Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Northern Region, Brazil: A Shift Towards NDM Producers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Selection of Bacterial Isolates
4.2. Presence of Carbapenemases Encoding Genes
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990-2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bertagnolio, S.; Dobreva, Z.; Centner, C.M.; Olaru, I.D.; Donà, D.; Burzo, S.; Huttner, B.D.; Chaillon, A.; Gebreselassie, N.; Wi, T.; et al. WHO global research priorities for antimicrobial resistance in human health. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sulayyim, H.J.; Ismail, R.; Al Hamid, A.; Ghafar, N.A. Antibiotic Resistance during COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, U.; Al-Anazi, M.; Alanazi, Z.; Rodríguez-Baño, J. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on multidrug resistant gram positive and gram negative pathogens: A systematic review. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaaban, T.; Ezzeddine, Z.; Ghssein, G. Antibiotic misuse during the COVID-19 pandemic in Lebanon: A cross-sectional study. COVID 2024, 4, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance, Fueled by the COVID-19 Pandemic. Policy Brief November 2021. 2022. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/55864 (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Kadri, S.S.; Adjemian, J.; Lai, Y.L.; Spaulding, A.B.; Ricotta, E.; Prevots, D.R.; Palmore, T.N.; Rhee, C.; Klompas, M.; Dekker, J.P.; et al. Difficult-to-treat resistance in gram-negative bacteremia at 173 US hospitals: Retrospective cohort analysis of prevalence, predictors, and outcome of resistance to all first-line agents. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. COVID-19: U.S. Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance, Special Report 2022; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022.
- Migliorini, L.B.; de Sales, R.O.; Koga, P.C.M.; Doi, A.M.; Poehlein, A.; Toniolo, A.R.; Menezes, F.G.; Martino, M.D.V.; Gales, A.C.; Brüggemann, H.; et al. Prevalence of blaKPC-2, blaKPC-3 and blaKPC-30—Carrying Plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated in a Brazilian Hospital. Pathogens 2021, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição-Neto, O.C.; da Costa, B.S.; Pontes Lda, S.; Silveira, M.C.; Justo-da-Silva, L.H.; de Oliveira Santos, I.C.; Teixeira, C.B.T.; Tavares e Oliveira, T.R.; Hermes, F.S.; Galvão, T.C.; et al. Polymyxin resistance in clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae in Brazil: Update on molecular mechanisms, clonal dissemination and relationship with KPC-producing strains. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 898125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.N.; Vitali, L.; Gaspar, G.G.; Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Martinez, R.; Darini, A.L.C. Expansion and evolution of a virulent, extensively drug-resistant (polymyxin B-resistant), QnrS1-, CTX-M-2-, and KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 international high-risk clone. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boralli, C.M.D.S.; Paganini, J.A.; Meneses, R.S.; da Mata, C.P.S.M.; Schürch, A.C.; Paganelli, F.L.; Willems, R.J.L.; Camargo, I.L.B.C. Characterization of blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1 plasmids of a K. pneumoniae ST11 outbreak clone. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.H. Current status of NDM-producing Enterobacterales in Brazil: A narrative review. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, Y.C.; Lobato, A.R.F.; Guerra, L.M.G.D.; Brasiliense, D.M. The spread of NDM-1 and NDM-7-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae is driven by multiclonal expansion of high-risk clones in healthcare institutions in the state of Pará, Brazilian Amazon region. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministério Brasil da Saúde; Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde e Ambiente. Boletim Epidemiológico: Resistência aos Antimicrobianos; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2024; Volume 55. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/epidemiologicos/edicoes/2024/boletim-epidem-vol-55-n-2 (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Pimentel, F.G.; Buchweitz, C.; Onocko Campos, R.T.; Hallal, P.C.; Massuda, A.; Kieling, C. Realising the future: Health challenges and achievements in Brazil. SSM Ment. Health 2023, 4, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeraud, C.; Mahamat, A.; Jousset, A.B.; Bernabeu, S.; Goncalves, T.; Pommier, C.; Girlich, D.; Birer, A.; Rodriguez, C.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; et al. Emergence and rapid dissemination of highly resistant NDM-14-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147, France, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2300095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Yin, D.; Sun, C.; Shen, Y.; Liu, D.; Bai, R.; Zhang, R.; Shen, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, Y. Clonal and horizontal transmission of blaNDM among Klebsiella pneumoniae in children’s intensive care units. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0157421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedišaletše, M.; Phumuzile, D.; Angela, D.; Andrew, W.; Mae, N.-F. Epidemiology, risk factors, and clinical outcomes of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in Africa: A systematic review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 35, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.H.; Yamada, A.Y.; Souza AR de Reis, A.D.; Santos, M.B.N.; de Assis, D.B.; de Carvalho, E.; Takagi, E.H.