Tigecycline Interferes with Fibrinogen Polymerization Independent of Peripheral Interactions with the Coagulation System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
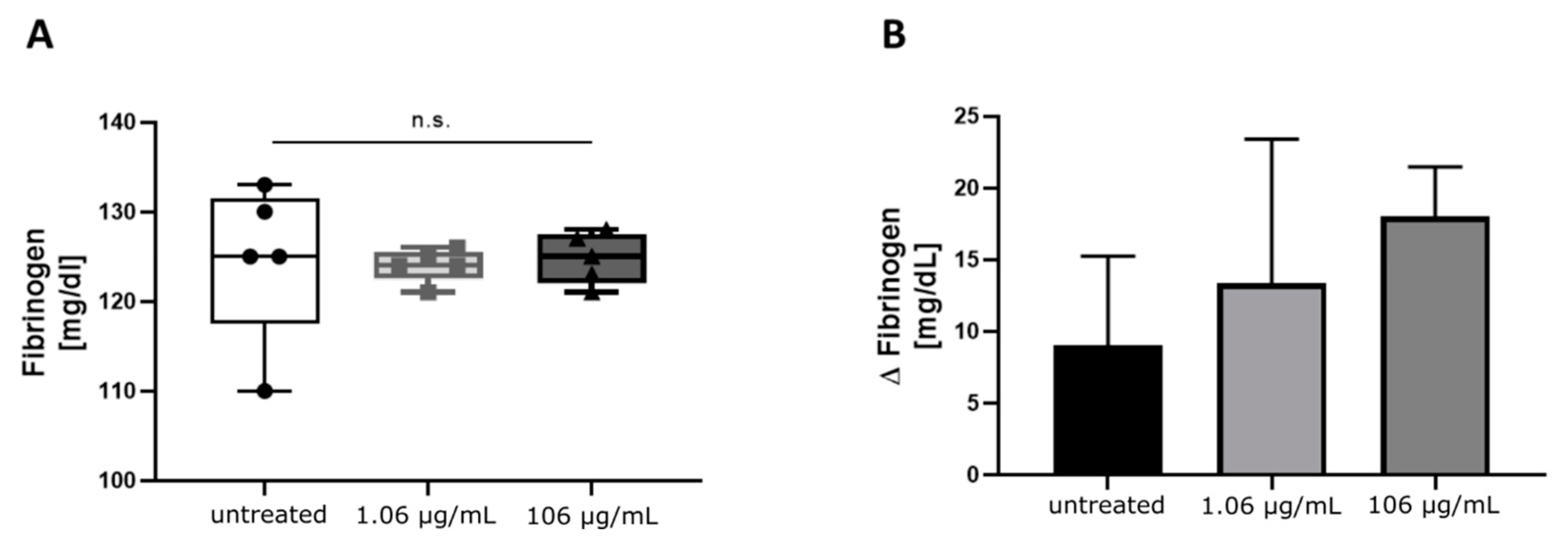
2.1. Influence of Increasing Concentrations of Tigecycline on Standard Coagulation Tests
2.2. Influence of Tigecycline on ROTEM® Measurements
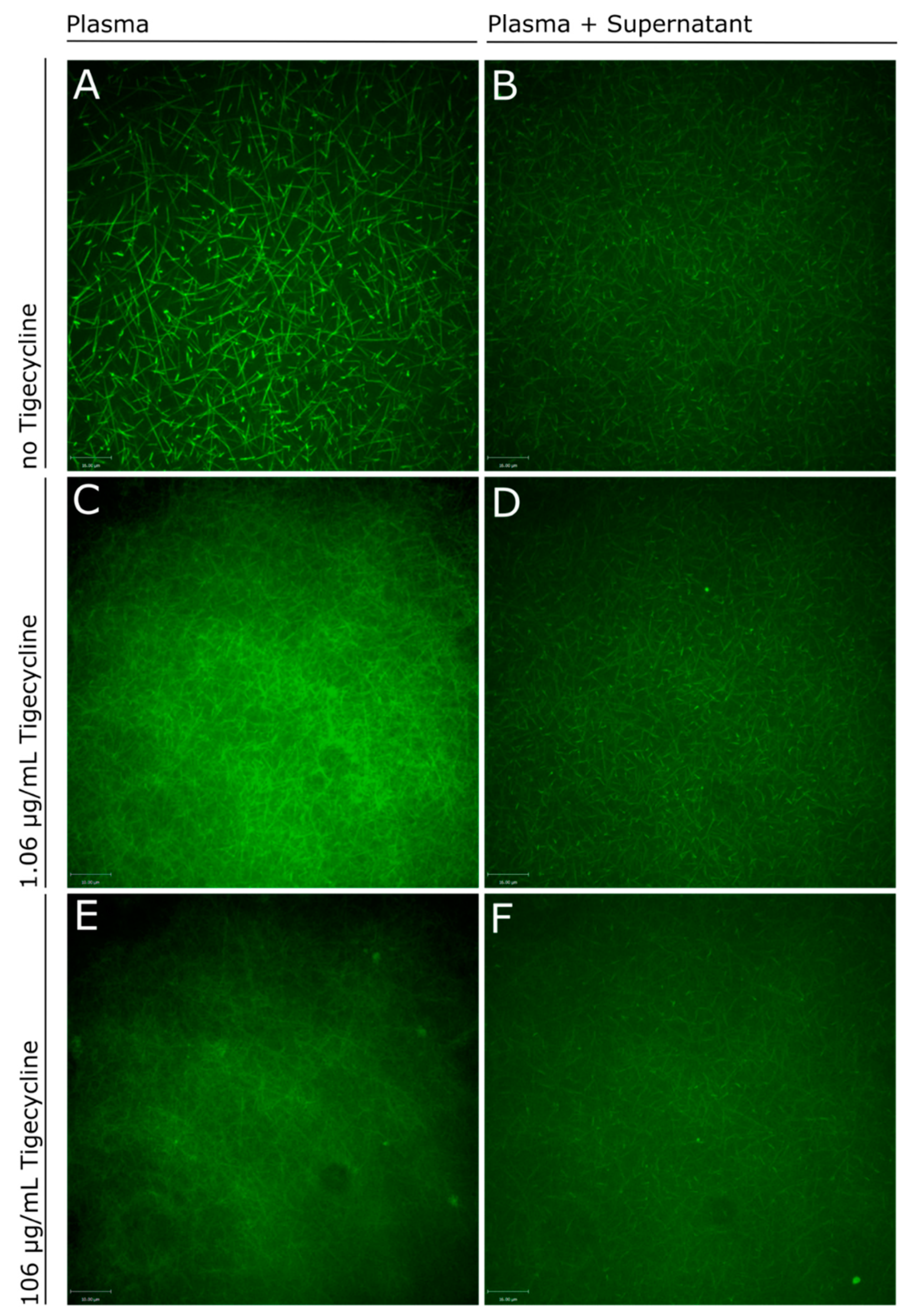
2.3. Influence of Tigecycline on Fibrin Polymerization
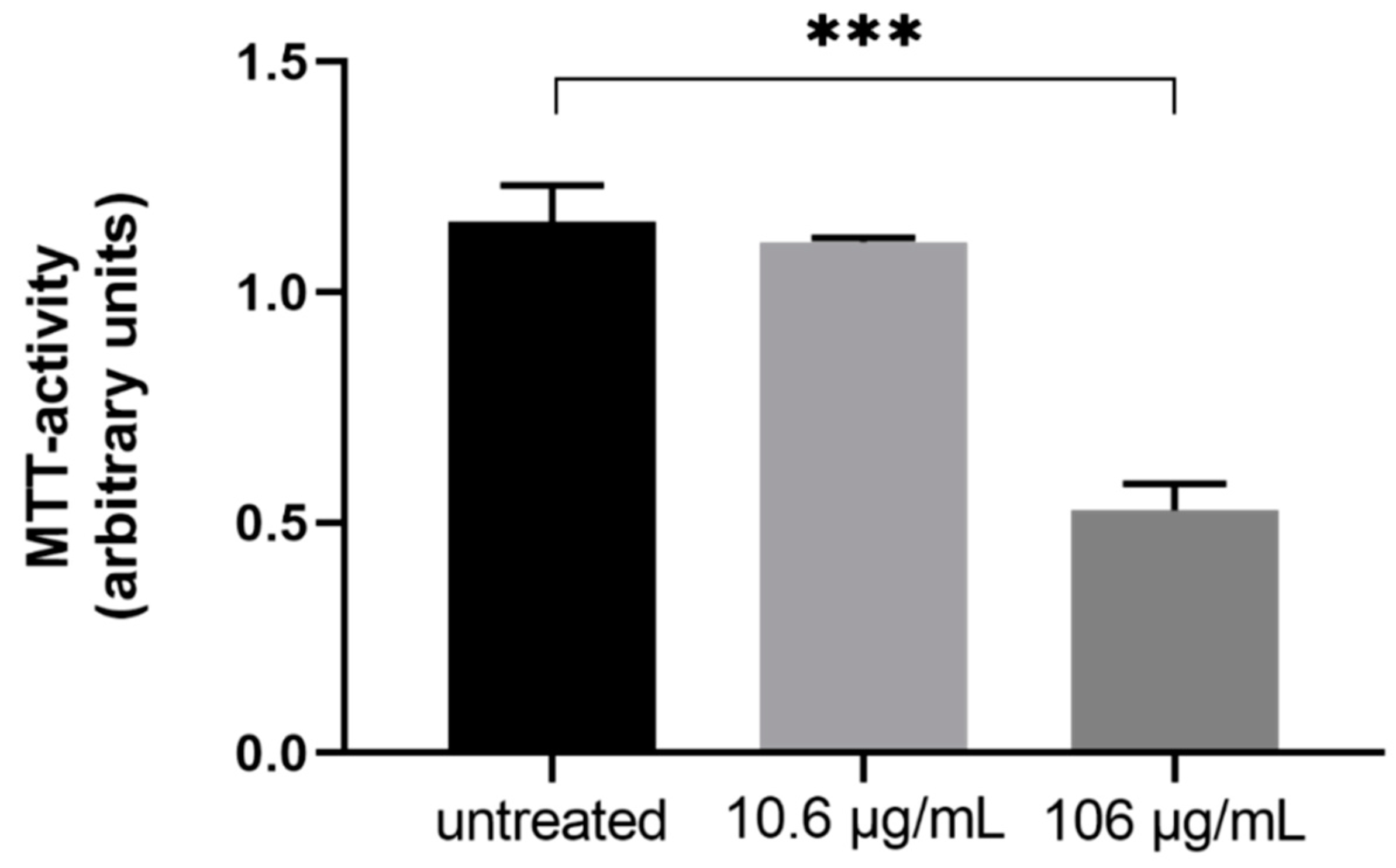
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Healthy Volunteers
4.2. Preparation of Blood Samples
4.3. Coagulation Tests
4.4. Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM®)
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. Stimulation of Hepatocytes
4.7. Real-Time Live Confocal Microscopy of Fibrin Formation
4.8. Cell Viability and Mitochondrial Activity (MTT)
4.9. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pankey, G.A. Tigecycline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, N.D. Tigecycline (Tygacil): The first in the glycylcycline class of antibiotics. Proc. (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.) 2006, 19, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, B.; Xue, Y.C.; Zhang, W.; Gao, T.T.; Yan, G.Q.; Tang, H. A Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of Tigecycline on Coagulation Function. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routsi, C.; Kokkoris, S.; Douka, E.; Ekonomidou, F.; Karaiskos, I.; Giamarellou, H. High-dose tigecycline-associated alterations in coagulation parameters in critically ill patients with severe infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, J. Tigecycline Treatment Causes a Decrease in Fibrinogen Levels. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakeam, H.A.; Duhailib, Z.A.; Salahuddin, N.; Amin, T. Impact of tigecycline versus imipenem–cilastatin on fibrinogen levels following cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC): A randomized-controlled study. J. Chemother. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giryes, S.; Azzam, Z.S.; Ismael-Badarneh, R.; Krivoy, N.; Berger, G. Severe Coagulation Disorder and Thrombocytopenia Associated with Tigecycline—Case Report and Review of Literature. Curr. Drug Saf. 2017, 12, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, J.; Moenster, R.P. Tigecycline-induced coagulopathy. