Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Composite Polyethylene Materials Reinforced with Neem and Turmeric
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
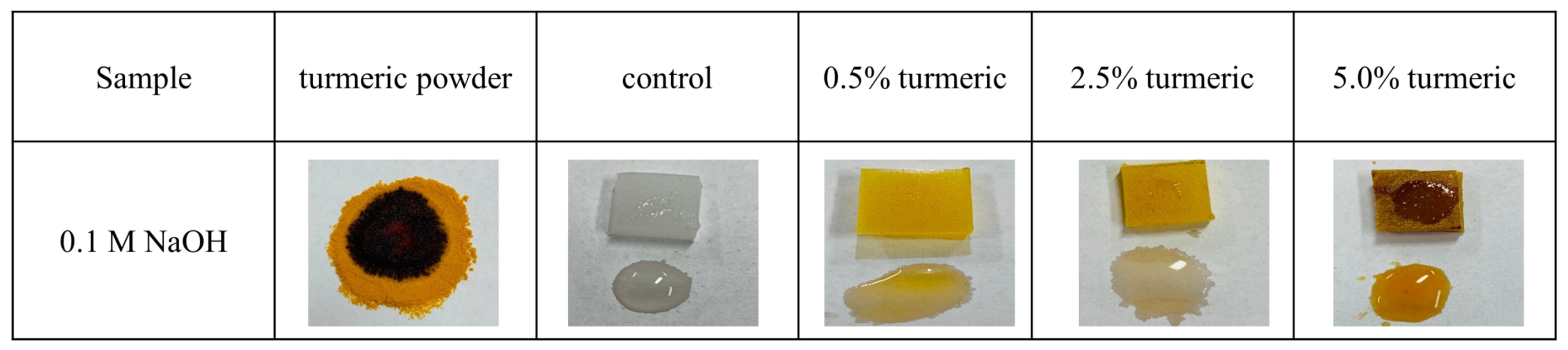
2.1. Samples Production
2.2. Samples’ Characterization
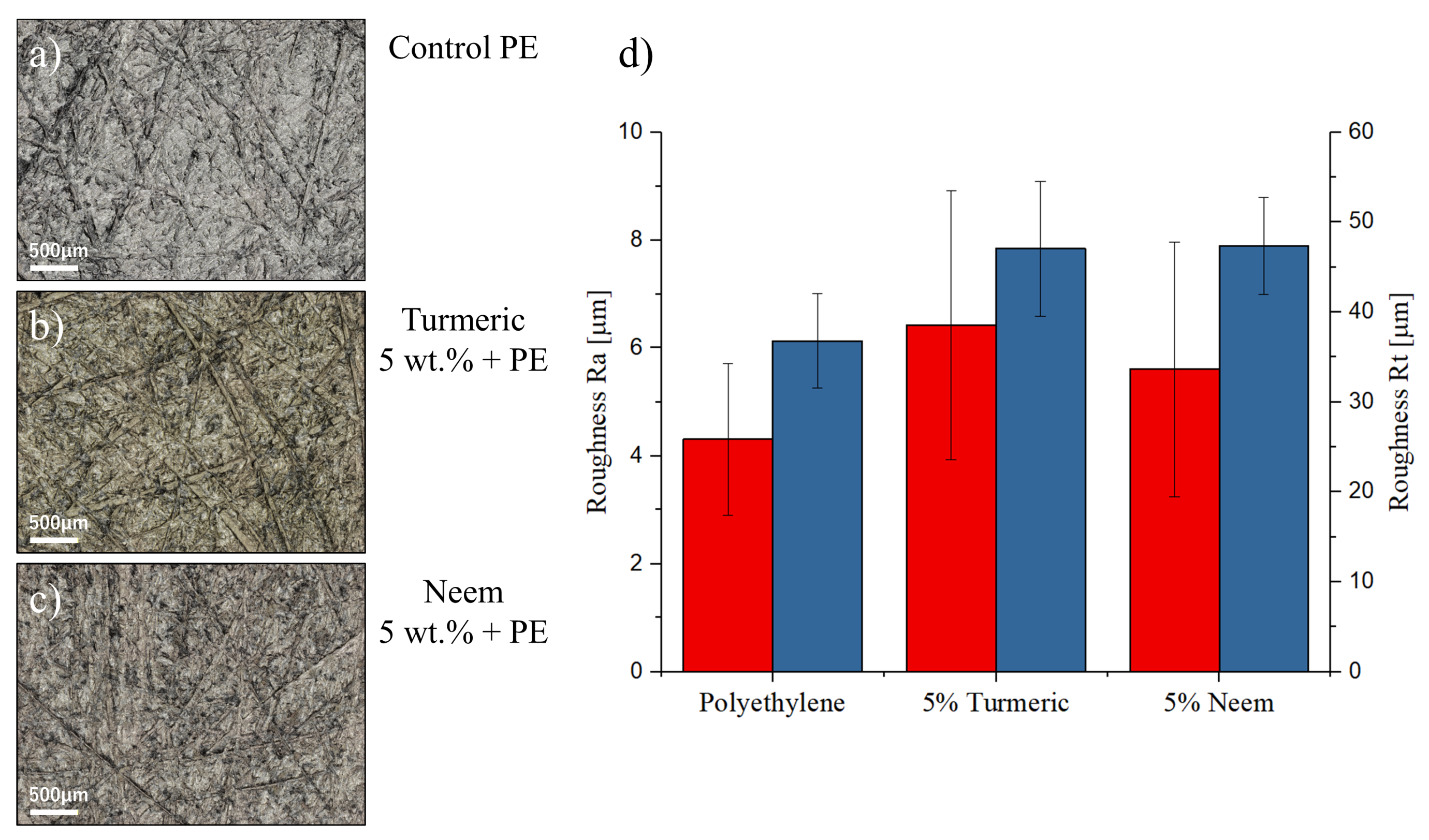
2.2.1. Laser Microscopy
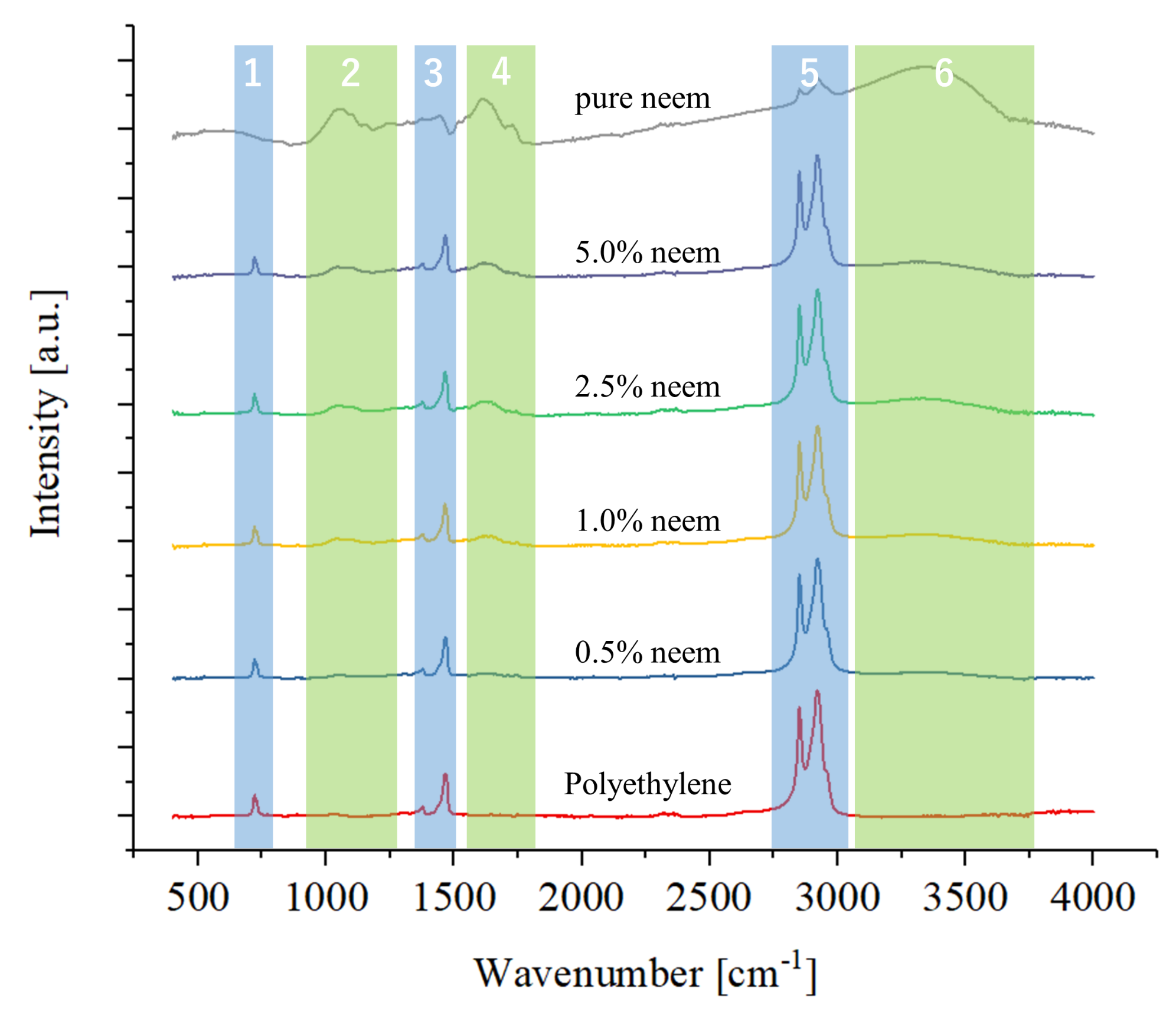
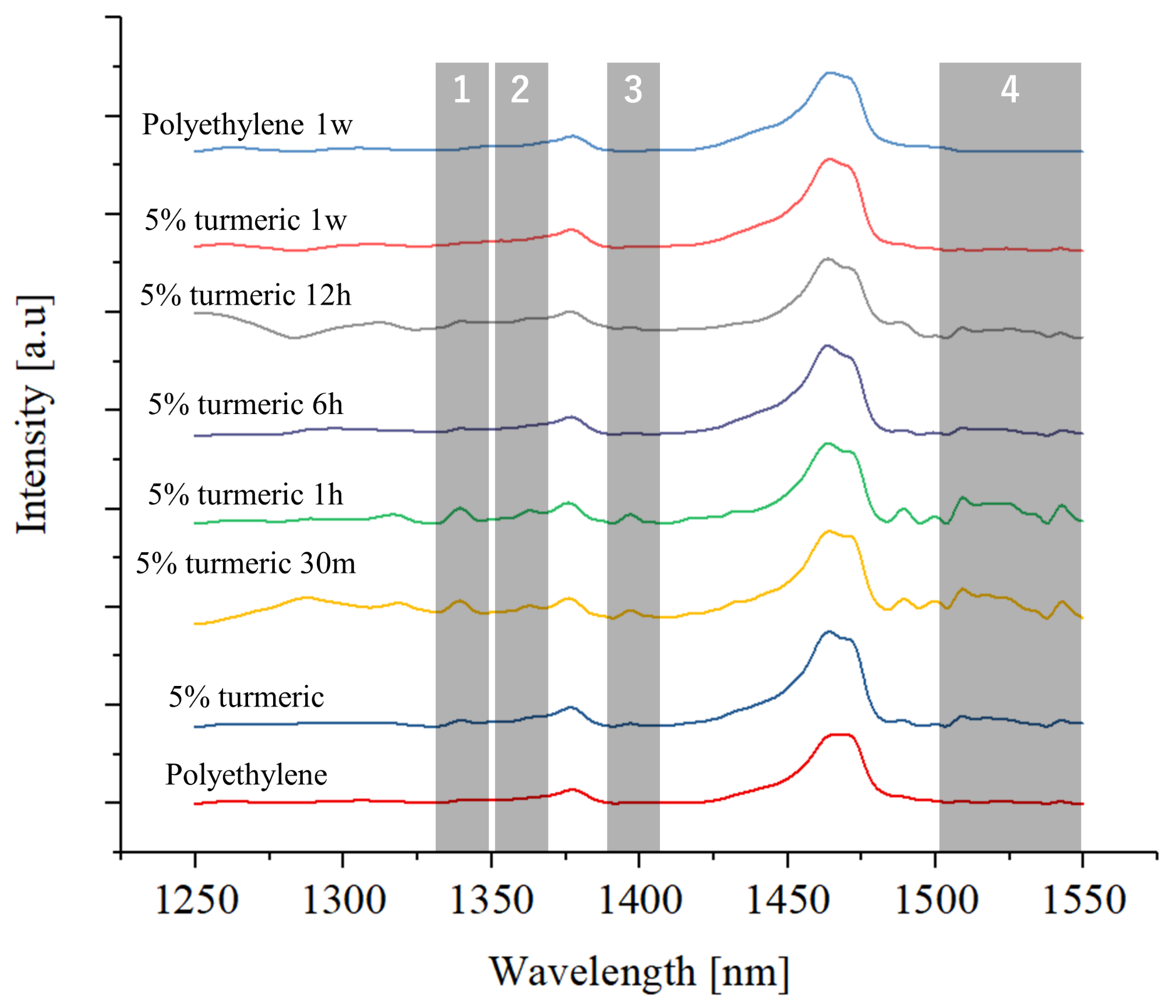
2.2.2. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
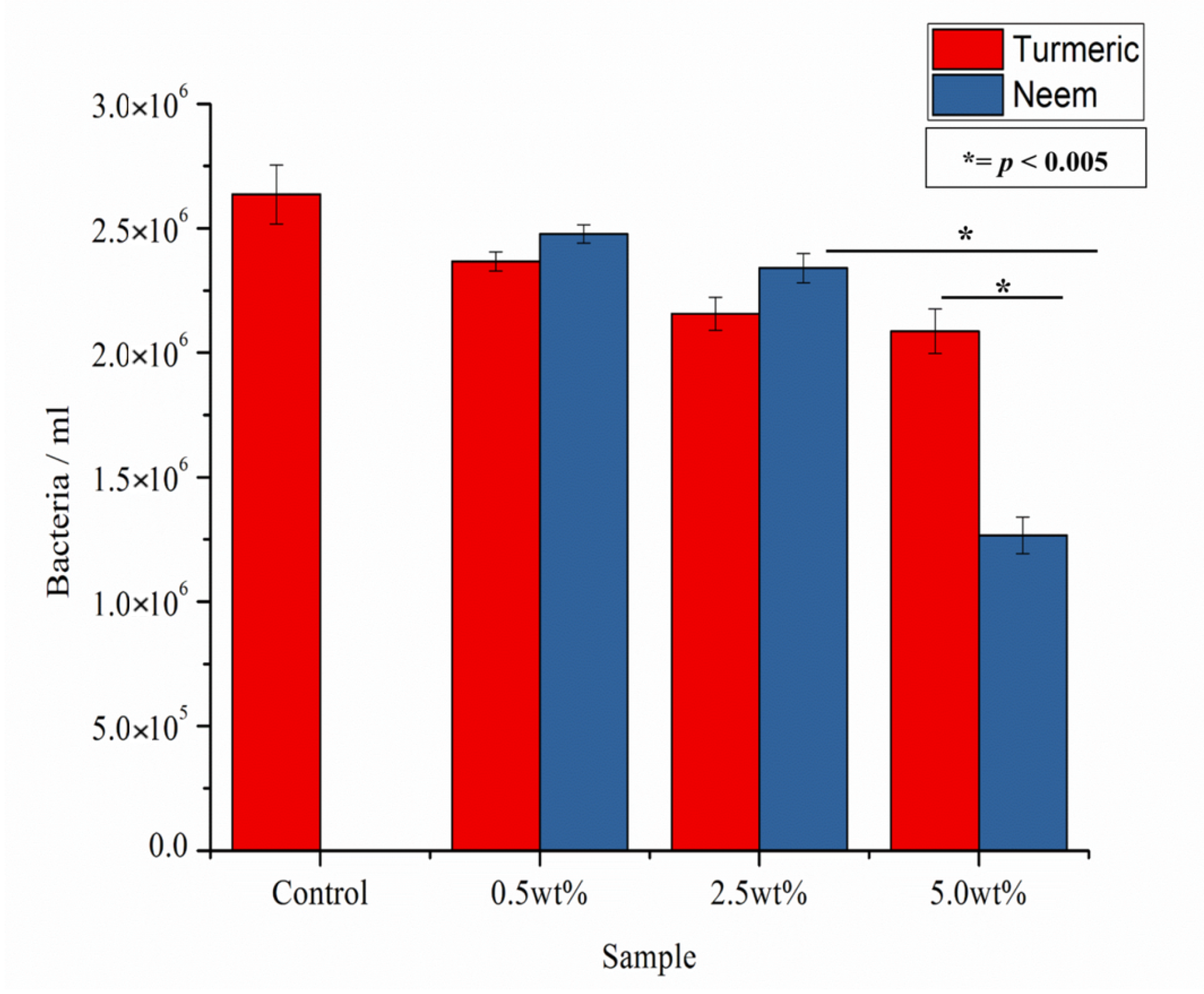
2.2.3. In Vitro Bacteria and Fungi Cultures
2.3. Biological Characterization
Colony Forming Units
2.4. Aging and Mechanical Testing
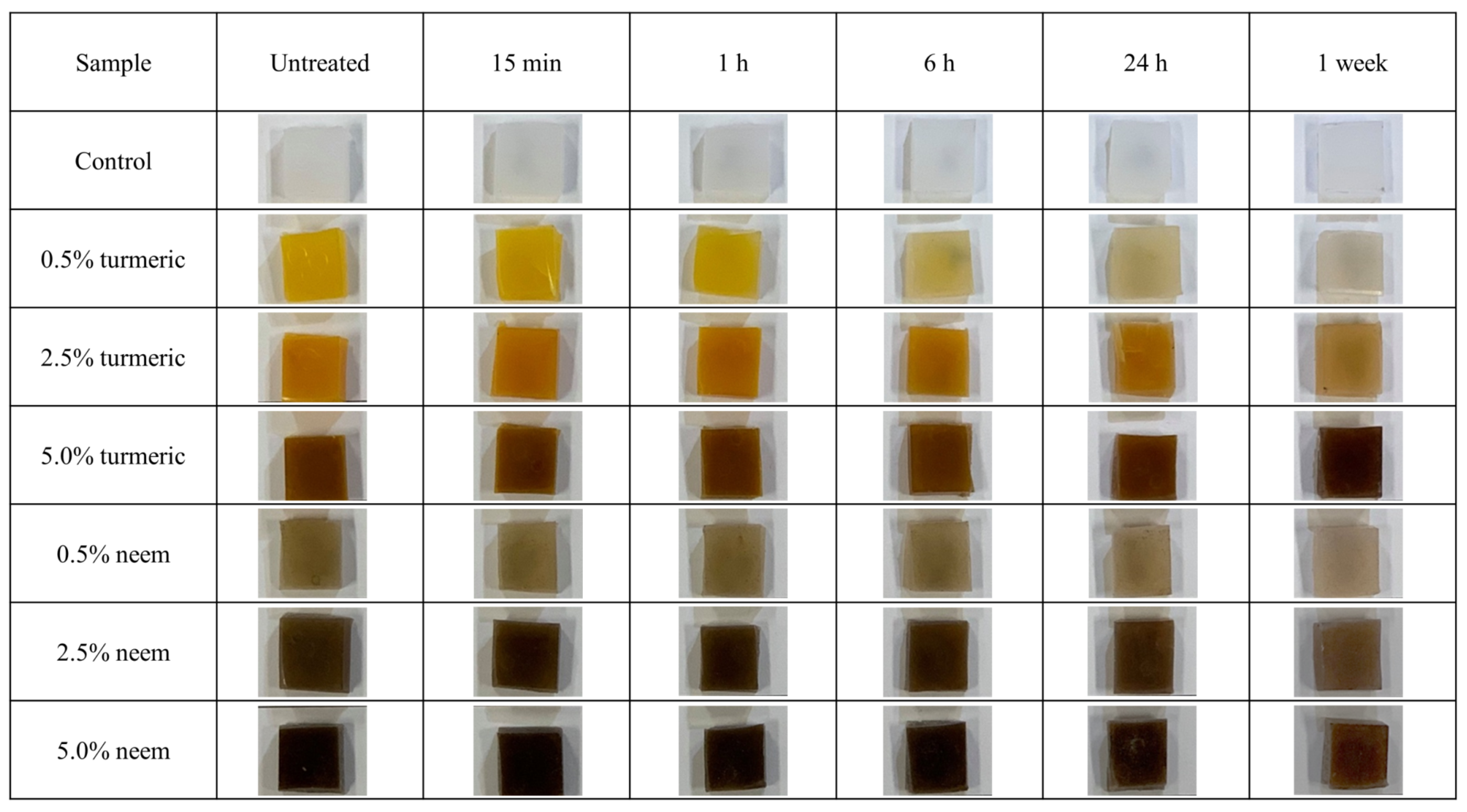
2.4.1. UV-Aging
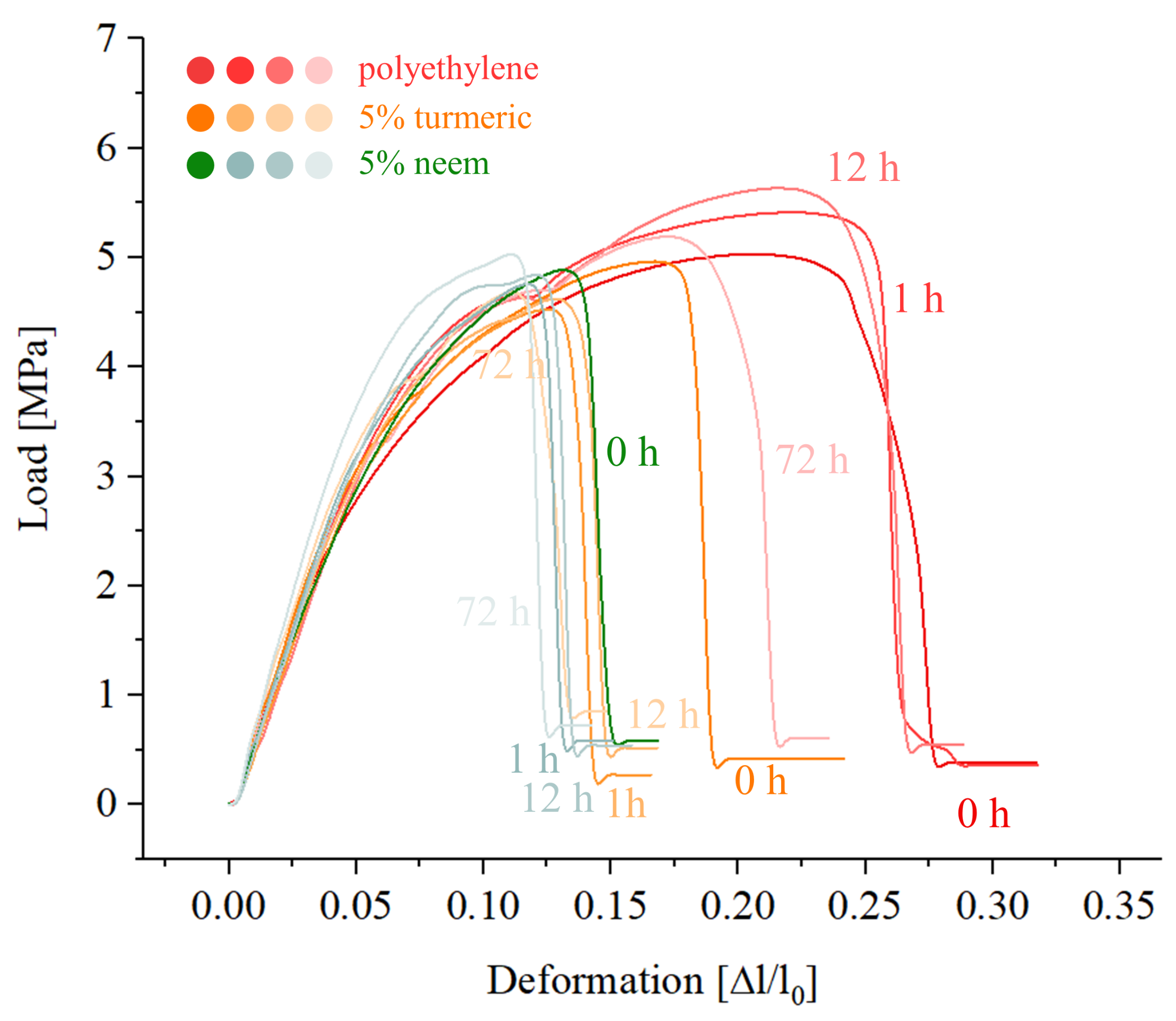
2.4.2. Mechanical Testing
3. Results
Surface Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cogan, J.A., Jr. The Uneasy Case for Food Safety Liability Insurance. Brook. L. Rev. 2015, 81, 1495. [Google Scholar]
- Estimates of Foodborne Illness in the United States, CTRS. For Disease Control & Prevention (Jan. 8, 2014) [Hereinafter Estimates of Foodborne Illness]. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden; https://perma.cc/986Y-VPZC; (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- “Enteric infections,” such as E. coli, Salmonella, Norovirus, and Listeria, “Enter the Body through