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Tiba-Casas, M.R. Genomic diversity of NDM-producing Klebsiella species from Brazil, 2013–2022. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavuzzi, A.M.L.; Firmo, E.F.; de Oliveira, É.M.; Lopes, A.C.d.S. Emergence of bla NDM-1 associated with the aac(6’)-Ib-cr, acrB, cps, and mrkD genes in a clinical isolate of multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from Recife-PE, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, e20180352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, P.L.; Martins, A.S.; Volpato, F.; Zavascki, A.P.; Barth, A.L. Increased frequency of blaNDM in a tertiary care hospital in southern Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.P.; Gonçalves, L.C.; Oliveira, A.C.C.; Queiroz, P.H.P.; Ito, C.R.M.; Santos, M.O.; Carneiro, L.C. Bacterial co-infection in patients with COVID-19 hospitalized (ICU and not ICU): Review and meta-analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2017, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, P.; Bose, P.; Rangnekar, A. NDM-beta-lactamase-1: Where do we stand? Indian J. Med. Res. 2022, 155, 243. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Feng, Y.; Tang, G.; Qiao, F.; McNally, A.; Zong, Z. NDM metallo-β-lactamases and their bacterial producers in health care settings. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00115–e00118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima das Chagas, A.; da Silva Araújo, J.C.; Serra, J.C.P.; de Araújo, K.M.; de Oliveira Cunha, M.; Correia, A.D.R.; Gonçalves, L.M.B.; Carneiro, L.C. Co-Infection of SARS-CoV-2 and Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, M.; Bostanshirin, N.; Hajikhani, B.; Yaslianifard, S.; van Belkum, A.; Goudarzi, M.; Hashemi, A.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D.; Dadashi, M. Global genotype distribution of human clinical isolates of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae; A systematic review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raro, O.H.F.; da Silva, R.M.C.; Filho, E.M.R.; Sukiennik, T.C.T.; Stadnik, C.; Dias, C.A.G.; Oteo Iglesias, J.; Pérez-Vázquez, M. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae From Transplanted Patients in Brazil: Phylogeny, Resistome, Virulome and Mobile Genetic Elements Harboring blaKPC–2 or blaNDM–1. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.S.D.; Rodrigues, Y.C.; de Melo, M.V.H.; Santos, P.A.S.D.; da Costa Oliveira, T.N.; Sardinha, D.M.; Lima, L.N.G.C.; Brasiliense, D.M.; Lima, K.V.B. First insights into clinical and resistance features of infections by Klebsiella pneumoniae among oncological patients from a referral center in Amazon region, Brazil. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2020, 12, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moolla, M.S.; Reddy, K.; Fwemba, I.; Nyasulu, P.S.; Taljaard, J.J.; Parker, A.; Louw, E.H.; Nortje, A.; Parker, M.A.; Lalla, U.; et al. Bacterial infection, antibiotic use and COVID-19: Lessons from the intensive care unit. S. Afr. Med. J. 2021, 111, 575–581. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, K.; Filipak, D.; da Silva, A.K.; Carneiro, M.B. Infecções bacterianas em pacientes com COVID-19 internados em UTI adulto: Incidência e atuação farmacêutica. Rev. Bras. Farm. Hosp. Serviços Saúde 2023, 14, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, R.F. The interface between COVID-19 and bacterial healthcare-associated infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Santos, J.V.; da Costa Júnior, S.D.; de Fátima Ramos Dos Santos Medeiros, S.M.; Cavalcanti, I.D.L.; de Souza, J.B.; Coriolano, D.L.; da Silva, W.R.C.; Alves, M.H.M.E.; Cavalcanti, I.M.F. Panorama of bacterial infections caused by epidemic resistant strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Lower Respiratory Infections Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality burden of non-COVID-19 lower respiratory infections and aetiologies, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 974–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedberg, P.; Ternhag, A.; Giske, C.G.; Strålin, K.; Özenci, V.; Johansson, N.; Spindler, C.; Hedlund, J.; Mårtensson, J.; Nauclér, P. Ventilator-associated lower respiratory tract bacterial infections in COVID-19 compared with non-COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Laterre, P.-F.; Luyt, C.-E.; Chastre, J. The challenge of ventilator-associated pneumonia diagnosis in COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.K.C.; Soares, C.F.; Ton, J.T.; Soares, N.; Peixoto, R.R.; Zimmerli, S.Â.; Vasconcelos, M.P. Perfil bacteriano de pacientes admitidos em unidade de terapia intensiva do centro de medicina tropical de Rondônia durante a pandemia do COVID-19. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 25, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UFTM. Prevenção E Controle Das Infecções E Colonizações Por Microrganismos Multirresistentes; UFTM: Uberaba, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira Rodrigues, A. Colonização por Microrganismos Multirresistentes em pacientes adultos com COVID-19 internados em Unidade de Terapia Intensiva. GOIÂNIA. 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.pucgoias.edu.br/jspui/handle/123456789/2511 (accessed on 1 November 2023).
