Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of an Antimicrobial Peptide Synthesized with D Amino Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Activity In Vitro
2.2. Frequency of Selection of Resistant Mutants after Exposure to SET-M33D
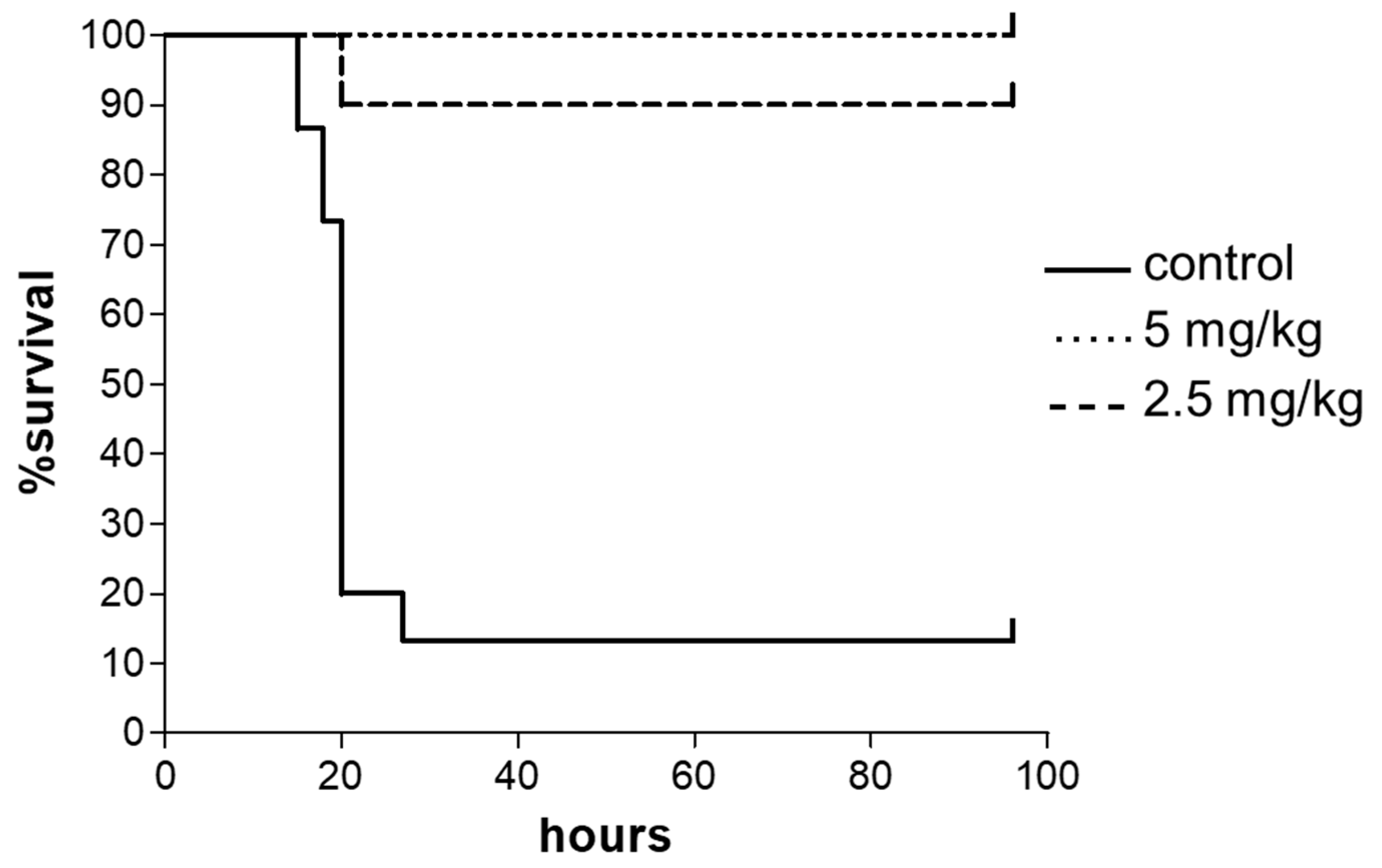
2.3. In Vivo Antimicrobial Efficacy of SET-M33D
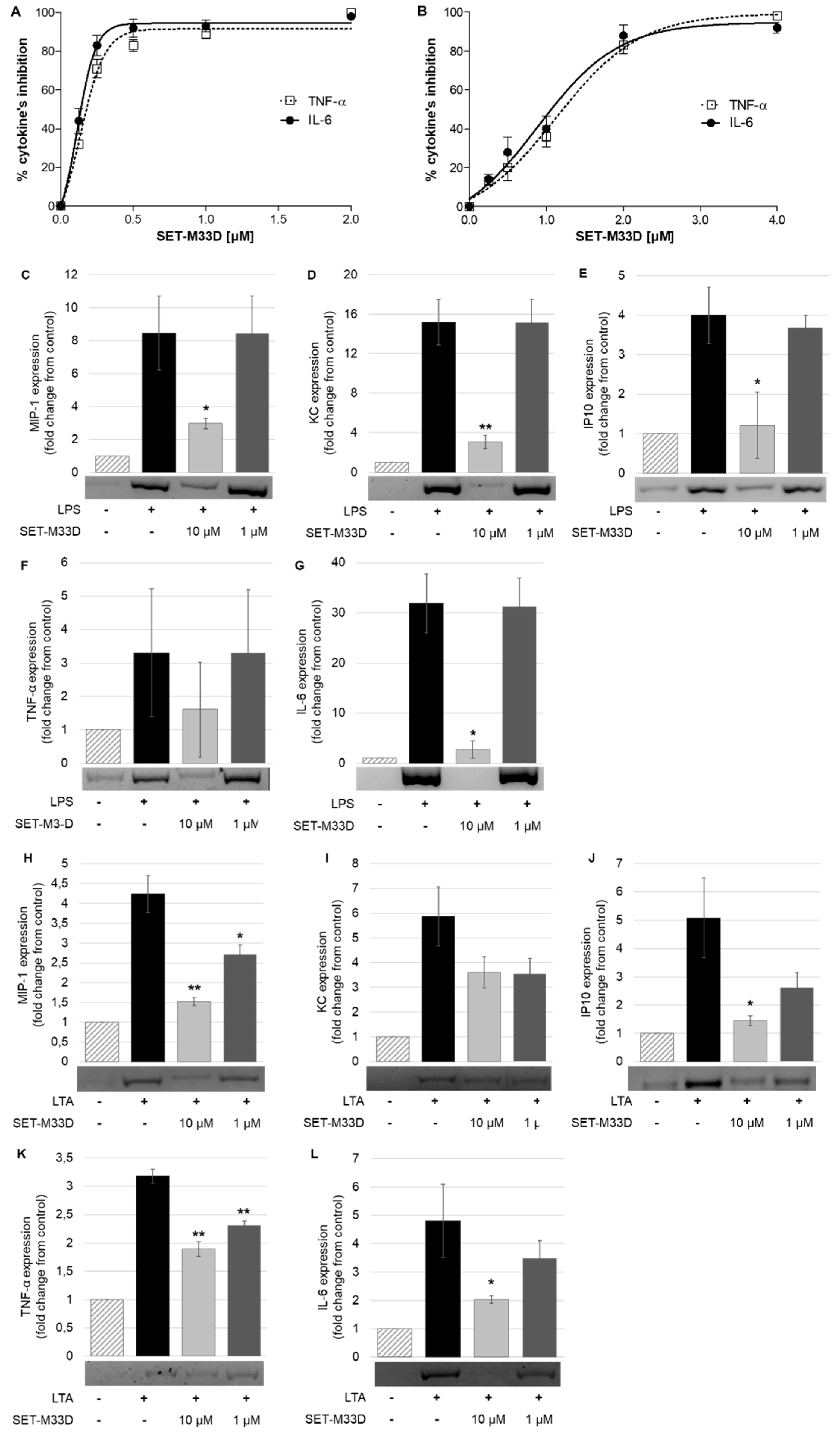
2.4. LPS and LTA Neutralization
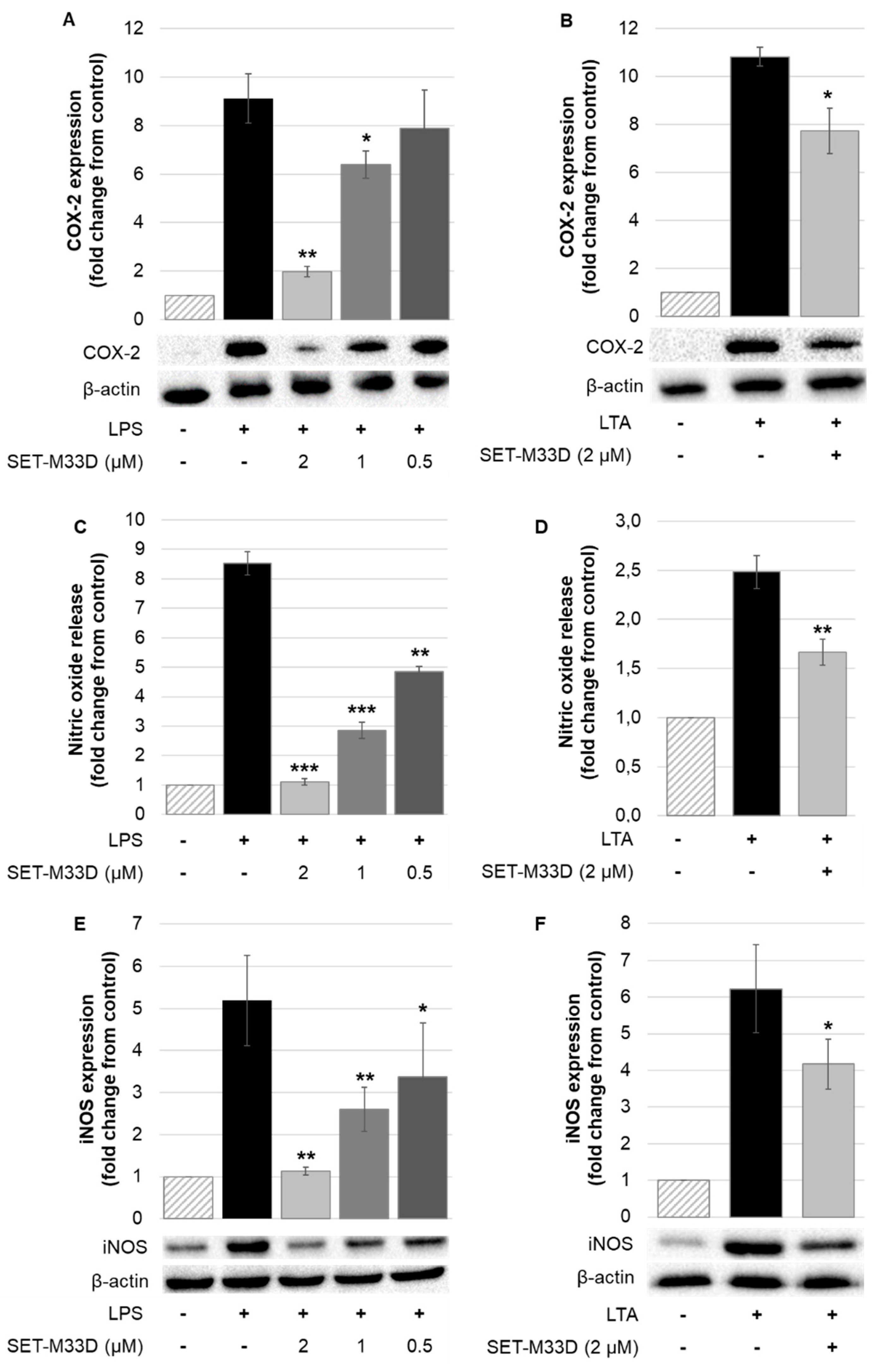
2.5. Inhibitory Effects of SET-M33D on COX-2 and iNOS Expression and Nitric Oxide Production
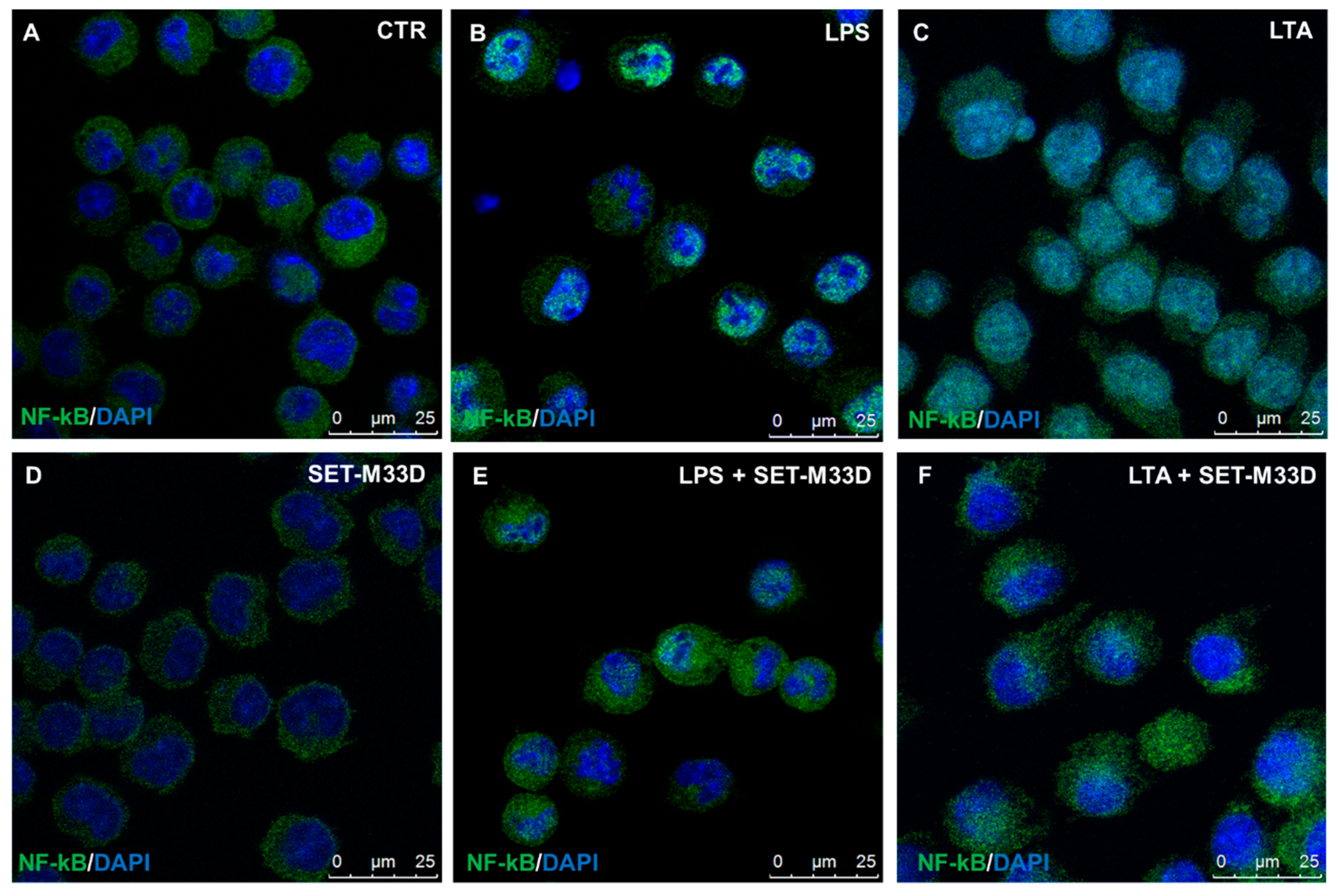
2.6. Effect of SET-M33D on NF-κB Nuclear Translocation
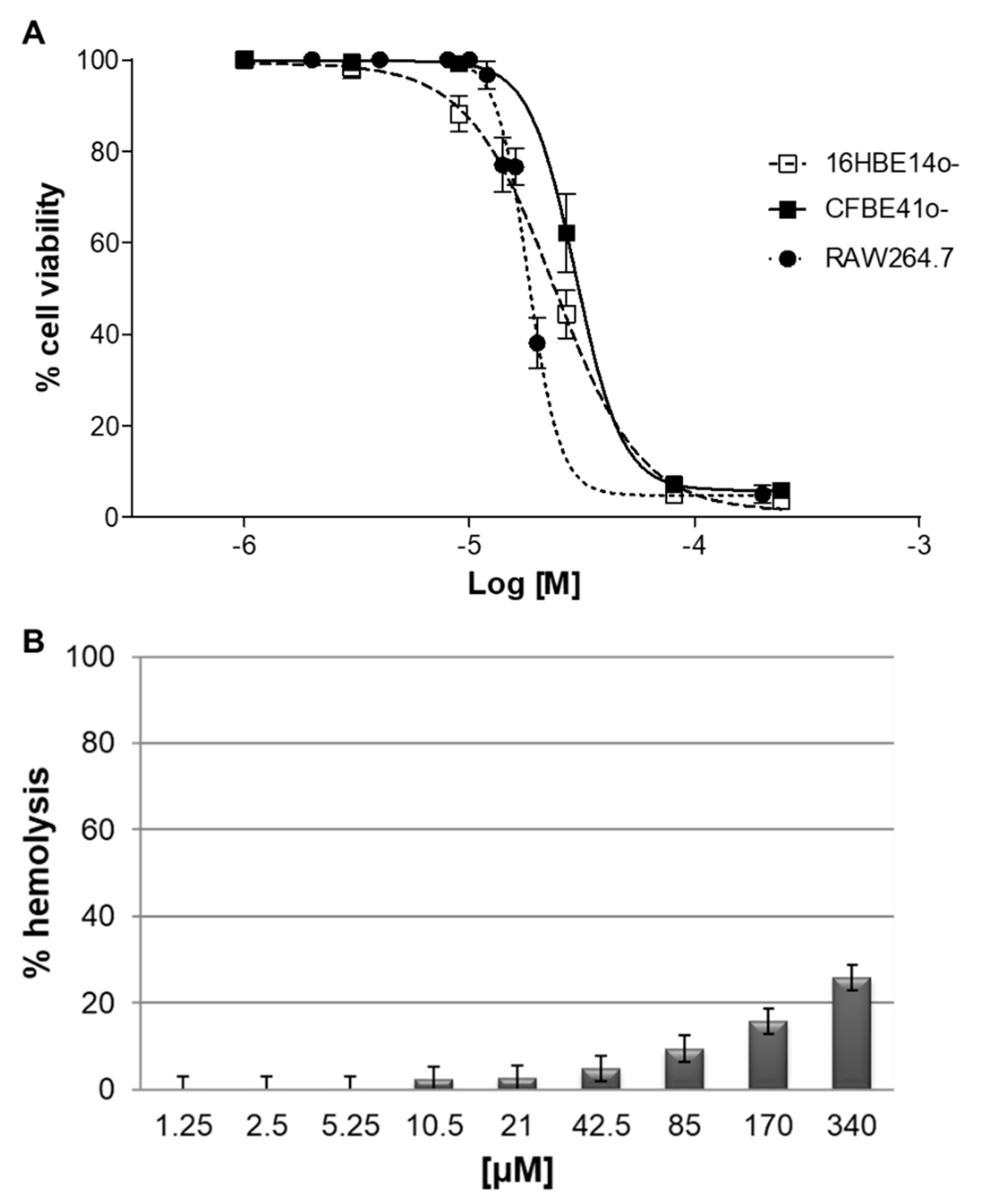
2.7. Cytotoxicity In Vitro
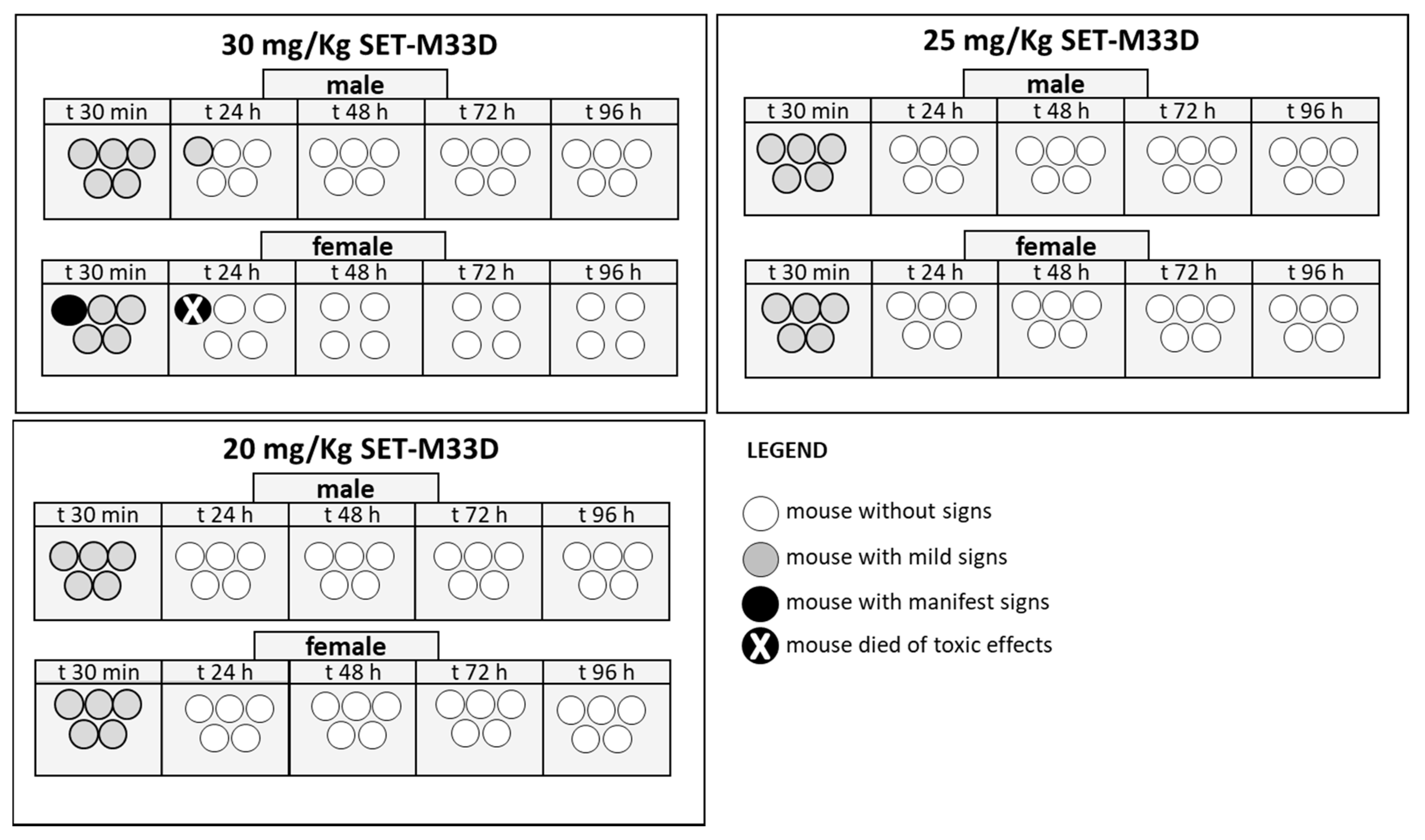
2.8. Acute Toxicity In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Peptide Synthesis
4.3. Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Selection of Resistant Mutants
4.5. In Vivo Efficacy
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. TNF-α and IL-6 Quantification
4.8. Gene Expression of Proinflammatory Factors
4.9. Nitrite Assay
4.10. Western Immunoblot Analysis
4.11. Immunofluorescence
4.12. Cell Viability Assay
4.13. Hemolytic Activity
4.14. Acute Toxicity In Vivo
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/112642 (accessed on 16 November 2019).
- Theuretzbacher, U. Global antibacterial resistance: The never-ending story. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2013, 1, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlapuu, M.; Hakansson, J.; Ringstad, L.; Bjorn, C. Antimicrobial peptides: An emerging category of therapeutic agents. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjya, S.; Straus, S.K. Design, Engineering and Discovery of Novel α-Helical and β-Boomerang Antimicrobial Peptides against Drug Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, A.M. Positively Charged Polymers as Promising Devices against Multidrug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensenn, H.; Hamill, P.; Hancock, R.E. Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, J.; Falciani, C.; Bracci, L.; Pini, A. Branched peptides as bioactive molecules for drug design. Pept. Sci. 2018, 110, e24089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.P. Synthetic peptide vaccine design: Synthesis and properties of a high density multiple antigenic peptide system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5409–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracci, L.; Falciani, C.; Lelli, B.; Lozzi, L.; Runci, Y.; Pini, A.; De Montis, M.G.; Tagliamonte, A.; Neri, P. Synthetic peptides in the form of dendrimers become resistant to protease activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46590–46595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciani, C.; Lozzi, L.; Pini, A.; Corti, F.; Fabbrini, M. Molecular basis of branched peptide resistance to enzyme proteolysis. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2007, 69, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, A.; Falciani, C.; Bracci, L. Branched peptides as therapeutics. Curr. Protein Pep. Sci. 2008, 9, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felício, M.R.; Silva, O.N.; Gonçalves, S.; Santos, N.C.; Franco, O.L. Peptides with Dual Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Front. Chem. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deslouches, B.; Di, Y.P. Antimicrobial peptides with selective antitumor mechanisms: Prospect for anticancer applications. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46635–46651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, D.W.; Heo, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Sim, E.J.; Kang, T.B.; Choi, J.W.; Sim, D.W.; Cheong, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Bang, J.K.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Action of an Antimicrobial Model Peptide That Suppresses the TRIF-Dependent Signaling Pathway via Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Endocytosis in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Pradeep, G.C.; Yoo, J.C.; Suh, J.W. A multifunctional alanine-rich anti-inflammatory peptide BCP61 showed potent inhibitory effects by inhibiting both NF-κB and MAPK expression. Inflammation 2017, 40, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Wong, G.C.L. Modulation of toll-like receptor signaling by antimicrobial peptides. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 88, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draing, C.; Sigel, S.; Deininger, S.; Traub, S.; Munke, R.; Mayer, C.; Hareng, L.; Hartung, T.; von Aulock, S.; Hermann, C. Cytokine induction by Gram-positive bacteria. Immunobiology 2008, 213, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.C.; Shen, S.C.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Prostaglandins as negative regulators against lipopolysaccharide, lipoteichoic acid, and peptidoglycan-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide production through reactive oxygen species-dependent heme oxygenase 1 expression in macrophages. Shock 2012, 38, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, A.; Giuliani, A.; Falciani, C.; Runci, Y.; Ricci, C.; Lelli, B.; Malossi, M.; Neri, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Bracci, L. Antimicrobial activity of novel dendrimeric peptides obtained by phage display selection and rational modification. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2665–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, A.; Giuliani, A.; Falciani, C.; Fabbrini, M.; Pileri, S.; Lelli, B.; Bracci, L. Characterization of the branched antimicrobial peptide M6 by analyzing its mechanism of action and in vivo toxicity. J. Pept. Sci. 2007, 13, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, A.; Falciani, C.; Mantengoli, E.; Bindi, S.; Brunetti, J.; Iozzi, S.; Rossolini, G.M.; Bracci, L. A novel tetrabranched antimicrobial peptide that neutralizes bacterial lipopolysaccharide and prevents septic shock in vivo. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, J.; Falciani, C.; Roscia, G.; Pollini, S.; Bindi, S.; Scali, S.; Arrieta, U.C.; Gómez-Vallejo, V.; Quercini, L.; Ibba, E.; et al. In vitro and in vivo efficacy, toxicity, bio-distribution and resistance selection of a novel antibacterial drug candidate. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quercini, L.; Brunetti, J.; Riolo, G.; Bindi, S.; Scali, S.; Lampronti, I.; D’Aversa, E.; Wronski, S.; Pollini, S.; Gentile, M.; et al. An antimicrobial molecule mitigates signs of sepsis in vivo and eradicates infections from lung tissue. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, J.; Roscia, G.; Lampronti, I.; Gambari, R.; Quercini, L.; Falciani, C.; Bracci, L.; Pini, A. Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Activity in Vitro and in Vivo of a Novel Antimicrobial Candidate. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25742–25748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Weide, H.; Brunetti, J.; Pini, A.; Bracci, L.; Ambrosini, C.; Lupetti, P.; Paccagnini, E.; Gentile, M.; Bernini, A.; Niccolai, N.; et al. Investigations into the killing activity of an antimicrobial peptide active against extensively antibiotic-resistant K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa. Biochim. Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciani, C.; Lozzi, L.; Pollini, S.; Luca, V.; Carnicelli, V.; Brunetti, J.; Lelli, B.; Bindi, S.; Scali, S.; Di Giulio, A.; et al. Isomerization of an Antimicrobial Peptide Broadens Antimicrobial Spectrum to Gram-Positive Bacterial Pathogens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, L.R.; Joshi, G.S.; Richardson, A.R. Virulence strategies of the dominant USA300 lineage of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, W.R.; Jarvis, A.A.; Chinn, R.Y. National prevalence of methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus in patients at United States health care facilities. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2010, 40, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, G.; Zhang, W.; Chen, K.; Bi, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, R. Structural design and antimicrobial properties of polypeptides and saccharide-polypeptide conjugates. J. Mater. Chem B. 2020, 8, 9173–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslouches, B.; Montelaro, R.C.; Urish, K.L.; Di, Y.P. Engineered Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides (eCAPs) to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Hall, K.N.; Aguilar, M.I. Antimicrobial peptide structure and mechanism of action: A focus on the role of membrane structure. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, E.F.; Straus, S.K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Reassessing the host defense peptide landscape. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Mitchell, J.A.; Appleton, I.; Tomlinson, A.; Bishop-Baley, D.; Croxtall, J.; Willoughby, D.A. Inducible form of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2046–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T. Pathogenesis of Septic Shock: Implications for Prevention and Treatment. J. Chemother. 