Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Camphorimine Complexes against Candida Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
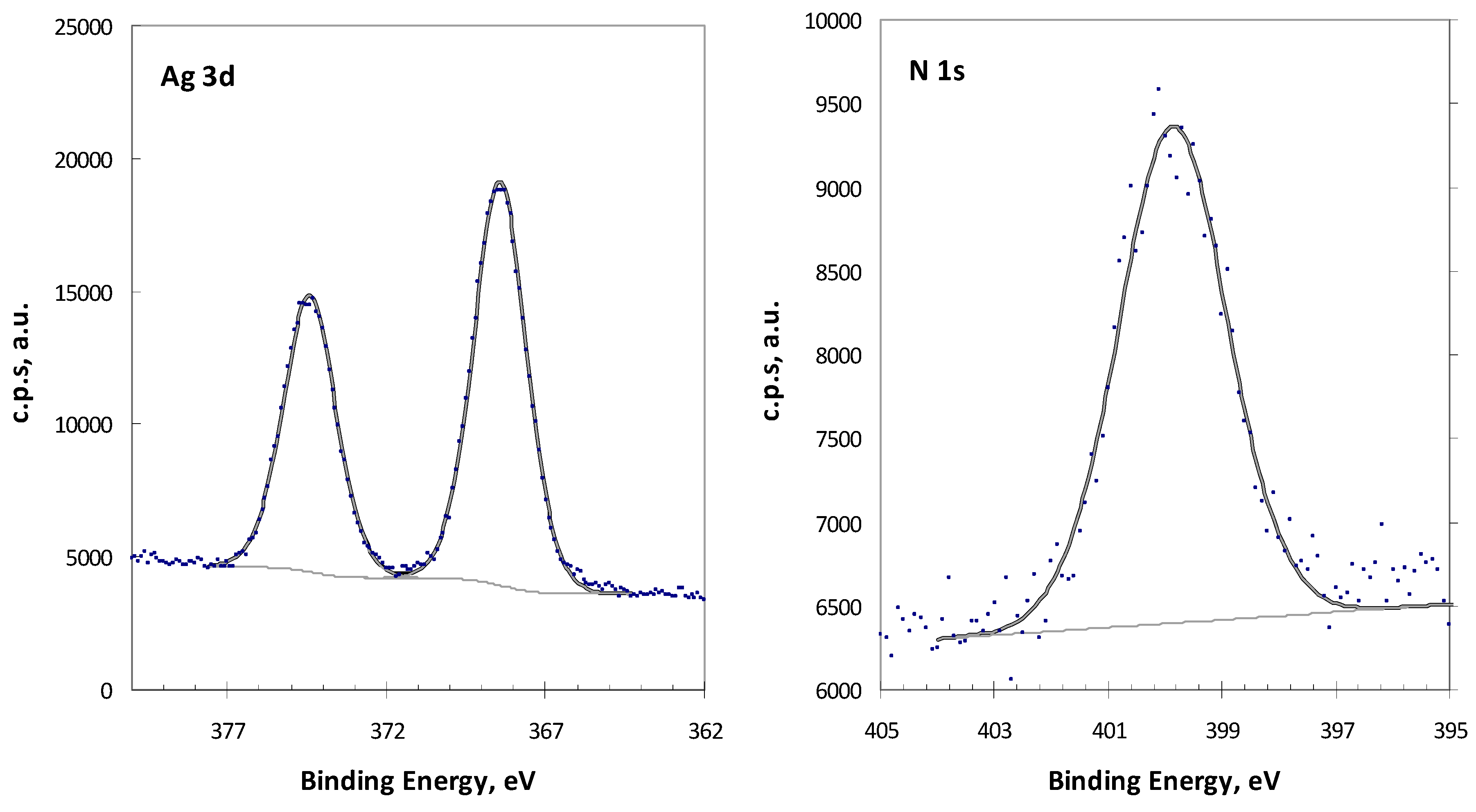
2.1. Analysis of Complex 1 by XPS
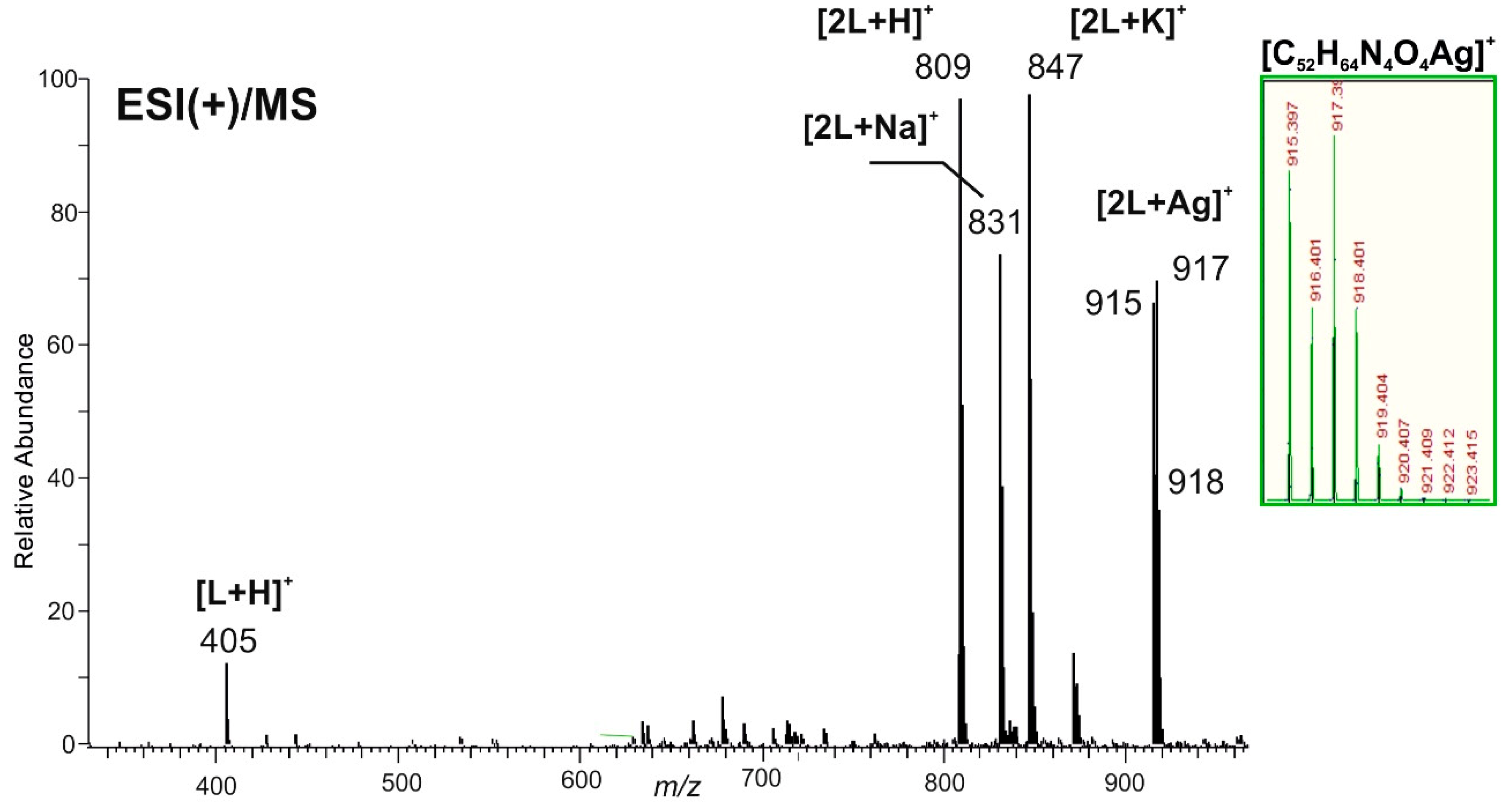
2.2. Silver Chloride Derived Complexes
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. Antibacterial Activity Determinations
3.4. Assessment of Complexes Anti-Candida Activity
3.5. Toxicity Assessment
3.6. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.S.; Rosli, R.; Seow, H.F.; Chong, P.P. Candida and invasive candidiasis: Back to basics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witherden, E.A.; Shoaie, S.; Hall, R.A.; Moyes, D.L. The Human Mucosal Mycobiome and Fungal Community Interactions. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J.; Gibbs, D.L.; Newell, V.A.; Ellis, D.; Tullio, V.; Rodloff, A.; Fu, W.; Ling, T.A.; Global Antifungal Surveillance Group. Results from the ARTEMIS DISK Global Antifungal Surveillance Study, 1997 to 2007: A 10.5-year analysis of susceptibilities of Candida Species to fluconazole and voriconazole as determined by CLSI standardized disk diffusion. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J.; Turnidge, J.D.; Castanheira, M.; Jones, R.N. Twenty Years of the SENTRY Antifungal Surveillance Program: Results for Candida Species From 1997–2016. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 15, S79–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theuretzbacher, U. Future antibiotics scenarios: Is the tide starting to turn? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.B.; Young, K.; Silver, L.L. What is an “ideal” antibiotic? Discovery challenges and path forward. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nett, J.E.; Andes, D.R. Antifungal Agents: Spectrum of Activity, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 51–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etubu, E.; Arikekpar, I. Antibiotics: Classification and mechanisms of action with emphasis on molecular perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2016, 4, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, G.; Saigal, S.; Elongavan, A. Action and resistance mechanisms of antibiotics: A guide for clinicians. