Unexplained High Prevalence of ESBL-Escherichia coli Among Cattle and Pigs in Peru
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
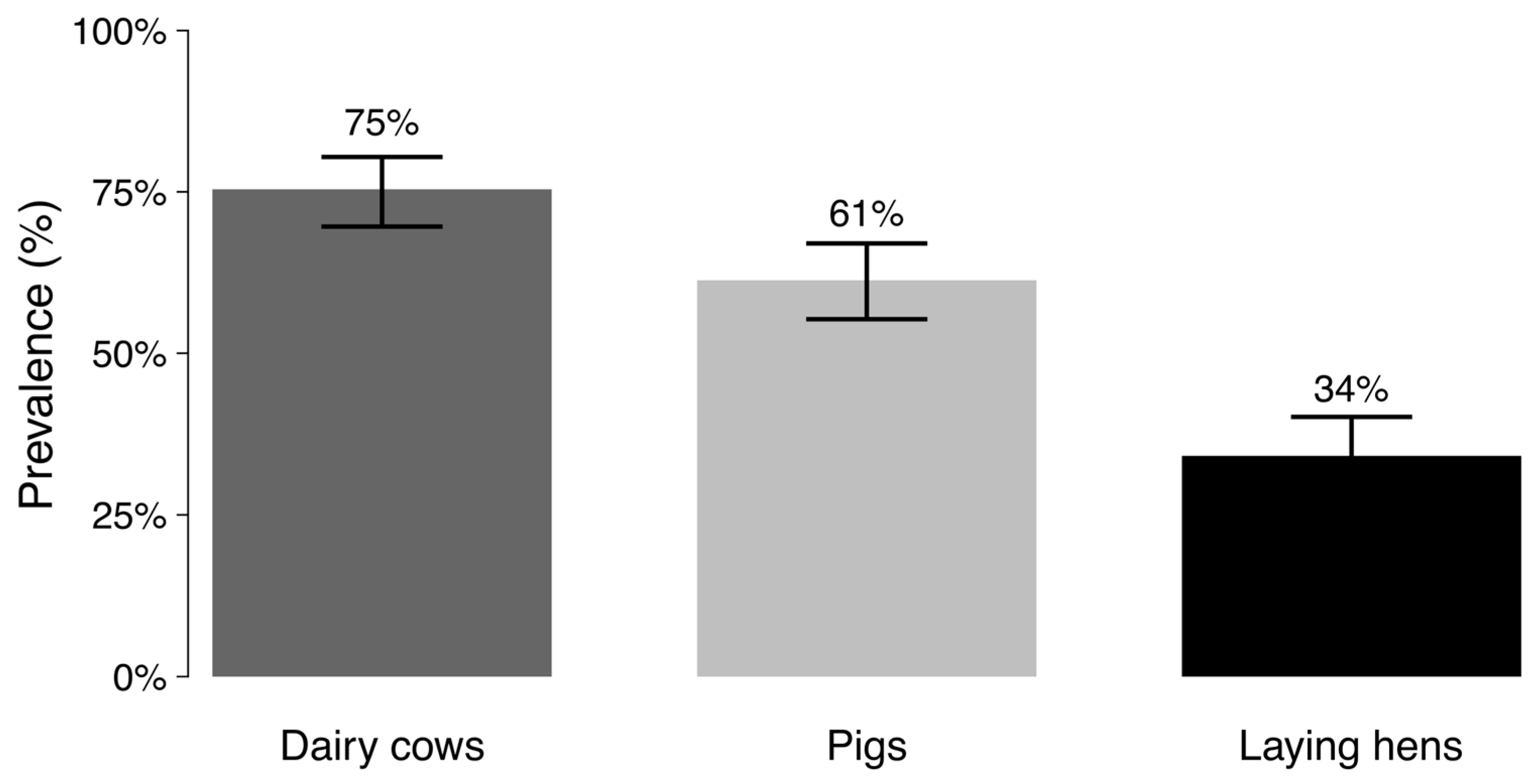
2.1. Prevalence of ESBL-E. coli Fecal Carriage by Livestock Species
2.2. Farmers’ Socioeconomic Characteristics
2.3. Differences Among Livestock Species
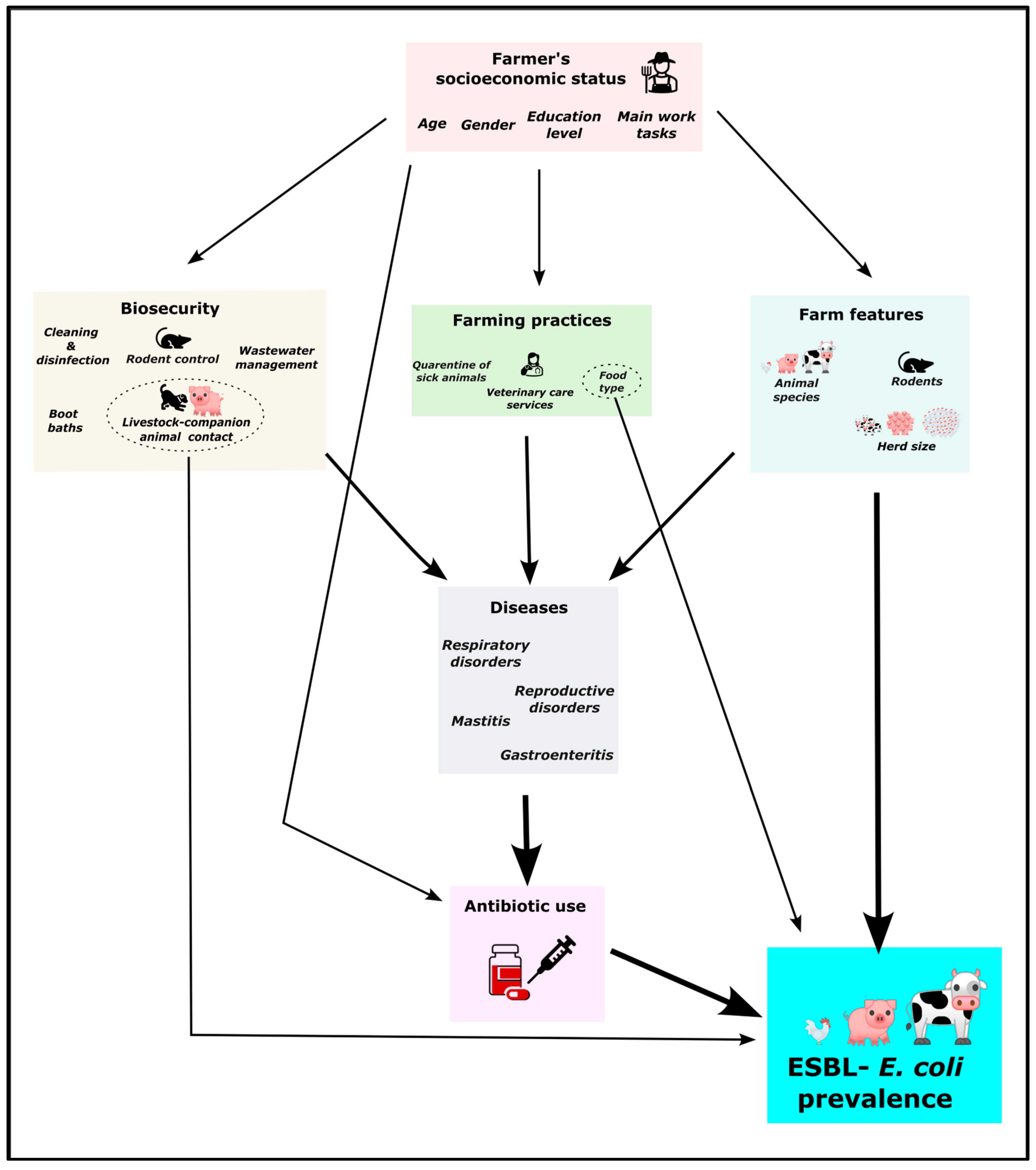
2.4. Statistical Analyses to Identify Factors Correlated to ESBL-E. coli Prevalence
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selected Study Regions
4.2. Livestock Sample Sizes and Farm Selection Design
4.3. Fecal Sampling and Detection of E. coli Isolates with ESBL Phenotype
4.4. ESBL Genes Detection
4.5. Questionnaires to Assess Farmers’ Socioeconomic Characteristics and Husbandry Practices
4.6. Statistical Analyses
4.6.1. ESBL-E. coli Prevalence Comparison Across Livestock Species
4.6.2. Association of ESBL-E. coli with Socioeconomic Characteristics and Husbandry Practices
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Sharara, F.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Davis Weaver, N.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Gershberg Hayoon, A.; et al. Global Mortality Associated with 33 Bacterial Pathogens in 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Khan, A.U. Global Economic Impact of Antibiotic Resistance: A Review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 19, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, I.N.; Laxminarayan, R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Duse, A.G.; Jenkins, P.; O’Brien, T.F.; Pablos-Mendez, A.; Klugman, K.P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Developing Countries. Part I: Recent Trends and Current Status. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandujano-Hernández, A.; Martínez-Vázquez, A.V.; Paz-González, A.D.; Herrera-Mayorga, V.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.; Lara-Ramírez, E.E.; Vázquez, K.; De Jesús De Luna-Santillana, E.; Bocanegra-García, V.; Rivera, G. The Global Rise of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli in the Livestock Sector: A Five-Year Overview. Animals 2024, 14, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, J.A.; Godreuil, S.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Mahamat, O.O.; Falcon, N.; Oravcova, K.; Streicker, D.G.; Shiva, C. Long-Term Maintenance of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Carried by Vampire Bats and Shared with Livestock in Peru. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, J.A.; Salgado-Caxito, M.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; González Muñoz, P.; Piñeiro, A.; Otto Medina, M.; Rivas, L.; Munita, J.; Millán, J. ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli Carrying CTX-M Genes Circulating among Livestock, Dogs, and Wild Mammals in Small-Scale Farms of Central Chile. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Liu, C.-W.; Liu, P.-Y. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBL) Producing Bacteria in Animals. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Pizzali, M.L.; Hartinger, S.M.; Salmon-Mulanovich, G.; Larson, A.; Riveros, M.; Mäusezahl, D. Antimicrobial Resistance in Rural Settings in Latin America: A Scoping Review with a One Health Lens. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.P.; Eisenberg, J.N.S.; Trueba, G.; Zhang, L.; Johnson, T.J. Small-Scale Food Animal Production and Antimicrobial Resistance: Mountain, Molehill, or Something in-Between? Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.C.; Keestra, S.; Tandon, P.; Chandler, C. WASH and Biosecurity Interventions for Reducing Burdens of Infection, Antibiotic Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in Animal Agricultural Settings: A One Health Mixed Methods Systematic Review; London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fagbamila, I.O.; Mancin, M.; Barco, L.; Ngulukun, S.S.; Jambalang, A.; Ajayi, O.T.; Sati, N.; Emennaa, P.; Ankeli, P.I.; Kwaga, J.; et al. Investigation of Potential Risk Factors Associated with Salmonella Presence in Commercial Laying Hen Farms in Nigeria. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 152, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Allaoui, A.; Rhazi Filali, F.; Ameur, N.; Bouchrif, B. Contamination of broiler turkey farms by Salmonella spp. in Morocco: Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and associated risk factors. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2017, 36, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michira, L.; Kagira, J.; Maina, N.; Waititu, K.; Kiboi, D.; Ongera, E.; Ngotho, M. Prevalence of Subclinical Mastitis, Associated Risk Factors and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Bacteria Isolated from Milk of Dairy Cattle in Kajiado Central Sub-county, Kenya. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Caxito, M.; Benavides, J.A.; Munita, J.M.; Rivas, L.; Garcia, P.; Listoni, F.J.P.; Moreno-Switt, A.I.; Paes, A.C. Risk Factors Associated with Faecal Carriage of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli among Dogs in Southeast Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 190, 105316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdieu, P.; Passeron, J.-C. La Reproducción. Elementos para una Teoría del Sistema de Enseñanza; Editorial Laia: Barcelona, Spain, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa Pérez, J.A.; Avalos, H.R.B.; Salazar, I.Y.V.; Carrasco Mamani, S.C. Social Programs and Socioeconomic Variables: Their Impact on Peruvian Regional Poverty (2013–2022). Economies 2024, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddens, A. Nuevas Reglas del Método Sociológico; Amorrortu: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Benavides, J.A.; Streicker, D.G.; Gonzales, M.S.; Rojas-Paniagua, E.; Shiva, C. Knowledge and Use of Antibiotics among Low-Income Small-Scale Farmers of Peru. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 189, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, L.E.; Cubas-Delgado, F.; Sammel, M.D.; Smith, G.; Galligan, D.T.; Levy, M.Z.; Hennessy, S. The Use of Antibiotics on Small Dairy Farms in Rural Peru. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávalos-Almeyda, M.; Guerrero, A.; Medina, G.; Dávila-Barclay, A.; Salvatierra, G.; Calderón, M.; Gilman, R.H.; Tsukayama, P. Antibiotic Use and Resistance Knowledge Assessment of Personnel on Chicken Farms with High Levels of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Ica, Peru. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIDAGRI, Ministerio de Desarrollo Agrario y Riego. Estadísticas|Boletines Anuales—Producción Ganadera y Avícola: “Anuario Estadístico—Producción Ganadera y Avícola 2023”. Available online: https://siea.midagri.gob.pe/portal/publicacion/boletines-anuales/5-ganadera-avicola (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- MIDAGRI, Ministerio de Desarrollo Agrario y Riego. Atlas de la Superficie Agrícola del Perú—Dirección General de Estadística, Evaluación y Seguimiento; MIDAGRI: Lima, Peru, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- MIDAGRI, Ministerio de Desarrollo Agrario y Riego. Estadística Agropecuaria: Agricultura Familiar. Available online: https://app.powerbi.com/view?r=eyJrIjoiNzVlYWIxNTYtZjE2MC00ODU4LTljZDgtNGI5ZGUxODk1ZjhjIiwidCI6IjdmMDg0NjI3LTdmNDAtNDg3OS04OTE3LTk0Yjg2ZmQzNWYzZiJ9 (accessed on 26 September 2024).
- INEI, Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática. Resultados Definitivos Censo Nacional Agropecuario 2012 (IV CENAGRO); Ministerio de Desarrollo Agrario y Riego (MIDAGRI): Lima, Peru, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Peru–Plan Multisectorial para Enfrentar la Resistencia a los Antimicrobianos. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/48559-plan-multisectorial-para-enfrentar-la-resistencia-a-los-antimicrobianos (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Benavides, J.A.; Shiva, C.; Virhuez, M.; Tello, C.; Appelgren, A.; Vendrell, J.; Solassol, J.; Godreuil, S.; Streicker, D.G. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Common Vampire Bats Desmodus Rotundus and Livestock in Peru. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, D.L.C.; de Souto Sobrinho, J.D.; de Godoy, B.L.V.; Neto, D.A.; Leandro, G.R.; Casella, T.; de Azevedo, S.S.; de Sousa Américo Batista Santos, C. Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Free-Range Chickens in the Caatinga Biome. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 3475–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeira, J.D.; Haenni, M.; Metayer, V.; Madec, J.-Y.; Ferreira, H.M.N. Epidemic Spread of IncI1/pST113 Plasmid Carrying the Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL) blaCTX-M-8 Gene in Escherichia coli of Brazilian Cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman-White, C.J.; Moran, D.; Peters, A.R.; Muwonge, A. A Review of the Predictors of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in European Food Animal Production. Front. Antibiot. 2023, 2, 1209552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; May, H.E.; AbuOun, M.; Stubberfield, E.; Gilson, D.; Chau, K.K.; Crook, D.W.; Shaw, L.P.; Read, D.S.; Stoesser, N.; et al. A Longitudinal Study Reveals Persistence of Antimicrobial Resistance on Livestock Farms Is Not Due to Antimicrobial Usage Alone. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1070340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhegghe, M.; Pletinckx, L.J.; Crombé, F.; Vandersmissen, T.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P.; Heyndrickx, M.; Rasschaert, G. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) ST398 in Pig Farms and Multispecies Farms. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuOun, M.; Jones, H.; Stubberfield, E.; Gilson, D.; Shaw, L.P.; Hubbard, A.T.M.; Chau, K.K.; Sebra, R.; Peto, T.E.A.; Crook, D.W.; et al. A Genomic Epidemiological Study Shows That Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterobacterales Is Associated with the Livestock Host, as Well as Antimicrobial Usage. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Silva, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Igrejas, G.; Valentão, P.; Falco, V.; Poeta, P. Antimicrobial Resistance and Clonal Lineages of Escherichia coli from Food-Producing Animals. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaru, I.D.; Walther, B.; Schaumburg, F. Zoonotic Sources and the Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance from the Perspective of Low and Middle-Income Countries. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2023, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruel, G.; Sellin, A.; Riveiro, H.; Pot, M.; Breurec, S.; Guyomard-Rabenirina, S.; Talarmin, A.; Ferdinand, S. Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Escherichia coli from Healthy Food-Producing Animals in Guadeloupe. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltgen, G.; Martak, D.; Valot, B.; Kamus, L.; Garrigos, T.; Verchere, G.; Gbaguidi-Haore, H.; Ben Cimon, C.; Ramiandrisoa, M.; Picot, S.; et al. One Health Compartmental Analysis of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli on Reunion Island Reveals Partitioning between Humans and Livestock. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.H.; Sukiman, M.Z.; Jasmy, N.; Zulkifly, N.A.; Mohd Yusof, N.A.S.; Mohamad, N.M.; Ariffin, S.M.Z.; Ghazali, M.F. Molecular Detection and Antibiogram of ESBL-Producing and Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli from Rabbit, Swine, and Poultry in Malaysia. Trop. Anim. Sci. J. 2022, 45, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, O.; Marchetti, L.; Parada, J.; Alarcón, L.V.; Aliverti, F.; Avison, M.B.; Ayala, C.S.; Ballesteros, C.; Best, C.M.; Bettridge, J.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology of Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli from Argentinian Pig and Dairy Farms Reveals Animal-Specific Patterns of Co-Resistance and Resistance Mechanisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e01791-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Widodo, A.; Effendi, M.H.; Khairullah, A.R. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli from Livestock. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emes, E.; Faye, A.; Naylor, N.; Belay, D.; Ngom, B.; Fall, A.G.; Knight, G.; Dione, M. Drivers of Antibiotic Use in Semi-Intensive Poultry Farms: Evidence from a Survey in Senegal. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boamah, V.E.; Agyare, C.; Odoi, H.; Dalsgaard, A. Practices and Factors Influencing the Use of Antibiotics in Selected Poultry Farms in Ghana. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 2, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Gong, G.; Yuan, J.; Sun, X. Antibiotic Use in Pig Farming and Its Associated Factors in L County in Yunnan, China. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, D.B.; Mellata, M. Escherichia coli Mastitis in Dairy Cattle: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 928346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegg, P.L. A 100-Year Review: Mastitis Detection, Management, and Prevention. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10381–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suojala, L.; Kaartinen, L.; Pyörälä, S. Treatment for Bovine Scherichia Coli Mastitis—An Evidence-Based Approach. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 36, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Mendoza, B.Y. Resistencia Antibiótica de Bacterias Causantes de Mastitis Clínica Bovina en el Distrito de Huanchaco de la Provincia de Trujillo, 2023. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12759/34591 (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Rodríguez Pérez, R.; Muñoz Ganoza, E. Frecuencia y Susceptibilidad Antimicrobiana de Bacterias Causantes de Mastitis En Bovinos de Un Establo de Trujillo, Perú. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2017, 28, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pyörälä, S.; Baptiste, K.E.; Catry, B.; van Duijkeren, E.; Greko, C.; Moreno, M.A.; Pomba, M.C.M.F.; Rantala, M.; Ružauskas, M.; Sanders, P.; et al. Macrolides and Lincosamides in Cattle and Pigs: Use and Development of Antimicrobial Resistance. Vet. J. 2014, 200, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWaal, K.; Deen, J. Global Trends in Infectious Diseases of Swine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11495–11500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A.; Grace, D.; Kock, R.; Alonso, S.; Rushton, J.; Said, M.Y.; McKeever, D.; Mutua, F.; Young, J.; McDermott, J.; et al. Zoonosis Emergence Linked to Agricultural Intensification and Environmental Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8399–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvêa, R.; dos Santos, F.; de Aquino, M.; de Pereira VL, A. Fluoroquinolones in Industrial Poultry Production, Bacterial Resistance and Food Residues: A Review. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorla, N.; Chiostri, E.; Ugnia, L.; Weyers, A.; Giacomelli, N.; Davicino, R.; García Ovando, H. HPLC Residues of Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Eggs of Laying Hens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1997, 8, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, J.; Lapierre, L.; Iragüen, D.; Cornejo, S.; Cassus, G.; Richter, P.; San Martín, B. Study of Enrofloxacin and Flumequine Residues Depletion in Eggs of Laying Hens after Oral Administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Liao, X.; Liang, J.; Wu, Y. The Excretion and Environmental Effects of Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, and Doxycycline Residues in Layer Chicken Manure. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on Pharmacologically Active Substances and Their Classification Regarding Maximum Residue Limits in Foodstuffs of Animal Origin (Relevant for the EEA); European Union: Strasbourg, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.-X.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, R.-F.; Fang, J. Detection of Fluoroquinolone and Sulfonamide Residues in Poultry Eggs in Kunming City, Southwest China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Lundkvist, Å.; Järhult, J.D.; Khan Nayem, M.R.; Tanzin, A.Z.; Badsha, M.R.; Khan, S.A.; Ashour, H.M. Residual Antimicrobial Agents in Food Originating from Animals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellaneda, E.M.M. Antibióticos Prohibidos en Estados Unidos (EE.UU.) y la Unión Europea (UE), Autorizados para uso Veterinario en Producción Avícola, Bovina y Porcina en el Perú; Tesis para optar el Título Profesional de Médico Veterinario Zootecnista; Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia: Lima, Peru, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio de Salud del Perú Resolución Ministerial. N° 372-2016/MINSA: Aprueba La NTS N° 120-MINSA/DIGESA-V.01 “Norma Sanitaria Que Establece Los Límites Máximos de Residuos (LMR) de Medicamentos Veterinarios En Alimentos de Consumo Humano”; Ministerio de Salud del Perú: Lima, Peru, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, M.; Quispe, K.; Paredes, M.; Quispe, K. Efectos de La Flor de Marigold (Tagetes erecta) y El Rizoma de Cúrcuma (Curcuma longa) Como Fuentes de Carotenoides Sobre El Rendimiento Productivo y Las Características de Carcasa de Pollos Doble Propósito En La Fase de Finalización. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2022, 33, e22590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuchon, F.N.V. Sistema de Crianza y Producción de Aves de Postura; Universidad Nacional de Educación Enrique Guzmán y Valle: Lima, Peru, 2021; Available online: https://repositorio.une.edu.pe/server/api/core/bitstreams/a44e20a5-5d73-48e5-b057-e2fb58d4d02a/content (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Shrestha, N. Detecting multicollinearity in regression analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2020, 8, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, J.I. Multicollinearity and regression analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 949, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIDAGRI, Ministerio de Desarrollo Agrario y Riego. Boletín Estadístico Mensual de La “Producción y Comercialización de Productos Avícolas”–Dirección General de Estadística, Seguimiento y Evaluación de Políticas/Dirección de Estadística e Información Agraria, No 3, Año: 2023; Portal Siea (Sistema Integrado de Estadísticas Agrarias); MIDAGRI: Lima, Peru, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- CDC Downloads|Support|Epi InfoTM|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/epiinfo/support/downloads.html (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- Khalil, C.A.; Conforti, P.; Ergin, I.; Gennari, P. Defining Small-Scale Food Producers to Monitor Target 2.3. of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Proposed International Definition of Small-Scale Food Producers for Monitoring the Sustainable Development Goal Indicators 2.3.1 and 2.3.2. 2018. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/statcom/49th-session/documents/BG-Item3j-small-scale-food-producers-definition-FAO-E.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Hartinger, S.M.; Medina-Pizzali, M.L.; Salmon-Mulanovich, G.; Larson, A.J.; Pinedo-Bardales, M.; Verastegui, H.; Riberos, M.; Mäusezahl, D. Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans, Animals, Water and Household Environs in Rural Andean Peru: Exploring Dissemination Pathways through the One Health Lens. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, C.; Burgess, C.M.; Brennan, F.P.; Münzenmaier, D.; Drissner, D.; Leigh, R.J.; Walsh, F. Genomic Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from Manure and Manured Agricultural Grasslands. npj Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procop, G.W.; Church, D.L.; Hall, G.S.; Janda, W.M. Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-56238-838-6. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A. When to Use the Bonferroni Correction. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2014, 34, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.P. Adjusted P-Values for Simultaneous Inference. Biometrics 1992, 48, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduzzi, P.; Concato, J.; Kemper, E.; Holford, T.R.; Feinstein, A.R. A Simulation Study of the Number of Events per Variable in Logistic Regression Analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.M.