2001, 1, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.H.; Jang, E.J.; Kwon, S.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, S.; Oh, S.R.; Lee, H.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Lee, H.J. A Novel Synthetic Compound, YH-1118, Inhibited LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response by Suppressing IkappaB Kinase/NF-kappaB Pathway in Raw 264.7 Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, K.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Kaur, J.; Venkatakrishnan, V.; Paulsen, I.T.; Nevalainen, H.; Molloy, M.P. Proteomics of hosts and pathogens in cystic fibrosis. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strain | Species | Relevant Features a | Relevant Resistance Genotype | MIC (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 700,699 Mu50 | Staphylococcus aureus | Reference strain, MR, GLY | 1.5 | |
| USA 300 | Staphylococcus aureus | MR | 1.5 | |
| SI-B | Staphylococcus aureus | MR | 3 | |
| SI-R | Staphylococcus aureus | MR | 1.5 | |
| FI-F | Staphylococcus aureus | none | 1.5 | |
| FI-4LNZ | Staphylococcus epidermidis | LIN | cfr | 0.7 |
| 4761/1 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | None | 0.3 | |
| ATCC 27840 | Staphylococcus capitis | Reference strain | 0.3 | |
| FI-1 | Staphylococcus saprophyticus | None | 0.7 | |
| FI-2 | Staphylococcus saprophyticus | None | 1.5 | |
| FI-3 | Staphylococcus saprophyticus | MR | 1.5 | |
| ATCC 29212 | Enterococcus faecalis | Reference strain | 3 | |
| FI-4 | Enterococcus faecalis | FQ, GLY | 1.5 | |
| FI-5 | Enterococcus faecalis | FQ | 3 | |
| FI-6 | Enterococcus faecalis | FQ | 3 | |
| FI81B1 | Enterococcus faecium | GLY | 0.7 | |
| FI81B2 | Enterococcus faecium | None | 0.7 | |