- Calderón-Parra, J.; Muiño-Miguez, A.; Bendala-Estrada, A.D.; Ramos-Mart’inez, A.; Muñez-Rubio, E.; Fernández Carracedo, E.; Tejada Montes, J.; Rubio-Rivas, M.; Arnalich-Fernandez, F.; Beato Pérez, J.L.; et al. Inappropriate antibiotic use in the COVID-19 era: Factors associated with inappropriate prescribing and secondary complications. Analysis of the registry SEMI-COVID. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitungo, I.; Dzinamarira, T.; Nyazika Tinashe, K.; Herrera, H.; Musuka, G.; Murewanhema, G. Inappropriate antibiotic use in Zimbabwe in the COVID-19 era: A perfect recipe for antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamara, I.F.; Kumar, A.M.V.; Maruta, A.; Fofanah, B.D.; Njuguna, C.K.; Shongwe, S.; Moses, F.; Tengbe, S.M.; Kanu, J.S.; Lakoh, S.; et al. Antibiotic use in suspected and confirmed COVID-19 patients admitted to health facilities in Sierra Leone in 2020–2021: Practice does not follow policy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Q.; Xu, Z.-E.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wei, H.; Hua, Z. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on neonatal admissions in a tertiary children’s hospital in southwest China: An interrupted time-series study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Medina, D.; Avalos-Huizar, L.M.; Bolio-Pontigo, W.; Soto-Castañeda, M.G.; Cárdenas-Valdez, J.C.; Medina-R’ios, C.K. Changes in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit statistics during the COVID-19 pandemic. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2024, 81, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cena, L.; Biban, P.; Janos, J.; Lavelli, M.; Langfus, J.; Tsai, A.; Youngstrom, E.A.; Stefana, A. The collateral impact of COVID-19 emergency on neonatal intensive care units and family-centered care: Challenges and opportunities. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 630594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.P.; Nunes, M.P.; Chaves Jde, R.A.B.; Justino Gda, C.; Chaves, N.M.; de Lima, V.G.; da Silva, A.S.; Marsola, L.R. Prevalência de carbapenemases em hospital Universitário na região amazônica no período de 2020 a 2022. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 27, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, G.; Carattoli, A. Global spread and evolutionary convergence of multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae high-risk clones. Pathog. Glob. Health 2023, 117, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Kong, X.; Hao, J.; Liu, J. Epidemiological Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Multidrug-Resistant Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 581543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmeiro, J.K.; de Souza, R.F.; Schörner, M.A.; Passarelli-Araujo, H.; Grazziotin, A.L.; Vidal, N.M.; Venancio, T.M.; Dalla-Costa, L.M. Molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a Brazilian tertiary hospital. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, C.A.M.; Pereira, P.S.; de Araujo, C.F.M.; Chagas, T.P.G.; Oliveira, J.C.R.; Buonora, S.N.; Albano, R.M.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D. Multiclonal expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates producing NDM-1 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01048-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzeddine, Z.; Ghssein, G. Towards new antibiotics classes targeting bacterial metallophores. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 182, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shbaklo, N.; Lupia, T.; De Rosa, F.G.; Corcione, S. Infection Control in the era of COVID-19: A narrative review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, H. Bacterial co-infections and antibiotic resistance in patients with COVID-19. GMS. Hyg. Infect. Control 2020, 15, Doc35. [Google Scholar]
- Vaneechoutte, M.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Tjernberg, I.; Elaichouni, A.; De Vos, P.; Claeys, G.; Verschraegen, G. Identification of Acinetobacter Genomic Species by Amplified Ribosomal DNA Restriction Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Shi, Q.; Wu, S.; Yin, D.; Peng, M.; Dong, D.