Concerted Efforts Are Needed to Control and Mitigate Antibiotic Pollution in Coastal Waters of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
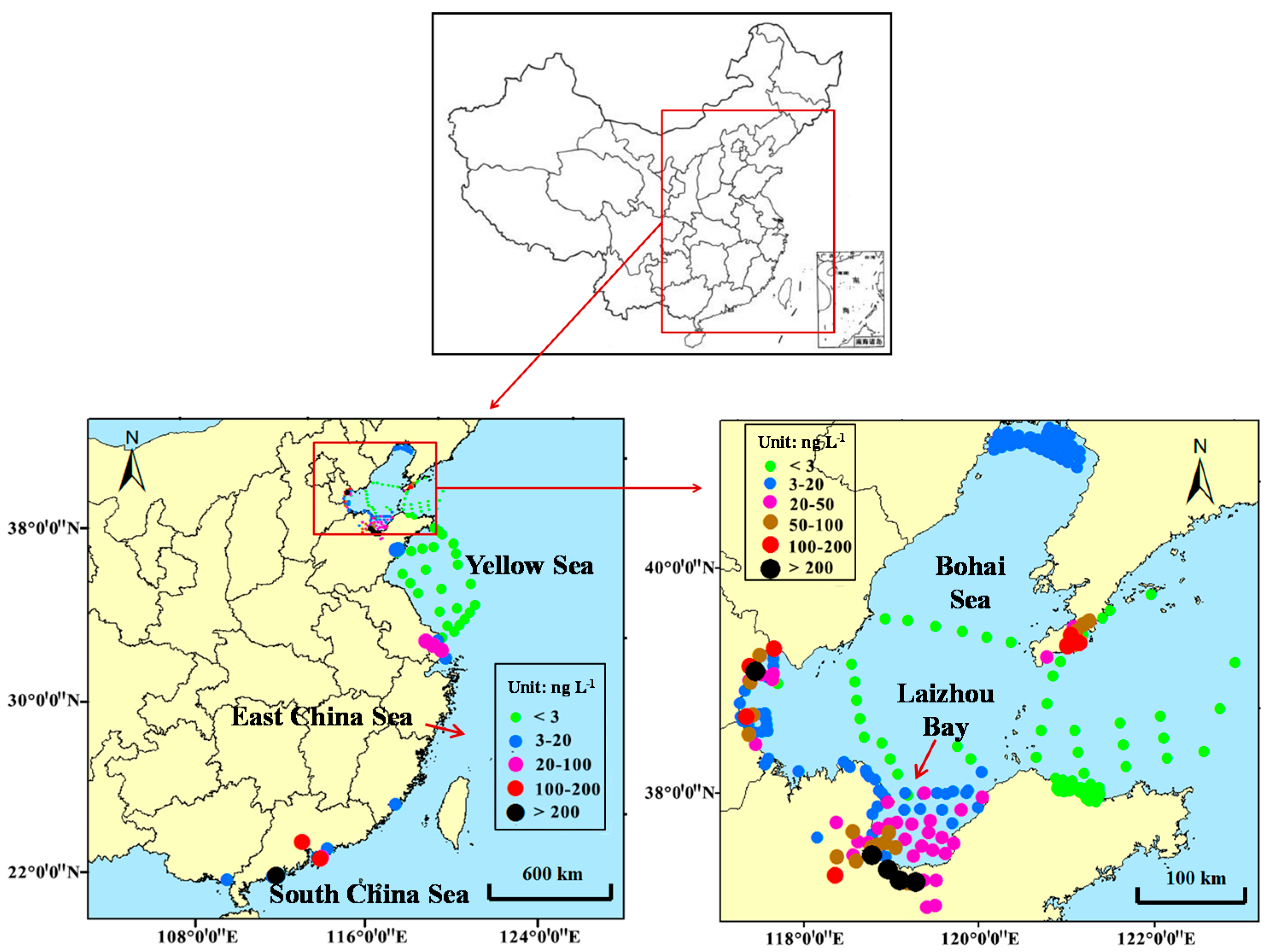
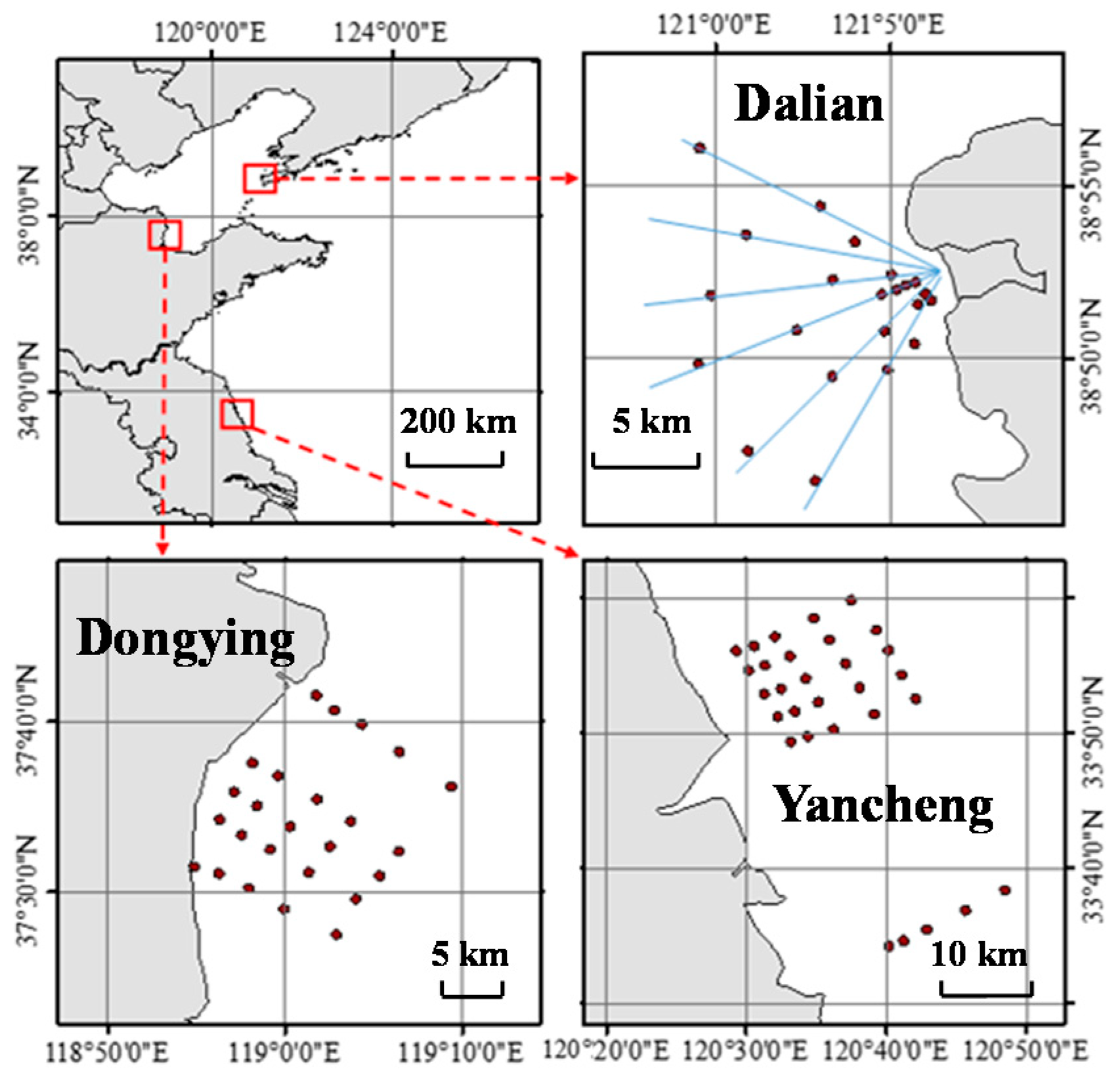
2. Occurrence and Distribution of Antibiotics in Coastal Waters of China
3. Potential Sources of Antibiotic Pollution in Coastal Waters
4. Risks of Antibiotics in Marine Environment
5. Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Liu, W. Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 32, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.K.; Chen, J.W.; Wei, X.X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Qiao, X.L.; Cai, X.Y.; Xie, Q. Aquatic photochemistry of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Kinetics, pathways, and multivariate effects of main water constituents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2400–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ge, L.; Qiao, X. Distinct photolytic mechanisms and products for different dissociation species of ciprofloxacin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4284–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, Y.N.; Uddin, M.; Guo, Z. Disparate effects of DOM extracted from coastal seawaters and freshwaters on photodegradation of 2,4-Dihydroxybenzophenone. Water Res. 2019, 151, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G. DOM from mariculture ponds exhibits higher reactivity on photodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics than from offshore seawaters. Water Res. 2018, 144, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S. Prediction of hydrolysis pathways and kinetics for antibiotics under environmental pH conditions: A quantum chemical study on cephradine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.C. River Hydrology in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.H.; Zhang, G.; Zou, S.C.; Li, X.D.; Liu, Y.C. Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Liu, S.S.; Zhou, G.J.; Sun, K.F.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioaccumulation and human dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulkowska, A.; He, Y.; So, M.K.; Yeung, L.W.; Leung, H.W.; Giesy, J.P.; Lam, P.K.; Martin, M.; Richardson, B.J. The occurrence of selected antibiotics in Hong Kong coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, A.; Hu, J.; Wu, X.; Peng, H.; Wu, S.; Dong, Z. Occurrence and source apportionment of sulfonamides and their metabolites in Liaodong Bay and the adjacent Liao River basin, North China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, G.; Fang, X.; Cai, Y.; Ge, L.; Zong, H.; Yuan, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Z. Occurrence, distribution, and bioaccumulation of antibiotics in coastal environment of Dalian, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Nie, M.; Liu, M.; Hochella, M.F., Jr. Selected emerging organic contaminants in the Yangtze Estuary, China: A comprehensive treatment of their association with aquatic colloids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Feng, Y.; Yang, F. Fate of antibiotics during wastewater treatment and antibiotic distribution in the effluent-receiving waters of the Yellow Sea, northern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Chaemfa, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Song, M.