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2017, 74, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieringer, H.; Schmekal, B.; Biesenbach, G.; Pohanka, E. Severe coagulation disorder with hypofibrinogenemia associated with the use of tigecycline. Ann. Hematol. 2010, 89, 1063–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossitto, G.; Piano, S.; Rosi, S.; Simioni, P.; Angeli, P. Life-threatening coagulopathy and hypofibrinogenaemia induced by tigecycline in a patient with advanced liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanis, N.; Paschou, E.; Gavriilaki, E.; Kalaitzoglou, A.; Vasileiou, S. Hypofibrinogenemia induced by tigecycline: A potentially life-threatening coagulation disorder. Infect. Dis. 2015, 47, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-C.; Wu, C.-C. Tigecycline-associated hypofibrinogenemia: A case report and review of the literature. IDCases 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, P.; Dong, L.; Zhang, X. A case report of patient with severe acute cholangitis with tigecycline treatment causing coagulopathy and hypofibrinogenemia. Medicine 2017, 96, e9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz Duran, F.; Yildirim, H.; Sen, E.M. A Lesser Known Side Effect of Tigecycline: Hypofibrinogenemia. Turk. J. Haematol. 2018, 35, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, D.; Madduri, R.P.; Sharma, R. The role of tigecycline in the treatment of infections in light of the new black box warning. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2014, 12, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; DeMaio, W.; Jordan, R.A.; Talaat, R.; Harper, D.; Speth, J.; Scatina, J. Metabolism, Excretion, and Pharmacokinetics of [14C] Tigecycline, a First-In-Class Glycylcycline Antibiotic, after Intravenous Infusion to Healthy Male Subjects. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenger-Eriksen, C.; Moore, G.W.; Rangarajan, S.; Ingerslev, J.; Sorensen, B. Fibrinogen estimates are influenced by methods of measurement and hemodilution with colloid plasma expanders. Transfusion 2010, 50, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, R.; Boer, K.; Poeschel, K.; Wolf, G.; Deufel, T.; Kiehntopf, M. Influence of direct thrombin inhibitor argatroban on coagulation assays in healthy individuals, patients under oral anticoagulation therapy and patients with liver dysfunction. