild boars in the north of Portugal. Are we facing a problem? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596–597, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Hotzel, H.; Peters, M.; Guenther, S.; Lazaris, A.; Loncaric, I.; Müller, E.; Reissig, A.; Ruppelt-Lorz, A.; et al. Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates in European Wildlife. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, J.; Gmeiner, M.; Mordmüller, B.; Matsiégui, P.-B.; Schaer, J.; Eckerle, I.; Weber, N.; Matuschewski, K.; Bletz, S.; Schaumburg, F. Bats are rare reservoirs of Staphylococcus aureus complex in Gabon. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 47, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmeť, V.; Čuvalová, A.; Stanko, M. Small mammals as sentinels of antimicrobial-resistant staphylococci. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Ziółkowska, G.; Zięba, P.; Gnat, S.; Wojtanowicz-Markiewicz, K.; Trościańczyk, A. Coagulase-positive Staphylococcus isolated from wildlife: Identification, molecular characterization and evaluation of resistance profiles with focus on a methicillin-resistant strain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 44, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C.; Joshi, P.R.; Greninger, A.L.; Melendez, D.; Paudel, S.; Acharya, M.; Bimali, N.K.; Koju, N.P.; No, D.; Chalise, M.; et al. The human clone ST22 SCCmec IV methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from swine herds and wild primates in Nepal: Is man the common source? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenburger, J.L.; Rousseau, J.D.; Weese, J.S.; Jardine, C.M. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile in wild Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) from Ontario swine farms. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 82, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Konicek, C.; Vodrážka, P.; Barták, P.; Knotek, Z.; Hess, C.; Račka, K.; Hess, M.; Troxler, S. Detection of zoonotic pathogens in wild birds in the cross-border region austria-czech republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrochen, D.M.; Schulz, D.; Fischer, S.; Jeske, K.; El Gohary, H.; Reil, D.; Imholt, C.; Trübe, P.; Suchomel, J.; Tricaud, E.; et al. Wild rodents and shrews are natural hosts of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversa, A.; Gariano, G.R.; Gallina, S.; Bianchi, D.M.; Orusa, R.; Domenis, L.; Cavallerio, P.; Fossati, L.; Serra, R.; Decastelli, L. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from food and wild animal carcasses in Italy. Food Microbiol. 2015, 52, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrero, M.C.; Mentaberre, G.; Sánchez, S.; Fernández-Llario, P.; Gómez-Barrero, S.; Navarro-Gonzalez, N.; Serrano, E.; Casas-Díaz, E.; Marco, I.; Fernández-Garayzabal, J.F.; et al. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carriage in different free-living wild animal species in Spain. Vet. J. 2013, 198, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feßler, A.T.; Thomas, P.; Mühldorfer, K.; Grobbel, M.; Brombach, J.; Eichhorn, I.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Schwarz, S. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from zoo and wild animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 218, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Larsen, J.; van Wijk, R.E.; Jones, O.R.; Berg, T.B.; Angen, Ø.; Larsen, A.R. European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) as a natural reservoir of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecC in Denmark. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Mattsson, R.; Rangstrup-Christensen, L.; Lazaris, A.; Coleman, D.C.; Shore, A.C.; Ehricht, R. Detection of mecC-Positive Staphylococcus aureus (CC130-MRSA-XI) in Diseased European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraushaar, B.; Fetsch, A. First description of PVL-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in wild boar meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 186, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, O.M.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; González-Barrio, D.; Ruiz-Fons, J.F.; Torres, C. High frequency of coagulase-positive staphylococci carriage in healthy wild boar with detection of MRSA of lineage ST398-t011. