Burden of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance in a Romanian Cardiovascular and Transplant Center: Factors Associated with Mortality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
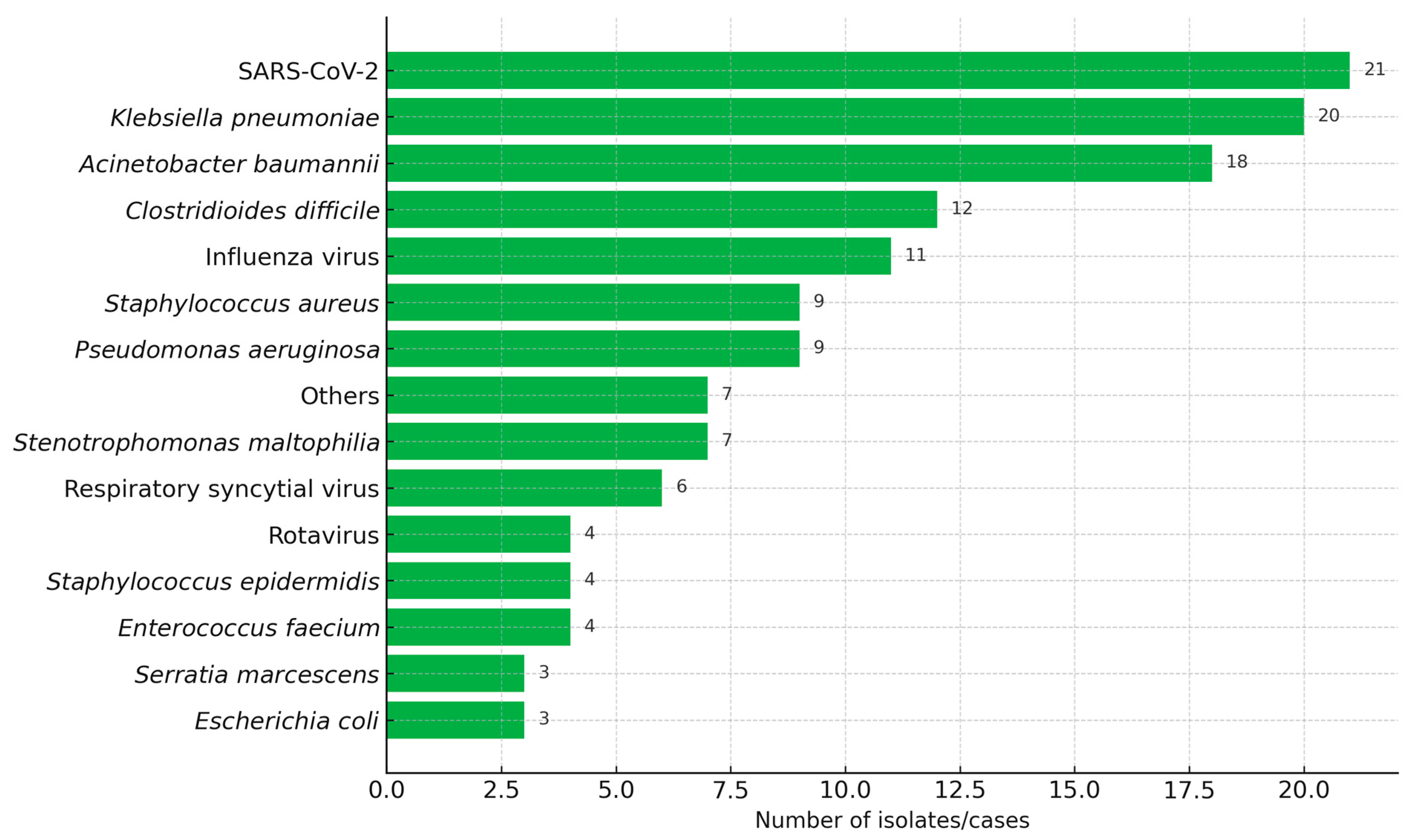
2.1. Sample Characteristics and Microorganisms
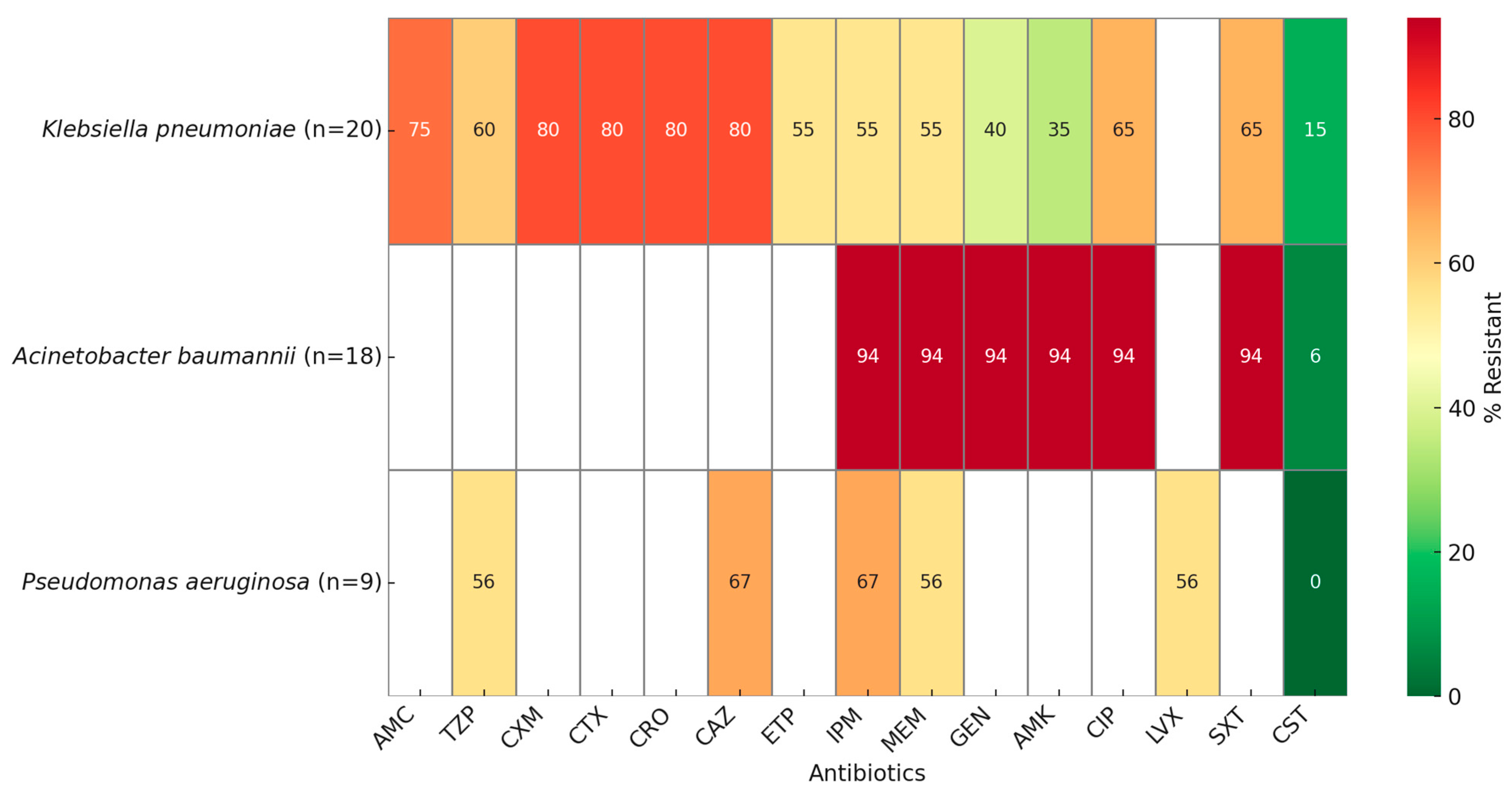
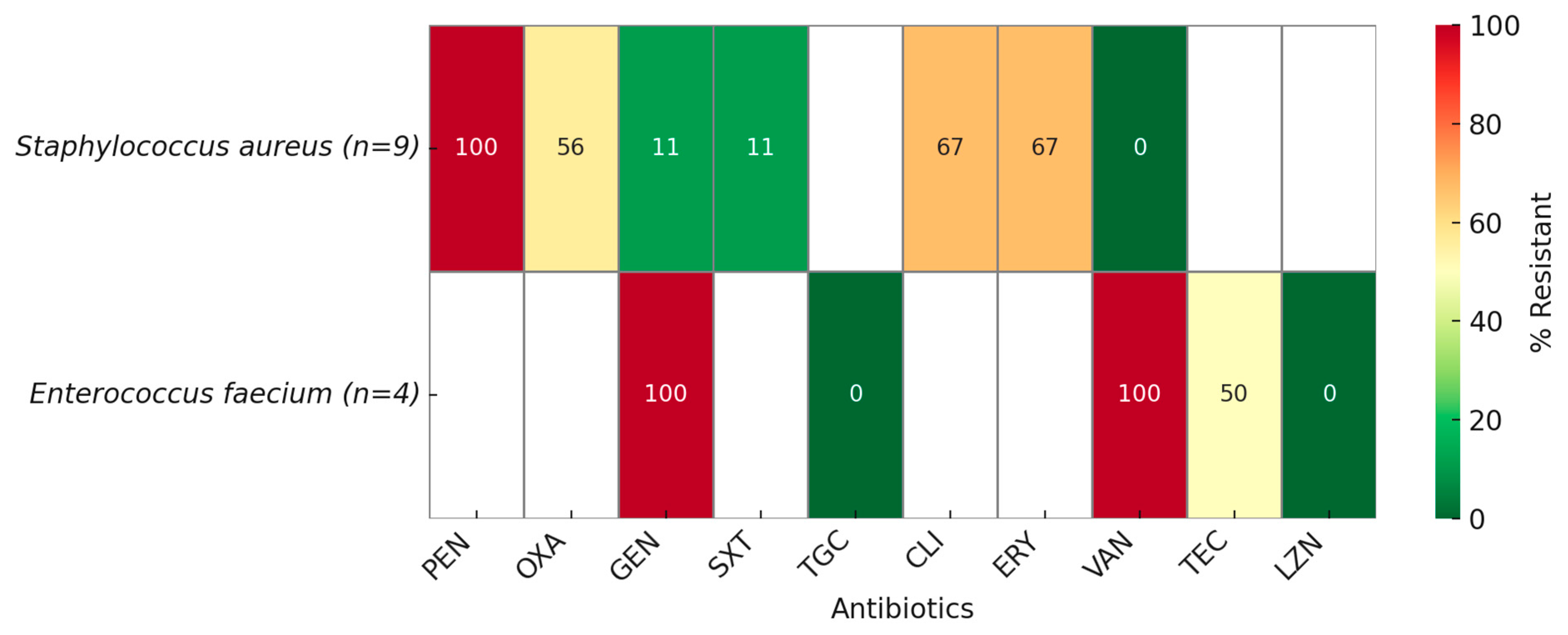
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance
2.3. Univariable Analysis of Factors Associated with Death Among Patients with Bacterial Infections
2.4. Multivariable Analysis of Factors Associated with Death Among Patients with Bacterial Infections
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Clinical Setting
4.2. Study Sample
4.3. Definitions
4.4. Data Collection
4.5. Ethics Approval
4.6. Microbiological Methods
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
| CPE | Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales |
| DDD | Defined Daily Dose |
| ECDC | European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control |
| ESBL | Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase |
| HAI | Healthcare-Associated Infection |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IPC | Infection Prevention and Control |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| MDR | Multidrug-Resistant |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| VRE | Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| XDR | Extensively Drug-Resistant |
References
- Raoofi, S.; Pashazadeh Kan, F.; Rafiei, S.; Hosseinipalangi, Z.; Noorani Mejareh, Z.; Khani, S.; Abdollahi, B.; Seyghalani Talab, F.; Sanaei, M.; Zarabi, F.; et al. Global prevalence of nosocomial infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0274248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.J.; Weldegiorgis, M.; Carter, E.; Brown, C.; Holmes, A.; Aylin, P. Economic Burden of Community-Acquired Antibiotic-Resistant Urinary Tract Infections: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024, 10, e53828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, S.; Cicala, M.; De Santo, C.; Mosconi, C.; Ciccacci, F.; Guarente, L.; Carestia, M.; Liotta, G.; Di Giovanni, D.; Buonomo, E.; et al. The financial burden of healthcare-associated infections: A propensity score analysis in an Italian healthcare setting. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2025, 7, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-H.; Chien, L.-J.; Fang, C.-T.; Chang, S.-C. Excess mortality and long-term disability from healthcare-associated carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: A nationwide population-based matched cohort study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Robertson, C.; Pan, J.; Kennedy, S.; Haahr, L.; Manoukian, S.; Mason, H.; Kavanagh, K.; Graves, N.; Dancer, S.J.; et al. Impact of healthcare-associated infection on length of stay. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 114, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoe, D.S.; Advani, S.D.; Anderson, D.J.; Babcock, H.M.; Bell, M.; Berenholtz, S.M.; Bryant, K.A.; Buetti, N.; Calderwood, M.S.; Calfee, D.P.; et al. Introduction to A Compendium of Strategies to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections in Acute-Care Hospitals: 2022 Updates. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, B.; Lamichhane, G.; Wamburu, A. Infection prevention and control: Critical strategies for nursing practice. Br. J. Nurs. Mark Allen Publ. 2024, 33, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzeffi, M.; Galvagno, S.; Rock, C. Prevention of Healthcare-associated Infections in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Anesthesiology 2021, 135, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoe, D.S.; Jackson, P. Saving lives through infection prevention, healthcare epidemiology, and antimicrobial stewardship: Getting back to preventing healthcare-associated infections. Am. J. Infect. Control 2024, 52, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, K.J.; Aureden, K.; Ham, D.C.; Harris, A.D.; Hessels, A.J.; Huang, S.S.; Maragakis, L.L.; Milstone, A.M.; Moody, J.; Yokoe, D.; et al. SHEA/IDSA/APIC Practice Recommendation: Strategies to prevent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus transmission and infection in acute-care hospitals: 2022 Update. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 1039–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Worthington, H.V.; Hua, F. Oral hygiene care for critically ill patients to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD008367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricchizzi, E.; Sasdelli, E.; Leucci, A.C.; Fabbri, E.; Caselli, L.; Latour, K.; Panis, L.I.; Baets, E.D.; den Abeele, A.-M.V.; D’Ambrosio, A.; et al. Incidence of health-care-associated infections in long-term care facilities in nine European countries: A 12-month, prospective, longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals—2022–2023. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/PPS-HAI-AMR-acute-care-europe-2022-2023 (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Healthcare-Associated Infections. 2023. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthcare-associated-infections (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Zacher, B.; Haller, S.; Willrich, N.; Walter, J.; Abu Sin, M.; Cassini, A.; Plachouras, D.; Suetens, C.; Behnke, M.; Gastmeier, P.; et al. Application of a new methodology and R package reveals a high burden of healthcare-associated infections (HAI) in Germany compared to the average in the European Union/European Economic Area, 2011 to 2012. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2019, 24, 1900135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kooi, T.; Lepape, A.; Astagneau, P.; Suetens, C.; Nicolaie, M.A.; de Greeff, S.; Lozoraitiene, I.; Czepiel, J.; Patyi, M.; Plachouras, D.; et al. Mortality review as a tool to assess the contribution of healthcare-associated infections to death: Results of a multicentre validity and reproducibility study, 11 European Union countries, 2017 to 2018. Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2021, 26, 2000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, T.J.; Kompithra, R.Z. Eco-epidemiology triad to explain infectious diseases. Indian J. Med. Res. 2023, 158, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voidazan, S.; Albu, S.; Toth, R.; Grigorescu, B.; Rachita, A.; Moldovan, I. Healthcare Associated Infections-A New Pathology in Medical Practice? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, A.; Pop, D.; Muresan, F.; Oprescu, F.; Fjaagesund, S. Surveillance and Reporting of Hospital-Associated Infections-A Document Analysis of Romanian Healthcare Legislation Evolution over 20 Years. Healthcare 2025, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, S.; Feier, B.; Capatina, D.; Tertis, M.; Cristea, C.; Popa, A. An Overview of Healthcare Associated Infections and Their Detection Methods Caused by Pathogen Bacteria in Romania and Europe. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, S.; Feier, B.; Mărginean, A.; Dumitrana, A.-E.; Costin, S.L.; Cristea, C.; Bolboacă, S.D. Evaluation of the Bacterial Infections and Antibiotic Prescribing Practices in the Intensive Care Unit of a Clinical Hospital in Romania. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iancu, D.; Moldovan, I.; Țilea, B.; Voidăzan, S. Evaluating Healthcare-Associated Infections in Public Hospitals: A Cross-Sectional Study. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abejew, A.A.; Wubetu, G.Y.; Fenta, T.G. Relationship between Antibiotic Consumption and Resistance: A Systematic Review. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. J. Can. Mal. Infect. Microbiol. Medicale 2024, 2024, 9958678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMC|European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Available online: https://qap.ecdc.europa.eu/public/extensions/AMC2_Dashboard/AMC2_Dashboard.html#eu-consumption-tab (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Ghiga, I.; Pitchforth, E.; Stålsby Lundborg, C.; Machowska, A. Family doctors’ roles and perceptions on antibiotic consumption and antibiotic resistance in Romania: A qualitative study. BMC Prim. Care 2023, 24, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Long, X.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y.; Ren, H. Global trend of antimicrobial resistance in common bacterial pathogens in response to antibiotic consumption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, I.; Godman, B.; Malaj, A.; Meyer, J.C. 11-Year Trend in Antibiotic Consumption in a South-Eastern European Country; the Situation in Albania and the Implications for the Future. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoom, A.; Donkor, E.S. Prevalence of Healthcare-Acquired Infections Among Adults in Intensive Care Units: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, K.; Gidey, M.T.; Hailu, B.Y.; Gebreamlak, Z.B.; Niriayo, Y.L. Clinical and economic burden of healthcare-associated infections: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Wei, N.; Zhang, J.; Ma, W.; Zhao, H.; Han, X. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of healthcare-associated infection in elderly patients in a large Chinese tertiary hospital: A 3-year surveillance study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurici, M.; D’Alò, G.L.; Fontana, C.; Santoro, V.; Gaziano, R.; Ciotti, M.; Cicciarella Modica, D.; De Filippis, P.; Sarmati, L.; De Carolis, G.; et al. Microbiology and Clinical Outcome of Hospital-Acquired Respiratory Infections in an Italian Teaching Hospital: A Retrospective Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, H.; Miranda-Novales, G.; Lorenzo-Hernández, L.M.; Luna, A.T. Risk factors for healthcare-associated infections in newborns after surgery in a neonatal intensive care unit. Gac. Med. Mex. 2023, 159, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, V.D.; Jin, Z.; Rodrigues, C.; Myatra, S.N.; Divatia, J.V.; Biswas, S.K.; Shrivastava, A.M.; Kharbanda, M.; Nag, B.; Mehta, Y.; et al. Risk factors for mortality over 18 years in 317 ICUs in 9 Asian countries: The impact of healthcare-associated infections. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ye, L.; Yu, Z.; Yao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, M. Epidemiology and outcomes of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in patients with hematological malignancies from 2014 to 2022. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1507908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarak-Qamsari, M.; Jenaghi, B.; Sahebi, L.; Norouzi-Shadehi, M.; Salehi, M.-R.; Shakoori-Farahani, A.; Khoshnevis, H.; Abdollahi, A.; Feizabadi, M.-M. Evaluation of Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus respiratory tract superinfections among patients with COVID-19 at a tertiary-care hospital in Tehran, Iran. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindu, M.; Moges, F.; Ashagrie, D.; Tigabu, Z.; Gelaw, B. Multidrug-resistant and carbapenemase-producing critical gram-negative bacteria isolated from the intensive care unit environment in Amhara region, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakobi, S.H.; Nwodo, U.U. Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae in the South African Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Surveillance Studies. MicrobiologyOpen 2025, 14, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, F.M.; Akinlade, E.A.; Yusuf-Omoloye, N.A.; Ajigbewu, O.H.; Dare, A.P.; Wahab, A.A.; Oyedara, O.O.; Isiaka, H.S.; Usamat, A.O. Carbapenem-resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Prevalence, antibiotic resistance profile and carbapenemase genes in clinical and hospital environmental strains. BMC Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. The burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in the WHO African region in 2019: A cross-country systematic analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e201–e216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance, to Guide Research, Development, and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zirpe, K.G.; Gurav, S.K.; Dhawad, P.A.; Tiwari, A.M.; Deshmukh, A.M.; Suryawanshi, P.B.; Kapse, U.S.; Wankhede, P.P.; Bhoyar, A.P.; Malhotra, R.V.; et al. Hospital-acquired Infections in the Adult Intensive Care Unit: Epidemiology, Resistance Patterns, and Risk Factors. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2025, 73, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Seifi, A.; Jaafaripooyan, E.; Jahangard-Rafsanjani, Z.; Afhami, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Emami Meybodi, M.M.; Salehi, M.; Mohammadnejad, E. Burden of nosocomial infections in intensive care units: Cost of antibiotics, the extra length of stay and mortality rate. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 15, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cındık, N.; Gökdemir, M.; Çelik, M.; Günaydın, A.Ç. Risk factors for and incidence of hospital-acquired infections after cardiac surgery in children with congenital heart disease: A single center experience. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2023, 65, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- One Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/one-health (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Brown, H.L.; Pursley, I.G.; Horton, D.L.; La Ragione, R.M. One health: A structured review and commentary on trends and themes. One Health Outlook 2024, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEFINIȚIA GENERALĂ A IAAM—Asociația Pentru Prevenirea și Controlul Infecțiilor—APCI. Available online: https://apci.ro/definitii-iaam/definitia-generala-a-iaam/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Survived n = 55 (%) | Deceased n = 41 (%) | OR * | 95%CI ** | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year of diagnosis | |||||
| 2023 | 23 (42) | 24 (58) | Reference | ||
| 2024 | 25 (45) | 15 (37) | 0.57 | 0.24–1.35 | 0.20 |
| 2025 | 7 (13) | 2 (5) | 0.27 | 0.05–1.45 | 0.12 |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 21 (38) | 16 (39) | Reference | ||
| Male | 34 (62) | 25 (61) | 0.96 | 0.42–2.21 | 0.93 |
