In Vivo Antibiotic Elution and Inflammatory Response During Two-Stage Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision: A Microdialysis Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
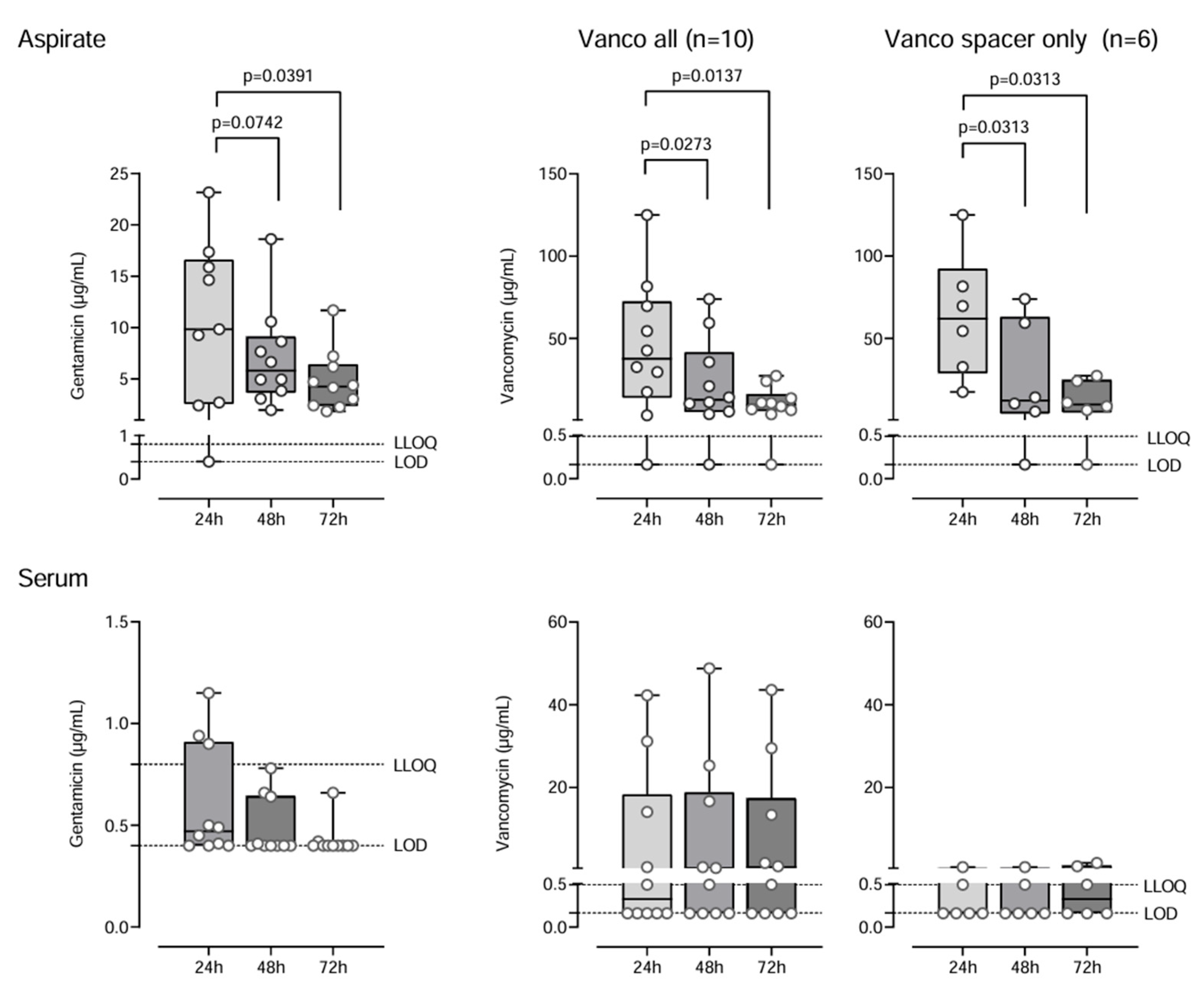
2. Results
2.1. Antibiotic Concentrations
2.2. Metabolic and Inflammatory Markers
3. Discussion
3.1. Microdialysis
3.2. Antibiotics
3.3. Antibiotic Elution Kinetics and Therapeutic Effects
3.4. Immunological and Metabolic Parameters
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
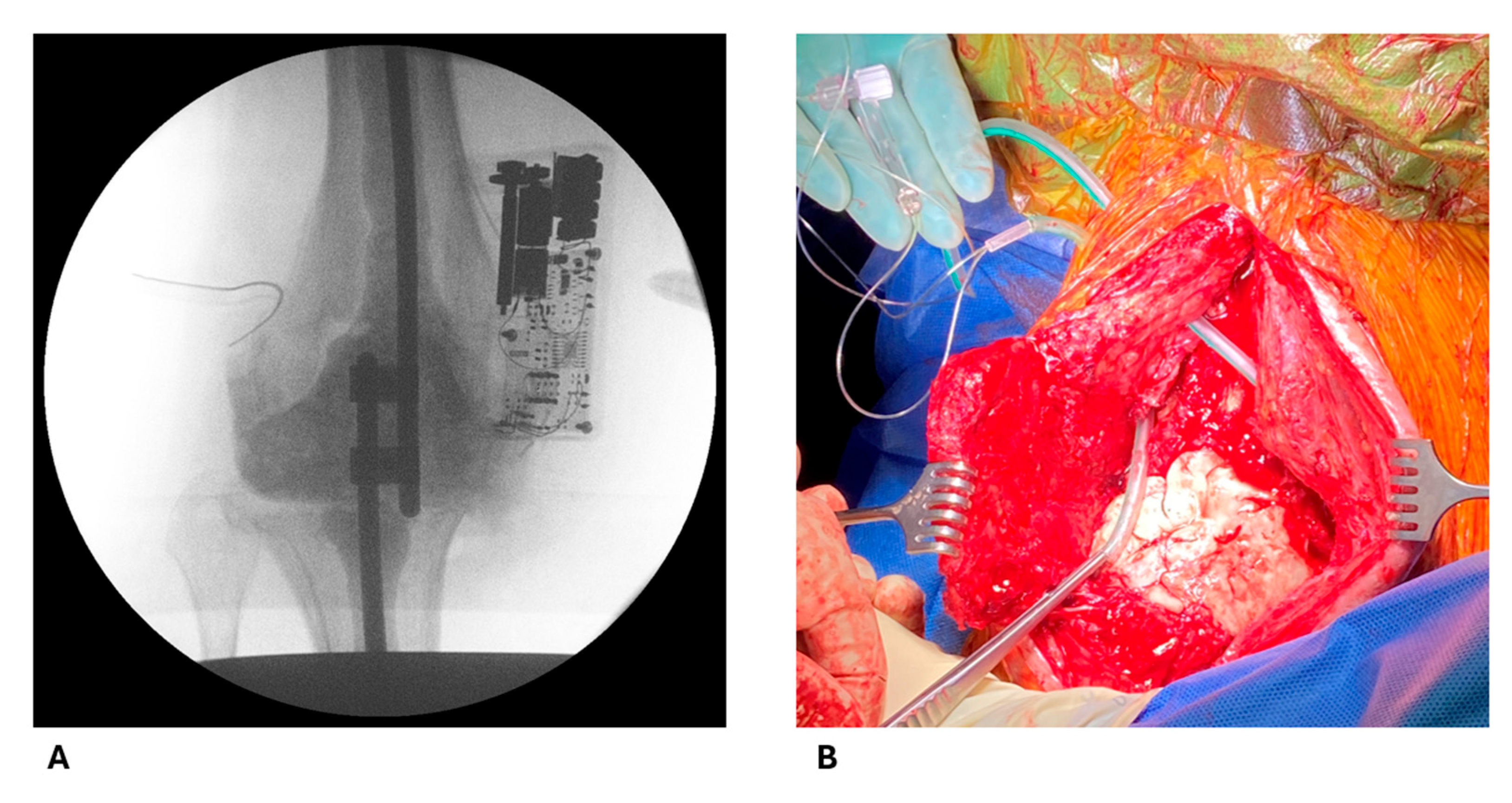
4.2. Intraoperative Procedures
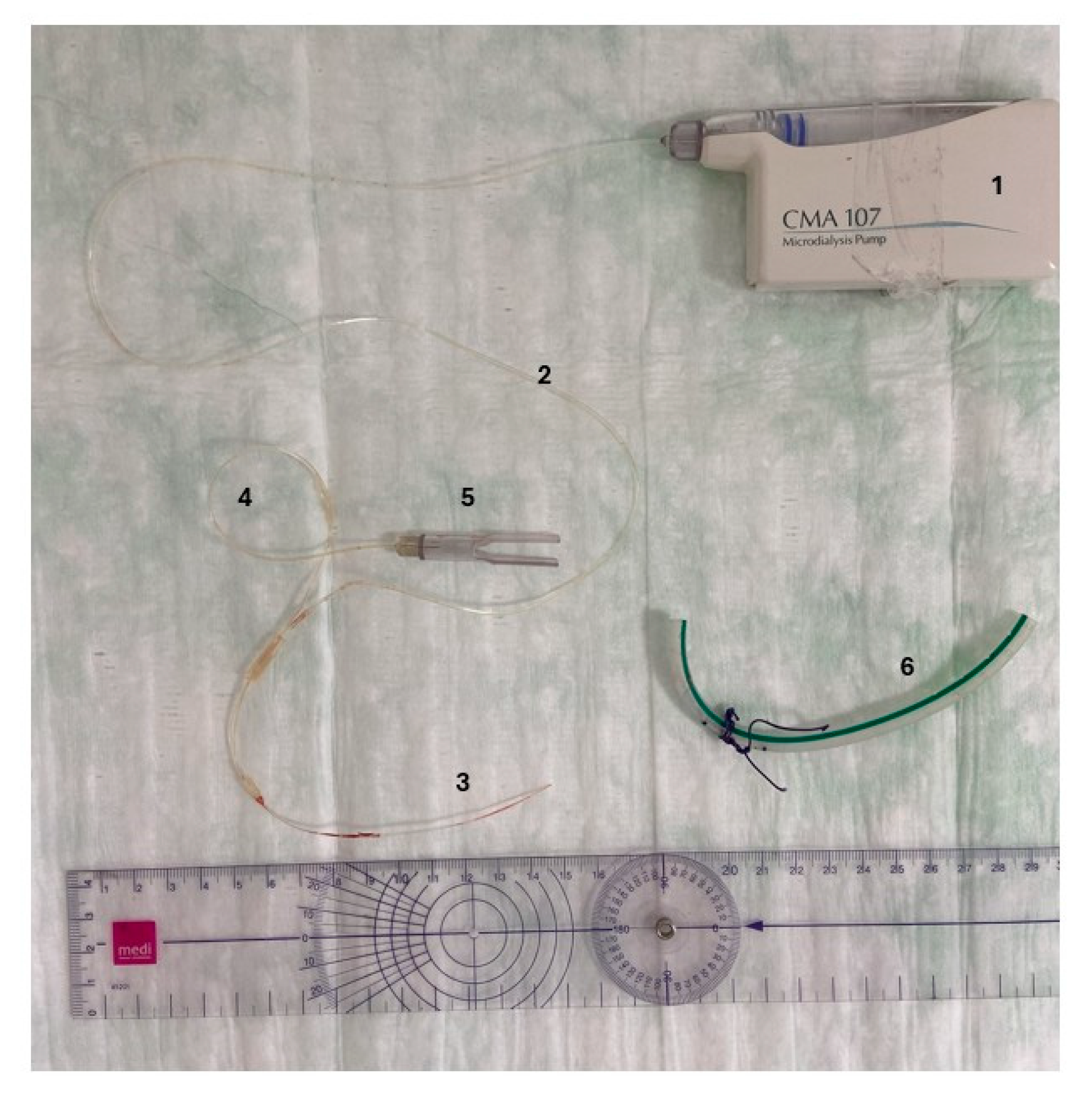
4.3. Sample Collection Protocol
4.4. Analysis
4.5. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PJI | Periprosthetic joint infection |
| TKA | Total knee arthroplasty |
| DAIR | Debridement, antibiotics, and implant retention |
| MD | Microdialysis |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
References
- Pabinger, C.; Berghold, A.; Boehler, N.; Labek, G. Revision rates after knee replacement: Cumulative results from worldwide clinical studies versus joint registers. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marang-van de Mheen, P.J.; Bragan Turner, E.; Liew, S.; Mutalima, N.; Tran, T.; Rasmussen, S.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; Gordon, A. Variation in Prosthetic Joint Infection and treatment strategies during 4.5 years of follow-up after primary joint arthroplasty using administrative data of 41397 patients across Australian, European and United States hospitals. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, M.; Lau, E.; Kurtz, S.M.; Alt, V. Projections of Primary TKA and THA in Germany from 2016 Through 2040. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, R.; Khan, T.; Alvand, A. Update on the diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection in hip and knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. 360 2019, 8, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, I.; Scheele, C.; Pohlig, F.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; Suren, C. Treatment options in PJI-is two-stage still gold standard? J. Orthop. 2021, 23, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangaud, C.; Ollivier, M.; Argenson, J.N. Outcome of single-stage versus two-stage exchange for revision knee arthroplasty for chronic periprosthetic infection. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenisch, M.; Ben Amar, S.; Babasiz, M.; Seuser, A.; Kohlhof, H.; Wirtz, D.C.; Randau, T.M. Temporary arthrodesis through static spacer implantation in two-stage treatment of periprosthetic joint infections of the knee. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 2023, 35, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostakos, K.; Meyer, C. Antibiotic Elution from Hip and Knee Acrylic Bone Cement Spacers: A Systematic Review. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4657874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yao, Z. Infection after total knee arthroplasty and its gold standard surgical treatment: Spacers used in two-stage revision arthroplasty. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2017, 6, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardi, E.M.; Franceschi, F. Prosthetic joint infection. A Relev. Public Health issue. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, J.L.; Shadbolt, B.; Scarvell, J.M.; Smith, P.N. Quality of Life after Infection in Total Joint Replacement. J. Orthop. Surg. 2008, 16, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmistowski, B.; Karam, J.A.; Durinka, J.B.; Casper, D.S.; Parvizi, J. Periprosthetic joint infection increases the risk of one-year mortality. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, T.N.; Dowsey, M.M.; Buising, K.L.; Liew, D.; Choong, P.F.M. Cost analysis of debridement and retention for management of prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymski, D.; Walter, N.; Hierl, K.; Rupp, M.; Alt, V. Direct Hospital Costs per Case of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Joint Infections in Europe—A Systematic Review. J. Arthroplast. 2024, 39, 1876–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostakos, K.; Fürst, O.; Kelm, J. Antibiotic-impregnated PMMA hip spacers: Current status. Acta Orthop. 2006, 77, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, C.S.; Müller, M.; Bashaw, E.D.; Benfeldt, E.; Bolinder, J.; Bullock, R.; Bungay, P.M.; DeLange, E.C.M.; Derendorf, H.; Elmquist, W.F.; et al. AAPS-FDA workshop white paper: Microdialysis principles, application and regulatory perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. Microdialysis as an Important Technique in Systems Pharmacology—A Historical and Methodological Review. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sutter, P.J.; Hermans, E.; De Cock, P.; van Bocxlaer, J.; Gasthuys, E.; Vermeulen, A. Penetration of Antibiotics into Subcutaneous and Intramuscular Interstitial Fluid: A Meta-Analysis of Microdialysis Studies in Adults. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2024, 63, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.J.; Park, J.H.; Park, H.K. Microdialysis applications in neuroscience. Neurol. Res. 2008, 30, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrono, D.; Roggio, D.; Mazzeo, A.T.; Catalano, G.; Mazza, E.; Rizza, G.; Gambella, A.; Rigo, F.; Leone, N.; Elia, V.; et al. Clinical assessment of liver metabolism during hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion using microdialysis. Artif. Organs 2022, 46, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langkilde, A.; Andersen, O.; Henriksen, J.H.; Langberg, H.; Petersen, J.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Assessment of in situ adipose tissue inflammation by microdialysis. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2015, 35, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, C.F.; Kwasnicki, A.; Lakka, S.S.; Engelhard, H.H. Cerebral Microdialysis as a Tool for Assessing the Delivery of Chemotherapy in Brain Tumor Patients. World Neurosurg. 2021, 145, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, J.; Stilling, M.; Hanberg, P.; Fichtner Bendtsen, M.A.; Jørgensen, A.R.; Søballe, K.; Jørgensen, N.P.; Bue, M. Moxifloxacin Concentrations in the Knee Joint, Tibial Bone, and Soft Tissue When Combined with Rifampicin: A Randomized Porcine Microdialysis Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2022, 104, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shippenberg, T.S.; Thompson, A.C. Overview of microdialysis. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2001, Chapter 7, Unit7.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bue, M.; Thomassen, M.B.; Larsen, O.H.; Jørgensen, A.R.; Stilling, M.; Søballe, K.; Hanberg, P. Local Vancomycin Concentrations after Intra-articular Injection into the Knee Joint: An Experimental Porcine Study. J. Knee Surg. 2021, 34, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, A.R.; Hanberg, P.; Bue, M.; Thomassen, M.B.; Pedersen Jørgensen, N.; Stilling, M. Double-dose cefuroxime concentrations in bone, synovial fluid of the knee joint and subcutaneous adipose tissue—A randomised porcine microdialysis study. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 160, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryun, K.; Suecof, L.A.; Sutherland, C.A.; Gao, L.; Kuti, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P. In Vivo Microdialysis Study of the Penetration of Daptomycin into Soft Tissues in Diabetic versus Healthy Volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelch, S.P.; Rueckl, K.; Fuchs, C.; Jordan, M.; Knauer, M.; Steinert, A.; Rudert, M.; Luedemann, M. Comparison of Elution Characteristics and Compressive Strength of Biantibiotic-Loaded PMMA Bone Cement for Spacers: Copal® Spacem with Gentamicin and Vancomycin versus Palacos® R+G with Vancomycin. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4323518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunz, A.; Schonhoff, M.; Omlor, G.W.; Knappe, K.; Bangert, Y.; Lehner, B.; Renkawitz, T.; Jaeger, S. Enhanced antibiotic release from bone cement spacers utilizing dual antibiotic loading with elevated vancomycin concentrations in two-stage revision for periprosthetic joint infection. Int. Orthop. 2023, 47, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.M.; Tetsworth, K.D.; Calhoun, J.H.; Mader, J.T. An articulated antibiotic spacer used for infected total knee arthroplasty: A comparative in vitro elution study of Simplex and Palacos bone cements. J. Orthop. Res. 2005, 23, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinder, A.; Zaatreh, S.; Ellenrieder, M.; Redanz, S.; Podbielski, A.; Reichel, T.; Bösebeck, H.; Mittelmeier, W.; Bader, R. Antibiotics release from cement spacers used for two-stage treatment of implant-associated infections after total joint arthroplasty. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moojen, D.J.F.; Hentenaar, B.; Charles Vogely, H.; Verbout, A.J.; Castelein, R.M.; Dhert, W.J.A. In vitro release of antibiotics from commercial PMMA beads and articulating hip spacers. J. Arthroplast. 2008, 23, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, K.D.; Renz, N.; Trampuz, A. Lokale Antibiotikatherapie. Unfallchirurg 2017, 120, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vugt, T.A.G.; Arts, J.J.; Geurts, J.A.P. Antibiotic-Loaded Polymethylmethacrylate Beads and Spacers in Treatment of Orthopedic Infections and the Role of Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutimer, J.; Gillespie, G.; Lovering, A.M.; Porteous, A.J. Measurements of in vivo intra-articular gentamicin levels from antibiotic loaded articulating spacers in revision total knee replacement. Knee 2009, 16, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, B.; Vogt, S.; Reinsch, M.; Büchner, H. Sufficient release of antibiotic by a spacer 6 weeks after implantation in two-stage revision of infected hip prostheses. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, S.H.; Ueng, S.W.N.; Shih, C.H. High concentration and bioactivity of vancomycin and aztreonam eluted from Simplex cement spacers in two-stage revision of infected hip implants: A study of 46 patients at an average follow-up of 107 days. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, M.J.; Lomaestro, B.M.; Rotschafer, J.C.; Moellering, R.C.; Craig, W.A.; Billeter, M.; Dalovisio, J.R.; Levine, D.P. Vancomycin therapeutic guidelines: A summary of consensus recommendations from the infectious diseases Society of America, the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barza, M.; Lauermann, M. Why monitor serum levels of gentamicin? Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1978, 3, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbysheva, S.; Yermak, K.; Grigoricheva, L.; Renz, N.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Synovial Fluid d-Lactate-A Novel Pathogen-Specific Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 2223–2229.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Ivy, M.; Block, D.R.; Abdel, M.P.; Hanssen, A.D.; Beauchamp, C.; Perry, K.I.; Rosemark, C.L.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Mandrekar, J.; et al. Comparative analysis of 23 synovial fluid biomarkers for hip and knee periprosthetic joint infection detection. J. Orthop. Res. 2020, 38, 2664–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Dai, K.; Qu, X.; Yan, M. Serum and Synovial Fluid Interleukin-6 for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josenhans, C.; Hahn, H. Bakterien: Vermehrung und Stoffwechsel. In Medizinische Mikrobiologie und Infektiologie; Suerbaum, S., Burchard, G.D., Kaufmann, S.H.E., Schulz, T.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 243–248. ISBN 978-3-662-61384-9. [Google Scholar]
- Faryna, A.; Goldenberg, K. Joint Fluid. In Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; Walker, H.K., Hall, W.D., Hurst, J.W., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1990; ISBN 0-409-90077-X. [Google Scholar]
- Kinugasa, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Satsuma, S.; Sakata, R.; Shinada, Y.; Kuroda, R. The predictive value of synovial glucose level in septic arthritis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2020, 29, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.W.; Mackenhauer, J.; Roberts, J.C.; Berg, K.M.; Cocchi, M.N.; Donnino, M.W. Etiology and therapeutic approach to elevated lactate levels. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, G.D.; Newman, R.J.; Slack, M.P. Synovial fluid lactate and the diagnosis of septic arthritis. J. Infect. 1983, 6, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfgott, D.C.; Tatter, S.B.; Santhanam, U.; Clarick, R.H.; Bhardwaj, N.; May, L.T.; Sehgal, P.B. Multiple forms of IFN-beta 2/IL-6 in serum and body fluids during acute bacterial infection. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirtz, D.C.; Heller, K.D.; Miltner, O.; Zilkens, K.W.; Wolff, J.M. Interleukin-6: A potential inflammatory marker after total joint replacement. Int. Orthop. 2000, 24, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawa, R.S.; Anillo, S.; Huntoon, K.; Baumann, H.; Kulaylat, M. Interleukin-6 in surgery, trauma, and critical care part II: Clinical implications. J. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 26, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Zmistowski, B.; Berbari, E.F.; Bauer, T.W.; Springer, B.D.; Della Valle, C.J.; Garvin, K.L.; Mont, M.A.; Wongworawat, M.D.; Zalavras, C.G. New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: From the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2992–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of Patients | n = 10 | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | 6 Male | |
| 4 Female | ||
| Age (years) | 71.5 | [67–78] |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 36.91 | [35.11–42.68] |
| Operated limb | 7 right | |
| 3 left | ||
| Amount of prepared cement (g) | 90 | [63–132] |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Arterial hypertension | 8 | |
| Type 2 diabetes | 5 | |
| Cardiac insufficiency | 5 | |
| Adipositas (Grade I/II/III) | 7 | (1/3/3) |
| Previous PJI | 5 |
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 95% CI | Median | 95% CI | Median | 95% CI | ||
| IL-6 [pg/mL] | serum | 24.83 | [7.46–126.2] | 17.18 | [0–116.4] | 11.85 | [0–122.8] |
| aspirate | 73.99 | [36.54–125.9] | 27.71 | [0–64.07] | 17.74 | [0–36.07] | |
| p-value | 0.275 | 0.734 | 0.652 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behrens, J.J.; Franz, A.; Schildberg, F.A.; Rudowitz, M.; Grote, S.; Fröschen, F.S. In Vivo Antibiotic Elution and Inflammatory Response During Two-Stage Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision: A Microdialysis Pilot Study. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080742
Behrens JJ, Franz A, Schildberg FA, Rudowitz M, Grote S, Fröschen FS. In Vivo Antibiotic Elution and Inflammatory Response During Two-Stage Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision: A Microdialysis Pilot Study. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(8):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080742
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehrens, Julika Johanna, Alexander Franz, Frank Alexander Schildberg, Markus Rudowitz, Stefan Grote, and Frank Sebastian Fröschen. 2025. "In Vivo Antibiotic Elution and Inflammatory Response During Two-Stage Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision: A Microdialysis Pilot Study" Antibiotics 14, no. 8: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080742
APA StyleBehrens, J. J., Franz, A., Schildberg, F. A., Rudowitz, M., Grote, S., & Fröschen, F. S. (2025). In Vivo Antibiotic Elution and Inflammatory Response During Two-Stage Total Knee Arthroplasty Revision: A Microdialysis Pilot Study. Antibiotics, 14(8), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14080742