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2008, 19, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.; Halvorsen, S.; Godal, H.C.; Sandset, P.M.; Skjoonsberg, O.H. Discrepancy between fibrinogen concentrations determined by clotting rate and clottability assays during the acute-phase reaction. Thromb. Res. 2000, 100, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.T.; Brandt, J.T.; Laposata, M.; Olson, J.D. Laboratory diagnosis of dysfibrinogenemia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2002, 126, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Binsack, R.; Stegmeier, K.; Dörge, L.; Völkl, A. Bezafibrate down-regulates fibrinogen biosynthesis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 28, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broeker, A.; Wicha, S.G.; Dorn, C.; Kratzer, A.; Schleibinger, M.; Kees, F.; Heininger, A.; Kees, M.G.; Häberle, H. Tigecycline in critically ill patients on continuous renal replacement therapy: A population pharmacokinetic study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, W.B. Some lessons in cardiovascular epidemiology from Framingham. Am. J. Cardiol. 1976, 37, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiserud, C.E.; Kierulf, P.; Høstmark, A.T. Effects of various fatty acids alone or combined with vitamin E on cell growth and fibrinogen concentration in the medium of HepG2 cells. Thromb. Res. 1995, 80, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-D.T.; Simpson-Haidaris, P.J. Cell Type–Specific Regulation of Fibrinogen Expression in Lung Epithelial Cells by Dexamethasone and Interleukin-1 β. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 22, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A. A SAF Binding Site in the Promoter Region of Human γ-Fibrinogen Gene Functions as an IL-6 Response Element. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 3411–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, M.; Nussbaumer, O.; Knofler, R.; Hengster, P.; Nussbaumer, W.; Streif, W. Real-Time Live Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy as a New Tool for Assessing Platelet Vitality. Transfus. Med. Hemotherapy: Off. Organ. Der Dtsch. Ges. Fur Transfus. Und Immunhamatol. 