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hu, F.; et al. Dissemination of Carbapenemases (KPC, NDM, OXA-48, IMP, and VIM) Among Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Adult and Children Patients in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, R.E.; Kiyota, K.A.; Monteiro, J.; Castanheira, M.; Andrade, S.S.; Gales, A.C.; Pignatari, A.C.C.; Tufik, S. Rapid detection and identification of metallo-beta-lactamase-encoding genes by multiplex real-time PCR assay and melt curve analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiffer, C.R.V.; Rezende, T.F.T.; Costa-Nobre, D.T.; Marinonio, A.S.S.; Shiguenaga, L.H.; Kulek, D.N.O.; Arend, L.N.V.S.; Santos, I.C.d.O.; Sued-Karam, B.R.; Rocha-de-Souza, C.M.; et al. A 7-Year Brazilian National Perspective on Plasmid-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance in Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii Complex and the Impact of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic on Their Occurrence. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 77, S29–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
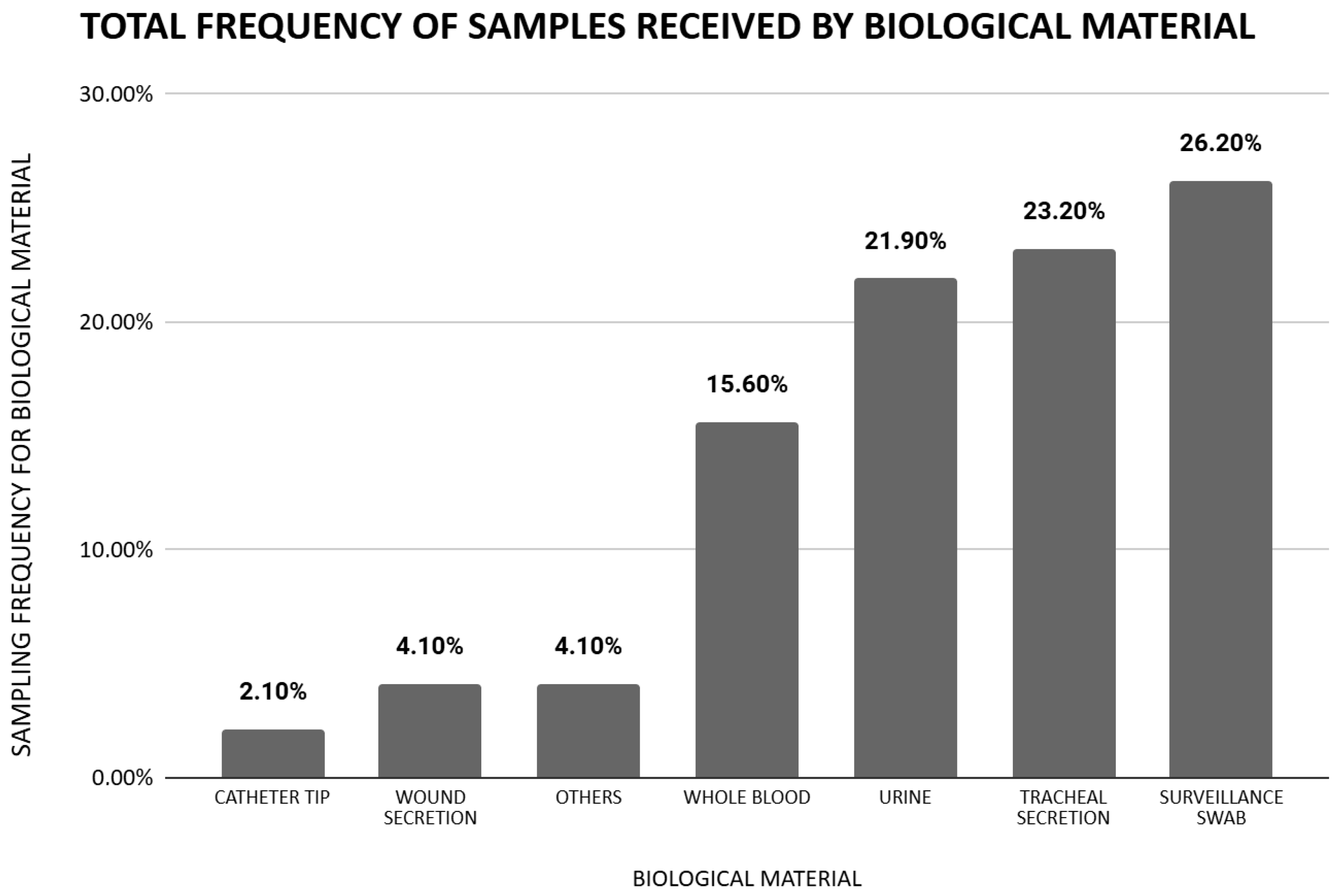
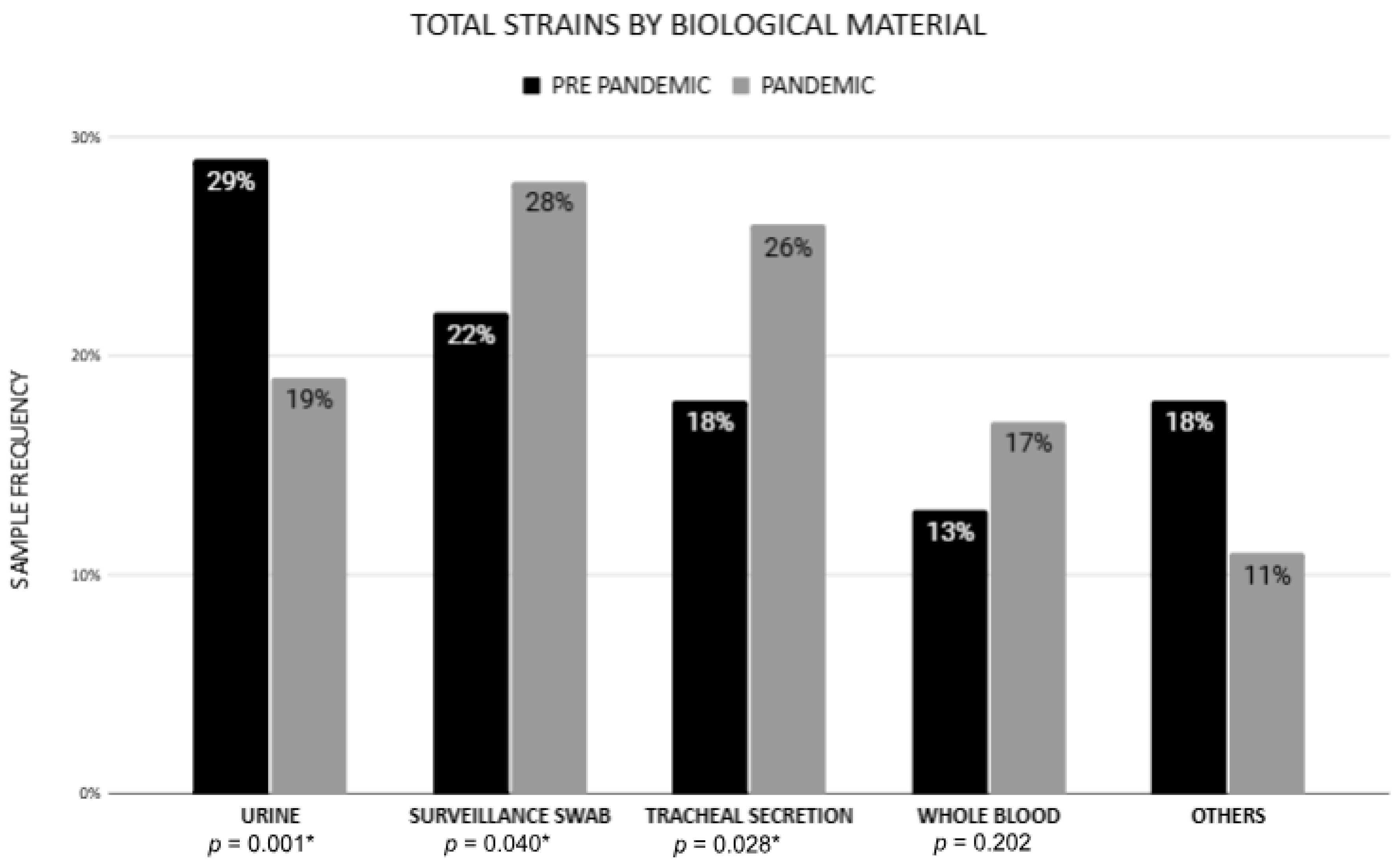
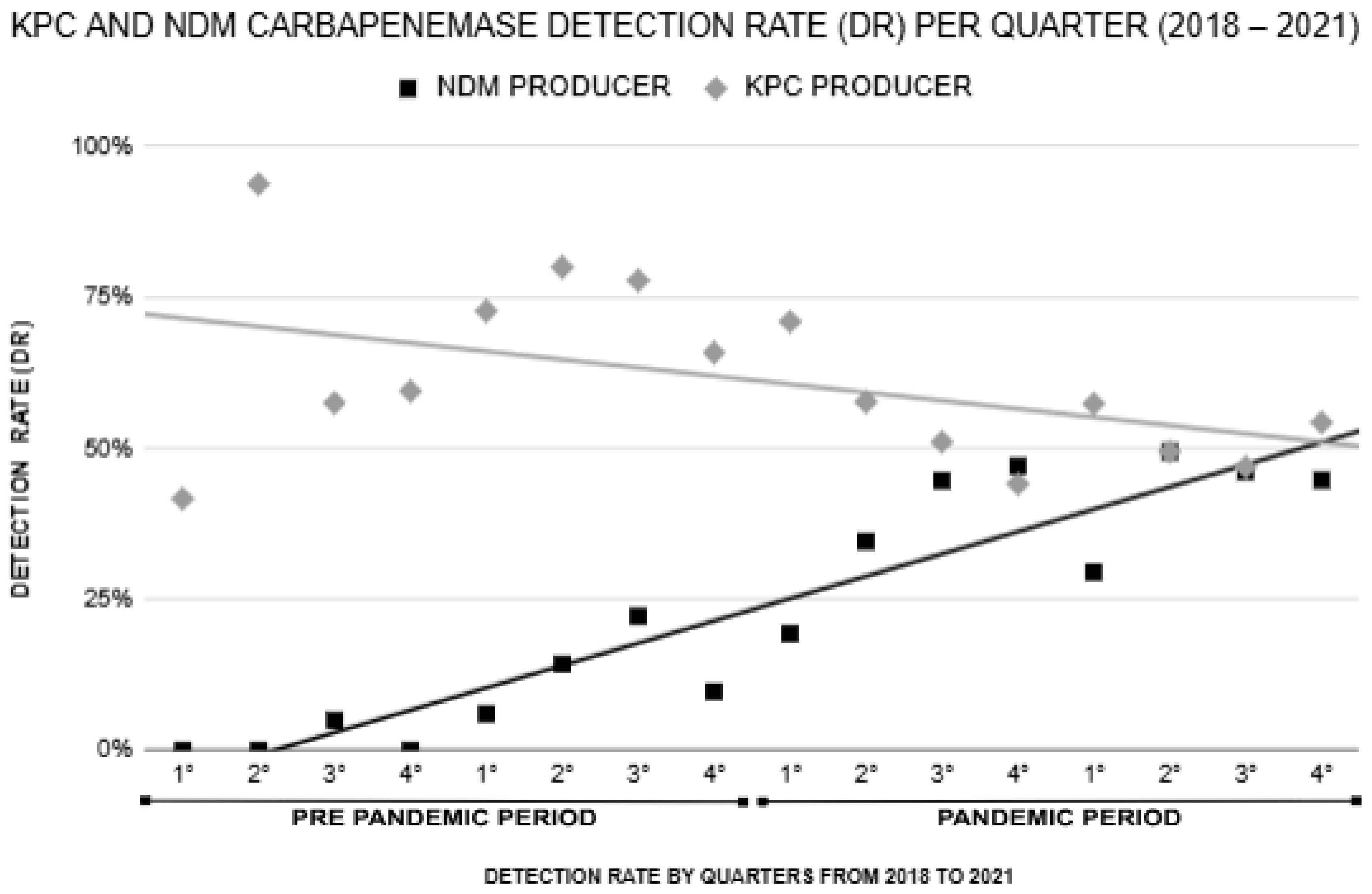
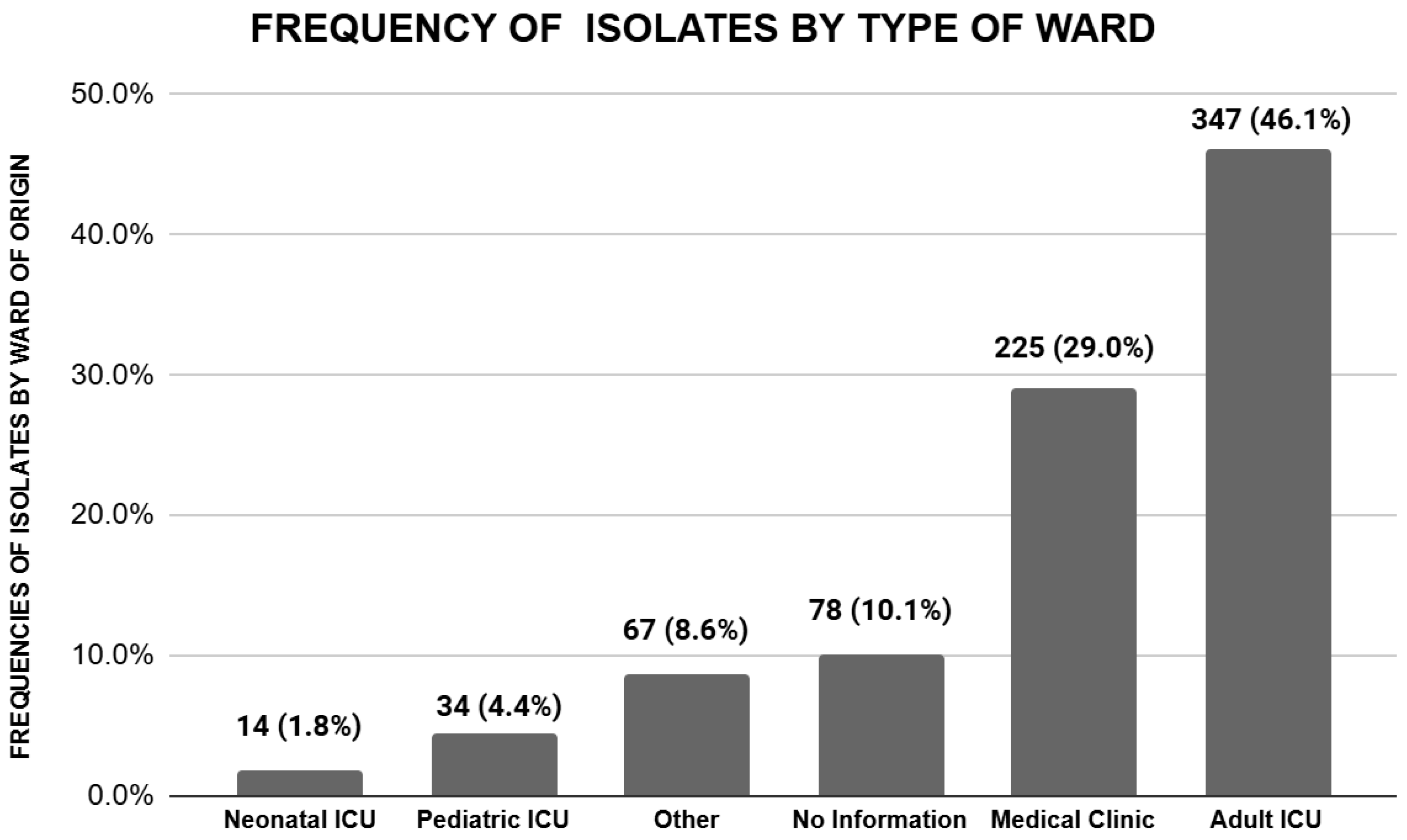
| Pre-Pandemic Period N (%) | Pandemic Period N (%) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation—Carbapenemases | |||
| Carbapenemase producer | 193 (77.2%) | 451 (85.9%) | 0.003 * |
| KPC producer | 172 (68.8%) | 274 (52.2%) | 0.000 * |
| NDM producer | 21 (8.4%) | 222 (42.3%) | 0.000 * |
| Correlation—Type of hospitalization ward | |||