| Age, years | |||||
| <18 | 25 (45) | 10 (24) | 0.28 | 0.10–0.76 | 0.01 |
| 18–34 | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | 0.35 | 0.02–4.24 | 0.41 |
| 35–49 | 4 (7) | 6 (15) | 1.05 | 0.24–4.42 | 0.94 |
| 50–64 | 10 (18) | 4 (10) | 0.28 | 0.07–1.07 | 0.06 |
| >65 | 14 (26) | 20 (49) | Base | ||
| ICU admission | |||||
| No | 28 (51) | 4 (10) | Reference | ||
| Yes | 27 (49) | 37 (90) | 9.59 | 3.00–30.57 | <0.001 |
| Antimicrobial resistance | |||||
| No | 34 (62) | 11 (27) | Reference | ||
| Yes | 21 (38) | 30 (73) | 4.41 | 1.83–10.63 | 0.001 |
| Phenotypic patterns of resistance *** | |||||
| No resistance | 34 (62) | 11 (27) | Reference | ||
| ESBL | 5 (9) | 6 (15) | 3.70 | 0.94–14.56 | 0.06 |
| CPE | 2 (4) | 7 (17) | 10.18 | 1.95–59.94 | 0.006 |
| MRSA | 4 (7) | 1 (2) | 0.77 | 0.07–7.66 | 0.82 |
| MDR | 1 (2) | 0 | |||
| VRE | 3 (5) | 1 (2) | 1.03 | 0.09–10.94 | 0.98 |
| XDR | 6 (11) | 15 (37) | 7.72 | 2.40–24.78 | 0.001 |
| Number of antibiotics | |||||
| 1–3 | 37 (67) | 6 (15) | Reference | <0.001 | |
| >3 | 18 (33) | 35 (85) | 11.99 | 4.26–33.69 |
| aOR * | 95%CI ** | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | |||
| <18 | 0.57 | 0.15–2.04 | 0.39 |
| 18–34 | 0.78 | 0.03–19.79 | 0.88 |
| 35–49 | 4.15 | 0.53–32.31 | 0.17 |
| 50–64 | 0.34 | 0.06–1.74 | 0.19 |
| >65 | Reference | ||
| ICU admission | |||
| No | Reference | ||
| Yes | 5.89 | 1.39–24.91 | 0.016 |
| Antimicrobial resistance | |||
| No | Reference | ||
| Yes | 1.52 | 0.47–4.84 | 0.47 |
| Number of antibiotics | |||
| 1–3 | Reference | 0.002 | |
| >3 | 6.79 | 2.00–23.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budianu, M.-A.; Ciurea, C.N.; Moraru, L.; Voidăzan, S. Burden of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance in a Romanian Cardiovascular and Transplant Center: Factors Associated with Mortality. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090926
Budianu M-A, Ciurea CN, Moraru L, Voidăzan S. Burden of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance in a Romanian Cardiovascular and Transplant Center: Factors Associated with Mortality. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090926
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudianu, Mihaela-Alexandra, Cristina Nicoleta Ciurea, Liviu Moraru, and Septimiu Voidăzan. 2025. "Burden of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance in a Romanian Cardiovascular and Transplant Center: Factors Associated with Mortality" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090926
APA StyleBudianu, M.-A., Ciurea, C. N., Moraru, L., & Voidăzan, S. (2025). Burden of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Resistance in a Romanian Cardiovascular and Transplant Center: Factors Associated with Mortality. Antibiotics, 14(9), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090926