2010, 37, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, M.; Pirkebner, D.; Draxl, A.; Margreiter, R.; Hengster, P. “Real-time” assessment of human islet preparations with confocal live cell imaging. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 3409–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Schenk, B.; Bachler, M.; Solomon, C.; Fries, D.; Hermann, M. FITC-linked Fibrin-Binding Peptide and real-time live confocal microscopy as a novel tool to visualize fibrin(ogen) in coagulation. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2017, 3, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
| Demographics | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 27.0 ± 6.1 |
| Height (cm) | 170.0 ± 9.7 |
| Weight (kg) | 64.3 ± 9.6 |
| Blood count | |
| Leukocytes (G/L) | 5.6 ± 1.0 |
| Erythrocytes (T/L) | 4.6 ± 0.4 |
| Haemoglobin (g/L) | 136.2 ± 10.7 |
| Haematocrit (L/L) | 0.4 ± 0.0 |
| MCH (pg) | 29.9 ± 1.1 |
| MCHC (g/L) | 343.5 ± 8.2 |
| MCV (fL) | 87.0 ± 3.30 |
| Red blood cell distribution (%) | 13.2 ± 0.8 |
| Thrombocytes (G/L) | 254.2 ± 51.1 |
| Mean platelet volume (f/L) | 10.8 ± 0.81 |
| Tigecycline Concentration (µg/mL) | Baseline | 0.106 | 1.06 | 10.6 | 106 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aPTT (s) | 29.38 ± 2.26 | 29.38 ± 2.10 | 29.62 ± 2.33 | 29.69 ± 2.56 | 38.92 ± 5.22 1 |
| Quick (%) | 91.46 ± 7.32 | 91.00 ± 6.40 | 89.46 ± 7.43 | 90.85 ± 8.29 | 85.00 ± 5.92 |
| International Normalized Ratio | 1.05 ± 0.07 | 1.05 ± 0.05 | 1.07 ± 0.06 | 1.05 ± 0.07 | 1.09 ± 0.06 |
| Fibrinogen by Clauss (mg/dL) | 266.69 ± 60.79 | 260.10 ± 61.23 | 258.20 ± 55.29 | 258.20 ± 49.57 | 258.10 ± 59.75 |
| Fibrinogen antigen (mg/dL) | 258.23 ± 34.47 | 245.20 ± 33.19 | 244.30 ± 33.73 | 241.50 ± 39.00 | 247.80 ± 34.76 |
| Thrombin time (s) | 20.38 ± 1.76 | 19.92 ± 1.80 | 20.15 ± 1.73 | 19.77 ± 1.88 | 20.38 ± 1.98 |
| Batroxobin time (s) | 16.38 ± 0.51 | 16.31 ± 0.75 | 16.23 ± 0.60 | 16.15 ± 0.55 | 16.23 ± 0.44 |
| F. XIII (%) | 108.44 ± 13.93 | 114.30 ± 16.06 | 113.70 ± 17.85 | 114.20 ± 15.85 | 112.20 ± 16.15 |
| F. XIII, immunologic (%) | 103.18 ± 9.23 | 106.10 ± 10.97 | 105.50 ± 10.42 | 105.90 ± 8.93 | 105.60 ± 9.12 |