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-K.; Kyung-Soo, H. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Peptide Structure and Mode of Action. BMB Rep. 2005, 38, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, C.; Sarkar, P.; Issa, R.; Aldar, J. Alternatives to Conventional Antibiotics in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.A.; Desai, S.D.; Singh, J. A Review on Plant Antimicrobials of Past Decade. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Worley, S.D.; Broughton, R. The chemistry and applications of antimicrobial polymers: A state-of-the-art review. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1359–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Luan, S.; Yin, Z.; He, M.; He, C.; Yin, L.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, L.; Song, X.; et al. Recent advances in the medical use of silver complex. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Lourenco, A.; Alves, M.M.; Montemor, M.F.; Mira, N.P.; Leitão, J.H.; Carvalho, M.F.N. Ag(I) camphorimine complexes with antimicrobial activity towards clinically important bacteria and species of the Candida genus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.F.N.; Leite, S.; Costa, J.P.; Galvão, A.M.; Leitão, J.H. Ag(I) camphor complexes: Antimicrobial activity by design. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 199, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.H.; Sousa, S.A.; Leite, S.A.; Carvalho, M.F.N. Silver Camphor Imine Complexes: Novel Antibacterial Compounds from Old Medicines. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Galvão, A.M.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Leitão, J.H.; Suarez, A.C.; Carvalho, M.F.N. Antibacterial activity of silver camphorimine coordination polymers. Dalton Trans 2016, 45, 7114–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, J.M.S.; Correia, I.; Galvão, A.M.; Marques, F.; Carvalho, M.F.N. Synthesis of Ag(I) camphor sulphonylimine complexes and assessment of their cytotoxic properties against cisplatin-resistant A2780cisR and A2780 cell lines. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 166, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordwell, F.G.; Algrim, D. Nitrogen acids. 1. Carboxamides and sulfonamides. J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 2507–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richau, J.A.; Leitão, J.H.; Sá-Correia, I. Enzymes leading to the nucleotide sugar precursors for exopolysaccharide synthesis in Burkholderia cepacia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doehmer, J. Predicting Drug Metabolism–dependent Toxicity for Humans with a Genetically Engineered Cell Battery. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2006, 34, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazu, T.K.; Bricker, B.A.; Flores-Rozas, H.; Ablordeppey, S.Y. The Mechanistic Targets of Antifungal Agents: An Overview. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.A.; Mendes, F.; Roseiro, A.P.S.; Santos, I.; Carvalho, M.F.N. Insight into the cytotoxicity of polynuclear Cu(I) camphor complexes. Polyhedron 2015, 87, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.F.N.; Costa, L.M.G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Schier, A.; Scherer, W.; Harbi, S.K.; Verfürth, U.; Herrmann, R. Synthesis, structure, and electrochemistry of palladium complexes with camphor-derived chiral ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 6270–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S.D.; Rivera, I. Asymmetric Carboalkoxyalkylidenation with a Chiral Horner-Wadsworth-Emmons Reagent. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 6887–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.A.; Feliciano, J.R.; Pita, T.; Guerreiro, S.I.; Leitão, J.H. Burkholderia cepacia Complex Regulation of Virulence Gene Expression: A Review. Genes 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendrup, M.C.