Comparative Evaluation of Tongue and Periodontal Pocket Microbiome in Relation to Helicobacter pylori Gastric Disease: 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Periodontal and Oral Health Conditions
2.2. Gastric Characteristics of Patients
2.3. Microbiome Analysis
2.4. Diversity Indexes
2.4.1. Alpha Diversity
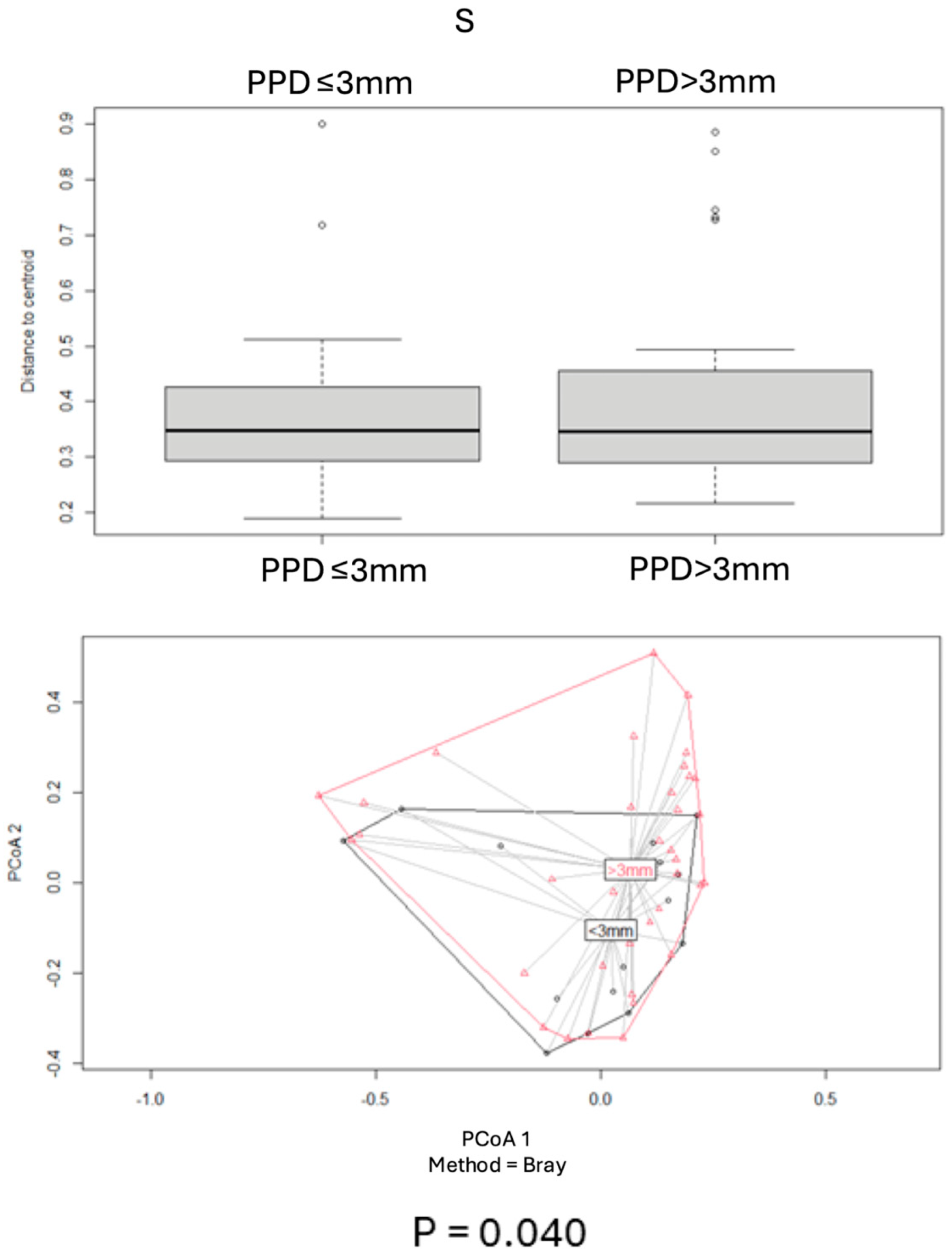
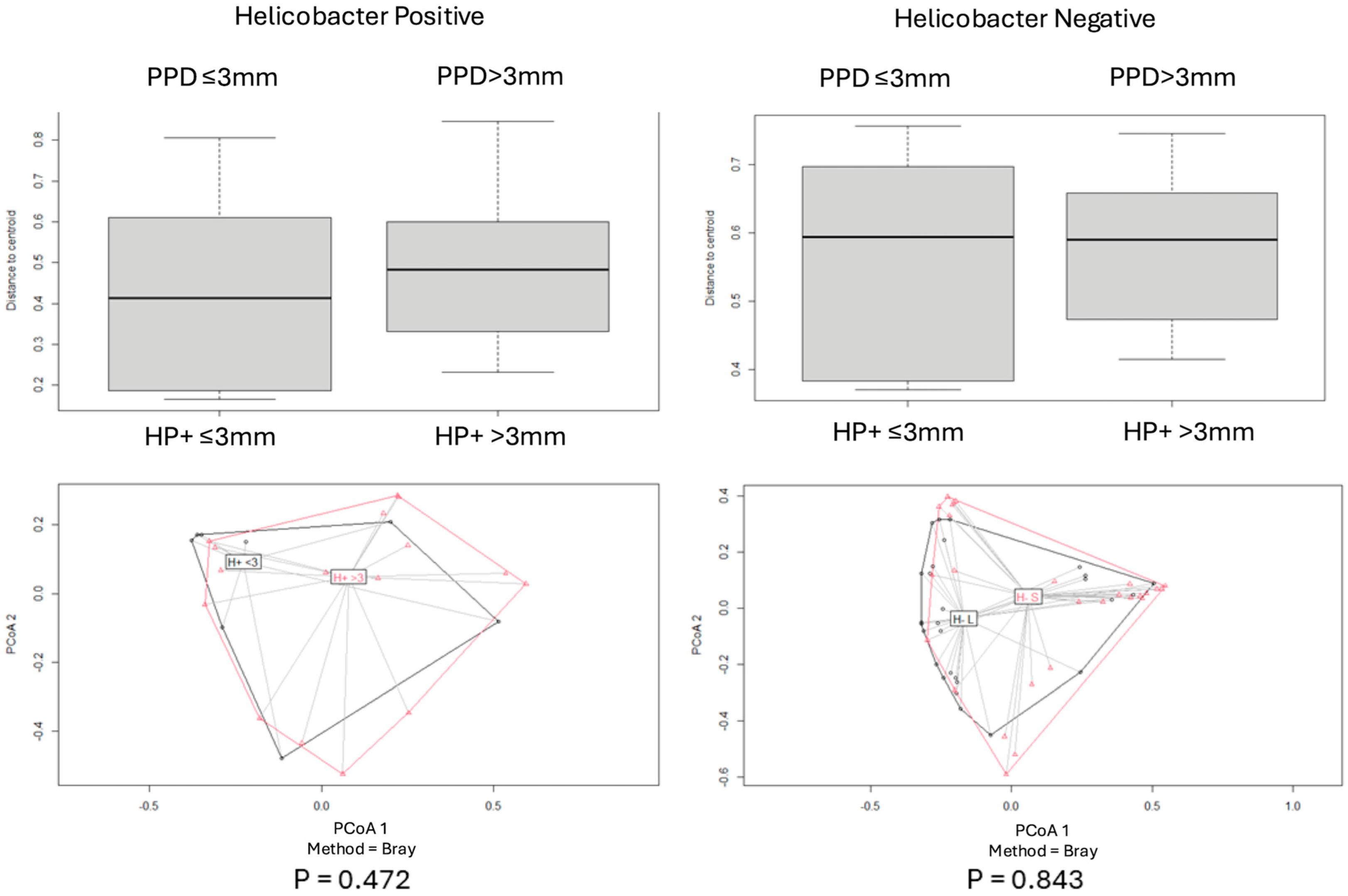
2.4.2. Beta Diversity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample
4.2. Patient Selection
- -
- Age between 35 and 85 years
- -
- Breath test performed within 1 week
- -
- Gastric biopsy
- -
- ASA status 1–2
- -
- Local geographic provenience
- -
- Age below 35 years
- -
- Negative breath test performed within 1 week+
- -
- Absence of gastric pathologies
- -
- Edentulous patients
4.3. Clinical Parameters
4.3.1. Dentition Status
4.3.2. Periodontal Status
- -
- Plaque score (plaque score): The presence of plaque or calculus was assessed at mesial, distal, vestibular and palatal sites around each tooth. The score was 0 = no plaque; 1 = thin layer of plaque; 2 = moderate layer of plaque and calculus; 3 = abundant plaque and calculus) [59].