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Nuttall, T.; McEwan, N.; Dawson, S.; Williams, N.J. Antimicrobial Resistance Risk Factors and Characterisation of Faecal E. coli Isolated from Healthy Labrador Retrievers in the United Kingdom. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 119, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedley, A.L.; Dawson, S.; Maddox, T.W.; Coyne, K.P.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Clegg, P.; Nuttall, T.; Kirchner, M.; Williams, N.J. Carriage of Antimicrobial Resistant Escherichia coli in Dogs: Prevalence, Associated Risk Factors and Molecular Characteristics. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupindu, A.M.; Dalsgaard, A.; Msoffe, P.L.M.; Ngowi, H.A.; Mtambo, M.M.; Olsen, J.E. Transmission of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli between Cattle, Humans and the Environment in Peri-Urban Livestock Keeping Communities in Morogoro, Tanzania. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 118, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iramiot, J.S.; Kajumbula, H.; Bazira, J.; Kansiime, C.; Asiimwe, B.B. Antimicrobial Resistance at the Human–Animal Interface in the Pastoralist Communities of Kasese District, South Western Uganda. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Jung, D.; Ronholm, J.; George, S. Prevalence and Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from Mastitic Dairy Cattle in Canada. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Category | Variable | Number of Farmers (n) (Total n = 59) | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Women | 26 | 44% |
| Men | 33 | 56% | |
| Age | 18–30 | 5 | 8% |
| 31–40 | 15 | 25% | |
| 41–50 | 12 | 20% | |
| 51–65 | 21 | 36% | |
| Over 65 years old | 6 | 10% | |
| Education level | None | 2 | 3% |
| Elementary | 17 | 29% | |
| Secondary | 26 | 44% | |
| Higher education | 14 | 24% | |
| Main work tasks | Administrative | 17 | 29% |
| Animal healthcare | 2 | 3% | |
| Animal husbandry | 24 | 41% | |
| Animal healthcare and husbandry | 16 | 27% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salgado-Caxito, M.; Léon, D.; Bardales, O.; Jara, L.M.; Medrano, P.; Murga, C.; Pérez, V.; Aylas-Jurado, B.; Su-Tello, R.; Najarro, J.; et al. Unexplained High Prevalence of ESBL-Escherichia coli Among Cattle and Pigs in Peru. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090867
Salgado-Caxito M, Léon D, Bardales O, Jara LM, Medrano P, Murga C, Pérez V, Aylas-Jurado B, Su-Tello R, Najarro J, et al. Unexplained High Prevalence of ESBL-Escherichia coli Among Cattle and Pigs in Peru. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090867
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalgado-Caxito, Marília, Daphne Léon, Olga Bardales, Luis M. Jara, Patricia Medrano, Clara Murga, Veronica Pérez, Brenda Aylas-Jurado, Roberto Su-Tello, Juana Najarro, and et al. 2025. "Unexplained High Prevalence of ESBL-Escherichia coli Among Cattle and Pigs in Peru" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090867
APA StyleSalgado-Caxito, M., Léon, D., Bardales, O., Jara, L. M., Medrano, P., Murga, C., Pérez, V., Aylas-Jurado, B., Su-Tello, R., Najarro, J., Salvador-Tasayco, E., Farrugia-Audri, J., Shiva, C., & Benavides, J. A. (2025). Unexplained High Prevalence of ESBL-Escherichia coli Among Cattle and Pigs in Peru. Antibiotics, 14(9), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090867






