Exploring the Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Focus on Cases with a Clinical Worse Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
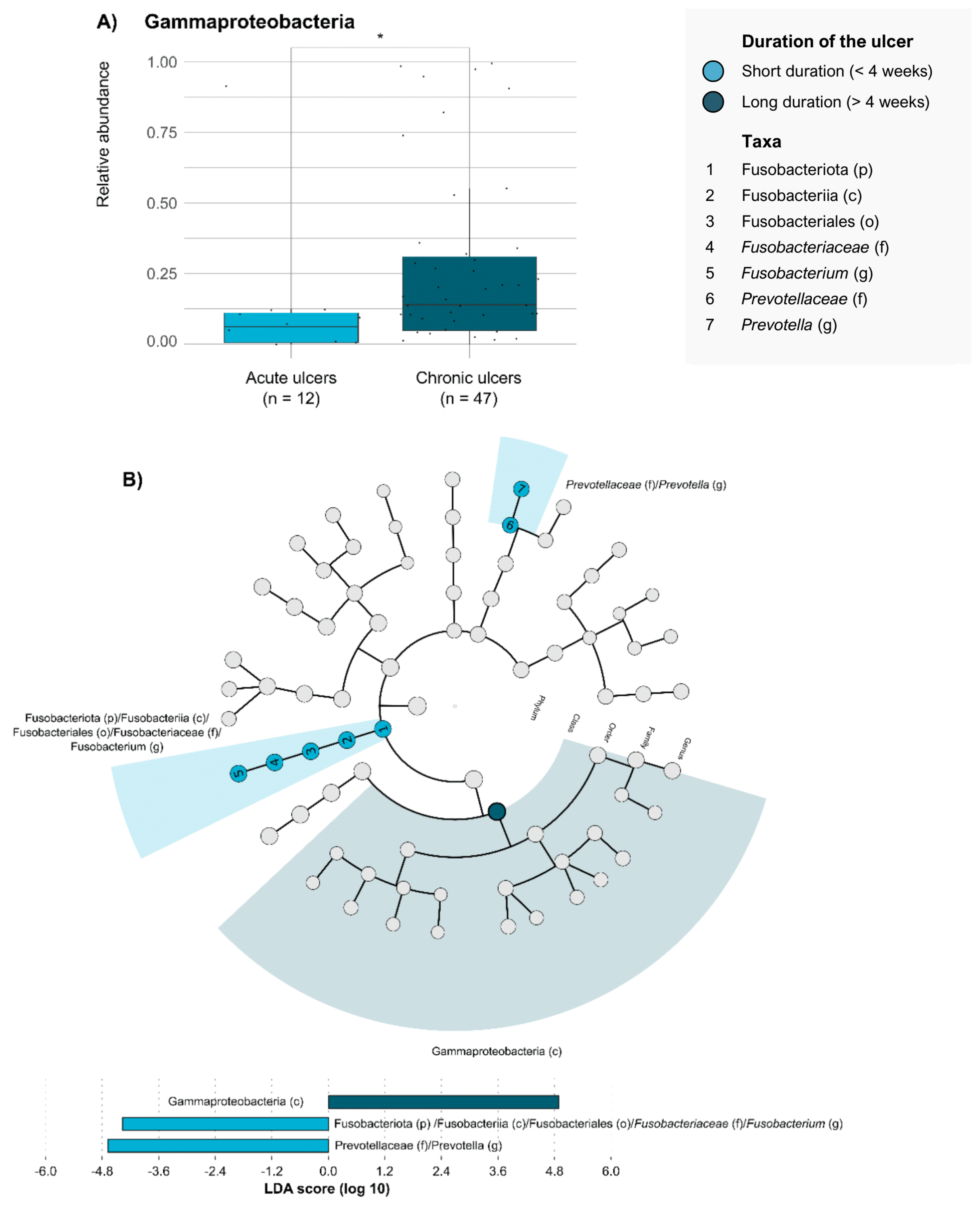
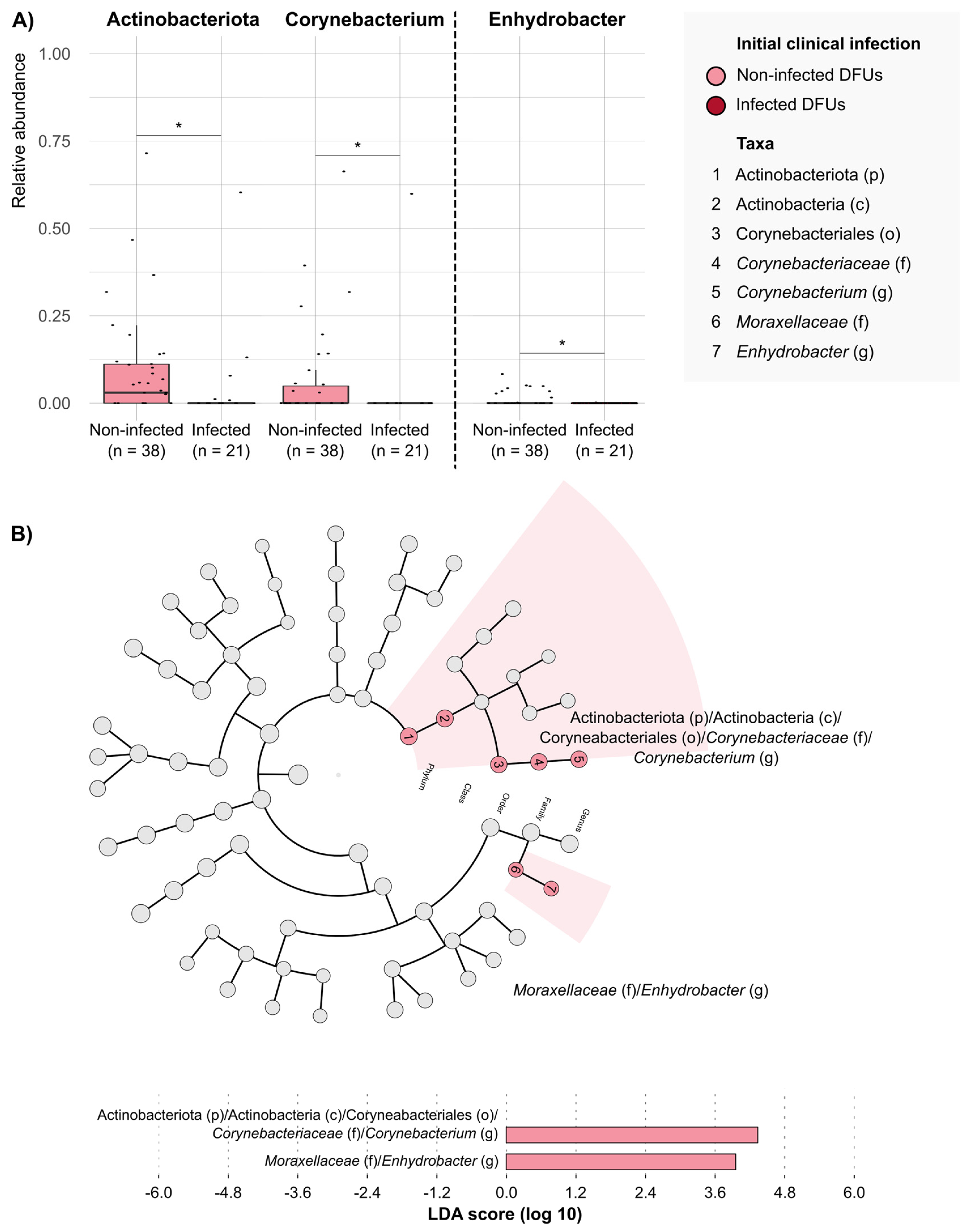
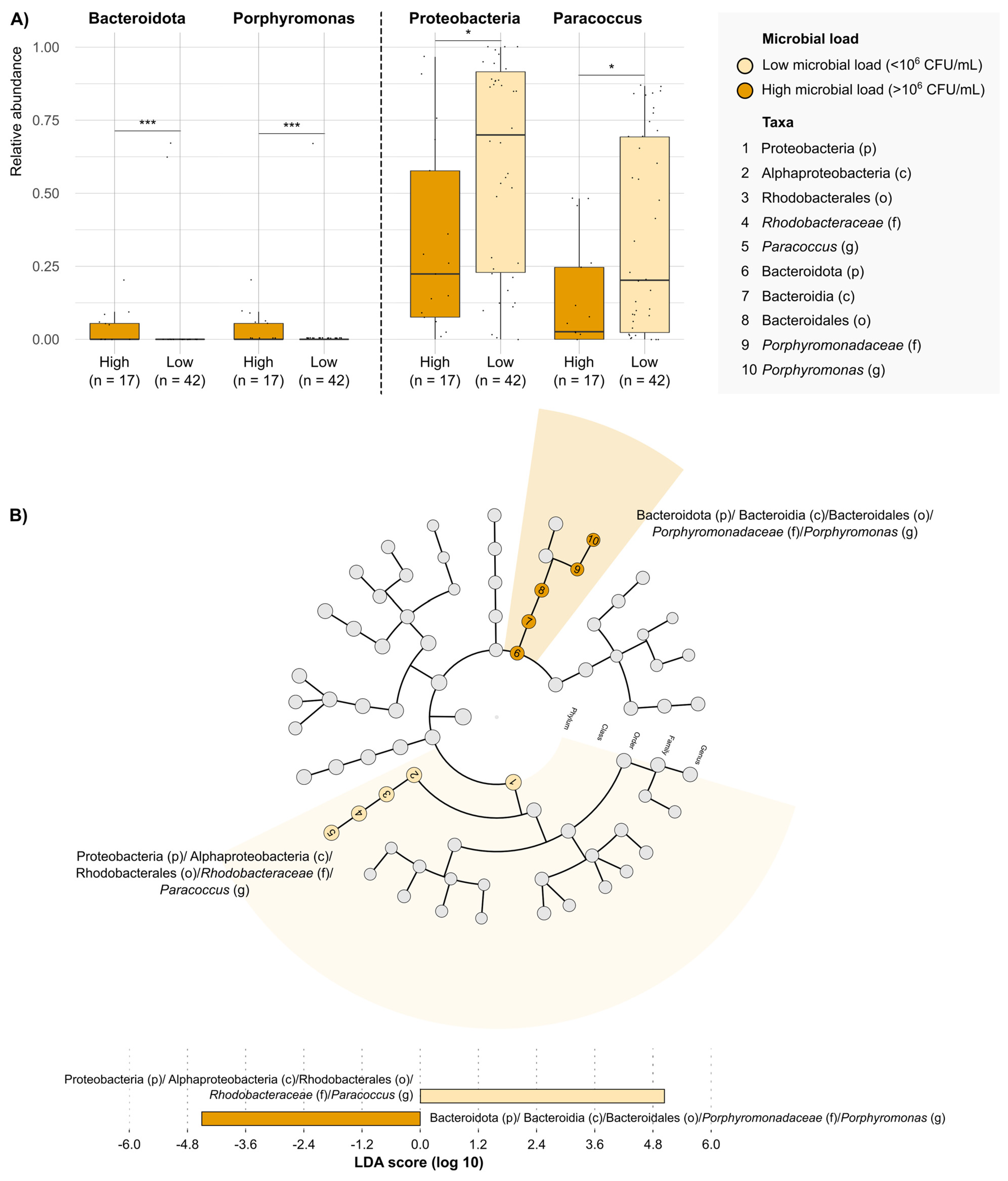
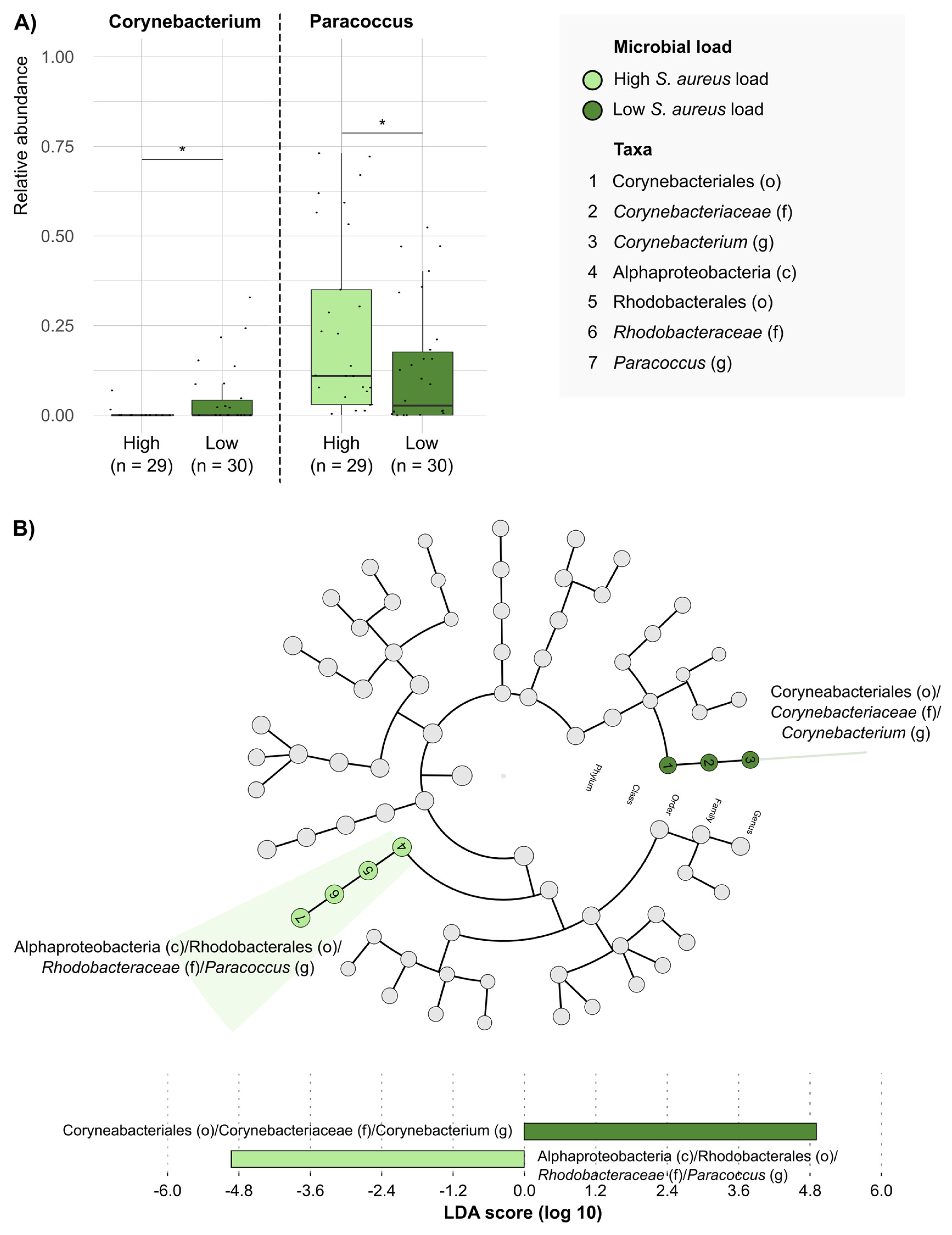
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design, Setting, and Patients
4.2. Definitions, Data Collection, and Clinical Management
4.3. Microbiological Studies and Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazzarini, P.A.; Hurn, S.E.; Fernando, M.E.; Jen, S.D.; Kuys, S.S.; Kamp, M.C.; Reed, L.F. Prevalence of Foot Disease and Risk Factors in General Inpatient Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, L.A.; Armstrong, D.G.; Wunderlich, R.P.; Mohler, M.J.; Wendel, C.S.; Lipsky, B.A. Risk Factors for Foot Infections in Individuals With Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Sheehan, P.; Armstrong, D.G.; Tice, A.D.; Polis, A.B.; Abramson, M.A. Clinical Predictors of Treatment Failure for Diabetic Foot Infections: Data from a Prospective Trial. Int. Wound J. 2007, 4, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, S.; Arda, B.; Taşbakan, M.I.; Çetinkalp, Ş.; Şimşir, I.Y.; Öztürk, A.M.; Uysal, A.; Ertam, İ. Risk Factors for Amputation in Patients with Diabetic Foot Infection: A Prospective Study. Int. Wound J. 2017, 14, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalan, L.R.; Meisel, J.S.; Loesche, M.A.; Horwinski, J.; Soaita, I.; Chen, X.; Uberoi, A.; Gardner, S.E.; Grice, E.A. Strain- and Species-Level Variation in the Microbiome of Diabetic Wounds Is Associated with Clinical Outcomes and Therapeutic Efficacy. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 641–655.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Demirdal, T.; Emir, B. Meta-Analysis of Risk Factors for Amputation in Diabetic Foot Infections. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2019, 35, e3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, K.E.; Boeckh, S.; Stacey, H.J.; Jones, J.D. The Microbiology of Diabetic Foot Infections: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, A.; Brodell, J.D.; Daiss, J.L.; Schwarz, E.M.; Oh, I. Evidence of Differential Microbiomes in Healing versus Non-Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Prior to and Following Foot Salvage Therapy. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldevila-Boixader, L.; Mur, I.; Morata, L.; Sierra, Y.; Rivera, A.; Bosch, J.; Montero-Saez, A.; Fernández-Reinales, A.J.; Martí, S.; Benito, N.; et al. Clinical Usefulness of Quantifying Microbial Load from Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 189, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ponsero, A.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Lipsky, B.A.; Hurwitz, B.L. The Dynamic Wound Microbiome. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jneid, J.; Lavigne, J.P.; La Scola, B.; Cassir, N. The Diabetic Foot Microbiota: A Review. Hum. Microb. J. 2017, 5–6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngba Essebe, C.; Visvikis, O.; Fines-Guyon, M.; Vergne, A.; Cattoir, V.; Lecoustumier, A.; Lemichez, E.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Dunyach-Remy, C. Decrease of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence by Helcococcus kunzii in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Front Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacy, A.; Everett, J.; Jorth, P.; Trivedi, U.; Rumbaugh, K.P.; Whiteley, M. Bacterial Fight-and-Flight Responses Enhance Virulence in a Polymicrobial Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7819–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redel, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, H.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Zhou, Y.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Weinstock, G.; Sodergren, E.; Blaser, M.J. Quantitation and Composition of Cutaneous Microbiota in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Men. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, A.; Bowling, F.L.; Boulton, A.J.M.; McBain, A.J. Molecular and Culture-Based Assessment of the Microbial Diversity of Diabetic Chronic Foot Wounds and Contralateral Skin Sites. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; McLennan, S.V.; Lo, L.; Natfaji, A.; Bolton, T.; Liu, Y.; Twigg, S.M.; Yue, D.K. Bacterial Load Predicts Healing Rate in Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.E.; Frantz, R.A. Wound Bioburden and Infection-Related Complications in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2008, 10, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.E.; Haleem, A.; Jao, Y.L.; Hillis, S.L.; Femino, J.E.; Phisitkul, P.; Heilmann, K.P.; Lehman, S.M.; Franciscus, C.L. Cultures of Diabetic Foot Ulcers without Clinical Signs of Infection Do Not Predict Outcomes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Egea-Zorrilla, A.