- -
- Bleeding on probing (BoP): The presence of bleeding on probing was measured at mesial, distal, vestibular, and palatal sites around each tooth. The scores were (0 = no bleeding; 1 = bleeding) [60]. The total percentage of sites with BoP = 1 was then recorded and grouped in quartiles: Q1 = 0–25%, Q2 = 26–50%, Q3 = 51–75%, and Q4 = 76–100% of sites.
- -
- Pocket probing depth (PPD): The measurements were made using a periodontal probe with a light force (approximately 0.25 N) in mesial distal vestibular and palatal sites [61]. The deepest PPD was recorded in mm.
- (1)
- No pockets exceeding 3 mm (PP < 3 mm), no calculus (plaque score = 0), but presence of bleeding on probing (BoP = 1).
- (2)
- No pockets exceeding 3 mm (PPD < 3 mm), but calculus or other plaque-retentive factors detected (PI = 1–3), with or without bleeding on probing (BoP = 0–1).
- (3)
- Pockets comprised within 3.5 mm and 5.5 mm (PPD= 3.5–5.5 mm) with or without plaque, calculus, or bleeding on probing.
- (4)
- Pocket comprised within 5.5 mm and 7 mm in depth (PPD = 5.5–7 mm) with or without plaque, calculus or bleeding on probing.
- (5)
- Pockets over 7 mm (PPD > 7 mm) and/or furcation involvement with or without plaque, calculus, or bleeding on probing.
4.4. Samples Collection and Microbiome Analysis
4.5. Genome Extraction
4.6. PCR Amplification of the 16SrDNA Gene and Nanopore Sequencing
4.7. Data Analysis and Visualization
4.7.1. Alpha Diversity
4.7.2. Beta Diversity
4.7.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, M.; Lei, L.; Zhao, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Hu, J.; Cheng, R.; Hu, T. The dynamic oral-gastric microbial axis connects oral and gastric health: Current evidence and disputes. NPJ Biofilm. Microbiomes 2025, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yuan, M.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Z. Association of oral microbiome and pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221123980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, Q.; Yu, S.; Xie, M.; Xie, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, L. Role of the oral microbiota in cancer evolution and progression. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 6306–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, P.D. Microbial ecology of dental plaque and its significance in health and disease. Adv. Dent. Res. 1994, 8, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, P.D. Are dental diseases examples of ecological catastrophes? Microbiology 2003, 149, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosier, B.T.; Marsh, P.D.; Mira, A. Resilience of the Oral Microbiota in Health: Mechanisms That Prevent Dysbiosis. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhibber-Goel, J.; Singhal, V.; Bhowmik, D.; Vivek, R.; Parakh, N.; Bhargava, B.; Sharma, A. Linkages between oral commensal bacteria and atherosclerotic plaques in coronary artery disease patients. NPJ Biofilm. Microbiomes 2016, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Iragavarapu, S.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Huang, R.; Erazo, M.; Bao, X.; Verghese, D.; Coca, S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Peter, I. Location-Specific Oral Microbiome Possesses Features Associated With CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 3, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilievski, V.; Zuchowska, P.K.; Green, S.J.; Toth, P.T.; Ragozzino, M.E.; Le, K.; Aljewari, H.W.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Reynolds, E.C.; Watanabe, K. Chronic oral application of a periodontal pathogen results in brain inflammation, neurodegeneration and amyloid beta production in wild type mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Liu, W.-J.; Cui, H.; Zou, K.-L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yu, G.-T. The role of oral microbiota in cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1253025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations General Assembly. Political Declaration of the High-Level Meeting of the General Assembly on the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases; Resolution A/66/L1; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, M. European workshop in periodontal health and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2010, 12, B2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, P.E.; Bourgeois, D.; Ogawa, H.; Estupinan-Day, S.; Ndiaye, C. The global burden of oral diseases and risks to oral health. Bull. World Health Organ. 2005, 83, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Richard, M.P., Jr.; Keith, T.W. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: Factors that modulate disease risk. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 713–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Taghvaei, T.; Mohabbati Mobarez, A.; Vaira, G.; Vaira, D. High correlation of babA 2-positive strains of Helicobacter pylori with the presence of gastric cancer. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullo, A.; Hassan, C.; Cristofari, F.; Andriani, A.; De Francesco, V.; Ierardi, E.; Tomao, S.; Stolte, M.; Morini, S.; Vaira, D. Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on early stage gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Gastroenterology Organisation. World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline: Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burucoa, C.; Axon, A. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e1240310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.H.; Xiao, S.D.; Megraud, F.; Leon-Barua, R.; Bazzoli, F.; van der Merwe, S.; Vaz Coelho, L.G.; Fock, M.; Fedail, S.; Cohen, H.; et al. Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. JGLD 2011, 20, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.Y.; Cheung, T.K.; Wong, B.C. Gastroesophageal reflux disease in Asian countries: Disorder of nature or nurture? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapstone, N.P.; Lynch, D.A.; Lewis, F.A.; Axon, A.T.; Tompkins, D.S.; Dixon, M.F.; Quirke, P. Identification of Helicobacter pylori DNA in the mouths and stomachs of patients with gastritis using PCR. J. Clin. Pathol. 1993, 46, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardo, P.G.; Tugnait, A.; Hassan, F.; Lynch, D.A.; West, A.P.; Mapstone, N.P.; Quirke, P.; Chalmers, D.M.; Kowolik, M.J.; Axon, A.T. Helicobacter pylori infection and dental care. Gut 1995, 37, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Haller, B.; Ulrich, D.; Wichelhaus, A.; Adler, G.; Bode, G. Quantitation of Helicobacter pylori in dental plaque samples by competitive polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000. 53, 218–222.
- Fritscher AFritscher, A.M.; Cherubini, K.; Chies, J.; Dias, A.C. Association between Helicobacter pylori and recurrent aphthous stomatitis in children and adolescents. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2004, 33, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loster, B.W.; Majewski, S.W.; Cze, M.; Bielanski, W.; Pierzchalski, P.; Konturek, S.J.; Gully, N.J. The relationship between the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the oral cavity and gastric in the stomach. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olivier, B.J.; Bond, R.P.; van Zyl, W.B.; Delport, M.; Slavik, T.; Ziady, C.; Terhaar Sive Droste, J.S.; Lastovica, A.; van der Merwe, S.W. Absence of Helicobacter pylori within the oral cavities of members of a healthy South African community. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Jakubovics, N.S.; Bächle, M.; Buchalla, W.; Hiller, K.A.; Maisch, T.; Hellwig, E.; Kirschneck, C.; Gessner, A.; Al-Ahmad, A.; et al. Colonization of Helicobacter pylori in the oral cavity—An endless controversy? Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Jithendra, K.D. Presence of Helicobacter pylori in subgingival plaque of periodontitis patients with and without dyspepsia, detected by polymerase chain reaction and culture. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2012, 16, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The human microbiome: At the interface of health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbert, S.A.; Mark Welch, J.L.; Borisy, G.G. Spatial ecology of the human tongue dorsum microbiome. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4003–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moradi, J.; Berggreen, E.; Bunæs, D.F.; Bolstad, A.I.; Bertelsen, R.J. Microbiome composition and metabolic pathways in shallow and deep periodontal pockets. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.S.; Kamath, K.P.; Gandhi, A.P.; Shamim, M.A.; Padhi, B.K.; Das, S. Dental plaque as an extra-gastric reservoir of Helicobacter pylori: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2025, 170, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, R.T.; Ochs, B.; Goodson, J.M. Temperature as a periodontal diagnostic. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1990, 17, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, S.C.; Ebersole, J.L. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia: The “red complex”, a prototype polybacterial pathogenic consortium in periodontitis. Periodontology 2000 2005, 38, 72–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N. Microbial ecosystem in the oral cavity: Metabolic diversity in an ecological niche and its relationship with oral diseases. Int. Congr. Ser. 2005, 1284, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, J.; Zilm, P.S.; Fuss, J.M.; Gully, N.J. A proteomic investigation of Fusobacterium nucleatum alkaline-induced biofilms. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y. Atlas of Oral Microbiology: From Healthy Microflora to Disease; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 145–210. [Google Scholar]
