Helicobacter pylori Infection and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases: The Role of Virulent Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prevalence of Overall H. pylori and CagA Positive H. pylori Infection
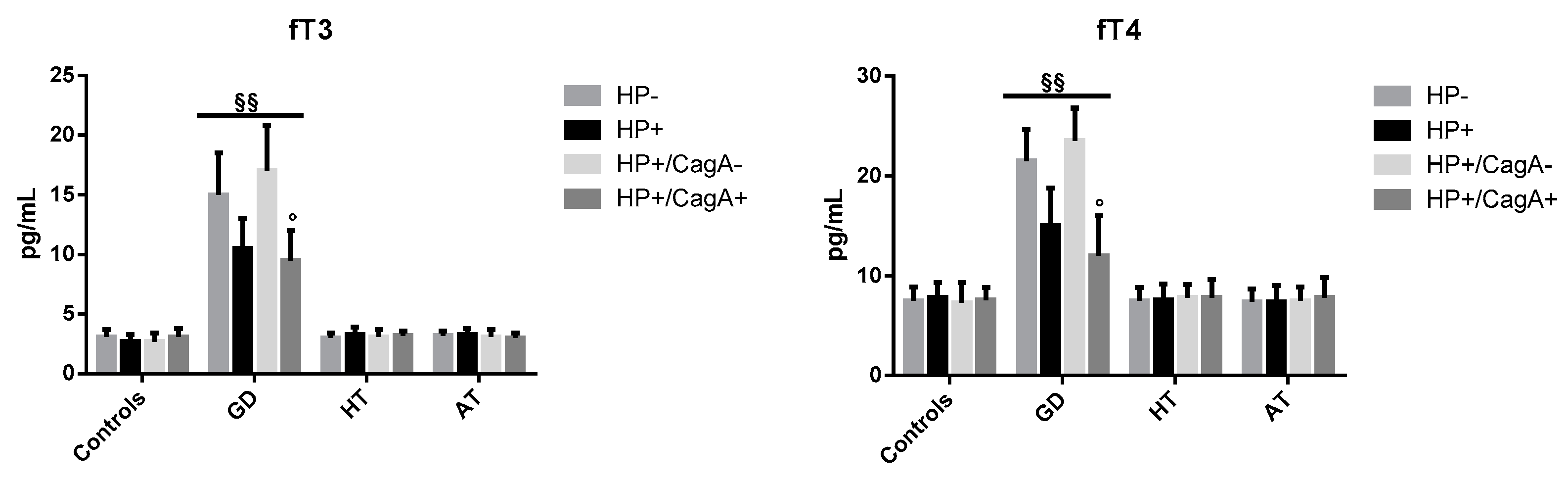
2.2. Levels of Thyroid Hormones
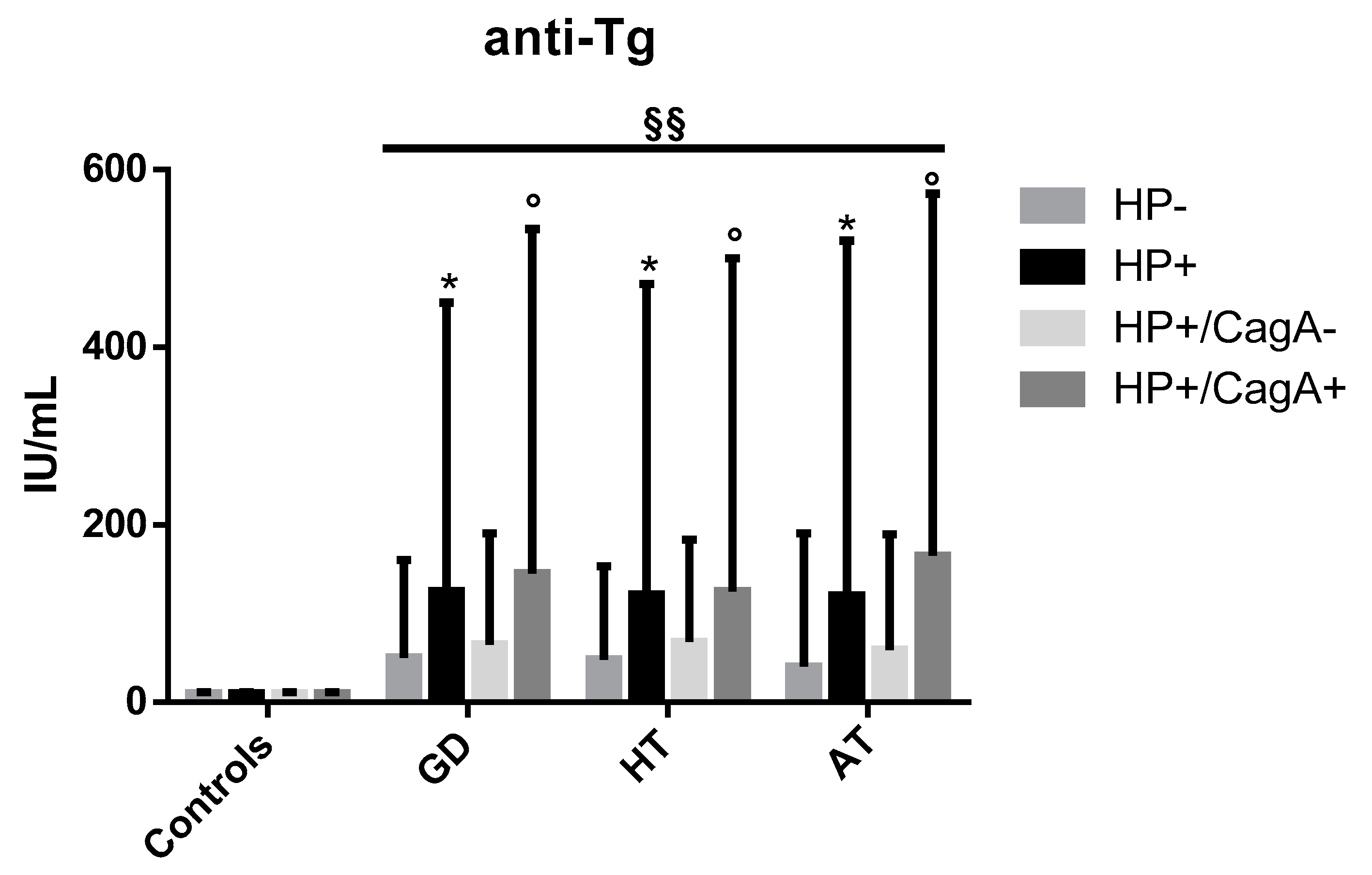
2.3. Levels of Anti-Tg Autoantibodies
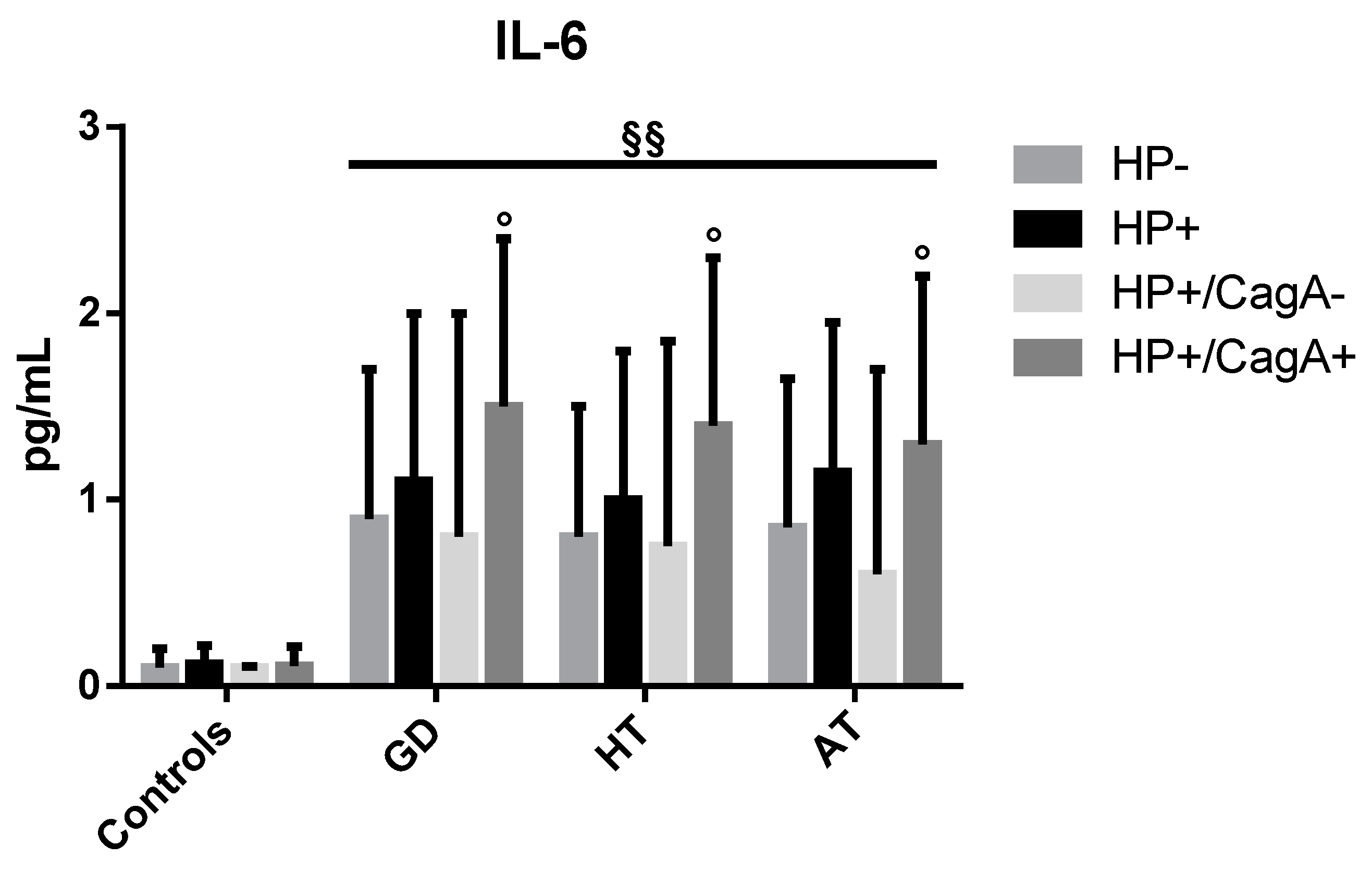
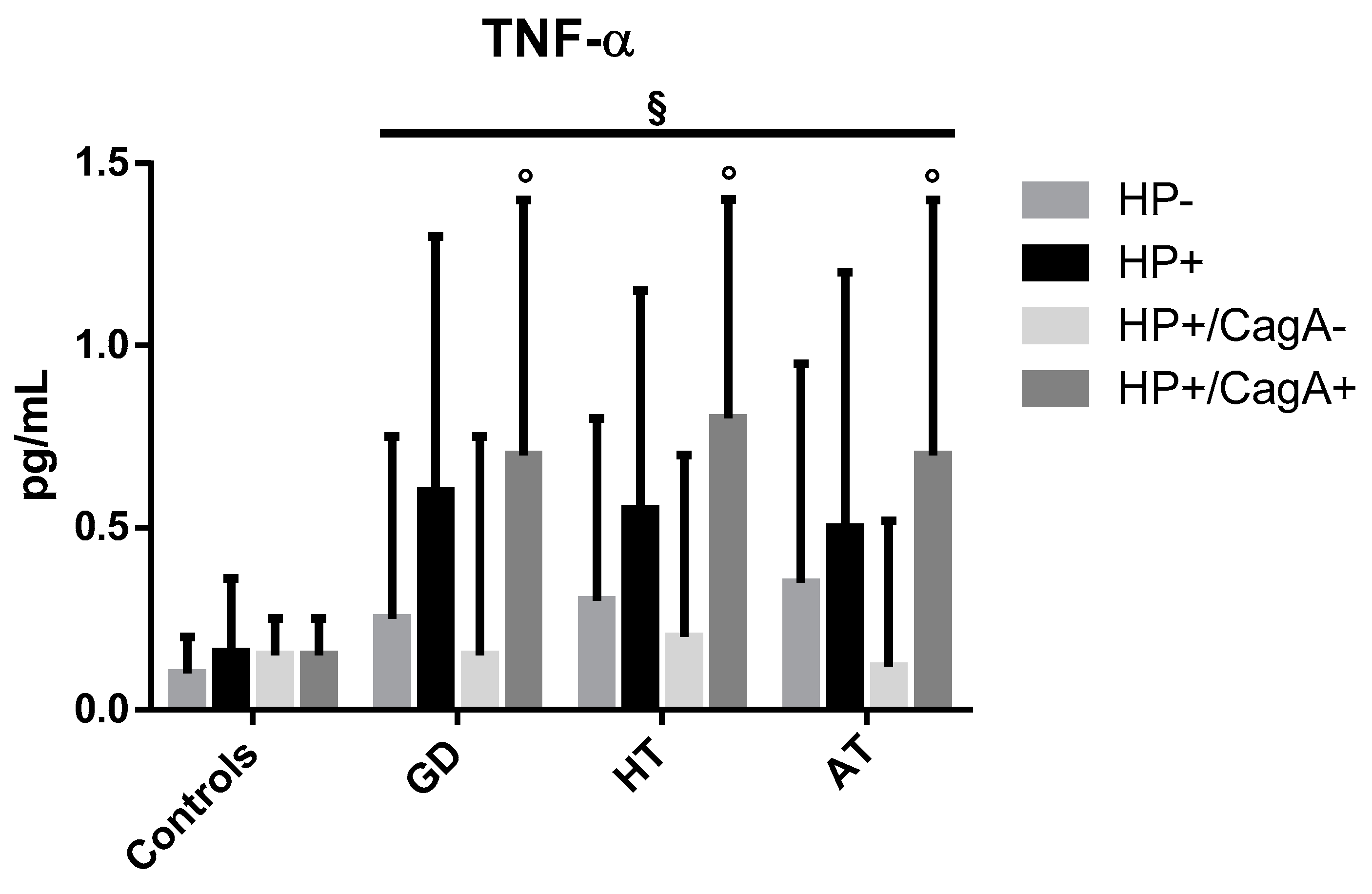
2.4. Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines
2.5. Alignments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Controls
4.2. Determination of Thyroid Hormones
4.3. Determination of Thyroid Autoantibodies
4.4. Determination of Inflammatory Cytokines
4.5. Diagnosis of Overall H. pylori Infection and CagA Status
4.6. Alignment (Bioinformatics)
- Thyroglobulin, 2767 aa protein, GenBank: CAA29104.1
- Thyroid peroxidase, 933 aa protein, GenBank: AAA61217.2
- Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor, 764 aa protein, GenBank: EAW81333.1
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooper, G.S.; Bynum, M.L.K.; Somers, E.C. Recent insights in the epidemiology of autoimmune diseases: Improved prevalence estimates and understanding of clustering of diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2009, 33, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.; Jeremias, P.; Matthias, T. The World Incidence and Prevalence of Autoimmune Diseases is Increasing. Int. J. Celiac Dis. 