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fny292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinige, D.; Von Altrock, A.; Kehrenberg, C. Genetic diversity and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from wild boars. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 54, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrero, M.C.; Mentaberre, G.; Sánchez, S.; Fernández-Llario, P.; Casas-Díaz, E.; Mateos, A.; Vidal, D.; Lavín, S.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.-F.; Domínguez, L. Carriage of Staphylococcus aureus by Free-Living Wild Animals in Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4865–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, P.; González-Barrio, D.; Benito, D.; García, J.T.; Viñuela, J.; Zarazaga, M.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Torres, C. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carrying the mecC gene in wild small mammals in Spain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvars-Larrive, A.; Ruppitsch, W.; Lepuschitz, S.; Szostak, M.P.; Spergser, J.; Feßler, A.T.; Schwarz, S.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Walzer, C.; et al. Urban brown rats (Rattus norvegicus) as possible source of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp., Vienna, Austria, 2016 and 2017. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1900149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Ferreira, E.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Diversity of methicillin-resistant staphylococci among wild Lepus granatensis: First detection of mecA-MRSA in hares. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 96, fiz204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Garcia, A.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; van Zeijl, J.H. Livestock-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a young harbour seal with endocarditis. Vet. Rec. Case Rep. 2019, 7, e000886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Stalder, G.L.; Mehinagic, K.; Rosengarten, R.; Hoelzl, F.; Knauer, F.; Walzer, C. Comparison of ESBL–And AmpC Producing Enterobacteriaceae and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Migratory and Resident Population of Rooks (Corvus frugilegus) in Austria. PLoS ONE 2014, 8, e84048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Camacho, M.C.; Lima-Barbero, J.-F.; Hernández, J.-M.; Zarazaga, M.; Höfle, Ú.; Torres, C. Detection of MRSA ST3061-t843-mecC and ST398-t011-mecA in white stork nestlings exposed to human residues. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.; Silva, N.; Igrejas, G.; Silva, F.; Sargo, R.; Alegria, N.; Benito, D.; Gómez, P.; Lozano, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance determinants in Staphylococcus spp. recovered from birds of prey in Portugal. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, G.; Varcasia, A.; Dessi, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Tamponi, C.; Saarma, U.; Laurimäe, T.; Kinkar, L.; Santoro, M.; Caputo, V.; et al. Cystic echinococcosis in wild boars (Sus scrofa) from southern Italy: Epidemiological survey and molecular characterization. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumburg, F.; Onwugamba, F.C.; Akulenko, R.; Peters, G.; Mellmann, A.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. A geospatial analysis of flies and the spread of antimicrobial resistant bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.M.; Paterson, G.K.; Holden, M.T.G.; Larsen, J.; Stegger, M.; Larsen, A.R.; Petersen, A.; Skov, R.L.; Christensen, J.M.; Bak Zeuthen, A.; et al. Whole genome sequencing identifies zoonotic transmission of MRSA isolates with the novel mecA homologue mecC. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplano, A.; Vandendriessche, S.; Nonhoff, C.; Denis, O. Genetic diversity among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates carrying the mecC gene in Belgium. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agersø, Y.; Hasman, H.; Cavaco, L.M.; Pedersen, K.; Aarestrup, F.M. Study of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Danish pigs at slaughter and in imported retail meat reveals a novel MRSA type in slaughter pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luini, M.; Cremonesi, P.; Magro, G.; Bianchini, V.; Minozzi, G.; Castiglioni, B.; Piccinini, R. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is associated with low within-herd prevalence of intra-mammary infections in dairy cows: Genotyping of isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász-Kaszanyitzky, E.; Jánosi, S.; Somogyi, P.; Dán, A.; van der Graaf-van Bloois, L.; van Duijkeren, E.; Wagenaar, J.A. MRSA transmission between cows and humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Müller, E.; Dorneanu, O.S.; Vremeră, T.; Ehricht, R. Molecular typing of MRSA and of clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Iaşi, Romania. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broens, E.M.; Graat, E.A.M.; van der Wolf, P.J.; van de Giessen, A.W.; van Duijkeren, E.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van Nes, A.; Mevius, D.J.; de Jong, M.C.M. MRSA CC398 in the pig production chain. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 98, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballhausen, B.; Kriegeskorte, A.; van Alen, S.; Jung, P.; Köck, R.; Peters, G.; Bischoff, M.; Becker, K. The pathogenicity and host adaptation of livestock-associated MRSA CC398. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Moreno, M.O.; Centelles-Serrano, M.J.; Nogales-López, J.; Domenech-Spanedda, M.F.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C. Unusual presence of the immune evasion gene cluster in livestock-associated MRSA of lineage CC398 causing peridural and psoas abscesses in a poultry farmer. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudín, M.A.; Deplano, A.; Vandendriessche, S.; Dodémont, M.; Nonhoff, C.; Denis, O.; Roisin, S. CC398 Staphylococcus aureus subpopulations in Belgian patients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, S.; Aspiroz, C.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Reynaga, E.; Azcona-Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rezusta, A.; Seral, C.; Antoñanzas, F.; Torres, L.; López, C.; et al. Epidemiology of MRSA CC398 in hospitals located in Spanish regions with different pig-farming densities: A multicentre study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2157–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.B.; Stegger, M.; Hasman, H.; Aziz, M.; Larsen, J.; Andersen, P.S.; Pearson, T.; Waters, A.E.; Foster, J.T.; Schupp, J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus CC398: Host adaptation and emergence of methicillin resistance in livestock. MBio 2012, 3, e00305-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, Y.; Leonard, F.C.; Markey, B.K. Detection of three distinct genetic lineages in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from animals and veterinary personnel. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, R.; Schaumburg, F.; Mellmann, A.; Köksal, M.; Jurke, A.; Becker, K.; Friedrich, A.W. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) as causes of human infection and colonization in Germany. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, D.; Nakaminami, H.; Miyajima, E.; Sugiyama, T.; Sasai, N.; Kitamura, Y.; Tamura, T.; Kawakubo, T.; Noguchi, N. Change in genotype of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) affects the antibiogram of hospital-acquired MRSA. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincze, S.; Stamm, I.; Kopp, P.A.; Hermes, J.; Adlhoch, C.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Walther, B. Alarming Proportions of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Wound Samples from Companion Animals, Germany 2010–2012. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S.; van Duijkeren, E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in veterinary medicine. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Lilliebridge, R.A.; Bishop, E.J.; Cheng, A.C.; Holt, D.C.; McDonald, M.I.; Giffard, P.M.; Currie, B.J.; Boutlis, C.S. Clinical Correlates of Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL), PVL Isoforms, and Clonal Complex in the Staphylococcus aureus Population of Northern Australia. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, L.; Holden, M.T.G.; Lindsay, H.; Webb, C.R.; Brown, D.F.J.; Curran, M.D.; Walpole, E.; Brooks, K.; Pickard, D.J.; Teale, C.; et al. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a novel mecA homologue in human and bovine populations in the UK and Denmark: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.; Stegger, M.; Heltberg, O.; Christensen, J.; Zeuthen, A.; Knudsen, L.K.; Urth, T.; Sorum, M.; Schouls, L.; Larsen, J.; et al. Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the novel mecC gene in Denmark corroborates a zoonotic reservoir with transmission to humans. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, E16–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K.; Morgan, F.J.E.; Harrison, E.M.; Cartwright, E.J.P.; Török, M.E.; Zadoks, R.N.; Parkhill, J.; Peacock, S.J.; Holmes, M.A. Prevalence and characterization of human mecC methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in England. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, A.-K.; Gustafsson, E.; Petersson, A.C.; Melander, E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with mecC: A description of 45 human cases in southern Sweden. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merialdi, G.; Feltrin, F.; Gaetarelli, B.; Lombardi, G.; Iurescia, M.; Alba, P.; Luppi, A.; Martinelli, N.; Ramini, M.; Carfora, V.; et al. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) spa type t127, Sequence Type (ST)1, quickly spreads and persists among young pigs. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftz033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earls, M.R.; Kinnevey, P.M.; Brennan, G.I.; Lazaris, A.; Skally, M.; O’Connell, B.; Humphreys, H.; Shore, A.C.; Coleman, D.C. The recent emergence in hospitals of multidrug-resistant community-associated sequence type 1 and spa type t127 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus investigated by whole-genome sequencing: Implications for screening. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatta, D.R.; Cavaco, L.M.; Nath, G.; Kumar, K.; Gaur, A.; Gokhale, S.; Bhatta, D.R. Association of Panton Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) genes with methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Western Nepal: A matter of concern for community infections (a hospital based prospective study). BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Gongora, C.; Harrison, E.M.; Moodley, A.; Guardabassi, L.; Holmes, M.A. MRSA carrying mecC in captive mara. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, G.K.; Harrison, E.M.; Holmes, M.A. The emergence of mecC methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Typing Methods | Principle | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| agr typing | Amplification of the hypervariable segment | [86] |
| spa typing | Amplification and sequencing of the 24 bp polymorphic zone X of the spa gene | [87] |
| Mutilocus sequence typing (MLST) | sequence analysis of the allelic variants of the seven housekeeping genes | [88] |
| SCCmec typing | Analysis of the structure of SCCmec region | [89] |
| Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) | Macro-restriction profiling based on the digestion of DNA with restriction enzymes | [90] |
| Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) | Unspecific binding with polymorphism of the whole chromosome | [91] |
| Multilocus variable-number tandem repeat (VNTR) analysis (MLVA) | Polymorphism of tandemly repeated DNA sequences | [92] |
| Multiple locus VNTR fingerprinting (MLVF) | polymorphism of tandemly repeated DNA sequences | [93] |
| Genome-scale DNA microarrays | Hybridization with genes on the chromossome | [94] |
| Whole genome sequencing (WGS) | Genome-wide variations | [95] |
| Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization - Time of Flight (MALDI-TOF) Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Generation of mass-spectral fingerprints | [96] |
| Animal | Location | MRSA/MSSA (Number of Isolates) | Clonal Lineages | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| spa-Type | ST/CC | ||||
| Hedgehog | Sweden | mecC-MRSA(35) | t843, t3391, t978, t10751 t10893, t11015; t9111, t15312 | CC130, CC2361 | [121] |
| Poland | MSSA (1) | n.d. | n.d. | [126] | |
| Austria | mecC-MRSA (1) | t3256 | CC130 | [51] | |
| Denmark | mecC-MRSA (114) | t528, t843, t1048, t3256, t3570, t6220, t17133, t978, t2345, t3391, t8835, t16868 | CC130 CC1943 | [134] | |
| Spain | mecA-MRSA (1) | t386 | CC1 | [54] | |
| Sweeden | mecC-MRSA (2) | t843, t5771 | CC130 | [135] | |
| Wild Boar | Spain | MSSA (11) | t1535, t7174, t1534, t6386, t3750, t11230 | CC130, CC5, CC522, CC425, ST2328 | [54] |
| Portugal | mecA-MRSA (1) MSSA (29) | t899, t3750, t1533, t286, t14312, t14311, t10668, t3583, t3750, t11230, t10712 | CC398, ST3220, ST1, ST3224, ST3223, ST3222, ST133, ST2328, ST1643 | [122] | |
| Germany | mecA-MRSA (28) | t011, t034, t1456, t1250, t015, t202, t008 | CC398, CC45, CC93, CC8 | [136] | |