- Idate, U.; Bhat, K.; Kotrashetti, V.; Kugaji, M.; Kumbar, V. Molecular identification of Capnocytophaga species from the oral cavity of patients with chronic periodontitis and healthy individuals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2020, 24, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, M.P.; Lennon, A. Identification of oral peptostreptococcus isolates by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of 16S rRNA genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4475–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ko, Y.; Lee, E.M.; Park, J.C.; Gu, M.B.; Bak, S.; Ji, S. Salivary microbiota in periodontal health and disease and their changes following nonsurgical periodontal treatment. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2020, 50, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, T.G.B.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Tsute Chen, G.; Colombo, A.P.V. Oral-gut bacterial profiles discriminate between periodontal health and diseases. J. Periodontal Res. 2022, 57, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antezack, A.; Etchecopar-Etchart, D.; La Scola, B.; Monnet-Corti, V. New putative periodontopathogens and periodontal health-associated species: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Periodontal Res. 2023, 58, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.M. The immune response to Prevotella bacteria in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, A.; Jin, J.O.; Johnston, C.D.; Yamazaki, H.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Rittling, S.R. Pathogenic bacterial species associated with endodontic infection evade innate immune control by disabling neutrophils. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4068–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Foschi, F.; Cavrini, F.; Montebugnoli, L.; Stashenko, P.; Sambri, V.; Prati, C. Detection of bacteria in endodontic samples by polymerase chain reaction assays and association with defined clinical signs in Italian patients. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 20, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elinav, E.; Strowig, T.; Kau, A.L.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Thaiss, C.A.; Booth, C.J.; Peaper, D.R.; Bertin, J.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. NLRP6 inflammasome regulates colonic microbial ecology and risk for colitis. Cell 2011, 145, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, N.W.; de Zoete, M.R.; Cullen, T.W.; Barry, N.A.; Stefanowski, J.; Hao, L.; Degnan, P.H.; Hu, J.; Peter, I.; Zhang, W.; et al. Immunoglobulin A coating identifies colitogenic bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2014, 158, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljazovic, A.; Roy, U.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Lesker, T.R.; Zhao, B.; Gronow, A.; Amend, L.; Will, S.E.; Hofmann, J.D.; Pils, M.C.; et al. Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, E.; Bachar, D.; Yasir, M.; Musso, D.; Djossou, F.; Gaborit, B.; Brah, S.; Diallo, A.; Ndombe, G.M.; Mediannikov, O.; et al. Treponema species enrich the gut microbiota of traditional rural populations but are absent from urban individuals. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 27, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Settem, R.P.; Honma, K.; Sharma, A.; Falkner, K.L.; Novak, J.M.; Sun, Y.; Kirkwood, K.L. Porphyromonas gingivalis indirectly elicits intestinal inflammation by altering the gut microbiota and disrupting epithelial barrier function through IL9-producing CD4+ T cells. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 37, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Africa, C.W.J.; Nel, J.; Stemmet, M. Anaerobes and bacterial vaginosis in pregnancy: Virulence factors contributing to vaginal colonisation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 6979–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, M.; Tohumcu, E.; Del Vecchio, L.E.; Porcari, S.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ianiro, G. The Influence of Helicobacter pylori on Human Gastric and Gut Microbiota. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Liao, B.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. The interactions between oral-gut axis microbiota and Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 914418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Calvo Henriquez, C.; Mouawad, F.; Ristagno, C.; Barillari, M.R.; Schindler, A.; Nacci, A.; Bouland, C.; Laino, L.; et al. Laryngopharyngeal reflux, gastroesophageal reflux and dental disorders: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbrouckel, J.P.; von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1628–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Shulman, J.D.; Cappelli, D.P. Prevention in Clinical Oral Health Care; Mosby Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Silness, J.; Löe, H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1964, 22, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosyn, J.; Eghbali, A.; Hermans, A.; Vervaeke, S.; De Bruyn, H.; Cleymaet, R. A 5-year prospective study on single immediate implants in the aesthetic zone. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefti, A.F. Periodontal probing. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1997, 8, 336–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, E.F. Oral diagnosis and treatment planning: Part 3. Periodontal disease and assessment of risk. Br. Dent. J. 2012, 213, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, S. Interactive Web-Based Data Visualization with R, Plotly, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]




