Clinical Characteristics, Outcomes, and Distribution Patterns of Pathogens Causing Respiratory Infections in Lung Retransplant Recipients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
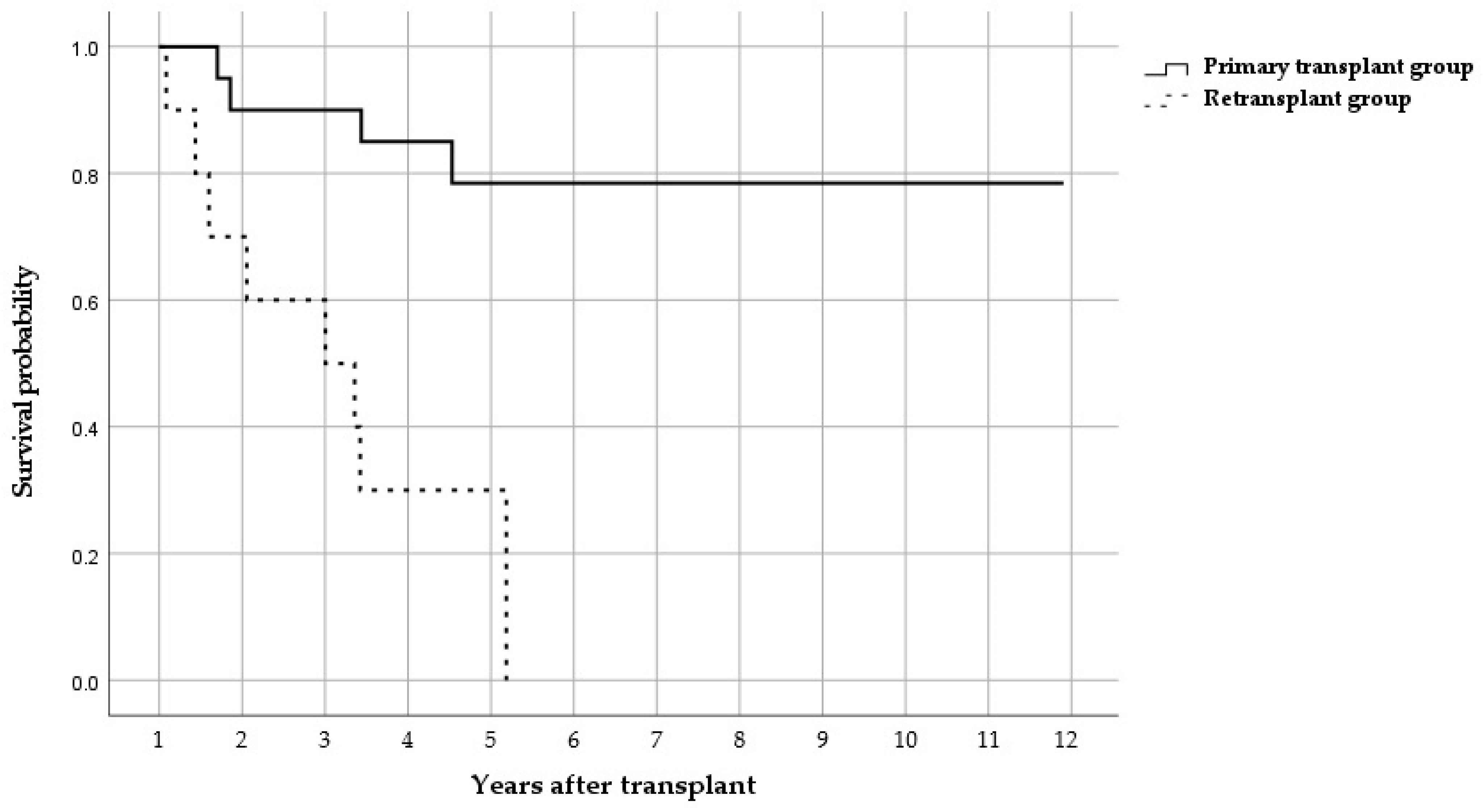
2.2. Clinical Outcomes
2.3. Microbiological Distribution of BAL Isolates
3. Discussion
3.1. Survival Outcomes
3.2. Microbiological Trends and Clinical Implication
3.3. Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Population and Data Collection
4.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Surveillance and Microbiological Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LT | Lung transplantation |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CTD | Connective tissue disease |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
References
- Gao, R.; Wang, W.; Qian, T.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, T.; Yu, H.; Man, L.; Xiong, M.; Chen, J. Pulmonary bacterial infection after lung transplantation: Risk factors and impact on short-term mortality. J. Infect. 2024, 89, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strueber, M.; Fischer, S.; Gottlieb, J.; Simon, A.R.; Goerler, H.; Gohrbandt, B.; Welte, T. Long-term outcome after pulmonary retransplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 132, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.J.; Belli, E.V.; Gregg, J.A.; Salgado, J.C.; Baz, M.A.; Staples, E.D.; Beaver, T.M.; Machuca, T.N. Two Decades of Lung Retransplantation: A Single-Center Experience. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Kaleekal, T.S.; Graviss, E.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Sinha, N.; Goodarzi, A.; Agboli, I.; Suarez, E.; Loebe, M.; Scheinin, S.; et al. Retransplantation Outcomes at a Large Lung Transplantation Program. Transplant. Direct 2018, 4, e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burguete, S.R.; Maselli, D.J.; Fernandez, J.F.; Levine, S.M. Lung transplant infection. Respirology 2013, 18, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Delden, C.; Stampf, S.; Hirsch, H.H.; Manuel, O.; Meylan, P.; Cusini, A.; Hirzel, C.; Khanna, N.; Weisser, M.; Garzoni, C.; et al. Burden and Timeline of Infectious Diseases in the First Year After Solid Organ Transplantation in the Swiss Transplant Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e159–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebano, G.; Geneve, C.; Tanaka, S.; Grall, N.; Atchade, E.; Augustin, P.; Thabut, G.; Castier, Y.; Montravers, P.; Desmard, M. Epidemiology and risk factors of multidrug-resistant bacteria in respiratory samples after lung transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2016, 18, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.B.; Panchanathan, R.; Walia, R.; Varsch, K.E.; Kang, P.; Huang, J.; Hashimi, A.S.; Mohanakumar, T.; Bremner, R.M.; Smith, M.A. Lung Retransplantation for Chronic Rejection: A Single-Center Experience. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osho, A.A.; Castleberry, A.W.; Snyder, L.D.; Palmer, S.M.; Ganapathi, A.M.; Hirji, S.A.; Lin, S.S.; Davis, R.D.; Hartwig, M.G. Differential outcomes with early and late repeat transplantation in the era of the lung allocation score. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 1914–1920; discussion 1920-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnecke, G.; Haverich, A. Lung re-transplantation: Review. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2012, 17, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Pan, X.; Fu, S.; Zhao, H. Pulmonary retransplantation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 4632–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, A.M.; Heh, V.; Rosenheck, J.P.; Keller, B.C.; Mokadam, N.A.; Lampert, B.C.; Whitson, B.A.; Henn, M.C. Thoracic retransplantation: Does time to retransplantation matter? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 166, 1529–1541.