Genomic Analysis of MRSA for Evaluating Local Transmission Dynamics in Geriatric Long-Term Care Facilities in Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
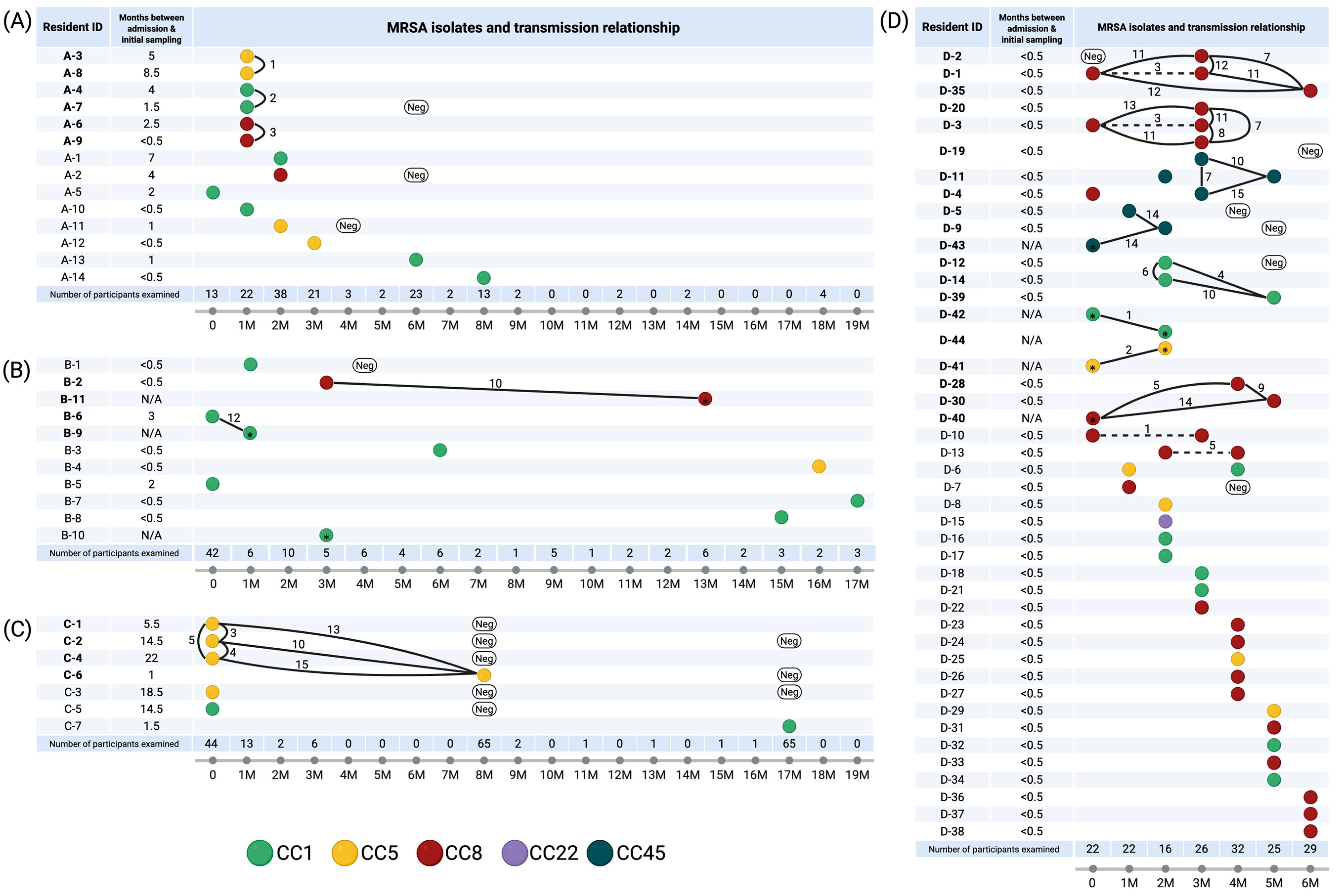
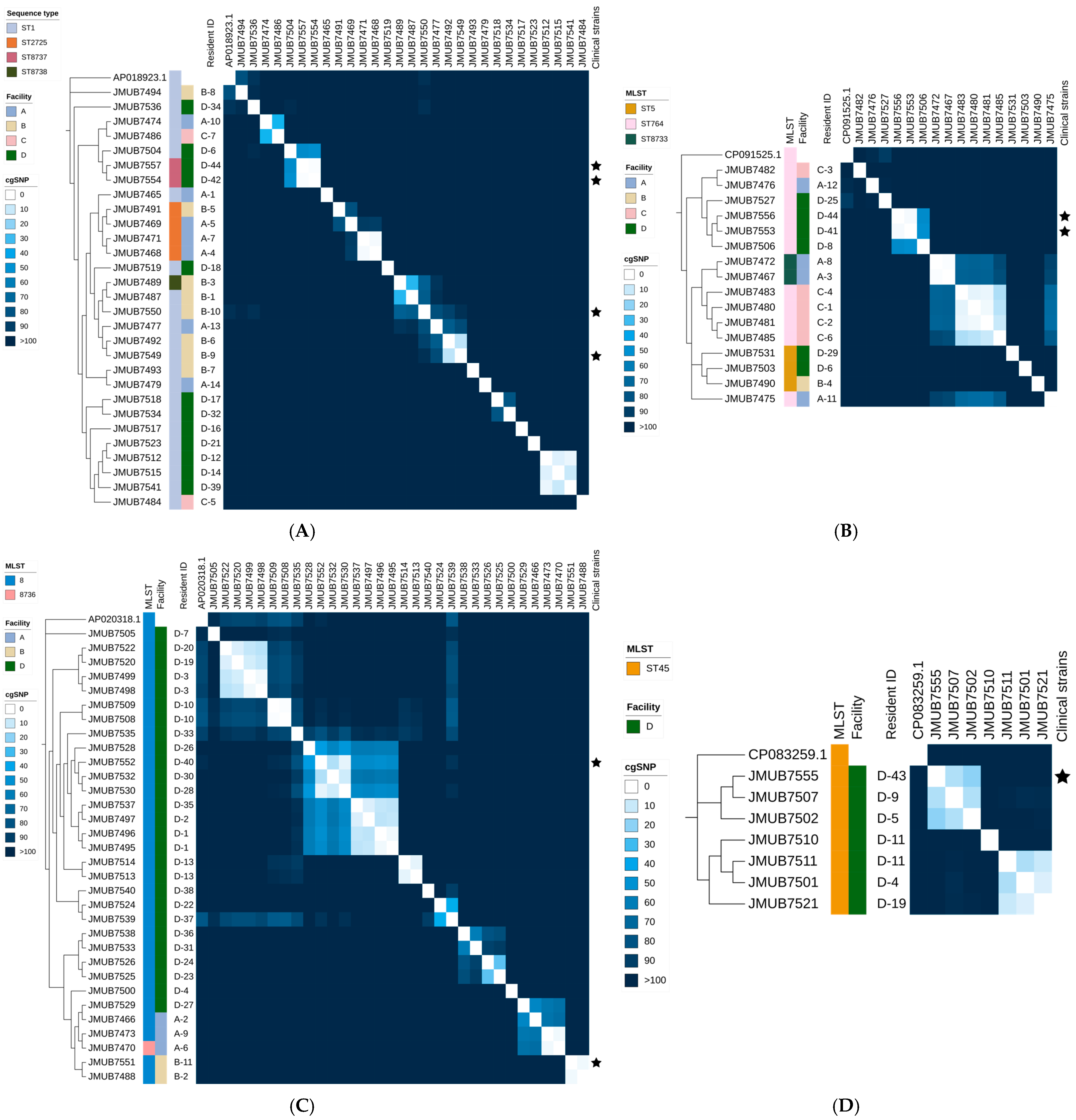
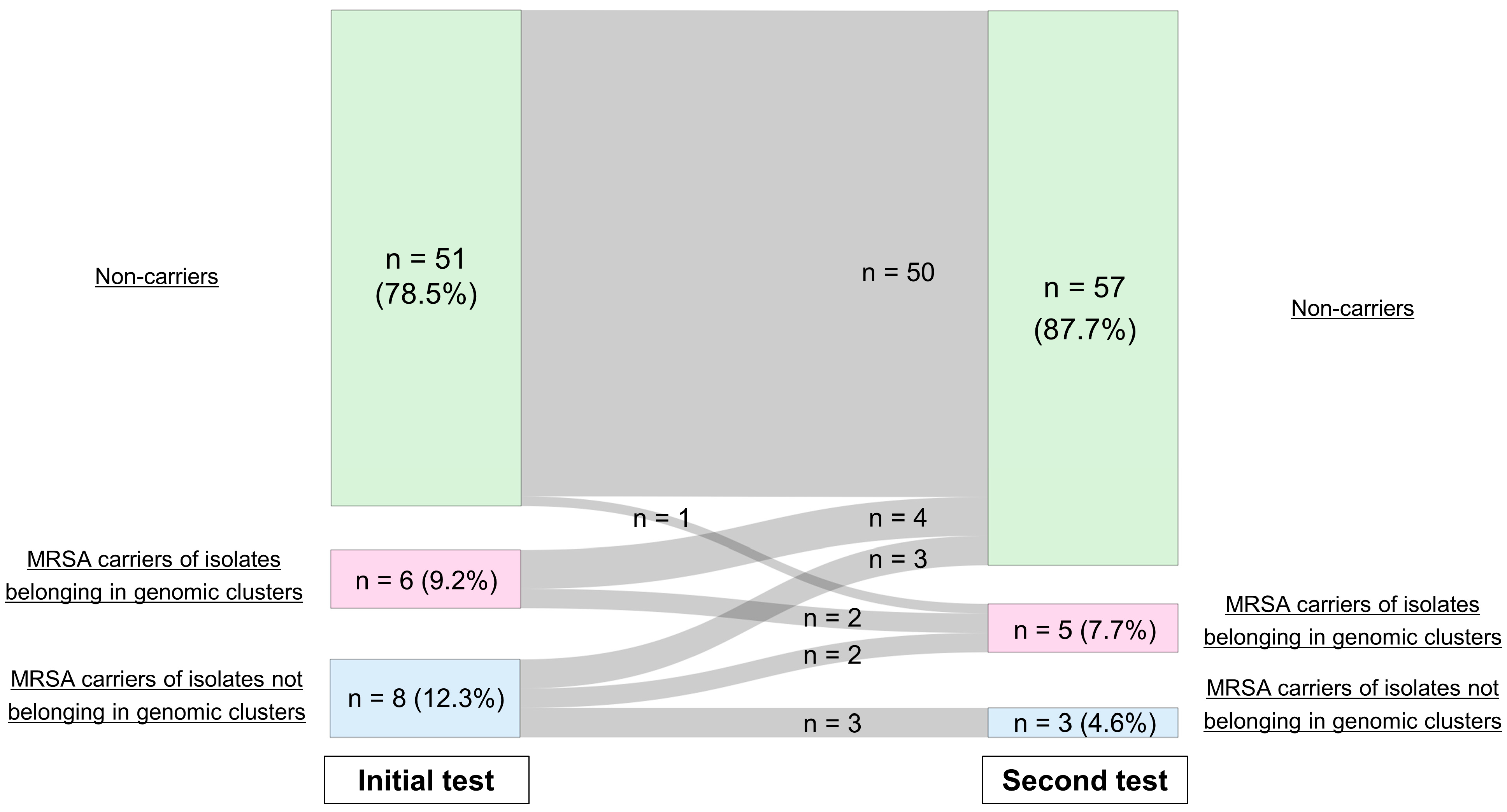
2. Results
2.1. Genetic Features of MRSA Isolates
2.2. SNP Analysis and Identification of Genomic Clusters
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Genetic AMR Profile
2.4. Virulence Gene Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates and Study Facilities
4.2. WGS and Transmission Analysis
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Detecting AMR Genes
4.4. Detection of Virulence Factor
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| LTCFs | Long-term care facilities |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| IPC | Infection prevention and control |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| CA-MRSA | Community-associated MRSA |
| MLST | Multi-locus sequence type |
| cgSNP | Core-genome SNP |
| pan-GWAS | Pan-genome-wide association study |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| RASi | Renin–angiotensin system inhibitor |
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [CrossRef]
- Safdar, N.; Maki, D.G. The Commonality of Risk Factors for Nosocomial Colonization and Infection with Antimicrobial-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus, Enterococcus, Gram-Negative Bacilli, Clostridium Difficile, and Candida. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, A.H.; Sepidarkish, M.; Mollalo, A.; Ardekani, A.; Almukhtar, M.; Mechaal, A.; Hosseini, S.R.; Bayani, M.; Javanian, M.; Rostami, A. The Global Prevalence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization in Residents of Elderly Care Centers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, A.; Aschbacher, R.; Dhanji, H.; Livermore, D.M.; Böttcher, A.; Sleghel, F.; Maggi, S.; Noale, M.; Larcher, C.; Woodford, N. Colonization of Residents and Staff of a Long-Term-Care Facility and Adjacent Acute-Care Hospital Geriatric Unit by Multiresistant Bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamblin, J.; Jefferies, J.M.; Harris, S.; Ahmad, N.; Marsh, P.; Faust, S.N.; Fraser, S.; Moore, M.; Roderick, P.; Blair, I.; et al. Nasal Self-Swabbing for Estimating the Prevalence of Staphylococcus Aureus in the Community. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, N.S.; Gilpin, D.F.; Tunney, M.M.; Kearney, M.P.; Crymble, L.; Cardwell, C.; Hughes, C.M. Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial of an Infection Control Education and Training Intervention Programme Focusing on Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Nursing Homes for Older People. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 76, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Lim, V.W.; Khan, A.; Pettigrew, K.; Lye, D.C.B.; Kanagasabai, K.; Phua, K.; Krishnan, P.; Ang, B.; Marimuthu, K.; et al. MRSA Transmission Dynamics Among Interconnected Acute, Intermediate-Term, and Long-Term Healthcare Facilities in Singapore. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, S76–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Brodrick, H.J.; Blane, B.; Brennan, G.; Morris, D.; Coll, F.; Reuter, S.; Brown, N.M.; Holmes, M.A.; et al. Transmission of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Long-Term Care Facilities and Their Related Healthcare Networks. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Arai, H. Long-Term Care System in Japan. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 2020, 24, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Population Estimates by Age (Five-Year Groups) and Sex-1 May 2023 (Final Estimates), 1 October 2023 (Provisional Estimates). Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/en/stat-search/files?page=1&layout=datalist&toukei=00200524&tstat=000000090001&cycle=1&year=20230&month=24101210&tclass1=000001011678&result_back=1&tclass2val=0 (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Sasahara, T.; Ae, R.; Yoshimura, A.; Kosami, K.; Sasaki, K.; Kimura, Y.; Akine, D.; Ogawa, M.; Hamabata, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; et al. Association between Length of Residence and Prevalence of MRSA Colonization among Residents in Geriatric Long-Term Care Facilities. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.S.; Singh, R.; McKinnell, J.A.; Park, S.; Gombosev, A.; Eells, S.J.; Gillen, D.L.; Kim, D.; Rashid, S.; Macias-Gil, R.; et al. Decolonization to Reduce Postdischarge Infection Risk among MRSA Carriers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.G.; McKinnell, J.A.; Singh, R.D.; Gussin, G.M.; Kleinman, K.; Saavedra, R.; Mendez, J.; Catuna, T.D.; Felix, J.; Chang, J.; et al. Decolonization in Nursing Homes to Prevent Infection and Hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, B.A.; Chambers, H.F.; Graber, C.J.; Szumowski, J.D.; Miller, L.G.; Han, L.L.; Chen, J.H.; Lin, F.; Lin, J.; Phan, T.H.; et al. Emergence of Multidrug-Resistant, Community-Associated, Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Clone USA300 in Men Who Have Sex with Men. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, T.; Gladman, J.; Gordon, A.L. The Treatment of Hypertension in Care Home Residents: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fralick, M.; Macdonald, E.M.; Gomes, T.; Antoniou, T.; Hollands, S.; Mamdani, M.M.; Juurlink, D.N. Canadian Drug Safety and Effectiveness Research Network Co-Trimoxazole and Sudden Death in Patients Receiving Inhibitors of Renin-Angiotensin System: Population Based Study. BMJ 2014, 349, g6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, N.; Sasaki, D.; Ota, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Yanagihara, K. Changing Molecular Epidemiology and Characteristics of MRSA Isolated from Bloodstream Infections: Nationwide Surveillance in Japan in 2019. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisatsune, J.; Kutsuno, S.; Iwao, Y.; Ishida-Kuroki, K.; Yahara, K.; Kitamura, N.; Kajihara, T.; Kayama, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Kitagawa, H.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus ST764-SCCmecII High-Risk Clone in Bloodstream Infections Revealed through National Genomic Surveillance Integrating Clinical Data. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Kitaoka, K.; Kimura, K.; Wachino, J.-I.; Kondo, T.; Iinuma, Y.; Murakami, N.; Fujimoto, S.; Arakawa, Y. Spread of Seb-Positive Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus SCCmec Type II-ST764 Among Elderly Japanese in Nonacute Care Settings. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Htun, H.L.; Hon, P.-Y.; Ang, B.; Kanagasabai, K.; Koh, J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Hsu, L.-Y. Comparative Epidemiology and Factors Associated with Major Healthcare-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Clones among Interconnected Acute-, Intermediate- and Long-Term Healthcare Facilities in Singapore. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 785.e9–785.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, A.; Kinnevey, P.; Shore, A.; Earls, M.; Poovelikunnel, T.T.; Brennan, G.; Humphreys, H.; Coleman, D.C. The Oral Cavity Revealed as a Significant Reservoir of Staphylococcus Aureus in an Acute Hospital by Extensive Patient, Healthcare Worker and Environmental Sampling. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnevey, P.M.; Kearney, A.; Shore, A.C.; Earls, M.R.; Brennan, G.; Poovelikunnel, T.T.; Humphreys, H.; Coleman, D.C. Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Transmission among Healthcare Workers, Patients and the Environment in a Large Acute Hospital under Non-Outbreak Conditions Investigated Using Whole-Genome Sequencing. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 118, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Total-Genome-Sequenced Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the Pubmlst.org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Hasman, H.; Larsen, J.; Stegger, M.; Johannesen, T.B.; Allesøe, R.L.; Lemvigh, C.K.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O.; Larsen, A.R. SCCmecFinder, a Web-Based Tool for Typing of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Mec in Staphylococcus Aureus Using Whole-Genome Sequence Data. mSphere 2018, 3, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, M.D.; Petersen, A.; Worning, P.; Nielsen, J.B.; Larner-Svensson, H.; Johansen, H.K.; Andersen, L.P.; Jarløv, J.O.; Boye, K.; Larsen, A.R.; et al. Comparing Whole-Genome Sequencing with Sanger Sequencing for Spa Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4305–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid Large-Scale Prokaryote Pan Genome Analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin-Hill, G. Pairsnp: A Set of Scripts for Calculating Pairwise SNP Distance. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/gtonkinhill/pairsnp (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Coll, F.; Raven, K.E.; Knight, G.M.; Blane, B.; Harrison, E.M.; Leek, D.; Enoch, D.A.; Brown, N.M.; Parkhill, J.; Peacock, S.J. Definition of a Genetic Relatedness Cutoff to Exclude Recent Transmission of Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: A Genomic Epidemiology Analysis. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e328–e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Treangen, T.J.; Melsted, P.; Mallonee, A.B.; Bergman, N.H.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. Mash: Fast Genome and Metagenome Distance Estimation Using MinHash. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynildsrud, O.; Bohlin, J.; Scheffer, L.; Eldholm, V. Rapid Scoring of Genes in Microbial Pan-Genome-Wide Association Studies with Scoary. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI Supplement M100. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for Predictions of Phenotypes from Genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A Novel Web Tool for WGS-Based Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Associated with Chromosomal Point Mutations in Bacterial Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malberg Tetzschner, A.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Lund, O.; Scheutz, F. In Silico Genotyping of Escherichia Coli Isolates for Extraintestinal Virulence Genes by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-Time Whole-Genome Sequencing for Routine Typing, Surveillance, and Outbreak Detection of Verotoxigenic Escherichia Coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| A | B | C | D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC and MLST, n (%) | ||||||
| CC1 | ||||||
| ST1 | 4 (28.6%) | 6 (54.5%) | 2 (28.6%) | 10 (18.9%) | ||
| ST2725 | 3 (21.4%) | 1 (9.1%) | - | - | ||
| ST8737 | - | - | - | 2 (3.8%) | ||
| ST8738 | - | 1 (9.1%) | - | - | ||
| CC5 | ||||||
| ST5 | - | 1 (9.1%) | - | 2 (3.8%) | ||
| ST764 | 2 (14.3%) | - | 5 (71.4%) | 4 (7.5%) | ||
| ST8733 | 2 (14.3%) | - | - | - | ||
| CC8 | ||||||
| ST8 | 2 (14.3%) | 2 (18.2%) | - | 27 (50.9%) | ||
| ST8736 | 1 (7.1%) | - | - | - | ||
| CC22 | ||||||
| ST22 | - | - | - | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| CC45 | ||||||
| ST45 | - | - | - | 7 (13.2%) | ||
| SCCmec type, n (%) | ||||||
| II | 4 (28.6%) | 1 (9.1%) | 5 (71.4%) | 7 (13.2%) | ||
| IVa | 10 (71.4%) | 8 (72.7%) | 2 (28.6%) | 13 (24.5%) | ||
| IVc | - | 2 (18.2%) | - | - | ||
| IVj | - | - | - | 27 (50.9%) | ||
| V | - | - | - | 6 (11.3%) | ||
| spa type, n (%) | ||||||
| t002 | 3 (21.4%) | - | 3 (42.9%) | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| t005 | - | - | - | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| t008 | 2 (14.3%) | 2 (18.2%) | - | 2 (3.8%) | ||
| t010 | - | - | 1 (14.3%) | - | ||
| t045 | 1 (7.1%) | - | - | 3 (5.7%) | ||
| t062 | - | - | - | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| t211 | - | - | - | 3 (5.7%) | ||
| t334 | - | - | - | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| t1062 | - | 1 (9.1%) | - | - | ||
| t1081 | - | - | - | 6 (11.3%) | ||
| t1767 | - | - | - | 2 (3.8%) | ||
| t1781 | - | - | 1 (14.3%) | - | ||
| t1784 | 7 (50.0%) | 5 (45.5%) | 2 (28.6%) | 11 (20.8%) | ||
| t2427 | - | - | - | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| t3081 | - | - | - | 2 (3.8%) | ||
| t4494 | - | 3 (27.3%) | - | - | ||
| t5071 | - | - | - | 15 (28.3%) | ||
| t7744 | - | - | - | 1 (1.9%) | ||
| t20946 | 1 (7.1%) | - | - | - | ||