the Mouth and Intestinal Tract and are Usually Spread through Contaminated Food and Water or by Contact with Vomit or Feces.” Enteric Diseases Epidemiology Branch, CTRS. For Disease Control & Prevention (Apr. 23, 2013). Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/dfwed/edeb/; http://perma.cc/7FK6-KK9X; (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Kovats, R.S.; Edwards, S.J.; Hajat, S.; Armstrong, B.G.; Ebi, K.L.; Menne, B. The effect of temperature on food poisoning: A time-series analysis of salmonellosis in ten European countries. Epidemiol. Infect. 2004, 132, 443–453. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, D. Food safety in low and middle income countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10490–10507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- James, S.J.; James, C. The food cold-chain and climate change. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Martins Alves, M. Discolouration Complaints in Minced Meat. Do the Food Miles Travelling affect the Customer Complaints? Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Plymouth, Plymouth, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Galgamuwa, L.S.; Iddawela, D.; Dharmaratne, S.D. Knowledge and practices of food hygiene among food handlers in plantation sector, Sri Lanka. Int. J. Sci. Rep. 2016, 2, 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahale, K.; Sousa, S.; Albuquerque, G.; Padrão, P.; Lunet, N. Street food research worldwide: A scoping review. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 32, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavico, F.J.; Mujtaba, B.G.; Muffler, S.; Samuel, M.; Polito, N.M. Manufacturer, supermarket, and grocer liability for contaminated food and beverages due to negligence, warranty, and liability laws. Economy 2018, 5, 17–39. [Google Scholar]
- Worsfold, D.; Worsfold, P.M.; Griffith, C.J. An assessment of food hygiene and safety at farmers’ markets. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2004, 14, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Mortlock, M.P.; Peters, A.C.; Griffith, C.J. A national survey of food hygiene training and qualification levels in the UK food industry. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2000, 10, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Redmond, E.C.; Griffith, C.J. Consumer perceptions of food safety risk, control and responsibility. Appetite 2004, 43, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission. Codex Alimentarius; Food & Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Roma, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Legnani, P.; Leoni, E.; Berveglieri, M.; Mirolo, G.; Alvaro, N. Hygienic