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Aragón-Vela, J.; Muñoz-Quezada, S.; Tercedor-Sánchez, L.; Abadia-Molina, F. The Gut Microbiota and Its Implication in the Development of Atherosclerosis and Related Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.M.; Clement, C.; Pogue, A.I.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lukiw, W.J. Pathogenic Microbes, the Microbiome, and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chia, D.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Paster, B.J.; Joshipura, K.; Wong, D.T.W. Variations of Oral Microbiota Are Associated with Pancreatic Diseases Including Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2012, 61, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, T.J.; Turton, J.C.; Tyson, J.; Musgrove, A.; Fleming, V.M.; Lister, M.M.; Loose, M.W.; Sockett, R.E.; Diggle, M.; Game, F.L.; et al. Examining Diabetic Heel Ulcers through an Ecological Lens: Microbial Community Dynamics Associated with Healing and Infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.K.; Patel, K.H.; Huang, R.Y.; Lee, C.N.; Moochhala, S.M. The Gut-Skin Microbiota Axis and Its Role in Diabetic Wound Healing—A Review Based on Current Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, M.M.; Freire, M.O.; Gabrilska, R.A.; Rumbaugh, K.P.; Lemon, K.P. Staphylococcus aureus Shifts toward Commensalism in Response to Corynebacterium Species. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, R.J.; Brownrigg, J.R.W.; Apelqvist, J.; Boyko, E.J.; Fitridge, R.; Mills, J.L.; Reekers, J.; Shearman, C.P.; Zierler, R.E.; Schaper, N.C. IWGDF Guidance on the Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Peripheral Artery Disease in Patients with Foot Ulcers in Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Bus, S.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, S.A.; Lavery, L.A.; Monteiro-Soares, M.; Rasmussen, A.; Raspovic, A.; Sacco, I.C.N.; van Netten, J.J. IWGDF Guideline on the Prevention of Foot Ulcers in Persons with Diabetes. IWGDF Guidel. 2019, 40, e3651. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Cornia, P.B.; Pile, J.C.; Peters, E.J.G.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; et al. 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e132-73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Senneville, É.; Abbas, Z.G.; Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Diggle, M.; Embil, J.M.; Kono, S.; Lavery, L.A.; Malone, M.; van Asten, S.A.; et al. Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot Infection in Persons with Diabetes (IWGDF 2019 Update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. S1), e3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n = 59 | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (median, IQR) | 65 years (59–71) |
| Male sex | 47 patients (80%) |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) | 52 patients (88%) |
| BMI (median, IQR) | 29 kg/m2 (25–33) |
| Years since diabetes diagnosis (median, IQR) | 17 years (8.5–25) |
| Diabetic neuropathy | 49 patients (83%) |
| Peripheral vasculopathy | 30 (51%) |
| DFU duration ≥ 4 weeks | 47 patients (80%) |