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the coastal aquatic environment of the Yellow Sea, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Antibiotics in the offshore waters of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea in China: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X. Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the Laizhou Bay, China: Impacts of river discharge. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, D.; Liu, G.; Liang, B.; Cui, B.; Bai, J. Temporal-spatial variation and partitioning prediction of antibiotics in surface water and sediments from the intertidal zones of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 78, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in coastal water of the Bohai Bay, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.R.; Na, G.S.; Lu, Z.H.; Gao, H.; Li, R.J.; Wu, X.; Zu, G.R.; Yao, Z.W. Distribution of sulfonamides and sulfonamide-resistant Escherichia coli in the coastal marine environment of northern Yellow Sea, China. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2014, 20, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Antibiotics in the coastal water of the South Yellow Sea in China: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Zhou, G.J.; Liu, S.S.; Yue, W.Z.; Sun, K.F.; Ying, G.G. Antibiotics in the coastal environment of the Hailing Bay region, South China Sea: Spatial distribution, source analysis and ecological risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhao, H. Persistence and risk of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in major mariculture sites in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitt, W.K.; Heslinga, G.A.; Watson, T.C. Use of antibiotics in the mariculture of giant clams (F. Tridacnidae). Aquaculture 1992, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Science 2008, 321, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, S.; Gao, H.; Lu, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Qiu, L.; Cai, Y.; Yao, Z. Sulfonamide antibiotics in the Northern Yellow Sea are related to resistant bacteria: Implications for antibiotic resistance genes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the coastal area of the Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Fu, C.; Tu, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Tang, J.; Luo, Y.; Christie, P. Levels, distributions and sources of veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Bohai Sea in China and surrounding estuaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, G. Fishmeal application induces antibiotic resistance gene propagation in mariculture sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10850–10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Ren, J.; Song, L.; Sun, S.; An, L. Dominant chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in coastal marine waters of Jiaozhou Bay, China. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 24, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Zhao, J.; Song, L.; Chen, M.; Chang, Y. Molecular characterizations of chloramphenicol- and oxytetracycline-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in mariculture waters of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Yue, Y.; Min, M.; Peng, S.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Y. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes from mariculture sites of China’s coastline. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhaus, T.; Karlsson, M. Screening level mixture risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in STP effluents. Water Res. 2014, 49, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Pleiter, M.; Gonzalo, S.; Rodea-Palomares, I.; Leganes, F.; Rosal, R.; Boltes, K.; Marco, E.; Fernandez-Pinas, F. Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: Implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, X.; Lang, X.; Qiao, X.; Li, X.; Chen, J. Insights into aquatic toxicities of the antibiotics oxytetracycline and ciprofloxacin in the presence of metal: Complexation versus mixture. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 166, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.M.; Ingerslev, F.; Baun, A. Ecotoxicity of mixtures of antibiotics used in aquacultures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 2208–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Lehmler, H.J.; Cai, X.; Chen, J. Antibiotic pollution in marine food webs in Laizhou Bay, North China: Trophodynamics and human exposure implication. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Lu, B.; Yu, Y.; Pei, J.; Yuan, D.; Gan, J. A novel active sampler coupling osmotic pump and solid phase extraction for in situ sampling of organic pollutants in surface water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davlson, W.H.Z. In situspeciation measurements of trace components in natural waters using thin-film gels. Nature 1994, 367, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.E.; Zhang, H.; Jones, K.C. A novel passive water sampler for in situ sampling of antibiotics. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.E.; Zhang, H.; Ying, G.G.; Jones, K.C. Evidence and recommendations to support the use of a novel passive water sampler to quantify antibiotics in wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13587–13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, C.L.; Du, J.; Tan, F.; Zhou, C. Development and evaluation of diffusive gradients in thin films technique for measuring antibiotics in seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.L.; Du, J. Investigation and application of diffusive gradients in thin-films technique for measuring endocrine disrupting chemicals in seawaters. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.N. Photodegradation mechanism of sulfonamides with excited triplet state dissolved organic matter: A case of sulfadiazine with 4-carboxybenzophenone as a proxy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, A.; He, L.; Xing, B. High adsorption of Sulfamethoxazole by an amine-modified Polystyrene-Divinylbenzene resin and its mechanistic insight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10015–10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, S. Modeling photodegradation kinetics of organic micropollutants in water bodies: A case of the Yellow River estuary. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 349, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Costanzo, S.D. Removal of antibiotics in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment: Implications for environmental discharge and wastewater recycling. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4164–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Goel, R. A comparative study on kinetics, process performance and microbial ecology for aerobic granular and conventional activated sludge reactors. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2017, 2017, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, R.; Jalilzadeh Yengejeh, R.; Babaei, A.A.; Derikvand, E.; Almasi, A. UV activation of hydrogen peroxide for removal of azithromycin antibiotic from aqueous solution: Determination of optimum conditions by response surface methodology. Toxin Rev. 2019, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, P.J.; Rico, A.; Zhang, W.; Ahmad-Al-Nahid, S.; Newton, R.; Phan, L.T.; Zhang, Z.; Jaithiang, J.; Dao, H.M.; Phu, T.M.; et al. Comparison of Asian aquaculture products by use of statistically supported life cycle assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14176–14183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antibiotic | Level Range | Mean Level | Antibiotic | Level Range | Mean Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonamides | Tetracycline | ||||
| Sulfadiazine | 0.1–209.0 | 14.2 | Tetracycline | 1.0–122.0 | 23.9 |
| Sulfacetamide | 0.3–56.8 | 14.7 | Doxycycline | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Sulfadiazole | 0.1–52.8 | 4.7 | Chlortetracycline | 0.6–5.0 | 1.8 |
| Sulfamethoxine | 0.2–41.7 | 8.4 | Methyl cyclin | 2.1–2.3 | 2.2 |
| Sulfachloropyridazine | 0.2–233.2 | 65.1 | Oxytetracycline | 2.5–15,163.0 | 578.9 |
| Sulfamethoxazine | 0.2–86.4 | 26.0 | Chloramphenicol | ||
| Sulfamonomethoxine | 0.1–28.9 | 7.3 | Chloramphenicol | 0.2–0.9 | 0.4 |
| Sulfadimethoxine | 0.3–108.4 | 20.4 | Thiamphenicol | 0.8–85.0 | 24.9 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 0.2–47.2 | 8.9 | Florfenicol | 0.5–40.0 | 11.6 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 0.1–527.0 | 19.1 | Macrolides | ||
| Acetyl Sulfamethoxazole | 5.9–52.8 | 25.6 | Roxithromycin | 0.1–630.0 | 38.4 |