control of mass catering establishments, microbiological monitoring of food and equipment. Food Control 2004, 15, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Betta, G.; Barbanti, D.; Massini, R. Food Hygiene in aseptic processing and packaging system: A survey in the Italian food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galotto, M.J.; Ulloa, P.A.; Hernández, D.; Fernández-Martín, F.; Gavara, R.; Guarda, A. Mechanical and thermal behaviour of flexible food packaging polymeric films materials under high pressure/temperature treatments. Packag. Technol. Sci. Int. J. 2008, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, D.; Turner, R.K. Packaging waste and the polluter pays principle: A taxation solution. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 1992, 35, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, V.; Rocculi, P.; Romani, S.; Dalla, R.M. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior, E.; Braganca, R.M.; Fowler, P. Lightweight compostable packaging: Literature review. Waste Resour. Action Programme 2006, 26, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Grigore, M.E. Methods of recycling, properties and applications of recycled thermoplastic polymers. Recycling 2017, 2, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, D.S.; Chinnan, M.S. Biopolymer-based antimicrobial packaging: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 223–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zorofchian Moghadamtousi, S.; Abdul Kadir, H.; Hassandarvish, P.; Tajik, H.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Shahab-Uddin, A.A.; Usmanghani, K.H.A.N.; Hannan, A.B.D.U.L.; Mohiuddin, E.; Asif, M. Curcuma longa and curcumin: A review article. Rom. J. Biol. Plant Biol. 2010, 55, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jaisinghani, R.N. Antibacterial properties of quercetin. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ododo, M.M.; Choudhury, M.K.; Dekebo, A.H. Structure elucidation of β-sitosterol with antibacterial activity from the root bark of Malva parviflora. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulmine, J.V.; Janissek, P.R.; Heise, H.M.; Akcelrud, L. Polyethylene characterization by FTIR. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, L.Q.; Niu, J.; Liu, W.; Peng, S.F.; Liu, C.M. The stability, sustained release and cellular antioxidant activity of curcumin nanoliposomes. Molecules 2015, 20, 14293–14311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, C.M.; Prabhawathi, V.; Sivakumar, P.M.; Doble, M. Design of a papain immobilized antimicrobial food package with curcumin as a crosslinker. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, O.N.; Schneider, C. Vanillin and ferulic acid: Not the major degradation products of curcumin. Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, O.N.; Luis, P.B.; Sintim, H.O.; Schneider, C. Unraveling curcumin degradation autoxidation proceeds through spiroepoxide and vinylether intermediates en route to the main bicyclopentadione. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 4817–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, S.; Zvezdanović, J.; Marković, D. Chlorophyll degradation in aqueous mediums induced by light and UV-B irradiation: An UHPLC-ESI-MS study. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2017, 141, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarabi, A.; Honarvar, M.; Mizani, M.; Faghihian, H.; Gerami, A. Extraction and purification of ferulic acid as an antioxidant from sugar beet pulp by alkaline hydrolysis. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2016, 28, 362. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, P.; Singh, M.; Kumari, H.; Kumari, A.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Bactericidal activity of curcumin I is associated with damaging of bacterial membrane. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praditya, D.; Kirchhoff, L.; Brüning, J.; Rachmawati, H.; Steinmann, J.; Steinmann, E. Anti-infective properties of the golden spice curcumin. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzohairy, M.A. Therapeutics role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and their active constituents in diseases prevention and treatment. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, W.C.; Maramba, C.C.; Gonzales, M.L.M. An in-vitro study on the antibacterial effect of neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf extract on methicillin-sensitive and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PIDSP J. 2011, 12, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Afrose, R.; Saha, S.K.; Banu, L.A.; Ahmed, A.U.; Shahidullah, A.S.; Gani, A.; Ali, M.Y. Antibacterial Effect of Curcuma longa (Turmeric) Against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Mymensingh Med. J. MMJ 2015, 24, 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, M.F.G.; Sales, J.A.; da Rocha, M.G.; Galdino, L.M.; de Aguiar, L.; Pereira-Neto, W.D.A.; Brilhante, R.S.N. Antifungal effects of the flavonoids kaempferol and quercetin: A possible alternative for the control of fungal biofilms. Biofouling 2019, 35, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Turmeric | Neem |
|---|---|
| wt.% | wt.% |
| 0% (reference) | |
| 0.5% | 0.5% |
| 1.0% | 1.0% |
| 2.5% | 2.5% |
| 5.0% | 5.0% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunthar, T.P.M.; Marin, E.; Boschetto, F.; Zanocco, M.; Sunahara, H.; Ramful, R.; Kamei, K.; Zhu, W.; Pezzotti, G. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Composite Polyethylene Materials Reinforced with Neem and Turmeric. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120857
Sunthar TPM, Marin E, Boschetto F, Zanocco M, Sunahara H, Ramful R, Kamei K, Zhu W, Pezzotti G. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Composite Polyethylene Materials Reinforced with Neem and Turmeric. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(12):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120857
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunthar, Thefye P. M., Elia Marin, Francesco Boschetto, Matteo Zanocco, Hirofumi Sunahara, Raviduth Ramful, Kaeko Kamei, Wenliang Zhu, and Giuseppe Pezzotti. 2020. "Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Composite Polyethylene Materials Reinforced with Neem and Turmeric" Antibiotics 9, no. 12: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120857
APA StyleSunthar, T. P. M., Marin, E., Boschetto, F., Zanocco, M., Sunahara, H., Ramful, R., Kamei, K., Zhu, W., & Pezzotti, G. (2020). Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Composite Polyethylene Materials Reinforced with Neem and Turmeric. Antibiotics, 9(12), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120857