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harhay, M.O.; Cherikh, W.S.; Toll, A.E.; Christie, J.D.; Stehlik, J.; Chambers, D.; Hayes, D.H.; Cantus, E. Epidemiology, risk factors, and outcomes of lung retransplantation: An analysis of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Thoracic Transplant Registry. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2022, 41, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, S.S.; Lee, W.S.; Chen, F.L.; Ou, T.Y.; Hsueh, P.R. Elizabethkingia meningoseptica: An important emerging pathogen causing healthcare-associated infections. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 86, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, S.; Thomas, B.; Shastry, B.A. Elizabethkingia meningoseptica: Emerging multidrug resistance in a nosocomial pathogen. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017-221076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajmi, A.; Teo, J.; Yeo, C.C. Epidemiology and Characteristics of Elizabethkingia spp. Infections in Southeast Asia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, M.; Stewart, A.; Tey, S.K.; Hajkowicz, K. Elizabethkingia bloodstream infections in severely immunocompromised patients: Persistent, relapsing and associated with high mortality. JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 6, dlae161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, P.; Razonable, R.R. Elizabethkingia species sepsis after lung transplantation: Case report and literature review. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, E229–E234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinckrodt, L.; Huis in’t Veld, R.; Rosema, S.; Voss, A.; Bathoorn, E. Review on infection control strategies to minimize outbreaks of the emerging pathogen Elizabethkingia anophelis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.E.; Schultz, H.H.L.; Johansen, H.K.; Pressler, T.; Lund, T.K.; Iversen, M.; Perch, M. Bacterial Re-Colonization Occurs Early after Lung Transplantation in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, M.; Rojas, L.J.; Marshall, S.H.; Hujer, A.M.; Cmolik, A.; Marshall, E.; Boucher, H.W.; Vila, A.J.; Soldevila, M.; Diene, S.M.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Pathogen in Immunocompromised Patients: Elizabethkingia anophelis-Exploring the Scope of Resistance to Contemporary Antimicrobial Agents and beta-lactamase Inhibitors. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofad014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCort, M.; MacKenzie, E.; Pursell, K.; Pitrak, D. Bacterial infections in lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 6654–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, C.C.; Razonable, R.R. Fungal Infection in Lung Transplantation. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 42, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 35th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Principles and Procedures for Detection and Culture of Fungi in Clinical Specimens, 2nd ed.; CLSI guideline M54; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Primary Transplant | Retransplant | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n = 20) | Patients (n = 10) | ||
| Age | 40.77 (12.35) | 49.00 (15.16) | 0.146 |
| Sex, male | 10 (50.0%) | 4 (40.0%) | 0.709 |
| BMI | 20.84 (2.88) | 19.21 (2.24) | 0.235 |
| Underlying pulmonary diseases | |||
| Idiopahtic pulmonary fibrosis | 8 (40.0%) | 2 (20.0%) | 0.419 |
| Chronic obtructive pulmonary disease | 3 (15.0%) | 4 (40.0%) | 0.181 |
| Acute respiratory ditress syndrome | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 0.667 |
| Tubeculosis | 6 (31.6%) | 3 (30.0%) | 1.000 |
| CPFE | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Diffuse panbronchiolitis | 2 (10.0%) | 0 | 0.540 |
| Bronchiolitis obliterans | 3 (15.0%) | 4 (40.0%) | 0.181 |