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Hope, W.; EUCAST-AFST. EUCAST technical note on the EUCAST definitive document EDef 7.2: Method for the determination of broth dilution minimum inhibitory concentrations of antifungal agents for yeasts EDef 7.2 (EUCAST-AFST). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E246–E247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Carapeto, A.P.; Ferraria, A.M.; do Rego, A.M.B. Unraveling the reaction mechanism of silver ions reduction by chitosan from so far neglected spectroscopic features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

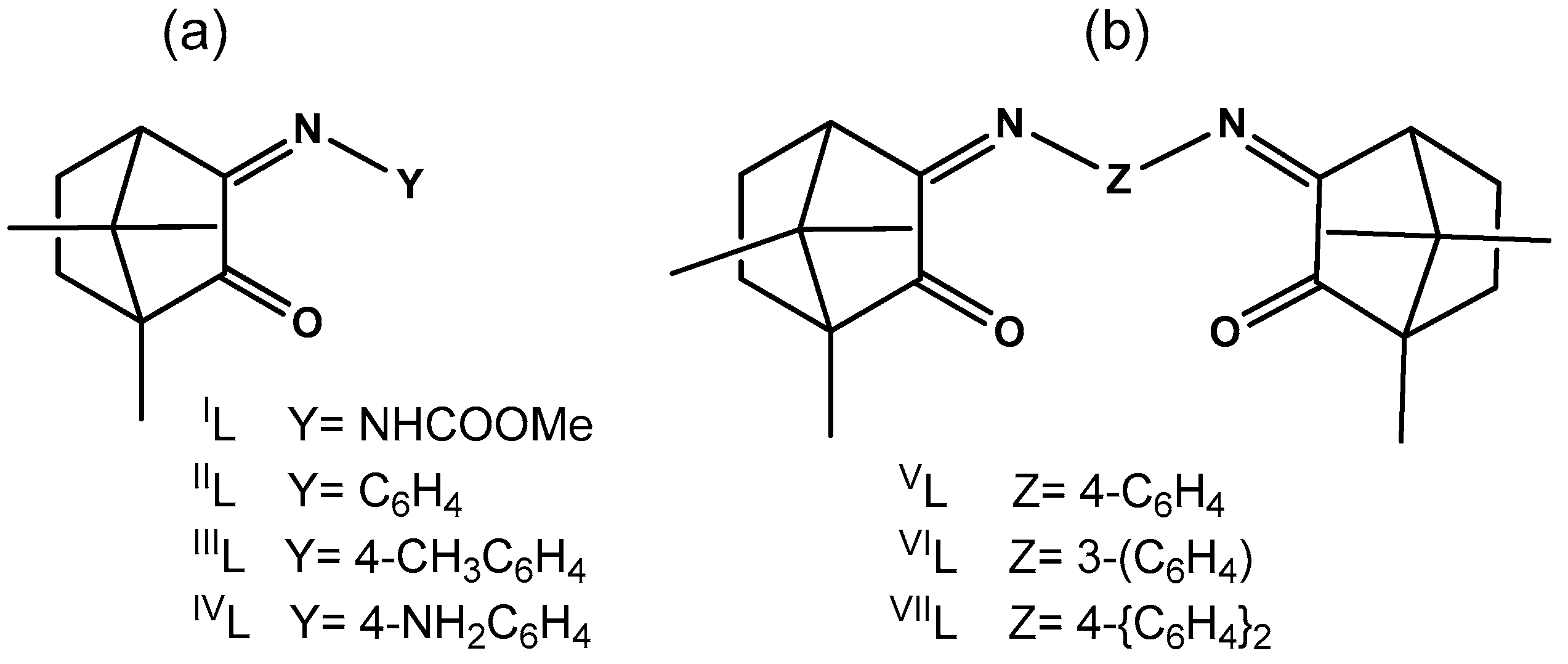

| COMPLEX | LIGAND (L) | IR (cm−1) a | 13C NMR (δ ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Z | νC=O | νC=N | C=O | C=N | ||
| [{AgIL}2(µ-O)] | IL (1) | NHCOOMe | 1722 | 1649 | (b) | ||
| [{Ag(IIL)}2(µ-O)] | IIL (2) | C6H5 | 1745 | 1652 | 207.4 | 173.3 c | |
| [{Ag(IIIL)}2(µ-O)] | IIIL (3) | 4-CH3C6H4 | 1747 | 1653 | 206.8 | 171.9 d | |
| [Ag(OH)(IVL´)] e | IVL (4) | 4-NH2C6H4 | 1733 | 1642 f | 207.8 | 169.1 c | |
| [{Ag(OH)}(VL)] | VL (5) | 4-C6H4 | 1754 | 1685 | 207.3 | 173.2 c | |
| [{Ag(OH)}3(VIL)2] | VIL (6) | 3-C6H4 | 1751 | 1668 | 206.6 | 173.0 g | |
| [Ag(OH)(VIIL)] | VIIL (7) | 4-(C6H4)2 | 1745 | 1660 | 206.7 | 172.5 g | |
| COMPLEX | LIGAND (L) | IR (cm−1) | 13C NMR (δ ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Z | νC=O | νC=N | C=O | C=N | ||
| [Ag(IIL)]Cl | IIL (8) | C6H5 | 1744 | 1651 | 207.5 | 173.2 a | |
| [{Ag(IIIL)}2(µ-O)] | IIIL (3) | 4-CH3C6H4 | 1747 | 1654 | 206.8 | 171.9 b | |
| [{Ag(NH3)}2(μ-VL)(μ-O)] | VL (9) | 4-C6H4 | 1744 | 1651 | 207.5 | 173.2 b | |
| [Ag(VIL)2]Cl | VIL (10) | 3-C6H4 | 1750 | 1661 | 207.2 | 173.8 a | |
| [Ag2(μ-VIL)(µ-O)] | VIL (10A) | 3-C6H4 | 1749 | 1660 | 207.3 | 173.9 a | |
| Complex. | MIC50 (µg/mL) | MIC (µg/mL) | IC50 a (µg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans | C. glabrata | E. coli ATCC25922 | B. contaminans IST408 | P. aeruginosa 477 | S. aureus Newman | V79 Cells | |
| 2 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 15.6 ± 0.1 | 59.4 ± 0.3 | 47 ± 7 | 19 ± 3 | 125 | 7 ± 5 |
| 3 | 31.3 ± 0.1 | 31.3 ± 0.1 | 56 ± 5 | 78 ± 2 | 43 ± 11 | 58 ± 2 | 8 ± 5 |
