Tobramycin Promotes Melanogenesis by Upregulating p38 MAPK Protein Phosphorylation in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
Abstract
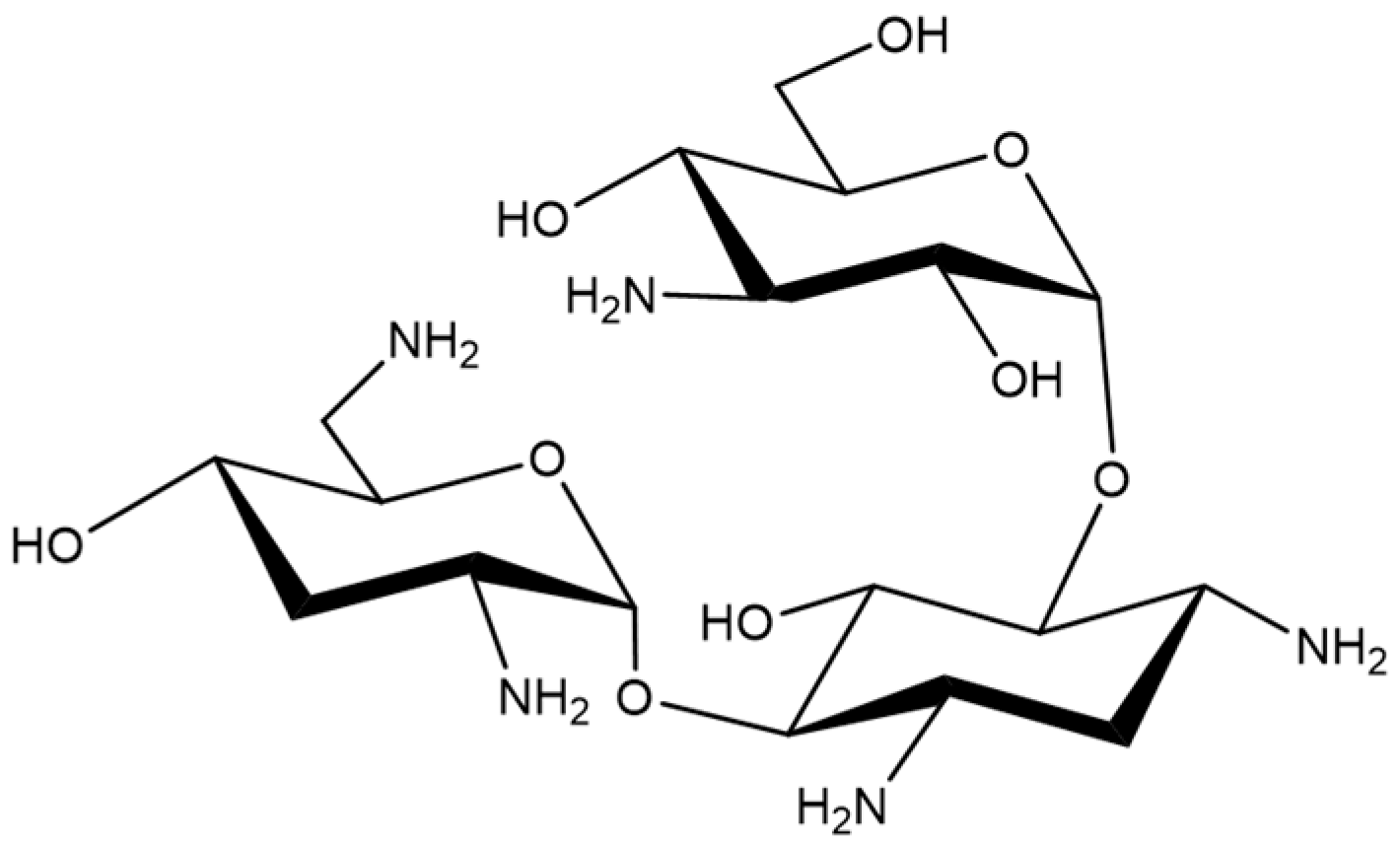
1. Introduction
2. Results
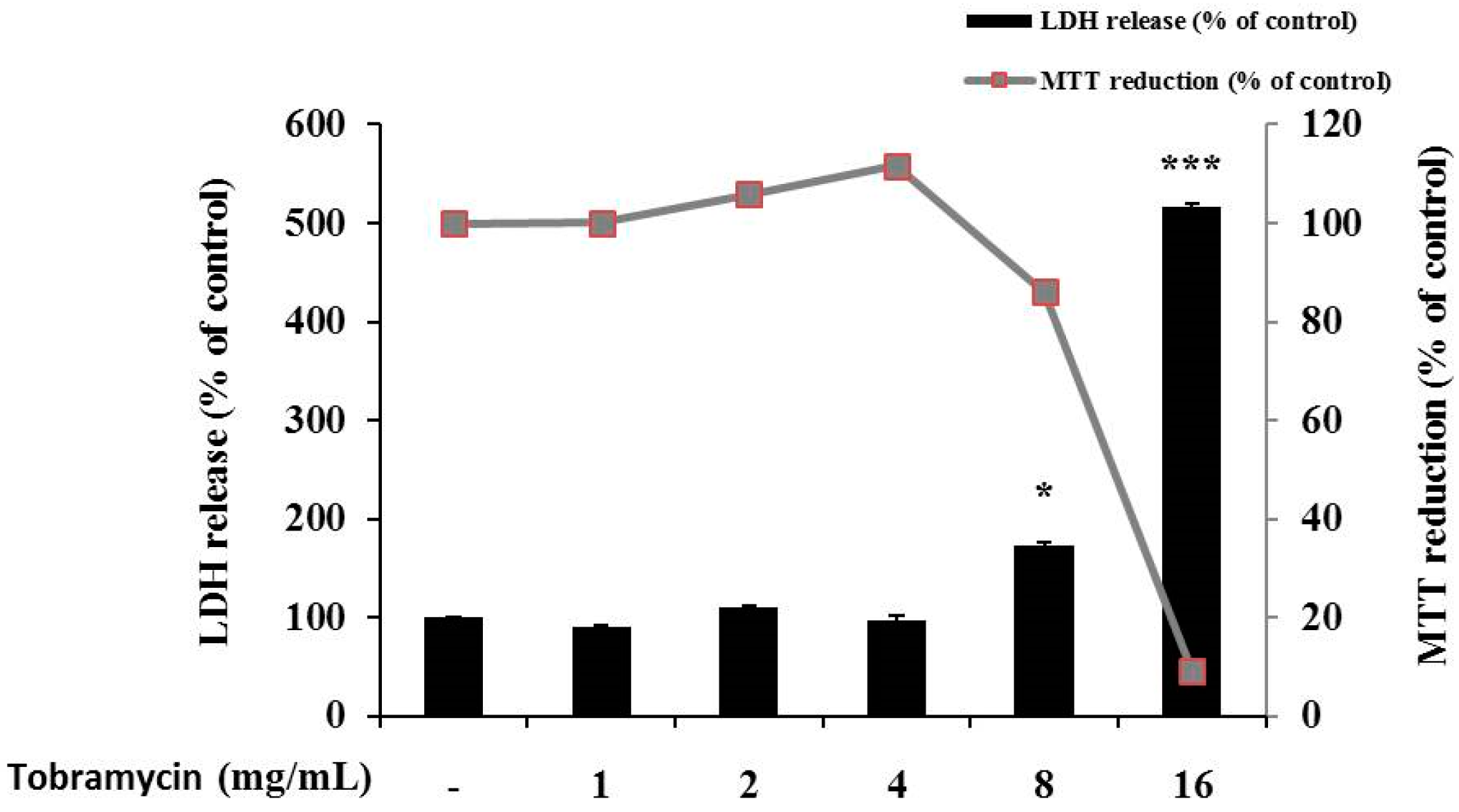
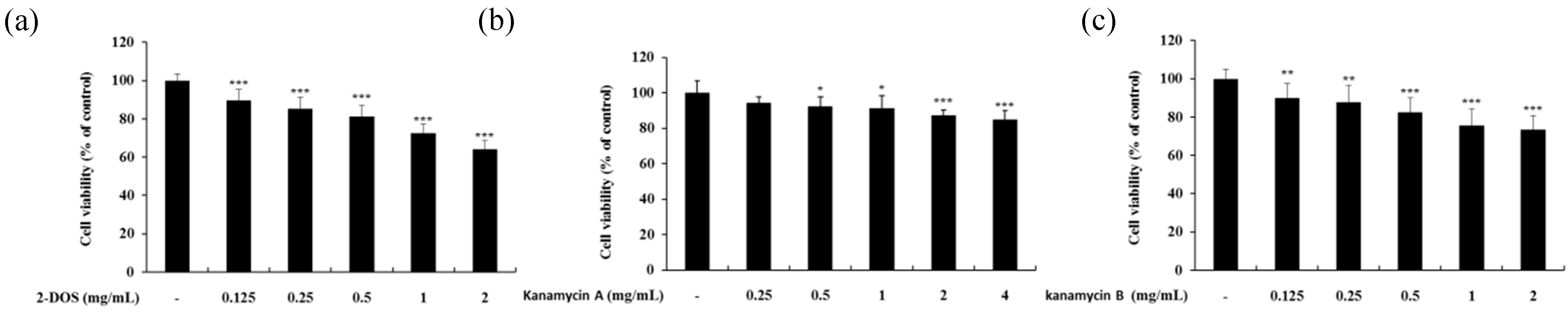
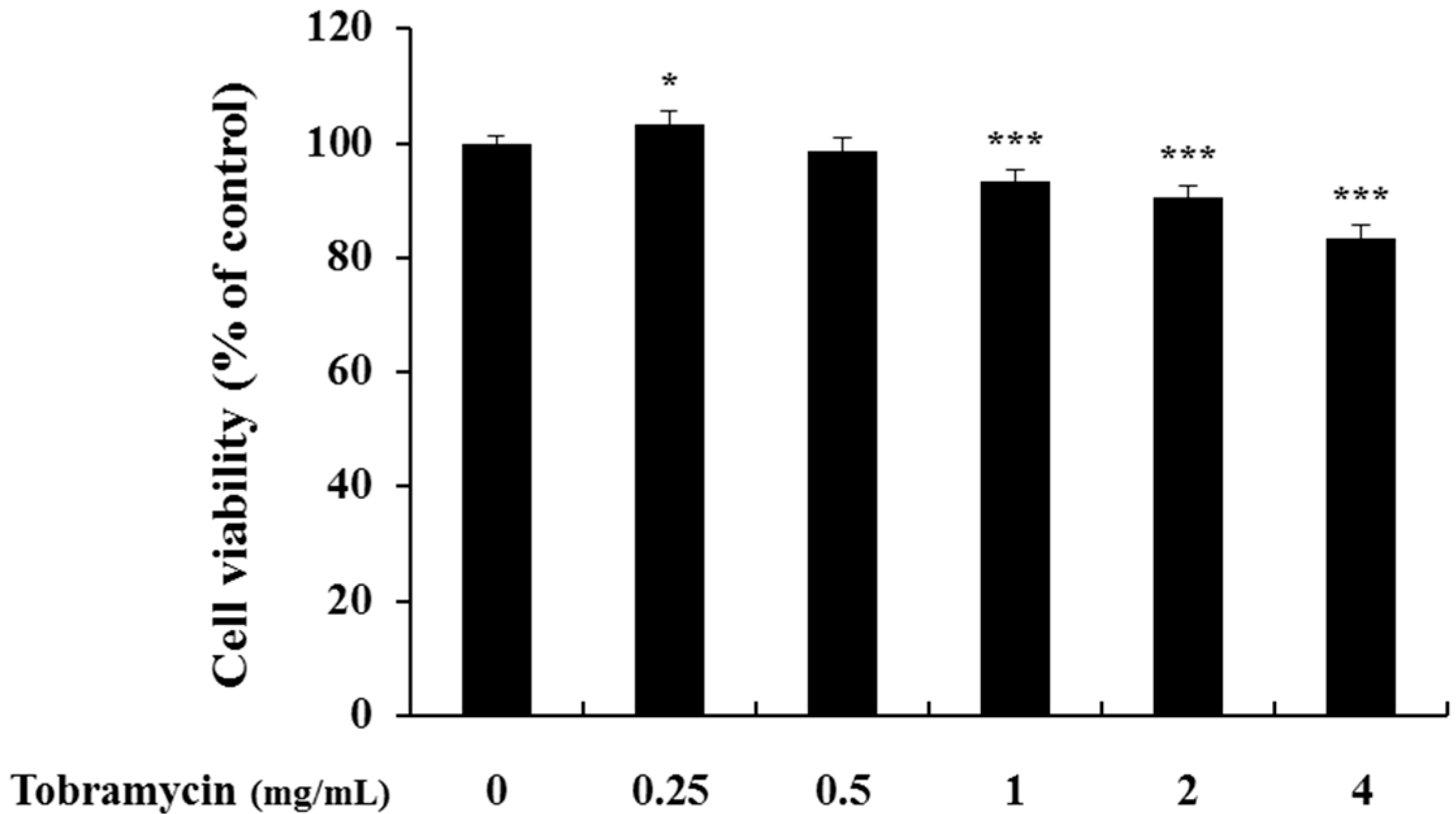
2.1. Cell Viability of B16F10 Melanoma Cells
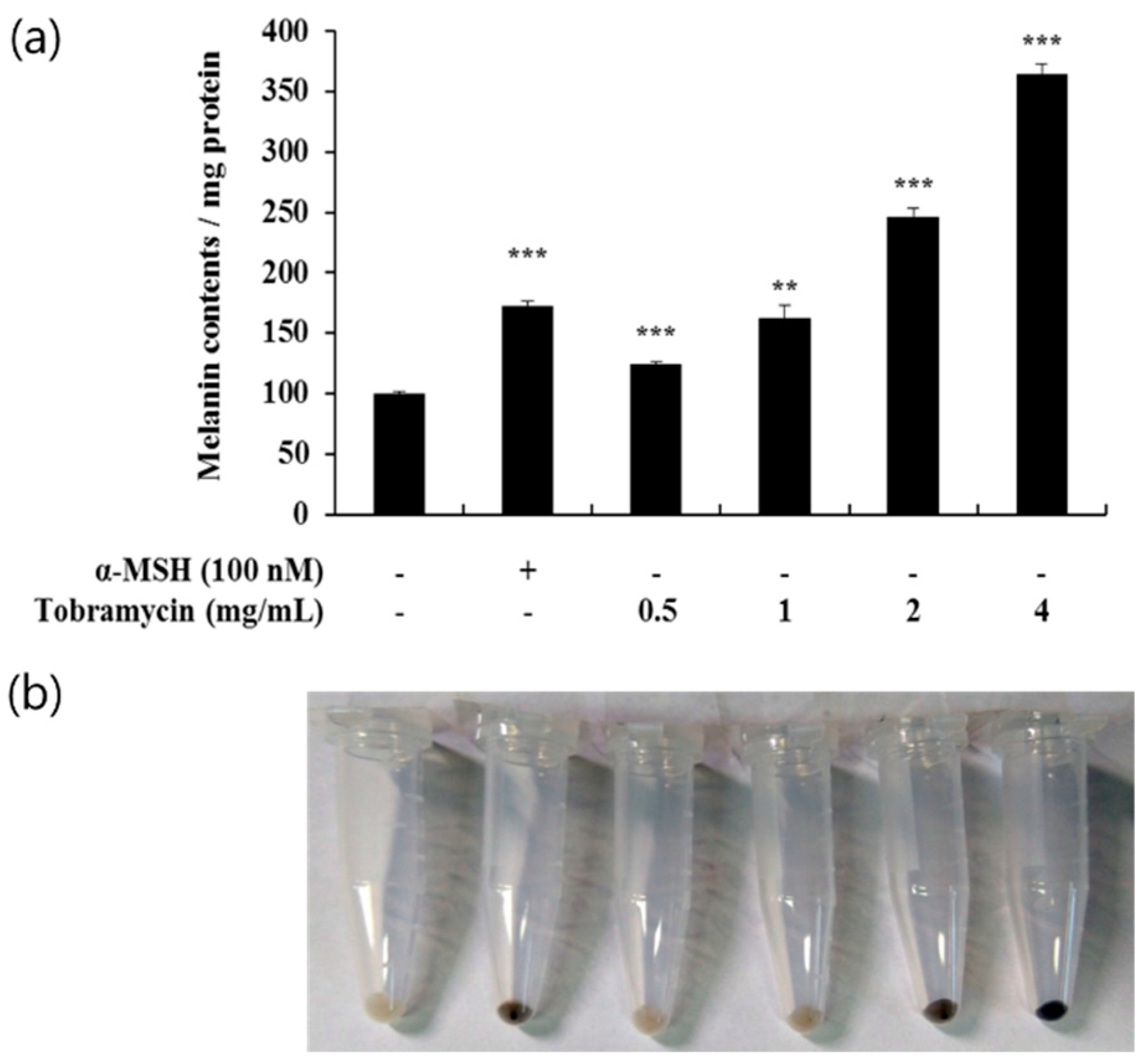
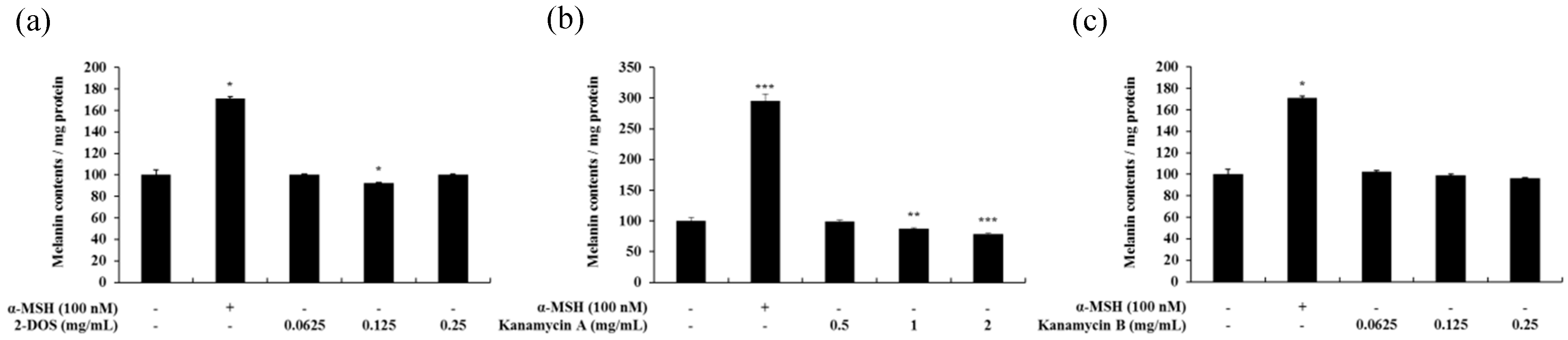
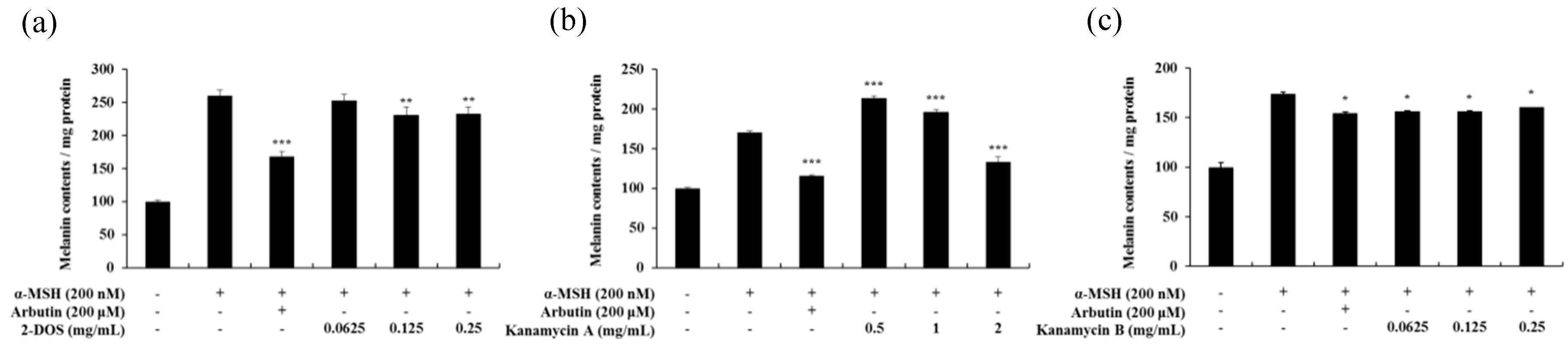
2.2. Effect of Tobramycin on Melanin Synthesis
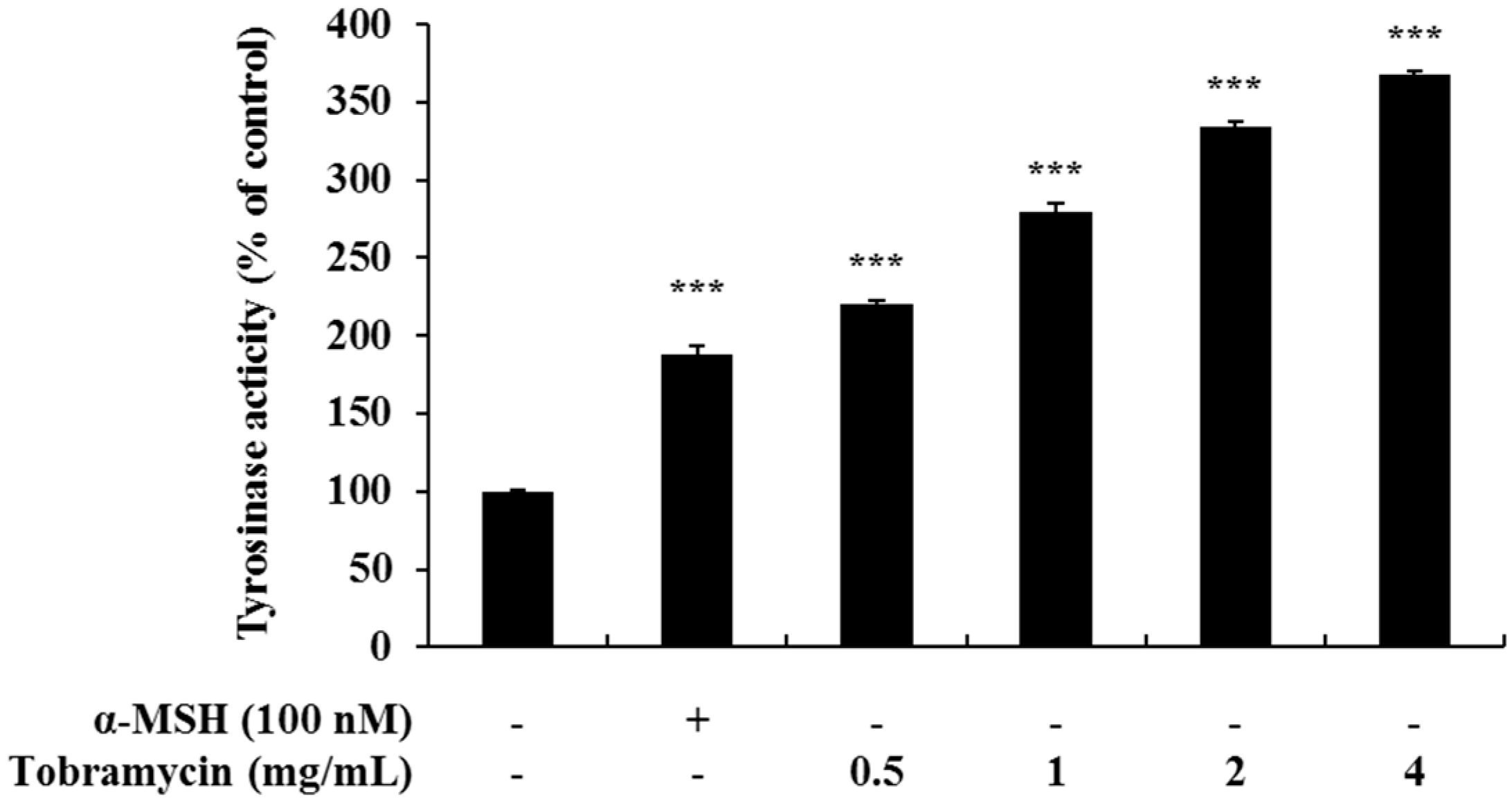
2.3. Effect of Tobramycin on Tyrosinase Activity
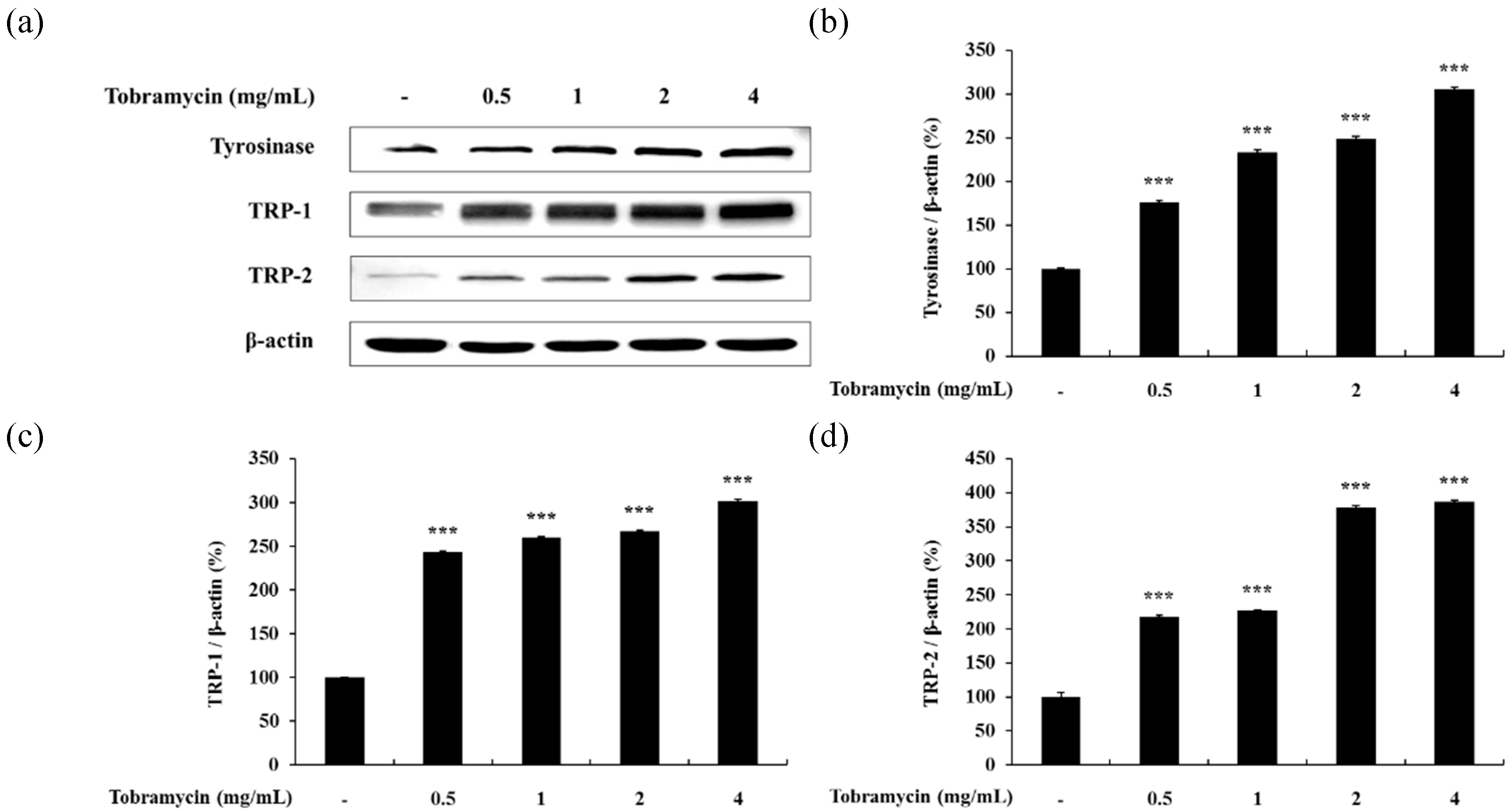
2.4. Expression of Proteins Related to Melanin Synthesis
2.4.1. Tyrosinase, TRP-1, TRP-2
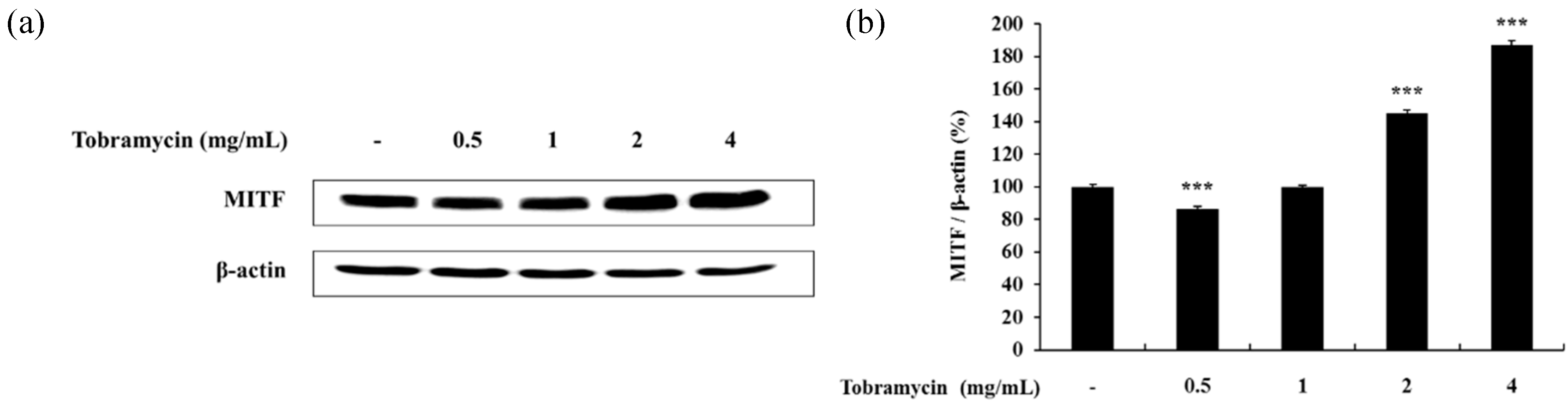
2.4.2. MITF
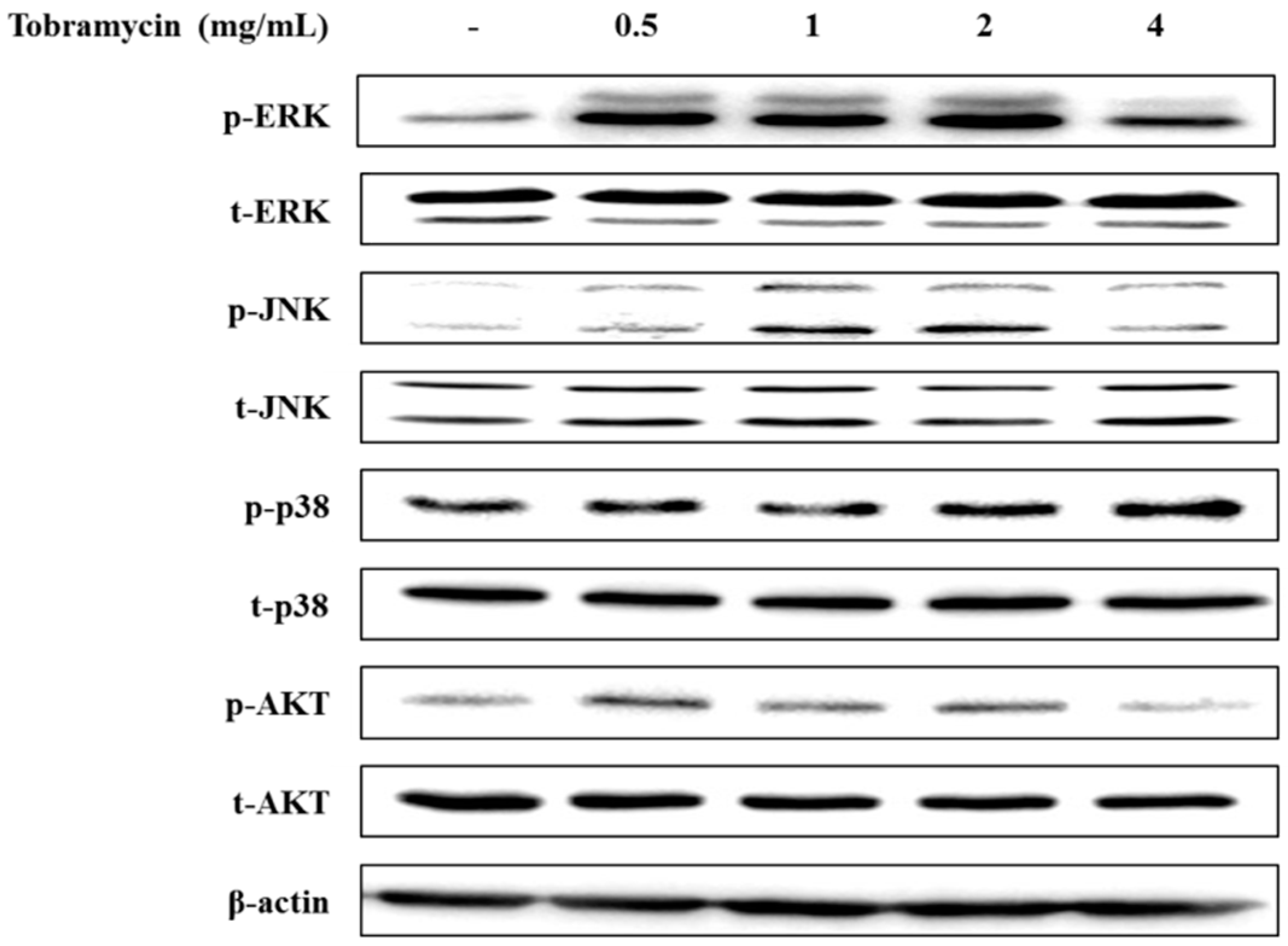
2.4.3. MAPKs and AKT
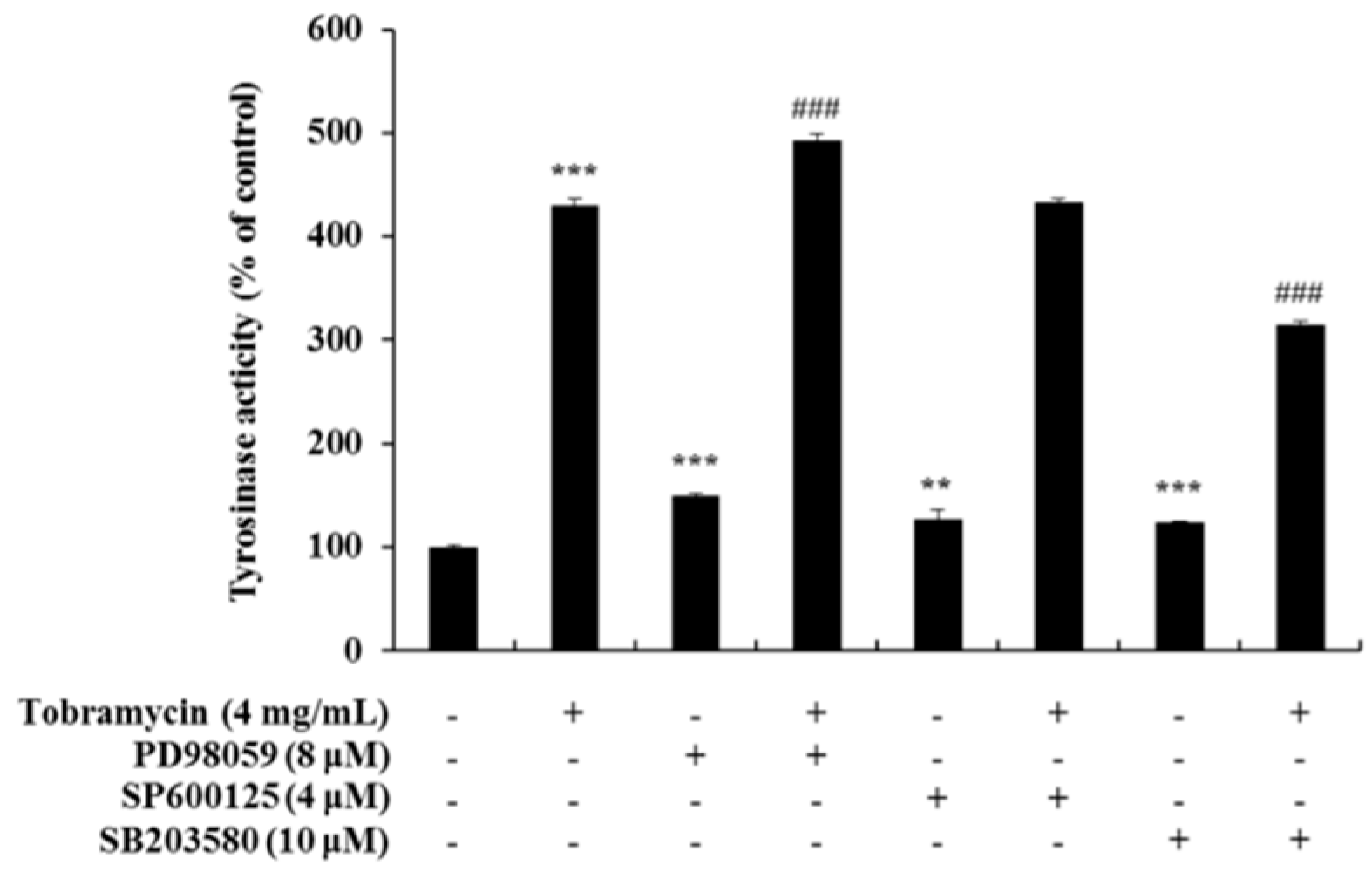
2.5. Tyrosinase Activity Assay with Protein Inhibitors
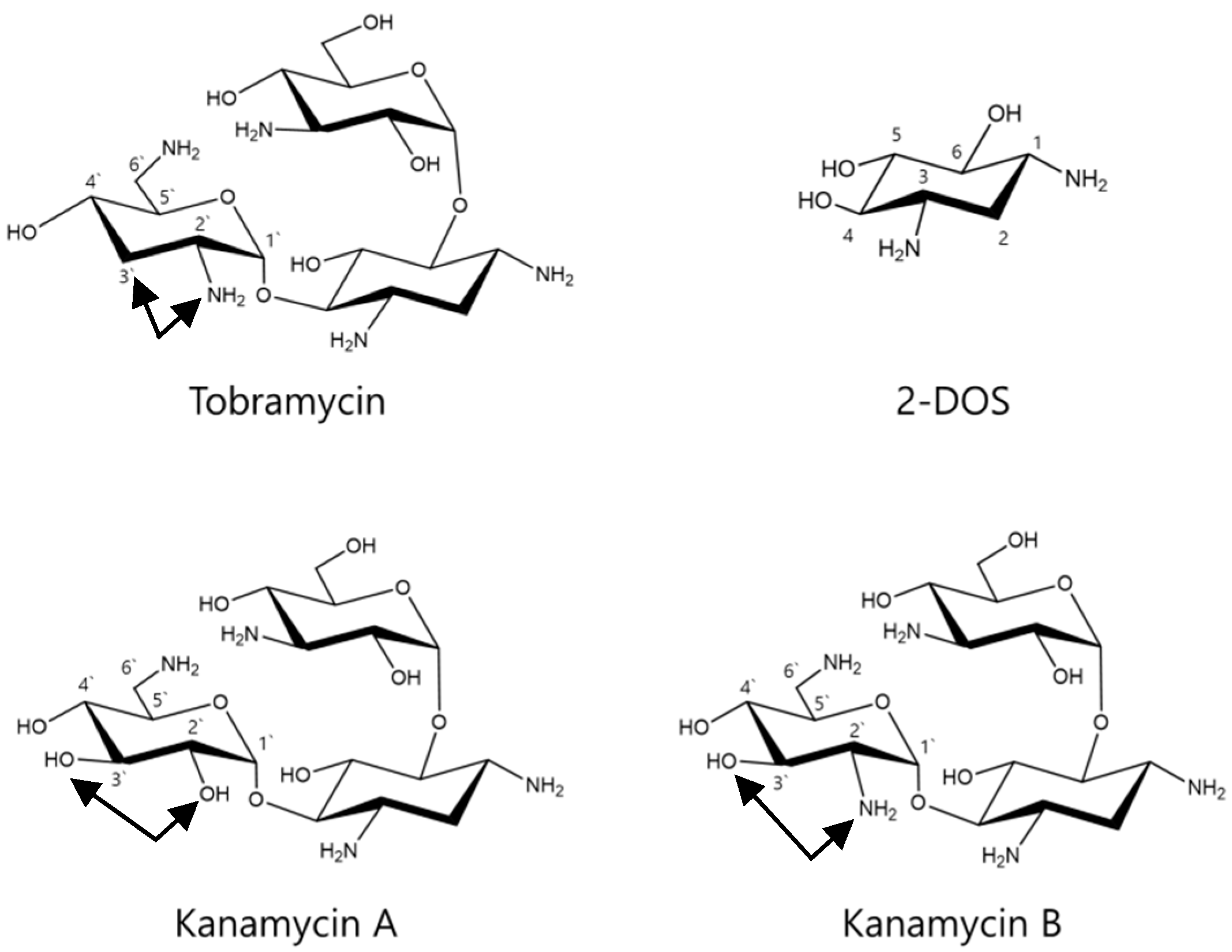
2.6. Effects of Tobramycin-Related Structures on Melanogenesis
2.7. Cell Viability of HaCaT Keratinocyte Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release Assay
