Identification of Anti-Persister Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a Clinical Drug Library
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of 14 Drug Candidates with High Anti-Persister Activity
| Drug name (50 μM) | MIC(μM) | Viability of Bacteria after 3 or 7 Days of Drug Exposure a | CFU/mL of Bacteria after 3 or 5 Days of Drug Exposure b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Days | 7 Days | 3 Days | 5 Days | ||
| Tosulfloxacin | 0.15 | − | − | 0 | 0 |
| Colistin | 0.6 | − | − | 0 | 0 |
| Gatifloxacin | 0.6 | − | − | 0 | 0 |
| Moxifloxacin | 0.6 | − | − | 0 | 0 |
| Sparfloxacin | 0.3 | − | − | 6000 | 0 |
| Enrofloxacin | 0.3 | +/− | − | 30,000 | 3300 |
| Sarafloxacin | 0.3 | +/− | − | 0 | 0 |
| Octodrine | ≥10 | + | − | >50,000 | 0 |
| Clofoctol | 10 | + | − | 12,000 | 2300 |
| Dibekacin | ≥40 | + | − | >50,000 | 0 |
| Cephalosporin C | 10 | + | − | 4000 | 0 |
| Pazufloxacin | 0.3 | + | − | 39,000 | 2700 |
| Streptomycin | ≥40 | + | − | >50,000 | 1000 |
| Neomycin | ≥40 | + | − | 41,000 | 0 |
| Drug-free control | − | + | + | 1,500,000,000 | 760,000,000 |
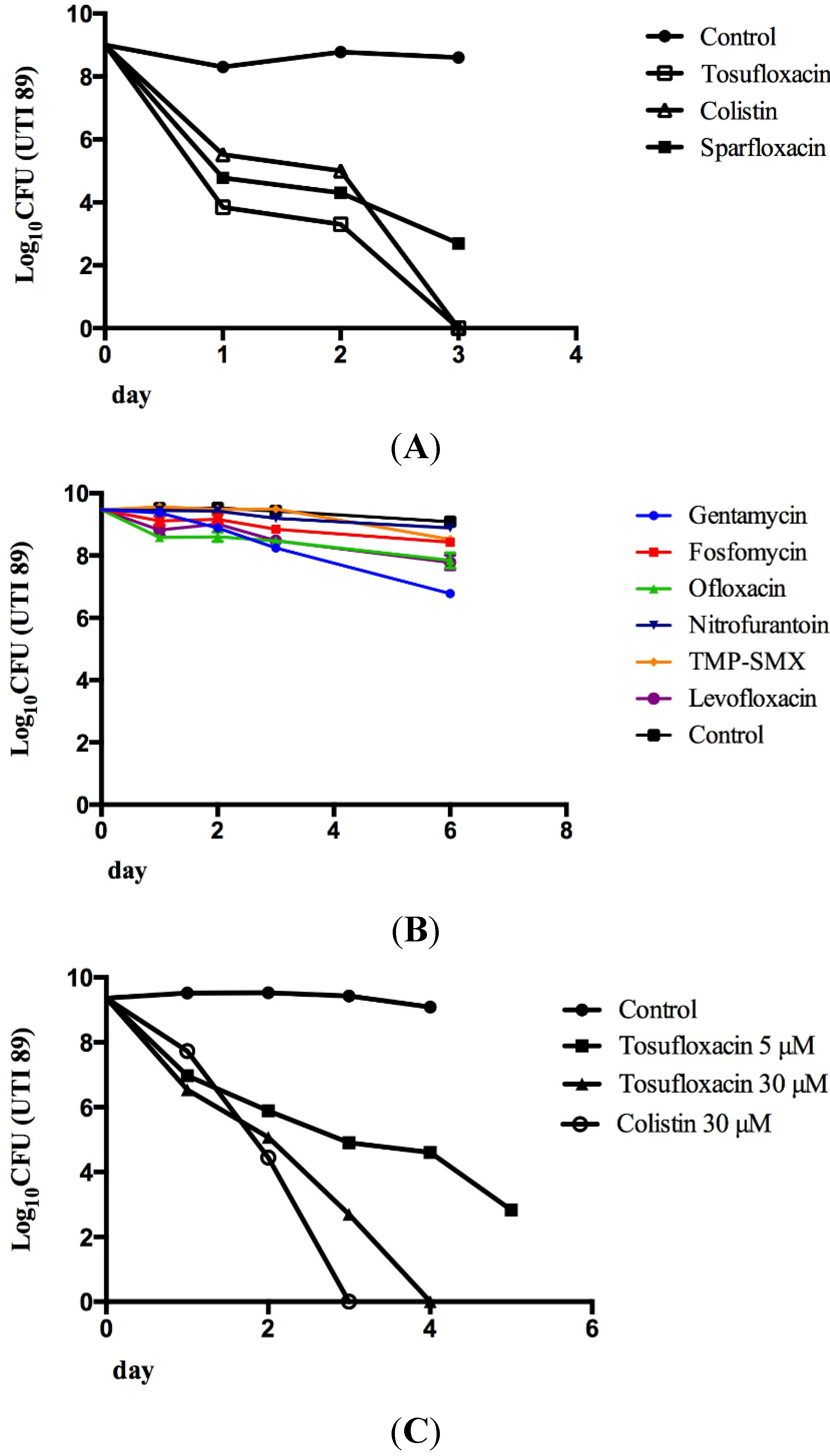
2.2. Tosufloxacin and Colistin Showed the Highest Anti-Persister Activity
2.3. Comparison of the Persister-Active Drug Candidates with Current UTI Antibiotics in Their Ability to Kill UPEC Persisters
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strain
3.2. Antibiotics and the Clinical Drug Library
3.3. Screening of the Clinical Drug Library in the UTI89 Stationary-Phase Persister Model
3.4. Validation of Active Drug Candidates by Colony Forming Unit (CFU) Count
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Event In 2014. http://www.cdc.gov/HAI/ca_uti/uti.html (accessed on 28 March 2015).