| Adult UCI | 99 (39.6%) | 258 (49.1%) | 0.013 * |
| Pediatric UCI | 16 (6.4%) | 18 (3.4%) | 0.059 |
| Neonatal UCI | 8 (3.2%) | 6 (1.1%) | 0.044 * |
| Medical clinics | 67 (26.8%) | 158 (30.1%) | 0.345 |
| Correlation—Clinical sample | |||
| Whole blood | 33 (13.2%) | 88 (16.8%) | 0.202 |
| Catheter tip | 5 (2%) | 11 (2.1%) | 0.931 |
| Tracheal secretion | 46 (18.4%) | 134 (25.5%) | 0.028 * |
| Urine | 72 (28.8%) | 98 (18.7%) | 0.001 * |
| Surveillance swab | 55 (22%) | 148 (28.2%) | 0.040 * |
| Wound secretion | 9 (3.6%) | 23 (4.4%) | 0.609 |
| Correlation—Age range | |||
| NB (Up to 1 month) | 7 (2.8%) | 5 (1%) | 0.051 |
| Child (0–12) | 45 (18%) | 38 (7.2%) | 0.001 * |
| Young (13–18) | 10 (4%) | 16 (3%) | 0.491 |
| Adult (19–59) | 80 (32%) | 209 (39.8%) | 0.036 * |
| Elderly (+60) | 105 (42%) | 196 (37.3%) | 0.213 |
| Year of Sample Collection | Carbapenemase Genes Detected | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaKPC | blaNDM | blaOXA-48 | blaIMP | blaVIM | Coproduction blaKPC + blaNDM | |
| 2018 | 64% (67/105) | 3% (3/105) | 0% (0/0) | 0% (0/0) | 0% (0/0) | 0% (0/0) |
| 2019 | 74% (107/145) | 13% (19/145) | 0% (0/0) | 0% (0/0) | 0% (0/0) | 1.3% (2/145) |
| 2020 | 55% (76/138) | 39% (54/138) | 0.7% (1/138) | 0% (0/0) | 0% (0/0) | 6.5% (9/138) |