4.5. Melanin Content Measurement
4.6. Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The protective role of melanin against UV damage in human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.T.; Schulman, J.; Fisher, D.E. UV and pigmentation: Molecular mechanisms and social controversies. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008, 21, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S.-H. Recent development of signaling pathways inhibitors of melanogenesis. Cell. Signal. 2017, 40, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S.H. Inhibitors of melanogenesis: A patent review (2009–2014). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca, P.; Urabe, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsukamoto, K.; Hearing, V.J. Melanin biosynthesis patterns following hormonal stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 25650–25655. [Google Scholar]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Plonka, P.M.; Schallreuter, K.U.; Paus, R.; Tobin, D.J. Hair follicle pigmentation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imesch, P.D.; Wallow, I.H.; Albert, D.M. The color of the human eye: A review of morphologic correlates and of some conditions that affect iridial pigmentation. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41 (Suppl. 2), S117–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidbey, K.H.; Agin, P.P.; Sayre, R.M.; Kligman, A.M. Photoprotection by melanin—A comparison of black and Caucasian skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1979, 1, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, A.J. The biochemical basis of disease. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 619–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, A.G., Jr. Skin manifestations of internal disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 93, 1265–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.J.; Bolognia, J.L. Disorders of hypopigmentation in children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 38, 991–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, R.; Pinder, R.; Sawyer, P.R.; Speight, T.; Avery, G. Tobramycin: A review of its antibacterial and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1976, 12, 