| HP+ n = 52 | HP− n = 15 | Total n = 67 | p-Value ** | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| BoP | 0–25 | 25 | 48.1 | 9 | 60.0 | 32 | 47.7 | 0.739 |
| 26–50 | 16 | 30.7 | 5 | 33.3 | 23 | 34.3 | ||
| 51–75 | 7 | 13.5 | 1 | 6.6 | 8 | 11.9 | ||
| >75 | 2 | 3.8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2.9 | ||
| NA * | 2 | 3.8 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5.8 | ||
| Plaque score | 0 | 4 | 7.6 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5.8 | 0.005 |
| 1 | 9 | 17.3 | 3 | 20.0 | 12 | 17.9 | ||
| 2 | 11 | 21.1 | 10 | 66.6 | 19 | 28.3 | ||
| 3 | 27 | 51.9 | 2 | 13.3 | 29 | 43.2 | ||
| NA * | 2 | 3.8 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5.8 | ||
| PPD (Mean ± SD) | 5.58 ± 2.9 | 5.53 ± 2.8 | 5.49 ± 2.9 | 0.95 | ||||
| HP+ n = 52 | HP− n = 15 | Total n = 67 | p-Value ** | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| PSE | 1 | 2 | 3.8 | 3 | 20.0 | 5 | 7.5 | 0.346 |
| 2 | 12 | 23.1 | 4 | 33.3 | 16 | 23.8 | ||
| 3 | 13 | 25.0 | 3 | 26.6 | 16 | 23.8 | ||
| 4 | 11 | 21.1 | 1 | 6.6 | 12 | 17.9 | ||
| 5 | 12 | 23.1 | 4 | 26.6 | 16 | 23.9 | ||
| NA * | 2 | 3.8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2.9 | ||
| Shallow Deep | ≤3 mm | 14 | 26.9 | 7 | 46.6 | 22 | 32.8 | 0.177 |
| >3 mm | 36 | 69.2 | 8 | 53.4 | 45 | 67.2 | ||
| NA * | 2 | 3.9 | ||||||
| HP+ n = 52 | HP− n = 15 | Total n = 67 | p-Value ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decayed (D) | 2.3 ± 3.2 | 1.2 ± 3.8 | 2.1 ± 3.1 | 0.012 |
| Missing (M) | 4.9 ± 4.9 | 2 ± 4.9 | 4.2 ± 5.9 | 0.060 |
| Filled (F) | 4.2 ± 4.9 | 6.93 ± 5.9 | 4.8 ± 4.9 | 0.058 |
| Implant (I) | 1.09 ± 2.1 | 0.93 ± 2.5 | 1.05 ± 2.1 | 0.800 |
| DMFI | 12.6 ± 6.8 | 11.5 ± 6.6 | 12.1 ± 7.9 | 0.441 |
| HP+ n = 52 | HP− n = 15 | Total n = 67 | p-Value ** | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Histology | Esophagitis | 1 | 1.9 | 3 | 20 | 4 | 5.9 | 0.001 |
| Healthy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Quiescent | 3 | 5.7 | 12 | 80 | 15 | 22.3 | ||
| Mild * | 23 | 44.2 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 34.3 | ||
| Moderate | 16 | 30.7 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 23.8 | ||
| Severe | 9 | 17.3 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 19.3 | ||
| Metaplasia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| HP | - | 1 | 19.2 | 15 | 100 | 16 | 23.8 | 0.001 |
| + | 4 | 7.6 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5.9 | ||
| ++ | 25 | 48.1 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 37.3 | ||
| +++ | 22 | 42.3 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 32.7 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamparini, F.; Buonavoglia, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Diakoudi, G.; Pavoni, M.; Fiorini, G.; Sambri, V.; Spinelli, A.; Vaira, D.; Gandolfi, M.G.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Tongue and Periodontal Pocket Microbiome in Relation to Helicobacter pylori Gastric Disease: 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080804
Zamparini F, Buonavoglia A, Pellegrini F, Diakoudi G, Pavoni M, Fiorini G, Sambri V, Spinelli A, Vaira D, Gandolfi MG, et al. Comparative Evaluation of Tongue and Periodontal Pocket Microbiome in Relation to Helicobacter pylori Gastric Disease: 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080804
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamparini, Fausto, Alessio Buonavoglia, Francesco Pellegrini, Georgia Diakoudi, Matteo Pavoni, Giulia Fiorini, Vittorio Sambri, Andrea Spinelli, Dino Vaira, Maria Giovanna Gandolfi, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Evaluation of Tongue and Periodontal Pocket Microbiome in Relation to Helicobacter pylori Gastric Disease: 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080804
APA StyleZamparini, F., Buonavoglia, A., Pellegrini, F., Diakoudi, G., Pavoni, M., Fiorini, G., Sambri, V., Spinelli, A., Vaira, D., Gandolfi, M. G., & Prati, C. (2025). Comparative Evaluation of Tongue and Periodontal Pocket Microbiome in Relation to Helicobacter pylori Gastric Disease: 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis. Antibiotics, 14(8), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080804