| Antibiotic use in the previous month | 28 patients (48%) |
| DFU infection | 21 (36%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soldevila-Boixader, L.; Carrera-Salinas, A.; Mur, I.; Morata, L.; Rivera, A.; Bosch, J.; Montero-Saez, A.; Castillejo, J.M.; Benito, N.; Martí, S.; et al. Exploring the Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Focus on Cases with a Clinical Worse Outcome. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070724
Soldevila-Boixader L, Carrera-Salinas A, Mur I, Morata L, Rivera A, Bosch J, Montero-Saez A, Castillejo JM, Benito N, Martí S, et al. Exploring the Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Focus on Cases with a Clinical Worse Outcome. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(7):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070724
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoldevila-Boixader, Laura, Anna Carrera-Salinas, Isabel Mur, Laura Morata, Alba Rivera, Jordi Bosch, Abelardo Montero-Saez, Jéssica Martínez Castillejo, Natividad Benito, Sara Martí, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Focus on Cases with a Clinical Worse Outcome" Antibiotics 14, no. 7: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070724
APA StyleSoldevila-Boixader, L., Carrera-Salinas, A., Mur, I., Morata, L., Rivera, A., Bosch, J., Montero-Saez, A., Castillejo, J. M., Benito, N., Martí, S., & Murillo, O. (2025). Exploring the Microbiome of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Focus on Cases with a Clinical Worse Outcome. Antibiotics, 14(7), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14070724