| PAO-1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Reference strain | 0.7 | |
| FI-8 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | 3 | |
| FI-9 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaVIM | 3 |
| FI-10 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | 3 | |
| FI-11 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaVIM | 3 |
| VR-143/97 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaVIM-1 | 3.0 |
| OBG6-1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaIMP-13 | 1.5 |
| RUH 875 | Acinetobacter baumannii | Reference strain, European clone I | 3.0 | |
| RUH 134 | Acinetobacter baumannii | Reference strain, European clone II | 3.0 | |
| MR 157 | Acinetobacter baumannii | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaOXA-58 | 6.0 |
| FI-13 | Escherichia coli | CARB, ESC, AG | blaKPC | 6 |
| FI-14 | Escherichia coli | ESC, FQ, AG | 1.5 | |
| FI-19 | Escherichia coli | AG, COL | mcr1.5 | 6 |
| FI-21 | Escherichia coli | COL | mcr1 | 6 |
| FI-22 | Escherichia coli | COL | mcr1 | 3 |
| FI-23 | Escherichia coli | COL | mcr1 | 3 |
| FI-24 | Escherichia coli | COL | mcr1 | 3 |
| MO-287 | Escherichia coli | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaNDM-1 | 3.0 |
| W03AN0041 | Enterobacter cloacae | ESC | blaSHV-12 | 1.5 |
| FI-15 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaKPC | 3 |
| FI-16 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaKPC | 3 |
| FI-17 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ | blaKPC | 6 |
| FI-18 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG | blaKPC | 3 |
| FI-20 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | CARB, β/I, ESC, FQ, AG, COL | mcr1.2, blaKPC | 6 |
| Strain | MIC SET-M33D (µM) | MIC Colistin (µM) | Mutation Frequency on SET-M33D | Mutation Frequency on Colistin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 1.5 | 0.35 | <6.6 × 10−10 * | 3.8 × 10−8 ± 1.9 × 10−8 |