| Tigecycline Concentration (µg/mL) | Baseline | 0.106 | 1.06 | 10.6 | 106 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INTEM | |||||
| Clotting Time (s) | 189.3 ± 19.4 | 194 ± 39 | 194 ± 27 | 182 ± 54 | 192 ± 22 |
| Maximum Clot Firmness (mm) | 56.5 ± 4.3 | 58 ± 5 | 57 ± 5 | 57 ± 5 | 58 ± 5 |
| Maximum Lysis (%) | 11.0 ± 2.2 | 10 ± 2 | 9 ± 2 | 10 ± 2 | 11 ± 2 |
| EXTEM | |||||
| Clotting Time (s) | 75.0 ± 9.2 | 76 ± 10 | 72 ± 6 | 72 ± 11 | 79 ± 12 |
| Maximum Clot Firmness (mm) | 61.2 ± 5.6 | 61 ± 6 | 59 ± 6 | 60 ± 6 | 61 ± 7 |
| Maximum Lysis (%) | 9.2 ± 1.9 | 9 ± 2 | 9 ± 2 | 9 ± 2 | 9 ± 3 |
| FIBTEM | |||||
| Clotting Time (s) | 63.8 ± 16.3 | 71 ± 7 | 68 ± 17 | 67 ± 10 | 72 ± 9 |
| Maximum Clot Firmness (mm) | 13.9 ± 5.3 | 11 ± 4 | 13 ± 2 | 15 ± 6 | 12 ± 2 |
| Maximum Lysis (%) | 3.6 ± 5.4 | 2 ± 4 | 4 ± 3 | 9 ± 11 | 2 ± 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandtner, A.; Bachler, M.; Fries, D.; Hermann, M.; Ruehlicke, J.; Fux, V.; Griesmacher, A.; Niederwanger, C.; Hell, T.; Treml, B. Tigecycline Interferes with Fibrinogen Polymerization Independent of Peripheral Interactions with the Coagulation System. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020084
Brandtner A, Bachler M, Fries D, Hermann M, Ruehlicke J, Fux V, Griesmacher A, Niederwanger C, Hell T, Treml B. Tigecycline Interferes with Fibrinogen Polymerization Independent of Peripheral Interactions with the Coagulation System. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020084
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandtner, Anna, Mirjam Bachler, Dietmar Fries, Martin Hermann, Jacqueline Ruehlicke, Vilmos Fux, Andrea Griesmacher, Christian Niederwanger, Tobias Hell, and Benedikt Treml. 2020. "Tigecycline Interferes with Fibrinogen Polymerization Independent of Peripheral Interactions with the Coagulation System" Antibiotics 9, no. 2: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020084
APA StyleBrandtner, A., Bachler, M., Fries, D., Hermann, M., Ruehlicke, J., Fux, V., Griesmacher, A., Niederwanger, C., Hell, T., & Treml, B. (2020). Tigecycline Interferes with Fibrinogen Polymerization Independent of Peripheral Interactions with the Coagulation System. Antibiotics, 9(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020084