| CTD-ILD | 3 (15.0%) | 0 | 0.532 |
| Other ILD | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Pulmonary arterial hypertension | 0 | 3 (30.0%) | 0.030 * |
| Others | 2 (10.0%) | 2 (20.0%) | 0.615 |
| Underlying diseases | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 10 (50.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | 0.440 |
| Hypertension | 7 (35.0%) | 2 (20.0%) | 0.675 |
| Coronary artery occlusive disease | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1 (5.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 1.000 |
| Cerebral vascular disease | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2 (10.0%) | 2 (20.0%) | 0.584 |
| Chronic liver disease | 1 (5.0%) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Connective tissue disease | 3 (15.0%) | 0 | 0.532 |
| Cancer | 4 (20.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 0.584 |
| Previous stem cell transplantation | 3 (15.0%) | 2 (20.0%) | 1.000 |
| Immunosuppressants | |||
| Tacrolimus | 20 (100%) | 10 (100%) | - |
| Mycophenolate | 20 (100%) | 8 (80.0%) | 0.103 |
| Prednisolone | 20 (100%) | 10 (100%) | - |
| Cyclosporine | 20 (100%) | 10 (100%) | - |
| Azathioprine | 0 | 2 (20.0%) | 0.103 |
| Basiliximab | 1 (5.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 1.000 |
| Primary Transplant | Retransplant | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n = 20) | Patients (n = 10) | ||
| Overall mortality n (%) | |||
| 30 days | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 0.333 |
| 90 days | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | 0.333 |
| 1 year | 2 (10.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | 0.300 |
| 5 years | 4 (20.0%) | 7 (70.0%) | 0.015 * |
| Infection-related mortality | 4 (20.0%) | 7 (70.0%) | 0.015 * |
| Other outcomes (days) | |||
| Length of stay | 38 (26–89) | 106 (55–188) | 0.035 * |
| ICU stay | 8 (5–15) | 23 (14–31) | 0.017 * |
| BAL at <1 Month Post-Transplantation (n = 49) | BAL Isolates in Primary Transplant Patients (n = 30) | BAL Isolates in Retransplant Patients (n = 19) | ||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Gram-negative species | 13 | 43.3% | 11 | 57.9% |
| Escherichia coli | 2 | 6.7% | 3 | 15.8% |
| Klebsiella | 1 | 3.3% | 2 | 10.5% |
| Other Enterobacterales | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Pseudomonas | 3 | 10.0% | 0 | - |
| Acinetobacter | 6 | 20.0% | 0 | - |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Elizabethkingia | 0 | - | 6 | 31.6% |
| Other Gram-negative species | 1 | 3.3% | 0 | - |
| Gram-positive species | 15 | 50.0% | 5 | 26.3% |
| Coagulase negative staphylococcus | 5 | 16.7% | 2 | 10.5% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 2 | 6.7% | 0 | - |
| Streptococcus | 2 | 6.7% | 0 | - |
| Enterococcus | 3 | 10.0% | 0 | - |
| Other Gram-positive species | 3 | 10.0% | 3 | 15.8% |
| Fungus | 2 | 6.7% | 3 | 15.8% |
| Candida | 1 | 3.3% | 1 | 5.3% |
| Others | 1 | 3.3% | 2 | 10.5% |
| BAL at 1–6 months post-transplantation (n = 79) | BAL isolates in primary transplant patients (n = 19) | BAL isolates in retransplant patients (n = 60) | ||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Gram-negative species | 5 | 26.3% | 48 | 80.0% |
| Escherichia coli | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Klebsiella | 4 | 21.1% | 1 | 1.7% |
| Other Enterobacterales | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Pseudomonas | 0 | - | 17 | 28.3% |
| Acinetobacter | 1 | 5.3% | 2 | 3.3% |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Elizabethkingia | 0 | - | 27 | 45.0% |
| Other Gram-negative species | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Gram-positive species | 12 | 63.2% | 12 | 20.0% |
| Coagulase negative staphylococcus | 1 | 5.3% | 1 | 1.7% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Streptococcus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Enterococcus | 8 | 42.1% | 2 | 3.3% |