| K. pneumoniae ATCC 13833 | 3 | 1.5 | <6.6 × 10−10 * | 3.2 × 10−8 ± 3.5 × 10−8 |
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 1.5 | - | 5.9 × 10 −9 ± 2.8 × 10−9 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brunetti, J.; Carnicelli, V.; Ponzi, A.; Di Giulio, A.; Lizzi, A.R.; Cristiano, L.; Cresti, L.; Cappello, G.; Pollini, S.; Mosconi, L.; et al. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of an Antimicrobial Peptide Synthesized with D Amino Acids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120840
Brunetti J, Carnicelli V, Ponzi A, Di Giulio A, Lizzi AR, Cristiano L, Cresti L, Cappello G, Pollini S, Mosconi L, et al. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of an Antimicrobial Peptide Synthesized with D Amino Acids. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(12):840. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120840
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunetti, Jlenia, Veronica Carnicelli, Alessia Ponzi, Antonio Di Giulio, Anna Rita Lizzi, Loredana Cristiano, Laura Cresti, Giovanni Cappello, Simona Pollini, Lara Mosconi, and et al. 2020. "Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of an Antimicrobial Peptide Synthesized with D Amino Acids" Antibiotics 9, no. 12: 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120840
APA StyleBrunetti, J., Carnicelli, V., Ponzi, A., Di Giulio, A., Lizzi, A. R., Cristiano, L., Cresti, L., Cappello, G., Pollini, S., Mosconi, L., Rossolini, G. M., Bracci, L., Falciani, C., & Pini, A. (2020). Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of an Antimicrobial Peptide Synthesized with D Amino Acids. Antibiotics, 9(12), 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120840