166–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, M.K.; Basnet, D.B.; Lee, H.C.; Liou, K.; Woo, J.S.; Kim, B.G.; Sohng, J.K. Isolation and characterization of the tobramycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces tenebrarius. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 230, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, H.C. Tobramycin: An overview. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 134, S3–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.E.; Kastner, R.E. Nebramycin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic complex. II. Description of Streptomyces tenebrarius. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, W.M.; Hoehn, M.M.; Knox, N.G. Nebramycin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic complex. I. Detection and biosynthesis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 314–323. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.Q.; Presti, E.A. Nebramycin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic complex. 3. Isolation and chemical-physical properties. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 332–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, W.E.; Welles, J.S. Nebramycin, a new broad-spectrum antibiotic complex. IV. In vitro and in vivo laboratory evaluation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 7, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Cannella, C.A.; Wilkinson, S.T. Acute renal failure associated with inhaled tobramycin. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2006, 63, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Mendiola, M.R.; Balda, A.G.; Delgado, M.C.; Montano, P.P.; De Olano, D.G.; Sanchez-Cano, M. Contact allergy from tobramycin eyedrops. Allergy 2005, 60, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, H.C.; Bendush, C.L. Ototoxicity of tobramycin: A clinical overview. J. Infect. Dis. 1976, 134, S206–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daschner, F.D.; Just, H.M.; Jansen, W.; Lorber, R. Netilmicin versus tobramycin in multi-centre studies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1984, 13 (Suppl. A), 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moellering, R.C., Jr.; Wennersten, C.; Kunz, L.J.; Poitras, J.W. Resistance to gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin among clinical isolates of bacteria. Am. J. Med. 1977, 62, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, M.L.; Begg, E.J.; Chambers, S.T.; Thornley, P.E.; Pattemore, P.K.; Grimwood, K. Adaptive resistance to tobramycin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1996, 37, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.S.; Lee, J.N.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.-G. Pratol, an O-methylated flavone, induces melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells via p-p38 and p-jnk upregulation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, G.-A.; Cho, S.K. Phytol suppresses melanogenesis through proteasomal degradation of MITF via the ROS-ERK signaling pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2018, 286, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, H.; Chu, J.H.; Chou, G.X.; Yu, Z.L. Activation of p38 MAPK pathway contributes to the melanogenic property of apigenin in B16 cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.R.; Lin, J.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Huang, T.K.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, M.O.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Su, C.C.; Wu, Y.J. Inhibition of melanogenesis by gallic acid: Possible involvement of the PI3K/Akt, MEK/ERK and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in B16F10 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20443–20458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratacap, B.; Attard, A.; Laurent, A.; Stoebner, P.; Smirou, D.; Charachon, R. Melanin in the inner ear. An experimental study with control and kanamycin-intoxicated colored guinea-pigs. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 1989, 246, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Bellei, C.; Costi, P.; Albertini, A.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L.; Gallorini, M.; Bergamaschi, L.; Moscatelli, A.; Turro, N.J.; et al. New melanic pigments in the human brain that accumulate in aging and block environmental toxic metals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17567–17572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesniok, D.; Otreba, M.; Beberok, A.; Buszman, E. Impact of kanamycin on melanogenesis and antioxidant enzymes activity in melanocytes—An in vitro study. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thingnes, J.; Lavelle, T.J.; Hovig, E.; Omholt, S.W. Understanding the melanocyte distribution in human epidermis: An agent-based computational model approach. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, S.-H.; Chung, Y.C.; Hyun, C.-G. Tobramycin Promotes Melanogenesis by Upregulating p38 MAPK Protein Phosphorylation in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030140
Moon S-H, Chung YC, Hyun C-G. Tobramycin Promotes Melanogenesis by Upregulating p38 MAPK Protein Phosphorylation in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(3):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030140
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Seung-Hyun, You Chul Chung, and Chang-Gu Hyun. 2019. "Tobramycin Promotes Melanogenesis by Upregulating p38 MAPK Protein Phosphorylation in B16F10 Melanoma Cells" Antibiotics 8, no. 3: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030140
APA StyleMoon, S.-H., Chung, Y. C., & Hyun, C.-G. (2019). Tobramycin Promotes Melanogenesis by Upregulating p38 MAPK Protein Phosphorylation in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Antibiotics, 8(3), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030140