| 2021 | 52% (200/387) | 44% (172/387) | 0% (0/0) | 0.2% (1/387) | 0% (0/0) | 10% (39/387) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barros, T.B.C.; Rodrigues, Y.C.; Lobato, A.R.F.; Dutra, L.M.G.; dos Reis, H.S.; Garcia, A.J.P.; Sagica, F.d.E.S.; Souza, C.d.O.; Brasiliense, D.M. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Northern Region, Brazil: A Shift Towards NDM Producers. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090866
Barros TBC, Rodrigues YC, Lobato ARF, Dutra LMG, dos Reis HS, Garcia AJP, Sagica FdES, Souza CdO, Brasiliense DM. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Northern Region, Brazil: A Shift Towards NDM Producers. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(9):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090866
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarros, Thalyta Braga Cazuza, Yan Corrêa Rodrigues, Amália Raiana Fonseca Lobato, Lívia Maria Guimarães Dutra, Herald Souza dos Reis, Ana Judith Pires Garcia, Fernanda do Espírito Santo Sagica, Cintya de Oliveira Souza, and Danielle Murici Brasiliense. 2025. "Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Northern Region, Brazil: A Shift Towards NDM Producers" Antibiotics 14, no. 9: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090866
APA StyleBarros, T. B. C., Rodrigues, Y. C., Lobato, A. R. F., Dutra, L. M. G., dos Reis, H. S., Garcia, A. J. P., Sagica, F. d. E. S., Souza, C. d. O., & Brasiliense, D. M. (2025). Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Northern Region, Brazil: A Shift Towards NDM Producers. Antibiotics, 14(9), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14090866