- Hooton, T.M.; Stamm, W.E. Diagnosis and treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 11, 551–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejrnaes, K. Bacterial characteristics of importance for recurrent urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli. Dan. Med. Bull. 2011, 58, B4187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foxman, B.; Zhang, L.; Tallman, P.; Palin, K.; Rode, C.; Bloch, C.; Gillespie, B.; Marrs, C.F. Virulence characteristics of Escherichia coli causing first urinary tract infection predict risk of second infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foxman, B. Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: Incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113, S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauner, A.; Jacobson, S.H.; Kuhn, I. Urinary Escherichia coli causing recurrent infections—A prospective follow-up of biochemical phenotypes. Clin. Nephrol. 1992, 38, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, L.; Guo, L.; Ye, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Similarity and divergence of phylogenies, antimicrobial susceptibilities, and virulence factor profiles of Escherichia coli isolates causing recurrent urinary tract infections that persist or result from reinfection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 4002–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koljalg, S.; Truusalu, K.; Vainumae, I.; Stsepetova, J.; Sepp, E.; Mikelsaar, M. Persistence of Escherichia coli clones and phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance in recurrent urinary tract infections in childhood. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; Stapleton, A.; Wenderoth, S.; Hooton, T.M.; Stamm, W.E. Chromosomal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of Escherichia coli strains causing recurrent urinary tract infections in young women. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjot-Rasmussen, L.; Hammerum, A.M.; Jakobsen, L.; Lester, C.H.; Larsen, P.; Frimodt-Moller, N. Persisting clones of Escherichia coli isolates from recurrent urinary tract infection in men and women. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Hooton, T.M.; Naber, K.G.; Wullt, B.; Colgan, R.; Miller, L.G.; Moran, G.J.; Nicolle, L.E.; Raz, R.; Schaeffer, A.J.; et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e103–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvey, M.A.; Schilling, J.D.; Martinez, J.J.; Hultgren, S.J. Bad bugs and beleaguered bladders: Interplay between uropathogenic Escherichia coli and innate host defenses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8829–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.R.; Chen, X.; Shi, L.; Liu, J.O.; Sullivan, D.J., Jr. A clinical drug library screen identifies astemizole as an antimalarial agent. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 415–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuyama, J. Structures of existing and new quinolones and relationship to bactericidal activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 44, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, R.E.; Chapple, D.S. Peptide antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.E.; Feola, D.J.; Rapp, R.P. Polymyxin B sulfate and colistin: Old antibiotics for emerging multiresistant gram-negative bacteria. Ann. Pharmacother. 1999, 33, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.; Sullivan, D.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Zhang, Y. Identification of Novel activity against Borrelia burgdorferi persisters using an FDA approved drug library. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2014, 2014, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Sugimura, Y.; Arima, K.; Kawamura, J.; Saitou, K.; Tajima, K.; Nakano, S.; Satani, H.; Nagano, M.; Hoshina, A.; et al. Study on clinical effects of tosufloxacin (TFLX) and the long-term low dose therapy for the prophylaxis of recurrent urinary tract infection. Hinyokika Kiyo 1994, 40, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Saitoh, H.; Negishi, T.; Yamada, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kawakami, S.; Tari, K.; Satake, I.; Ozawa, K.; et al. Clinical efficacy of tosufloxacin on the patients with urinary tract infections. Hinyokika Kiyo 1992, 38, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Hung, C.S.; Xu, J.; Reigstad, C.S.; Magrini, V.; Sabo, A.; Blasiar, D.; Bieri, T.; Meyer, R.R.; Ozersky, P.; et al. Identification of genes subject to positive selection in uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli: A comparative genomics approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5977–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blango, M.G.; Mulvey, M.A. Persistence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in the face of multiple antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, H.; Cui, P.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Sullivan, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y. Identification of Anti-Persister Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a Clinical Drug Library. Antibiotics 2015, 4, 179-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4020179
Niu H, Cui P, Shi W, Zhang S, Feng J, Wang Y, Sullivan D, Zhang W, Zhu B, Zhang Y. Identification of Anti-Persister Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a Clinical Drug Library. Antibiotics. 2015; 4(2):179-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4020179
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Hongxia, Peng Cui, Wanliang Shi, Shuo Zhang, Jie Feng, Yong Wang, David Sullivan, Wenhong Zhang, Bingdong Zhu, and Ying Zhang. 2015. "Identification of Anti-Persister Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a Clinical Drug Library" Antibiotics 4, no. 2: 179-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4020179
APA StyleNiu, H., Cui, P., Shi, W., Zhang, S., Feng, J., Wang, Y., Sullivan, D., Zhang, W., Zhu, B., & Zhang, Y. (2015). Identification of Anti-Persister Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a Clinical Drug Library. Antibiotics, 4(2), 179-187. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics4020179