| Spain | mecA-MRSA (1) MSSA (50) | t011, t3750, t16741, t3583, t742, t11232, t6292, t11212, t002, t1094, t127, t843, t12923, t208, t1951, t1200, t073, t12827, t16740, t548, t3293 | CC398, CC133, CC425, CC5, CC1, CC130, CC49, CC88, CC97 | [137] | |
| Germany | MSSA (41) | t127, t091, t14149, t021, t1773, t11226, t1181, t7674, t12042, t10856, t3369, t15002, t6902, t15001, t15000, t3583, t742, t14999, t571 | ST1, ST7, ST30, ST890, ST3237, ST3238, ST3369, ST425, ST3255, ST133, ST804 | [138] | |
| Spain | mecA-MRSA (7) | t011, t127 | CC398 | [132] | |
| Spain | MSSA (126) | t098, t127, t607, t1407, t2601, t11223, t548, t2516, t7174, t11210, t11214, t11219, t084, t11218, t6220, t3583, t10476, t11220, t189, t034,t742, t6909, t11222, t11225, t11232, t10712, t3750, t11227, t11230, t11229, t359, t11209, t11502, t015, t6384, t011 | ST1, ST5, ST15, ST96, ST130, ST133, ST188, ST398, ST425, ST1643, ST2328, ST2641, ST2672, ST2675, ST2678, ST2681, ST2682, ST2729, | [139] | |
| Rodent | Spain | mecC-MRSA (2) MSSA (11) | t1535, t120, t12365, t12752, t9303, t3750, t12363, t12364 | CC130, CC5, CC1956, ST2328 ST2766, ST2767 | [140] |
| Slovakia | mecA-MRSA (3) MSSA (4) | n.d. | n.d. | [125] | |
| Germany | mecC-MRSA (1) 39 MSSA | t843, t208, t4189, t1773, t2311, t15027, t3058 | CC130, CC49, ST890, CC88, CC1956 | [130] | |
| Austria | mecA-MRSA (1) | t011 | CC398 | [141] | |
| Deer | Spain | MSSA (4) | t1535 | CC130 | [54] |
| Germany | MSSA (1) | t15473 | CC425 | [133] | |
| Spain | MSSA (54) | t098, t127, t11223, t548, t11210, t342, t2678, t11215, t571, t1077, t6386, t6909, t11208, t11212, t11228, t11231, t528, t1534, t3576, t742, t11211, t11226, t11233, t015, t11217 | ST1, ST5, ST30, ST133, ST350, ST398, ST425, ST522, ST2640, ST2671, ST2681 | [139] | |
| Hare | Portugal | mecA-MRSA (3) | t1190 | ST2855 | [142] |
| Germany | mecC-MRSA (3) | t10513, t843 | CC130 | [51] | |
| Marten | Poland | mecA-MRSA (1) MSSA (2) | t1635 | CC8 | [126] |
| Red Foxe | Poland | MSSA (2) | n.d. | n.d. | [126] |
| Otter | Austria | mecC-MRSA (1) | t4335 | CC130 | [51] |
| Shrew | Germany | MSSA (5) | t9909, t1125, t11225 | ST3033 CC5, CC425 | [130] |
| Rabbit | Spain | mecC-MRSA (3) | t843 | CC130 | [54] |
| Mouflon | Spain | MSSA (4) | t6056, t11233 | CC133, ST3237 | [54] |
| Ibex | Spain | MSSA (36) | t002, t1736, t3369, t528, t843, t1535, t3750, t11501, t11221, t7229, t11216, t528 | ST5, ST130, ST425, ST581, ST2328, ST2637, ST2639, ST2673 | [139] |
| Spain | MRSA (2) | t011, t1451 | CC1, CC398 | [132] | |
| Squirrel | Germany | MSSA (4) | t208, t307, t528 | CC49, CC22, ST4310 | [133] |
| Beaver | Germany | MSSA (1) | t3058 | CC1956 | [133] |
| Seal | The Neatherlands | MRSA (1) | t1430 | CC9 | [143] |
| Bat | Germany | MSSA (1) | t164 | CC20 | [133] |
| Rook | Austria | mecA-MRSA (5) | t127, t852 | CC1, CC22 | [144] |
| Stork | Spain | mecC-MRSA (1) mecA-MRSA (2) MSSA (35) | t843, t002, t011, t1818, t1166, t6384, t6606, t571, t012, t688, t126, t209, t045, t015, t1945, t091, t3625, t774, t005, t216, t14445 | CC130 CC5 CC398 CC7, CC22, CC30, CC45, CC59, CC133 | [145] |
| Eagle | Germany | MSSA (1) | t1422 | CC692 | [133] |
| Kite | Germany | MSSA (1) | t14745 | CC692 | [133] |
| Magpie | Spain | mecC-MRSA (7) | t843 | CC130 | [53] |
| Vulture | Spain | mecC-MRSA (5) mecA-MRSA (1) MSSA (2) | t843, t011, t1535, t267 | CC130, CC398, C97 | [53] |
| Spain | MSSA (2) | t7304 | ST133 | [139] | |
| Buzzard | Portugal | MSSA (1) | t012 | CC30 | [146] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, V.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Wild Animals in Europe: A Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030122
Silva V, Capelo JL, Igrejas G, Poeta P. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Wild Animals in Europe: A Review. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(3):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030122
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Vanessa, José L. Capelo, Gilberto Igrejas, and Patrícia Poeta. 2020. "Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Wild Animals in Europe: A Review" Antibiotics 9, no. 3: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030122
APA StyleSilva, V., Capelo, J. L., Igrejas, G., & Poeta, P. (2020). Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus Lineages in Wild Animals in Europe: A Review. Antibiotics, 9(3), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9030122