| Sulfadiazine | 0.1–30.0 | 3.4 | Azithromycin | 0.1–396.0 | 45.2 |
| Sulfaguanidine | 0.6–3.7 | 1.5 | Erythromycin | 0.1–486.0 | 16.9 |
| Sulfanilamide | 0.5–7.9 | 2.5 | Clarithromycin | 0.2–32.9 | 3.1 |
| Sulfaquinoxaline | 0.5–7.0 | 1.9 | β-lactam | ||
| Quinolone | Cephalexin | 10.0–182.0 | 43.7 | ||
| Norfloxacin | 2.3–6800.0 | 129.3 | Cefradine | 5.3–90.0 | 41.8 |
| Enoxacin | 23.4–508.0 | 98.8 | Others | ||
| Ofloxacin | 0.8–5100.0 | 57.0 | Salinomycin | 1.3–36.9 | 9.9 |
| Enrofloxacin | 1.9–24.6 | 111.5 | Trimethoprim | 1.3–13,600.0 | 416.1 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 3.3–39.0 | 9.7 |
| Antimicrobial Resistance Genes | Geographic Locations | Local Factors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| cat I, cat III | Jiaozhou Bay | Surface seawater | [33] |
| cat II, cat IV, floR, tetB, tetD, tetE, tetM | Around Dalian | Maricultural environments | [34] |
| sul1, sul2, tetA, tetC, tetD, qnrS, qnrB, qnrA | Around Dalian | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul2, sul3, sulP, tetA, tetB, tetC, tetD, qnrS, qnrB | Around Tangshan | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul2, sulP, tetA, tetB, tetC, tetD, qnrD, qnrB, qnrA | Around Penglai | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sulP, tetA, tetC, qnrD, qnrB | Around Lianyungang | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul3, sulP, tetB, tetC, tetD, qnrD, qnrB | Around Qidong | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul2, sulP, tetA, tetC, tetD, qnrS, qnrA | Around Xiangshan | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul2, sul3, tetA, tetC, tetD, qnrS, qnrA | Around Ningde | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul2, sulP, tetA, tetC, tetD, qnrD, qnrB, qnrA | Around Dongshan | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul1, sul3, tetB, tetC, tetD, qnrD, qnrS, qnrB | Around Zhanjiang | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| sul2, sul3, tetA, tetB, tetC, tetD, qnrD, qnrS, qnrB, qnrA | Around Lingshui | Maricultural environments | [35] |
| tetA, tetB | Around Meijijiao | Maricultural environments | [35] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Du, J.; Chen, J. Concerted Efforts Are Needed to Control and Mitigate Antibiotic Pollution in Coastal Waters of China. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020088
Xie H, Du J, Chen J. Concerted Efforts Are Needed to Control and Mitigate Antibiotic Pollution in Coastal Waters of China. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020088
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Huaijun, Jing Du, and Jingwen Chen. 2020. "Concerted Efforts Are Needed to Control and Mitigate Antibiotic Pollution in Coastal Waters of China" Antibiotics 9, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020088
APA StyleXie, H., Du, J., & Chen, J. (2020). Concerted Efforts Are Needed to Control and Mitigate Antibiotic Pollution in Coastal Waters of China. Antibiotics, 9(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020088