| Other Gram-positive species | 3 | 15.8% | 9 | 15.0% |
| Fungus | 2 | 10.5% | 0 | - |
| Candida | 2 | 10.5% | 0 | - |
| Others | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| BAL at 6–12 months post-transplantation (n = 54) | BAL isolates in primary transplant patients (n = 7) | BAL isolates in retransplant patients (n = 47) | ||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Gram-negative species | 4 | 57.1% | 32 | 68.1% |
| Escherichia coli | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Klebsiella | 2 | 28.6% | 0 | - |
| Other Enterobacterales | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Pseudomonas | 1 | 14.3% | 17 | 36.2% |
| Acinetobacter | 0 | - | 2 | 4.3% |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 0 | - | 2 | 4.3% |
| Elizabethkingia | 0 | - | 10 | 21.3% |
| Other Gram-negative species | 1 | 14.3% | 1 | 2.1% |
| Gram-positive species | 4 | 57.1% | 15 | 31.9% |
| Coagulase negative staphylococcus | 1 | 14.3% | 8 | 17.0% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Streptococcus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Enterococcus | 0 | - | 4 | 8.5% |
| Other Gram-positive species | 3 | 42.9% | 4 | 8.5% |
| Fungus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Candida | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Others | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| BAL at 1–2 years post-transplantation (n = 57) | BAL isolates in primary transplant patients (n = 6) | BAL isolates in retransplant patients (n = 51) | ||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Gram-negative species | 5 | 83.3 | 40 | 78.4% |
| Escherichia coli | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Klebsiella | 1 | 20.0% | 2 | 3.9% |
| Other Enterobacterales | 0 | - | 6 | 11.8% |
| Pseudomonas | 0 | - | 27 | 52.9% |
| Acinetobacter | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Elizabethkingia | 0 | - | 2 | 3.9% |
| Other Gram-negative species | 3 | 60.0% | 3 | 5.9% |
| Gram-positive species | 1 | 20.0% | 11 | 21.6% |
| Coagulase negative staphylococcus | 1 | 20.0% | 2 | 3.9% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Streptococcus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Enterococcus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Other Gram-positive species | 0 | - | 9 | 17.6% |
| Fungus | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Candida | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Others | 0 | - | 0 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.; Kim, J.H.; Woo, A.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Kim, H.E.; Lee, J.G.; Park, M.S.; Jeong, S.J. Clinical Characteristics, Outcomes, and Distribution Patterns of Pathogens Causing Respiratory Infections in Lung Retransplant Recipients. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090927
Han M, Kim JH, Woo A, Kim SY, Yang YH, Kim HE, Lee JG, Park MS, Jeong SJ. Clinical Characteristics, Outcomes, and Distribution Patterns of Pathogens Causing Respiratory Infections in Lung Retransplant Recipients. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):927. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090927
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Min, Jae Hoon Kim, Ala Woo, Song Yee Kim, Young Ho Yang, Ha Eun Kim, Jin Gu Lee, Moo Suk Park, and Su Jin Jeong. 2025. "Clinical Characteristics, Outcomes, and Distribution Patterns of Pathogens Causing Respiratory Infections in Lung Retransplant Recipients" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090927
APA StyleHan, M., Kim, J. H., Woo, A., Kim, S. Y., Yang, Y. H., Kim, H. E., Lee, J. G., Park, M. S., & Jeong, S. J. (2025). Clinical Characteristics, Outcomes, and Distribution Patterns of Pathogens Causing Respiratory Infections in Lung Retransplant Recipients. Antibiotics, 14(9), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090927