2016, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.J.; Rau, L.M. Autoimmune diseases: A leading cause of death among young and middle-aged women in the United States. Am. J. Public Health 2000, 90, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderpump, M.P.J. The epidemiology of thyroid disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 99, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrogan, A.; Seaman, H.E.; Wright, J.W.; de Vries, C.S. The incidence of autoimmune thyroid disease: A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Endocrinol. Oxf. 2008, 69, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, D.S.A.; Cooper, D.S. The incidence and prevalence of thyroid autoimmunity. Endocrine 2012, 42, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larizza, D.; Calcaterra, V.; Martinetti, M.; Negrini, R.; De Silvestri, A.; Cisternino, M.; Iannone, A.M.; Solcia, E. Helicobacter pylori infection and autoimmune thyroid disease in young patients: The disadvantage of carrying the human leukocyte antigen-DRB1*0301 allele. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, S.; Caturegli, P.; Piccolo, P.; Barbesino, G.; Pinchera, A. Antithyroid peroxidase autoantibodies in thyroid diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 71, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chardès, T.; Chapal, N.; Bresson, D.; Bès, C.; Giudicelli, V.; Lefranc, M.P.; Péraldi-Roux, S. The human anti-thyroid peroxidase autoantibody repertoire in Graves’ and Hashimoto’s autoimmune thyroid diseases. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, M.; Faustino, L.C. Genetics of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor—Relevance for Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. Front. Endocrinol. Lausanne 2017, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, G.; Figura, N.; Ponzetto, A.; Marzocchi, B.; Santucci, A. Application of proteomics to the study of Helicobacter pylori and implications for the clinic. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, D.; Ferraccioli, G.F.; De Vita, S.; Labombarda, A.; Boiocchi, M.; Bartoli, E. Helicobacter pylori infection and autoimmune processes: An emerging field of study. Ital. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 30, S310–S312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hyjek, E.; Isaacson, P.G. Primary B cell lymphoma of the thyroid and its relationship to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Hum. Pathol. 1988, 19, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, C.M.; Daniels, G.H. Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomb, J.F.; White, O.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Clayton, R.A.; Sutton, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Ketchum, K.A.; Klenk, H.P.; Gill, S.; Dougherty, B.A.; et al. The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 1997, 388, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, G.H.; Park, H.B.; Shin, M.K.; Park, C.K.; Lee, J.H.; Youn, H.S.; Cho, M.J.; Lee, W.K.; Rhee, K.H. Monoclonal antibodies against Helicobacter pylori cross-react with human tissue. Helicobacter 1997, 2, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figura, N.; Di Cairano, G.; Lorè, F.; Guarino, E.; Gragnoli, A.; Cataldo, D.; Giannace, R.; Vaira, D.; Bianciardi, L.; Kristodhullu, S.; et al. The infection by Helicobacter pylori strains expressing CagA is highly prevalent in women with autoimmune thyroid disorders. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 50, 817–826. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, N.; Granger, D.N.; Evans, D.J.; Evans, D.G.; Graham, D.Y.; Anderson, D.C.; Wolf, R.E.; Kvietys, P.R. Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collodel, G.; Moretti, E.; Campagna, M.S.; Capitani, S.; Lenzi, C.; Figura, N. Infection by CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains may contribute to alter the sperm quality of men with fertility disorders and increase the systemic levels of TNF-alpha. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, C.A.; Marques, C.R.; dos Santos Costa, R.; da Silva, H.B.F.; Alcantara-Neves, N.M. Cytokines, cytokine gene polymorphisms and Helicobacter pylori infection: Friend or foe? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5235–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, G.; Braconi, D.; Lusini, P.; Santucci, A. Helicobacter pylori: Immunoproteomics related to different pathologies. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2007, 4, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Osato, M.S.; Olson, C.A.; Zhang, J.; Figura, N. Effect of H. pylori infection and CagA status on leukocyte counts and liver function tests: Extra-gastric manifestations of H. pylori infection. Helicobacter 1998, 3, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yan, F. Chemokines as novel therapeutic targets in autoimmune thyroiditis. Recent Pat. DNA Gene Seq. 2010, 4, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Jang, E.K.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, W.G.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, W.B. Association between thyroid autoimmunity and Helicobacter pylori infection. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delitala, A.P.; Pes, G.M.; Errigo, A.; Maioli, M.; Delitala, G.; Dore, M.P. Helicobacter pylori CagA antibodies and thyroid function in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar]
- Bassi, V.; Marino, G.; Iengo, A.; Fattoruso, O.; Santinelli, C. Autoimmune thyroid diseases and Helicobacter pylori: The correlation is present only in Graves’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobsley, M.; Tovey, F.I.; Holton, J. How labile is gastric infection with H pylori? World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 4665–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weetman, A.; DeGroot, L.J. Autoimmunity to the Thyroid Gland; NCBI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2000.