| 6 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 15.6 ± 0.1 | 125 | 125 | 60 ± 7 | 125 | 3 ± 1 |
| 7 | 15.6 ± 0.1 | 15.6 ± 0.1 | 54 ± 3 | >125 | 61 ± 4 | >125 | 12 ± 5 |
| 8 | 125 ± 1 | 250 ± 1 | 250 | >250 | 112± 14 | 250 | 25 ± 14 |
| 9 | 3.9 ± 0.4 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 32 ± 1 | 125 | 19 ± 3 | 125 | 2 ± 1 |
| 10 | - | - | >250 | >250 | >250 | >250 | - |
| 10A | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 15.6 ± 0.1 | 52.2 ± 0.2 | 23 ± 3 | 43 ± 10 | 125 | 1.7 ± 0.9 |
| Ag(OAc) | >500 | >500 | 30.9 ± 0.4 | 12 ± 2 | 16 ± 3 | 29.5 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.2 |
| AgCl | 500 ± 1 | >500 | 14 ± 2 | 10 ± 1 | 12 ± 1 | 30 ± 2 | >30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, J.P.; Pinheiro, M.J.F.; Sousa, S.A.; Botelho do Rego, A.M.; Marques, F.; Oliveira, M.C.; Leitão, J.H.; P. Mira, N.; N. N. Carvalho, M.F. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Camphorimine Complexes against Candida Strains. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030144
Costa JP, Pinheiro MJF, Sousa SA, Botelho do Rego AM, Marques F, Oliveira MC, Leitão JH, P. Mira N, N. N. Carvalho MF. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Camphorimine Complexes against Candida Strains. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(3):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030144
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Joana P., M. Joana F. Pinheiro, Sílvia A. Sousa, Ana M. Botelho do Rego, Fernanda Marques, M. Conceição Oliveira, Jorge H. Leitão, Nuno P. Mira, and M. Fernanda N. N. Carvalho. 2019. "Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Camphorimine Complexes against Candida Strains" Antibiotics 8, no. 3: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030144
APA StyleCosta, J. P., Pinheiro, M. J. F., Sousa, S. A., Botelho do Rego, A. M., Marques, F., Oliveira, M. C., Leitão, J. H., P. Mira, N., & N. N. Carvalho, M. F. (2019). Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Camphorimine Complexes against Candida Strains. Antibiotics, 8(3), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030144