| Unknown type | - | - | - | 3 (5.7%) | ||
| A | B | C | D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Facility type | HSF | HSF | SNH | HSF | ||
| Resident capacity, n | 100 | 50 | 60 | 150 | ||
| Region of Japan | Eastern | Eastern | Eastern | Western | ||
| Number of participants, n | 128 | 99 | 89 | 135 | ||
| Number of participants with at least one MRSA isolation, n | 14 | 11 | 7 | 44 | ||
| Number of isolates, n | 14 | 11 | 7 | 53 | ||
| Source of samples, n | ||||||
| Nasal swab | ||||||
| Clinical specimen | ||||||
| Airway tract secretions | - | - | - | 5 | ||
| Urine | - | - | - | 1 | ||
| Otitis externa | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Skin abscess | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Dacryocystitis | - | 1 | - | - | ||
| Number of participants sorted by test frequency, n | ||||||
| 1 time | 109 | 90 | 18 | 96 | ||
| 2 times | 19 | 9 | 30 | 39 | ||
| 3 times | - | - | 41 | - | ||
| Frequency of nasal swab tests, median (IQR) | 1 (1–1) | 1 (1–1) | 2 (2–3) | 1 (1–2) | ||
| Timing of the first nasal swab test from admission, median (IQR), month | 2.5 (1.0–7.4) | <0.5 (<0.5–4.3) | 7.0 (1.0–25.5) | <0.5 (<0.5–<0.5) | ||
| Duration of the study, month | 20 | 18 | 20 | 7 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suzuki, T.; Sasahara, T.; Watanabe, S.; Kosami, K.; Akine, D.; Kinoshita, Y.; Cui, L.; Hatakeyama, S. Genomic Analysis of MRSA for Evaluating Local Transmission Dynamics in Geriatric Long-Term Care Facilities in Japan. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090874
Suzuki T, Sasahara T, Watanabe S, Kosami K, Akine D, Kinoshita Y, Cui L, Hatakeyama S. Genomic Analysis of MRSA for Evaluating Local Transmission Dynamics in Geriatric Long-Term Care Facilities in Japan. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090874
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuzuki, Takayuki, Teppei Sasahara, Shinya Watanabe, Koki Kosami, Dai Akine, Yumi Kinoshita, Longzhu Cui, and Shuji Hatakeyama. 2025. "Genomic Analysis of MRSA for Evaluating Local Transmission Dynamics in Geriatric Long-Term Care Facilities in Japan" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090874
APA StyleSuzuki, T., Sasahara, T., Watanabe, S., Kosami, K., Akine, D., Kinoshita, Y., Cui, L., & Hatakeyama, S. (2025). Genomic Analysis of MRSA for Evaluating Local Transmission Dynamics in Geriatric Long-Term Care Facilities in Japan. Antibiotics, 14(9), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090874