- Gribetz, D.; Talbot, N.B.; Crawford, J.D. Goiter due to lymphocytic thyroiditis (Hashimoto’s struma); its occurrence in preadolescent and adolescent girls. N. Engl. J. Med. 1954, 250, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.S.; Ekiz, F.; Deveci, M.; Sahin, M.; Topaloglu, O.; Karbek, B.; Tutal, E.; Ginis, Z.; Cakal, E.; Ozbek, M.; et al. The relationship between cytotoxin-associated gene A positive Helicobacter pylori infection and autoimmune thyroid disease. Endocr. Res. 2015, 40, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, X.Y.; Ye, F.; Zhang, G.X. Associations of Helicobacter pylori infection and cytotoxin-associated gene A status with autoimmune thyroid diseases: A meta-analysis. Thyroid 2013, 23, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Qin, L.; Liu, T. Meta-analysis of the correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115691–115700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perri, F.; Clemente, R.; Festa, V.; De Ambrosio, C.C.; Quitadamo, M.; Fusillo, M.; Grossi, E.; Andriulli, A. Serum tumour necrosis factor-alpha is increased in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection and CagA antibodies. Ital. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 290–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmet, N.; Refik, M.; Harputluoglu, M.; Ersoy, Y.; Aydin, N.E.; Yildirim, B. Serum and gastric fluid levels of cytokines and nitrates in gastric diseases infected with Helicobacter pylori. New Microbiol. 2004, 27, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gianoukakis, A.G.; Khadavi, N.; Smith, T.J. Cytokines, Graves’ disease, and thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. Thyroid 2008, 18, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretz, J.D.; Arscott, P.L.; Myc, A.; Baker, J.R. Inflammatory cytokine regulation of Fas-mediated apoptosis in thyroid follicular cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25433–25438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafillidis, J.K.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Gikas, A.; Merikas, E.; Peros, G.; Sofroniadou, K.; Cheracakis, P.; Sklavaina, M.; Tzanidis, G.; Konstantellou, E. Relation between Helicobacter pylori infection, thyroid hormone levels and cardiovascular risk factors on blood donors. Hepatogastroenterology 2003, 50, cccxviii–cccxx. [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Fukuma, K.; Kuribayashi, K.; Masuda, T. Organ-specific autoimmune diseases induced in mice by elimination of T cell subset. I. Evidence for the active participation of T cells in natural self-tolerance; deficit of a T cell subset as a possible cause of autoimmune disease. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 161, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Lim, C.W.; Park, J.S.; Yeom, J.S.; Lim, J.Y.; Jun, J.S.; Woo, H.O.; Youn, H.S.; Baik, S.C.; Lee, W.K.; et al. Correlations between the CagA Antigen and Serum Levels of Anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG and IgA in Children. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, J.E.; Shallcross, T.M.; Heatley, R.V.; Wyatt, J.I. Mucosal tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut 1991, 32, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, J.E.; Lindley, I.J. Mucosal interleukin-8 and Helicobacter pylori-associated gastroduodenal disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1994, 6, S33–S38. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kita, M.; Kodama, T.; Sawai, N.; Kashima, K.; Imanishi, J. Induction of various cytokines and development of severe mucosal inflammation by cagA gene positive Helicobacter pylori strains. Gut 1997, 41, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Tsai, H.F.; Kuo, S.H.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, C.W.; Hsu, P.I.; Cheng, A.L.; Hsu, P.N. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into Human B lymphocytes, the origin of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5740–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mini, R.; Annibale, B.; Lahner, E.; Bernardini, G.; Figura, N.; Santucci, A. Western blotting of total lysate of Helicobacter pylori in cases of atrophic body gastritis. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahner, E.; Bernardini, G.; Possenti, S.; Renzone, G.; Scaloni, A.; Santucci, A.; Annibale, B. Immunoproteomics of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with atrophic body gastritis, a predisposing condition for gastric cancer. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| H. pylori/CagA Status | GD (%) | HT (%) | AT (%) | Controls (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HP+ | 26 (66.6) | 49 (64.4) | 15 (34.0) | 40 (29.4) |
| HP− | 13 (33.3) | 27 (35.5) | 29 (65.9) | 96 (70.5) |
| Total | 39 | 76 | 44 | 136 |
| HP+/CagA+ | 12 (46.1) | 23 (46.9) | 7 (46.6) | 8 (20.0) |
| HP+/CagA− | 14 (53.8) | 26 (53.0) | 8 (53.3) | 32 (80.0) |
| HP+ vs. HP− | Significance (p) | OR (95% CI) |
| GD vs. Controls | p < 0.001 | 4.8 (2.32–9.95) |
| HT vs. Controls | p < 0.001 | 4.36 (2.43–7.8) |
| GD vs. AT | p < 0.01 | 3.87 (1.57–9.51) |
| HT vs. AT | p < 0.001 | 3.51 (1.63–7.57) |
| HP+/CagA+ vs. HP+/CagA− | Significance (p) | OR (95% CI) |
| GD vs. Controls | p < 0.05 | 3.43 (1.17–10.07) |
| HT vs. Controls | p < 0.01 | 3.54 (1.38–9.05) |
| Human Proteins Aligned | Most Significantly Aligning Bacterial Proteins | Expectation Value | % of Identity | % of Positivity | % of Gaps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroglobulin | Toxin outer membrane protein (Sequence ID: WP_000713656.1) | 4.4 | 29 | 45 | 18 |
| Thyroid peroxidase | Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate synthase (sequence ID: WP_001210902.1) | 1.5 | 39 | 64 | 0 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor | NADH dehydrogenase subunit L (Sequence ID: WP_001200218.1) | 0.34 | 34 | 50 | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figura, N.; Di Cairano, G.; Moretti, E.; Iacoponi, F.; Santucci, A.; Bernardini, G.; Gonnelli, S.; Giordano, N.; Ponzetto, A. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases: The Role of Virulent Strains. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010012
Figura N, Di Cairano G, Moretti E, Iacoponi F, Santucci A, Bernardini G, Gonnelli S, Giordano N, Ponzetto A. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases: The Role of Virulent Strains. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigura, Natale, Giovanni Di Cairano, Elena Moretti, Francesca Iacoponi, Annalisa Santucci, Giulia Bernardini, Stefano Gonnelli, Nicola Giordano, and Antonio Ponzetto. 2020. "Helicobacter pylori Infection and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases: The Role of Virulent Strains" Antibiotics 9, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010012
APA StyleFigura, N., Di Cairano, G., Moretti, E., Iacoponi, F., Santucci, A., Bernardini, G., Gonnelli, S., Giordano, N., & Ponzetto, A. (2020). Helicobacter pylori Infection and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases: The Role of Virulent Strains. Antibiotics, 9(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010012









